Submitted:
01 October 2024
Posted:
02 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
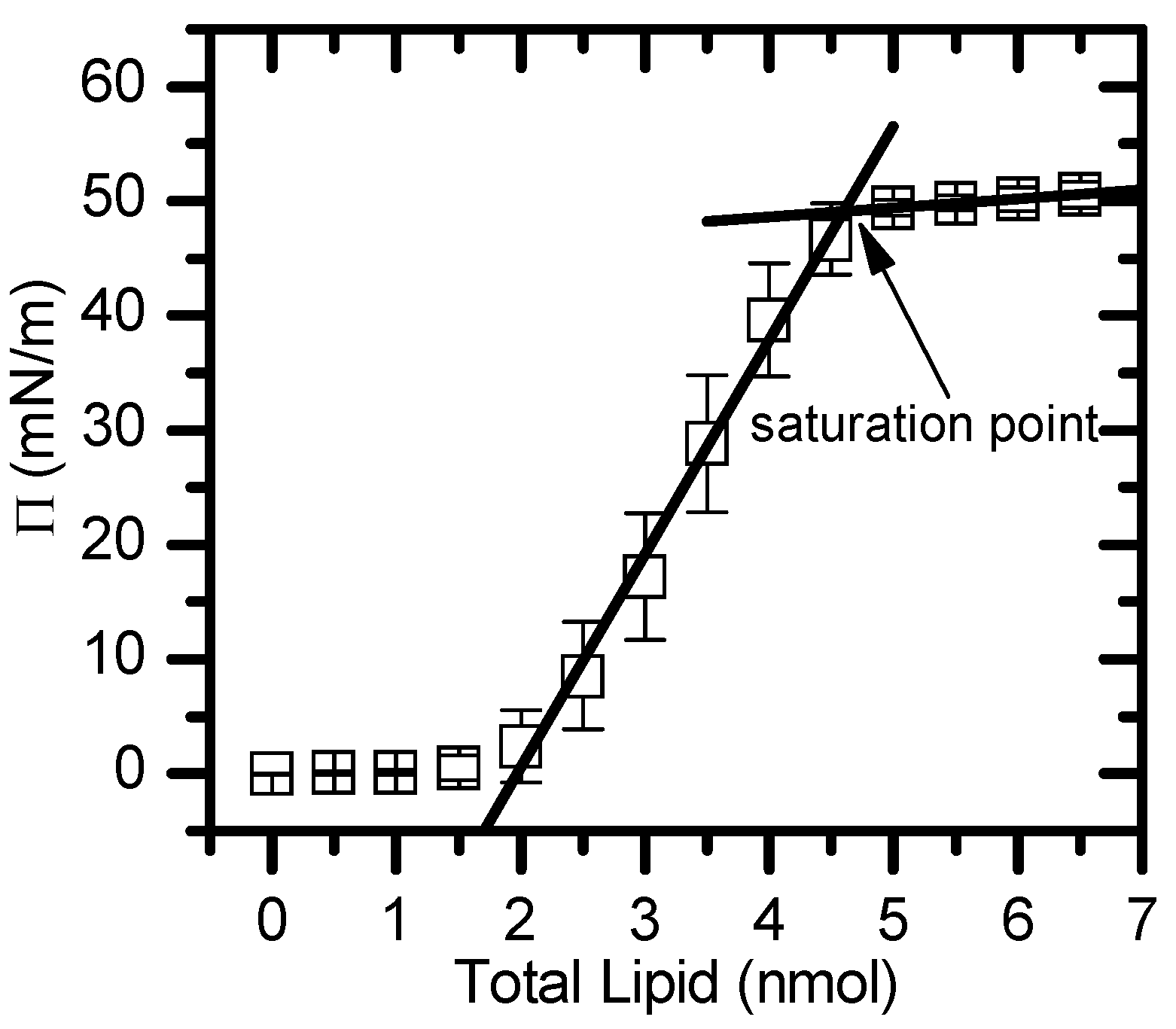
2.1. Area per Lipid in Monolayers
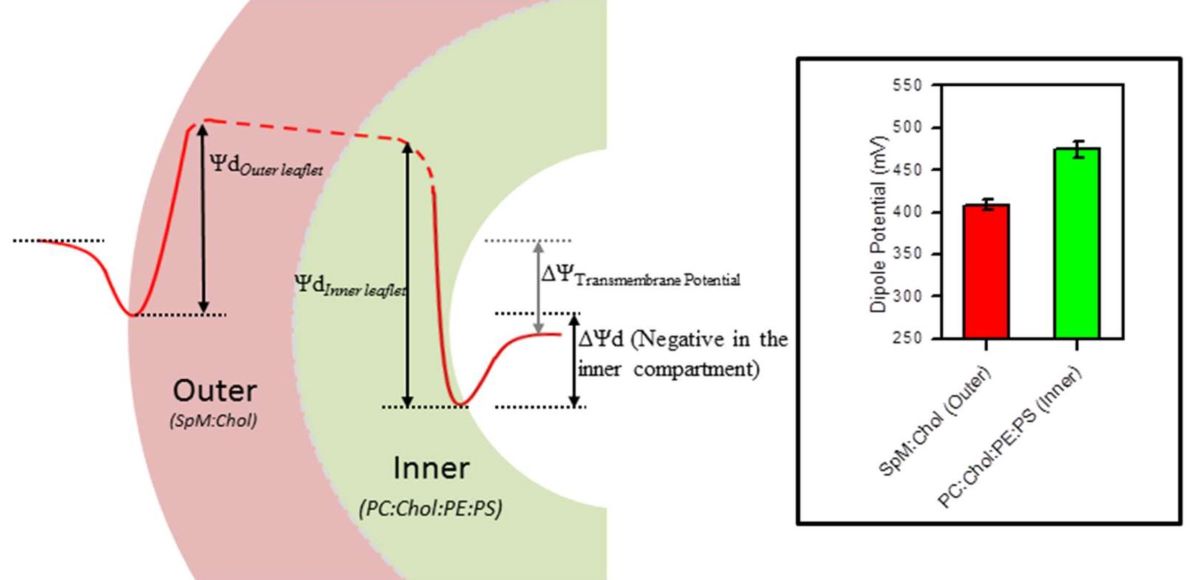
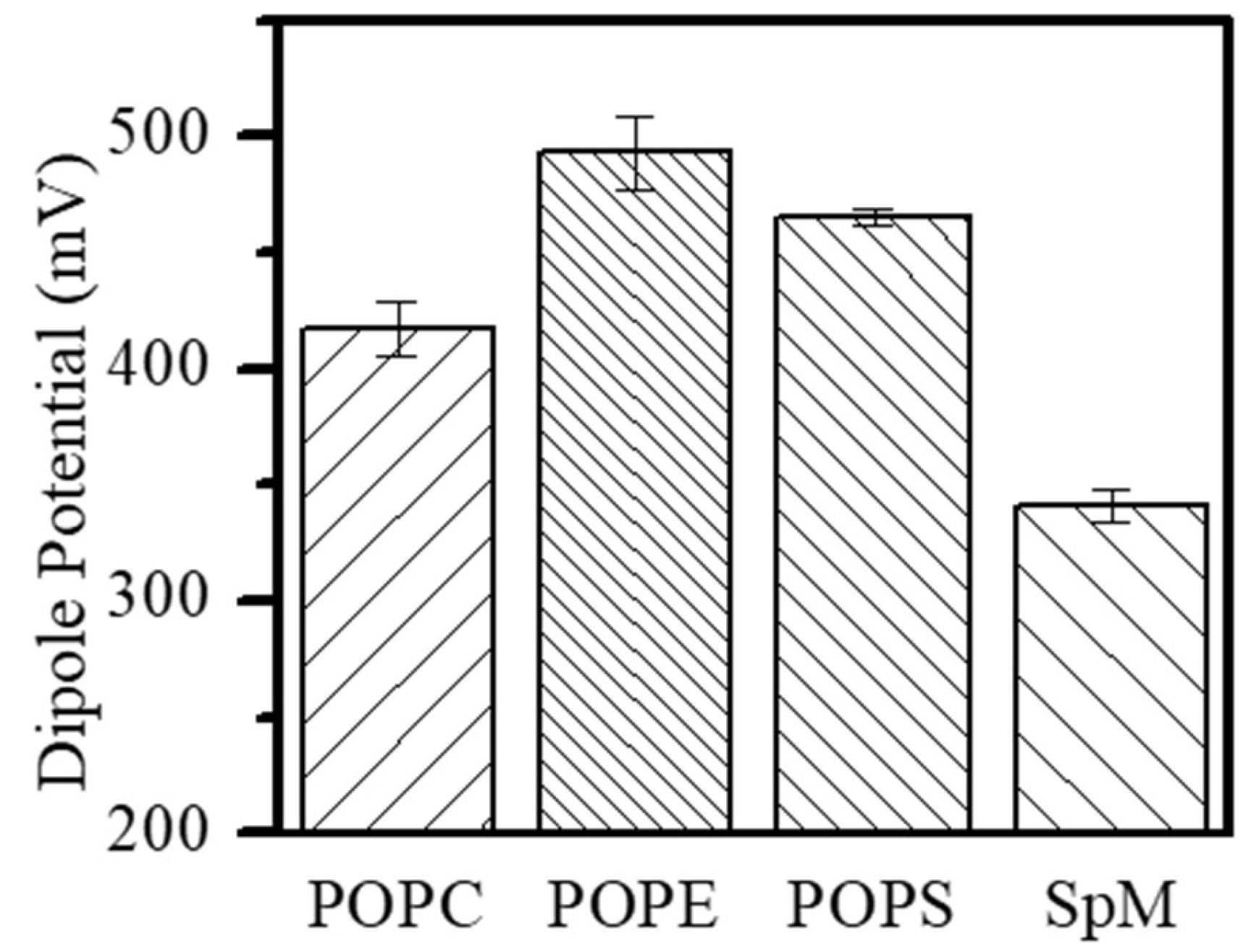
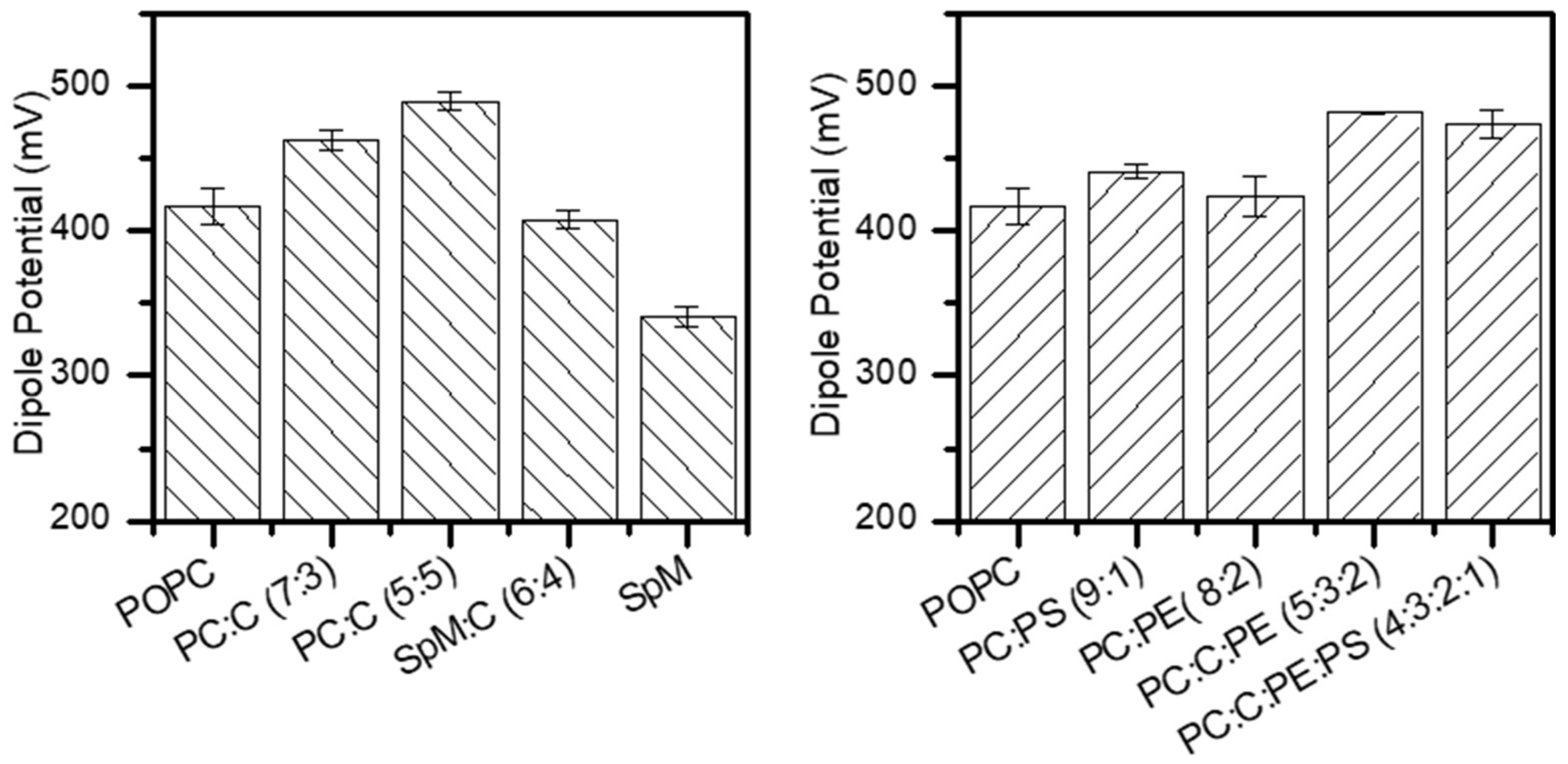
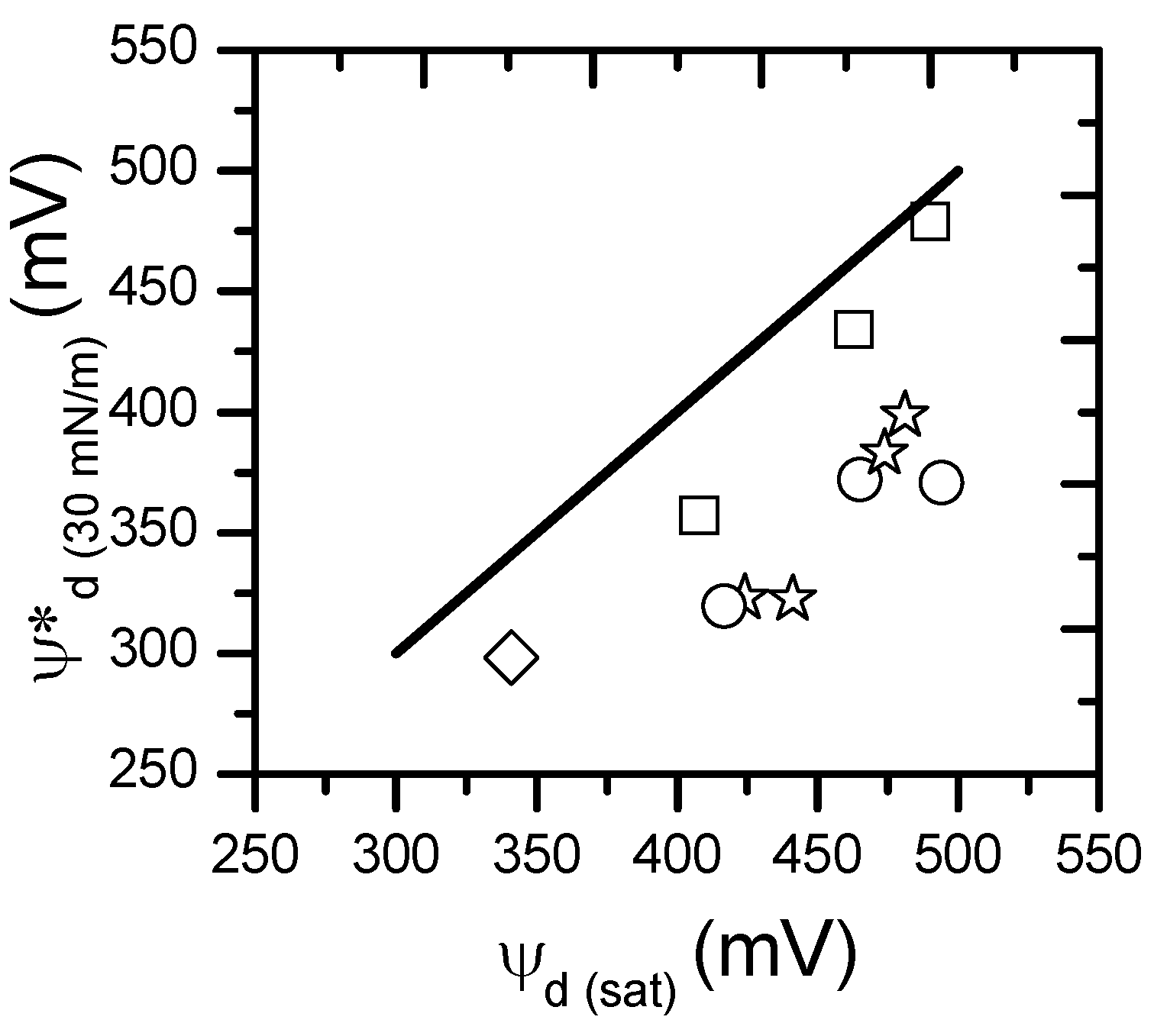
2.2. Dipole Potential in Lipid Monolayers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Monolayer Surface Pressure Experiments
4.3. Measurement of the Potential Difference across Lipid Monolayers
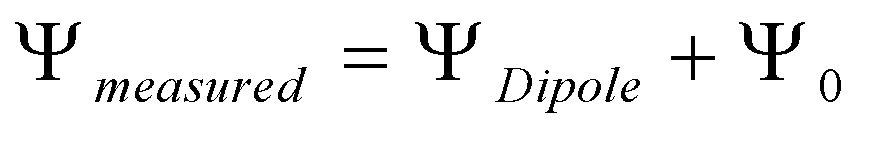 (2)
(2)
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McLaughlin, S. Electrostatic Potentials at Membrane-Solution Interfaces. In; Bronner, F., Kleinzeller, A., Eds.; Current Topics in Membranes and Transport; Academic Press, 1977; Vol. 9, pp. 71–144.
- Honig, B.H.; Hubbell, W.L.; Flewelling, R.F. Electrostatic Interactions In Membranes And Proteins. Annu Rev Biophys 1986, 15, 163–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, S. The Electrostatic Properties of Membranes. Annu Rev Biophys 1989, 18, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevc, G. Membrane Electrostatics. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Biomembranes 1990, 1031, 311–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, Y.A.; Topaly, V.P. Permeability Of Bimolecular Phospholipid Membranes For Fat-Soluble Ions. BIOPHYSICS-USSR 1969, 14, 477. [Google Scholar]
- Lairion, F.; Disalvo, E.A. Effect of Dipole Potential Variations on the Surface Charge Potential of Lipid Membranes. J Phys Chem B 2009, 113, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawrisch, K.; Ruston, D.; Zimmerberg, J.; Parsegian, V.A.; Rand, R.P.; Fuller, N. Membrane Dipole Potentials, Hydration Forces, and the Ordering of Water at Membrane Surfaces. Biophys J 1992, 61, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, M.A.; Cejas, J.P.; Rosa, A.S.; Disalvo, E.A. Relevance of Water in Biological Membranes. Chem Phys 2023, 566, 111784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, X. The Structure of Water Bonded to Phosphate Groups at the Electrified Zwitterionic Phospholipid Membranes/Aqueous Interface. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2020, 59, 6627–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.L.; Derreumaux, P.; Nguyen, P.H. Structure and Elasticity of Mitochondrial Membranes: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. J Phys Chem B 2023, 127, 10778–10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Lazaridis, T. Influence of the Membrane Dipole Potential on Peptide Binding to Lipid Bilayers. Biophys Chem 2012, 161, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cladera, J.; O’Shea, P. Intramembrane Molecular Dipoles Affect the Membrane Insertion and Folding of a Model Amphiphilic Peptide. Biophys J 1998, 74, 2434–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, R.M.S.; Martins, P.A.T.; Ramos, C. V; Cordeiro, M.M.; Leote, R.J.B.; Razi Naqvi, K.; Vaz, W.L.C.; Moreno, M.J. Effect of Dipole Moment on Amphiphile Solubility and Partition into Liquid Ordered and Liquid Disordered Phases in Lipid Bilayers. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2020, 1862, 183157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G. Dual Mechanism for the Action of Cholesterol on Membrane Permeability. Nature 1974, 252, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flewelling, R.F.; Hubbell, W.L. Hydrophobic Ion Interactions with Membranes. Thermodynamic Analysis of Tetraphenylphosphonium Binding to Vesicles. Biophys J 1986, 49, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, H.A.L.; Loura, L.M.S.; Moreno, M.J. Permeation of a Homologous Series of NBD-Labeled Fatty Amines through Lipid Bilayers: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Membranes (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchian, T.; Mereuta, L. Phlorizin- and 6-Ketocholestanol-Mediated Antagonistic Modulation of Alamethicin Activity in Phospholipid Planar Membranes. Langmuir 2006, 22, 8452–8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotelle-Bunner, A.; Beaunier, P.; Tandori, J.; Maroti, P.; Clarke, R.J.; Sebban, P. The Local Electric Field within Phospholipid Membranes Modulates the Charge Transfer Reactions in Reaction Centres. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 2009, 1787, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amazon, J.J.; Feigenson, G.W. Lattice Simulations of Phase Morphology on Lipid Bilayers: Renormalization, Membrane Shape, and Electrostatic Dipole Interactions. Phys Rev E 2014, 89, 22702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.J. Effect of Lipid Structure on the Dipole Potential of Phosphatidylcholine Bilayers. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1997, 1327, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bose, P.S.; Sigworth, F.J. Using Cryo-EM to Measure the Dipole Potential of a Lipid Membrane. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2006, 103, 18528–18533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almgren, M.; Gimel, J.C.; Wang, K.; Karlsson, G.; Edwards, K.; Brown, W.; Mortensen, K. SDS Micelles at High Ionic Strength. A Light Scattering, Neutron Scattering, Fluorescence Quenching, and CryoTEM Investigation. J Colloid Interface Sci 1998, 202, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.; Chattopadhyay, A. Membrane Dipole Potential: An Emerging Approach to Explore Membrane Organization and Function. J Phys Chem B 2022, 126, 4415–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockman, H. Dipole Potential of Lipid Membranes. Chem Phys Lipids 1994, 73, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, O.S.; Finkelstein, A.; Katz, I.; Cass, A. Effect of Phloretin on the Permeability of Thin Lipid Membranes. Journal of General Physiology 1976, 67, 749–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.C.; Cafiso, D.S. Internal Electrostatic Potentials in Bilayers: Measuring and Controlling Dipole Potentials in Lipid Vesicles. Biophys J 1993, 65, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, S.A.; McIntosh, T.J.; Magid, A.D.; Needham, D. Modulation of the Interbilayer Hydration Pressure by the Addition of Dipoles at the Hydrocarbon/Water Interface. Biophys J 1992, 61, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, T.J.; Magid, A.D.; Simon, S.A. Cholesterol Modifies the Short-Range Repulsive Interactions between Phosphatidylcholine Membranes. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaby, J.M.; Brockman, H.L.; Brown, R.E. Cholesterol’s Interfacial Interactions with Sphingomyelins and-Phosphatidylcholines: Hydrocarbon Chain Structure Determines the Magnitude of Condensation. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 9135–9142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlikowska-Rzeznik, H.; Versluis, J.; Bakker, H.J.; Piatkowski, L. Cholesterol Changes Interfacial Water Alignment in Model Cell Membranes. J Am Chem Soc 2024, 146, 13151–13162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Kamp, J.A.F. Lipid Asymmetry in Membranes. Annu Rev Biochem 1979, 48, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, P.F. Protein Involvement in Transmembrane Lipid. Annu Rev Biophys 1992, 21, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, J.E.; Lenard, J. Membrane Asymmetry. Science (1979) 1977, 195, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leidl, K.; Liebisch, G.; Richter, D.; Schmitz, G. Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Lipid Species of Human Circulating Blood Cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 2008, 1781, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodge, J.T.; Phillips, G.B. Composition of Phospholipids and of Phospholipid Fatty Acids and Aldehydes in Human Red Cells. J Lipid Res 1967, 8, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkleij, A.J.; Zwaal, R.F.A.; Roelofsen, B.; Comfurius, P.; Kastelijn, D.; van Deenen, L.L.M. The Asymmetric Distribution of Phospholipids in the Human Red Cell Membrane. A Combined Study Using Phospholipases and Freeze-Etch Electron Microscopy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1973, 323, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiessling, V.; Wan, C.; Tamm, L.K. Domain Coupling in Asymmetric Lipid Bilayers. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2009, 1788, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starke-Peterkovic, T.; Turner, N.; Vitha, M.F.; Waller, M.P.; Hibbs, D.E.; Clarke, R.J. Cholesterol Effect on the Dipole Potential of Lipid Membranes. Biophys J 2006, 90, 4060–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkovich, S.G.; Martinez-Seara, H.; Nesterenko, A.M.; Vattulainen, I.; Gurtovenko, A.A. What Can We Learn about Cholesterol’s Transmembrane Distribution Based on Cholesterol-Induced Changes in Membrane Dipole Potential? J Phys Chem Lett 2016, 7, 4585–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Deng, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.; Cen, C. Effect of Cholesterol on Membrane Dipole Potential: Atomistic and Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J Chem Theory Comput 2018, 14, 3780–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, V.; Domene, C. Stereospecific Interactions of Cholesterol in a Model Cell Membrane: Implications for the Membrane Dipole Potential. J Membr Biol 2018, 251, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.J. Effect of Cholesterol on the Dipole Potential of Lipid Membranes. In Cholesterol Modulation of Protein Function: Sterol Specificity and Indirect Mechanisms; Rosenhouse-Dantsker, A., Bukiya, A.N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; ISBN 978-3-030-04278-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zakany, F.; Kovacs, T.; Panyi, G.; Varga, Z. Direct and Indirect Cholesterol Effects on Membrane Proteins with Special Focus on Potassium Channels. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 2020, 1865, 158706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, P.T.; Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Vaz, W.L.C.; Cardoso, R.M.S.; Valério, J.; Moreno, M.J. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Chlorpromazine Interaction with Lipid Bilayers: Effect of Charge and Cholesterol. J Am Chem Soc 2012, 134, 4184–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, J.L.; Moreno, M.J.; Vaz, W.L.C. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Association of a Fluorescent Lysophospholipid Derivative with Lipid Bilayers in Liquid-Ordered and Liquid-Disordered Phases. Biophys J 2005, 88, 4064–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coreta-Gomes, F.M.; Vaz, W.L.C.; Moreno, M.J. Effect of Acyl Chain Length on the Rate of Phospholipid Flip-Flop and Intermembrane Transfer. J Membr Biol 2018, 251, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Filipe, H.A.L.; Geraldes, C.F.G.C.; Voth, G.A.; Moreno, M.J.; Loura, L.M.S. Interaction of MRI Contrast Agent [Gd(DOTA)]− with Lipid Membranes: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Inorg Chem 2024, 63, 10897–10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, M.M.; Filipe, H.A.L.; Santos, P. dos; Samelo, J.; Ramalho, J.P.P.; Loura, L.M.S.; Moreno, M.J. Interaction of Hoechst 33342 with POPC Membranes at Different PH Values. Molecules 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães, N.; Simões, G.M.; Ramos, C.; Samelo, J.; Oliveira, A.C.; Filipe, H.A.L.; Ramalho, J.P.P.; Moreno, M.J.; Loura, L.M.S. Interactions between Rhodamine Dyes and Model Membrane Systems—Insights from Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estronca, L.M.B.B.; João Moreno, M.; Abreu, M.S.C.; Melo, E.; Vaz, W.L.C. Solubility of Amphiphiles in Membranes: Influence of Phase Properties and Amphiphile Head Group. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002, 296, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejas, J. del P.; Rosa, A.S.; González Paz, A.N.; Disalvo, E.A.; Frías, M. de los A. Impact of Chlorogenic Acid on Surface and Phase Properties of Cholesterol-Enriched Phosphatidylcholine Membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys 2024, 753, 109913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.; Nguyen, M.-A.; Koner, S.; Freeman, E.; Collier, C.P.; Sarles, S.A. Electrophysiological Interrogation of Asymmetric Droplet Interface Bilayers Reveals Surface-Bound Alamethicin Induces Lipid Flip-Flop. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2019, 1861, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, L.; Zhu, M.; Cheng, X.; Jiang, X. Effect of Dipole Potential on the Orientation of Voltage-Gated Alamethicin Peptides Regulated by Chaotropic Anions. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 2022, 904, 115880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos, A.M.; Blázquez-Sánchez, M.T.; Sousa, C.; Oliveira, M.C.; de Almeida, R.F.M.; Rauter, A.P. C-Glucosylation as a Tool for the Prevention of PAINS-Induced Membrane Dipole Potential Alterations. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohl, E.E.; Krylov, A. V; Block, M.; Pohl, P. Changes of the Membrane Potential Profile Induced by Verapamil and Propranolol. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1998, 1373, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafiso, D.S. Dipole Potentials and Spontaneous Curvature: Membrane Properties That Could Mediate Anesthesia. Toxicol Lett 1998, 100–101, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, T.O.; Bastos, A.E.P.; Marquês, J.T.; Viana, A.S.; Lima, P.A.; de Almeida, R.F.M. M-Cresol Affects the Lipid Bilayer in Membrane Models and Living Neurons. RSC Adv 2016, 6, 105699–105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.J. Dipole-Potential-Mediated Effects on Ion Pump Kinetics. Biophys J 2015, 109, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, B. Modulation of Phospholipase A2 by Electrostatic Fields and Dipole Potential of Glycosphingolipids in Monolayers. J Lipid Res 1999, 40, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, D. Lateral Pressure in Membranes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Biomembranes 1996, 1286, 183–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantzsch, G.; Binder, H.; Heerklotz, H. Surface Area per Molecule in Lipid/C12Enmembranes as Seen by Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer. J Fluoresc 1994, 4, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, B.; Dietrich, U.; Klose, G. Hydration and Structural Properties of Mixed Lipid/Surfactant Model Membranes. Langmuir 1997, 13, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Monticelli, L.; Tieleman, D.P. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of a Palmitoyl-Oleoyl Phosphatidylserine Bilayer with Na+ Counterions and NaCl. Biophys J 2004, 86, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand, R.P.; Parsegian, V.A. Hydration Forces between Phospholipid Bilayers. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Biomembranes 1989, 988, 351–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaby, J.M.; Momsen, M.M.; Brockman, H.L.; Brown, R.E. Phosphatidylcholine Acyl Unsaturation Modulates the Decrease in Interfacial Elasticity Induced by Cholesterol. Biophys J 1997, 73, 1492–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaby, J.M.; Brockman, H.L. Surface Dipole Moments of Lipids at the Argon-Water Interface. Similarities among Glycerol-Ester-Based Lipids. Biophys J 1990, 58, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, R.C.; Simon, S.A. Lipid Monolayer States and Their Relationships to Bilayers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1987, 84, 4089–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.M.; De Oliveira, O.N.; Morgan, H. Models for Interpreting Surface Potential Measurements and Their Application to Phospholipid Monolayers. J Colloid Interface Sci 1990, 139, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, R.C.; Simon, S.A.; Baer, E. Ionic Influences on the Phase Transition of Dipalmitoylphosphatidylserine. Biochemistry 1976, 15, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Palaiokostas, M.; Wang, W.; Orsi, M. Effects of Lipid Composition on Bilayer Membranes Quantified by All-Atom Molecular Dynamics. J Phys Chem B 2015, 119, 15263–15274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, T.J.; Simon, S.A.; Needham, D.; Huang, C.H. Interbilayer Interactions between Sphingomyelin and Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Bilayers. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 2020–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund-Katz, S.; Laboda, H.M.; McLean, L.R.; Phillips, M.C. Influence of Molecular Packing and Phospholipid Type on Rates of Cholesterol Exchange. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 3416–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahane, G.; Ding, W.; Palaiokostas, M.; Orsi, M. Physical Properties of Model Biological Lipid Bilayers: Insights from All-Atom Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J Mol Model 2019, 25, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, T.J.; Simon, S.A.; Needham, D.; Huang, C.H. Structure and Cohesive Properties of Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Bilayers. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 2012–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemelä, P.; Hyvönen, M.T.; Vattulainen, I. Structure and Dynamics of Sphingomyelin Bilayer: Insight Gained through Systematic Comparison to Phosphatidylcholine. Biophys J 2004, 87, 2976–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.W.; Vasudevan, S.; Jakobsson, E.; Mashl, R.J.; Scott, H.L. Structure of Sphingomyelin Bilayers: A Simulation Study. Biophys J 2003, 85, 3624–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevc, G.; Watts, A.; Marsh, D. Titration of the Phase Transition of Phosphatidylserine Bilayer Membranes. Effects of PH, Surface Electrostatics, Ion Binding, and Head-Group Hydration. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 4955–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, F.C.; Ojcius, D.M.; Hubbell, W.L. The Intrinsic PKa Values for Phosphatidylserine and Phosphatidylethanolamine in Phosphatidylcholine Host Bilayers. Biophys J 1986, 49, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelig, A. Local Anesthetics and Pressure: A Comparison of Dibucaine Binding to Lipid Monolayers and Bilayers. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1987, 899, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, A. A Comparative Study of the Phase Transitions of Phospholipid Bilayers and Monolayers. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1979, 557, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demel, R.A.; Geurts van Kessel, W.S.M.; Zwaal, R.F.A.; Roelofsen, B.; van Deenen, L.L.M. Relation between Various Phospholipase Actions on Human Red Cell Membranes and the Interfacial Phospholipid Pressure in Monolayers. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1975, 406, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paré, C.; Lafleur, M. Polymorphism of POPE/Cholesterol System: A 2H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Infrared Spectroscopic Investigation. Biophys J 1998, 74, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohvo-Rekilä, H.; Ramstedt, B.; Leppimäki, P.; Peter Slotte, J. Cholesterol Interactions with Phospholipids in Membranes. Prog Lipid Res 2002, 41, 66–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sostarecz, A.G.; McQuaw, C.M.; Ewing, A.G.; Winograd, N. Phosphatidylethanolamine-Induced Cholesterol Domains Chemically Identified with Mass Spectrometric Imaging. J Am Chem Soc 2004, 126, 13882–13883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, R.; Hall, J.E. Dipole Potential Measurements in Asymmetric Membranes. Nature 1976, 264, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurtovenko, A.A.; Vattulainen, I. Lipid Transmembrane Asymmetry and Intrinsic Membrane Potential: Two Sides of the Same Coin. J Am Chem Soc 2007, 129, 5358–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubay, G. Biochemistry; 3rd ed.; William C Brown: Dubuque, Iowa, 1993.
- Schlegel, R.A.; Williamson, P. Phosphatidylserine, a Death Knell. Cell Death Differ 2001, 8, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzardo, M. del C.; Peltzer, G.; Disalvo, E.A. Surface Potential of Lipid Interfaces Formed by Mixtures of Phosphatidylcholine of Different Chain Lengths. Langmuir 1998, 14, 5858–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ). The lines are a guide to
the eye.
). The lines are a guide to
the eye.
 ). The lines are a guide to
the eye.
). The lines are a guide to
the eye.
 , (b). The line is
the best fit of a polynomial equation for areas smaller than 100 Å2
in the liquid expanded state.
, (b). The line is
the best fit of a polynomial equation for areas smaller than 100 Å2
in the liquid expanded state.
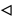 , (b). The line is
the best fit of a polynomial equation for areas smaller than 100 Å2
in the liquid expanded state.
, (b). The line is
the best fit of a polynomial equation for areas smaller than 100 Å2
in the liquid expanded state.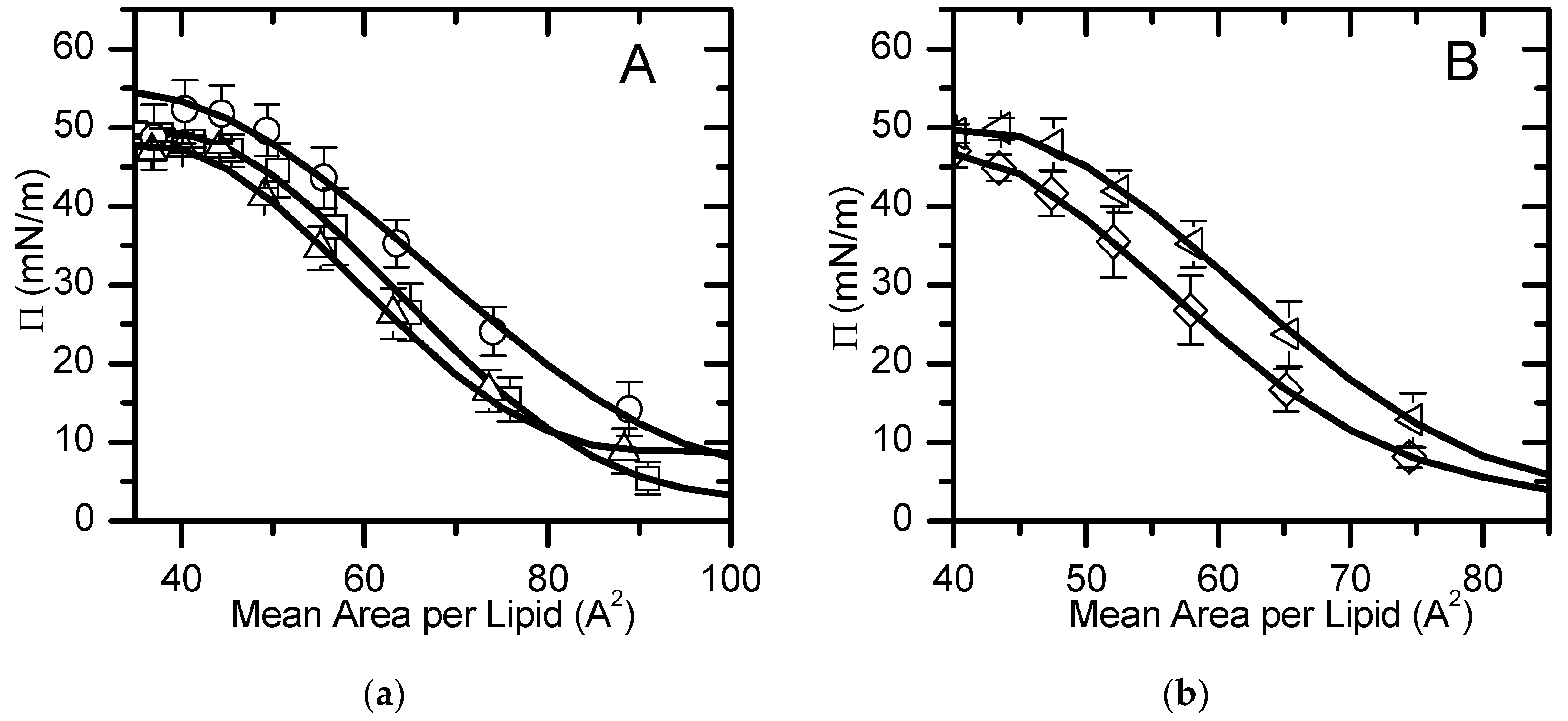
| Area per lipid at π = 30 mN/m (Å2) | Area per lipid at πsat (Å2) | Saturation Pressure (mN/m) | Dipole Potential at πsat (mV) | |
| POPC | 64.5 | 49.4±3.4 | 50 | 417±12 |
| POPS | 55.0a | 44f | - | 465±4.2e |
| POPE | 56.0b | 42f | - | 494±16 |
| SPM | 48.0c | 42c | - | 341±7.1 |
| POPC:POPS (9:1) | 69.8 | 51.0±4.0 | 51 | 441±2.5e |
| POPC:POPE (8:2) | 59.6 | 45.4±3.0 | 47 | 424±15 |
| POPC:CHOL (7:3) | 48.0d | 45d | - | 463±6.9 |
| POPC:CHOL (5:5) | 44.0d | 43d | - | 490±5.7 |
| POPC:CHOL:POPE (5:3:2) | 56.0 | 46.4±2.7 | 46 | 481±1.4 |
| POPC:CHOL:POPE:POPS (4:3:2:1) Inner | 61.5 | 49.7±2.6 | 49 | 474±11e |
| SPM:CHOL (6:4)outer | 39.0 c | - | - | 408±6.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





