Submitted:
30 September 2024
Posted:
01 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Questions
- How are digital technologies being used or adopted in different industries (such as manufacturing, healthcare, etc.)?
- What are the key digital technologies and channels that have significantly impacted competitive advantage in recent years?
- What are the obstacles preventing SMEs from adopting digital technologies?
- What are the measurable performance metrics used to evaluate the effectiveness of digital technologies?
- How will the long-term adoption of digital technologies impact societal structures, particularly in terms of workforce transformation, privacy, and digital inequality, and what regulatory measures are necessary to mitigate these challenges?
1.2. Research Motivation
1.3. Research Novelty
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources
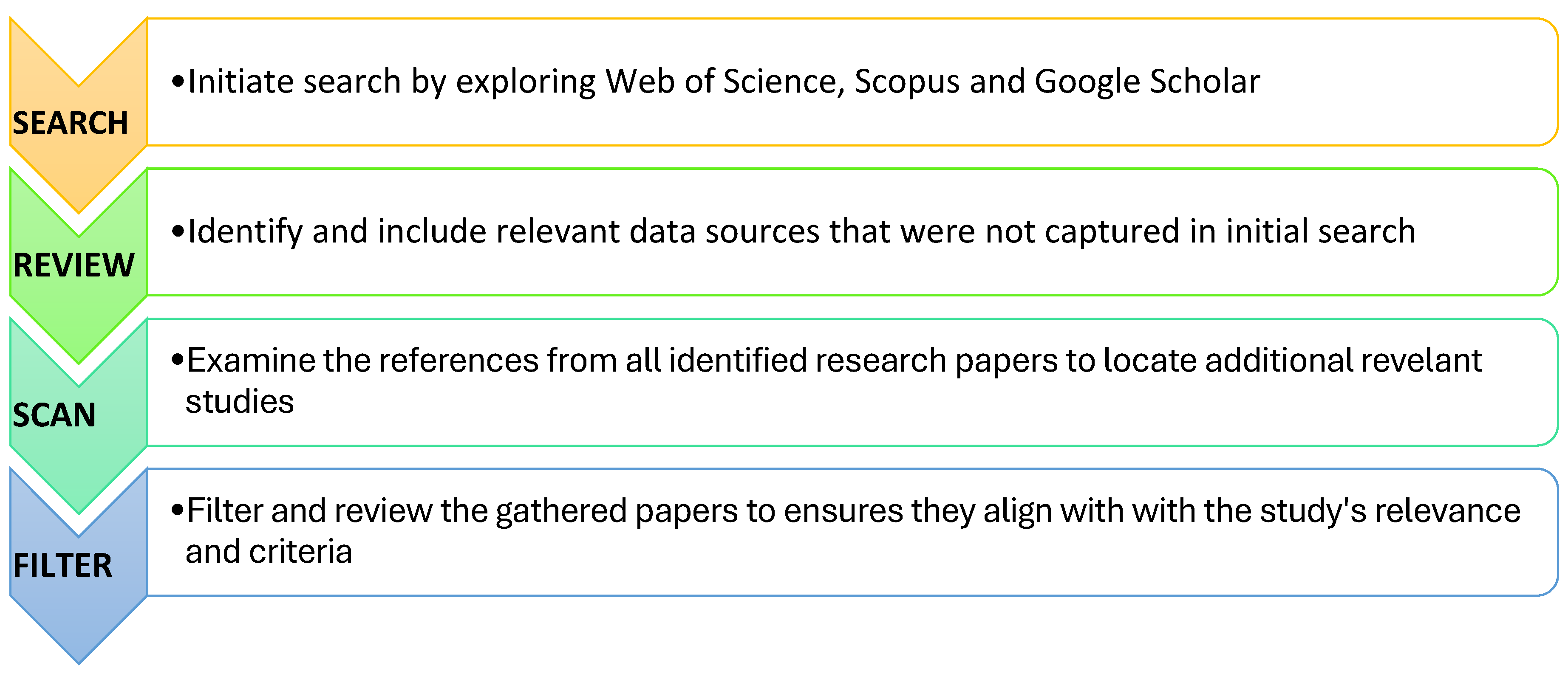
2.3. Search Strategy
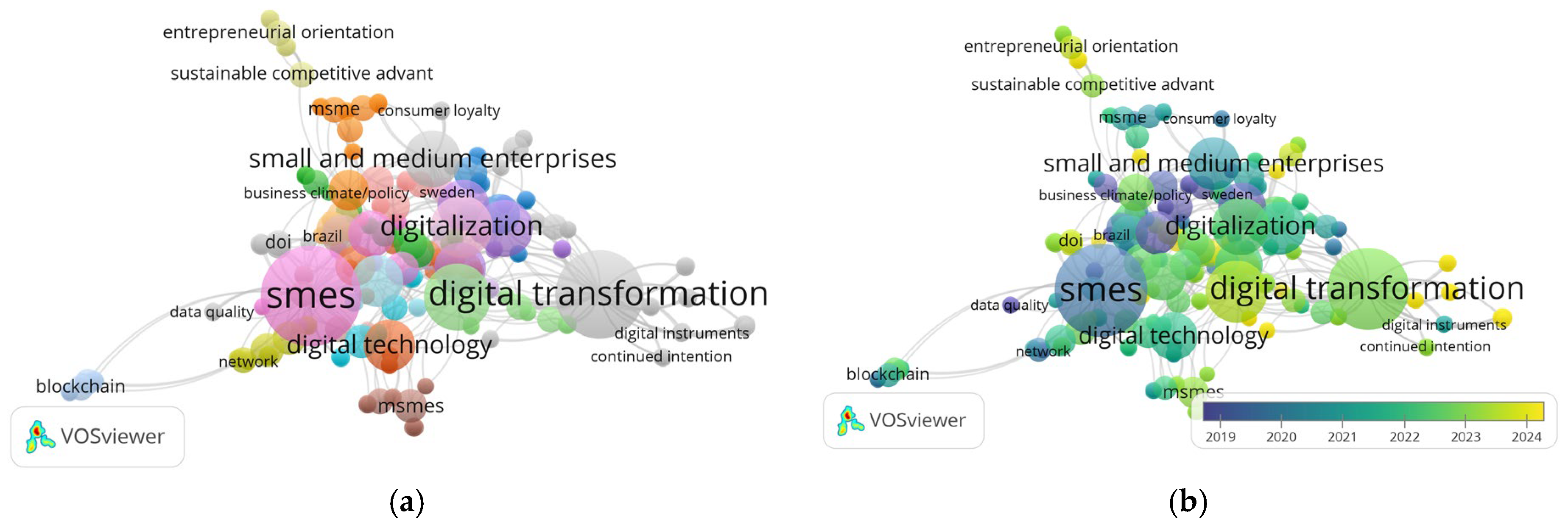
2.4. Selection Process
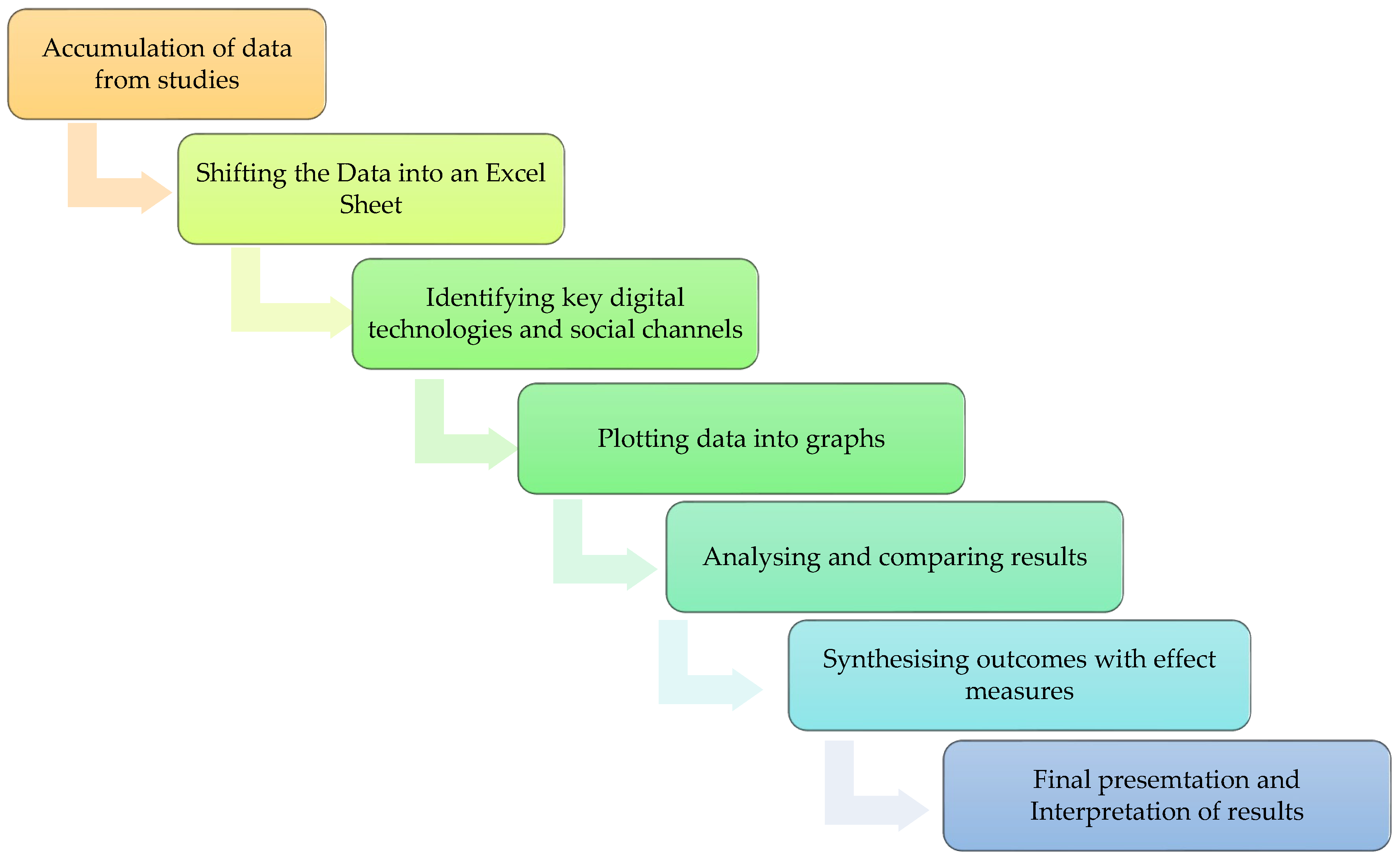
2.5. Data Collection Process
2.6. Data Items
2.7. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.8. Effect Measures
2.9. Synthesis Methods
2.10. Reporting Bias Assessment
2.11. Certainty Assessment
| Paper ID | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Total | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [15] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 100% |
| [16] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
| [17] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
| [18] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 100% |
| [19] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
| [20] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
| [21] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
| [22] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
| [23] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 100% |
| [24] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 100% |
| …. | …. | …. | …. | …. | …. | …. | …. | …. |
| …. | …. | …. | …. | …. | …. | …. | …. | …. |
| [52] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 100% |
| [53] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 100% |
| [54] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 100% |
| [55] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 100% |
| [56] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
| [57] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
| [58] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
| [59] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
| [60] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
| [61] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 91.67% |
3. Results
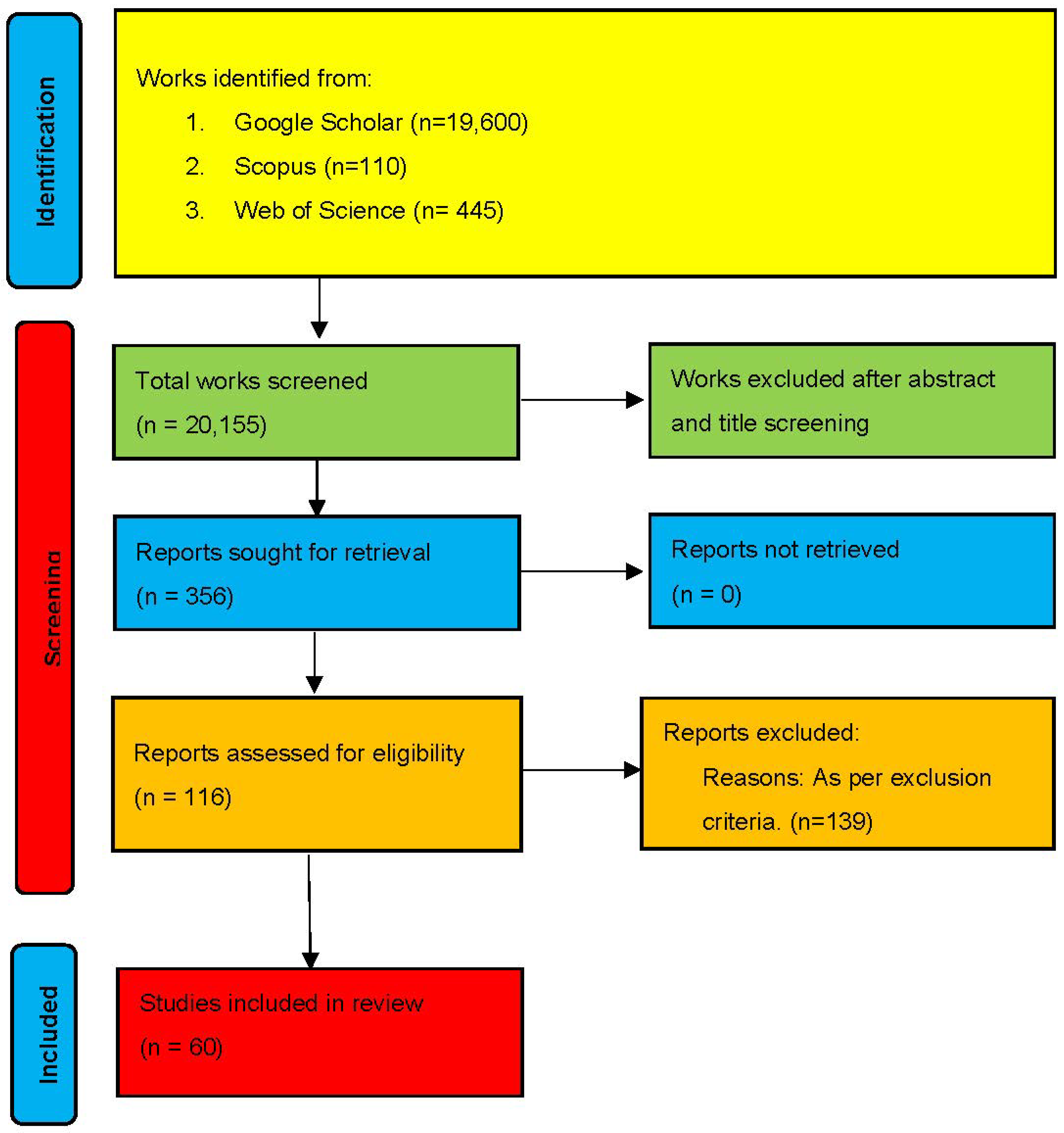
3.1. Study Selection
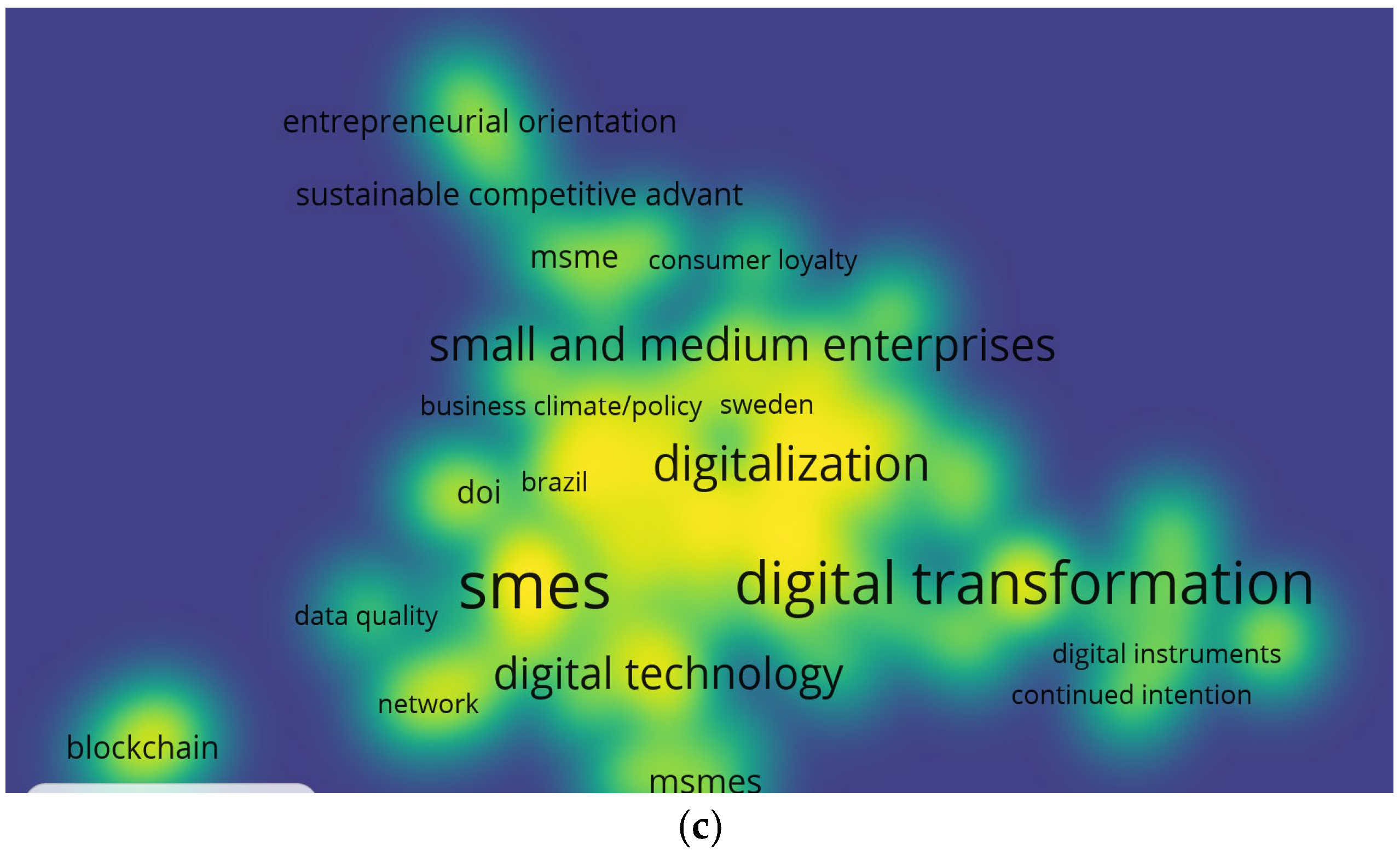
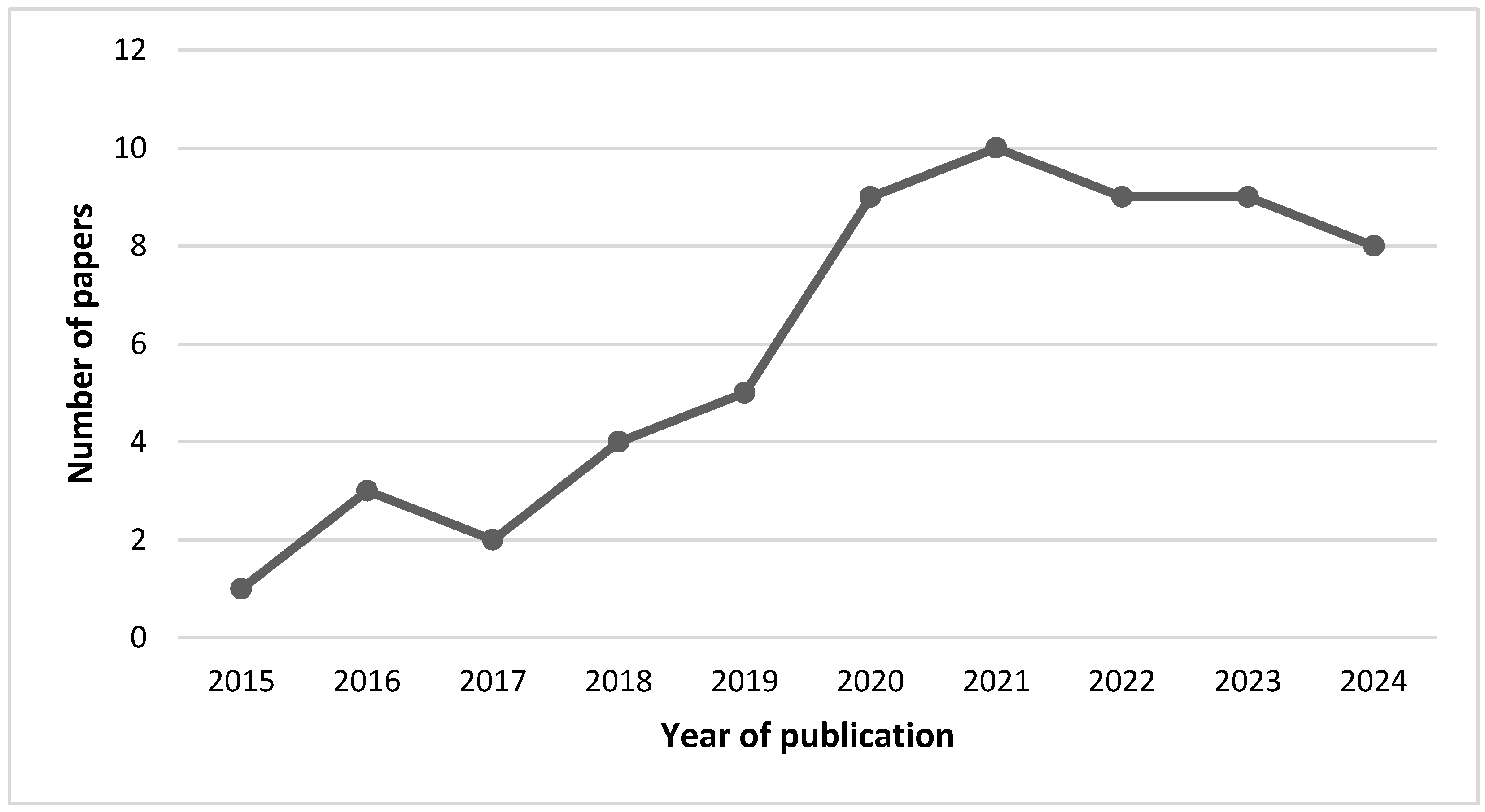
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
3.5. Results of Synthesis
3.5.1. Study Characteristics and Bias Assessment
3.5.2. Statistical Syntheses
3.5.3. Statistical Syntheses
3.5.4. Sensitivity Analyses
3.6. Reporting Biases
3.7. Certainty of Evidence
4. Discussion
- RQ 1: How are digital technologies being used or adopted in different industries (such as manufacturing, healthcare etc.)?
- RQ 2: What are the key digital technologies and channels that have significantly impacted competitive advantage in recent years?
- RQ 3: What are the obstacles preventing SMEs from adopting digital technologies?
- RQ 4: What are the measurable performance metrics used to evaluate the effectiveness of digital technologies?
- RQ 5: How will the long-term adoption of digital technologies impact societal structures, particularly in terms of workforce transformation, privacy, and digital inequality, and what regulatory measures are necessary to mitigate these challenges?
5. Real-World Case Studies in Digital Transformation for SMEs and Large Enterprises
Case 1: Pakistan’s SME Adoption of IoT and Big Data Analytics for Value Creation
Case 2: AI-Driven Innovations in Indian SMEs
Case 3: Netflix and AWS for Scalability
Case 4: MakeMyTrip’s Cost Optimization Using AWS
Case 5: Domino’s Pizza and Azure Cloud for Customer Experience
Case 6: Airbnb’s Cloud-Based Infrastructure
Case 7: Zapier: A Remote Work Success with Cloud and Collaboration Tools
Case 8: Amazon’s IoT-Powered Warehousing
Case 9: General Electric’s Predix Platform on AWS
6. Practical Implications for Decision-Makers
7. Decision-Making Framework for Implementing Proposed Study Topic
8. Best Practices for Successful Implementation
9. Metrics and KPIs for Measuring Study Topic Performance
11. Roadmap for SMEs Businesses and Policy Recommendations
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kraus, S.; Jones, P.; Kailer, N.; Weinmann, A.; Banegas, N.C.; Tierno, N.R. Digital Transformation: An Overview of the Current State of the Art of Research. SAGE Open 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-gharbawy, H.M.S.; Ragab, A.A.; Ragheb, M.A.; Farouk, M. The Effect of Information Technology on Innovative Performance with Mediation Role of Process Innovation Capability: Evidence from Egyptian SMEs. J. Bus. Manag. Sci. 2024, 12, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, E.C.; Soriano, D.R. The Role of Digitalization in Business and Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2023, 18, 449–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, G. Understanding Digital Transformation: A Review and a Research Agenda. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2021, 28, 118–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, A.; El Sawy, O.A.; Pavlou, P.A.; Venkatraman, N. Digital Business Strategy: Toward a Next Generation of Insights. MIS Q. 2013, 37, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, P.; Nwankpa, J.K. Digital Transformation and the COVID-19 Crisis Continuity Planning. ResearchGate Mar. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350187882_Digital_transformation_and_the_COVID-19_crisis_continuity_planning.
- Behl, A.; Gaur, J.; Pereira, V.; Yadav, R.; Laker, B. Role of Big Data Analytics Capabilities to Improve Sustainable Competitive Advantage of MSME Service Firms during COVID-19 – A Multi-Theoretical Approach. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 148, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bughin, J.; Hazan, E.; Ramaswamy, S.; Allas, T.; Dahlstrom, P.; Henke, N.; Trench, M. Artificial Intelligence: The Next Digital Frontier. McKinsey Global Institute, 2017. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=3043572.
- Davenport, T.H. Competing on Analytics. ResearchGate. 2006. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7327312_Competing_on_Analytics.
- Grewal, D.; Roggeveen, A.L.; Nordfält, J. The Future of Retailing. J. Retailing 2017, 93, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtner, S.; Reinhardt, R. Ambidextrous Idea Generation-Antecedents and Outcomes. J. Product Innov. Manag. 2016, 33, 34–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamba, S.F. Research Directions on the Adoption, Usage, and Impact of the Internet of Things through the Use of Big Data Analytics. 2015 48th Hawaii Int. Conf. Syst. Sci., 2015. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/29640377/Research_Directions_on_the_Adoption_Usage_and_Impact_of_the_Internet_of_Things_through_the_Use_of_Big_Data_Analytics (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- How Big Old Companies Navigate Digital Transformation. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319929433_How_big_old_companies_navigate_digital_transformation (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Teece, D.J. Business Models and Dynamic Capabilities. Long Range Planning 2018, 51, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, H.; Lu, L.; Ma, G.; Gao, X. How Firms Cope with Social Crisis: The Mediating Role of Digital Transformation as a Strategic Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic. PLOS ONE 2023, 18, e0282854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, Z.; Radulescu, M.; Sinisi, C.I.; Serbanescu, L.; Păunescu, L.M. Towards Sustainable Digital Innovation of SMEs from the Developing Countries in the Context of the Digital Economy and Frugal Environment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.M.S. Do Industry 4.0 Technologies Improve Cantabrian Manufacturing SMEs Performance? The Role Played by Industry Competition. Aug. 2022. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160791X22001609?via%3Dihub.
- Alaskari, O.; Pinedo-Cuenca, R.; Ahmad, M.M. Framework for Implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): A Case Study. Procedia Manufacturing 2021, 55, 424–430. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2351978921002559. [CrossRef]
- Peretz-Andersson, E.; Tabares, S.; Mikalef, P.; Parida, V. Artificial Intelligence Implementation in Manufacturing SMEs: A Resource Orchestration Approach. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2024, 77, 102781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marneros, S.; Papageorgiou, G.; Efstathiades, A. Sustainability Management, Technological Innovation and Corporate Social Responsibility for Social Media Small to Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs). Eur. Conf. Innov. Entrep. 2023, 18, 571–579. Available online: https://papers.academic-conferences.org/index.php/ecie/article/view/1848 (accessed on 6 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Skare, M.; de las Mercedes de Obesso, M.; Ribeiro-Navarrete, S. Digital Transformation and European Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): a Comparative Study Using Digital Economy and Society Index Data. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2023, 68, 102594. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0268401222001281. [CrossRef]
- Sjachriatin, E.; Riyadi, S.; Mujanah, S. The Effects of Knowledge-Oriented Leadership Style, Digital Transformation, and Human Resource Development on Sustainable Competitive Advantage in East Java MSMEs. Uncertain Supply Chain Manag. 2023, 11, 1685–1694. Available online: https://growingscience.com/beta/uscm/6305-the-effects-of-knowledge-oriented-leadership-style-digital-transformation-and-human-resource-development-on-sustainable-competitive-advantage-in-east-java-msmes.html (accessed on 6 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Al-shanableh, N.; et al. The Adoption of Big Data Analytics in Jordanian SMEs: An Extended Technology Organization Environment Framework with Diffusion of Innovation and Perceived Usefulness. Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 2024, 8, 753–764. Available online: https://growingscience.com/beta/ijds/6661-the-adoption-of-big-data-analytics-in-jordanian-smes-an-extended-technology-organization-environment-framework-with-diffusion-of-innovation-and-perceived-usefulness.html (accessed on 6 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Heckelei, T.; Gerullis, M.K.; Börner, J.; Rasch, S. Adoption and Diffusion of Digital Farming Technologies - Integrating Farm-Level Evidence and System Interaction. Agric. Syst. 2021, 190, 103074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Wu, Z.; Yang, F. Research on the Relationship between Digital Transformation and Performance of SMEs. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham Quang Huy; Vu, Phuc Kien. Big Data in Relation with Business Intelligence Capabilities and E-Commerce during COVID-19 Pandemic in Accountant’s Perspective. Fut. Bus. J. 2023, 9. [CrossRef]
- Belitski, M.; Liversage, B. E-Leadership in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in the Developing World. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2019, 9, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, S.S.; Samantha, T. Social Media Adoption: Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises’ Perspective in Sri Lanka. J. Asian Finance Econ. Bus. 2021, 8, 759–766. Available online: http://ir.lib.seu.ac.lk/bitstream/123456789/5249/1/Social%20Media%20Adoption-%20Small%20and%20Medium-sized%20Enterprises%27%20Perspective%20in%20Sri%20Lanka.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Hojnik, B.B.; Huđek, I. Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in the Digital Age: Understanding Characteristics and Essential Demands. Inf. 2023, 14, 606. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2078-2489/14/11/606. [CrossRef]
- Makanyeza, C.; Dzvuke, G. The Influence of Innovation on the Performance of Small and Medium Enterprises in Zimbabwe. J. Afr. Bus. 2015, 16, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, A.; et al. The Role of Digital Technologies in Supporting the Implementation of Circular Economy Practices by Industrial Small and Medium Enterprises. Bus. Strat. Environ. 2023, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE.org. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=9765158 (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- IEEE.org. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=8372725 (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- Adam, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Ikramuddin, I.; Syahputra, H. The Role of Digital Marketing Platforms on Supply Chain Management for Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) at Indonesia. Int. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2020, 9, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Haseeb, M.; Hussain, H.I.; Kot, S.; Androniceanu, A.; Jermsittiparsert, K. Role of Social and Technological Challenges in Achieving a Sustainable Competitive Advantage and Sustainable Business Performance. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiu, S.; Ngobeni, M.; Mathabela, L.; Thango, B. Applications and Competitive Advantages of Data Mining and Business Intelligence in SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eller, R.; Alford, P.; Kallmünzer, A.; Peters, M. Antecedents, Consequences, and Challenges of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprise Digitalization. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 112, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, S.; Durst, S.; Ferreira, J.J.; Veiga, P.; Kailer, N.; Weinmann, A. Digital Transformation in Business and Management Research: An Overview of the Current Status Quo. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2022, 63, 102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroudi, P.; Gupta, S.; Duda, M. Digital Technology and Marketing Management Capability: Achieving Growth in SMEs. Available online: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/QMR-01-2017-0014/full/pdf (accessed on 10 February 2017).
- Radicic, D.; Petković, S. Impact of Digitalization on Technological Innovations in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs). Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 191, 122474. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040162523001592. [CrossRef]
- Cenamor, J.; Parida, V.; Wincent, J. How Entrepreneurial SMEs Compete through Digital Platforms: The Roles of Digital Platform Capability, Network Capability and Ambidexterity. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 100, 196–206. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0148296319302188?via%3Dihub. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yan, D.; Umair, M. Assessing the Role of Competitive Intelligence and Practices of Dynamic Capabilities in Business Accommodation of SMEs. Econ. Anal. Policy 2022, 77. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0313592622002089. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Caro, E.; Cegarra-Navarro, J.G.; Alfonso-Ruiz, F.J. Digital Technologies and Firm Performance: The Role of Digital Organisational Culture. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 154, 119962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, W.A. Digital Marketing Competencies as a Factor in the Success of E-Commerce Small Businesses in International Markets. IEEE Xplore 2022. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10041460 (accessed on 1 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Rumengan, A.; Rumengan, J.; Wibisono, C.; Bambang, W.; Otok, B. Structural Equation Modeling in Business Performance through Competitive Advantage with Information Technology as Moderating. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. (IJMET) 2018, 9, 632–644. Available online: https://iaeme.com/MasterAdmin/Journal_uploads/IJMET/VOLUME_9_ISSUE_10/IJMET_09_10_066.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2024).
- Chan, C.M.L.; Teoh, S.Y.; Yeow, A.; Pan, G. Agility in Responding to Disruptive Digital Innovation: Case Study of an SME. Inf. Syst. J. 2018, 29, 436–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, D.; Szabó, R. Zs. Driving Forces and Barriers of Industry 4.0: Do Multinational and Small and Medium-Sized Companies Have Equal Opportunities? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 146, 119–132. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040162518315737. [CrossRef]
- Scuotto, V.; Nicotra, M.; Del Giudice, M.; Krueger, N.; Gregori, G.L. A Microfoundational Perspective on SMEs’ Growth in the Digital Transformation Era. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 129, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troise, C.; Corvello, V.; Ghobadian, A.; O’Regan, N. How Can SMEs Successfully Navigate VUCA Environment: The Role of Agility in the Digital Transformation Era. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 174, 121227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhize, A.; Mokhothu, K.; Tshikhotho, M.; Thango, B. Evaluating the Impact of Cloud Computing on SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Su, F.; Zhang, W.; Mao, J.-Y. Digital Transformation by SME Entrepreneurs: A Capability Perspective. Inf. Syst. J. 2018, 28, 1129–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulia, M.R. Digital Competencies and Experience in Partnership Program on SMEs Performance. J. Res. Soc. Sci. Econ. Manag. 2023, 2, 1416–1425. Available online: https://jrssem.publikasiindonesia.id/index.php/jrssem/article/view/385/1014 (accessed on 16 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.-W.; Leong, L.-Y.; Hew, J.-J.; Tan, G.W.-H.; Ooi, K.-B. Time to Seize the Digital Evolution: Adoption of Blockchain in Operations and Supply Chain Management among Malaysian SMEs. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 52, 101997. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0268401219304347. [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.-H.; Foo, A.T.-L.; Leong, L.-Y.; Ooi, K.-B. Can Competitive Advantage Be Achieved through Knowledge Management? A Case Study on SMEs. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 65, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farida, I.; Setiawan, D. Business Strategies and Competitive Advantage: The Role of Performance and Innovation. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2022, 8, 163. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2199853122007648. [CrossRef]
- Chinakidzwa, M.; Phiri, M. Impact of Digital Marketing Capabilities on Market Performance of Small to Medium Enterprise Agro-Processors in Harare, Zimbabwe. Bus. Theory Pract. 2020, 21, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, T.; Sonntag, P. Industry 4.0: Adoption Challenges and Benefits for SMEs. Comput. Ind. 2020, 121, 103261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovska, I.; Josimovski, S.; Edwards, C. Digital Channels Diminish SME Barriers: The Case of the UK. Econ. Res.-Ekon. Istraživanja 2016, 29, 217–232. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/1331677X.2016.1164926. [CrossRef]
- Pramono, R.; Sondakh, L.W.; Bernarto, I.; Juliana, J.; Purwanto, A. Determinants of the Small and Medium Enterprises Progress: A Case Study of SME Entrepreneurs in Manado, Indonesia. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2021, 8, 881–889. Available online: https://www.koreascience.or.kr/article/JAKO202100569459356.page. [CrossRef]
- Priyono, A.; Moin, A.; Putri, V.N.A.O. Identifying Digital Transformation Paths in the Business Model of SMEs during the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 6, 104. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2199-8531/6/4/104. [CrossRef]
- Kgakatsi, M.; Galeboe, O.; Molelekwa, K.; Thango, B. The Impact of Big Data on SME Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B. Lean Principles, Practices, and Impacts: A Study on Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs). Ann. Oper. Res. 2012, 241, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah. Linking Social Media Usage and SME’s Sustainable Performance: The Role of Digital Leadership and Innovation Capabilities. Technol. Soc. 2022, 68. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/a/eee/teinso/v68y2022ics0160791x22000410.html (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- Bouncken, R.; Schmitt, F. SME Family Firms and Strategic Digital Transformation: Inverting Dualisms Related to Overconfidence and Centralization. J. Small Bus. Strateg. 2022, 32, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Saarikko, T.; Westergren, U.H.; Blomquist, T. Digital Transformation: Five Recommendations for the Digitally Conscious Firm. Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 825–839. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0007681320300975. [CrossRef]
- Molete, O.B.; Mokhele, S.E.; Ntombela, S.D.; Thango, B.A. The Impact of IT Strategic Planning Process on SME Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardito, L.; Raby, S.; Albino, V.; Bertoldi, B. The Duality of Digital and Environmental Orientations in the Context of SMEs: Implications for Innovation Performance. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 123, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adwan, S.; Saleem, A.; et al. The Adoption of Digital Technologies by Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises for Sustainability and Value Creation in Pakistan. Sustain. 2024. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/16/17/7351.
- Vrontis, D.; Chaudhuri, R.; Chatterjee, S. Adoption of Digital Technologies by SMEs for Sustainability and Value Creation: Moderating Role of Entrepreneurial Orientation. Sustain. 2022. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/13/7949. [CrossRef]
- Toromade, A.S.; Chiekezie, N.R. Driving sustainable business practices in SMEs: Innovative approaches for environmental and economic synergy. Int. J. Manag. Entrep. Res. 2024, 6, 2637–2647. Available online: https://fepbl.com/index.php/ijmer/article/view/1411 (accessed on 16 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.; Marques, J. Value Creation in Technology-Driven Ecosystems: Role of Coopetition in Industrial Networks. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commerce Res. 2024, 19, 2343–2359. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/0718-1876/19/3/113#:~:text=The%20Service%2DDominant%20Logic%20(S%2DD%20Logic)%20literature%2C%20which (accessed on 12 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Mothapo, M.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Tracking and Measuring Social Media Activity: Key Metrics for SME Strategic Success – A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, S. The Role of Digital Marketing in Small Business Success in India. Tuijin Jishu/Journal Propulsion Technol. 2024, 45, 443–449. Available online: https://www.propulsiontechjournal.com/index.php/journal/article/view/7191 (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Aslam, W.; Gasmi, S. The Role of Academic Technology Entrepreneurship in Technopreneur Development: A Focus on SMEs Adoption of E-Commerce Technologies. ResearchGate, Aug. 2024. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/383183536_The_Role_of_Academic_Technology_Entrepreneurship_in_Technopreneur_Development_A_Focus_on_SMEs_Adoption_of_E-Commerce_Technologies (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Al-Adwan, S.; Saleem, A.; et al. The Adoption of Digital Technologies by Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises for Sustainability and Value Creation in Pakistan. Sustain. 2024. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/16/17/7351.
- Ngcobo, K.; Bhengu, S.; Mudau, A.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Enterprise Data Management: Types, Sources, and Real-Time Applications to Enhance Business Performance - A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Role of Cloud Computing in Digital Transformation: Case Studies and Success Stories. Studytonight. 2024. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://vorecol.com/blogs/blog-the-role-of-cloud-computing-in-accelerating-digital-transformation-180497%23:~:text%3DCloud%2520computing%2520offers%2520a%2520treasure,i%2520into%2520a%2520dynamic%252C%2520adaptable%2520environment.&ved=2ahUKEwjT7K6UzL-IAxUz3wIHHRHYLYQQFnoECBYQAw&usg=AOvVaw2OyKtaIMrHaWKUkm505_oO.
- Cloud Computing Case Studies and Success Stories. Knowledgehut. 2024. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://www.knowledgehut.com/blog/cloud-computing/cloud-computing-case-studies&ved=2ahUKEwjZwJnGzL-IAxXY3AIHHUbDLvsQFnoECBMQAQ&usg=AOvVaw1JncFcJHVe-1PXcp0dpV5s.
- Digital Transformation - 5 Success Stories Driven by IT Solutions. Business Computer Solutions. 2024. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://perception-point.io/guides/digital-transformation/digital-transformation-for-business-5-big-success-stories/&ved=2ahUKEwip48LWzb-IAxUaywIHHZpSDVsQFnoECBwQAQ&usg=AOvVaw3eIqxXqbg4oAuqqd-RYtVH.
- Mohlala, T.T.; Mehlwana, L.L.; Nekhavhambe, U.P.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Strategic Innovation in HRIS and AI for Enhancing Workforce Productivity in SMEs: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloud-Based Industrial Transformation. Studytonight. 2024. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://www.technologyreview.com/2024/05/29/1092342/industry-and-ai-focused-cloud-transformation/&ved=2ahUKEwjkg4r4zr-IAxUT3AIHHf1-CSgQFnoECBQQAQ&usg=AOvVaw17FXo1NV5emWhbp2wLml76.
- McKinsey Global Institute. The Future of AI and the Global Economy: How AI Will Impact Business. 2023. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai-in-2023-generative-ais-breakout-year (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- PwC. Sizing the Prize: What’s the Real Value of AI for Your Business and How Can You Capitalize? 2023. Available online: https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/issues/analytics/assets/pwc-ai-analysis-sizing-the-prize-report.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Gartner. IoT Projections for 2030: Market Growth and Technology Trends. 2023. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/internet-things-iot-market-overview#:~:text=CAGR%20and%20Revenue%3A%20%E2%80%9CThe%20global,%2C%20during%20the%20forecast%20period.%E2%80%9D (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- IoT Analytics. Internet of Things – Global Forecast to 2030: Key Trends and Insights. 2023. Available online: https://data.gsmaintelligence.com/research/research/research-2023/iot-connections-forecast-to-2030 (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Deloitte. Blockchain’s Role in the Future of Supply Chain and Finance. 2023. Available online: https://www2.deloitte.com/kz/en/pages/operations/articles/blockchain-supply-chain-innovation.html (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- World Economic Forum. Blockchain Technology for Inclusive Financial Systems. 2023. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2023/05/setting-blockchain-on-a-net-zero-path/ (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Accenture. Cloud Computing: A Roadmap for Accelerating Digital Transformation. 2023. Available online: https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insights/digital-transformation-index (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Ericsson. The 5G Revolution: How It Will Transform Industries and Societies by 2030. 2023. Available online: https://www.ericsson.com/en/5g (accessed on 15 September 2024).



| Ref. | Cites | Year | Contribution | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [8] | 1,523 | 2017 | Highlights the role of artificial intelligence in shaping digital transformation and business advantage. | Provides industry insights and practical applications. | The report focused on AI might overlook other technologies in digital transformation. |
| [9] | 12,362 | 2017 | Explores how analytics-driven strategies can lead to competitive advantages. | Focuses on real-world applications of data analytics for competitive success. | Primarily focuses on analytics, lacking discussion on other digital tools like AI or IoT.#break# |
| [10] | 527 | 2020 | Explores the future of retailing, focusing on how digital technologies shape retail experiences. | Industry-specific analysis for retail, with actionable insights for digital transformation | Limited to the retail industry, lacks broader cross-industry insights. |
| [11] | 235 | 2016 | Discusses how ambidextrous idea generation influences innovation and competitive advantage | Highlights the importance of ambidexterity in innovation. | Less focused on digital transformation, and more on innovation processes.#break# |
| [12] | 1,047 | 2015 | Explores the role of IoT and big data analytics in shaping business strategies | Combines two key emerging trends -IoT and big data offering a future-looking analysis | Focused on emerging technologies; practical implications may still be unclear for business.#break# |
| [13] | 987 | 2017 | Explores how large companies navigate digital transformation | Case studies of big firms provide practical insights. | Focuses on large organizations and may not be as relevant to SMEs or startups.#break# |
| [14] | 14,498 | 2018 | Discusses the role of business models and dynamic capabilities in driving competitive advantage | Provides a dynamic view of how companies can adapt their business models to capture value from technology. | More theoretical; lacks direct practical guidance for implementing specific digital strategies.#break# |
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Topic | Articles must focus on Digital Technologies and Channels for Competitive Business Advantage | Articles Unrelated to Digital Technologies and Channels for Competitive Business Advantage |
| Research Framework | Articles must include a research framework or methodology for digital technologies in SMEs | Articles lacking a clear research framework or methodology for digital technologies in SMEs |
| Language | Articles written in English | Articles published in languages other than English |
| Period | Publications between 2014 and 2024 | Publications outside 2014 and 2024 |
| Data Items | Description |
|---|---|
| Title | The title of research related to digital technologies as it channels for competitive advantage in SMEs |
| Year | The year in which the research on digital technologies and SMEs was published |
| #break#Online Database (Google Scholar, SCOPUS, Web of Science, IEEE Explore, ERIC) | The platform or database where the research on digital technology and SMEs is indexed or available. |
| Journal Name | The name of the journal where the study on digital technologies for SMEs was published.#break# |
| Research Type (Article Journal, Conference Paper, Book Chapter, Dissertation, Thesis) | The type of research publication focused on SMEs and digital technologies. |
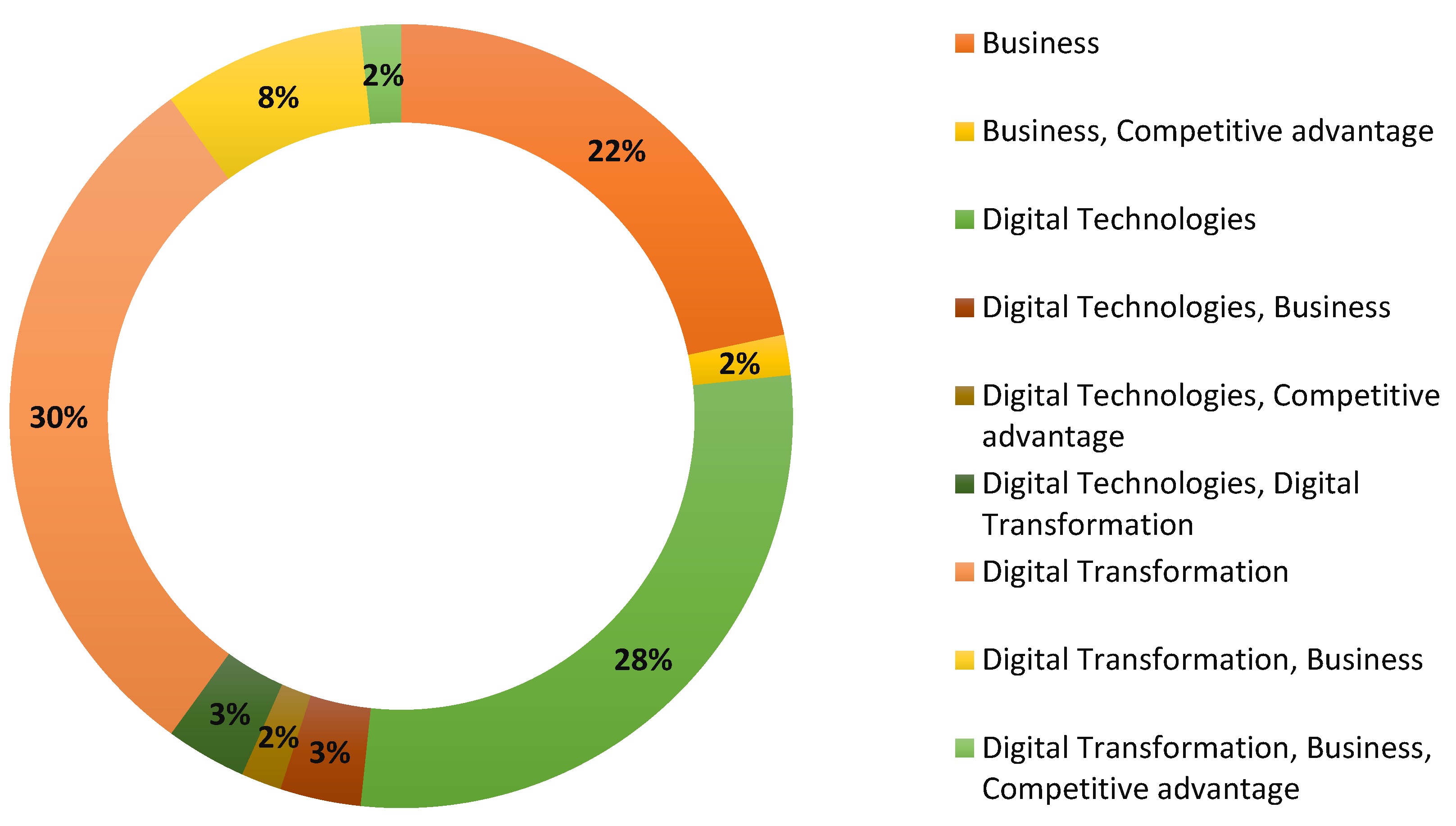
| Discipline or Subject Area (e.g., digital technologies, competitive advantage, business) | The academic field, such as digital technology or competitive advantage, is related to the research in SMEs.#break# |
| Industry Context (e.g., SMEs, startups, small businesses) | The industry focus of the research, specifically on SMEs and how they leverage digital technologies.#break# |
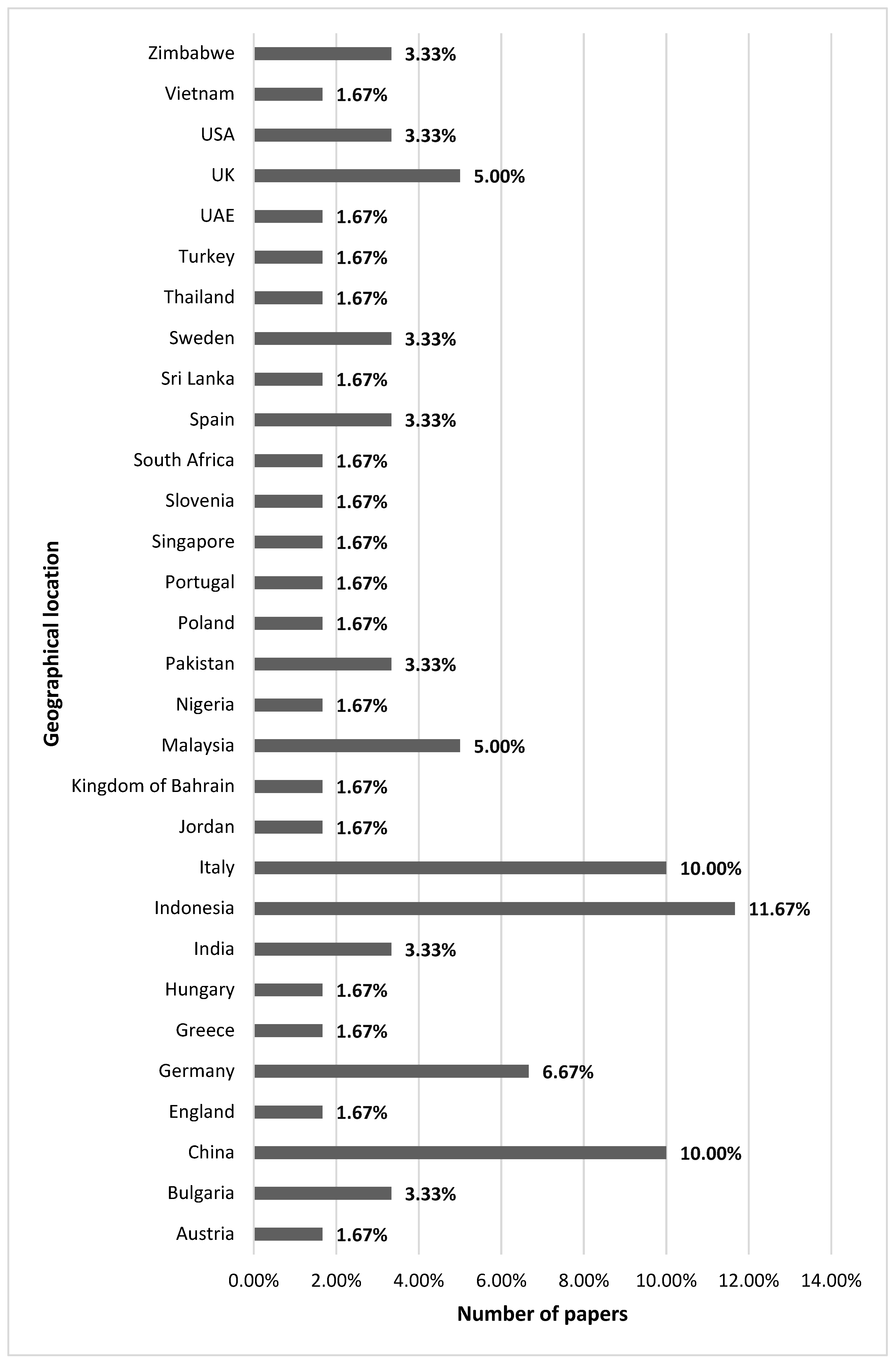
| Geographic Location | The geographical focus of the research, such as specific regions or countries where SMEs are analyzed.#break# |
| Economic Context (e.g., developed vs. developing countries) | The economic setting, whether the research focuses on SMEs in developed or developing countries.#break# |
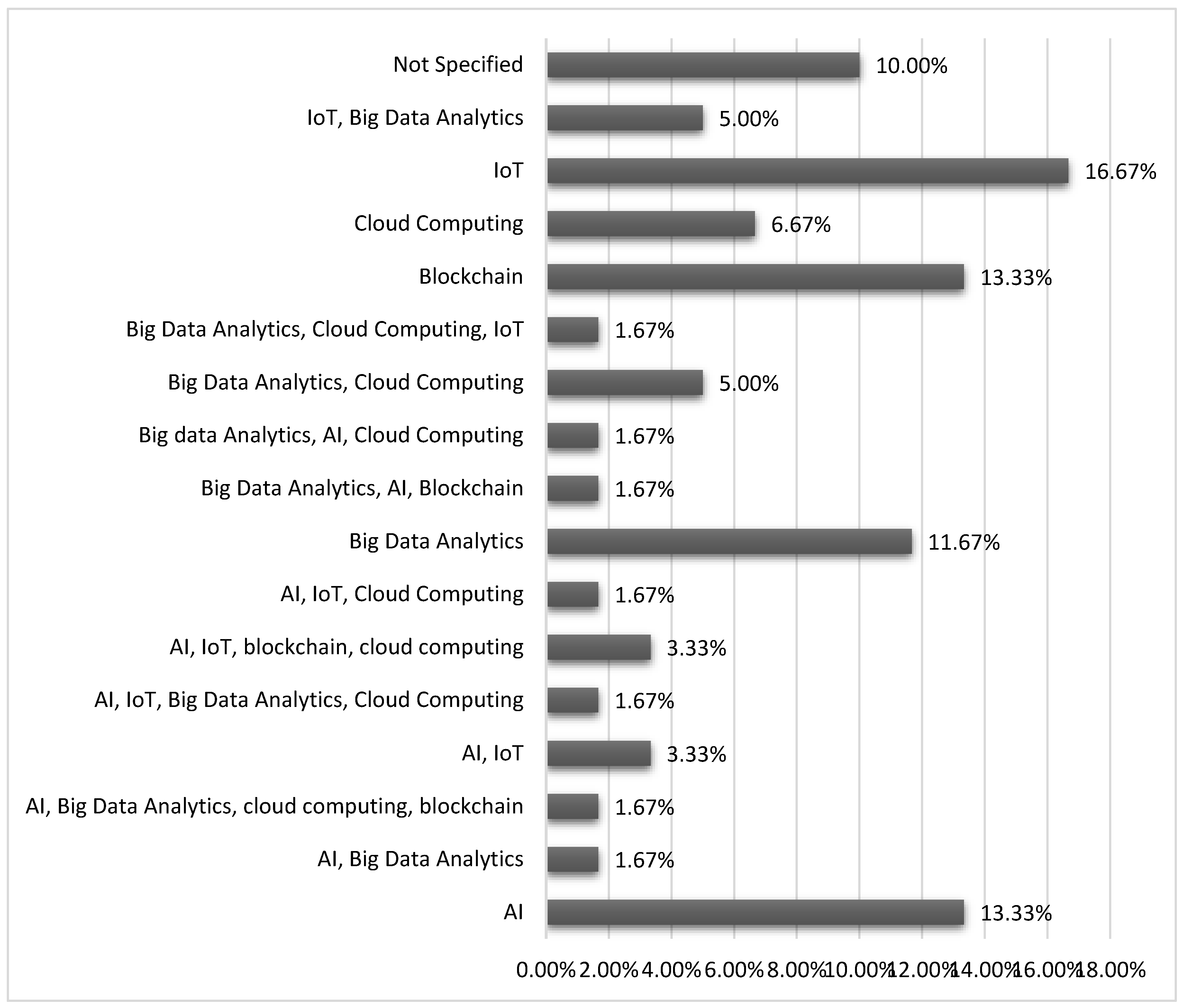
| Types of Digital Technologies (e.g., AI, IoT, blockchain) | The digital technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain are explored as competitive channels for SMEs.#break# |
| Technology Providers (e.g., AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud) | The technology service providers offering platforms to SMEs, such as AWS or Microsoft Azure, for competitive advantage.#break# |
| Technology Implementation Model (e.g., on-premises, cloud-based, hybrid) | The deployment models for digital technologies, like cloud-based or hybrid, are used by SMEs.#break# |
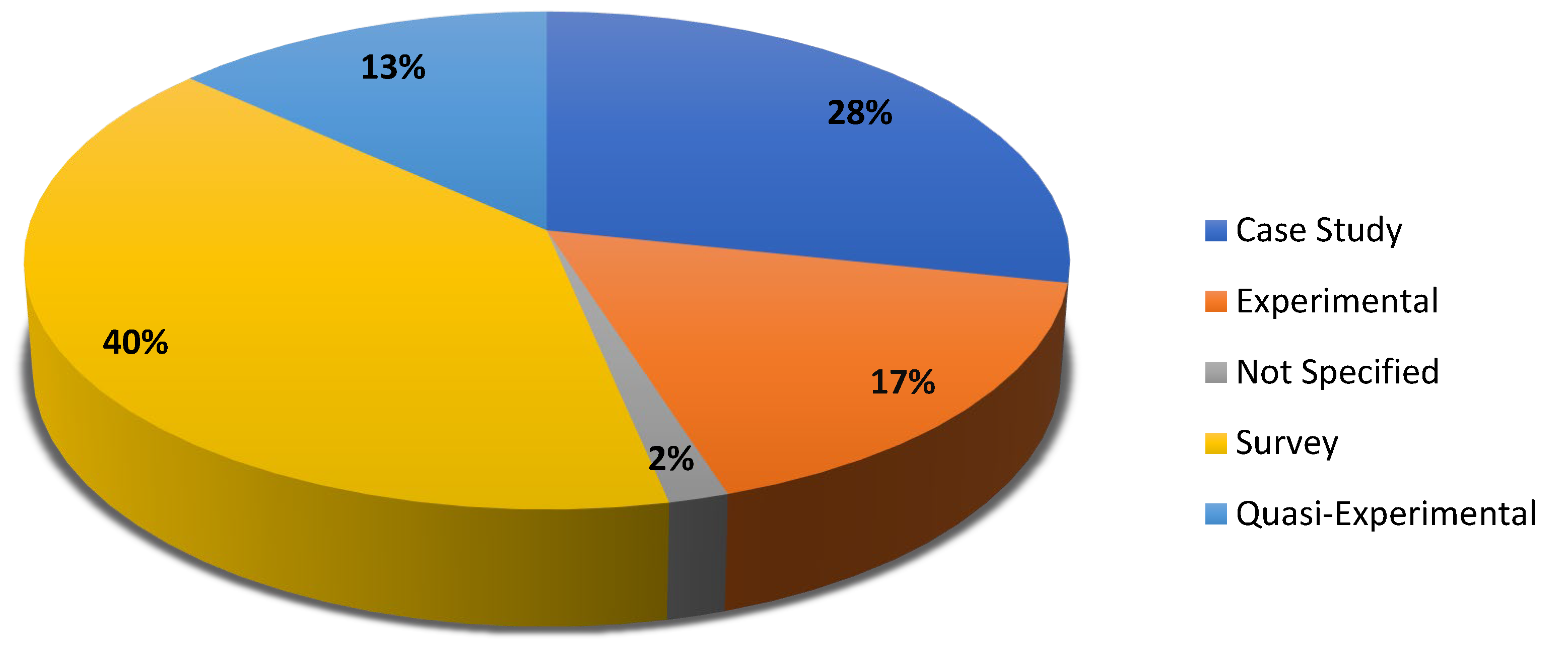
| Research Design (experimental, quasi-experimental, case study, survey, etc.) | The research methodology is used to analyze the adoption and impact of digital technologies in SMEs.#break# |
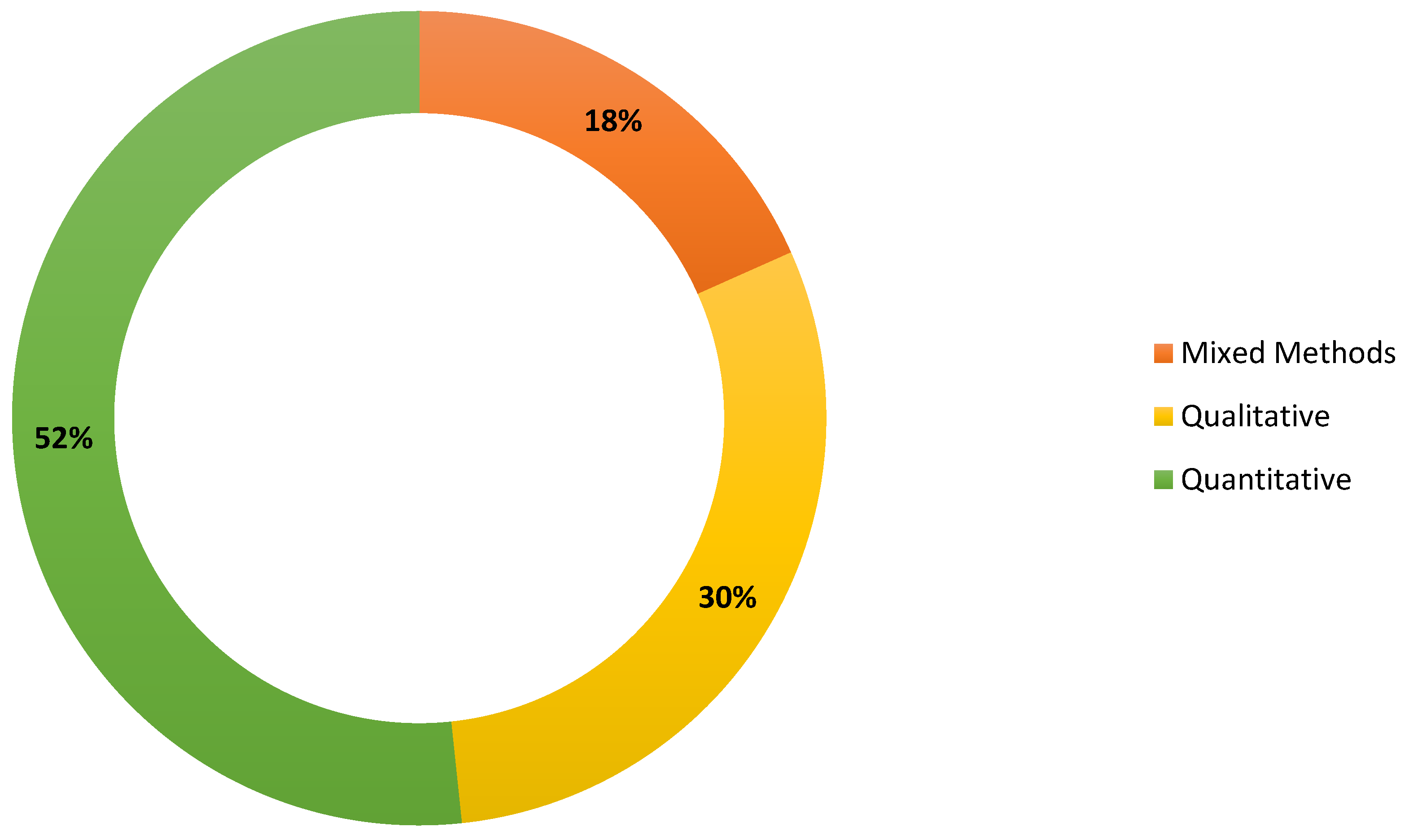
| Type of Study (quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods) | The study approach, such as quantitative or mixed methods, is applied to research on digital technology and competitive advantage for SMEs.#break# |
| Sample Size | The number of SMEs or stakeholders surveyed or analyzed in the research.#break# |
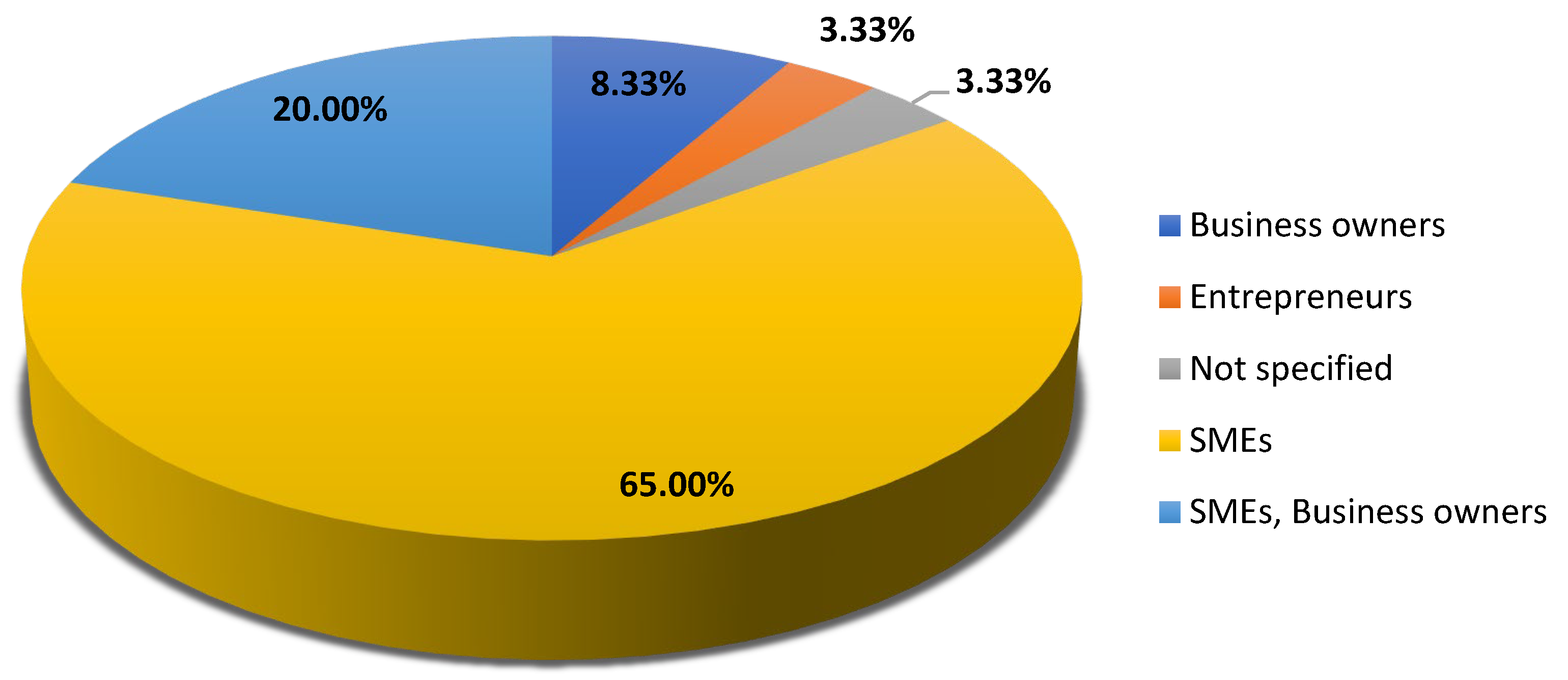
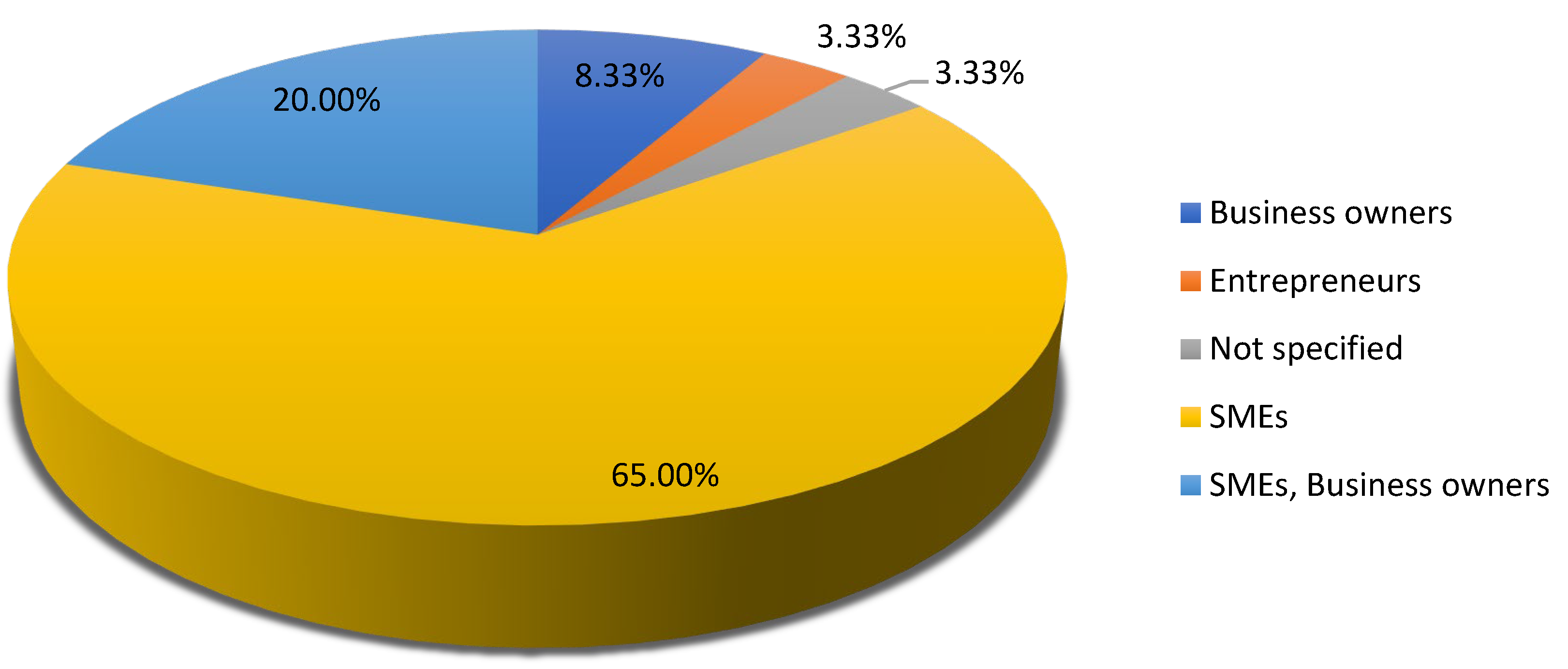
| Sample Characteristics (e.g., SMEs, entrepreneurs, business owners) | Specific attributes of the participants, like entrepreneurs or business owners in the SME sector.#break# |
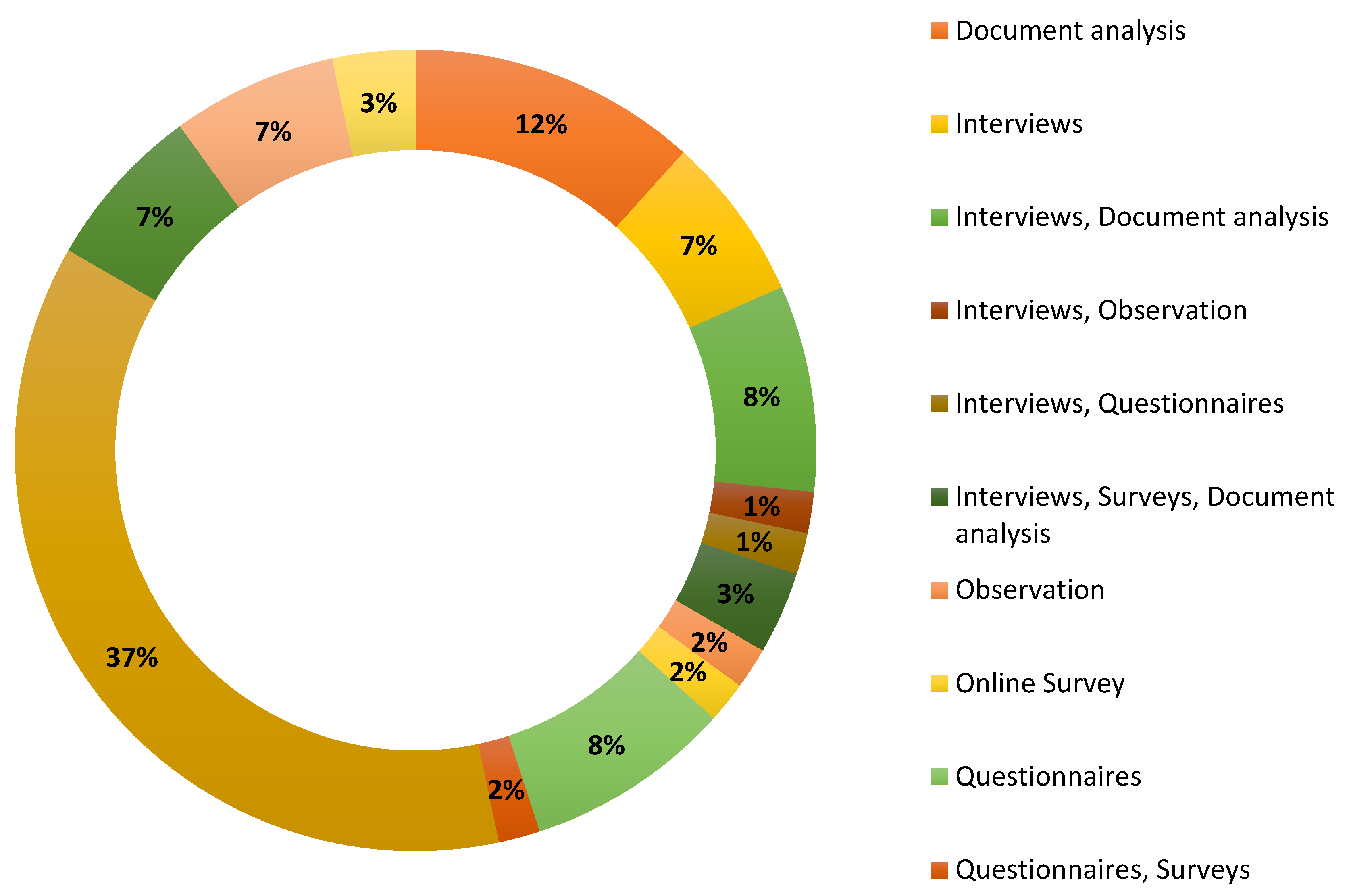
| Data Collection Methods (e.g., interviews, surveys, observations, document analysis) | The methods used to gather data, such as surveys or interviews, from SMEs regarding digital technology use.#break# |
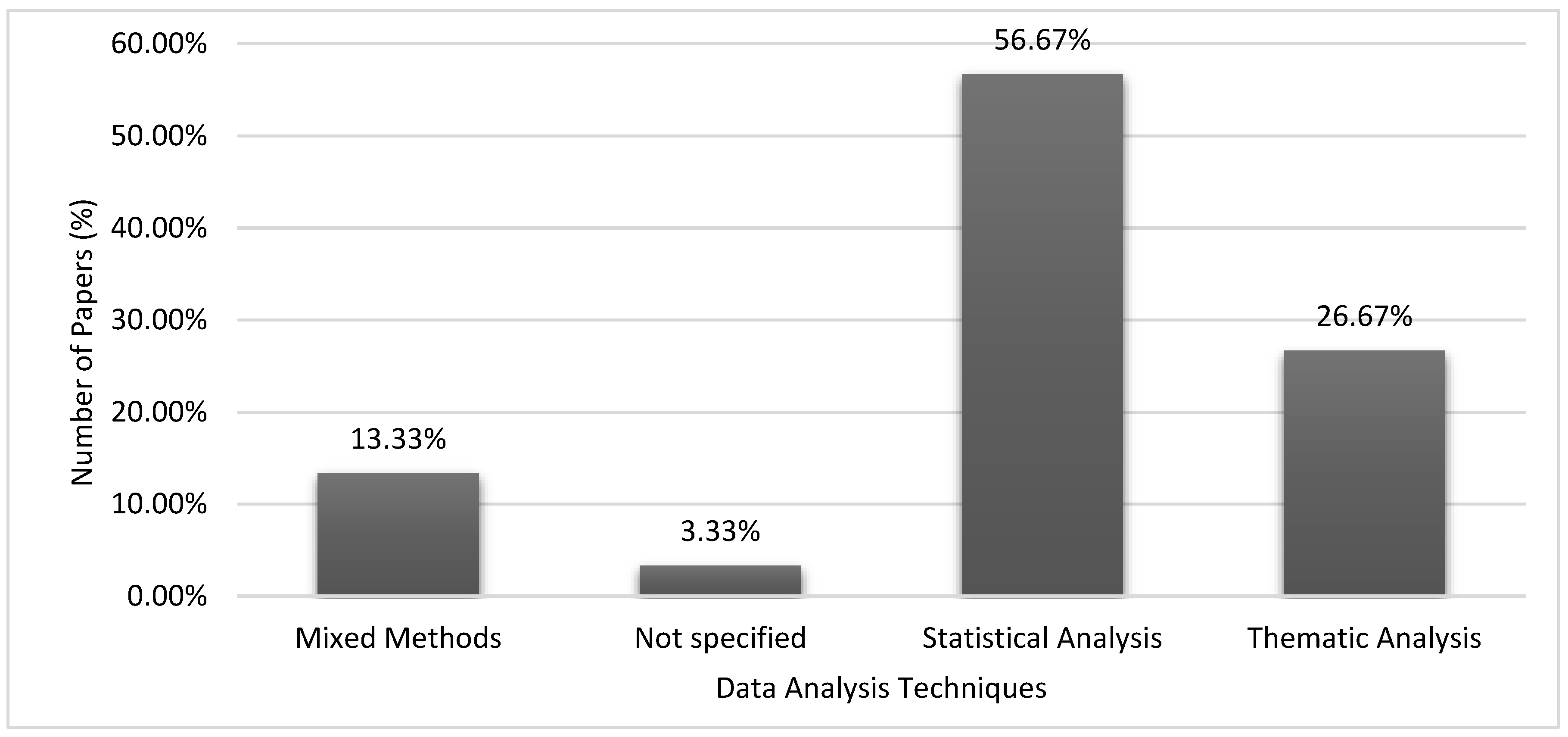
| Data Analysis Techniques (e.g., statistical analysis, thematic analysis) | Techniques used to analyze data, such as statistical analysis or thematic analysis, in the context of digital technology in SMEs.#break# |
| Business Performance Metrics (e.g., revenue growth, market share, customer base) | Key performance indicators like revenue growth or market share used to measure competitive advantage from digital technology in SMEs.#break# |
| Technical Performance Metrics (e.g., system uptime, user engagement, scalability) | Metrics related to technical success, like scalability or user engagement, in the digital technology adopted by SMEs.#break# |
| Organizational Outcomes (e.g., employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction) | The impact of digital technologies on organizational outcomes like customer or employee satisfaction in SMEs.#break# |
| Long-term Impacts (e.g., business growth, competitive advantage) | The lasting effects of digital technologies, such as sustained competitive advantage or long-term business growth for SMEs. |
| Study | Selection (Max 4 Stars) | Comparability (Max 2 stars) | Outcome/Exposure (Max 3 stars) | Total Score (Max 9 stars) | Quality Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [15] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 8 | High quality |
| [16] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 8 | High quality |
| [17] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | High quality |
| [18] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | High quality |
| [19] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [20] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [21] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [22] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 8 | High quality |
| [23] | ★★★★ | ★ | ★★★ | 8 | High quality |
| [24] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [25] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [26] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [27] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [28] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [29] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★ | 6 | Moderate quality |
| [30] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 6 | Moderate quality |
| [31] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | High quality |
| [32] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | High quality |
| [33] | ★★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 7 | High quality |
| [34] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [35] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [36] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | High quality |
| [37] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [38] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [39] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 8 | High quality |
| [40] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 6 | Moderate quality |
| [41] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | High quality |
| [42] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | High quality |
| [43] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [44] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 6 | Moderate quality |
| [45] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [46] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [47] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [48] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [49] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 6 | Moderate quality |
| [50] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [51] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | High quality |
| [52] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 8 | High quality |
| [53] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 6 | Moderate quality |
| [54] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [55] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [56] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | High quality |
| [57] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 8 | High quality |
| [58] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 6 | Moderate quality |
| [59] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | High quality |
| [60] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| [61] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High quality |
| Synthesis Step | Description | Methods Applied |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility Assessment | Studies were evaluated based on relevance to SMEs and digital technologies, with characteristics coded for grouping. | Criteria coding, logical comparison, grouping by predefined criteria. |
| Data Preparation | Data was standardized and missing information was imputed or interpolated to ensure uniformity for synthesis. | Statistical conversions, imputation, interpolation. |
| Tabulation and Visual Display | Results were presented in structured tables and forest plots, ordered by study quality and relevance. | Structured tables, forest plots, graphical representation of effect estimates. |
| Synthesis Methods | Meta-analysis using fixed-effects or random-effects models, with heterogeneity testing. Alternative methods were used for non-meta-analyzed data. | Meta-analysis models, heterogeneity tests, alternative synthesis methods, statistical software. |
| Question (Q) | Research Quality Questions |
|---|---|
| Q1 | Are the research objectives clearly defined? |
| Q2 | Is the methodology of the study well-explained? |
| Q3 | Is the research model clearly presented? |
| Q4 | Are the data collection methods thoroughly described? |
| Q5 | Is the study’s context or discipline clearly identified? |
| Q6 | Do the results contribute to the existing body of literature? |
| Published Year | Book Chapter | Conference Paper | Dissertation | Journal article |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2015 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 2016 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 2017 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 2018 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| 2019 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 2020 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| 2021 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| 2022 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| 2023 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 8 |
| 2024 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| Industry | Category | Subcategory | Findings | Strategic Drivers | Barriers | Opportunities | Strategic Implications for Business Leaders |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retail SMEs | Digital Marketing | AI-based Marketing Automation | 25% increase in customer engagement using AI-driven marketing automation | Personalization and real-time engagement critical for customer retention | High cost of implementing AI-driven tools, lack of expertise | AI can boost customer retention and ROI in marketing campaigns | Invest in AI-driven CRM systems that automate customer engagement and integrate inventory systems |
| Predictive Analytics | Inventory Management | 30% improvement in inventory management and forecasting | Real-time data analysis for adjusting stock levels | Lack of integration across digital platforms, siloed data | Optimized inventory reduces waste, prevents stockouts during peak seasons | Prioritize predictive analytics in supply chain management to reduce costs and optimize operations | |
| E-commerce | Omnichannel Integration | 40% sales increase with omnichannel integration | Seamless cross-channel integration improves customer experience | Difficulty in synchronizing data across physical, online, and mobile channels | Enhanced brand loyalty and revenue growth with omnichannel options | Invest in omnichannel platforms for a frictionless, consistent customer experience | |
| Healthcare SMEs | Patient Data Management | IoT-based Patient Monitoring | 25% reduction in emergency response times using IoT devices | Real-time data supports quick medical decisions | Data privacy concerns, compliance with regulations (HIPAA, GDPR) | IoT enhances early diagnosis and patient care through real-time monitoring | Ensure IoT systems comply with healthcare regulations and leverage real-time data for better outcomes |
| Data Security | Blockchain for Data Transactions | Blockchain improved data transparency and security | Secure, tamper-proof data transactions are essential | High implementation costs, technical complexity | Blockchain facilitates secure data sharing in healthcare collaborations | Leverage blockchain for regulatory compliance and secure data sharing among healthcare institutions | |
| Finance SMEs | Fraud Detection | AI-powered Fraud Detection | 50% reduction in fraudulent transactions using AI | Real-time fraud detection systems improve trust and compliance | High upfront investment, lack of skilled professionals | AI-powered fraud detection can reduce financial crimes | Prioritize AI systems for fraud detection to enhance trust and meet compliance standards |
| Data Security | Blockchain for Financial Records | 30% faster audits using blockchain for financial transactions | Blockchain secures tamper-proof transaction records | Limited knowledge of blockchain, high cost of implementation | Blockchain ensures transparency and security in international trade | Invest in blockchain to create tamper-proof transaction records and ensure compliance | |
| Manufacturing SMEs | Production Optimization | IoT for Predictive Maintenance | 20% reduction in machine downtime using IoT for predictive maintenance | Real-time machine monitoring ensures operational efficiency | High cost of IoT implementation, lack of technical expertise | IoT improves efficiency by reducing operational downtimes and optimizing production | Implement IoT for real-time production monitoring and predictive maintenance to reduce downtime and costs |
| Supply Chain Management | AI-Driven Supply Chain Analytics | 35% improvement in demand forecasting and supply chain optimization | AI-driven insights optimize supply chain management | Integration challenges across supply chain, lack of data standards | AI can optimize supply chain forecasting and inventory management | Adopt AI for optimizing supply chain management and improving overall operational efficiency | |
| Logistics SMEs | Fleet Management | IoT for Real-Time Fleet Tracking | 30% improvement in fleet efficiency through IoT-based tracking systems | Real-time vehicle monitoring ensures efficient fleet management | Integration with existing logistics systems, data privacy concerns | IoT can optimize fleet routes and reduce fuel consumption | Invest in IoT-based tracking systems to improve fleet management and optimize delivery schedules |
| Supply Chain Visibility | Blockchain for Transparency | 40% improvement in supplier trust and transparency using blockchain | Blockchain ensures secure, transparent supply chains | Lack of expertise, high blockchain adoption costs | Blockchain can enhance trust and visibility in supply chain management | Implement blockchain to secure and streamline the supply chain, improving transparency and efficiency | |
| Hospitality SMEs | Customer Engagement | AI-Powered Personalization | 30% increase in customer satisfaction through personalized services using AI | Personalization increases customer loyalty and brand differentiation | High cost of AI tools, lack of expertise | AI enhances guest experience through personalized recommendations | Invest in AI tools for personalized guest experiences and services, improving loyalty and satisfaction |
| Booking and Property Management | Cloud-Based Booking Systems | 25% improvement in booking efficiency through cloud-based management | Cloud systems enable seamless booking and property management | High implementation costs, lack of system integration | Cloud systems improve booking efficiency and streamline property management | Leaders should prioritize cloud-based booking systems to improve efficiency and customer experience | |
| Energy SMEs | Grid Performance Monitoring | IoT for Smart Grids | 15% improvement in grid performance with real-time IoT monitoring | Real-time grid monitoring enables energy efficiency improvements | High cost of IoT infrastructure, lack of skilled professionals | IoT enables predictive maintenance and energy efficiency in grid operations | Invest in IoT systems for smart grid monitoring and predictive maintenance to optimize energy use |
| Renewable Energy Adoption | AI for Energy Management | 20% reduction in energy costs through AI-based energy management systems | AI optimizes energy consumption and cost management | High cost of AI solutions, technical expertise required | AI can reduce energy costs and optimize resource allocation | Leaders should invest in AI-driven energy management systems to reduce costs and optimize resource use | |
| Education SMEs | Learning Management | Cloud-Based LMS Systems | 35% improvement in student engagement through cloud-based LMS | Cloud LMS systems improve learning outcomes and student accessibility | Integration challenges with existing platforms, data privacy concerns | Cloud-based LMS offers scalability and improved student engagement | Invest in cloud-based LMS platforms to enhance digital learning experiences and student outcomes |
| Research Data Management | AI for Research Analytics | 25% improvement in research output using AI for data analysis | AI accelerates research data processing and analysis | High cost of AI adoption, limited data integration capabilities | AI can improve research productivity and data analysis capabilities | Leaders should integrate AI systems into research platforms to enhance data analysis and research productivity |
| Industry | Key Decision Points | Sub-Decision Points | Technologies to Implement | Evaluation Metrics | Risks to Consider | Strategic Benefits | Long-term Implications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retail SMEs | Personalization vs. Process Optimization | Should SMEs prioritize customer personalization over internal process optimization? | AI-driven CRM for personalized marketing, ERP for process optimization | Customer satisfaction, sales conversion rates, inventory turnover rates | High cost of AI implementation, data privacy concerns | AI improves personalized marketing, while ERP optimizes operational efficiency | Long-term improvements in customer loyalty and operational scalability |
| Mobile-First vs. Omnichannel Strategy | Is it better to invest in mobile-first technology or an omnichannel strategy? | Mobile-responsive platforms, omnichannel e-commerce integration | Customer acquisition cost (CAC), mobile engagement metrics, omnichannel conversion rates | Inconsistent customer experiences across channels | Omnichannel strategy provides flexibility across sales platforms, boosting customer retention | Strategic long-term growth through diversified sales channels and customer engagement | |
| Data-Driven Insights vs. Traditional Models | Should data analytics be prioritized over traditional retail forecasting methods? | AI-powered data analytics, predictive analytics for inventory management | Forecast accuracy, revenue growth, operational cost reduction | Risk of data misinterpretation, high setup costs | Predictive analytics improves demand forecasting, inventory optimization | Long-term operational efficiency and reduction of waste | |
| Healthcare SMEs | Real-Time Monitoring vs. Data Security | Should SMEs focus on real-time patient monitoring or improving data security? | IoT-based patient monitoring systems, blockchain for secure data sharing | Patient outcome metrics, HIPAA/GDPR compliance, emergency response times | High cost of compliance, regulatory and data privacy challenges | IoT-based monitoring improves patient outcomes, while blockchain secures data transactions | Enhanced patient care, data security, and long-term regulatory compliance |
| In-House Data Storage vs. Cloud Solutions | Should SMEs invest in in-house data storage or transition to cloud-based systems? | Cloud-based EHR systems, AI for medical diagnostics | Patient data accessibility, cost efficiency, system reliability | Data privacy concerns, ongoing cloud service costs | Cloud solutions offer scalable data storage and real-time access to patient records | Long-term cost savings, increased scalability, and improved patient care | |
| Patient Experience vs. Operational Efficiency | Should the focus be on improving patient experience or optimizing internal operations? | AI-driven patient care systems, ERP for hospital management | Patient satisfaction scores, operational cost reductions | Resistance to adopting new technologies, high cost of training healthcare professionals | AI-driven patient care systems improve healthcare experiences and outcomes | Long-term improvements in patient satisfaction, healthcare delivery efficiency | |
| Finance SMEs | Compliance vs. Fraud Detection | Should SMEs invest in compliance measures or fraud detection technologies first? | AI-driven fraud detection systems, blockchain for secure transactions | Fraud detection rates, compliance violations, customer trust metrics | High initial costs, complexity of implementation | AI systems reduce fraud, blockchain ensures regulatory compliance | Long-term cost savings from reduced fraud and increased customer trust |
| Automation vs. Customer Service | Should SMEs prioritize automating processes or improving customer service? | AI-powered customer service bots, robotic process automation (RPA) | Customer service response times, operational cost savings | Loss of personal touch with customers, complexity of automation | Automation improves operational efficiency, while AI enhances customer interactions | Long-term operational savings and customer satisfaction improvements | |
| Data Centralization vs. Decentralization | Should data be centralized for control or decentralized for security and flexibility? | Blockchain for decentralized ledgers, cloud-based financial systems | Transaction processing times, data security breaches, audit accuracy | High cost of blockchain implementation, integration challenges | Decentralized ledgers increase data security and transparency | Long-term trust and transparency in financial transactions | |
| Manufacturing SMEs | Automation vs. Workforce Expansion | Should SMEs automate processes or focus on workforce expansion? | IoT for smart manufacturing, AI-driven robotics | Production efficiency, labor cost reductions, downtime minimization | Resistance to automation, high upfront investment in robotics | Automation reduces costs, improves production rates, and minimizes errors | Long-term scalability and operational efficiency gains |
| Predictive Maintenance vs. Reactive Repair | Should SMEs adopt predictive maintenance technologies or continue with traditional repair strategies? | IoT-based predictive maintenance, AI-powered equipment monitoring | Machine downtime rates, maintenance cost savings, equipment lifespan | High cost of IoT and AI adoption, technical expertise requirement | Predictive maintenance improves uptime, reduces operational costs, and extends equipment life | Long-term reduction in maintenance costs and increased operational efficiency | |
| Global Supply Chain vs. Local Optimization | Should SMEs focus on global supply chain optimization or local market efficiencies? | AI for global supply chain management, blockchain for supply chain transparency | Delivery accuracy, supplier trust, cost savings from optimized logistics | High costs of blockchain and AI integration, complexity in global coordination | AI and blockchain improve supply chain transparency, trust, and efficiency | Long-term improvements in global logistics and operational transparency | |
| Logistics SMEs | Route Optimization vs. Delivery Speed | Should SMEs prioritize route optimization technologies over reducing delivery times? | AI-powered route optimization tools, IoT for real-time fleet tracking | Delivery time reduction, fuel cost savings, fleet efficiency | Data privacy concerns, high cost of AI and IoT tools | Route optimization reduces delivery times and fuel costs | Long-term fuel cost savings and operational efficiency improvements |
| Real-Time Tracking vs. Supply Chain Visibility | Should SMEs focus on real-time tracking of assets or improving supply chain visibility? | Blockchain for supply chain transparency, IoT for asset tracking | Supply chain efficiency, inventory accuracy, tracking system reliability | High blockchain implementation costs, integration challenges | Blockchain and IoT improve supply chain visibility and tracking accuracy | Long-term transparency and operational control in supply chain management | |
| Hospitality SMEs | Customer Personalization vs. Booking Efficiency | Should SMEs focus on personalizing guest experiences or improving booking processes? | AI-driven personalization, cloud-based booking systems | Guest satisfaction, booking conversion rates, occupancy rates | High cost of AI tools, integration challenges with legacy systems | AI improves customer engagement and personalized services | Long-term guest loyalty and increased occupancy rates |
| Dynamic Pricing vs. Standard Pricing Models | Should SMEs adopt dynamic pricing models or stick to traditional pricing strategies? | AI-driven dynamic pricing tools, revenue management systems | Revenue growth, occupancy rates, guest satisfaction | Resistance to dynamic pricing models, customer dissatisfaction with price fluctuations | Dynamic pricing optimizes revenue and ensures maximum occupancy | Long-term revenue optimization and pricing efficiency | |
| Energy SMEs | Energy Efficiency vs. Grid Expansion | Should SMEs focus on improving energy efficiency or expanding grid capacity? | IoT for energy usage monitoring, AI-driven energy management systems | Energy cost savings, grid reliability, operational efficiency | High cost of IoT and AI tools, regulatory challenges | IoT improves energy efficiency, while AI optimizes resource allocation | Long-term energy savings and grid reliability improvements |
| Renewable Energy vs. Traditional Sources | Should SMEs invest in renewable energy systems or continue with traditional energy sources? | Solar power systems, AI-driven energy forecasting | Carbon footprint reduction, energy cost savings, regulatory compliance | High initial cost of renewable energy systems, lack of technical expertise | Renewable energy reduces costs, improves sustainability, and ensures regulatory compliance | Long-term cost savings and regulatory compliance with sustainability standards | |
| Education SMEs | Remote Learning vs. In-Person Instruction | Should SMEs invest in remote learning platforms or maintain traditional in-person instruction models? | Cloud-based LMS platforms, AI for personalized learning | Student engagement metrics, learning outcomes, cost per student | Resistance to adopting new technology, high initial investment in platforms | Remote learning offers scalability and flexibility | Long-term improvements in learning accessibility and student engagement |
| Digital Resource Management vs. Traditional Systems | Should SMEs digitize resource management or continue with traditional systems? | Cloud-based research data management platforms, AI for research analysis | Research output, data accessibility, collaboration efficiency | Data security concerns, high cost of AI and cloud integration | Cloud systems and AI improve research collaboration and data analysis | Long-term improvements in research efficiency and collaboration |
| Industry | Category | Sub-Category | Best Practices | Challenges to Overcome | Strategic Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retail SMEs | Digital Marketing | Personalization | Leverage AI-driven marketing automation to personalize customer experiences across digital and physical channels. | High cost of AI tools, need for data-driven marketing strategy | Improved customer retention, higher conversion rates, and increased customer lifetime value through personalized interactions. |
| Customer Analytics | Predictive Analytics | Implement predictive analytics for demand forecasting and inventory optimization to reduce stockouts and overstocking. | Integration across sales platforms and data silos | Optimized inventory levels, reduced waste, and higher operational efficiency during peak seasons or sales events. | |
| Omnichannel Strategy | E-Commerce Integration | Ensure seamless integration across all customer touchpoints, including online, mobile, and in-store shopping experiences. | Data synchronization across channels, consistency in customer experiences | Increased customer satisfaction, improved sales performance across multiple platforms, and better customer loyalty. | |
| Healthcare SMEs | Patient Data Management | IoT and Blockchain Integration | Use IoT devices for real-time patient monitoring and blockchain for secure, transparent data sharing between healthcare providers. | Regulatory compliance (HIPAA/GDPR), security concerns, and high costs of IoT and blockchain adoption | Enhanced patient outcomes, improved efficiency in patient data sharing, and higher trust in data security protocols. |
| Compliance and Security | Data Privacy & Compliance Automation | Automate compliance management using AI-driven systems to handle patient data in line with healthcare regulations. | Ensuring AI-based compliance tools meet regulatory standards | Improved data security, reduced compliance risks, and a more streamlined approach to handling patient information. | |
| Operational Efficiency | Cloud-Based EHR | Deploy cloud-based Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems to improve real-time accessibility and reduce on-premise IT costs. | Data privacy concerns and potential for breaches during cloud migration | Cost savings on IT infrastructure, improved healthcare delivery through faster data access, and compliance with data privacy laws. | |
| Finance SMEs | Financial Security | AI-Driven Fraud Detection | Implement AI-driven fraud detection systems to monitor transactions and flag anomalies in real-time, ensuring compliance and reducing fraud risks. | High initial investment in AI systems and difficulty in integrating with legacy financial systems | Reduction in fraudulent activities, improved compliance with financial regulations, and stronger customer trust in the company’s security systems. |
| Data Transparency | Blockchain for Transactions | Use blockchain to create secure, tamper-proof financial ledgers for transparent transactions and streamlined auditing. | High cost and complexity of blockchain systems | Secure financial transactions, faster audits, and reduced risk of fraud, improving operational efficiency and trust in financial transactions. | |
| Regulatory Compliance | Automation of Regulatory Reporting | Automate compliance reporting using AI to ensure adherence to financial regulations (e.g., PCI DSS, AML). | High cost of setting up AI-based compliance systems and lack of internal expertise | Reduced risk of non-compliance, faster reporting times, and fewer penalties from regulatory bodies. | |
| Manufacturing SMEs | Operational Efficiency | IoT-Driven Automation | Leverage IoT to monitor real-time production data, track machine performance, and optimize production schedules through predictive maintenance. | Resistance to automation and high initial setup costs for IoT infrastructure | Reduced machine downtime, lower operational costs, and improved production efficiency through predictive maintenance systems. |
| Supply Chain Management | AI for Supply Chain Optimization | Implement AI to optimize supply chain logistics, demand forecasting, and real-time tracking of goods and inventory. | Complexity in integrating AI with existing supply chain systems | Enhanced supply chain visibility, reduced inventory holding costs, and improved delivery times, leading to higher customer satisfaction and operational savings. | |
| Digital Manufacturing | Cloud-Based ERP | Deploy cloud-based ERP systems to streamline production, inventory, and sales data management for better decision-making and resource allocation. | Integration issues with legacy systems and data migration challenges | Improved resource allocation, real-time production visibility, and seamless integration of various operational departments, leading to better decision-making and reduced operational bottlenecks. | |
| Logistics SMEs | Route Optimization | AI-Powered Route Optimization | Use AI-powered tools to optimize delivery routes, reducing delivery times and fuel costs while improving fleet management efficiency. | High cost of AI adoption, resistance to technological change among drivers | Lower fuel costs, improved delivery times, and higher fleet efficiency, resulting in reduced operational expenses and improved customer satisfaction. |
| Asset Tracking | IoT for Real-Time Tracking | Implement IoT systems to monitor real-time asset location and condition, ensuring better management of inventory and shipments. | High cost of IoT adoption, data privacy concerns regarding asset tracking information | Real-time visibility of goods in transit, improved inventory management, and faster identification of logistical bottlenecks, resulting in optimized delivery performance. | |
| Digital Supply Chain Management | Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency | Use blockchain to create transparent, secure supply chain records, ensuring end-to-end tracking of goods from source to delivery. | Complexity in blockchain implementation and high setup costs | Improved transparency and security in the supply chain, reduced risk of fraud, and faster issue resolution, leading to higher trust among suppliers and customers. | |
| Hospitality SMEs | Customer Experience Management | AI for Personalized Guest Services | Use AI to personalize guest services, from customized room preferences to dynamic pricing based on guest behavior and preferences. | Data privacy concerns, cost of AI implementation in customer-facing systems | Increased guest satisfaction, higher retention rates, and optimized revenue through personalized guest experiences and dynamic pricing models. |
| Booking Systems | Cloud-Based Booking Systems | Implement cloud-based booking engines integrated with AI to predict demand and adjust pricing strategies in real-time. | Resistance to dynamic pricing models, integration challenges with legacy booking systems | Increased booking efficiency, improved pricing strategies, and enhanced guest satisfaction through real-time data-driven booking optimization. | |
| Sustainability | Energy-Efficient Smart Systems | Use IoT-driven smart energy management systems to optimize energy usage across properties, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. | High initial costs of IoT systems and reluctance to adopt energy-saving technologies | Reduced energy costs, compliance with sustainability regulations, and improved brand reputation as a sustainable hospitality provider. | |
| Energy SMEs | Energy Management | AI for Predictive Energy Management | Deploy AI-driven energy management systems to optimize energy consumption and predict future energy needs, improving grid efficiency. | High cost of AI and IoT implementation, need for technical expertise | Improved energy usage, lower operational costs, and increased grid efficiency, reducing the overall environmental footprint of energy usage. |
| Renewable Energy Integration | IoT and Smart Grids | Use IoT-enabled smart grids to manage and optimize renewable energy integration, ensuring real-time visibility into energy distribution networks. | Integration challenges with existing grids and high upfront costs for smart grid systems | Optimized renewable energy distribution, reduced energy loss, and better management of energy demand and supply, leading to greater sustainability and regulatory compliance. | |
| Regulatory Compliance | AI for Automated Reporting | Implement AI for automated reporting to regulatory bodies, ensuring compliance with environmental and energy regulations. | Complexity of AI tools and high setup costs | Faster regulatory reporting, reduced risk of penalties for non-compliance, and improved trust in energy reporting systems. | |
| Education SMEs | Remote Learning Systems | AI for Personalized Learning | Use AI to offer personalized learning experiences for students based on their performance, preferences, and learning styles. | High cost of AI tools and reluctance to transition fully from traditional methods | Improved student engagement, better learning outcomes, and increased scalability of educational resources. |
| Research Data Management | Cloud-Based Research Platforms | Implement cloud-based research platforms to manage and share research data securely and efficiently across academic institutions. | Data security concerns and integration with existing research management systems | Enhanced collaboration between researchers, better data management, and faster access to research findings, resulting in improved academic output and innovation. | |
| Learning Management Systems (LMS) | Cloud-Based LMS | Deploy cloud-based LMS to offer a scalable, flexible platform for both students and instructors, improving access to educational materials. | Resistance to online learning methods, data privacy concerns for student information | Increased flexibility in learning options, better access to educational resources, and improved student satisfaction with learning environments. |
| Industry | Category | Sub-Category | KPIs | Metrics | Performance Insights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retail SMEs | Digital Marketing | AI-Driven Personalization | Customer Conversion Rate, Return on Investment (ROI) on Marketing Campaigns, Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) | Percentage of customers engaging with personalized marketing, overall sales increases due to targeted campaigns | High customer conversion rates and increased CLV indicate that AI-driven personalization efforts are effective at driving sales and fostering long-term customer loyalty. |
| Inventory Management | Predictive Analytics | Inventory Turnover Rate, Stockout Rate, Inventory Holding Costs | Days inventory is held, percentage of stockouts during peak sales periods | A low stockout rate and high inventory turnover indicate efficient inventory management driven by predictive analytics, reducing waste and optimizing stock availability during high-demand periods. | |
| Sales Performance | Omnichannel Sales Integration | Sales Growth by Channel, Customer Satisfaction Scores, Average Order Value (AOV) | Sales contribution per channel (online, mobile, in-store), customer ratings on experience across channels | Higher customer satisfaction scores and sales growth per channel show the effectiveness of omnichannel strategies in delivering a seamless and satisfying customer experience. | |
| Healthcare SMEs | Patient Outcomes | IoT-Enabled Monitoring | Patient Readmission Rates, Response Time to Emergencies, Patient Satisfaction Scores | Time to respond to medical emergencies, reduction in patient readmission rates | Faster response times and lower readmission rates reflect the positive impact of IoT-enabled monitoring on healthcare outcomes, improving operational efficiency and patient care. |
| Data Security and Compliance | Blockchain for Data Transparency | Number of Data Breaches, Compliance Violation Reports, Time for Cross-Institutional Data Sharing | Percentage of data securely shared across healthcare providers, compliance audits | Fewer data breaches and faster data sharing across institutions show that blockchain technology is successfully enhancing data security and compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. | |
| Financial Performance | Cloud-Based EHR Implementation | Cost Savings from Reduced On-Premise IT Infrastructure, Time to Access Patient Records | IT infrastructure cost reductions, time to retrieve patient information | Reductions in IT infrastructure costs and faster access to patient data demonstrate the operational and financial benefits of adopting cloud-based EHR systems in healthcare SMEs. | |
| Finance SMEs | Fraud Detection and Prevention | AI-Driven Fraud Detection Systems | Fraud Detection Rate, Time to Detect Fraudulent Transactions, Customer Trust Metrics | Percentage of fraudulent transactions flagged in real-time, customer satisfaction scores related to security | Higher fraud detection rates and faster detection times signal that AI-driven fraud prevention systems are improving financial security and protecting customer trust in finance-related SMEs. |
| Financial Security | Blockchain for Secure Transactions | Reduction in Audit Time, Transaction Error Rate, Compliance with PCI DSS Standards | Percentage of secure blockchain transactions, audit time reductions | Lower transaction error rates and reduced audit times indicate that blockchain systems are streamlining transaction security and improving financial compliance in SMEs. | |
| Customer Retention | AI for Personalized Banking Services | Customer Churn Rate, Average Revenue Per User (ARPU), Customer Satisfaction with Personalization | Customer feedback on personalized banking services, revenue growth per user | A reduction in customer churn and an increase in ARPU demonstrate that personalized AI-driven banking services are successfully enhancing customer engagement and loyalty. | |
| Manufacturing SMEs | Operational Efficiency | IoT for Predictive Maintenance | Machine Downtime, Cost of Maintenance, Time Between Failures (MTBF) | Percentage reduction in downtime, cost savings from predictive maintenance efforts | Lower machine downtime and higher MTBF indicate that IoT-driven predictive maintenance systems are improving operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs in manufacturing SMEs. |
| Supply Chain Management | AI for Supply Chain Optimization | Order Fulfillment Rate, Supply Chain Lead Time, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) | Percentage of orders fulfilled on time, supply chain delays reduced by AI optimization | Improved order fulfillment rates and shorter lead times signal the effectiveness of AI-driven supply chain optimization in enhancing logistical efficiency and reducing the cost of goods sold. | |
| Production Performance | Cloud-Based ERP for Production | Production Cycle Time, Scrap Rate, Resource Utilization Efficiency | Percentage reduction in production times, scrap rate per production batch | Shorter production cycles and lower scrap rates show that cloud-based ERP systems are improving production planning, reducing waste, and optimizing resource utilization in manufacturing SMEs. | |
| Logistics SMEs | Delivery Optimization | AI-Powered Route Planning | Delivery Times, Fuel Consumption per Route, Customer Satisfaction with Delivery Experience | Percentage reduction in delivery times, fuel savings per delivery route | Faster deliveries and reduced fuel consumption reflect the success of AI-powered route planning in optimizing logistical operations for logistics SMEs. |
| Real-Time Shipment Tracking | IoT for Asset Monitoring | Shipment Accuracy, Percentage of Lost or Delayed Goods, Real-Time Shipment Visibility | Reduction in lost or delayed goods, real-time tracking visibility percentages | Higher shipment accuracy and increased visibility show that IoT-based asset monitoring systems are improving logistics management and reducing the number of lost or delayed shipments. | |
| Supply Chain Transparency | Blockchain for Supply Chain Security | Time to Resolve Supply Chain Disruptions, Supplier Trust Ratings, Percentage of Secure Transactions | Percentage reduction in supply chain disputes, number of secure blockchain transactions | Fewer disruptions and higher supplier trust ratings demonstrate that blockchain technology is enhancing supply chain transparency and security for logistics SMEs. | |
| Hospitality SMEs | Customer Satisfaction | AI for Guest Personalization | Guest Retention Rate, Average Customer Satisfaction Scores, Return Booking Rates | Percentage of repeat guests, guest satisfaction with personalized services | Higher guest retention rates and improved satisfaction scores highlight the effectiveness of AI-driven guest personalization in enhancing customer experiences and driving repeat bookings. |
| Booking System Performance | Cloud-Based Booking Systems | Booking Conversion Rate, System Uptime, Revenue Per Booking | Percentage uptime of booking systems, conversion rates across booking platforms | Higher booking conversion rates and consistent system uptime indicate that cloud-based booking systems are improving booking performance and revenue generation for hospitality SMEs. | |
| Sustainability and Energy Management | IoT for Smart Energy Monitoring | Energy Cost Savings, Percentage Reduction in Energy Usage, Compliance with Sustainability Goals | Percentage reductions in energy consumption, operational cost savings from smart energy systems | Lower energy usage and higher compliance with sustainability goals reflect the successful implementation of IoT-based smart energy systems in reducing operational costs and promoting eco-friendly practices in hospitality SMEs. | |
| Energy SMEs | Grid Efficiency | AI-Driven Energy Management Systems | Grid Downtime, Energy Efficiency Metrics, Renewable Energy Utilization Rate | Percentage improvement in grid uptime, energy efficiency gains | Reduced grid downtime and increased renewable energy utilization demonstrate the positive impact of AI-driven energy management systems in optimizing energy distribution for energy SMEs. |
| Renewable Energy Management | IoT for Smart Grids | Real-Time Monitoring Accuracy, Renewable Energy Integration Rate, Energy Loss Percentage | Percentage of renewable energy sources integrated into the grid, energy loss reduction metrics | Higher integration rates of renewable energy sources and lower energy losses show that IoT-based smart grids are enhancing energy management and promoting sustainability in energy SMEs. | |
| Regulatory Compliance | AI for Automated Compliance Reporting | Compliance Violation Rates, Time to Submit Regulatory Reports, Compliance Cost Savings | Percentage reduction in regulatory reporting times, compliance-related cost savings | Faster regulatory reporting and reduced compliance costs reflect the benefits of AI-driven automated compliance systems in ensuring that energy SMEs adhere to industry standards while minimizing operational costs. | |
| Education SMEs | Learning Outcomes | AI for Personalized Learning Systems | Student Satisfaction Scores, Completion Rates of Online Courses, Average Learning Performance Improvement | Percentage of students completing courses, improvement in student performance | Higher course completion rates and improved learning outcomes show that AI-driven personalized learning systems are increasing student engagement and success in education SMEs. |
| Research Collaboration | Cloud-Based Research Data Platforms | Data Sharing Speed, Number of Collaborative Research Projects, Research Publication Rates | Percentage reduction in time for data sharing, increase in collaborative research outputs | Faster research data sharing and increased collaborative projects reflect the positive impact of cloud-based research platforms in enhancing academic collaboration and research outputs for education SMEs. | |
| Operational Efficiency | Cloud-Based Learning Management Systems (LMS) | System Uptime, Student Engagement Metrics, Instructor Satisfaction Rates | Percentage of system availability during peak times, student and instructor satisfaction scores | Improved student engagement and higher system uptime indicate that cloud-based LMS systems are enhancing learning experiences and operational efficiency in education SMEs. |
| Stage | Industry | Category | Subcategories | Key Actions for SMEs | Policy Recommendations | Expected Outcomes |
| Stage 1: Digital Awareness | Retail SMEs | Digital Marketing Adoption | Basic CRM Implementation, Online Presence | Develop digital literacy and awareness programs. Implement basic customer relationship management (CRM) systems and establish a strong online presence via websites and social media. | Provide funding for digital literacy programs aimed at retail SMEs. Offer tax incentives for investments in basic digital marketing tools and e-commerce platforms. | Improved online presence, customer engagement, and sales through basic digital marketing channels. |
| Healthcare SMEs | Telemedicine and EHR Awareness | Telemedicine Integration, Cloud EHR | Conduct awareness campaigns about the potential of telemedicine and cloud-based electronic health records (EHR). Start implementing simple digital health solutions for remote care. | Provide subsidies for healthcare SMEs to adopt telemedicine platforms. Enforce data security policies to help SMEs comply with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR. | Increased access to healthcare services through telemedicine, improved patient data management, and adherence to security standards. | |
| Finance SMEs | Financial Technology (FinTech) Adoption | Blockchain Basics, AI for Fraud Detection | Raise awareness of blockchain and AI technologies in finance. Start small-scale implementations of blockchain for secure transactions and AI for basic fraud detection. | Provide grants for SMEs in finance to experiment with AI and blockchain for secure transactions. Collaborate with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with financial regulations during the digital transformation process. | Enhanced transaction security, early-stage adoption of fraud detection technologies, and increased regulatory compliance awareness. | |
| Stage 2: Digital Integration | Manufacturing SMEs | IoT and Automation Integration | IoT for Predictive Maintenance, ERP Systems | Implement IoT devices for predictive maintenance and begin integrating ERP systems for better supply chain and production management. | Provide financial support for SMEs to adopt IoT solutions, focusing on automation and predictive maintenance. Establish tax deductions for investments in ERP systems that improve supply chain transparency and operational efficiency. | Reduced operational downtime, optimized production processes, and improved supply chain visibility. |
| Logistics SMEs | Real-Time Data Integration | AI-Powered Route Planning, IoT Shipment Tracking | Integrate IoT-based real-time shipment tracking and use AI for optimizing delivery routes. Start using predictive analytics for demand forecasting. | Offer grants for logistics SMEs to invest in AI-powered route planning tools and IoT tracking systems. Encourage the development of smart logistics hubs with integrated real-time tracking capabilities. | Improved delivery times, enhanced route optimization, and reduced shipping costs. | |
| Hospitality SMEs | Customer Experience Transformation | AI for Personalized Services, CRM for Loyalty | Integrate AI for personalized guest experiences and advanced CRM systems for loyalty programs. Build multi-channel booking systems to improve customer experience. | Provide subsidies for SMEs in hospitality to implement AI for customer personalization and CRM tools. Offer incentives for cloud-based booking platforms that integrate with various customer engagement tools. | Enhanced customer satisfaction through personalized services, increased customer retention, and streamlined booking management systems. | |
| Stage 3: Digital Optimization | Retail SMEs | E-Commerce and Omnichannel Optimization | Inventory Management, Omnichannel Strategies | Implement advanced e-commerce systems with omnichannel integration. Use predictive analytics for inventory management to optimize stock levels and reduce waste. | Support SMEs with financial incentives for adopting omnichannel e-commerce platforms. Facilitate access to advanced data analytics tools for optimizing inventory and customer management. | Higher sales growth from omnichannel platforms, reduced stockouts, and better inventory management practices. |
| Healthcare SMEs | Data Security and Compliance | Blockchain for Data Security, AI for Diagnostics | Ensure full integration of blockchain for secure data management and AI for diagnostic tools. Improve patient data security while optimizing healthcare outcomes with AI solutions. | Offer financial assistance to healthcare SMEs for integrating blockchain technologies and ensuring full compliance with healthcare data regulations. Promote the use of AI diagnostics through government-funded research and development (R&D) initiatives. | Enhanced patient care, improved data security, and better diagnostic accuracy through AI and blockchain technologies. | |
| Finance SMEs | Advanced FinTech Implementation | AI for Risk Management, Cloud-Based Systems | Fully integrate AI tools for real-time risk management and fraud detection. Adopt cloud-based systems for flexible and scalable financial operations. | Provide tax incentives for SMEs adopting cloud-based financial management systems and AI tools for fraud detection. Collaborate with financial regulatory bodies to ensure cloud solutions comply with industry standards and regulations. | Improved fraud detection, enhanced scalability of financial operations, and better compliance with financial regulations. | |
| Stage 4: Digital Expansion | Manufacturing SMEs | AI for Production and Automation | AI-Driven Production Lines, IoT for Real-Time Monitoring | Scale the use of AI-driven production systems and IoT for real-time monitoring of equipment and production processes. | Governments should offer subsidies and grants for manufacturing SMEs adopting AI and IoT at scale. Provide regulatory frameworks for the safe integration of automation technologies that do not displace workers. | Scaled production lines with minimized downtime, increased productivity, and optimized resource allocation. |
| Logistics SMEs | Global Supply Chain Visibility | Blockchain for Supply Chain, AI for Global Route Optimization | Adopt blockchain for end-to-end supply chain visibility and use AI to optimize global logistics operations. | Encourage cross-border logistics hubs powered by blockchain technology for supply chain transparency. Offer export-related tax incentives for SMEs adopting AI-driven global supply chain management systems. | Increased transparency across global supply chains, reduced logistical inefficiencies, and enhanced scalability of operations. | |
| Education SMEs | Digital Learning Expansion | AI for Personalized Learning, Cloud-Based Research Platforms | Scale the use of AI for personalized learning and cloud platforms for collaborative research across institutions. | Governments should provide funding for SMEs in education to expand their digital learning systems. Offer grants for cloud-based research management tools that enable cross-institutional collaboration and data sharing. | Expanded reach of digital education programs, improved student outcomes through personalized learning, and increased academic collaboration. | |
| Stage 5: Sustainability and Global Competitiveness | Energy SMEs | Renewable Energy and IoT Integration | IoT-Enabled Smart Grids, AI for Energy Efficiency | Fully integrate IoT for smart energy grids and AI tools for optimizing energy usage and reducing waste. Ensure full compliance with sustainability standards. | Provide tax incentives for renewable energy investments and IoT adoption in energy management. Encourage public-private partnerships to accelerate the development of smart grid infrastructure for SMEs. | Reduced energy costs, improved grid efficiency, and enhanced compliance with sustainability goals. |
| Healthcare SMEs | Sustainable Healthcare Solutions | IoT for Remote Healthcare, AI for Sustainable Operations | Use IoT and AI for sustainable healthcare delivery, including remote patient care and energy-efficient hospital operations. | Governments should offer financial support for sustainable healthcare technologies and provide incentives for reducing operational carbon footprints in healthcare facilities. | Improved healthcare access through IoT-enabled remote care, reduced operational costs, and lower environmental impact. | |
| Finance SMEs | Global Competitiveness and Digital Payments | Blockchain for Cross-Border Transactions, AI for Global Financial Operations | Adopt blockchain for cross-border transactions and integrate AI for managing global financial operations and regulatory compliance. | Promote global financial collaboration through blockchain-based secure payment systems. Provide export financing and support for SMEs looking to expand their financial operations internationally. | Enhanced global financial competitiveness, reduced costs of cross-border transactions, and improved regulatory compliance. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





