Submitted:
29 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Invasive Blood Glucose Monitoring
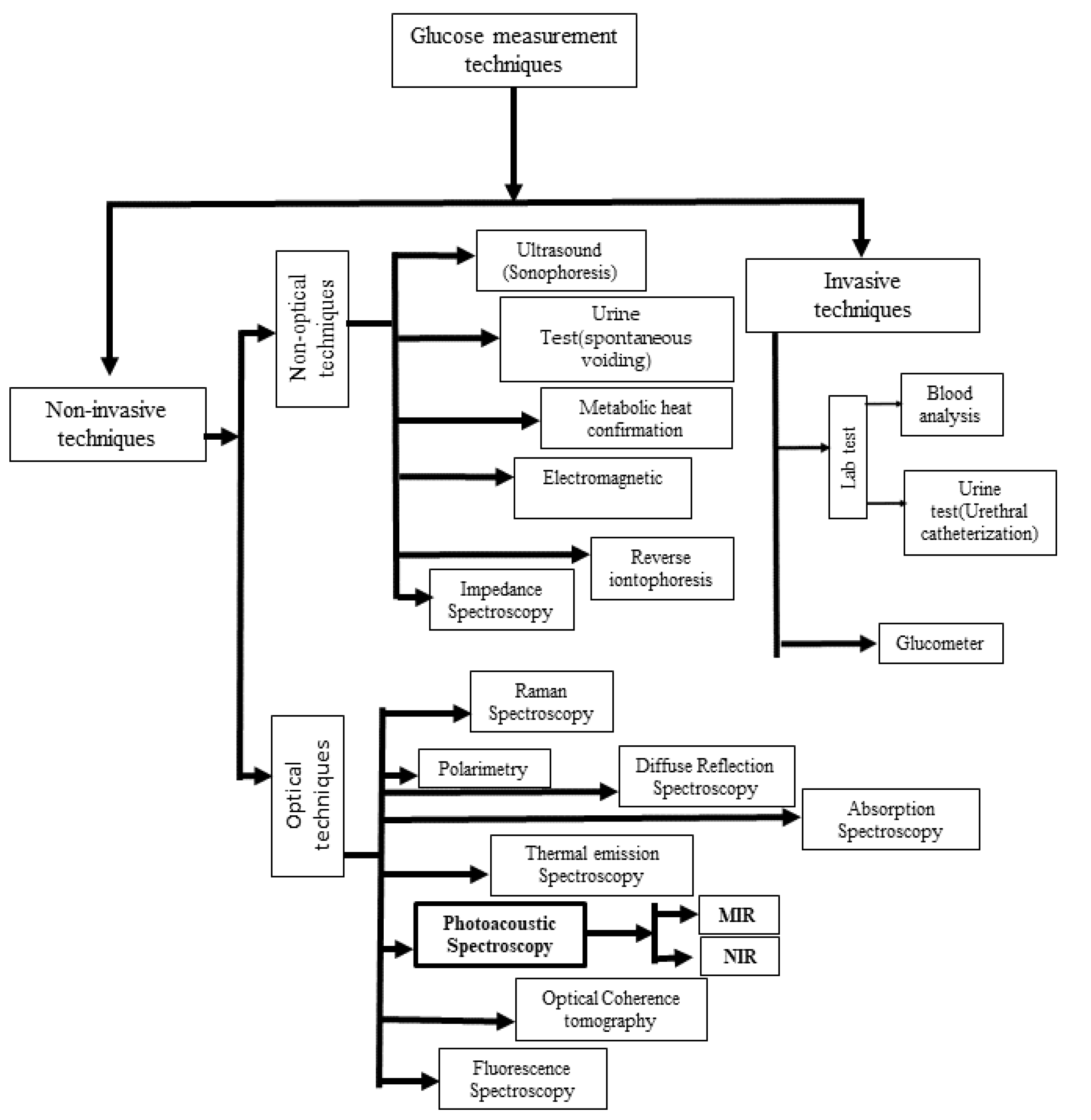
1.2. Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Monitoring
- Sensitivity: This denotes the minimum concentration that a sensor can detect. A blood glucose sensor should be capable of identifying glucose levels as low as 30 mg/dL [11].
- Stability: This pertains to the performance of a measurement device over an extended period. The device should exhibit high precision, ensuring that measurements remain consistent for the same concentration. Additionally, it should offer a high level of accuracy, meaning that measurements should not fluctuate over time.
- Selectivity: The measurement method must be able to distinguish the glucose signal from signals generated by other substances. Since glucose in the human body is present in aqueous solutions that also contain ions or proteins, which could produce interfering signals, the sensor must effectively isolate the glucose signal.
- Portability: The measurement device should be compact and convenient to carry.
2. Principle of Photoacoustic Spectroscopy for Noninvasive Glucose Detection
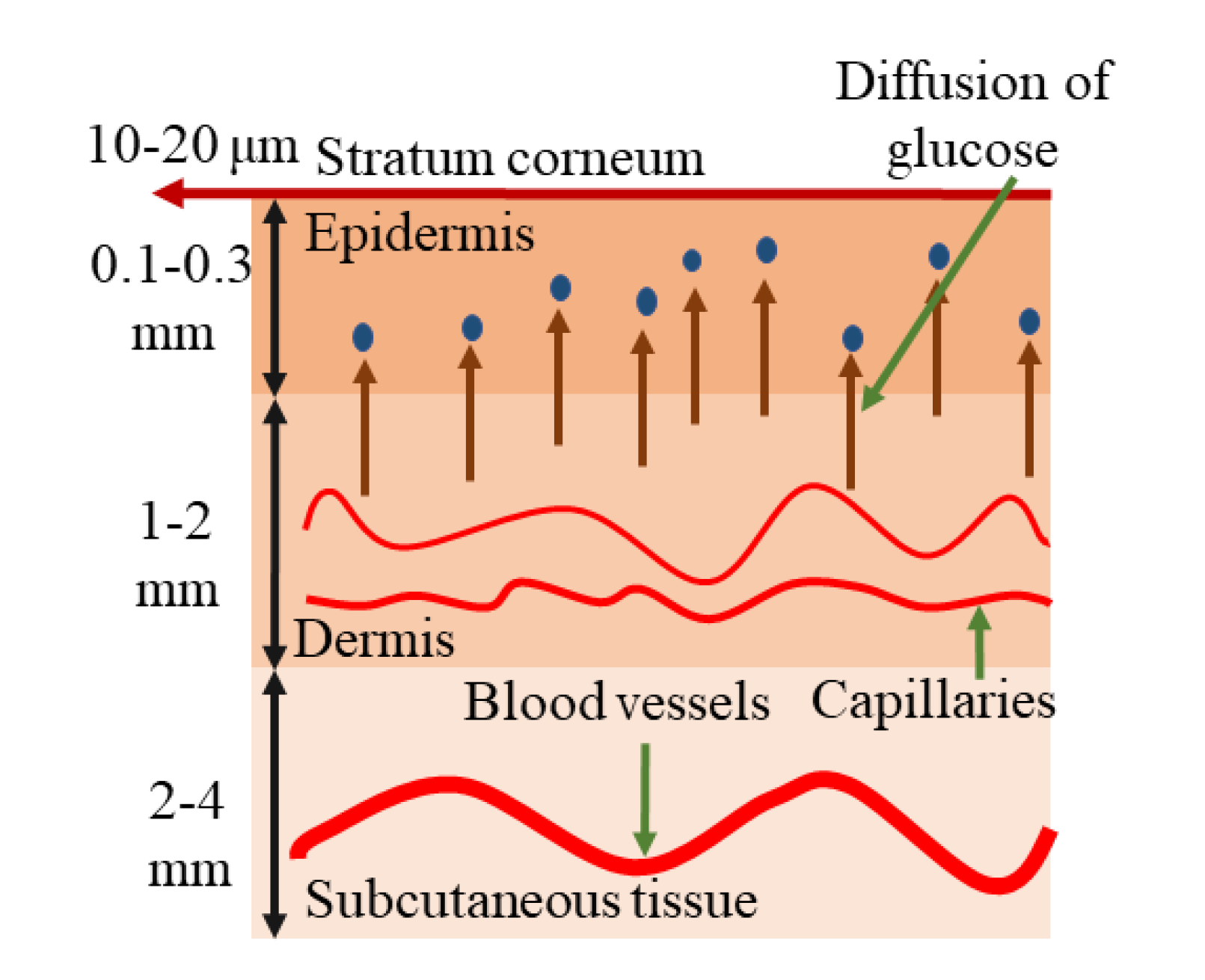
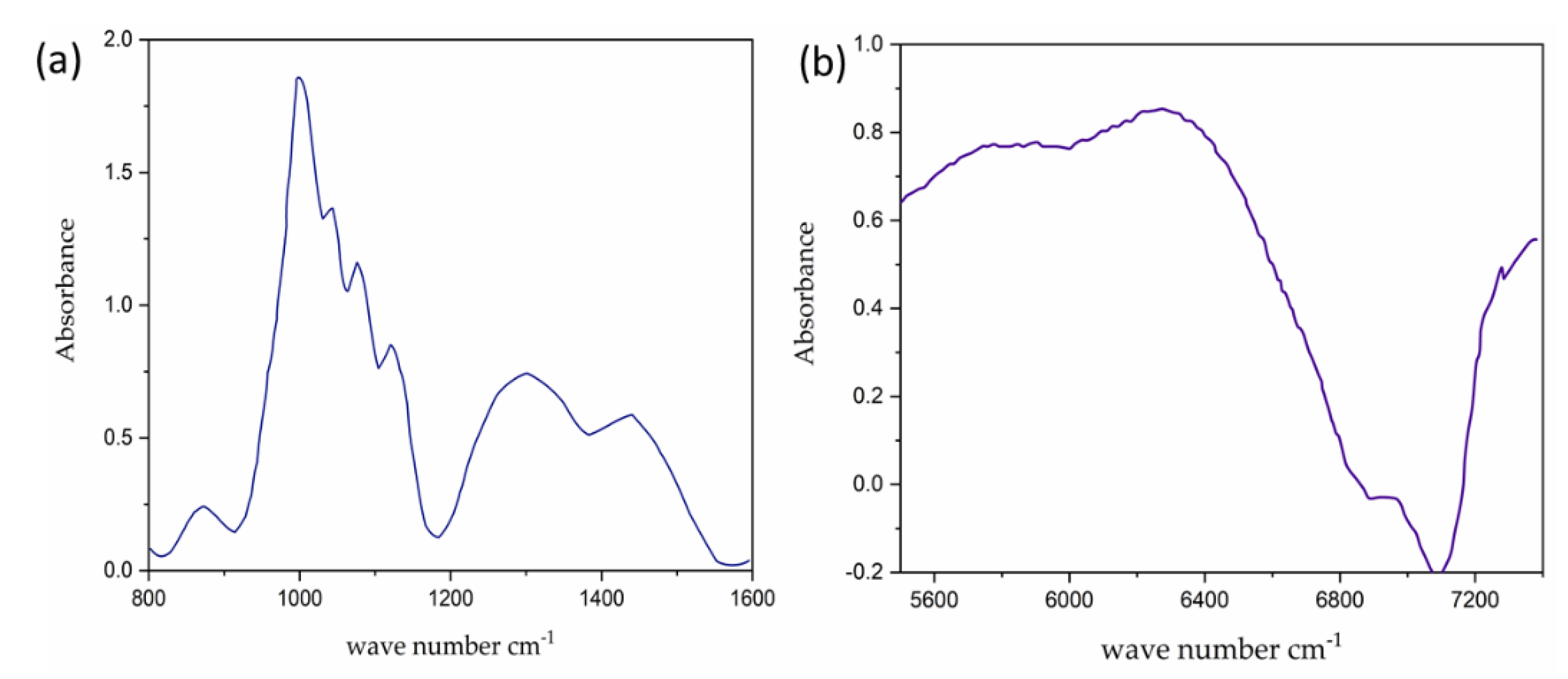
2.1. Basic Interaction of IR Light with Human Skin/Tissue
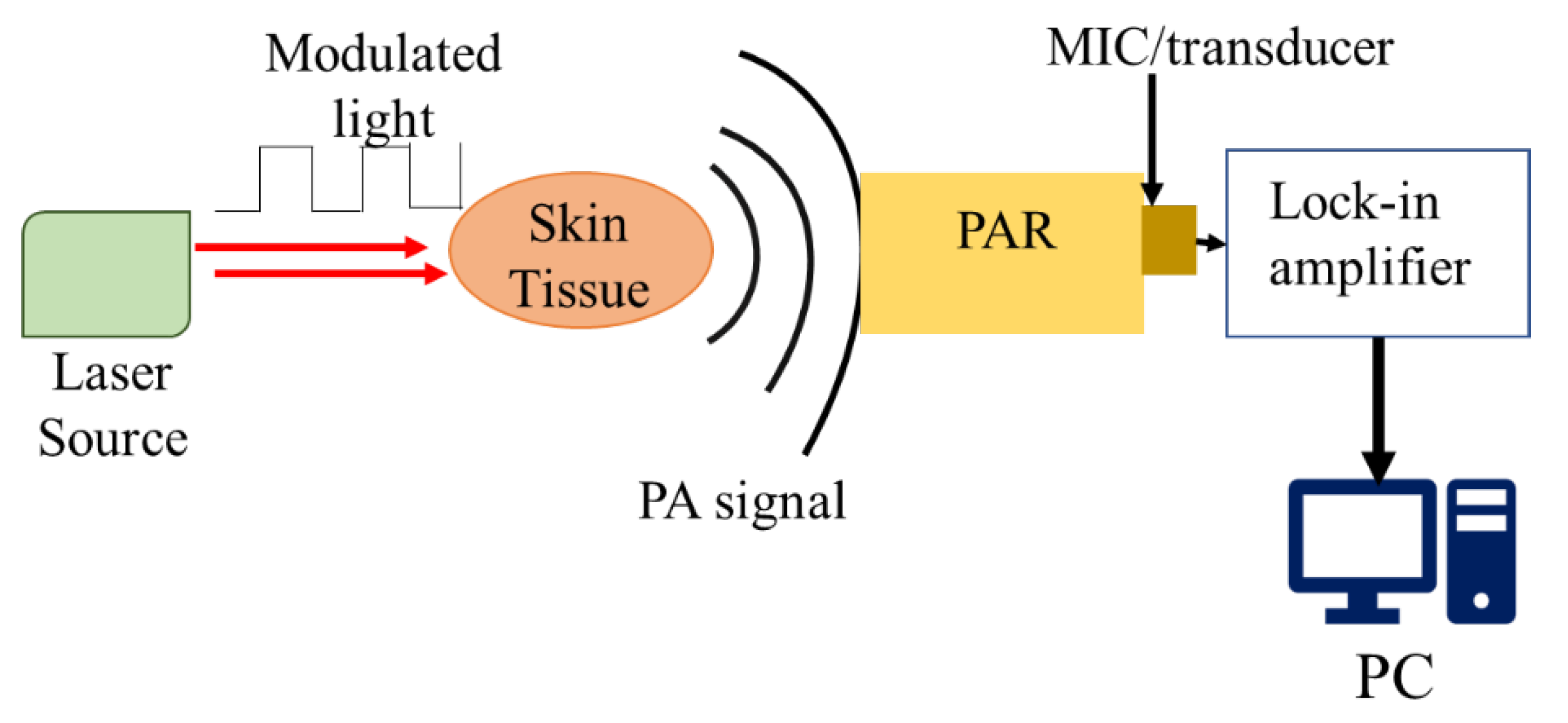
2.2. Principle of Generating and Detecting Photoacoustic Signals
2.3. Amplification Mechanism of Photoacoustic Resonator (PAR)
2.4. Design and Modeling of Photoacoustic Resonator
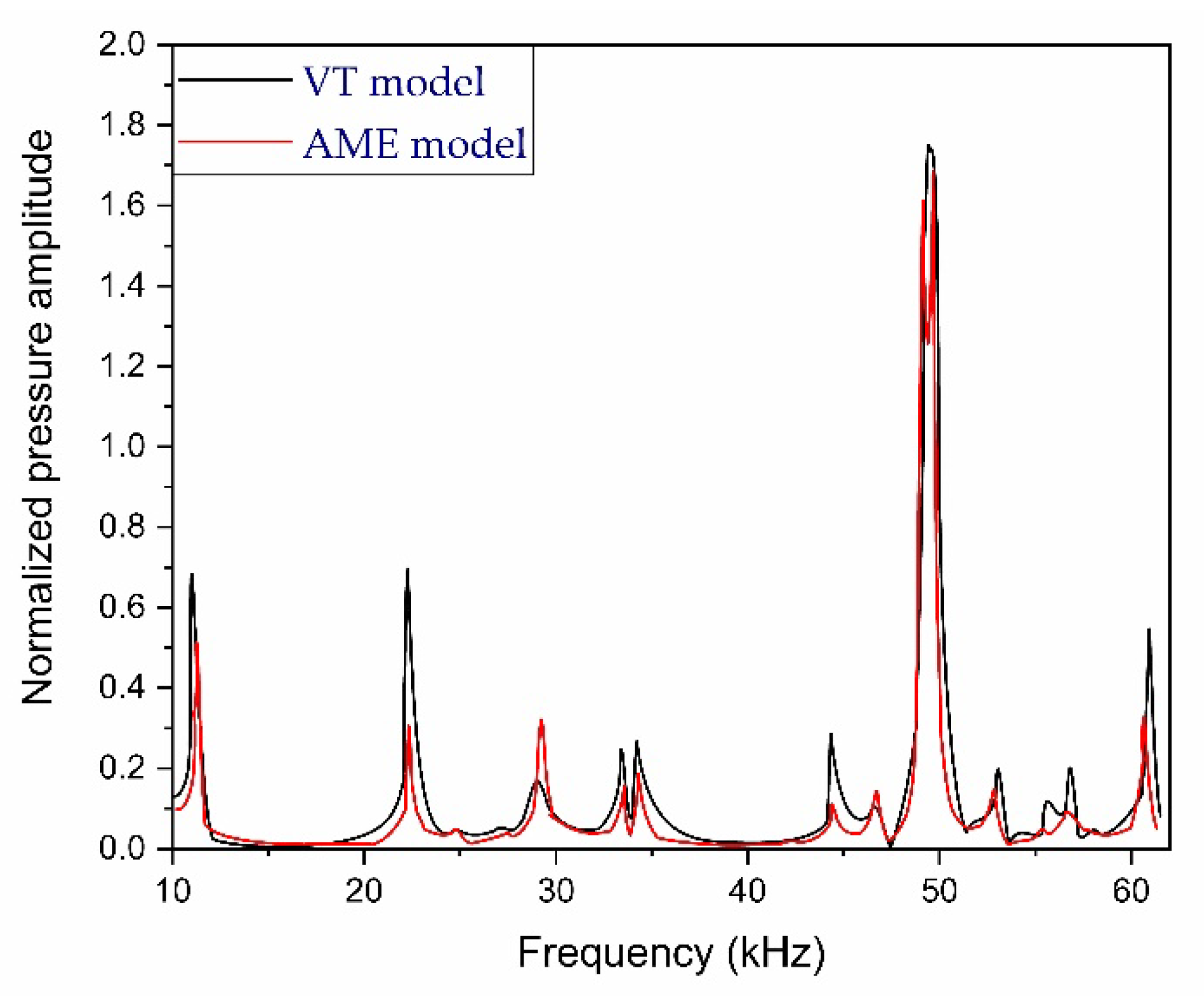
2.5. Requirements of PAR for Noninvasive Glucose Detection
- Humidity issue:
- Volume and surface loss:
- Location and position of light source & cylinders:
3. History of PA Cells Used in PAS for Noninvasive Blood Glucose Detection
| Year of Publication |
Excitation Wavelength (nm) |
Type of PA Cell | Frequency Range (kHz) |
Q-factor | Investigated Sample | Glucose level (mg/dL) |
Schematic of PA cell |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 [65] | 1382 & 1610 | Cylindrical shaped Fiber-coupled |
300-500 | ----- | Acquous Glucose solution |
50,100,150 |
 |
| 2012 [67] | 8196 to 10000 | T shaped | 50-54 | 102 | Fingertips of healthy&diabetes affected volunteers | <50, and <300 |  |
| 2013 [66] | 1382 to 1610 | Cylindrical shaped Fiber-coupled |
300-500 | ------ | Aqueous Glucose solution |
0-100 |
 |
| 2013 [39] | 9090 to 9132 | Conically shaped | ------ | ------- | Both in aqueous glucose soln and different body sites of human |
30–500 |
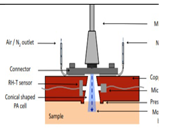 |
| 2013 [68] | 8032 to 10000 | T shaped |
50-60 | ------ | Fingertips of healthy&diabetes affected volunteers |
30-500 |
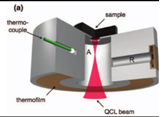 |
| 2015 [70] | 1550 | T shaped |
5.05 (resonance frequency of PA cell) |
------ | Aqueous Glucose solution |
30-500 |
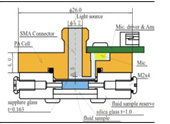 |
| 2016 [71] | 8064 to 11111 | T shaped |
51 (resonance frequency of PA cell) |
------ | Carbon black tape As reference sample |
1000 |
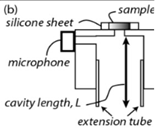 |
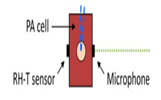
| 2016 [69] | 8032 to 10000 | conically-shaped | ------- | ------- | Both in aqueous glucose solution and fingertips of human |
0–440 |
 |
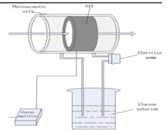
| 2017 [73] | 1064 | Cylindrical shaped |
310 (resonant peak of PZT) |
------ | Aqueous Glucose solution |
20-100 |
 |
| 2018 [72] | 8000 to 11111 | T shaped | 47.5 (resonant Peak of PA cell) |
------ | Index fingertip |
------ |
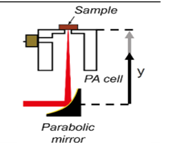 |
| 2020 [74] | ----- | T shaped | 10-60 | ----- | ------ |
----- |
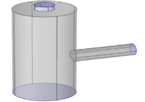 |
| 2022 [75] | 1535 | bowl-shaped structure |
0-5 ( for bandpass signal processing) |
------ | Aqueous Glucose solution |
30 to 500 |
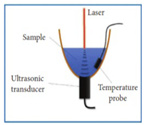 |
| 2023 [76] | 9250 | T shaped |
10 to 40 (With a frequency step of 0.15 kHz) |
------ | Biomedical skin phantom |
100 to 275 |
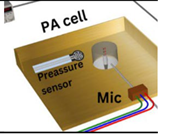 |
4. Prospects of PAR for Noninvasive Glucose Detection
- Finding proper geometry:
- Identifying proper resonant frequency of cell:
- Observation of detection sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratio(SNR):
- Importance of Manufacturing Accuracy:
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- “Diabetes.” Accessed: Jul. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes?gad_source=1#tab=tab_1.
- “Diabetes Facts and Figures | International Diabetes Federation.” Accessed: Jul. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://idf.org/about-diabetes/diabetes-facts-figures/.
- N. H. Cho et al., “IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045,” Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract., vol. 138, pp. 271–281, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Lin et al., “Projection of the future diabetes burden in the United States through 2060,” Popul. Health Metr., vol. 16, no. 1, p. 9, Dec. 2018. [CrossRef]
- “Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2010,” Diabetes Care, vol. 33, no. Supplement_1, pp. S11–S61, Jan. 2010. [CrossRef]
- L. C. Clark and C. Lyons, “ELECTRODE SYSTEMS FOR CONTINUOUS MONITORING IN CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY,” Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., vol. 102, no. 1, pp. 29–45, Oct. 1962. [CrossRef]
- W. Villena Gonzales, A. W. Villena Gonzales, A. Mobashsher, and A. Abbosh, “The Progress of Glucose Monitoring—A Review of Invasive to Minimally and Non-Invasive Techniques, Devices and Sensors,” Sensors, vol. 19, no. 4, p. 800, Feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- “Phenobarbital - Health Encyclopedia - University of Rochester Medical Center.” 2017. Accessed: Jul. 29, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=167&ContentID=glucose_urine.
- D. G. Ross, “Urinalysis,” in Imaging and Technology in Urology, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023, pp. 171–175. [CrossRef]
- L. Tang, S. J. L. Tang, S. J. Chang, C.-J. Chen, and J.-T. Liu, “Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Monitoring Technology: A Review,” Sensors, vol. 20, no. 23, p. 6925, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. von Lilienfeld-Toal, M. H. von Lilienfeld-Toal, M. Weidenmüller, A. Xhelaj, and W. Mäntele, “A novel approach to non-invasive glucose measurement by mid-infrared spectroscopy: The combination of quantum cascade lasers (QCL) and photoacoustic detection,” Vib. Spectrosc., vol. 38, no. 1–2, pp. 209–215, Jul. 2005. [CrossRef]
- H. D. Park, K. J. Lee, H. R. Yoon, and H. H. Nam, “Design of a portable urine glucose monitoring system for health care,” Comput. Biol. Med., vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 275–286, May 2005. [CrossRef]
- S. Panchbhai, “Correlation of Salivary Glucose Level with Blood Glucose Level in Diabetes Mellitus,” J. Oral Maxillofac. Res., vol. 3, no. 3, Jul. 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Iguchi et al., “A flexible and wearable biosensor for tear glucose measurement,” Biomed. Microdevices, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 603–609, Jul. 2007. [CrossRef]
- J. Moyer, D. Wilson, I. Finkelshtein, B. Wong, and R. Potts, “Correlation Between Sweat Glucose and Blood Glucose in Subjects with Diabetes,” Diabetes Technol. Ther., vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 398–402, May 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Delbeck, T. S. Delbeck, T. Vahlsing, S. Leonhardt, G. Steiner, and H. M. Heise, “Non-invasive monitoring of blood glucose using optical methods for skin spectroscopy—opportunities and recent advances,” Anal. Bioanal. Chem., vol. 411, no. 1, pp. 63–77, Jan. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Pleitez, H. M. Pleitez, H. von Lilienfeld-Toal, and W. Mäntele, “Infrared spectroscopic analysis of human interstitial fluid in vitro and in vivo using FT-IR spectroscopy and pulsed quantum cascade lasers (QCL): Establishing a new approach to non invasive glucose measurement,” Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc., vol. 85, no. 1, pp. 61–65, Jan. 2012. [CrossRef]
- “Definition of biomarker - NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms - NCI.” Accessed: Aug. 19, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/biomarker.
- J. Huang, Y. J. Huang, Y. Zhang, and J. Wu, “Review of non-invasive continuous glucose monitoring based on impedance spectroscopy,” Sensors Actuators A Phys., vol. 311, p. 112103, Aug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. A. Buehler et al., “Noninvasive Glucose Monitor Using Dielectric Spectroscopy,” Endocr. Pract., vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 142–147, Feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Sieg, R. H. Guy, and M. B. Delgado-Charro, “Noninvasive Glucose Monitoring by Reverse Iontophoresis in Vivo: Application of the Internal Standard Concept,” Clin. Chem., vol. 50, no. 8, pp. 1383–1390, Aug. 2004. [CrossRef]
- F. Tang, X. Wang, D. Wang, and J. Li, “Non-Invasive Glucose Measurement by Use of Metabolic Heat Conformation Method,” Sensors, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 3335–3344, May 2008. [CrossRef]
- J. Kost, “Ultrasound-Assisted Insulin Delivery and Noninvasive Glucose Sensing,” Diabetes Technol. Ther., vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 489–497, Aug. 2002. [CrossRef]
- M. R. Kaysir, J. M. R. Kaysir, J. Song, S. Rassel, A. Aloraynan, and D. Ban, “Progress and Perspectives of Mid-Infrared Photoacoustic Spectroscopy for Non-Invasive Glucose Detection,” Biosensors, vol. 13, no. 7, p. 716, Jul. 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. Ballerstadt, C. R. Ballerstadt, C. Evans, A. Gowda, and R. McNichols, “In Vivo Performance Evaluation of a Transdermal Near- Infrared Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Affinity Sensor for Continuous Glucose Monitoring,” Diabetes Technol. Ther., vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 296–311, Jun. 2006. [CrossRef]
- W. March, D. W. March, D. Lazzaro, and S. Rastogi, “Fluorescent Measurement in the Non-Invasive Contact Lens Glucose Sensor,” Diabetes Technol. Ther., vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 312–317, Jun. 2006. [CrossRef]
- R. O. Esenaliev, K. V. R. O. Esenaliev, K. V. Larin, I. V. Larina, and M. Motamedi, “Noninvasive monitoring of glucose concentration with optical coherence tomography,” Opt. Lett., vol. 26, no. 13, p. 992, Jul. 2001. [CrossRef]
- M. K. Enejder et al., “Raman spectroscopy for noninvasive glucose measurements,” J. Biomed. Opt., vol. 10, no. 3, p. 031114, 2005. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Lambert, C. C. J. L. Lambert, C. C. Pelletier, and M. Borchert, “Glucose determination in human aqueous humor with Raman spectroscopy,” J. Biomed. Opt., vol. 10, no. 3, p. 031110, 2005. [CrossRef]
- K. Maruo, M. K. Maruo, M. Tsurugi, M. Tamura, and Y. Ozaki, “In Vivo Noninvasive Measurement of Blood Glucose by Near-Infrared Diffuse-Reflectance Spectroscopy,” Appl. Spectrosc., vol. 57, no. 10, pp. 1236–1244, Oct. 2003. [CrossRef]
- R. Marbach, T. R. Marbach, T. Koschinsky, F. A. Gries, and H. M. Heise, “Noninvasive Blood Glucose Assay by Near-Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy of the Human Inner Lip,” Appl. Spectrosc., vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 875–881, Jul. 1993. [CrossRef]
- H. Malik and G. L. Coté, “Real-time, closed-loop dual-wavelength optical polarimetry for glucose monitoring,” J. Biomed. Opt., vol. 15, no. 1, p. 017002, 2010. [CrossRef]
- G. Purvinis, B. D. G. Purvinis, B. D. Cameron, and D. M. Altrogge, “Noninvasive Polarimetric-Based Glucose Monitoring: An in Vivo Study,” J. Diabetes Sci. Technol., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 380–387, Mar. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Vrančić et al., “Continuous glucose monitoring by means of mid-infrared transmission laser spectroscopy in vitro,” Analyst, vol. 136, no. 6, p. 1192, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0an00537a. [CrossRef]
- G. Spanner and R. Nie�ner, “New concept for the non-invasive determination of physiological glucose concentrations using modulated laser diodes,” Anal. Bioanal. Chem., vol. 354, no. 3, pp. 306–310, Jan. 1996. [CrossRef]
- J. Kottmann, J. M. J. Kottmann, J. M. Rey, and M. W. Sigrist, “New photoacoustic cell design for studying aqueous solutions and gels,” Rev. Sci. Instrum., vol. 82, no. 8, Aug. 2011. [CrossRef]
- G. Spanner and R. Niessner, “Noninvasive determination of blood constituents using an array of modulated laser diodes and a photoacoustic sensor head,” Anal. Bioanal. Chem., vol. 355, no. 3–4, pp. 327–328, Jun. 1996. [CrossRef]
- P. P. Pai, P. K. Sanki, and S. Banerjee, “A photoacoustics based continuous non-invasive blood glucose monitoring system,” in 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA) Proceedings, IEEE, May 2015, pp. 106–111. [CrossRef]
- J. Kottmann, U. J. Kottmann, U. Grob, J. Rey, and M. Sigrist, “Mid-Infrared Fiber-Coupled Photoacoustic Sensor for Biomedical Applications,” Sensors, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 535–549, Jan. 2013. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Pleitez, T. M. A. Pleitez, T. Lieblein, A. Bauer, O. Hertzberg, H. von Lilienfeld-Toal, and W. Mäntele, “In Vivo Noninvasive Monitoring of Glucose Concentration in Human Epidermis by Mid-Infrared Pulsed Photoacoustic Spectroscopy,” Anal. Chem., vol. 85, no. 2, pp. 1013–1020, 2013. [CrossRef]
- P. Beard, “Biomedical photoacoustic imaging,” Interface Focus, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 602–631, Aug. 2011. [CrossRef]
- J. Kottmann, J. J. Kottmann, J. Rey, and M. Sigrist, “Mid-Infrared Photoacoustic Detection of Glucose in Human Skin: Towards Non-Invasive Diagnostics,” Sensors, vol. 16, no. 10, p. 1663, Oct. 2016. [CrossRef]
- G. B. Christison and H. A. MacKenzie, “Laser photoacoustic determination of physiological glucose concentrations in human whole blood,” Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 284–290, May 1993. [CrossRef]
- R. Fakhlaei et al., “Application, challenges and future prospects of recent nondestructive techniques based on the electromagnetic spectrum in food quality and safety,” Food Chem., vol. 441, p. 138402, May 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. Yadav, A. J. Yadav, A. Rani, V. Singh, and B. M. Murari, “Prospects and limitations of non-invasive blood glucose monitoring using near-infrared spectroscopy,” Biomed. Signal Process. Control, vol. 18, pp. 214–227, Apr. 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. J. Burmeister and M. A. Arnold, “Evaluation of Measurement Sites for Noninvasive Blood Glucose Sensing with Near-Infrared Transmission Spectroscopy,” Clin. Chem., vol. 45, no. 9, pp. 1621–1627, Sep. 1999. [CrossRef]
- J. T. Olesberg, M. A. J. T. Olesberg, M. A. Arnold, C. Mermelstein, J. Schmitz, and J. Wagner, “Tunable Laser Diode System for Noninvasive Blood Glucose Measurements,” Appl. Spectrosc., vol. 59, no. 12, pp. 1480–1484, Dec. 2005. [CrossRef]
- V. V. Tuchin, Ed., Handbook of Optical Sensing of Glucose in Biological Fluids and Tissues. CRC Press, 2008. [CrossRef]
- S. N. Thennadil, J. L. S. N. Thennadil, J. L. Rennert, B. J. Wenzel, K. H. Hazen, T. L. Ruchti, and M. B. Block, “Comparison of Glucose Concentration in Interstitial Fluid, and Capillary and Venous Blood During Rapid Changes in Blood Glucose Levels,” Diabetes Technol. Ther., vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 357–365, Sep. 2001. [CrossRef]
- S. Liakat, K. A. S. Liakat, K. A. Bors, T.-Y. Huang, A. P. M. Michel, E. Zanghi, and C. F. Gmachl, “In vitro measurements of physiological glucose concentrations in biological fluids using mid-infrared light,” Biomed. Opt. Express, vol. 4, no. 7, p. 1083, Jul. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Rosencwaig, “Photoacoustic Spectroscopy of Biological Materials,” Science (80-. )., vol. 181, no. 4100, pp. 657–658, Aug. 1973. [CrossRef]
- K. Maruo and Y. Yamada, “Near-infrared noninvasive blood glucose prediction without using multivariate analyses: introduction of imaginary spectra due to scattering change in the skin,” J. Biomed. Opt., vol. 20, no. 4, p. 047003, 2015. [CrossRef]
- H. A. MacKenzie et al., “Advances in Photoacoustic Noninvasive Glucose Testing,” Clin. Chem., vol. 45, no. 9, pp. 1587–1595, Sep. 1999. [CrossRef]
- S. El-Busaidy, B. S. El-Busaidy, B. Baumann, M. Wolff, L. Duggen, and H. Bruhns, “Experimental and Numerical Investigation of a Photoacoustic Resonator for Solid Samples: Towards a Non-Invasive Glucose Sensor,” Sensors, vol. 19, no. 13, p. 2889, Jun. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Cox, J. G. Laufer, S. R. Arridge, and P. C. Beard, “Quantitative spectroscopic photoacoustic imaging: a review,” J. Biomed. Opt., vol. 17, no. 6, p. 061202, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, V. Ntziachristos, and D. Razansky, “Model-based optoacoustic inversion with arbitrary-shape detectors,” Med. Phys., vol. 38, no. 7, pp. 4285–4295, Jul. 2011. [CrossRef]
- L. Nie and X. Chen, “Structural and functional photoacoustic molecular tomography aided by emerging contrast agents,” Chem. Soc. Rev., vol. 43, no. 20, pp. 7132–7170, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Baumann, B. Kost, M. Wolff, and H. Groning, “Modeling and Numerical Investigation of Photoacoustic Resonators,” Model. Simul., 2008. [CrossRef]
- L. Duggen, N. L. Duggen, N. Lopes, M. Willatzen, and H.-G. Rubahn, “Finite Element Simulation of Photoacoustic Pressure in a Resonant Photoacoustic Cell Using Lossy Boundary Conditions,” Int. J. Thermophys., vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 774–785, Apr. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Glière, J. Rouxel, M. Brun, B. Parvitte, V. Zéninari, and S. Nicoletti, “Challenges in the Design and Fabrication of a Lab-on-a-Chip Photoacoustic Gas Sensor,” Sensors, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 957–974, Jan. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M. Wolff, B. Kost, and H. Groninga, “Finite element calculation of photoacoustic signals,” Appl. Opt., vol. 46, no. 7, p. 1120, Mar. 2007. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Pleitez, T. M. A. Pleitez, T. Lieblein, A. Bauer, O. Hertzberg, H. von Lilienfeld-Toal, and W. Mäntele, “Windowless ultrasound photoacoustic cell for in vivo mid-IR spectroscopy of human epidermis: Low interference by changes of air pressure, temperature, and humidity caused by skin contact opens the possibility for a non-invasive monitoring of glucose in th,” Rev. Sci. Instrum., vol. 84, no. 8, Aug. 2013. [CrossRef]
- J. Y. Sim, C.-G. J. Y. Sim, C.-G. Ahn, E.-J. Jeong, and B. K. Kim, “In vivo Microscopic Photoacoustic Spectroscopy for Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring Invulnerable to Skin Secretion Products,” Sci. Rep., vol. 8, no. 1, p. 1059, Jan. 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. El-Busaidy, B. S. El-Busaidy, B. Baumann, M. Wolff, and L. Duggen, “Shape optimization of an open photoacoustic resonator,” Appl. Sci., vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 1–11, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Camou, T. S. Camou, T. Haga, T. Tajima, and E. Tamechika, “Detection of aqueous glucose based on a cavity size- and optical-wavelength-independent continuous-wave photoacoustic technique,” Anal. Chem., vol. 84, no. 11, pp. 4718–4724, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Sensors Council, Annual IEEE Computer Conference, M. IEEE Sensors Conference 12 2013.11.03-06 Baltimore, and M. IEEE Sensors Conference 12 2013.11.04-06 Baltimore, IEEE sensors, 2013 3-6 Nov. 2013, Baltimore, Maryland, USA ; proceedings ; the 12th IEEE Sensors Conference.
- M. A. Pleitez, T. M. A. Pleitez, T. Lieblein, A. Bauer, O. Hertzberg, H. von Lilienfeld-Toal, and W. Mäntele, “In Vivo Noninvasive Monitoring of Glucose Concentration in Human Epidermis by Mid-Infrared Pulsed Photoacoustic Spectroscopy,” Anal. Chem., vol. 85, no. 2, pp. 1013–1020, Jan. 2013. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Pleitez, T. M. A. Pleitez, T. Lieblein, A. Bauer, O. Hertzberg, H. Von Lilienfeld-Toal, and W. Mäntele, “Windowless ultrasound photoacoustic cell for in vivo mid-IR spectroscopy of human epidermis: Low interference by changes of air pressure, temperature, and humidity caused by skin contact opens the possibility for a non-invasive monitoring of glucose in th,” Rev. Sci. Instrum., vol. 84, no. 8, 2013. [CrossRef]
- J. Kottmann, J. M. J. Kottmann, J. M. Rey, and M. W. Sigrist, “Mid-infrared photoacoustic detection of glucose in human skin: Towards non-invasive diagnostics,” Sensors (Switzerland), vol. 16, no. 10, Oct. 2016. [CrossRef]
- N. Wadamori, “Behavior of long-period measurements using a small-sized photoacoustic cell for aqueous glucose monitoring,” in 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), IEEE, Aug. 2015, pp. 1267–1270. [CrossRef]
- J. Y. Sim, C.-G. J. Y. Sim, C.-G. Ahn, E. Jeong, and B. K. Kim, “Photoacoustic spectroscopy that uses a resonant characteristic of a microphone for in vitro measurements of glucose concentration,” in 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), IEEE, Aug. 2016, pp. 4861–4864. [CrossRef]
- J. Y. Sim, C. G. J. Y. Sim, C. G. Ahn, E. J. Jeong, and B. K. Kim, “In vivo Microscopic Photoacoustic Spectroscopy for Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring Invulnerable to Skin Secretion Products,” Sci. Rep., vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 1–11, 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhao, W. S. Zhao, W. Tao, Q. He, H. Zhao, and H. Yang, “Glucose solution determination based on liquid photoacoustic resonance,” Appl. Opt., vol. 56, no. 2, p. 193, 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. A. S. El-Busaidy, B. Baumann, M. Wolff, and L. Duggen, “Modelling of open photoacoustic resonators,” Photoacoustics, vol. 18, no. December 2019, 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Yang, C. L. Yang, C. Chen, Z. Zhang, and X. Wei, “Glucose Determination by a Single 1535 nm Pulsed Photoacoustic Technique: A Multiple Calibration for the External Factors,” J. Healthc. Eng., vol. 2022, pp. 1–10, Sep. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Aloraynan, S. Rassel, M. R. Kaysir, and D. Ban, “Dual quantum cascade lasers for noninvasive glucose detection using photoacoustic spectroscopy,” Sci. Rep., vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 1–9, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. ISHIHARA and N. WADAMORI, “A Study on Enhancement of Sensitivity of a PhotoAcoustic Detector Cell for Non-invasive Measurements Based on Finite Element Method Analysis(Symposium on Biomedical Engineering 2007),” Trans. Japanese Soc. Med. Biol. Eng. BME, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 238–245, 2008.
- K. Tachibana, K. K. Tachibana, K. Okada, R. Kobayashi, and Y. Ishihara, “Development of a high-sensitivity and portable cell using Helmholtz resonance for noninvasive blood glucose-level measurement based on photoacoustic spectroscopy,” Proc. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. EMBS, vol. 2016-October, pp. 6477–6480, 2016. [CrossRef]
- R. Takamoto, R. R. Takamoto, R. Namba, M. Matsuoka, and T. Sawada, “Human in vivo percutaneous absorptiometry using the laser-photoacoustic method,” Anal. Chem., vol. 64, no. 21, pp. 2661–2663, Nov. 1992. [CrossRef]
- R. Takamoto, S. R. Takamoto, S. Yamamoto, R. Namba, T. Takamatsu, M. Matsuoka, and T. Sawada, “In vivo Percutaneous Absorptiometry by a Laser Photoacoustic Method Using a Novel Open-Ended Cell Combined with Light Guide,” Anal. Chem., vol. 66, no. 14, pp. 2267–2271, Jul. 1994. [CrossRef]
- Tang Z, Ni W, Li Z, Hou J, Chen S, Shum PP, Yang C. Performance Enhancement of Opened Resonance Photoacoustic Cells Based on Three Dimensional Topology Optimization. Photonics. 2021; 8(9):380. [CrossRef]
- J. Y. Sim, C. J. Y. Sim, C. -G. Ahn, E. Jeong and B. K. Kim, “Photoacoustic spectroscopy that uses a resonant characteristic of a microphone for in vitro measurements of glucose concentration,” 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 2016, pp. 4861-4864. [CrossRef]
- Haouari, R.; Rochus, V.; Lagae, L.; Rottenberg, X. Topology Optimization of an Acoustical Cell for Gaseous Photoacoustic Spectroscopy using COMSOL Multiphysics. In Proceedings of the 2017 COMSOL Conference in Rotterdam, Rotherdam, UK, 16 November 2017.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





