Submitted:
29 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Machine Learning
2.1. Supervised Learning
2.2. Semi-Supervised Learning
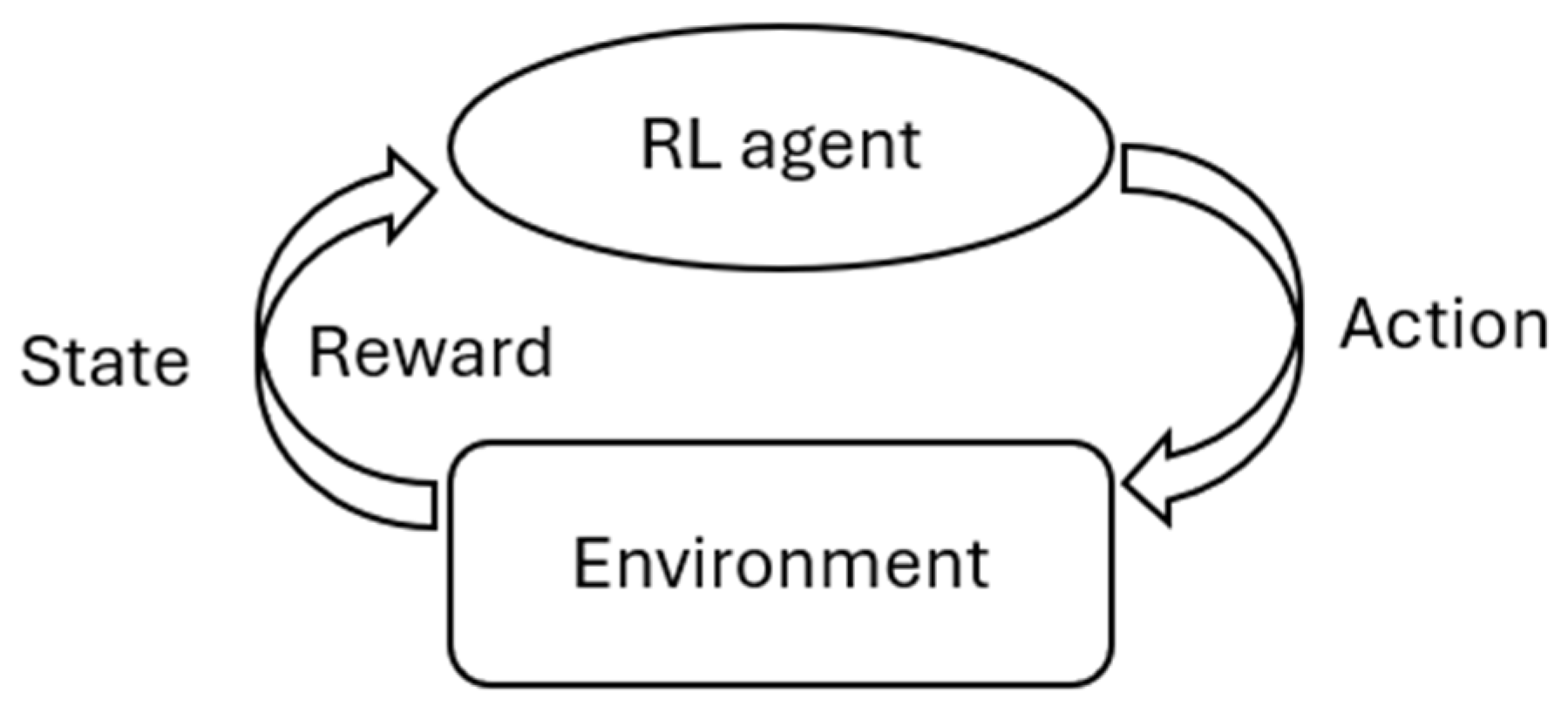
2.3. Reinforcement Learning
3. Applications of Supervised Learning in Additive Manufacturing
3.1. Fatigue Life Prediction
3.2. Quality Detection
3.3. Process Modeling and Control
4. Applications of Semi-Supervised Learning in Additive Manufacturing
5. Applications of Reinforcement Learning in Additive Manufacturing
5.1. Quality Control
5.2. Scheduling
6. Conclusions and Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethics Statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Tao, F.; Fang, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Freiheit, T. Smart Manufacturing and Intelligent Manufacturing: A Comparative Review. Engineering 2020, 7, 738–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Li, G.; Kamarthi, S.; Jin, X.; Moghaddam, M. Trends in intelligent manufacturing research: a keyword co-occurrence network based review. J. Intell. Manuf. 2022, 33, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuyal, S.; Bista, D.; Bista, R. Challenges, Opportunities and Future Directions of Smart Manufacturing: A State of Art Review. Sustain. Futur. 2020, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinez, J.F.; Chang, Q.; Gao, R.X.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J. Artificial Intelligence in Advanced Manufacturing: Current Status and Future Outlook. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2020, 142, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Kong, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, S. Recent Advances of Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing Industrial Sectors: A Review. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2021, 23, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yi, X.; Lu, S.; Johansson, K.H.; Chai, T. Intelligent Manufacturing for the Process Industry Driven by Industrial Artificial Intelligence. Engineering 2021, 7, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, R.X.; Wu, D. Deep learning for smart manufacturing: Methods and applications. J. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 48, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Xu, X.; Klotz, E.; Newman, S.T. Intelligent Manufacturing in the Context of Industry 4.0: A Review. Engineering 2017, 3, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Krishna, C.; Rajesh, R.; Ananthakrishnan, A.; Vishnuvardhan, A.; Patel, S.S.; Kapruan, C.; Brahmbhatt, S.; Kataray, T.; Narayanan, D.; et al. Industrial internet of things in intelligent manufacturing: a review, approaches, opportunities, open challenges, and future directions. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Liu, X.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Lu, W.F.; Li, B. Embodied intelligence in manufacturing: leveraging large language models for autonomous industrial robotics. J. Intell. Manuf. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evjemo, L.D.; Gjerstad, T.; Grøtli, E.I.; Sziebig, G. Trends in Smart Manufacturing: Role of Humans and Industrial Robots in Smart Factories. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2020, 1, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.; Lima, R.; Eckhardt, T.; Paiva, S. Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence in Industry 4.0 – A Literature review. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 181, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievano-Martínez, F.A.; Fernández-Ledesma, J.D.; Burgos, D.; Branch-Bedoya, J.W.; Jimenez-Builes, J.A. Intelligent Process Automation: An Application in Manufacturing Industry. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, R. Big data analytics for intelligent manufacturing systems: A review. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 62, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Shang, Y. A review of industrial big data for decision making in intelligent manufacturing. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2022, 29, 101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozjek, D.; Vrabič, R.; Rihtaršič, B.; Lavrač, N.; Butala, P. Advancing manufacturing systems with big-data analytics: A conceptual framework. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2020, 33, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imad, M.; Hopkins, C.; Hosseini, A.; Yussefian, N.; Kishawy, H. Intelligent machining: a review of trends, achievements and current progress. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2021, 35, 359–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.; Kennedy, J.V.; Potgieter, J. A comparison of traditional manufacturing vs additive manufacturing, the best method for the job. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 30, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhameed, O.; Al-Ahmari, A.; Ameen, W.; Mian, S.H. Additive manufacturing: Challenges, trends, and applications. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiawan, R.B.; Imaduddin, F.; Ariawan, D.; Ubaidillah, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Arifin, Z. A review on the fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing: Filament processing, materials, and printing parameters. Open Eng. 2021, 11, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Qin, Q.; Wang, J. A Review of Stereolithography: Processes and Systems. Processes 2020, 8, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Jabri, A. Ouballouch, L. Lasri. A Review on Selective Laser Sintering 3D Printing Technology for Polymer Materials. Proceedings of CASICAM 2022; Zarbane, K., Beidouri, Z., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, K.V.; Nandini, V.V. Direct Metal Laser Sintering: A Digitised Metal Casting Technology. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2013, 13, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, D.-G. Directed Energy Deposition (DED) Process: State of the Art. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 8, 703–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, M. Chapter 8 - Electron beam melting process: a general overview. In Additive Manufacturing; Pou, J., Riveiro, A., Davim, J.P., Eds.; Elsevier, 2021; pp. 277–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafaei, A.; Elliott, A.M.; Barnes, J.E.; Li, F.; Tan, W.; Cramer, C.L.; Nandwana, P.; Chmielus, M. Binder jet 3D printing—Process parameters, materials, properties, modeling, and challenges. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 119, 100707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkaseer, A.; Chen, K.J.; Janhsen, J.C.; Refle, O.; Hagenmeyer, V.; Scholz, S.G. Material jetting for advanced applications: A state-of-the-art review, gaps and future directions. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Amouzandeh, R.; Vogts, H.; Luallen, E.; Arzani, M. A brief review on the mechanisms and approaches of silk spinning-inspired biofabrication. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1252499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Li, Y.; Ling, S.; Huang, W.; Cebe, P.; Hsu, H.; De Ferrari, F.; Jiang, X.; et al. 3D Printing of Silk Protein Structures by Aqueous Solvent-Directed Molecular Assembly. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 20, 1900191–e1900191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M.; Mathur, A. Toward intelligent training of supervised image classifications: directing training data acquisition for SVM classification. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Jain, V.; Mishra, A. An Analysis Of Convolutional Neural Networks For Image Classification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 132, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, D.; Koli, A.; Khatter, K.; Singh, S. Natural language processing: state of the art, current trends and challenges. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2022, 82, 3713–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anumanchipalli, G.K.; Chartier, J.; Chang, E.F. Speech synthesis from neural decoding of spoken sentences. Nature 2019, 568, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Hu, R.; Li, Z.; Attarian, S.; Björk, K.-M.; Lendasse, A. A machine-learning-enhanced hierarchical multiscale method for bridging from molecular dynamics to continua. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 32, 14359–14373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Li, J.; Bordas, S.P.A.; Kim, A.M. Artificial neural networks and their applications in computational materials science: A review and a case study. In Advances in Applied Mechanics; Elsevier, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, F.; Mudireddy, A.; Mantilla, R.; Xiao, S. Using a physics-based hydrological model and storm transposition to investigate machine-learning algorithms for streamflow prediction. J. Hydrol. 2023, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.; Wiegratz, K. Machine learning methods in finance: Recent applications and prospects. Eur. Financial Manag. 2023, 29, 1657–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R.; Rab, S. Significance of machine learning in healthcare: Features, pillars and applications. Int. J. Intell. Networks 2022, 3, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Liu, J.; Nemati, S.; Yin, G. Reinforcement Learning in Healthcare: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 55, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yao, L.; McAuley, J.; Zhou, G.; Wang, X. Deep reinforcement learning in recommender systems: A survey and new perspectives. Knowledge-Based Syst. 2023, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V. Playing Atari with Deep Reinforcement Learning. 2013. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.5602v1 (accessed on 19 September 2021).
- Cai, M.; Xiao, S.; Li, J.; Kan, Z. Safe reinforcement learning under temporal logic with reward design and quantum action selection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cai, M.; Kan, Z.; Xiao, S. Model-free reinforcement learning for motion planning of autonomous agents with complex tasks in partially observable environments. Auton. Agents Multi-Agent Syst. 2024, 38, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambly, B.; Xu, R.; Yang, H. Recent advances in reinforcement learning in finance. Math. Finance 2023, 33, 437–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, C.; Shahidehpour, M.; Yang, T.; Zeng, Z.; Chai, T. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Smart Grid Operations: Algorithms, Applications, and Prospects. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 1055–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Li, C. Applying Neural-Network-Based Machine Learning to Additive Manufacturing: Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Engineering 2019, 5, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; McWilliams, B.; Jarosinski, W.; Park, H.-Y.; Jung, Y.-G.; Lee, J.; Zhang, J. Machine Learning in Additive Manufacturing: A Review. JOM 2020, 72, 2363–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, G.; Khairallah, S.; Matthews, M.; King, W.E.; Elwany, A. Gaussian process-based surrogate modeling framework for process planning in laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing of 316L stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 94, 3591–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffar, M.; Paul, A.; Al-Bahrani, R.; Wolff, S.; Choudhary, A.; Agrawal, A.; Ehmann, K.; Cao, J. Data-driven prediction of the high-dimensional thermal history in directed energy deposition processes via recurrent neural networks. Manuf. Lett. 2018, 18, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.; Bian, L. Deep Learning for Distortion Prediction in Laser-Based Additive Manufacturing using Big Data. Manuf. Lett. 2019, 20, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Mahadevan, S. Uncertainty quantification and management in additive manufacturing: current status, needs, and opportunities. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 2855–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Shang, X.; Zhao, M.; Dong, X.; Xiong, G.; Wang, F.-Y. A Learning-Based Framework for Error Compensation in 3D Printing. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 4042–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tootooni, M.S.; Dsouza, A.; Donovan, R.; Rao, P.K.; Kong, Z.; Borgesen, P. Classifying the Dimensional Variation in Additive Manufactured Parts From Laser-Scanned Three-Dimensional Point Cloud Data Using Machine Learning Approaches. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2017, 139, 091005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, C.; Reutzel, E.W.; Petrich, J.; Nassar, A.R.; Phoha, S. Application of supervised machine learning for defect detection during metallic powder bed fusion additive manufacturing using high resolution imaging. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 21, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Gopi, T.; Harikeerthana, N.; Gupta, M.K.; Gaur, V.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Wu, C. Machine learning techniques in additive manufacturing: a state of the art review on design, processes and production control. J. Intell. Manuf. 2022, 34, 21–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M. Industry 4.0, digitization, and opportunities for sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 252, 119869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, D.; Constantinescu, C.; Westkämper, E. Smart Factory - A Step towards the Next Generation of Manufacturing. In Manufacturing Systems and Technologies for the New Frontier; Mitsuishi, M., Ueda, K., Kimura, F., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2008; pp. 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Behzadi, M.M.; Ilieş, H.T. Real-Time Topology Optimization in 3D via Deep Transfer Learning. Comput. Des. 2021, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.X.; Chen, C.-T.; Richmond, D.J.; Buehler, M.J. Bioinspired hierarchical composite design using machine learning: simulation, additive manufacturing, and experiment. Mater. Horizons 2018, 5, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, K.; Wang, H.; Sudo, H.; Chiba, A. Simple method to construct process maps for additive manufacturing using a support vector machine. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, D. Prediction of melt pool temperature in directed energy deposition using machine learning. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 37, 101692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Data-driven cost estimation for additive manufacturing in cybermanufacturing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 46, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.C.-Y. Machine learning approaches to knowledge synthesis and integration tasks for advanced engineering automation. Comput. Ind. 1990, 15, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Wu, C. Eliminating intermetallic compounds via Ni interlayer during friction stir welding of dissimilar Mg/Al alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 4353–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzadeh, M.; Chowdhury, S.; Tschopp, M.A.; Doude, H.R.; Marufuzzaman, M.; Bian, L. In-situ monitoring of melt pool images for porosity prediction in directed energy deposition processes. IISE Trans. 2018, 51, 437–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, G.; Elwany, A.; Sang, H. Prediction of porosity in metal-based additive manufacturing using spatial Gaussian process models. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 12, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, F.; Witherell, P.; Lane, B. Identifying Uncertainty in Laser Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing Models. J. Mech. Des. 2016, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-W.; Lin, C.-J. A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 2002, 13, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning; 2010; pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Cowan, C.; Grant, P. Orthogonal least squares learning algorithm for radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 1991, 2, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 378, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heess, N.; Hunt, J.J.; Lillicrap, T.P.; Silver, D. Memory-based control with recurrent neural networks. 2015. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.04455v1 (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 1994, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, N.; Jockisch, A. Are GRU Cells More Specific and LSTM Cells More Sensitive in Motive Classification of Text? Front. Artif. Intell. 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q. Are Transformers Effective for Time Series Forecasting? Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 11121–11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Engelen, J.E.; Hoos, H.H. A survey on semi-supervised learning. Mach. Learn. 2019, 109, 373–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarowsky, D. Unsupervised word sense disambiguation rivaling supervised methods. The 33rd annual meeting; pp. 189–196.
- D. Berthelot, N. Carlini, I. Goodfellow, A. Oliver, N. Papernot, and C. Raffel, “MixMatch: a holistic approach to semi-supervised learning,” in Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Red Hook, NY, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2019.
- Q. Xie, Z. Dai, E. Hovy, M.-T. Luong, and Q. V. Le, “Unsupervised data augmentation for consistency training,” in Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, in NIPS ’20. Red Hook, NY, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2020.
- D. Berthelot et al., “ReMixMatch: Semi-Supervised Learning with Distribution Matching and Augmentation Anchoring,” in International Conference on Learning Representations, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:213757781.
- K. Sohn et al., “FixMatch: simplifying semi-supervised learning with consistency and confidence,” in Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, in NIPS ’20. Red Hook, NY, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2020.
- Cascante-Bonilla, P.; Tan, F.; Qi, Y.; Ordonez, V. Curriculum Labeling: Revisiting Pseudo-Labeling for Semi-Supervised Learning. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 6912–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. I. J. Guo, Z. Liu, S. M. I. T. Zhang, and F. I. C. L. P. Chen, “Incremental Self-training for Semi-supervised Learning,” 2024. [Online]. Available: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:269283005.
- Blum, A.; Mitchell, T. Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training. In Proceedings of the eleventh annual conference on Computational learning theory-COLT’ 98. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Tao, D.; Wang, Y. A general framework for co-training and its applications. Neurocomputing 2015, 167, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Cai, W.; Zhang, L.; Yu, L.; Li, W. A review of research on co-training. Concurr. Comput. Pr. Exp. 2021, 35, e6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Balcan, A. Blum, and K. Yang, “Co-Training and Expansion: Towards Bridging Theory and Practice,” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, L. Saul, Y. Weiss, and L. Bottou, Eds., MIT Press, 2004. [Online]. Available: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2004/file/9457fc28ceb408103e13533e4a5b6bd1-Paper.pdf.
- Nigam, K.; Ghani, R. Analyzing the effectiveness and applicability of co-training. CIKM00: Ninth International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, United StatesDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 86–93.
- S. A. Goldman and Y. Zhou, “Enhancing Supervised Learning with Unlabeled Data,” in International Conference on Machine Learning, 2000. [Online]. Available: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:1215747.
- Zhou, Z.-H.; Li, M. Tri-training: exploiting unlabeled data using three classifiers. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2005, 17, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W. Xi-l, “Semi-supervised regression based on support vector machine co-training,” Comput. Eng. Appl., 2011, [Online]. Available: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:201894734.
- Ferreira, R.E.P.; Lee, Y.J.; Dórea, J.R.R. Using pseudo-labeling to improve performance of deep neural networks for animal identification. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Smith, S.L.; Belta, C.; Rus, D. Optimal Control of Markov Decision Processes With Linear Temporal Logic Constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2014, 59, 1244–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ravenzwaaij, D.; Cassey, P.; Brown, S.D. A simple introduction to Markov Chain Monte–Carlo sampling. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2016, 25, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beranek, W.; Howard, R.A. Dynamic Programming and Markov Processes. Technometrics 1961, 3, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, C.J.C.H.; Dayan, P. Q-learning. Mach. Learn. 1992, 8, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. van Hasselt, A. Guez, and D. Silver, “Deep Reinforcement Learning with Double Q-Learning,” in AAAI’16: Proceedings of the Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2016, pp. 2094–2100.
- S. Kakade and J. Langford, “Approximately optimal approximate reinforcement learning,” in In Proc. 19th International Conference on Machine Learning, Citeseer, 2002.
- J. Schulman, F. Wolski, P. Dhariwal, A. Radford, and O. Klimov, “Proximal policy optimization algorithms,” arXiv. arXiv, Jul. 19, 2017. Accessed: Nov. 23, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06347v2.
- Dang, L.; He, X.; Tang, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, T. A fatigue life prediction approach for laser-directed energy deposition titanium alloys by using support vector regression based on pore-induced failures. Int. J. Fatigue 2022, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, X.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. Internal pores in DED Ti-6.5Al-2Zr-Mo-V alloy and their influence on crack initiation and fatigue life in the mid-life regime. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 28, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y. Murakami, “18 - Additive manufacturing: effects of defects,” in Metal Fatigue (Second Edition), Y. Murakami, Ed., Academic Press, 2019, pp. 453–483. [CrossRef]
- Salvati, E.; Tognan, A.; Laurenti, L.; Pelegatti, M.; De Bona, F. A defect-based physics-informed machine learning framework for fatigue finite life prediction in additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 2022, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, S.; Brückner-Foit, A.; Brandão, A.; Gumpinger, J.; Ghidini, T.; Beretta, S. Fatigue properties of AlSi10Mg obtained by additive manufacturing: Defect-based modelling and prediction of fatigue strength. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2017, 187, 165–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, S.-P.; Luo, C.; Liao, D.; Wang, Q. Physics-guided machine learning frameworks for fatigue life prediction of AM materials. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, P.; Erdogan, F. A Critical Analysis of Crack Propagation Laws. J. Basic Eng. 1963, 85, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, Z.; Ogawa, Y.; Akebono, H.; Sugeta, A.; Hayashi, Y. Machine-learning-based investigation into the effect of defect/inclusion on fatigue behavior in steels. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 155, 106597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Wu, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, G. Defect-correlated fatigue resistance of additively manufactured Al-Mg4.5Mn alloy with in situ micro-rolling. J. Mech. Work. Technol. 2021, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. Microstructure and fatigue behavior of a laser additive manufactured 12CrNi2 low alloy steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Shi, D.; Yang, X. A tensile properties-related fatigue strength predicted machine learning framework for alloys used in aerospace. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2024, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yue, X.; Wang, H. Predictability of Different Machine Learning Approaches on the Fatigue Life of Additive-Manufactured Porous Titanium Structure. Metals 2024, 14, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhilash, P.M.; Ahmed, A. Convolutional neural network–based classification for improving the surface quality of metal additive manufactured components. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 3873–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Crampton, A.; Parkinson, S. A Layer-Wise Surface Deformation Defect Detection by Convolutional Neural Networks in Laser Powder-Bed Fusion Images. Materials 2022, 15, 7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banadaki, Y.; Razaviarab, N.; Fekrmandi, H.; Li, G.; Mensah, P.; Bai, S.; Sharifi, S. Automated Quality and Process Control for Additive Manufacturing using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Recent Prog. Mater. 2021, 4, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, J.; Rodriguez, S.; Omidvarkarjan, D.; Ferchow, J.; Meboldt, M. Recognition of Additive Manufacturing Parts Based on Neural Networks and Synthetic Training Data: A Generalized End-to-End Workflow. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L. “MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, Jun. 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. CoRR 2015, abs/1512.03385.
- K. Simonyan and A. Zisserman, “Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition,” CoRR, vol. abs/1409.1556, 2014, [Online]. Available: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:14124313.
- Wenzel, S.; Slomski-Vetter, E.; Melz, T. Optimizing System Reliability in Additive Manufacturing Using Physics-Informed Machine Learning. Machines 2022, 10, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.Q. Orthogonal Column Latin Hypercubes and Their Application in Computer Experiments. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1998, 93, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusuzoglu, B.; Mahadevan, S. Physics-Informed and Hybrid Machine Learning in Additive Manufacturing: Application to Fused Filament Fabrication. JOM 2020, 72, 4695–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoerk, M.; Gonzalez-Gutierrez, J.; Lichal, C.; Cajner, H.; Berger, G.R.; Schuschnigg, S.; Cardon, L.; Holzer, C. Optimisation of the Adhesion of Polypropylene-Based Materials during Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing. Polymers 2018, 10, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perani, M.; Jandl, R.; Baraldo, S.; Valente, A.; Paoli, B. Long-short term memory networks for modeling track geometry in laser metal deposition. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1156630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inyang-Udoh, U.; Chen, A.; Mishra, S. A Learn-and-Control Strategy for Jet-Based Additive Manufacturing. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2022, 27, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang-Udoh, U.; Mishra, S. A Physics-Guided Neural Network Dynamical Model for Droplet-Based Additive Manufacturing. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2021, 30, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xie, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, Z. A Transfer Learning-Based Multi-Fidelity Point-Cloud Neural Network Approach for Melt Pool Modeling in Additive Manufacturing. ASCE-ASME J Risk Uncert Engrg Sys Part B Mech Engrg 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Jiang, P.; Zhou, Q.; Shao, X.; Hu, J.; Meng, X. An on-line variable fidelity metamodel assisted Multi-objective Genetic Algorithm for engineering design optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 66, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; He, S.; Yang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Peng, Y.; et al. Identification of cladding layer offset using infrared temperature measurement and deep learning for WAAM. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, S. Automatic quality inspection in additive manufacturing using semi-supervised deep learning. J. Intell. Manuf. 2022, 34, 3091–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, D.; Ikami, D.; Yamasaki, T.; Aizawa, K. Joint Optimization Framework for Learning with Noisy Labels. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 5552–5560.
- Westphal, E.; Seitz, H. A machine learning method for defect detection and visualization in selective laser sintering based on convolutional neural networks. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. N. Rizve, K. Duarte, Y. S. Rawat, and M. Shah, “In Defense of Pseudo-Labeling: An Uncertainty-Aware Pseudo-label Selection Framework for Semi-Supervised Learning,” ArXiv, vol. abs/2101.06329, 2021, [Online]. Available: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:231632854.
- Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, X. A new graph-based semi-supervised method for surface defect classification. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2020, 68, 102083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lv, S.; Deng, Y.; Li, X. A Weakly Supervised Surface Defect Detection Based on Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 42285–42296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Yuan, K. A Compact Convolutional Neural Network for Surface Defect Inspection. Sensors 2020, 20, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scime, L.; Beuth, J. A multi-scale convolutional neural network for autonomous anomaly detection and classification in a laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H. Predicting the Printability in Selective Laser Melting with a Supervised Machine Learning Method. Materials 2020, 13, 5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.J.; Li, H. A machine learning guided investigation of quality repeatability in metal laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 2021, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.V.; Hum, A.J.W.; Tran, T. A semi-supervised machine learning approach for in-process monitoring of laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Today: Proc. 2022, 70, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.V.; Hum, A.J.W.; Do, T.; Tran, T. Semi-supervised machine learning of optical in-situ monitoring data for anomaly detection in laser powder bed fusion. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2022, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaro, I.A.; Jayasinghe, S.; Sutcliffe, C.; Black, K.; Paoletti, P.; Green, P.L. Automatic fault detection for laser powder-bed fusion using semi-supervised machine learning. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.A.; Ivanoff, T.A.; Dagel, D.; Madison, J.D.; Jared, B. Linking pyrometry to porosity in additively manufactured metals. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 31, 100946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scime, L.; Beuth, J. Using machine learning to identify in-situ melt pool signatures indicative of flaw formation in a laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 25, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Giera, B.; Guss, G.; Matthews, I.; Mcmains, S. Semi-Supervised Convolutional Neural Networks for In-Situ Video Monitoring of Selective Laser Melting. 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, United StatesDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 744–753.
- Larsen, S.; Hooper, P.A. Deep semi-supervised learning of dynamics for anomaly detection in laser powder bed fusion. J. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 33, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiyan, V.; Drissi-Daoudi, R.; Shevchik, S.; Masinelli, G.; Le-Quang, T.; Logé, R.; Wasmer, K. Semi-supervised Monitoring of Laser powder bed fusion process based on acoustic emissions. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2021, 16, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondara, L. Medical Image Denoising Using Convolutional Denoising Autoencoders. 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, SpainDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 241–246.
- Mahmud, M.S.; Huang, J.Z.; Fu, X. Variational Autoencoder-Based Dimensionality Reduction for High-Dimensional Small-Sample Data Classification. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Appl. 2020, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hahn, T.; Mechefske, C.K. Self-supervised learning for tool wear monitoring with a disentangled-variational-autoencoder. Int. J. Hydromechatronics 2021, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegl, T.; Seeböck, P.; Waldstein, S.M.; Langs, G.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. f-AnoGAN: Fast unsupervised anomaly detection with generative adversarial networks. Med Image Anal. 2019, 54, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Standfield, B.; Dou, C.; Law, A.C.; Kong, Z.J. Real-time process monitoring and closed-loop control on laser power via a customized laser powder bed fusion platform. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmawan, A.G.; Xiong, Y.; Foong, S.; Soh, G.S. A Model-Based Reinforcement Learning and Correction Framework for Process Control of Robotic Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, FranceDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 4030–4036.
- Knaak, C.; Masseling, L.; Duong, E.; Abels, P.; Gillner, A. Improving Build Quality in Laser Powder Bed Fusion Using High Dynamic Range Imaging and Model-Based Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 55214–55231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoke, F.; Farimani, A.B. Thermal control of laser powder bed fusion using deep reinforcement learning. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, H.; Lane, B.; Donmez, M.; Fox, J.; Neira, J. Implementation of Advanced Laser Control Strategies for Powder Bed Fusion Systems. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 26, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Chang, H.; Wu, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhai, Z. An intelligent process parameters optimization approach for directed energy deposition of nickel-based alloys using deep reinforcement learning. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 120, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. Rosenthal, “Mathematical Theory of Heat Distribution during Welding and Cutting,” Weld. J., vol. 20, pp. 220–234, 1941.
- Dharmadhikari, S.; Menon, N.; Basak, A. A reinforcement learning approach for process parameter optimization in additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. W. Eagar and N.-S. Tsai, “Temperature Fields Produced by Travelling Distributed Heat Sources.,” Weld. J. Miami Fla, vol. 62, no. 12, pp. 346–355, 1983.
- Chung, J.; Shen, B.; Law, A.C.C.; Kong, Z. (. Reinforcement learning-based defect mitigation for quality assurance of additive manufacturing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 65, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicastro, M.; Ferone, D.; Festa, P.; Fugaro, S.; Pastore, T. A reinforcement learning iterated local search for makespan minimization in additive manufacturing machine scheduling problems. Comput. Oper. Res. 2021, 131, 105272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, K.-C.; Lin, S.-W. Minimizing makespan in two-stage assembly additive manufacturing: A reinforcement learning iterated greedy algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukkoc, I. MILP models to minimise makespan in additive manufacturing machine scheduling problems. Comput. Oper. Res. 2019, 105, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kucukkoc, I.; Zhang, D.Z. Production planning in additive manufacturing and 3D printing. Comput. Oper. Res. 2017, 83, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




