Submitted:
26 September 2024
Posted:
27 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
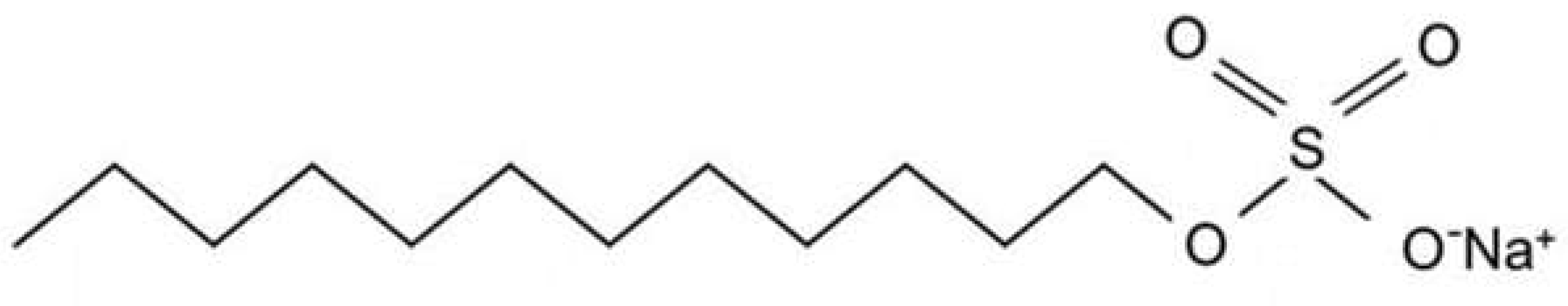
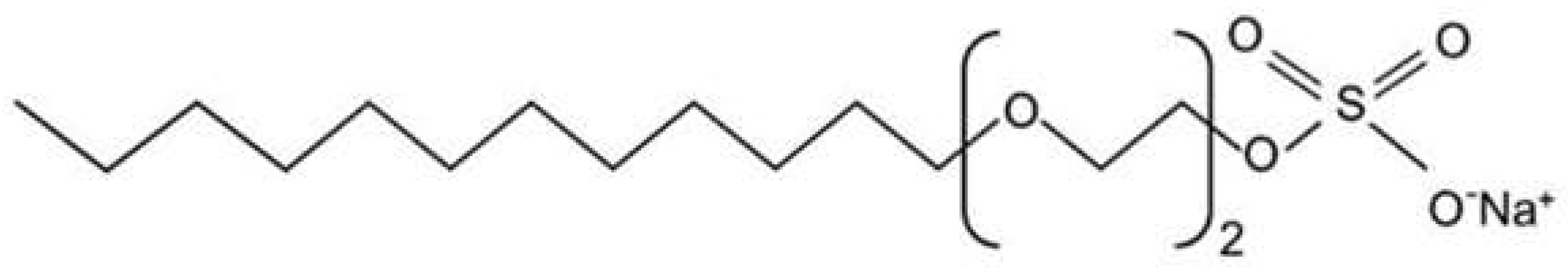
1.1. What Are Sulfates?
1.2. Issues with Sulfates
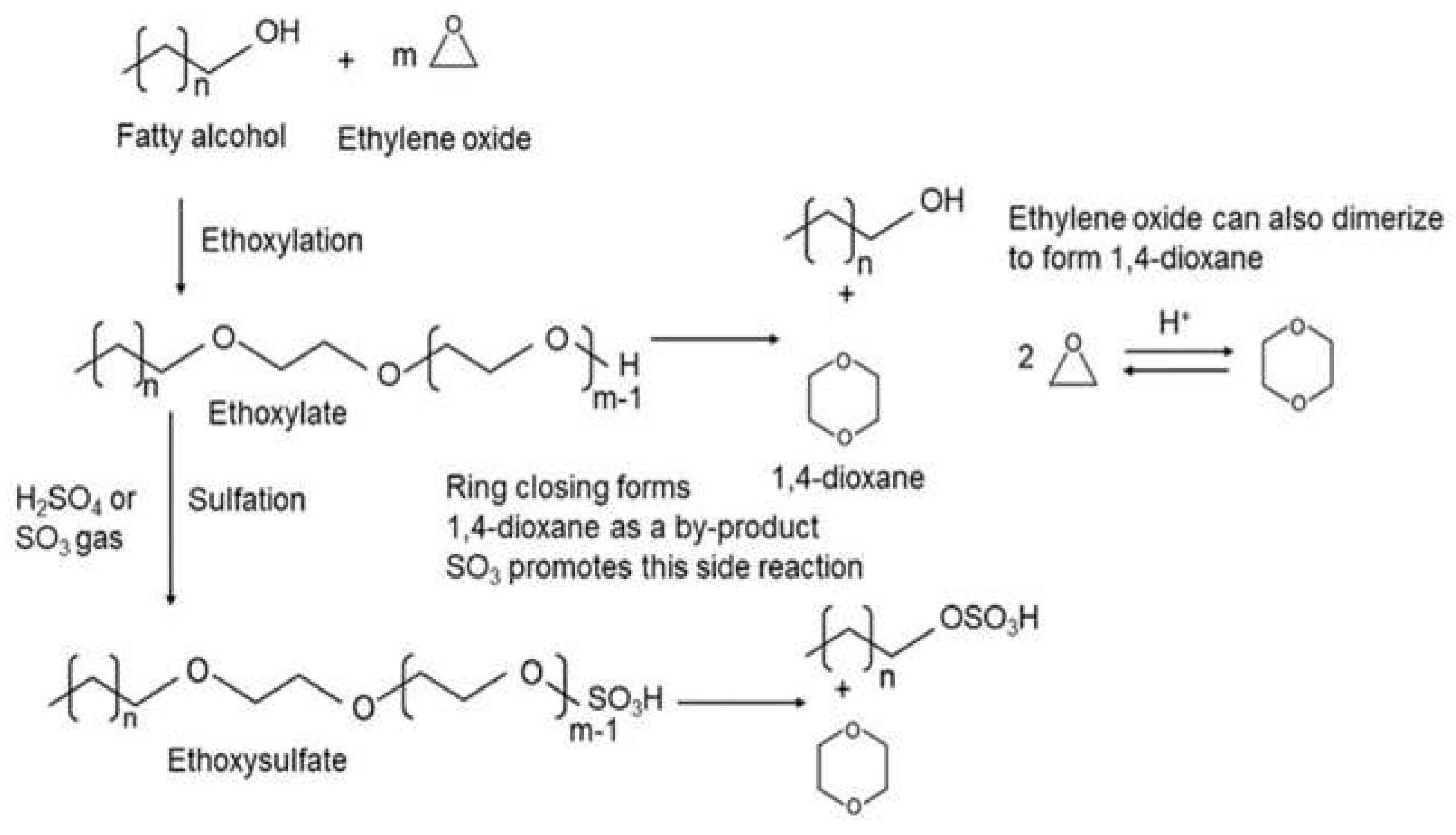
1.3. 1,4-Dioxane
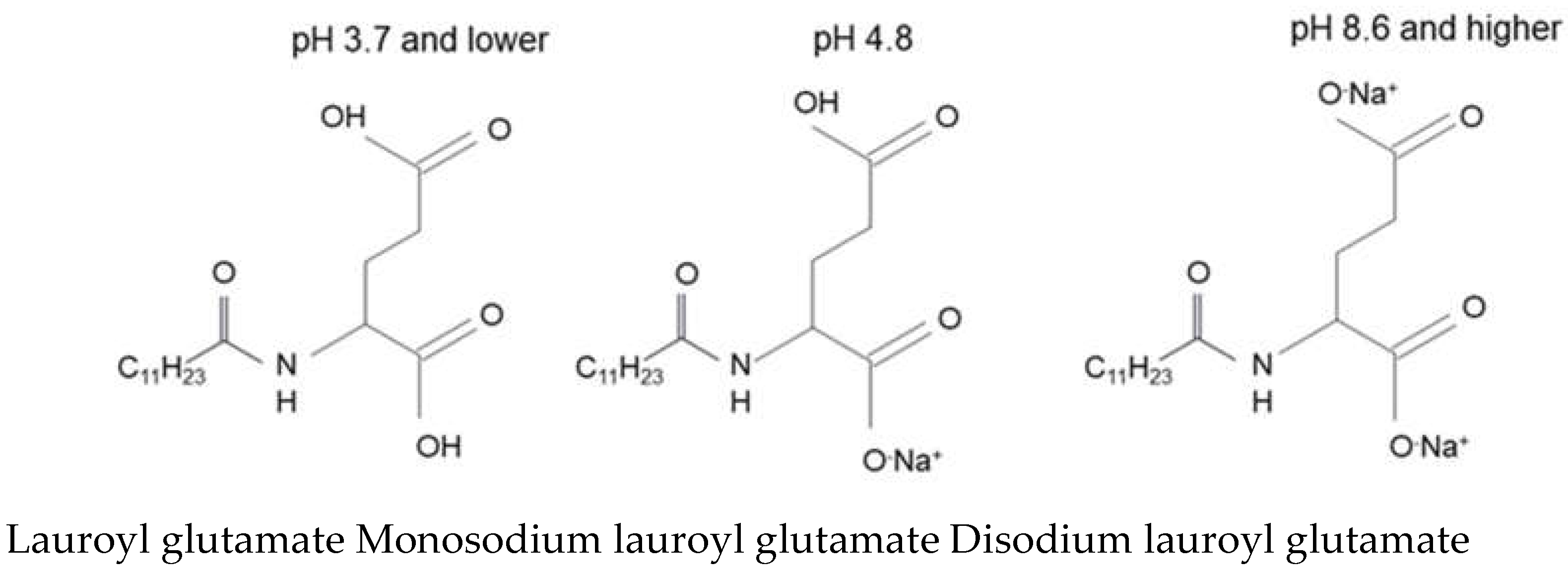
1.4. Amino Acid-Based Surfactants
1.5. Current Sulfate-Free Commercial Products
| Ingredient | No. of Times Cited |
|---|---|
| Cocoamidopropyl Betaine | 15 |
| Isothionates | 11 |
| C14-16 Olefin Sulfonate (AOS) | 9 |
| Sulfosuccinate | 6 |
| Hydroxysultaine | 5 |
| Cocamide mipa/dipa | 5 |
| Taurate | 3 |
2. Personal Cleansing Technology of the Future: the People Perspective
2.1. Safety
2.2. Mildness
2.3. Sensory -Foam and Foam Stability
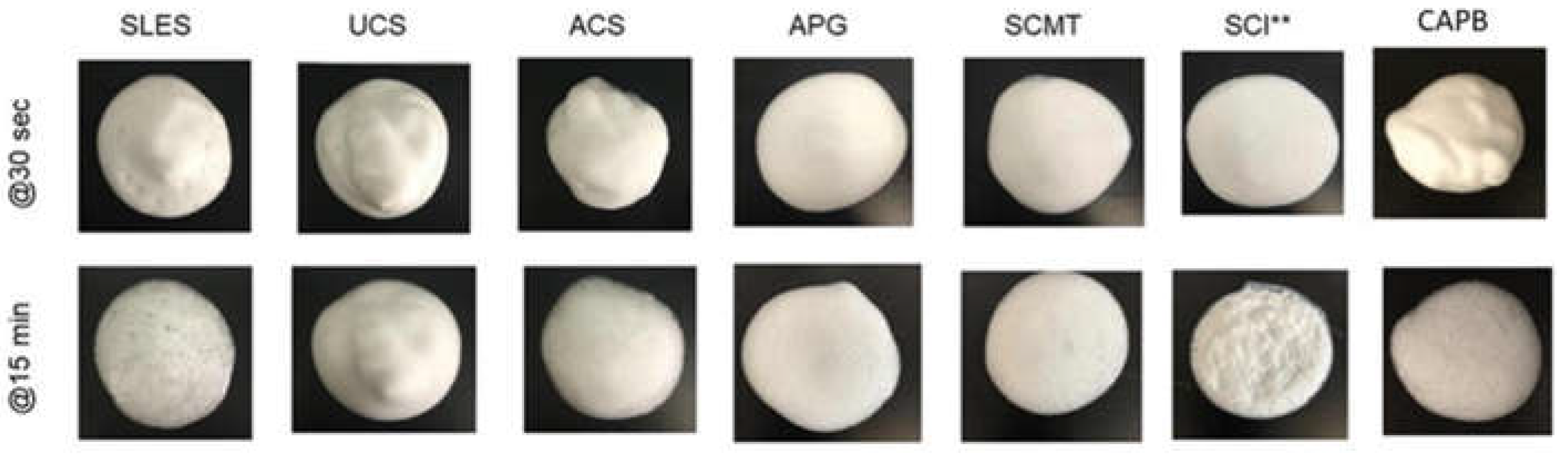
2.4. Skin Absorption
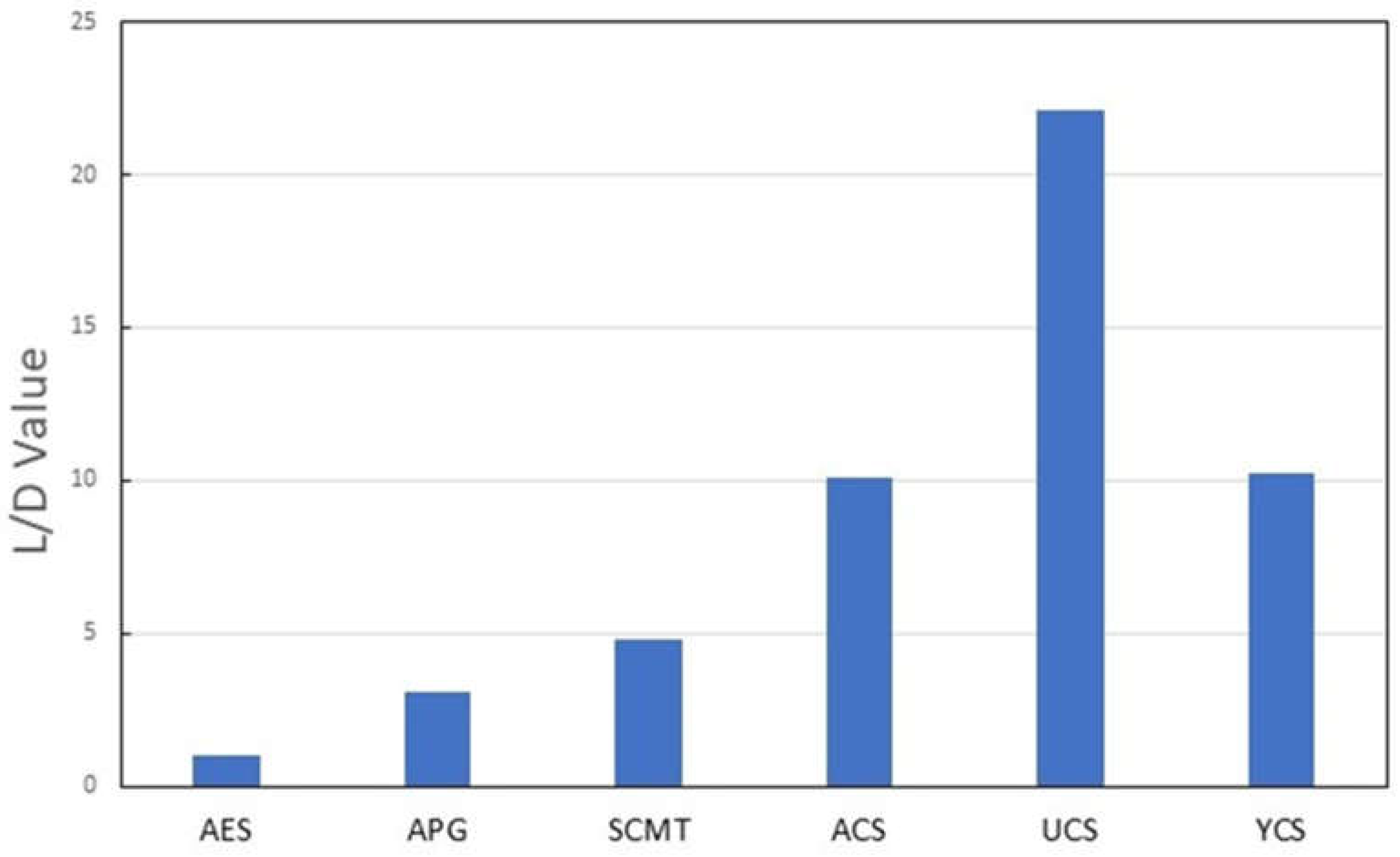
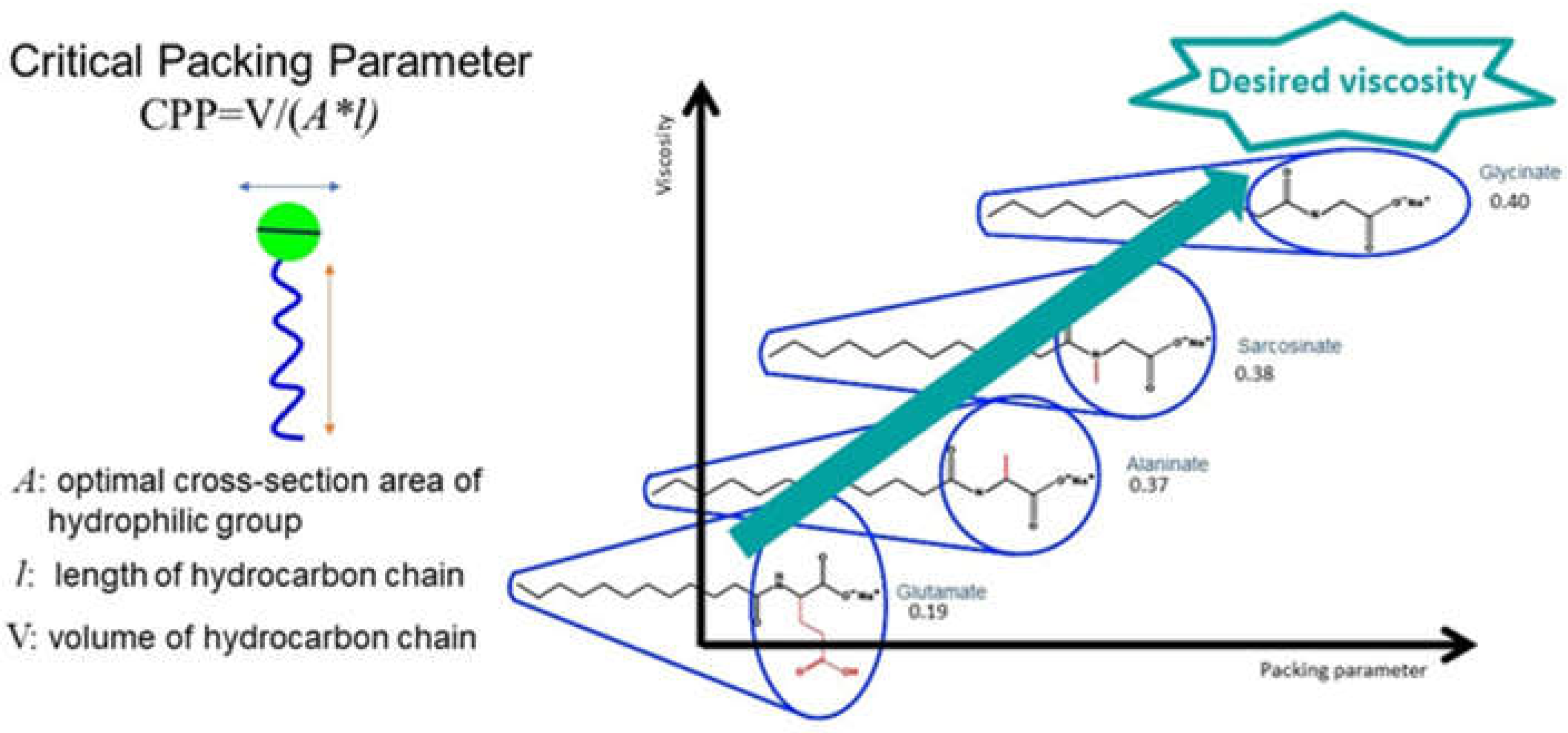
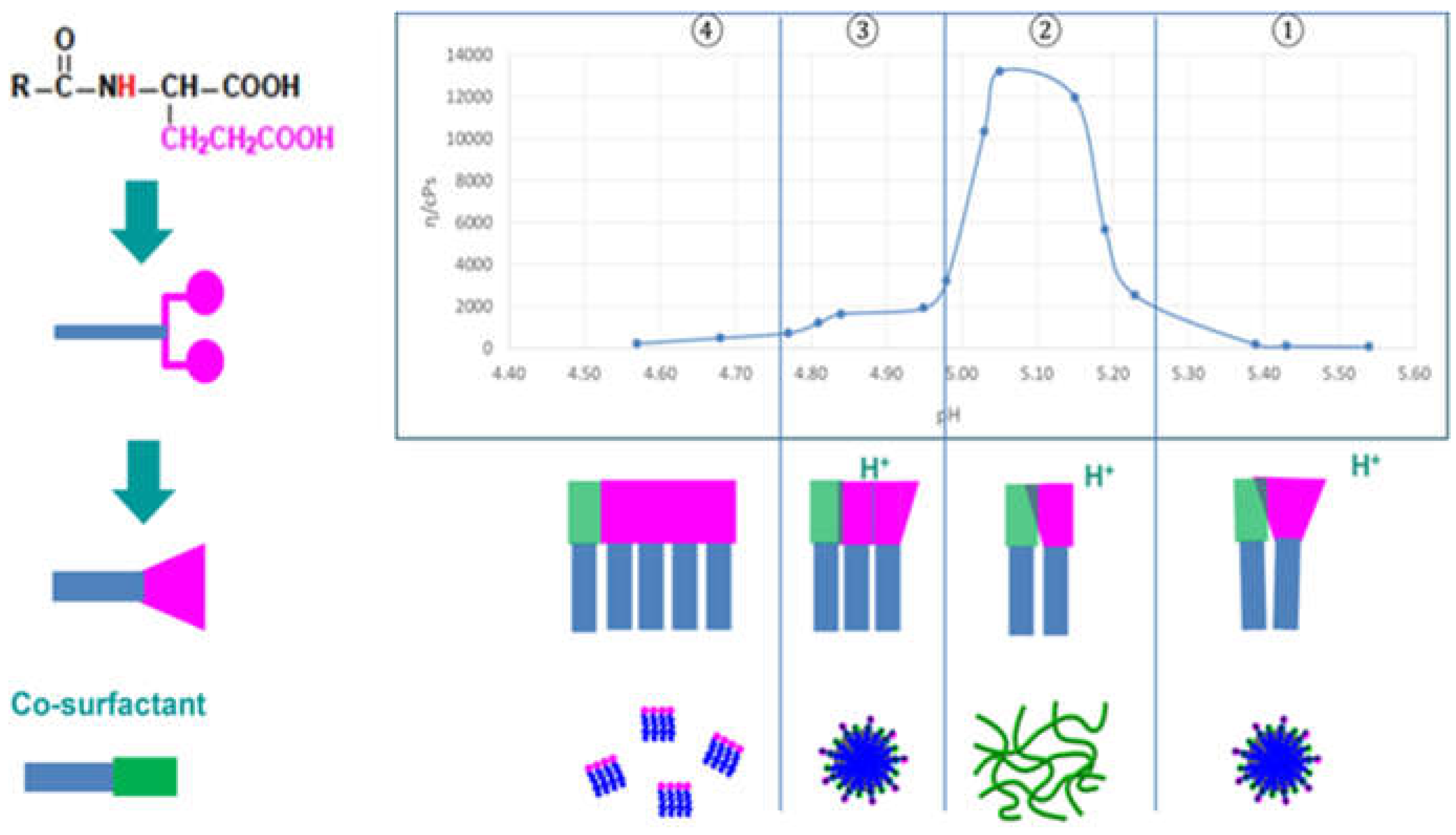
2.5. Thickening
3. Personal Cleansing Technology of the Future: The Planet Perspective
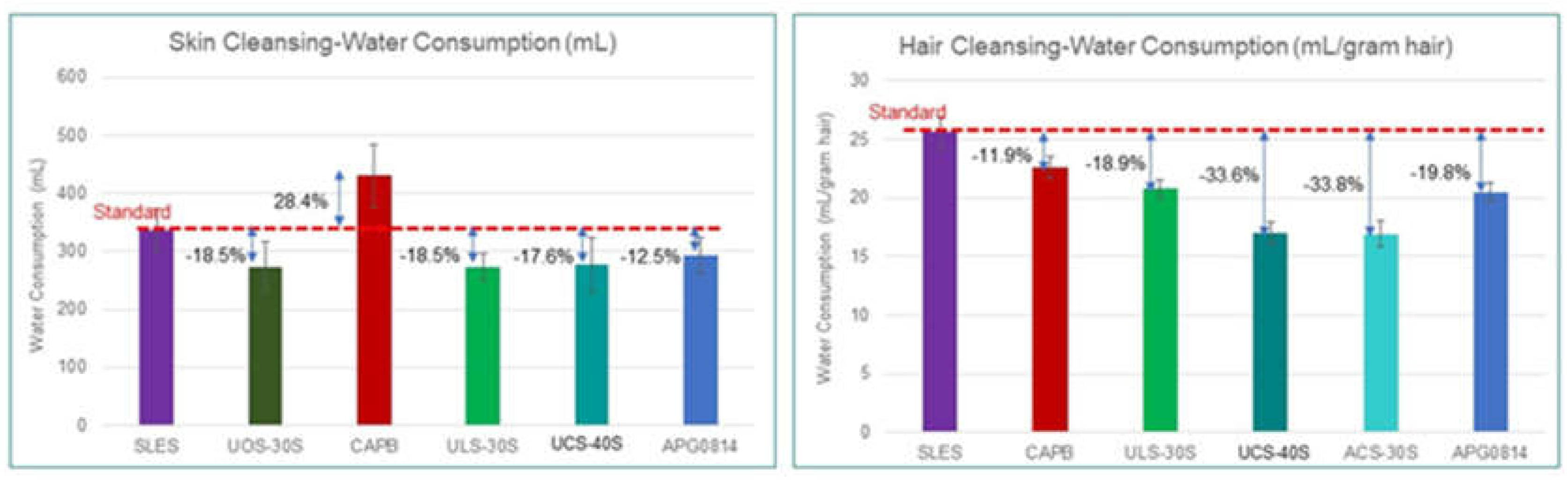
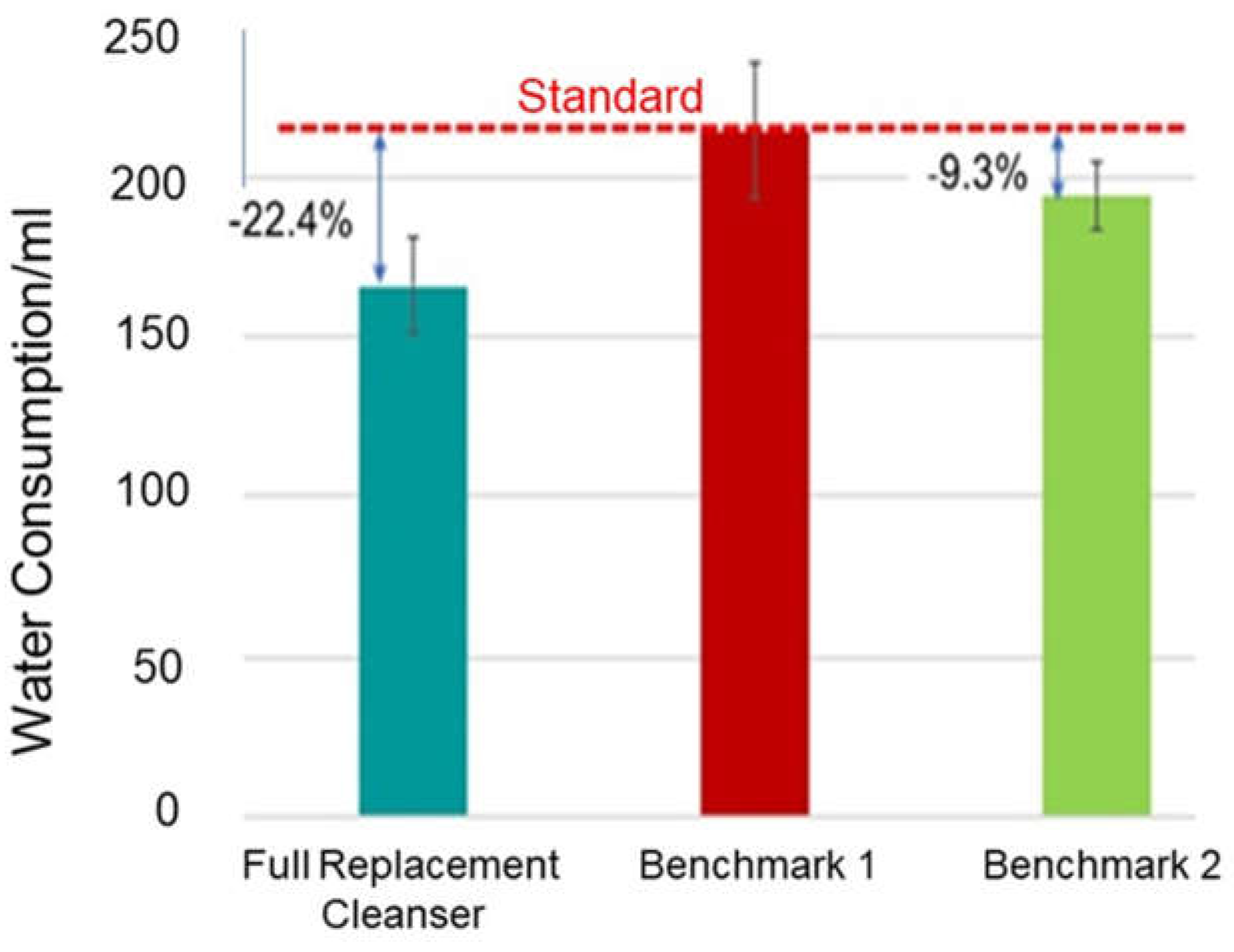
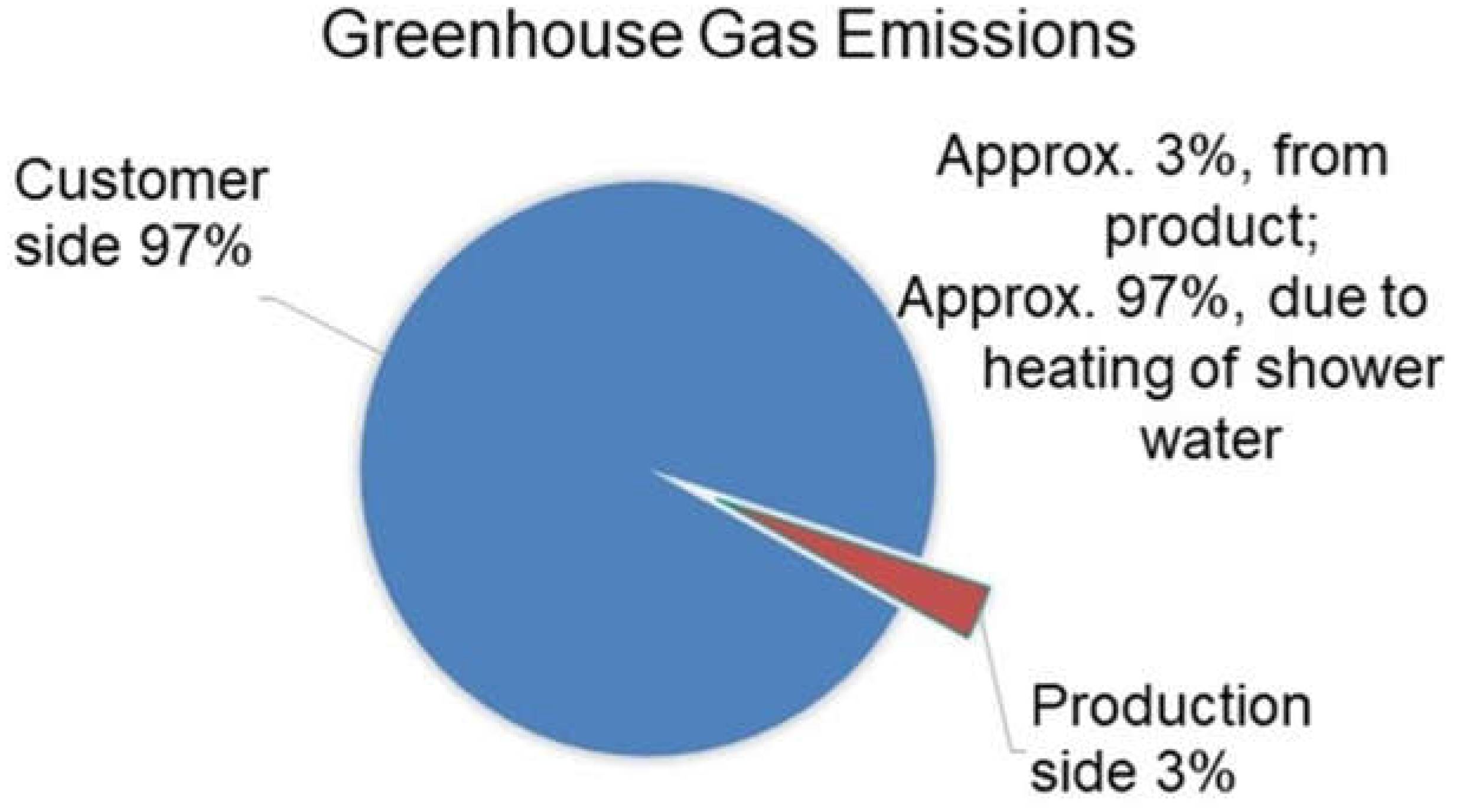
3.1. Water Savings
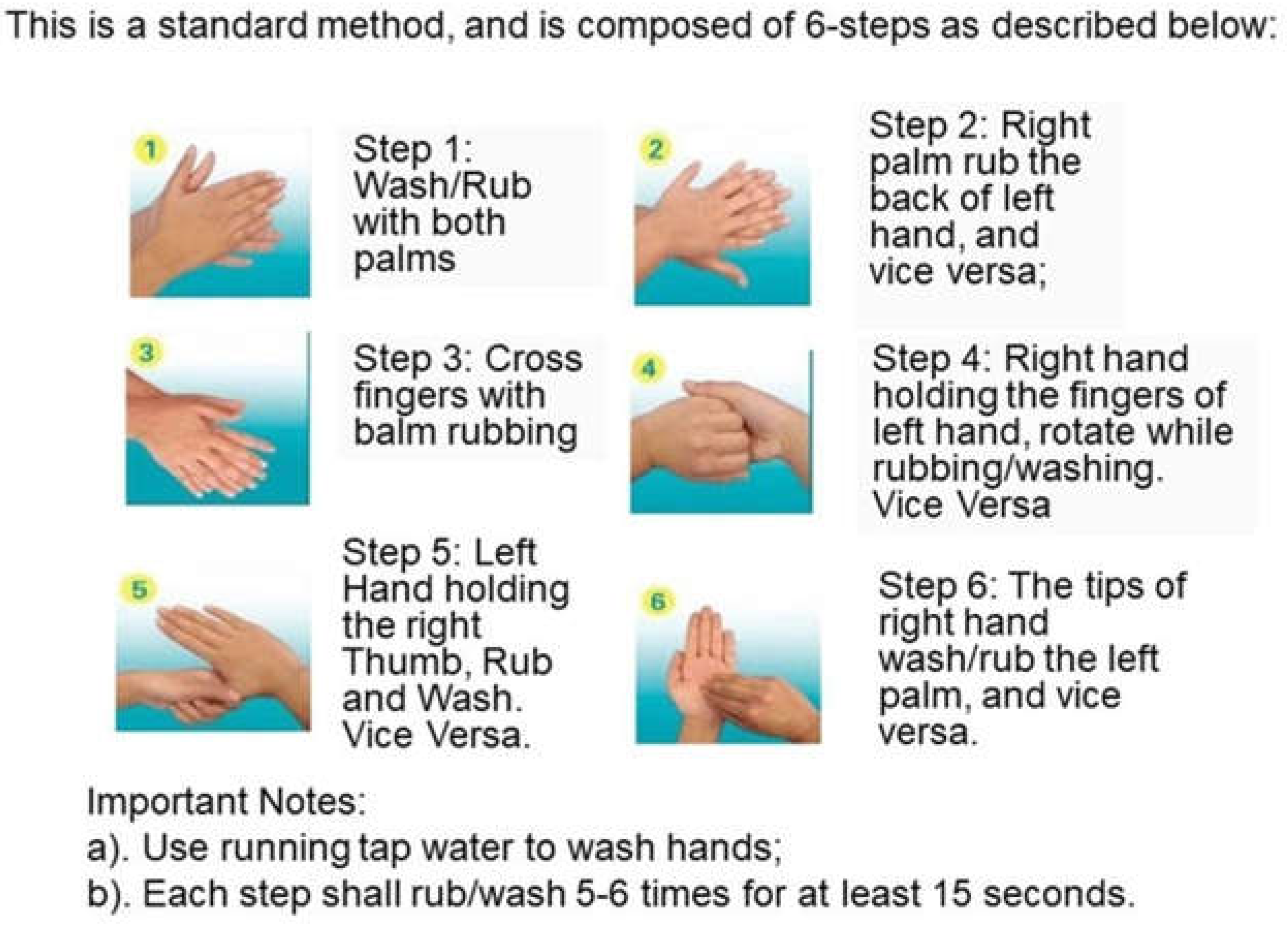
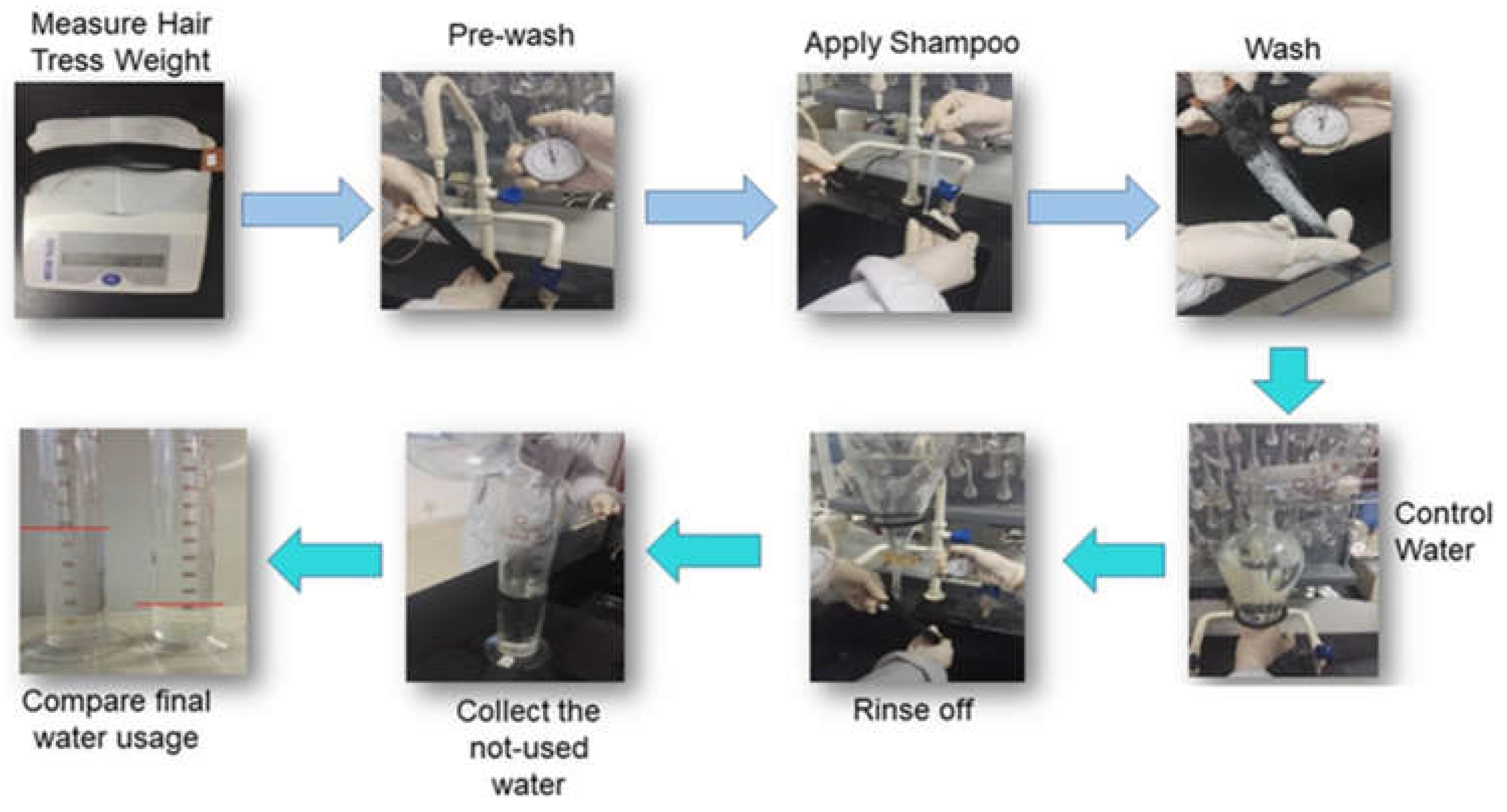
- 1Measurement hair tress weight
- 2Pre-wash tresses
- 3Apply shampoo
- 4Wash tress
- Control water
- Rinse tress
- Collect unused water
- Calculate final water usage
| Ingredient | % w/w | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Glutamix™A-50 | 40.00 | Glutamate Surfactant Blend |
| Linoleamidopropyl PG-Dimonium Chloride Phosphate | 1.00 | Emollient |
| Deionized Water | 55.00 | Medium |
| Citric Acid (50% Solution) | q.s. | pH Adjuster |
| Total | 100 |
Water/Energy Consumption Analysis
3.2. Natural Origin Index (NOI) and Sustainability
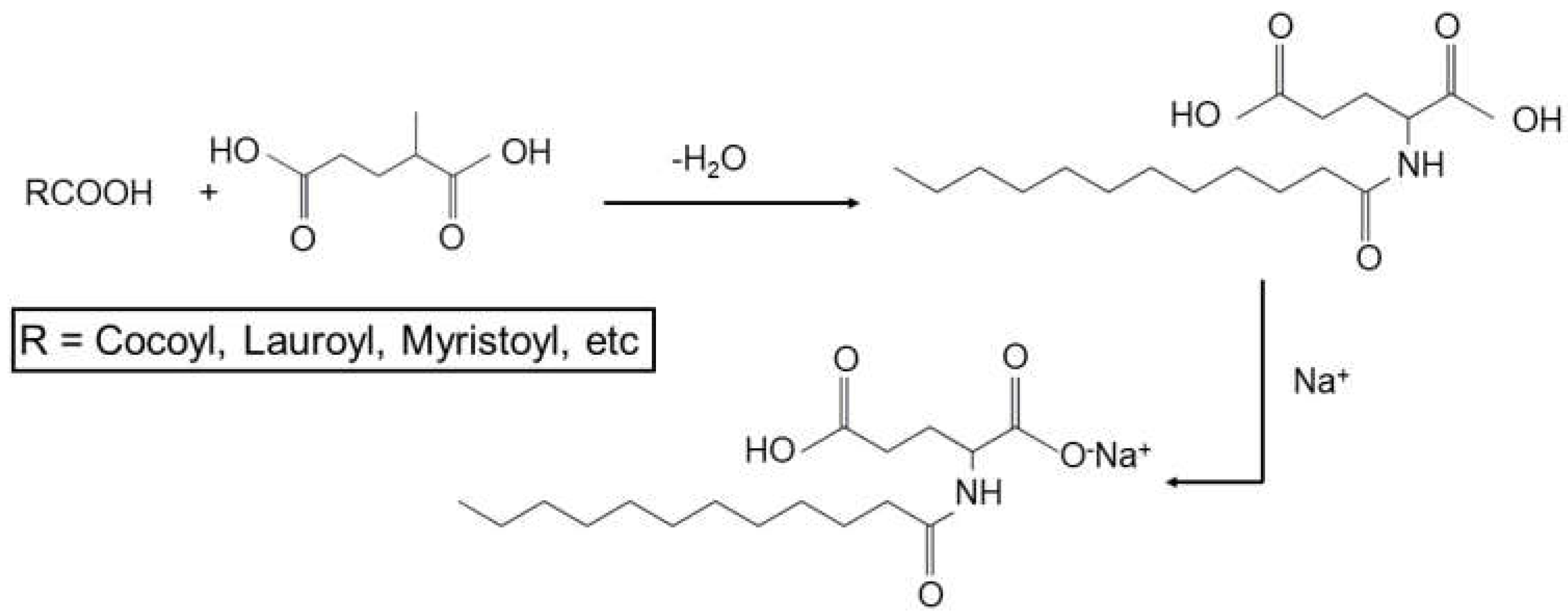
3.3. Biodegradation
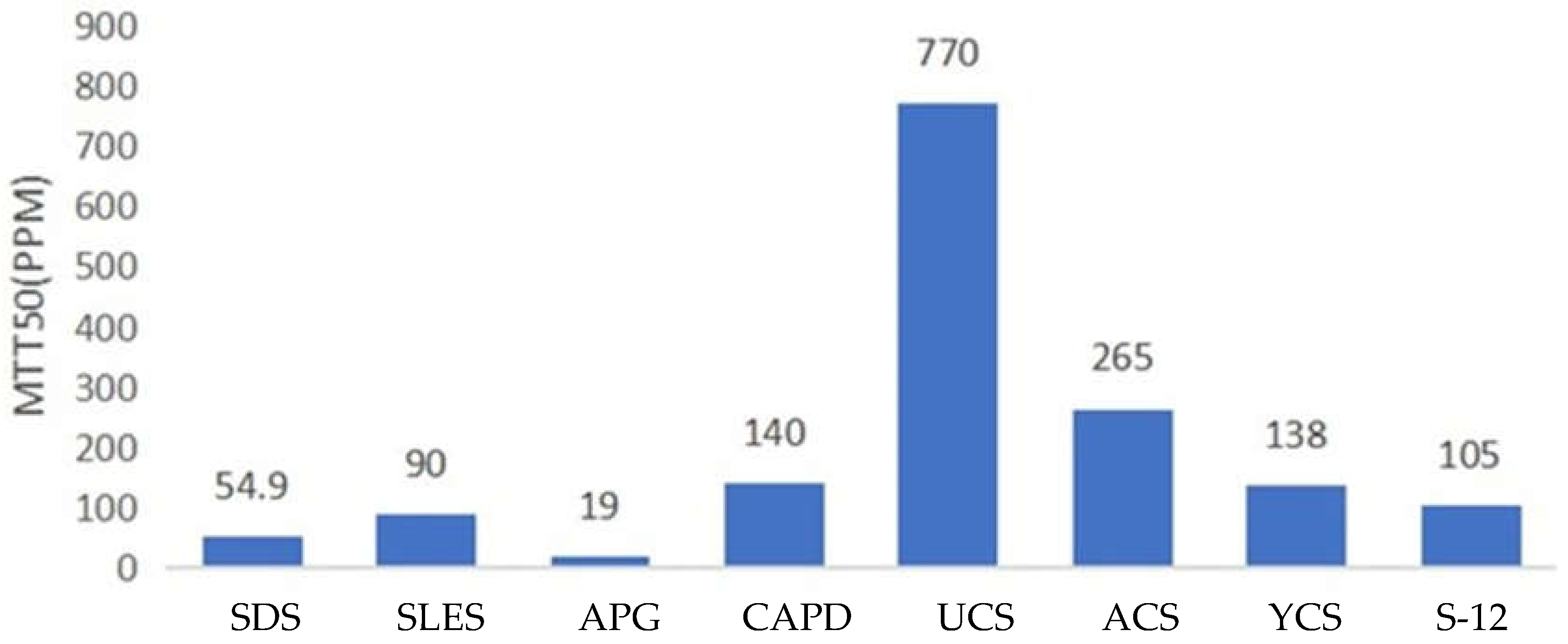
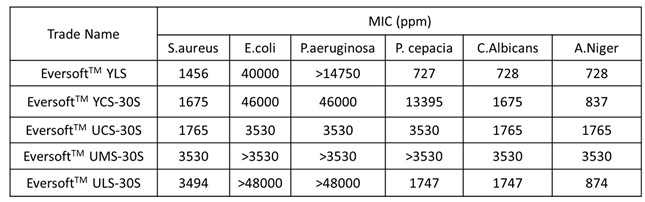
1.4. Antibacterial Properties
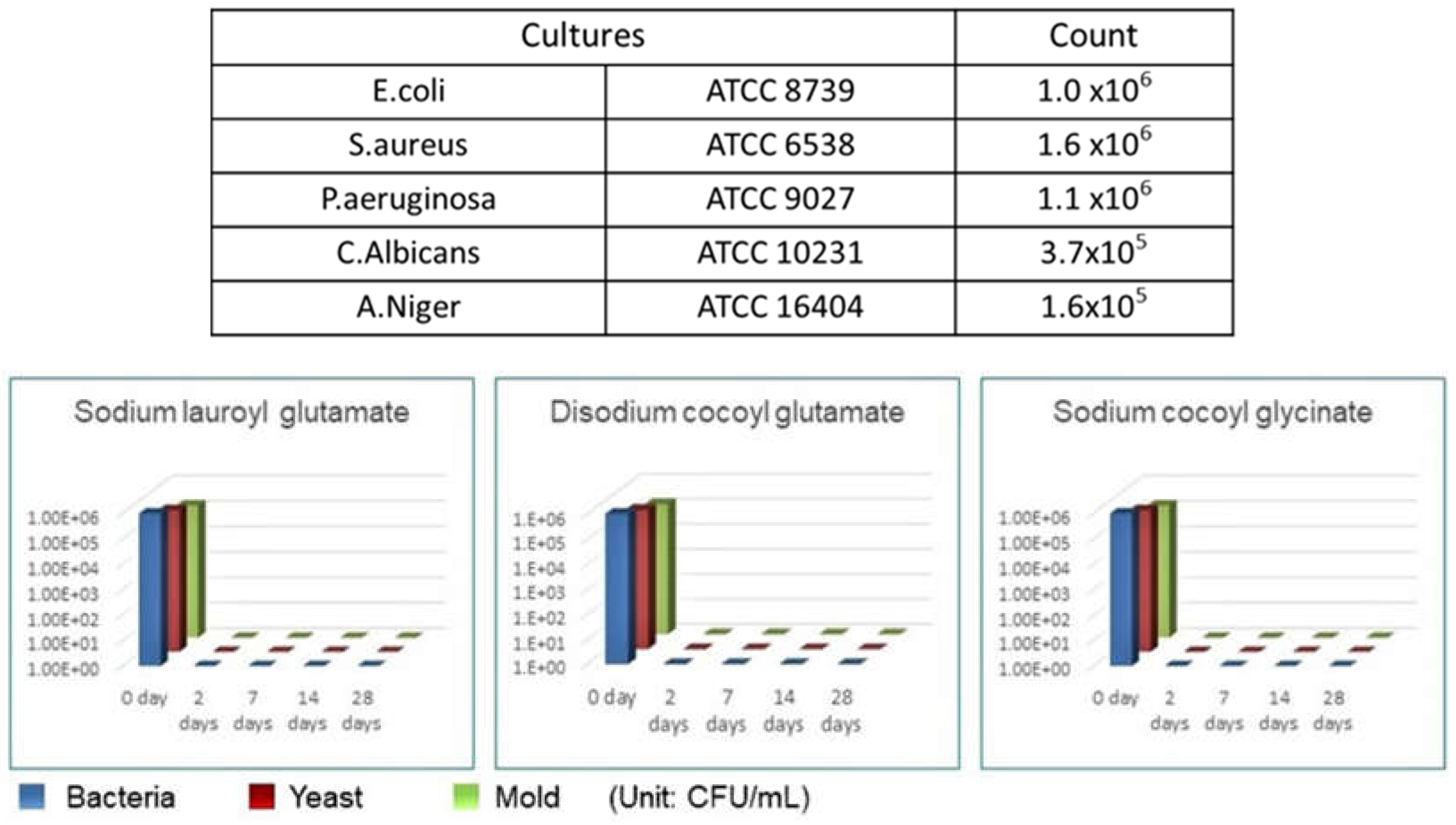
4. Discussion and Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anastas, P. T. & Warner, J. C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice. (New York: Oxford University Press, 1998).
- Moran, M. C. et al., “Green” amino acid-based surfactants, Green Chem. 2004, 6(5), 233-240. [CrossRef]
- Bhadani, A. et al., Current perspective of sustainable surfactants based on renewable building blocks. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 45, 124–135. [CrossRef]
- Reznik, G. O. et al., Use of sustainable chemistry to produce an acyl amino acid surfactant, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86(5), 1387-1397. [CrossRef]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P. et al., Cleansing without compromise: the impact of cleansers on the skin barrier and the technology of mild cleansing, Dermatol. Ther. 2004, 17 Suppl 1, 16-25. [CrossRef]
- Lukic, M., Pantelic, I., Savic, S., An overview of novel surfactants for for-mulation of cosmetics with certain emphasis on acidic active substances, Tenside, Surfactants, Deterg., 2016, 53, 1. [CrossRef]
- Schoenberg, T., Sulfate-free Cleansers, Cosmet. & Toil., 2006, 121, (12).
- Löffler, H., Happle, R. (2003), Profile of irritant patch testing with detergents: sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium laureth sulfate and alkyl polyglucoside. Contact Dermatitis, 48: 26-32. [CrossRef]
- Aramaki, J. et al. (2001), Irritant patch testing with sodium lauryl sulphate: interrelation between concentration and exposure time. British Journal of Dermatology, 145: 704-708. [CrossRef]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, K. P. et al., Binding of surfactants to stratum corneum, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1996, 47(4), 185-200.
- Morris, S. A. et al., Mechanisms of anionic surfactant penetration into hu-man skin: Investigating monomer, micelle and submicellar aggregate penetra-tion theories, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2019, 41(1), 55-66. [CrossRef]
- Coots, R., Sodium Laurylglucosides Hydroxypropyl Sulfonate for Sulfate-free Formulations, Cosmet. & Toil., 2011, 126, (4).
- Kemp, B. and Reng, A., Developing Ether Sulfate-Free Surfactant Formu-lations, Cosmet. & Toil., 1989, 104, (4).
- Marimon, N., IFSCC Webinar Series, Key Factors When Choosing Sulfate-free Surfactants- Webinar 23 August. Available online: https://ifscc.org/news/key-factors-when-choosing-sulfate-free-surfactants-webinar-23-august/ 2023.
- Bettenhausen, C. A. How companies are getting 1,4-dioxane out of home and personal care products, C & EN, 2020 98 11 (110).
- NY State Senate Bill 4389B. https://legisla tion.nysenate.gov/pdf/bills/2019/S4389B.
- Foster, N. C. Foster, N. C. Sulfonation and Sulfation Processes, Chemithon, 1997. Available online: www.chemithon.com/Resources/pdfs/Technical_papers/Sulfo%20and%20Sulfa%201.pdf.
- Nagtode, V. S. et al., Green Surfactants (Biosurfactants): A Petroleum-Free Substitute for Sustainability-Comparison, Applications, Market, and Future Prospects, ACS Omega 2023, 8(13), 11674-11699. [CrossRef]
- Takehara, M. et al., Surface active N-acylglutamate: I. Preparation of long chain N-acylglutamic acid, JAOCS 1972, 49 (3). [CrossRef]
- akehara, M. et al., Surface active N-acylglutamate: II. Physicochemical properties of long chain N-acylglutamic acids and their sodium salts, JAOCS 1972 49 (3). [CrossRef]
- Takehara, M. et al., Surface active N-acylglutamate: III. Physicochemical properties of sodium long chain N-acylglutamates, JAOCS 1973 50, (7). [CrossRef]
- akehara, M., Yoshimura, I., Yoshida, R., Surface-active N-acylglutamate: IV. Physicochemical properties of triethanolamine long chain N-acylglutamates, JOACS 1974 51 (9). [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R. et al., Surface active N-acylglutamate: V. Application of N-acylglutamates to detergent bars, JAOCS 1976 53 (4). [CrossRef]
- Takehara, M., Properties and applications of amino acid-based surfactants, Coll. Surf. 1989, 38(1-3), 149-67. [CrossRef]
- Bordes, R., Holmberg, K., Amino acid-based surfactants - do they deserve more attention?, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 79-91. [CrossRef]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P., Amino-acid surfactants in personal cleansing (review), Tenside, Surfactants, Deterg. 2019, 56(5), 378-386. [CrossRef]
- Chandra, Nimisha; Tyagi, V. K., Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Amino Acids Based Surfactants: A Review, J. Dispersion Sci. Tech. 2013, 34(6), 800-808. [CrossRef]
- Infante, M. R. et al., Amino acid-based surfactants, C. R. Chim 2004, 7(6-7), 583-592. [CrossRef]
- Pinazo, A. et al., Amino Acids as Raw Material for Biocompatible Surfac-tants, Industrial & Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50(9), 4805-4817. [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, D.B. et al., Synthesis, chemistry, physicochemical properties and industrial applications of amino acid surfactants: A review, C. R. Chimie 2018, 2, 112-130. [CrossRef]
- Clapes, P., Infante, M. R., Amino acid-based surfactants: enzymatic synthesis, properties and potential applications, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1999, 63, 215-233. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. et al., Study on foaming properties of Nacyl amino acid surfac-tants: sodium N-acyl glycinate and sodium N-acyl phenylalaninate, Colloids Surf. A 567 2019, 240–248. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. et al., Synthesis and properties of pH dependent N-acylglutamate/aspartate surfactants, Colloids Surf., A 640 2022, 128474. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., et al., Effects of fatty acyl chains on the interfacial rheological behaviors of amino acid surfactants, J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 114823. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y et al., The α-Substituent effect of amino acids on performance of N-Lauroyl amino acid surfactants, J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 49, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y., Skin Irritation Potential Study of Anionic Surfactants using Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Spectroscopy, PhD Thesis, Chiba Institute of Science, 2014.
- Lee, C. H.; Kawasaki, Y.; Maibach, H. I., Effect of surfactant mixtures on irritant contact dermatitis potential in man: sodium lauroyl glutamate and sodium lauryl sulphate, Contact Derm. 1994, 30, 205-209. [CrossRef]
- Sugar, M., Schmucker, R., Reduction of Skin’s Surfactant Adsorption: An Effective Way to Improve Mildness and Performance of Bath Care Products, XXIth IFSCC International Congress 2000, Berlin – Proceedings.
- Kanari, M., Kawasaki, Y., Sakamoto, K., Acylglutamate as an anti-irritant for mild detergent system, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. Jpn. 1993, 27(3), 498-15. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J., , Greener Surface Active Reagents Structure, Property and Performance Relationships, PhD thesis, Columbia University, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Su, E.; Wang, H.; Sha, J. Thickening Cleansing Compositions and Applications and Method of Preparation Thereof (US Patent No. 11,045,404).
- Sakai, K. et al., Wormlike Micelle Formation by Acylglutamic Acid with Alkylamines, Langmuir 2012, 28(51), 17617-17622. [CrossRef]
- Lu, H. et al., Wormlike Micelles in Mixed Amino Acid-Based Anionic Surfactant and Zwitterionic Surfactant Systems, J. Surfact. Deterg. 2015, 18(4), 589-596. [CrossRef]
- Su, E. et al., Water Saving Grace, Cosmet. & Toil. 2020 135, (2).
- Zhang, G. et al., Green Synthesis, Composition Analysis and Surface Active Properties of Sodium Cocoyl Glycinate, Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 4(9), 445-450. [CrossRef]
- Regan, J., Mollica, l-M., Ananthapadmanabhan, K. P., A Novel Glycinate-based Body Wash: Clinical Investigation into Ultra-mildness, Effective Conditioning, and Improved Consumer Benefits. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2013, 6(6), 23-30.
- Huang, J., Xu, H., Investigation of the synergistic effect and the mor-phology of the binary compound systems with potassium N-lauroyl glycinate, Tenside, Surfactants, Deterg. 2022, 59(2), 159-167. [CrossRef]
- Preparation Method and Use of N-Acyl Acidic Amino Acid or Salt Thereof (US Patent No. 9,629,787).
- Valivety, R., Jauregi, P., Gill I., Evgeny Vulfson, E., Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of amino acid-based surfactants,1997, JOCS 74, 7. [CrossRef]
- Joondan, N., Jhaumeer Laulloo, S., Caumul, P., Amino acids: Building blocks for the synthesis of greener amphiphiles, J. Disper. Sci. Technol., 2018, 39(11), 1550-1564. [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/20719.
- Xia, J.; Xian, Y.; Nnanna, I. A., Structure-Function Relationship of Acyl Amino Acid Surfactants: Surface Activity and Antimicrobial properties, J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 867-871. [CrossRef]
- Pinazo, A. et al., Amino acid-based surfactants: New antimicrobial agents, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2016, 228 17-39. [CrossRef]
- Boshui C., Zhang, N., Sun, X., Enhanced Biodegradation of Lubricating Oil by Fatty Acyl Amino Acids, Proceedings of 2011 China Functional Materials Technology and Industry Forum (CTMTIF 2011).
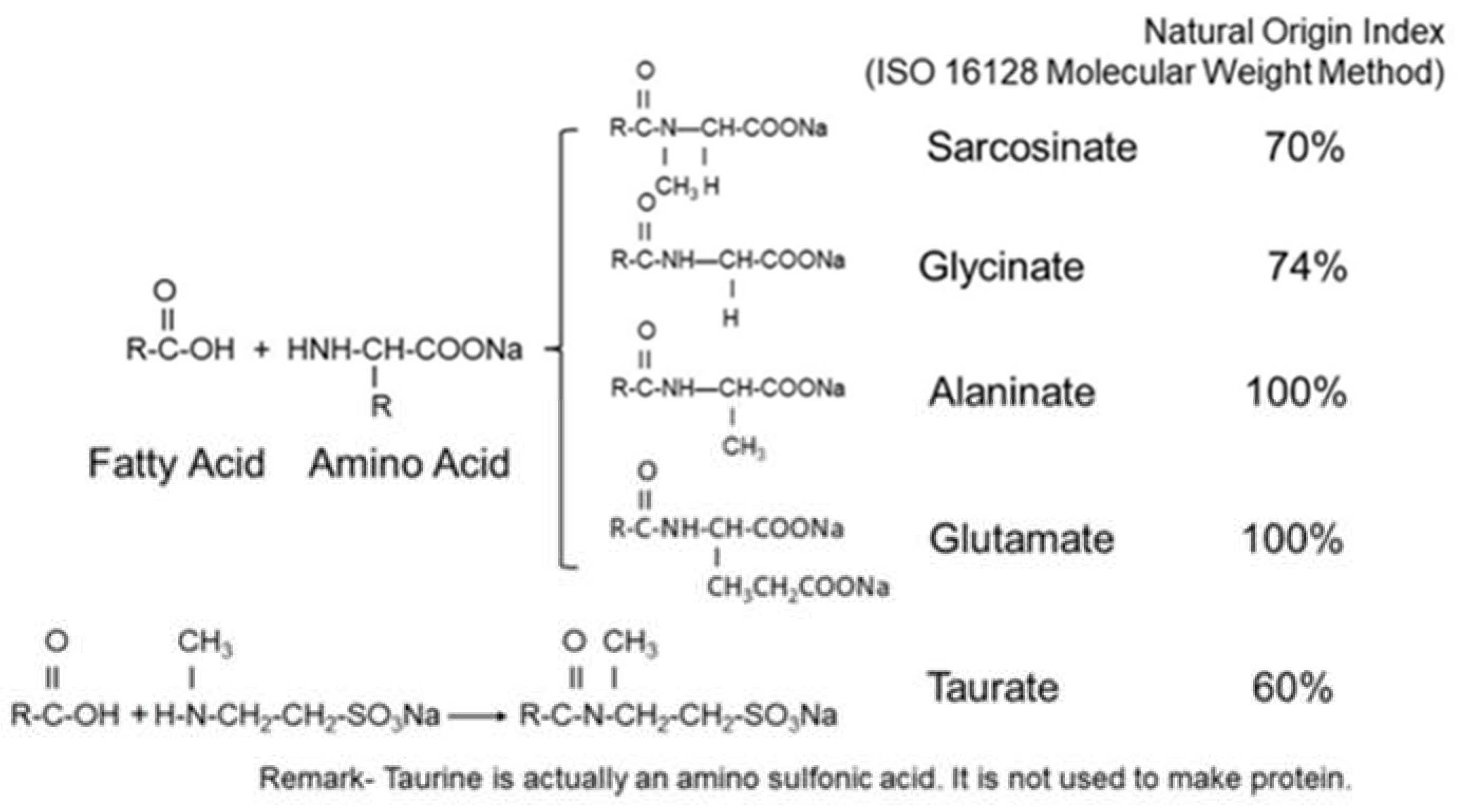
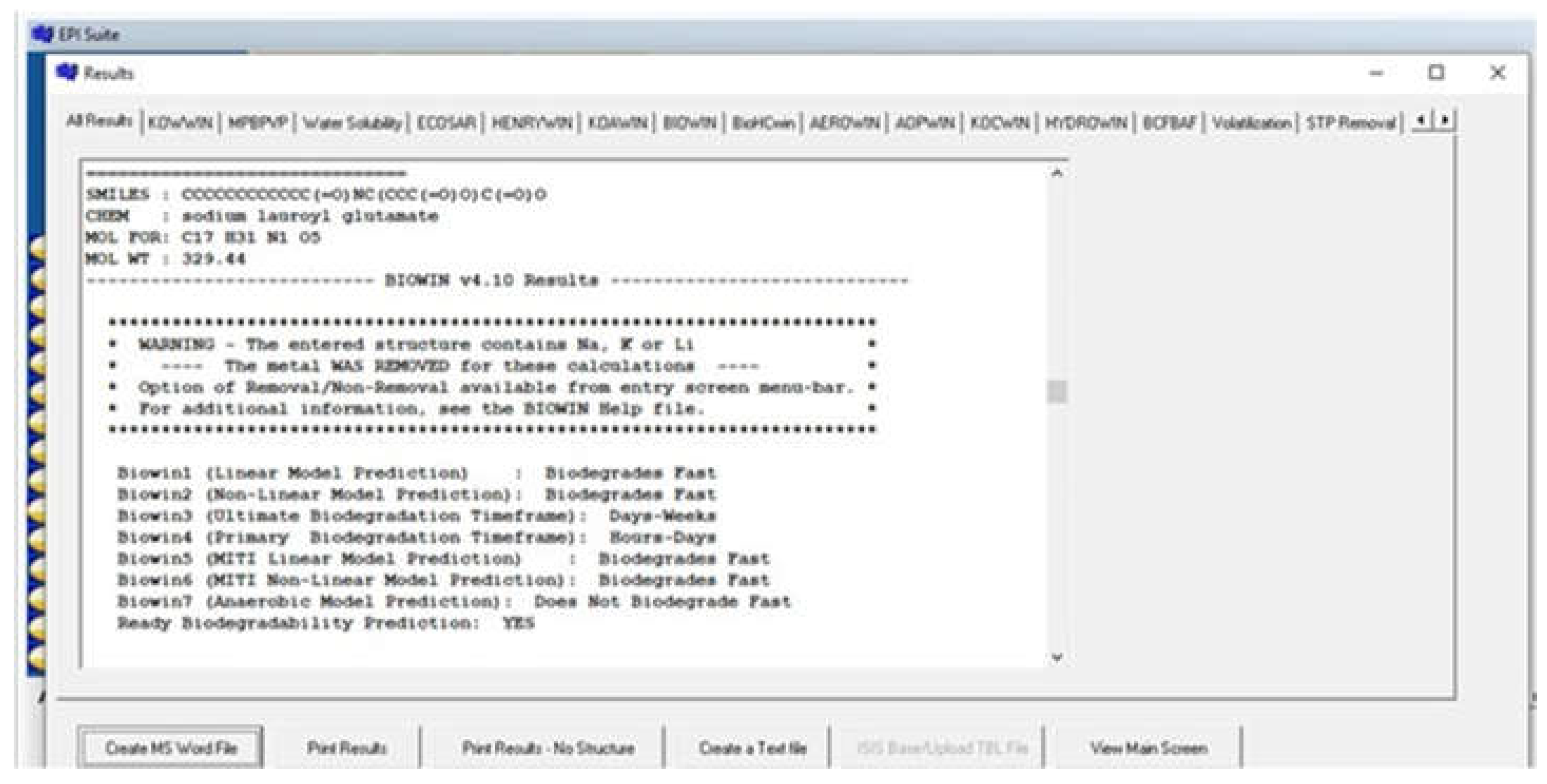
| Surfactant | Main Feed Stocks | Main Impurities |
|---|---|---|
| Glutamate, Alaninate | Fatty acids, amino acids | Amino acids, fatty acids, sodium chloride |
| APG | Fatty alcohol, glucose | Fatty alcohol, glucose |
| Betaines | Fatty amine, sodium chloroacetate, epichorohydrin | Fatty amine, sodium chloroacetate, epichorohydrin |
| Alkyl sulfosuccinate | Fatty acid, maleic anhydride, ethanolamine | Sodium maleate |
| Isethionates/ taurates | Fatty acid, EO, sodium sulfite/ same + methylamine | Dioxane, sodium isethionate/ same + sodium methyltaurine |
| SLES | Fatty alcohols, EO, SO3 | Dioxane |
| Imidazolidine/AmphoacetatesAOS | Fatty acid, alkyl diamine, sodium chloroacetateAlpha olefins, sulfur | Alkyl diamine, sodium chloroacetateSultone |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




