Submitted:
20 September 2024
Posted:
23 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel variant of the Tsetlin Machine called Regularized Tsetlin Machine (RegTM) that implements regularization based on past clause sums and weights to improve the accuracy of the TM by increasing its generalizability, making it highly suitable for few-shot learning and meta-learning optimization tasks.
- We propose to use the Sigmoid function as an alternative to the unit-step function.
- We perform different experiments using benchmark image datasets to show the efficiency of RegTM with the different regularizers and sigmoid function.
2. Related Works
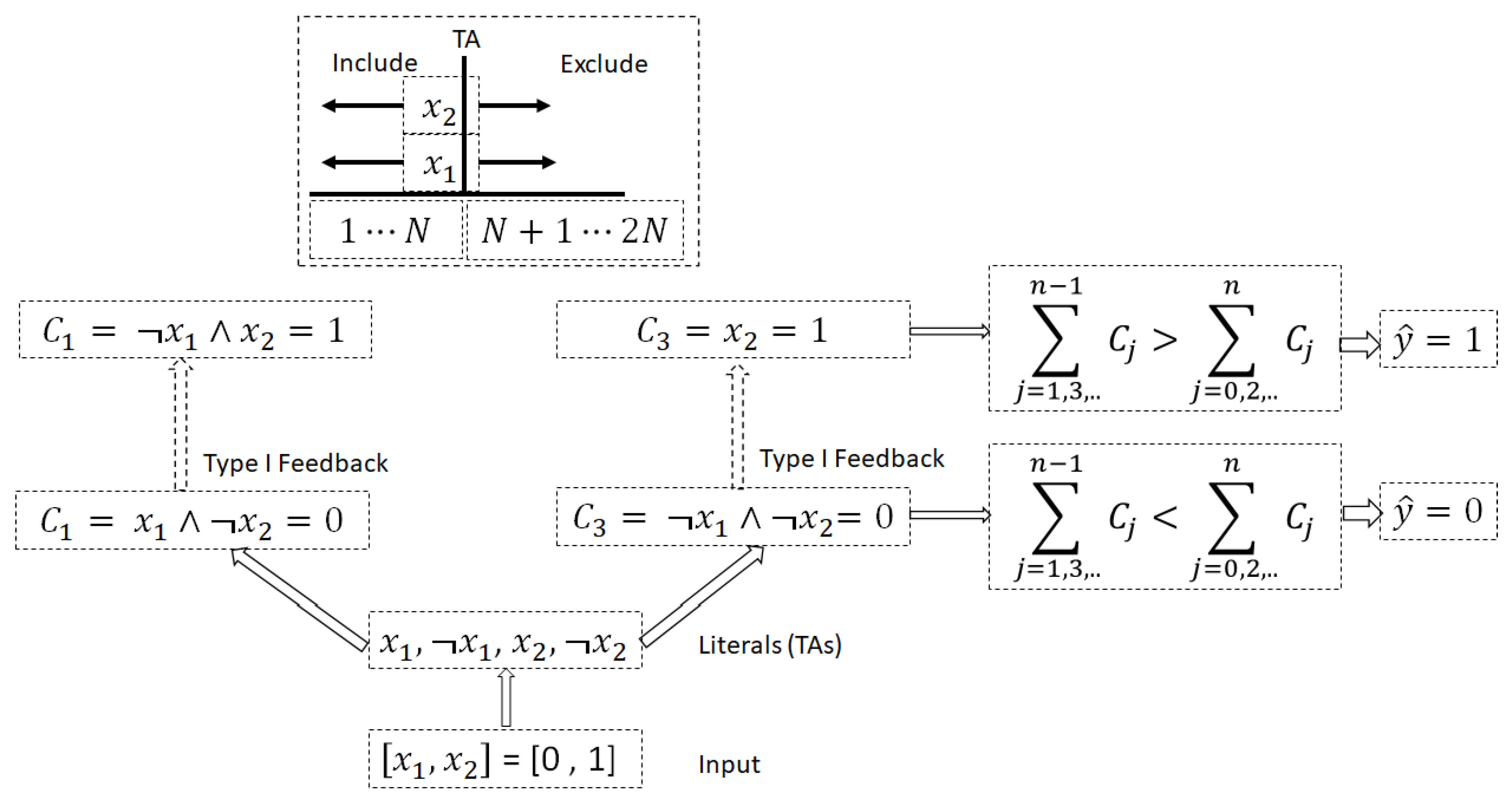
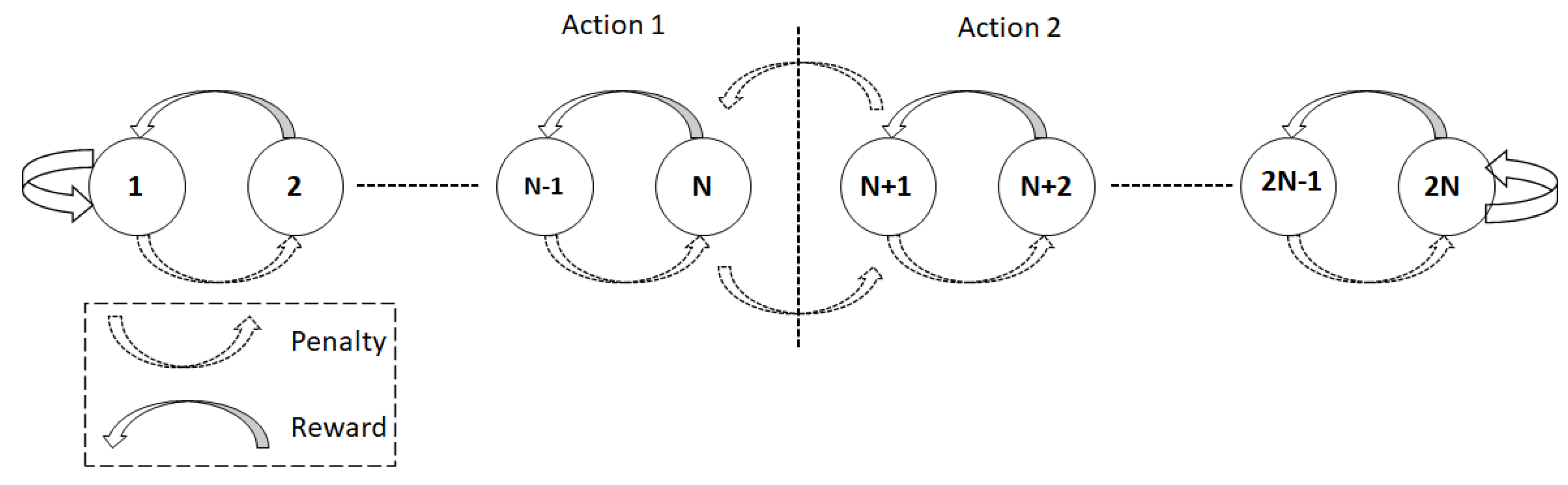
3. Preliminary: Vanilla Tsetline Macnhine
4. Methodology
5. Experiments
5.1. Experimental Design
5.2. Experiment Results
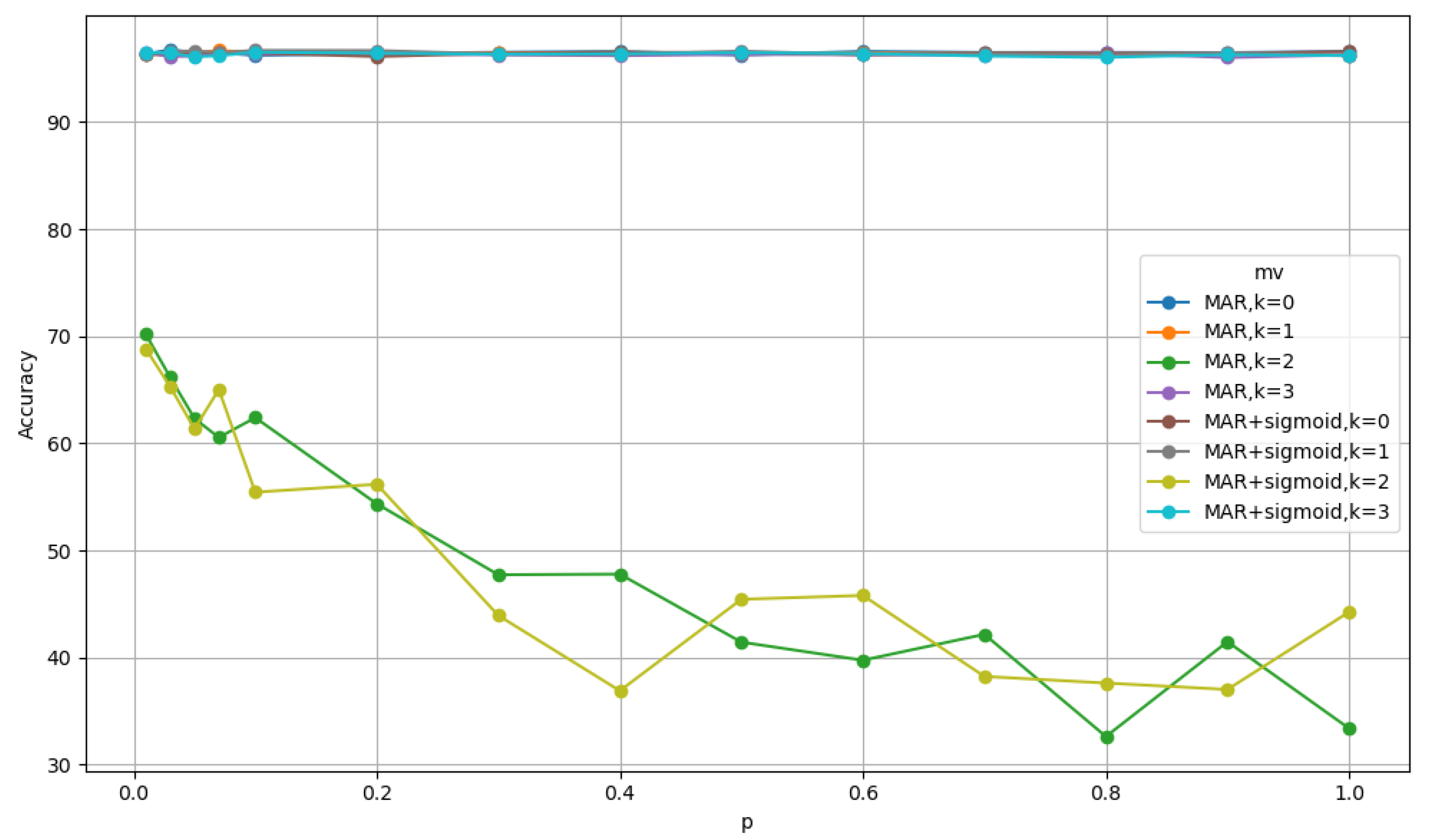
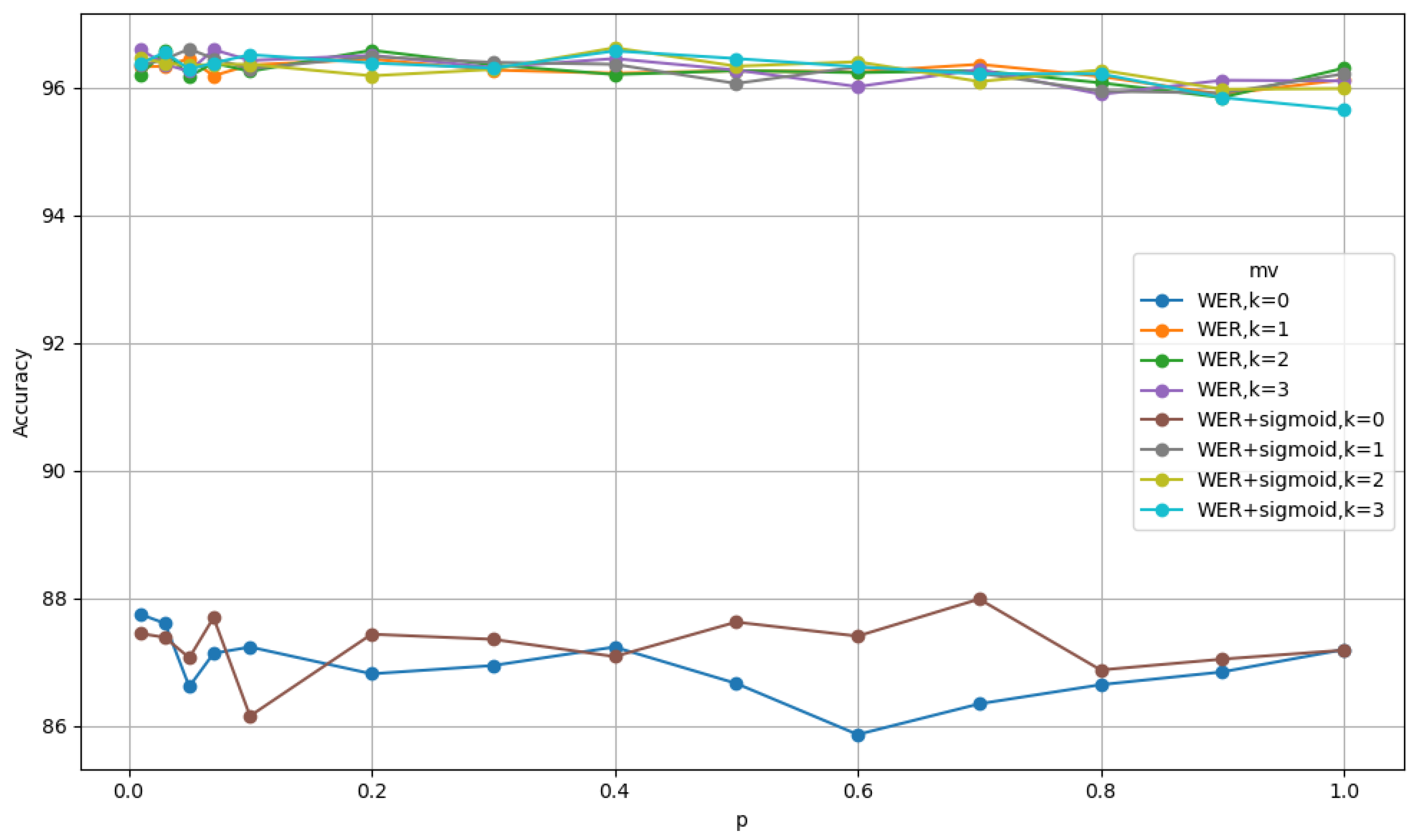
5.3. Ablation Studies
6. Conclusion
References
- Granmo, O.C. The Tsetlin Machine–A Game Theoretic Bandit Driven Approach to Optimal Pattern Recognition with Propositional Logic. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.01508. [Google Scholar]
- Abeyrathna, K.D.; Bhattarai, B.; Goodwin, M.; Gorji, S.R.; Granmo, O.C.; Jiao, L.; Saha, R.; Yadav, R.K. Massively parallel and asynchronous tsetlin machine architecture supporting almost constant-time scaling. International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR. 2021; 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.; Wheeldon, A.; Shafik, R.; Yakovlev, A.; Granmo, O.C. From arithmetic to logic based ai: A comparative analysis of neural networks and tsetlin machine. 2020 27th IEEE international conference on electronics, circuits and systems (ICECS). IEEE. 2020; 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.; Vasudevan, D.; Kirst, C. Super-Tsetlin: Superconducting Tsetlin Machines. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.; Rafiev, A.; Xia, F.; Shafik, R.; Yakovlev, A.; Brown, A. An alternate feedback mechanism for tsetlin machines on parallel architectures. 2022 International Symposium on the Tsetlin Machine (ISTM). IEEE. 2022; 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Uszkoreit, H.; Du, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhao, D.; Zhu, J. Explainable AI: A brief survey on history, research areas, approaches and challenges. In Proceedings of the Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing: 8th CCF International Conference, NLPCC 2019, Dunhuang, China, October 9–14, 2019; Proceedings, Part II 8. Springer, 2019; pp. 563–574. [Google Scholar]
- Došilović, F.K.; Brčić, M.; Hlupić, N. Explainable artificial intelligence: A survey. 2018 41st International convention on information and communication technology, electronics and microelectronics (MIPRO). IEEE. 2018; 0210–0215. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, U.; Zadorozhny, V.; Krishnamurthy, P. Localization of Unidentified Events with Raw Microblogging Data. Online Social Networks and Media 2022, 29, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, F.; Borgelt, C.; Kuehne, H.; Deussen, O. Deep differentiable logic gate networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, 35, 2006–2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y. A comprehensive survey on regularization strategies in machine learning. Information Fusion 2022, 80, 146–166. [Google Scholar]
- Dombi, J.; Jónás, T. The generalized sigmoid function and its connection with logical operators. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 2022, 143, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.R.; Singh, S.K.; Chaudhuri, B.B. Activation functions in deep learning: A comprehensive survey and benchmark. Neurocomputing 2022, 503, 92–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bouneffouf, D. Multi-armed Bandit Problem and Application. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bouneffouf, D.; Rish, I.; Aggarwal, C. Survey on applications of multi-armed and contextual bandits. 2020 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). IEEE. 2020; 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Seraj, R.; Sharma, J.; Granmo, O.C. Tsetlin Machine for Solving Contextual Bandit Problems. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, 35, 30194–30205. [Google Scholar]
- Tunheim, S.A.; Jiao, L.; Shafik, R.; Yakovlev, A.; Granmo, O.C. Convolutional Tsetlin Machine-based Training and Inference Accelerator for 2-D Pattern Classification. Microprocessors and Microsystems 2023, 103, 104949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granmo, O.C.; Glimsdal, S.; Jiao, L.; Goodwin, M.; Omlin, C.W.; Berge, G.T. The convolutional Tsetlin machine. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.09688. [Google Scholar]
- Darshana Abeyrathna, K.; Granmo, O.C.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, L.; Goodwin, M. The regression Tsetlin machine: a novel approach to interpretable nonlinear regression. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A 2020, 378, 20190165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glimsdal, S.; Granmo, O.C. Coalesced multi-output tsetlin machines with clause sharing. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07594. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, B.; Granmo, O.C.; Jiao, L.; Yadav, R.; Sharma, J. Tsetlin Machine Embedding: Representing Words Using Logical Expressions. arXiv, 2023; arXiv:2301.00709. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, R.; Granmo, O.C.; Zadorozhny, V.I.; Goodwin, M. A relational tsetlin machine with applications to natural language understanding. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems 2022, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.; Granmo, O.C.; Goodwin, M. Using Tsetlin machine to discover interpretable rules in natural language processing applications. Expert Systems 2023, 40, e12873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, G.T.; Granmo, O.C.; Tveit, T.O.; Goodwin, M.; Jiao, L.; Matheussen, B.V. Using the Tsetlin machine to learn human-interpretable rules for high-accuracy text categorization with medical applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 115134–115146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.K.; Jiao, L.; Granmo, O.C.; Goodwin, M. Human-Level Interpretable Learning for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis. The Thirty-Fifth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-21). AAAI. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolae, D.C. Question Classification using Interpretable Tsetlin Machine. The 1st International Workshop on Machine Reasoning (MRC 2021). 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, B.; Granmo, O.C.; Jiao, L. Explainable Tsetlin Machine Framework for Fake News Detection with Credibility Score Assessment. Proceedings of the Language Resources and Evaluation Conference; European Language Resources Association: Marseille, France, 2022; pp. 4894–4903. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, L.; Granmo, O.C.; Qian, Y.; Pan, F. Interpretable Tsetlin Machine-based Premature Ventricular Contraction Identification. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10181. [Google Scholar]
- Jenul, A.; Bhattarai, B.; Liland, K.H.; Jiao, L.; Schrunner, S.; Futsaether, C.; Granmo, O.C.; Tomic, O. Component Based Pre-filtering of Noisy Data for Improved Tsetlin Machine Modelling. 2022 International Symposium on the Tsetlin Machine (ISTM). IEEE. 2022; 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Abouzeid, A.; Granmo, O.C.; Goodwin, M.; Webersik, C. Label-Critic Tsetlin Machine: A Novel Self-supervised Learning Scheme for Interpretable Clustering. 2022 International Symposium on the Tsetlin Machine (ISTM). IEEE. 2022; 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.; Yadav, R.; Granmo, O.C.; Jiao, L. Drop clause: enhancing performance, robustness and pattern recognition capabilities of the Tsetlin machine. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2023, 37, 13547–13555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoulady, A.; Granmo, O.C.; Gorji, S.R.; Phoulady, H.A. The weighted tsetlin machine: compressed representations with weighted clauses. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.12607. [Google Scholar]
- Glimsdal, S.; Saha, R.; Bhattarai, B.; Giri, C.; Sharma, J.; Tunheim, S.A.; Yadav, R.K. Focused Negative Sampling for Increased Discriminative Power in Tsetlin Machines. 2022 International Symposium on the Tsetlin Machine (ISTM). IEEE. 2022; 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Granmo, O.C.; Andersen, P.A.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, X.; Blakely, C.; Berge, G.T.; Tveit, T. Learning Minimalistic Tsetlin Machine Clauses with Markov Boundary-Guided Pruning. 2023 International Symposium on the Tsetlin Machine (ISTM). IEEE. 2023; 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, B.; Granmo, O.C.; Jiao, L.; Andersen, P.A.; Tunheim, S.A.; Shafik, R.; Yakovlev, A. Contracting Tsetlin Machine with Absorbing Automata. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.11481. [Google Scholar]
- Abeyrathna, K.D.; Abouzeid, A.A.O.; Bhattarai, B.; Giri, C.; Glimsdal, S.; Granmo, O.C.; Jiao, L.; Saha, R.; Sharma, J.; Tunheim, S.A. ; others. Building concise logical patterns by constraining tsetlin machine clause size. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.08190. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, T.; Maheshwari, S.; Shafik, R.; Yakovlev, A.; Das, S. MILEAGE: An Automated Optimal Clause Search Paradigm for Tsetlin Machines. 2022 International Symposium on the Tsetlin Machine (ISTM). 2022; 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsetlin, M.L. On behaviour of finite automata in random medium. Avtomat. i Telemekh 1961, 22, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, H. Some aspects of the sequential design of experiments. 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Gittins, J.C. Bandit processes and dynamic allocation indices. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B: Statistical Methodology 1979, 41, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, K.S.; Thathachar, M.A. Learning automata:anintroduction; Courier corporation, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, R.; Berangi, R.; Minaei, B. A survey of regularization strategies for deep models. Artificial Intelligence Review 2020, 53, 3947–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.D. Time series analysis; Princeton university press, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Q.; Kwok, J.T.; Ni, L.M. Generalizing from a few examples: A survey on few-shot learning. ACM computing surveys (csur) 2020, 53, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, C.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks. International conference on machine learning. PMLR. 2017; 1126–1135. [Google Scholar]
- stby, S.; Brambo, T.M.; Glimsdal, S. The Sparse Tsetlin Machine: Sparse Representation with Active Literals. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.02375. [Google Scholar]
- Abeyrathna, K.D.; Granmo, O.C.; Zhang, X.; Goodwin, M. A scheme for continuous input to the Tsetlin machine with applications to forecasting disease outbreaks. Advances and Trends in Artificial Intelligence. Proceedings of the From Theory to Practice: 32nd International Conference on Industrial, Engineering and Other Applications of Applied Intelligent Systems, IEA/AIE 2019, Graz, Austria, July 9–11, 2019, Proceedings 32. Springer, 2019; 564–578. [Google Scholar]
- Mathisen, E.; Smørvik, H.S. Analysis of binarization techniques and Tsetlin machine architectures targeting image classification. Master’s thesis, University of Agder, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Simard, P.; Victorri, B.; LeCun, Y.; Denker, J. Tangent prop-a formalism for specifying selected invariances in an adaptive network. Advances in neural information processing systems 1991, 4. [Google Scholar]
| 1 |
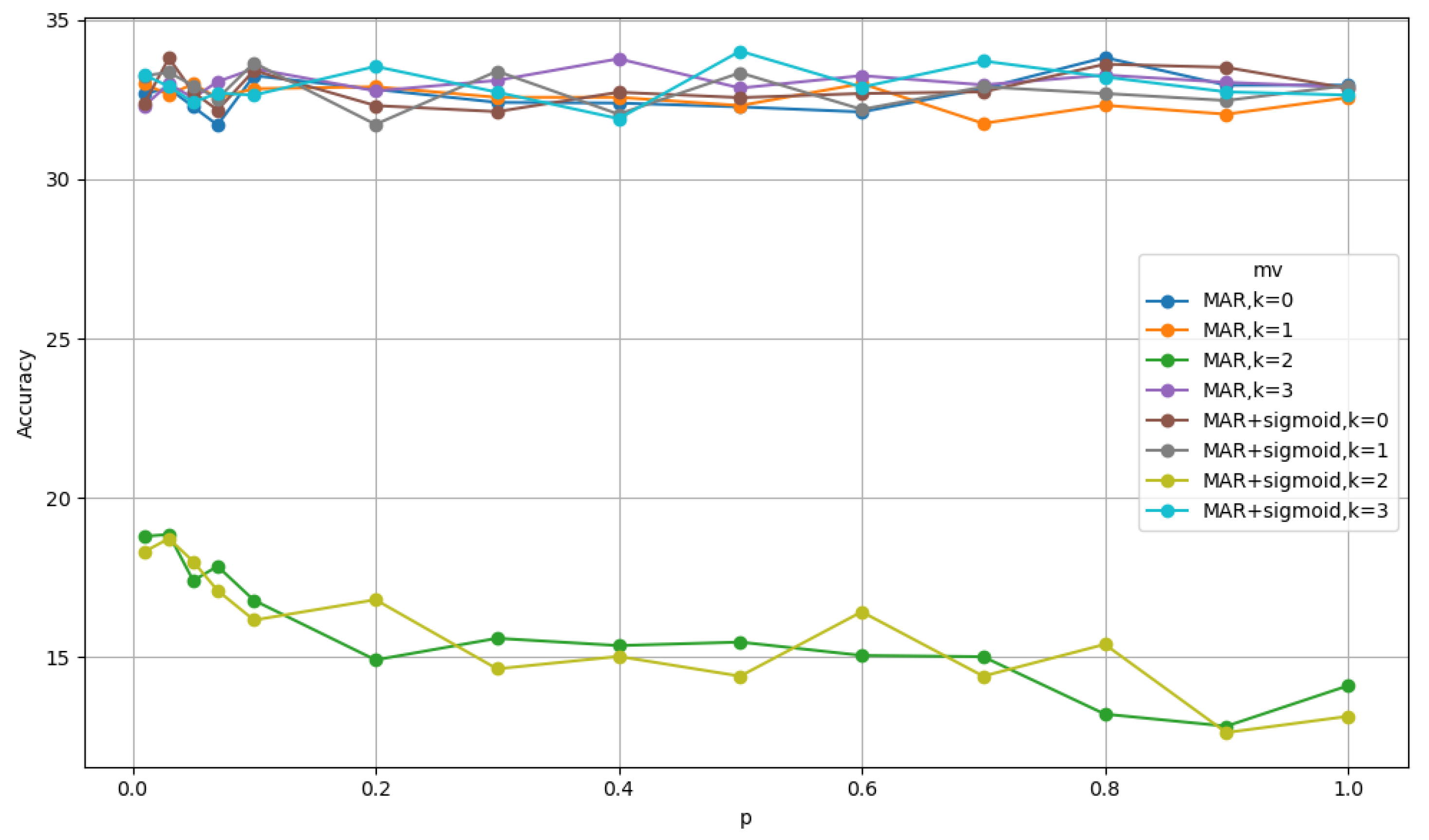
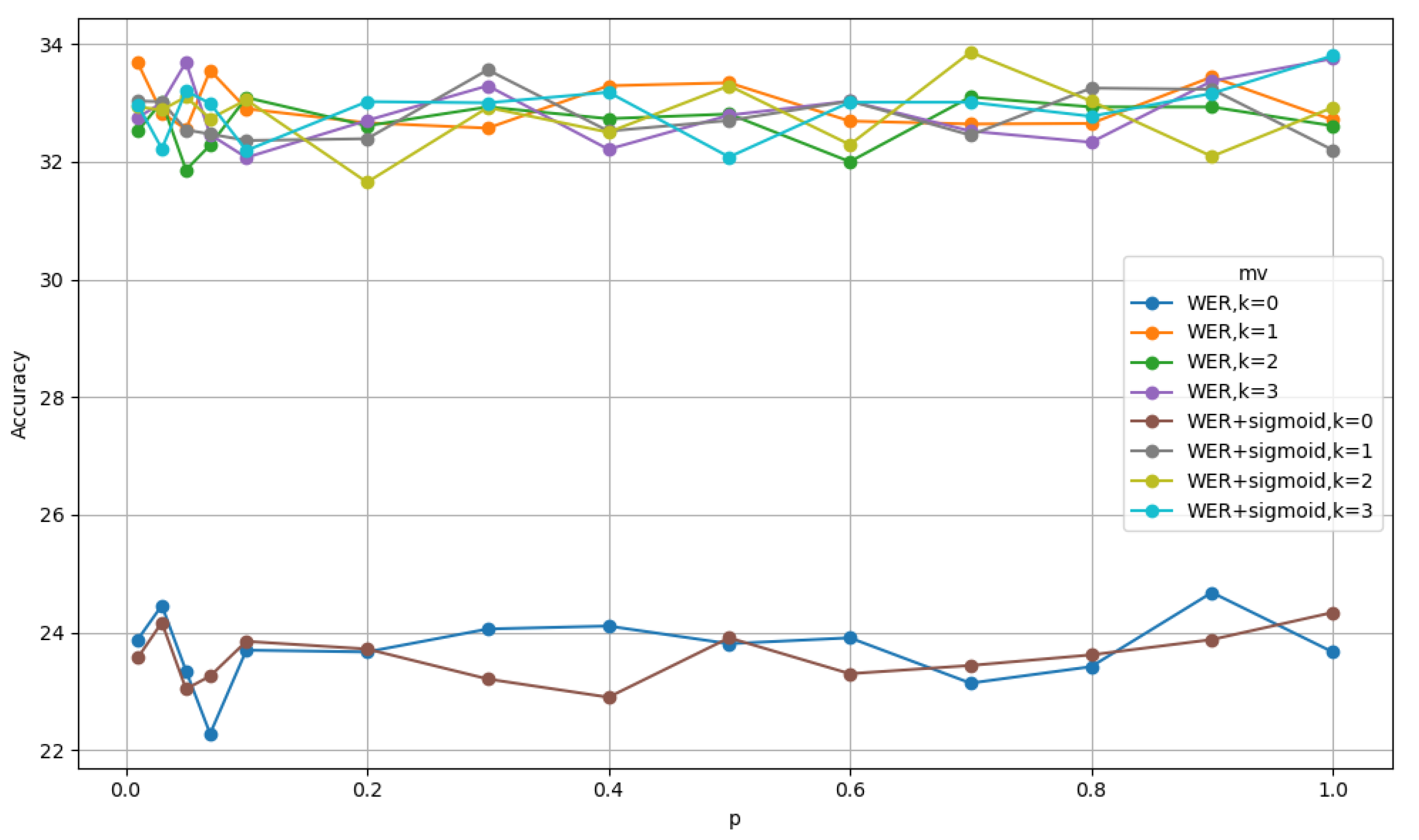
| Method (C=100, T=5000) | TM | with drop probability |
|---|---|---|
| No RegTM | 96.43 | 96.54 |
| Sigmoid | 96.45 | 96.15 |
| MAR only (k=0, p=0.03) | 96.75 | 95.48 |
| MAR + sigmoid (k=1, p=0.1) | 96.68 | 96.42 |
| WER (k=2, p=0.4) | 96.59 | 96.23 |
| WER + sigmoid (k=3, p=0.01) | 96.63 | 96.23 |
| Method (C=200, T=5000) | TM | with drop probability |
| No RegTM | 97.28 | 97.08 |
| Sigmoid | 97.09 | 97.24 |
| MAR only (k=0, p=0.03) | 97.19 | 97.06 |
| MAR + sigmoid (k=1, p=0.1) | 97.29 | 97.21 |
| WER (k=2, p=0.4) | 97.10 | 97.17 |
| WER + sigmoid (k=3, p=0.01) | 97.24 | 97.04 |
| Method (C=100, T=5000) | TM | with drop probability |
|---|---|---|
| No RegTM | 32.75 | 33.72 |
| Sigmoid | 32.92 | 33.84 |
| MAR only (k=0, p=0.8) | 33.82 | 32.27 |
| MAR + sigmoid (k=3, p=0.5) | 34.02 | 33.26 |
| WER (k=3, p=1.0) | 33.75 | 33.65 |
| WER + sigmoid (k=2, p=0.7) | 33.86 | 33.01 |
| Method (C=200, T=5000) | TM | with drop probability |
| No RegTM | 34.37 | 35.63 |
| Sigmoid | 35.89 | 36.31 |
| MAR only (k=0, p=0.8) | 34.84 | 36.45 |
| MAR + sigmoid (k=3, p=0.5) | 34.73 | 34.15 |
| WER (k=3, p=1.0) | 36.21 | 35.57 |
| WER + sigmoid (k=2, p=0.7) | 36.54 | 36.57 |
| Method | MNIST | CIFAR10 |
|---|---|---|
| Vanilla TM | 00:08:10 | 00:21:10 |
| Vanilla TM with drop clause | 00:08:37 | 00:22:07 |
| sigmoid only | 00:08:18 | 00:22:12 |
| MAR only | 00:08:14 | 00:21:36 |
| MAR + sigmoid | 00:08:18 | 00:22:10 |
| WER | 00:08:10 | 00:21:25 |
| WER + sigmoid | 00:08:23 | 00:23:41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





