Submitted:
18 September 2024
Posted:
19 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Inorganic-Based Nanoparticles and Biomaterials as Scaffolds in Regenerative Medicine
3. Nanotechnology Strategies in Regenerative Medicine and Wound Healing
3.1. Engineered Nanomaterials
3.2. Carbon Nanomaterials
3.3. Bioactive Glass-Ceramic Nanoparticles and Nano-Silica Hydrogels
3.4. Hydroxyapatites
3.5. Magnesium Oxide Alloys
3.6. Gold Nanoparticles
3.7. Biomimetic Natural Biomaterials
4. Challenges with the Application of Inorganic Biomaterials in Regenerative Medicine
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, A.S.; Mooney, D.J. Regenerative Medicine: Current Therapies and Future Directions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2015, 112(47), 14452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, C.; Dunnill, P. A Brief Definition of Regenerative Medicine. Regen. Med. 2008, 3(1), 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Li, S.; Yu, Q.; Chen, T.; Liu, D. Application of Stem Cells in Regeneration Medicine. MedComm (2020) 2023, 4(4), e291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinley, K.L.; Longaker, M.T.; Naik, S. Emerging Frontiers in Regenerative Medicine. Science 2023, 380(6647), 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, E.; Vigani, B.; Viseras, C.; Ferrari, F.; Rossi, S.; Sandri, G. Inorganic Nanomaterials in Tissue Engineering. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, A.J.; Oliveira, J.M.; Martins, A.; Teixeira, F.G.; Silva, N.A.; Neves, N.M.; Sousa, N.; Reis, R.L. Chapter One - Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: Past, Present, and Future. International Review of Neurobiology, Academic Press 2013, 108, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Brien, F.J. Biomaterials & Scaffolds For Tissue Engineering. Materials Today 2011, 14(3), 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikada, Y. Challenges in Tissue Engineering. J. R. Soc. Interface 2006, 3(10), 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yao, Q. Copper-based Biomaterials For Bone and Cartilage Tissue Engineering. J. Orthop. Translat. 2021, 29, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.R.; Won, J.E.; Jeon, E.; Lee, S.; Kang, W.; Jo, H.; Jang, J.H.; Shin, U.S.; Kim, H.W. Fibroblast Growth Factors: Biology, Function, and Application For Tissue Regeneration. J. Tissue Eng. 2010, 2010, 218142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh. Z.; Javaid, M.A.; Hamdan, N.; Hashmi, R. Bone Regeneration Using Bone Morphogenetic Proteins and Various Biomaterial Carriers. Materials (Basel), 2015, 8(4), 1778. [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, T.; Watabe, T. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8(6), a021899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lademann, F.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Rauner, M. The Bone Morphogenetic Protein Pathway: The Osteoclastic Perspective. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 586031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrzewski, W.; Dobrzyński, M.; Szymonowicz, M.; Rybak, Z. Stem Cells: Past, Present, and Future. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10(1), 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolios, G.; Moodley, Y. Introduction to stem cells and regenerative medicine. Respiration 2013, 85(1), 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal Dayem, A.M.; Saadeldin, I.M.; Zhang, S. Editorial: Crosslinking ROS signaling and stem cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1101802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.R., Laurencin, C.T.; Nukavarapu, S.P. Bone Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and Challenges. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40(5), 363. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.P.; Fu, X.B. Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells in Skin Repair and Regeneration. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2008, 11(4), 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, X. Stem Cell-Based Drug Delivery Strategy For Skin Regeneration and Wound Healing: Potential Clinical Applications. Inflamm. Regen. 2023, 43(1), 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duscher, D.; Barrera, J.; Wong, V.W.; Maan, Z.N.; Whittam, A.J.; Januszyk, M.; Gurtner, G.C. Stem Cells in Wound Healing: The Future of Regenerative Medicine? A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2016, 62(2), 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.M.; et al., Stem Cell-Based Therapy For Human Diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022. 7(1), 272. [CrossRef]
- Rajabzadeh, N.; Fathi, E.; Farahzadi, R. Stem Cell-Based Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cell Investig. 2019, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.T.; Badowski, M.; Ahmad, N.; Gaballa, M.A. The potential of cord blood stem cells for use in regenerative medicine. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2007, 7(9), 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Bongale, A.M.; Tefera, M.A.; Dixit, P.; Bhanap, P. Fresh Umbilical Cord Blood-A Source of Multipotent Stem Cells, Collection, Banking, Cryopreservation, and Ethical Concerns. Life (Basel), 2023, 13(9), 1794. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Petitto, G.; Rezvani, K.; Daher, M.; Rafei, H.; Kebriaei, P.; Shpall, E.J.; Olson, A. Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Connecting Its Origin to Its Future. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2023, 12(2), 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.N.; Byam, C.E.; Kernan, N.A.; Lee, S.S.; Hawke, R.M.; Doshi, K.A.; Wells, D.S.; Heller, G.; Papadopoulos, E.B.; Scaradavou, A.; Young, J.W.; van den Brink, M.R. Availability of Cord Blood Extends Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Access to Racial and Ethnic Minorities. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant 2010, 16(11), 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gragert, L.; et al. HLA Match Likelihoods For Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Grafts in the U.S. Registry. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371(4), 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.L.; Troyer, D.L. Stem Cells in the Umbilical Cord. Stem Cell Rev. 2006, 2(2), 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzberg, J.; Lyerly, A.D.; Sugarman, J. Untying the Gordian Knot: Policies, Practices, and Ethical Issues Related to Banking of Umbilical Cord Blood. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115(10), 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover-Plow, J.; Gong, Y. Challenges For Heart Disease Stem Cell Therapy. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2012, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, A.; Zwacka, R. The Future of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapeutic Approaches For Cancer - From Cells to Ghosts. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhao, E.R.; Hableel, G.; Hu, T.; Kim, T.; Li, J.; Gonzalez-Pech, N.I.; Cheng, D.J.; Lemaster, J.E.; Xie, Y.; Grassian, V.H.; Sen, G.L.; Jokerst, J.V. Increasing the Efficacy of Stem Cell Therapy via Triple-Function Inorganic Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2019, 13(6), 6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourian Dehkordi, A.; Mirahmadi Babaheydari, F.; Chehelgerdi, M.; Raeisi Dehkordi, S. Skin Tissue Engineering: Wound Healing Based on Stem-Cell-Based Therapeutic Strategies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10(1), 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, K.L.; Goverman, J.; Ma, H.; Fischman, A.; Yu, Y.M.; Bilodeau, M.; Rad, A.M.; Bonab, A.A.; Tompkins, R.G.; Fagan, S.P. Stem Cells and Burns: Review and Therapeutic Implications. J. Burn Care Res. 2010, 31(6), 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, H.Y.; Chan, M.H.; Gau, C.S.; Weng, S.M. Stem Cell Therapy on Skin: Mechanisms, Recent Advances and Drug Reviewing Issues. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26(1), 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojeh, N.; Pastar, I.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Stojadinovic, O. Cells in Skin Regeneration, Wound Healing, and Their Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16(10), 25476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-García, D.; Filipová, A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. A Beginner's Introduction to Skin Stem Cells and Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22(20), 11030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound Repair and Regeneration. Nature 2008, 453(7193), 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H. Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling in Development and Disease. Cell 2006, 127(3), 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, C.Y.; Nusse, R. The Wnt Signaling Pathway in Development and Disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.D.; Klaus, A.; Garratt, A.N.; Birchmeier, W. Wnt Signaling in Stem and Cancer Stem Cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25(2), 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tottoli, E.M.; Dorati, R.; Genta, I.; Chiesa, E.; Pisani, S.; Conti, B. Skin Wound Healing Process and New Emerging Technologies for Skin Wound Care and Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12(8), 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, M.M.; Ibrahium, A.M.; Abdelgalil, A.I.; El-Saied, M.A.; El-Bably, S.H. Regenerative Strategies in Treatment of Peripheral Nerve Injuries in Different Animal Models. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 20(6), 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frausin, S.; Viventi, S.; Verga Falzacappa, L.; Quattromani, M.J.; Leanza, G.; Tommasini, A.; Valencic, E. Wharton's Jelly Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Biological Properties, Induction of Neuronal Phenotype and Current Applications in Neurodegeneration Research. Acta Histochem. 2015, 117(4-5), 329. [CrossRef]
- Karimi, H. Nerve Regeneration and Stem Cells. Biomedical. J. Sci. & Tech. Res. 2019, 18(3). [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, S.; Wen, J.; Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Qian, C.; Qin, Z.; Li, Z.; Tan, D.; Fan, Z.; Wu, W.; Guo, J. Tissue Engineering With Peripheral Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes the Regeneration of Injured Peripheral Nerves. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 292, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.C.; Du, W.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yu, S.X.; Lu, F.Z.; Ding, H.M.; Cheng, Y.B.; Ren, C.; Geng, D.Q. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment For Peripheral Nerve Injury: A Narrative Review. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16(11), 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, K.; Qian, T.; Gu, X. Application of Stem Cells in Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Burns. Trauma 2020, 8, tkaa002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.W.; Zhang, C.L. Neuronal Regeneration After Injury: A New Perspective on Gene Therapy. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1181816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. A Review of Clinical Translation of Inorganic Nanoparticles. AAPS J, 2015, 17(5), 1041. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, P.; Fu, Z.; Meng, S.; Dai, L.; Yang, H. Applications of Nanomaterials in Tissue Engineering. RSC Adv. 2021, 11(31), 19041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brokesh, A.M.; Gaharwar, A.K. Inorganic Biomaterials for Regenerative Medicine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12(5), 5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Luan, Z.; Li, J. Inorganic Nanoparticles-Based Systems in Biomedical Applications of Stem Cells: Opportunities and Challenges. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Fan, C. Advances in Graphene-Based 2D Materials for Tendon, Nerve, Bone/Cartilage Regeneration and Biomedicine. iScience 2024, 27(7), 110214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Sindhu, A.; Dilbaghi, N.; Chaudhury, A.; Rajakumar, G.; Rahuman, A.A. Nano-Regenerative Medicine Towards Clinical Outcome of Stem Cell and Tissue Engineering in Humans. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2012, 16(9), 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Vijayavenkataraman, S.; Cidonio, G. Biomaterials and Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. BMC Methods 2024, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.P.; Leong, K.W. Scaffolding in Tissue Engineering: General Approaches and Tissue-Specific Considerations. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 17, Suppl 4(Suppl 4), 467. [CrossRef]
- Krishani, M.; Shin, W.Y.; Suhaimi, H.; Sambudi, N.S. Development of Scaffolds from Bio-Based Natural Materials for Tissue Regeneration Applications: A Review. Gels 2023, 9(2), 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering Precision Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20(2), 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, G.S.R.; Dariya, B.; Mungamuri, S.K.; Chalikonda, G.; Kang, S.M.; Khan, I.N.; Sushma, P.S.; Nagaraju, G.P.; Pavitra, E.; Han, Y.K. Nanomaterials Multifunctional Behavior For Enlightened Cancer Therapeutics. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 69, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.J.; Jiang, X.C.; Li, Y.S.; Gao, J.Q. Inorganic Nanoparticle-Integrated Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Potential Biological Agent For Multifaceted Applications. MedComm (2020), 2023, 4(4), e313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhuis, T.J.; Arts, J.J. Bioactive and Osteoinductive Bone Graft Substitutes: Definitions, Facts and Myths. Injury 2011, 42 Suppl 2, S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.R.; Laurencin, C.T.; Nukavarapu, S.P. Bone Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and Challenges. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40(5), 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devin, J.E.; Attawia, M.A.; Laurencin, C.T. Three-Dimensional Degradable Porous Polymer-Ceramic Matrices For Use in Bone Repair. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1996, 7(8), 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Morshed, M.; Memic, A.; Hassan, S.; Webster, T.J.; Marei, H.E. Nanoparticles in Tissue Engineering: Applications, Challenges and Prospects. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2018, 13, 5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, T.G.; Park, H.S.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Yoon, S.C.; Nam, J.D. Thermal and Mechanical Characteristics of Poly(L-lactic acid) Nanocomposite Scaffold. Biomaterials. 2003, 24(16), 2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Rahaman, K.A.; Kim, Y.C.; Jeon, H.; Han, H.S. Fostering Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine to Treat Musculoskeletal Disorders in Bone and Muscle. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 40, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, L.; Xiao, Y. Porous Nanomaterials Targeting Autophagy in Bone Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13(10), 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friggeri, G.; et al. Multifunctional Scaffolds For Biomedical Applications: Crafting Versatile Solutions with Polycaprolactone Enriched by Graphene Oxide. APL Bioeng. 2024, 8(1), 016115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadian, H.; Khastar, H.; Ehterami, A.; Salehi, M. Bioengineered 3D Nanocomposite Based on Gold Nanoparticles and Gelatin Nanofibers for Bone Regeneration: In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11(1), 13877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadian, H.; et al. Electrospun Cellulose Acetate/Gelatin Nanofibrous Wound Dressing Containing Berberine for Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10(1), 8312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhimathi, C.; Quek, Y.J.; Ezhilarasu, H.; Ramakrishna, S.; Bay, B.H.; Srinivasan, D.K. Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Silica-Coated Gold Nanoparticles for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20(20), 5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedel-Grzenda, A.; Fraczek-Szczypta, A.; Terrones, M.; Elias, A.L. Lekka, M.; Menaszek, E.; Blazewicz, S. Polysulphone composite membranes modified with two types of carbon additives as a potential material for bone tissue regeneration. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2017, 40(1), 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithole, M.N.; Kumar, P.; Du Toit, L.C.; Erlwanger, K.H.; Ubanako, P.N.; Choonara, Y.E. A 3D-Printed Biomaterial Scaffold Reinforced with Inorganic Fillers for Bone Tissue Engineering: In Vitro Assessment and In Vivo Animal Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(8), 7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Rathnam, C.; Hou, Y.; Patel, M.; Cai, L.; Lee, K.-B. Rapid and Controllable Multilayer Cell Sheet Assembly via Biodegradable Nanochannel Membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 2403367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chueng, S.D.; Li, Y.; Patel, M.; Rathnam, C.; Dey, G.; Wang, L.; Cai, L.; Lee, K.B. A Biodegradable Hybrid Inorganic Nanoscaffold for Advanced Stem Cell Therapy. Nat Commun. 2018, 9(1), 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydar, S.Y.; Ay, H.F.; Cakir, R. Frontiers of Stem Cell Engineering For Nanotechnology-Mediated Drug Delivery Systems. ADMET DMPK, 2024, 12(2), 225. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Leong, K.W. Nanoscale Surfacing For Regenerative Medicine. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 2, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovkina, O.; Dashinimaev, E. Advances and Complications of Regenerative Medicine in Diabetes Therapy. PeerJ, 2020, 8, e9746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Wu, N. Application Progress of Nanotechnology in Regenerative Medicine of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 190, 109966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreadi, A.; Lodeserto, P.; Todaro, F.; Meloni, M.; Romano, M.; Minasi, A.; Bellia, A.; Lauro, D. Nanomedicine in the Treatment of Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwakoti, P.; Rennie, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.J.; Tuch, B.E.; McClements, L.; Xu, X. Challenges with Cell-based Therapies for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Stem Cell. Rev. Rep. 2023, 19(3), 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Ji, K.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Wang, J. Materials and Carriers Development for Glucose-Responsive Insulin. Acc. Mater. Res. 2022, 3(9), 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhru, S.H.; Furtado, S.; Morello, A.P.; Mathiowitz, E. Oral Delivery of Proteins by Biodegradable Nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabanel, J.M.; Aoun, V.; Elkin, I.; Mokhtar, M.; Hildgen, P. Drug-Loaded Nanocarriers- Passive Targeting and Crossing of Biological Barriers. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiseh, O.; Tang, B.C.; Whitehead, K.A.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Managing Diabetes with Nanomedicine: Challenges and Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14(1), 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Borah, S.J.; Bhawna, Kumar, S.; Gupta, A.; Kumari, V.; Kumar, R.; Dubeyg, K.K.; Kumar, V. Emerging Trends in Nano-Based Antidiabetic Therapeutics: A Path to Effective Diabetes Management. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4(15), 3091. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, S.; Ji, W.; Yao, H.; Lin, L.; Cui, H.; Santos, H.A.; Pan, G. Emerging Theranostic Nanomaterials in Diabetes and Its Complications. Adv. Sci. (Weinh). 2022, 9(3), e2102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonomoto, K.; Yamaoka, K.; Kaneko, H.; Yamagata, K.; Sakata, K.; Zhang, X.; Kondo, M.; Zenke, Y.; Sabanai, K.; Nakayamada, S.; Sakai, A.; Tanaka, Y. Spontaneous Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Poly-Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid Nano-Fiber Scaffold. PLoS One. 2016, 11(4), e0153231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, A.; Ghouri, M.D.; Muyizere, T.; Aqib, R.M.; Muhaymin, A.; Cai, R.; Chen, C. Engineered Nano-Bio Interfaces for Stem Cell Therapy. Precis. Chem. 2023, 1(6), 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, B.K.; Wong, S.T.; Lim, C.K.; Kung, T.Y.; Yap, C.H.; Ramagopal, Y.; Romer, L.H.; Yim, E.K. Nanotopography Modulates Mechanotransduction of Stem Cells and Induces Differentiation Through Focal Adhesion Kinase. ACS Nano 2013, 7(6), 4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludin, A.; Gur-Cohen, S.; Golan, K.; Kaufmann, K.B.; Itkin, T.; Medaglia, C.; Lu, X.J.; Ledergor, G.; Kollet, O.; Lapidot, T. Reactive Oxygen Species Regulate Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal, Migration and Development, as well as their Bone Marrow Microenvironment. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21(11), 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Sun, J.; Feng, W.; Liang, X.J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. Defect-Related Luminescent Hydroxyapatite-Enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Via an ATP-Induced cAMP/PKA Pathway. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2016, 8(18), 11262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przekora, A. Current Trends in Fabrication of Biomaterials for Bone and Cartilage Regeneration: Materials Modifications and Biophysical Stimulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20(2), 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.N.; Law, J.B.; He, A.Y.; Low, H.Y.; Hui, J.H.; Lim, C.T.; Yang, Z.; Lee, E.H. Substrate Topography Determines the Fate of Chondrogenesis from Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Resulting in Specific Cartilage Phenotype Formation. Nanomedicine 2014, 10(7), 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.N.; Yang, Z.; Hui, J.H.; Ouyang, H.W.; Lee, E.H. Cartilaginous ECM Component-Modification of the Micro-Bead Culture System For Chondrogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Biomaterials 2007, 28(28), 4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.; Hwang, N.S.; Canver, A.C.; Theprungsirikul, P.; Lin, D.W.; Elisseeff, J. Chondroitin Sulfate Based Niches For Chondrogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Matrix Biol. 2008, 27(1), 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.M.; Lozovik, Y.E.; Fiorito, S.; Yahia, L. Biocompatibility and Applications of Carbon Nanotubes in Medical Nanorobots. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2(3), 361. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, S.W.; Shau, Y.H.; Wu, P.C.; Yang, Y.S.; Shieh, D.B.; Chen, C.C. In Vitro and in Vivo Studies of FePt Nanoparticles for Dual Modal CT/MRI Molecular Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132(38), 13270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ding, Z.; Yang, C.; Chen, L. Exploration of the Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes’ Influence for Cartilage Repair, Colloid. Surf. A: Physicochemi. Engr. Aspects. 2020, 606, 125520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymański, T.; Semba, J.A.; Mieloch, A.A.; Cywoniuk, P.; Kempa, M.; Rybka, J.D. Hyaluronic Acid and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes as Bioink Additives for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13(1), 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, C.J.; Wan, Y.; Smith, P.; Shang, G.; Cui, Q. Antioxidative Fullerol Promotes Osteogenesis of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elídóttir, K.L.; Scott, L.; Lewis, R.; Jurewicz, I. Biomimetic Approach to Articular Cartilage Tissue Engineering Using Carbon Nanotube-Coated and Textured Polydimethylsiloxane Scaffolds. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2022, 1513(1), 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.Q.; Yan, K.; Shi, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Li, R.; Dong, W.; Zheng, J. Neurogenic Differentiation of Adipose Derived Stem Cells on Graphene-Based Mat. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 90, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, F.; Tamjid, E.; Behmanesh, M. Drug-Eluting PCL/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Scaffolds For Enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 115, 111102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S., et al., Carbon Nanomaterials in the Treatment of Infectious Bone Defects and Wound Scars after Wushu Fractures. Journal of Chemistry, 2020. 2020: p. 1-9.
- Shen, Y.; Wu, L.; Qin, D.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X. Carbon Black Suppresses the Osteogenesis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: The Role of Mitochondria. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15(1), 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, S.; Verdoliva, V.; Kargozar, S.; Baino, F. Bioactive Glass-Ceramic Scaffolds Coated with Hyaluronic Acid-Fatty Acid Conjugates: A Feasibility Study. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14(1), 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannio, M.; Bellucci, D.; Roether, J.A.; Boccaccini, D.N.; Cannillo, V. Bioactive Glass Applications: A Literature Review of Human Clinical Trials. Materials (Basel). 2021, 14(18), 5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, R.; Bellucci, D.; Cannillo, V. A Review of Bioactive Glass/Natural Polymer Composites: State of the Art. Materials (Basel). 2020, 13(23), 5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rashidy, A.A.; Roether, J.A.; Harhaus, L.; Kneser, U.; Boccaccini, A.R. Regenerating Bone with Bioactive Glass Scaffolds: A Review of in vivo Studies in Bone Defect Models. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiume, E.; Barberi, J.; Verné, E.; Baino, F. Bioactive Glasses: From Parent 45S5 Composition to Scaffold-Assisted Tissue-Healing Therapies. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9(1), 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hench, L.L. The Story of Bioglass. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17(11), 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, L.C.; Boccaccini, A.R. Bioactive Glass and Glass-Ceramic Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials (Basel) 2010, 3(7), 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.R. Bioactive Ceramics and Glasses. In: Boccaccini A.R., G.J.E., editors. Tissue Engineering Using Ceramics and Polymers. 1st ed. Volume 1. Woodhead Publishing Limited CRC Press; Cambridge, UK: 2007. pp. 52–71.
- Xynos, I.D.; Hukkanen, M.V.; Batten, J.J.; Buttery, L.D.; Hench, L.L.; Polak, J.M. Bioglass 45S5 Stimulates Osteoblast Turnover and Enhances Bone Formation In vitro: Implications and Applications for Bone Tissue Engineering. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2000, 67(4), 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreanca, A., et al., The Evaluation of the Osteopromoting Capabilities of Composites Based on Biopolymers and Gold/Silver Nanoparticles Doped Bioactive Glasses on an Experimental Rat Bone Defect. Biomed Mater. 2023, 18(5). [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Chen, M.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Luo, M.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Lei, B. A Multifunctional Bioactive Glass-Ceramic Nanodrug for Post-Surgical Infection/Cancer Therapy-Tissue Regeneration. ACS Nano 2021, 15(9), 14323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, N.; Khoshfetrat, A.B.; Khaksar, M.; Zamani, A.R.N.; Rahbarghazi, R. Collagen-Alginate-Nano-Silica Microspheres Improved the Osteogenic Potential of Human Osteoblast-Like MG-63 Cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120(9), 15069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.A.; El-Sayed, M.M.H.; Emam, A.N.; Abd-Rabou, A.A.; Dawood, R.M.; Oudadesse, H. Bioactive Glass Doped with Noble Metal Nanoparticles for Bone Regeneration: in vitro Kinetics and Proliferative Impact on Human Bone Cell Line. RSC Adv. 2021, 11(41), 25628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, A.; Castro, J.P.O.; Habibovic, P.; van Rijt, S.H. Injectable, Self-Healing Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposite Hydrogels with Improved Mechanical Properties. Nanoscale 2021, 13(2), 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, X.; Wang, T.; Zhao, X.; Lu, B.; Chen, F.; Zheng, L. Calcium Phosphate-Based Biomaterials for Bone Repair. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13(4), 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Barbieri, D.; Yuan, H.; Moroni, L.; Feng, G. The Role of Calcium Phosphate Surface Structure in Osteogenesis and the Mechanisms Involved. Acta Biomater. 2020, 106, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, H.; Qingling, F.; Bo, Y.; Songjian, L. Biomimetic Properties of an Injectable Chitosan/Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Collagen Composite. Mater. Sci. Eng.: C 2011, 31(3), 683. [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, S.; Ozawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Izuo, N.; Toda, T.; Yokote, K.; Shimizu, T. Palladium and Platinum Nanoparticles Attenuate Aging-Like Skin Atrophy via Antioxidant Activity in Mice. PLoS One 2014, 9(10), e109288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, F.; Nirwan, V.; Gonçalves, A.M.; Panitschewski, N.; Filová, E.; Fahmi, A.; Costa, P.F. (2023). Bio-Inspired Nanoporous Scaffold: Electrospun Hybrid Fibers Based on Self-Assembled Block Copolymer Mineralized with Inorganic Nanoparticles for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2023, 73(12), 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.Y.S.; Isloor, A.M.; Kumar, G.C.M.; Inamuddin Asiri, A.M. Nanohydroxyapatite Reinforced Chitosan Composite Hydrogel with Tunable Mechanical and Biological Properties for Cartilage Regeneration. Sci Rep. 2019, 9(1), 15957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumai, T.; Yui, N.; Yatabe, K.; Sasaki, C.; Fujii, R.; Takenaga, M.; Fujiya, H.; Niki, H.; Yudoh, K. A Novel, Self-Assembled Artificial Cartilage-Hydroxyapatite Conjugate for Combined Articular Cartilage and Subchondral Bone Repair: Histopathological Analysis of Cartilage Tissue Engineering in Rat Knee Joints. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boller, L.A.; Shiels, S.M.; Florian, D.C.; Peck, S.H.; Schoenecker, J.G.; Duvall, C.; Wenke, J.C.; Guelcher, S.A. Effects of Nanocrystalline Hydroxyapatite Concentration and Skeletal Site on Bone and Cartilage Formation in Rats. Acta Biomater. 2021, 130, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; et al. 3D Printed Gelatin/Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds for Stem Cell Chondrogenic Differentiation and Articular Cartilage Repair. Biomater Sci. 2021, 9(7), 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaweł, J.; Milan, J.; Żebrowski, J.; Płoch, D.; Stefaniuk, I.; Kus-Liśkiewicz, M. Biomaterial Composed of Chitosan, Riboflavin, and Hydroxyapatite for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13(1), 17004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Leal, D.; Noris-Suarez, K.; Gonzalez, G. Chitosan-Collagen-Hydroxyapatite Membranes for Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2022, 33(2), 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wei, Y.; Sun, R.; Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Lian, X.; Ma, X.; Huang, D. Calcium Phosphate Bone Cements Incorporated with Black Phosphorus Nanosheets Enhanced Osteogenesis. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9(1), 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F.; Kaese, V.; Haferkamp, H.; Switzer, E.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Wirth, C.J.; Windhagen, H. In vivo Corrosion of Four Magnesium Alloys and the Associated Bone Response. Biomaterials 2005, 26(17), 3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Fu, X.; Pan, H.; Wan, P.; Wang, L.; Tan, L.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, K.; Chu, P.K. Biodegradable Mg-Cu Alloys with Enhanced Osteogenesis, Angiogenesis, and Long-Lasting Antibacterial Effects. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.W.; Kirkland, N.T.; Truong, J.; Wang, J.; Smith, P.N.; Birbilis, N.; Nisbet, D.R. The Influence of Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys on the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2014, 102(12), 4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischerauer, S.F.; Kraus, T.; Wu, X.; Tangl, S.; Sorantin, E.; Hänzi, A.C.; Löffler, J.F.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Weinberg, A.M. In vivo Degradation Performance of Micro-Arc-Oxidized Magnesium Implants: A Micro-CT Study in Rats. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9(2), 5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Wu, J.; Han, Y.; Wu, C. Immunomodulatory Multicellular Scaffolds For Tendon-to-Bone Regeneration. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10(10), eadk6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Filho, G.B.; Atoche-Medrano, J.J.; Aragón, F.F.H.; Mantilla Ochoa, J.C.; Pacheco-Salazar, D.G.; da Silva, S.W.; Coaquira, J.A.H. Core-Shell Au/Fe3O4 Nanocomposite Synthesized by Thermal Decomposition Method: Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties . Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 563, 150290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.H.; et al. Favorable Biological Performance Regarding the Interaction between Gold Nanoparticles and Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24(1), 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H. Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles: A Novel Nanomaterial for Various Medical Applications and Biological Activities. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Rai, B. Effect of Size and Surface Charge of Gold Nanoparticles on their Skin Permeability: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, K.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Seo, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, E.M. Gold Nanoparticles Attenuates Antimycin A-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in MC3T3-E1 Osteoblastic Cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 153(1-3), 428. [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.A.; Zhu, J.; Gootee, J.; Snider, C.L.; Bellrichard, M.; Grant, D.A. Gold Nanoparticle-Collagen Gels for Soft Tissue Augmentation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018, 24(13-14), 1091. [CrossRef]
- Nunan, R.; Harding, K.G.; Martin, P. Clinical Challenges of Chronic Wounds: Searching for an Optimal Animal Model to Recapitulate their Complexity. Dis Model Mech. 2014, 7(11), 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, C.; et al. Microcurrent and Gold Nanoparticles Combined with Hyaluronic Acid Accelerates Wound Healing. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022; 11, 11, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poomrattanangoon, S.; Pissuwan, D. Gold Nanoparticles Coated with Collagen-I and Their Wound Healing Activity in Human Skin Fibroblast Cells. Heliyon 2024, 10(13), e33302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yu, J.M.; Gan, Y.C.; Qiu, X.Z.; Gao, Z.C.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.X.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, G.H.; Lin, S.E.; McCarthy, A.; John, J.V.; Wei, D.X.; Hou, H.H. Biomimetic Natural Biomaterials For Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: New Biosynthesis Methods, Recent Advances, and Emerging Applications. Mil. Med. Res. 2023, 10(1), 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; et al. Prospects and Challenges For the Application of Tissue Engineering Technologies in the Treatment of Bone Infections. Bone Res. 2024, 12(1), 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senra, M.R.; Marques, M.F.V.; Monteiro, S.N. Poly (Ether-Ether-Ketone) For Biomedical Applications: From Enhancing Bioactivity to Reinforced-Bioactive Composites-An Overview. Polymers (Basel), 2023, 15(2), 373. [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Ding, J. Recent Advances in Regenerative Biomaterials. Regen. Biomater. 2022, 9, rbac098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Tan, J.; Lv. D.; Song, W.; Su, R.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, L.; Liao, Y. Strontium Ranelate Incorporated 3D Porous Sulfonated PEEK Simulating MC3T3-E1 Cell Differentiation. Regen. Biomater. 2020, 8(1), rbaa043. [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, D.P.; Águas, A.P.; Barbosa, M.A.; Pelegrín, P.; Barbosa, J.N. The Inflammasome in Host Response to Biomaterials: Bridging Inflammation and Tissue Regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
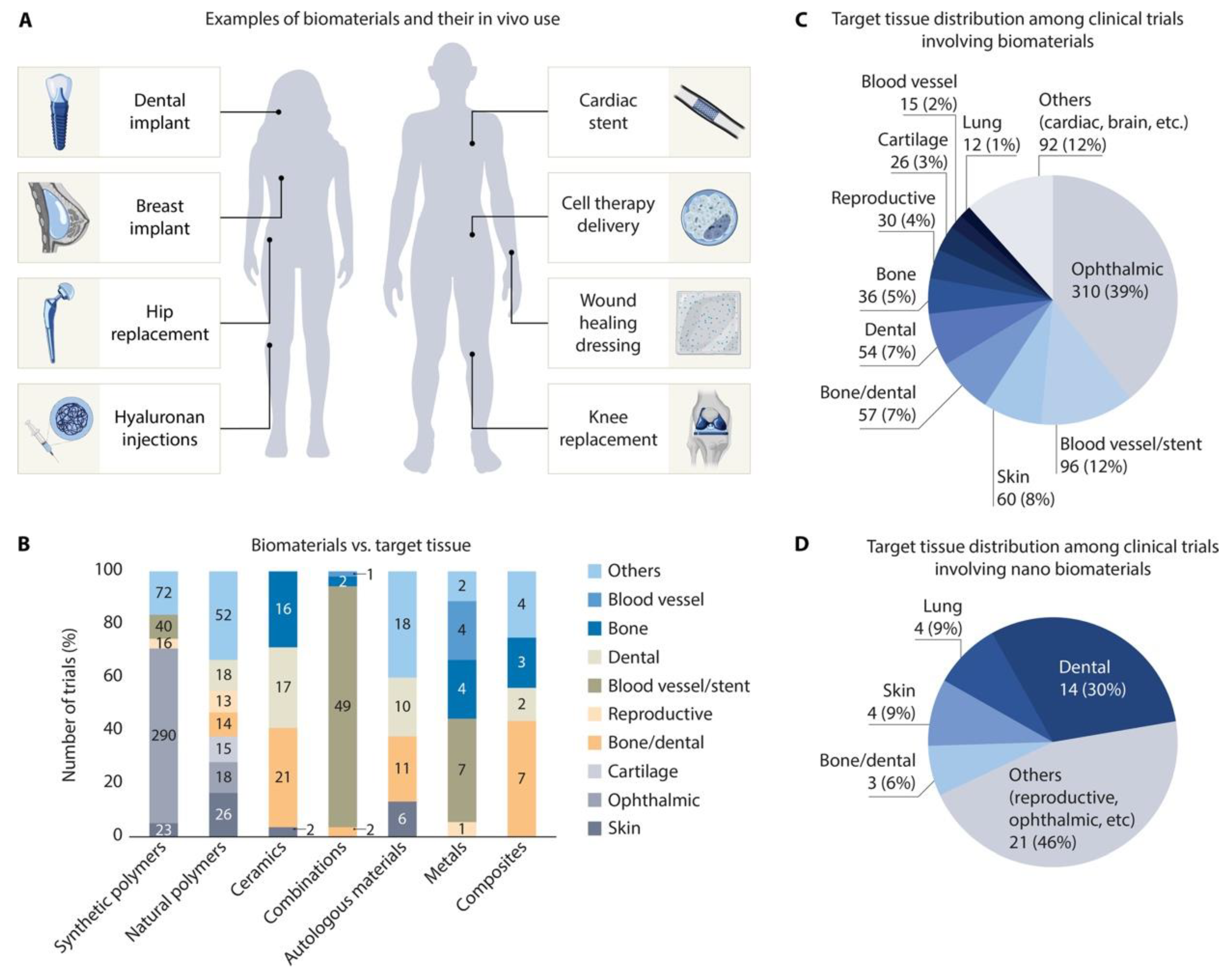
- Lele, M.; Kapur, S.; Hargett, S.; Sureshbabu, N.M.; Gaharwar, A.K. Global Trends in Clinical Trials Involving Engineered Biomaterials. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10(29), eabq0997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elson, E.L.; Genin, G.M. Tissue Constructs: Platforms for Basic Research and Drug Discovery. Interface Focus 2016, 6(1), 20150095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L.; Thompson, I. Twenty-First Century Challenges for Biomaterials. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7 Suppl 4(Suppl 4), S379. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, R.; Bhatt, V.D.; Dhot, P.S. Tissue Engineering; Current Status & Futuristic Scope. J. Med. Life 2019, 12(3), 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.K.; Soker, S.; Atala, A. Chapter 1—Tissue Engineering: Current Status and Future Perspectives. In: Lanza, R., Langer, R., Vacanti, J.P., and Atala, A., eds. Principles of Tissue Engineering (Fifth Edition). London, UK: Academic Press, 2020, pp. 1–35.
- Ashammakhi, N.; GhavamiNejad, A.; Tutar, R.; Fricker, A.; Roy, I.; Chatzistavrou, X.; Hoque Apu, E.; Nguyen, K.L.; Ahsan, T.; Pountos, I.; Caterson, E.J. Highlights on Advancing Frontiers in Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2022, 28(3), 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badylak, S.F.; Nerem, R.M. Progress in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2010, 107(8), 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
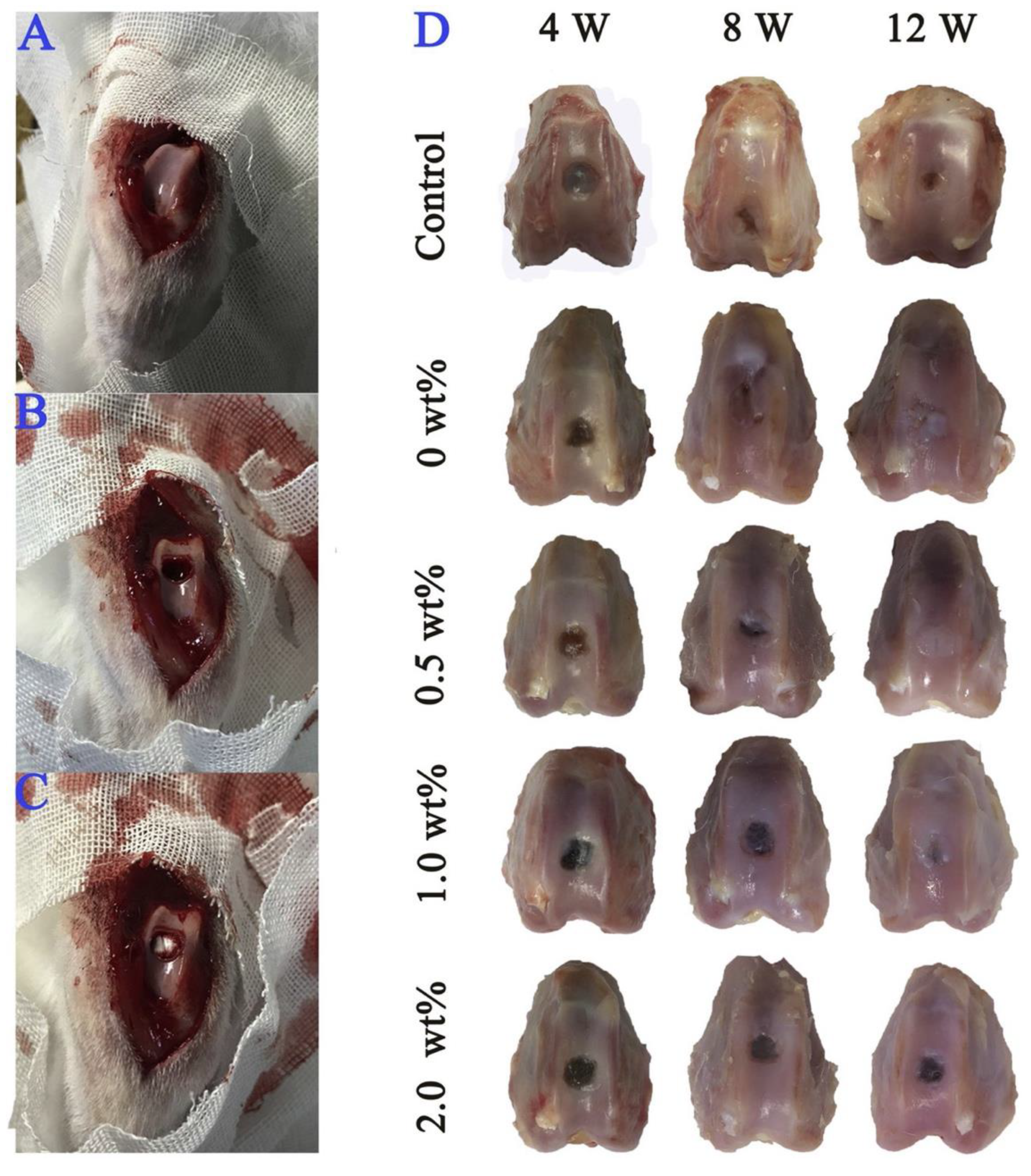
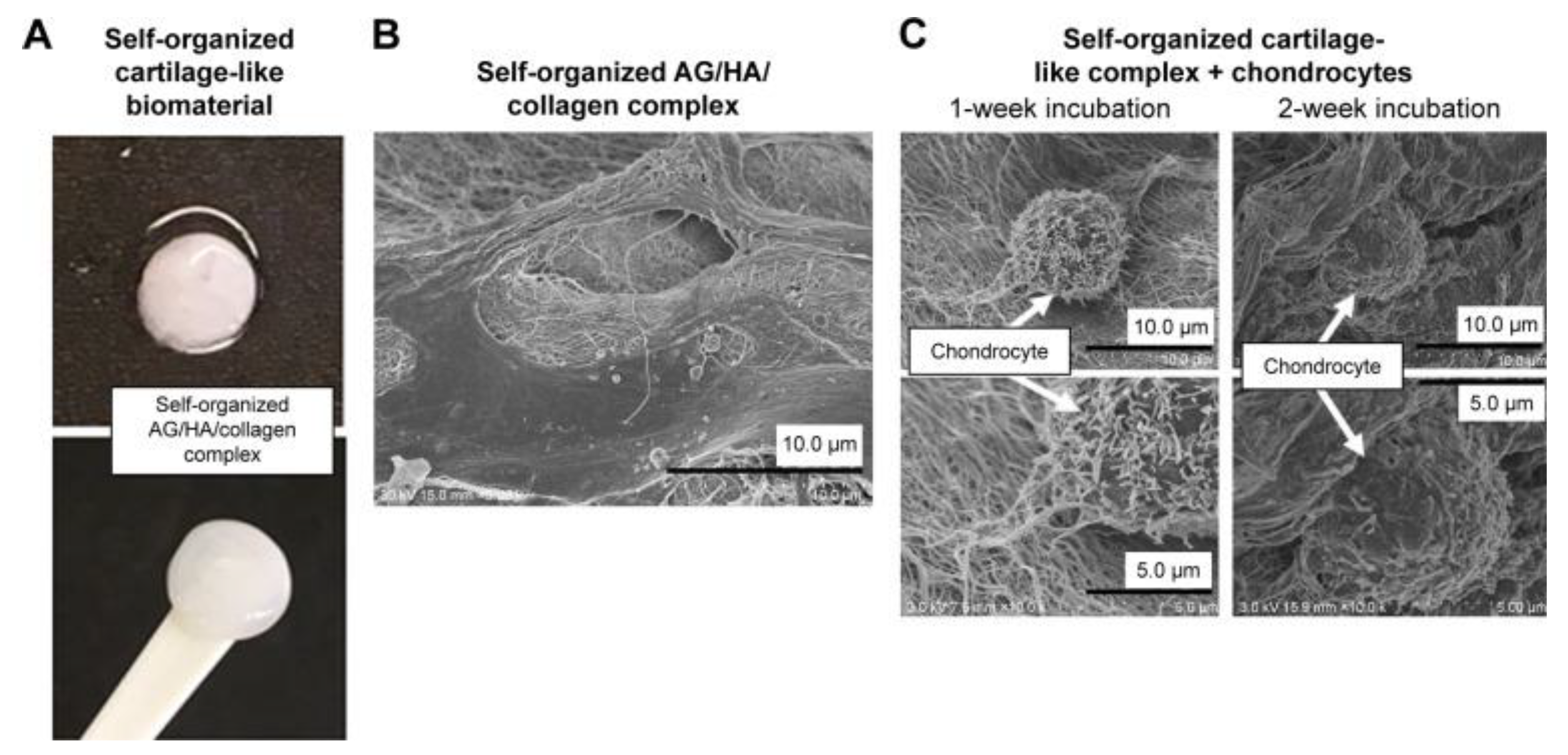
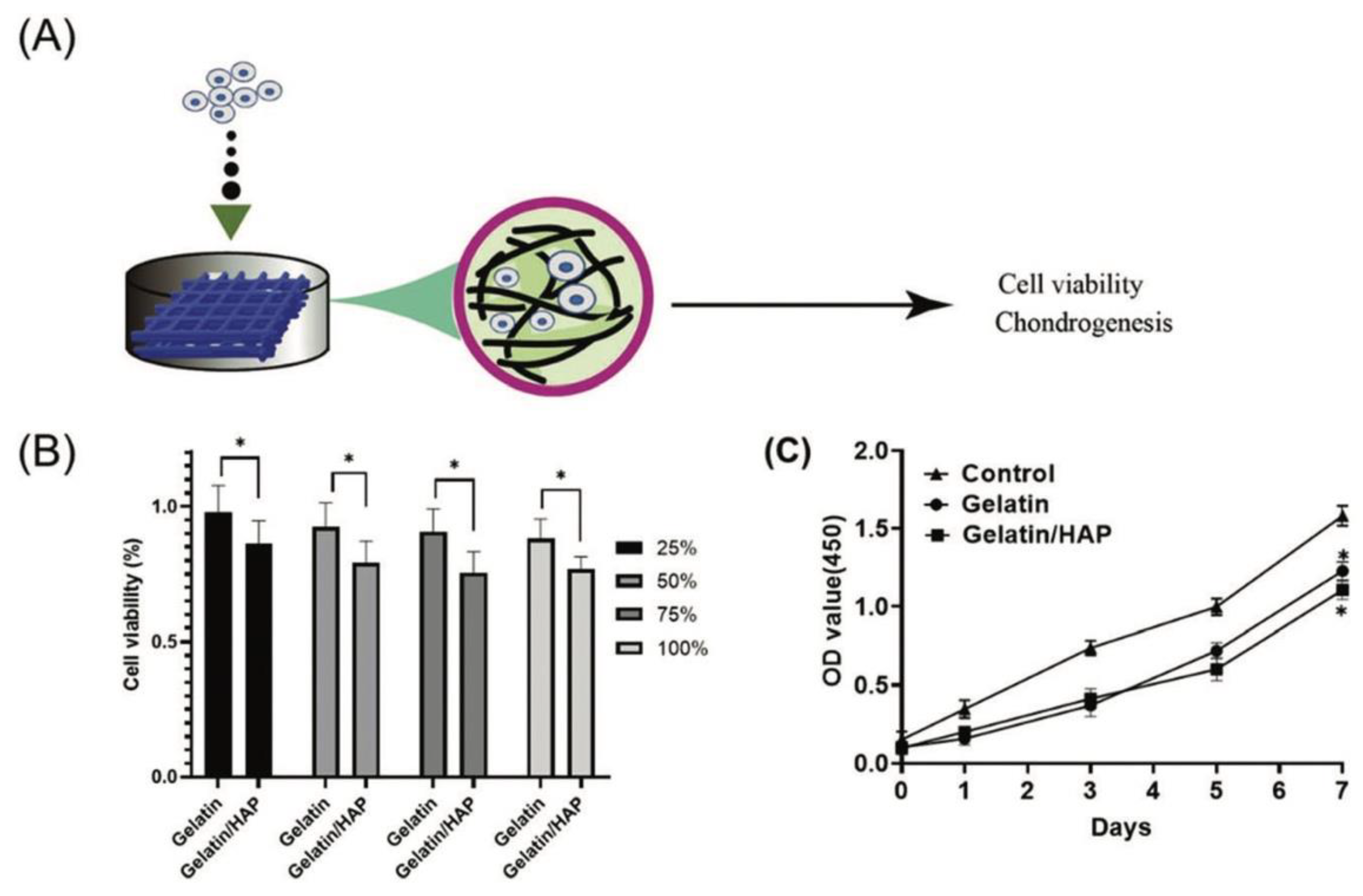
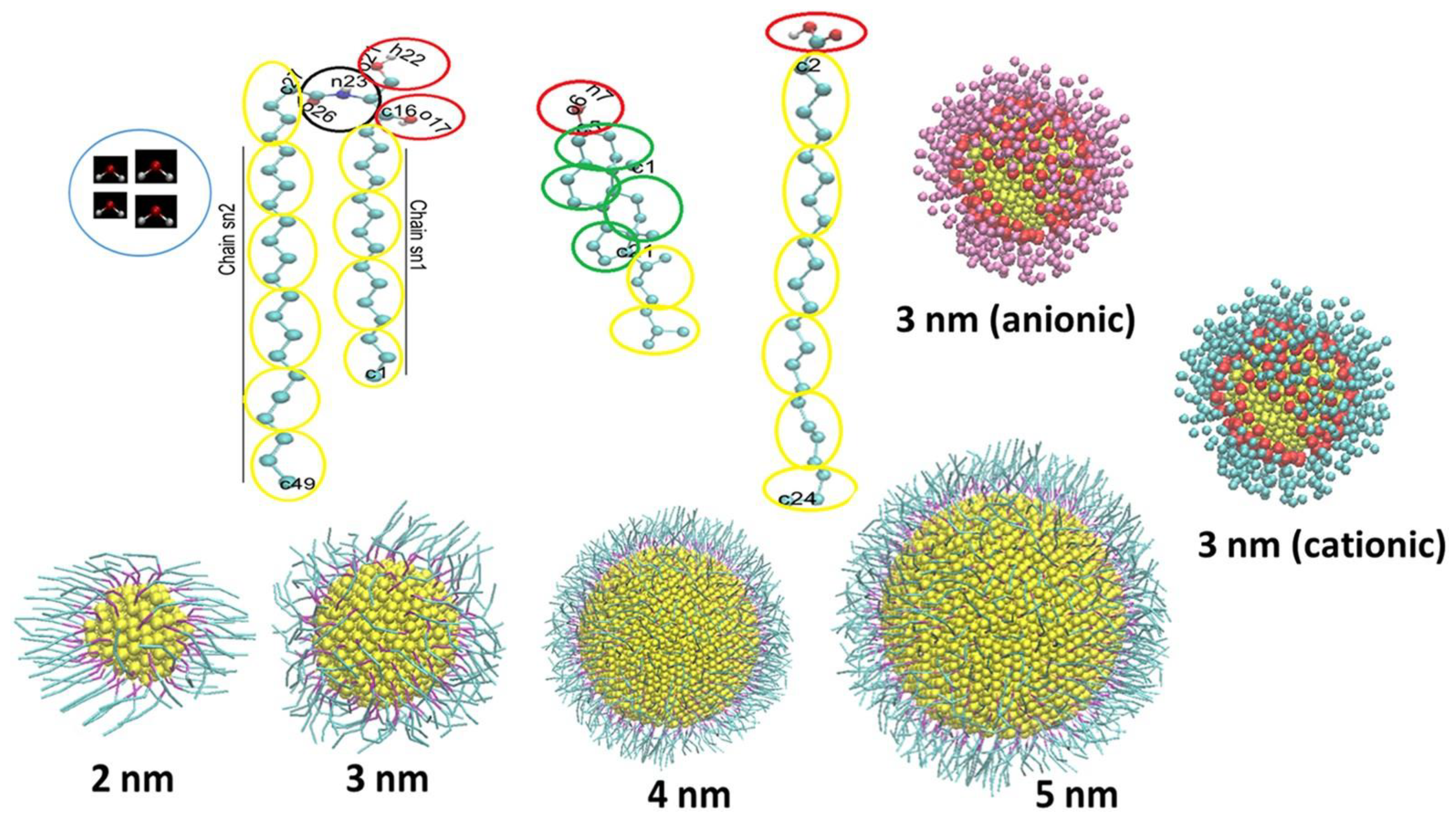
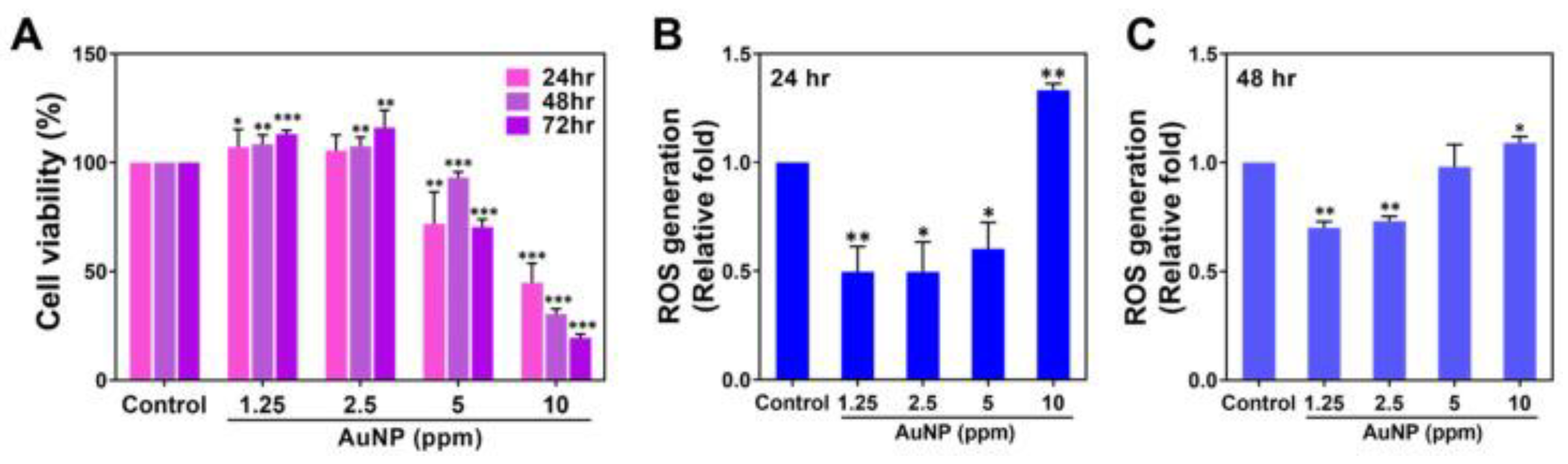
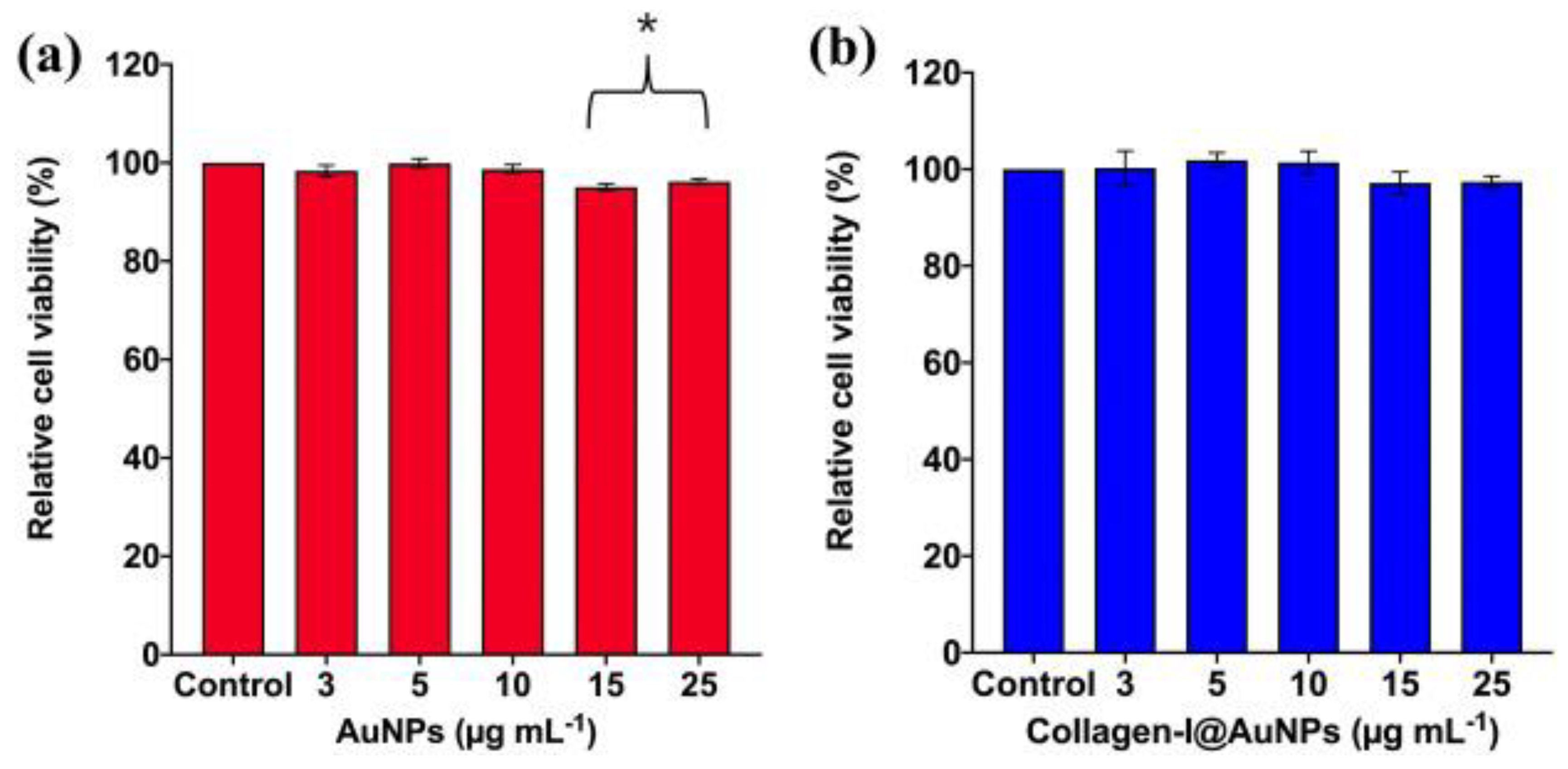
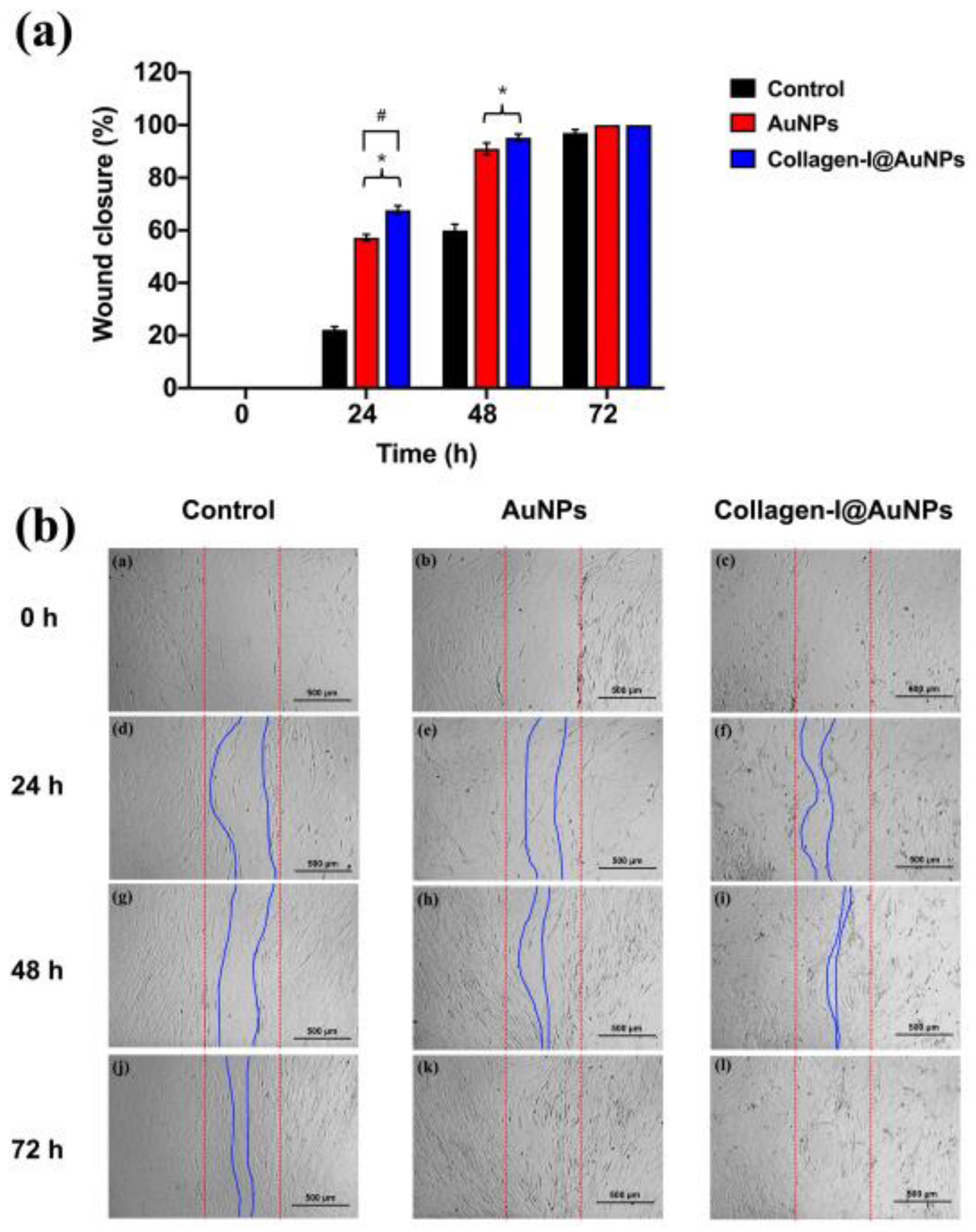
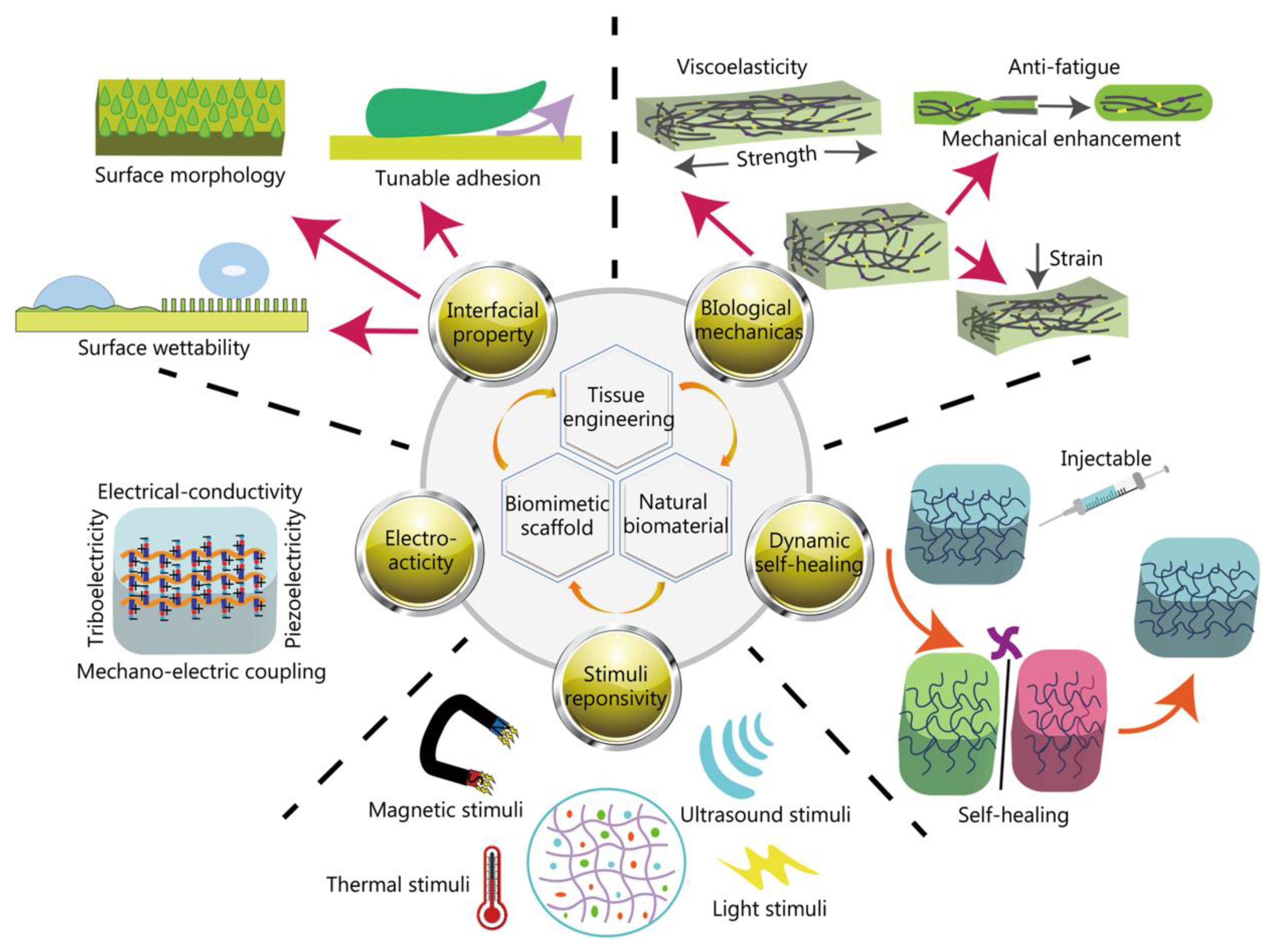
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



