Submitted:
18 September 2024
Posted:
19 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- How are GWS developed as a sustainable tool to mitigate urban flooding defined?
- Are GWS a viable alternative to combat pluvial flooding in Peru? Are they the best tool available?
- What are the design parameters and characteristics of a GWS with applicability to Peru?
- Is it feasible to develop a “Design Code” proposal for SuDS for an urban context in Peru?
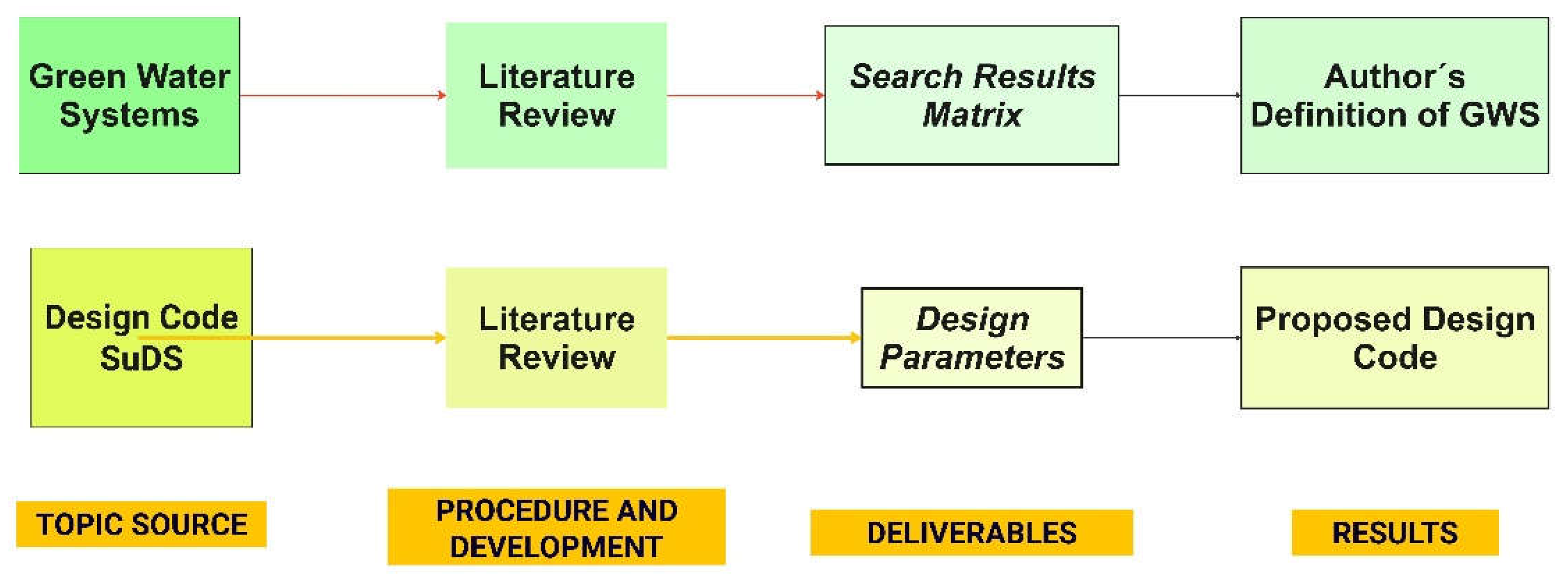
2. Materials and Methods
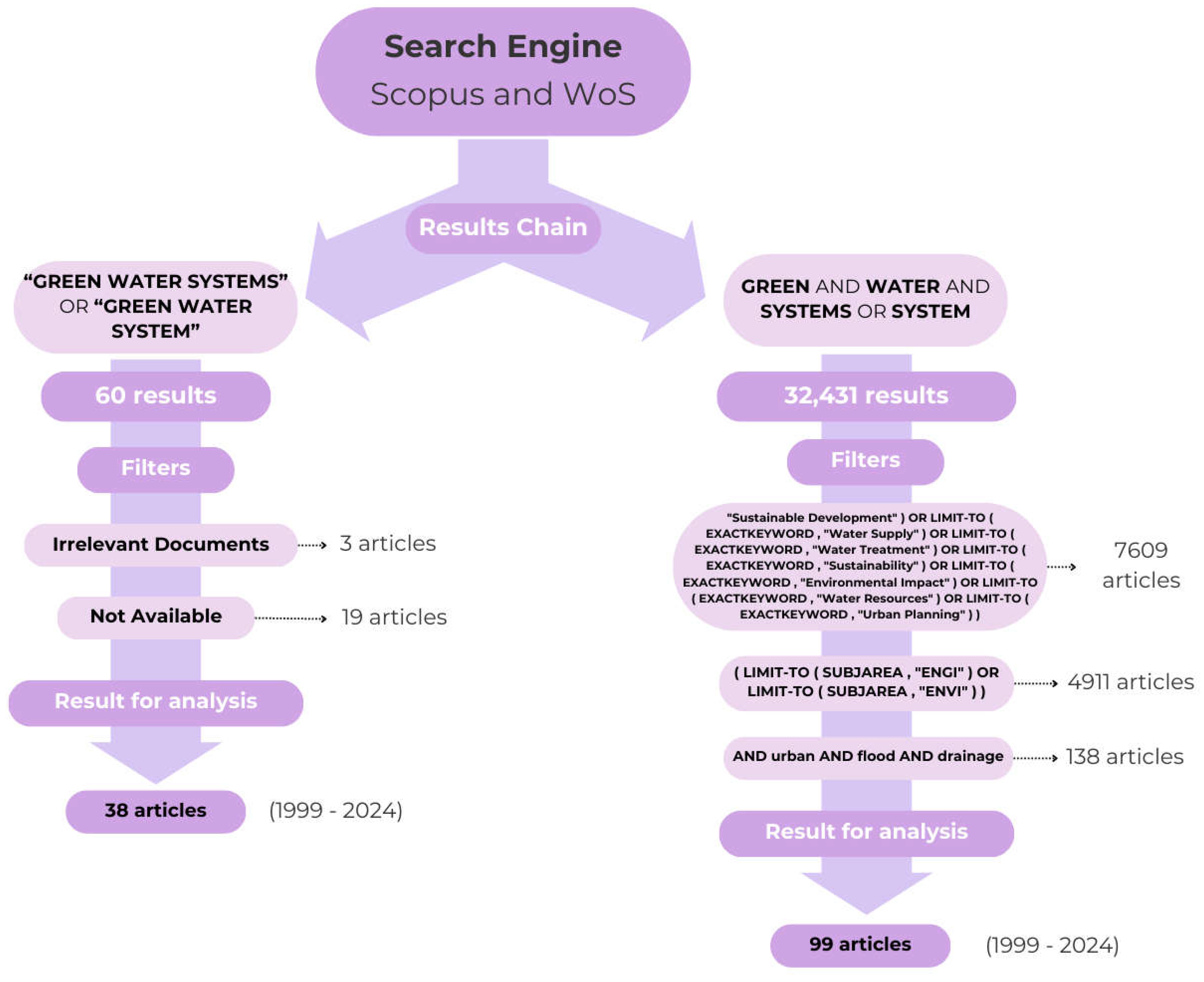
2.1. Literature Review: Green Water Systems
2.1.1. Literature Review
2.1.2. Design Codes SuDS
- United Kingdom: The SuDS Manual (C753) [25]
- Canada: Stormwater Management Planning and Design Manual [160]
- Colombia: EAAB – Norma Técnica de criterios para diseño y construcción de sistemas urbanos de drenaje sostenible (NS-166) [26]
- El Salvador: Guía Técnica para el diseño de SuDS [161]
- France: Guide de Gestion des eaux pluviales [162]
- Malaysia: Urban Stormwater Management Manual [163]
- Spain: Guía Básica para el Diseño de Sistemas Urbanos de Drenaje Sostenible [164]
3. Results
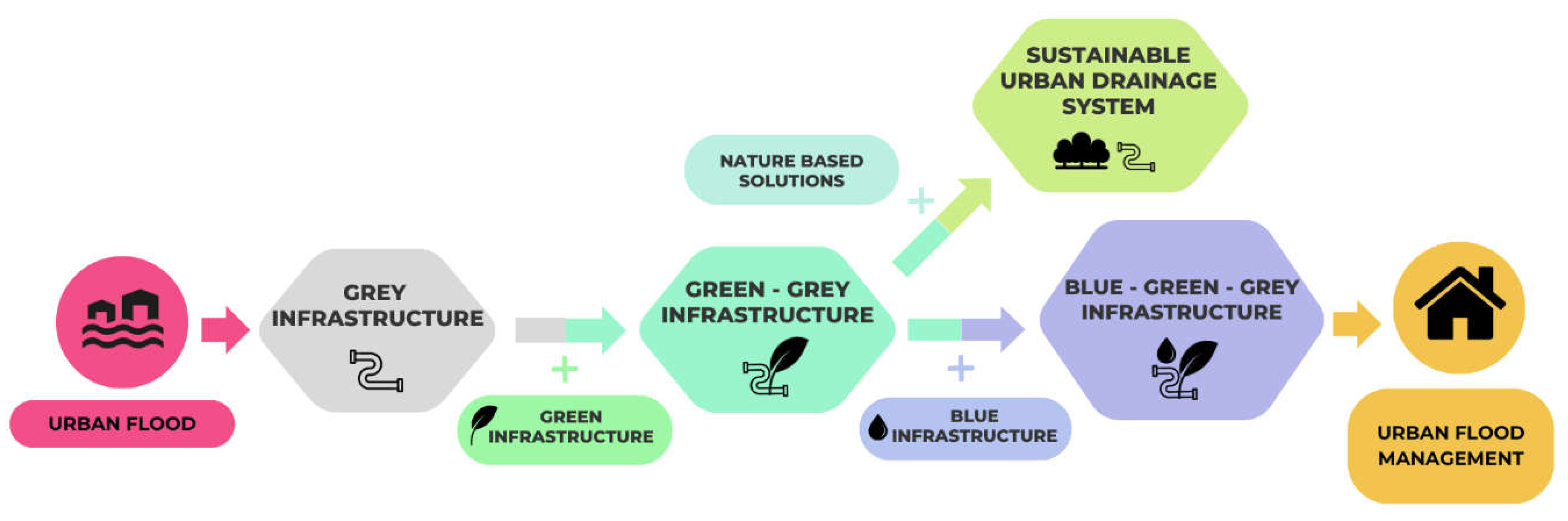
3.1. Proposed GWS Definition
3.2. International Review of SuDS Regulations
3.3. Aplication in Peruvian Context
4. Discussion
- How are GWS developed as a sustainable tool to mitigate urban flooding defined?
- Are GWS a viable alternative to combat pluvial flooding in Peru? Are they the best tool available?
- What are the design parameters and characteristics of a GWS type with applicability to Peru?
- Is it feasible to develop a “Design Code” proposal for SuDS in an urban context in Peru?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maiolo, M.; Palermo, S.A.; Brusco, A.C.; Pirouz, B.; Turco, M.; Vinci, A.; Spezzano, G.; Piro, P. On the Use of a Real-Time Control Approach for Urban Stormwater Management. Water 2020, 12, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oorschot, J.; Slootweg, M.; Remme, R.P.; Sprecher, B.; van der Voet, E. Optimizing green and gray infrastructure planning for sustainable urban development. npj Urban Sustain. 2024, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobini, S.; Becker, P.; Larsson, R.; Berndtsson, R. Systemic Inequity in Urban Flood Exposure and Damage Compensation. Water 2020, 12, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T.G.; Scheid, C. Evaluation and communication of pluvial flood risks in urban areas. WIREs Water 2020, 7, e1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, M.; Martina, M.L.V.; Creaco, E.; Figueiredo, R. Indirect impact assessment of pluvial flooding in urban areas using a graph-based approach: The Mexico city case study. Water (Switzerland) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rojas, M.I.; Garrido-Jiménez, F.J.; Abarca-Álvarez, F.J.; Vallecillos-Siles, M.R. Advances in the Integration of Sustainable Drainage Systems into Urban Planning: A Case Study. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delforge, D.; Wathelet, V.; Below, R.; Sofia, C.L.; Tonnelier, M.; Loenhout, J.v.; Speybroeck, N. EM-DAT: the Emergency Events Database. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
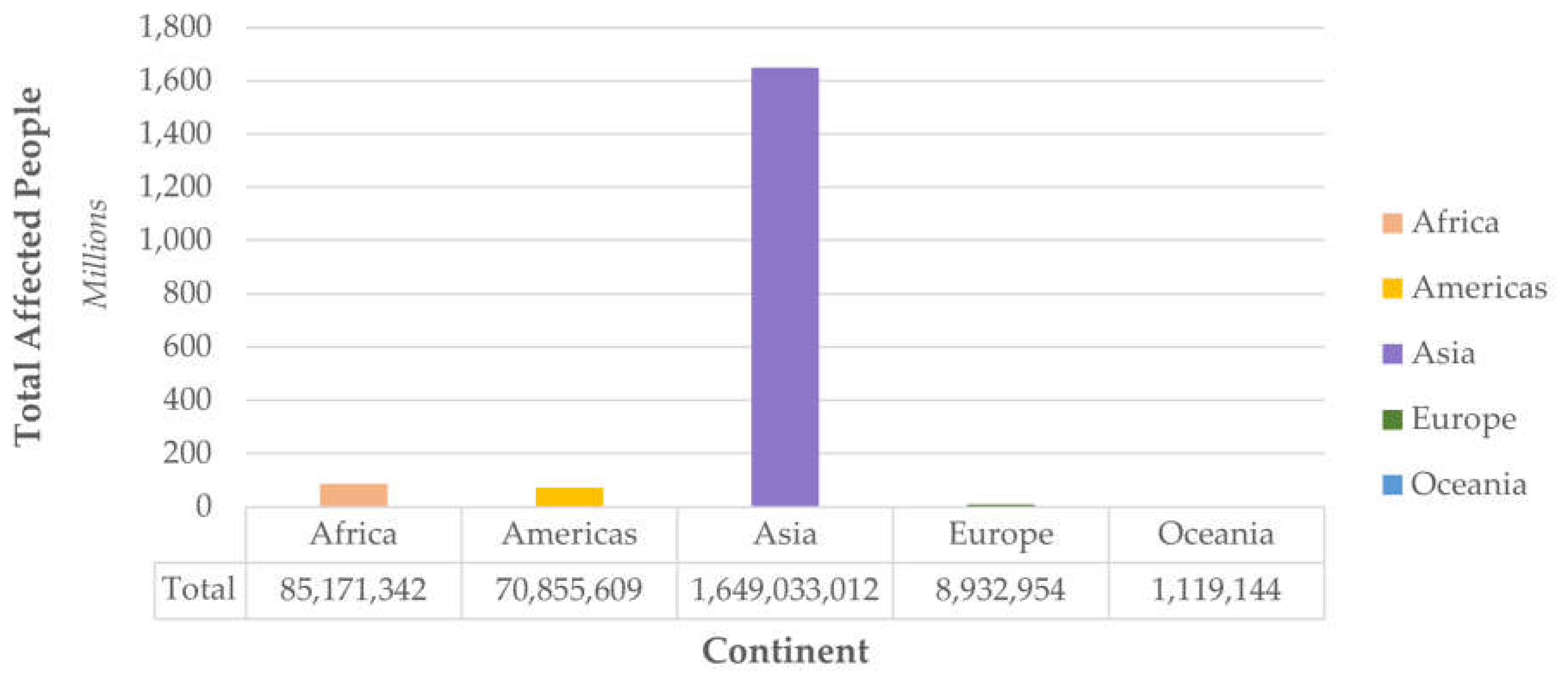
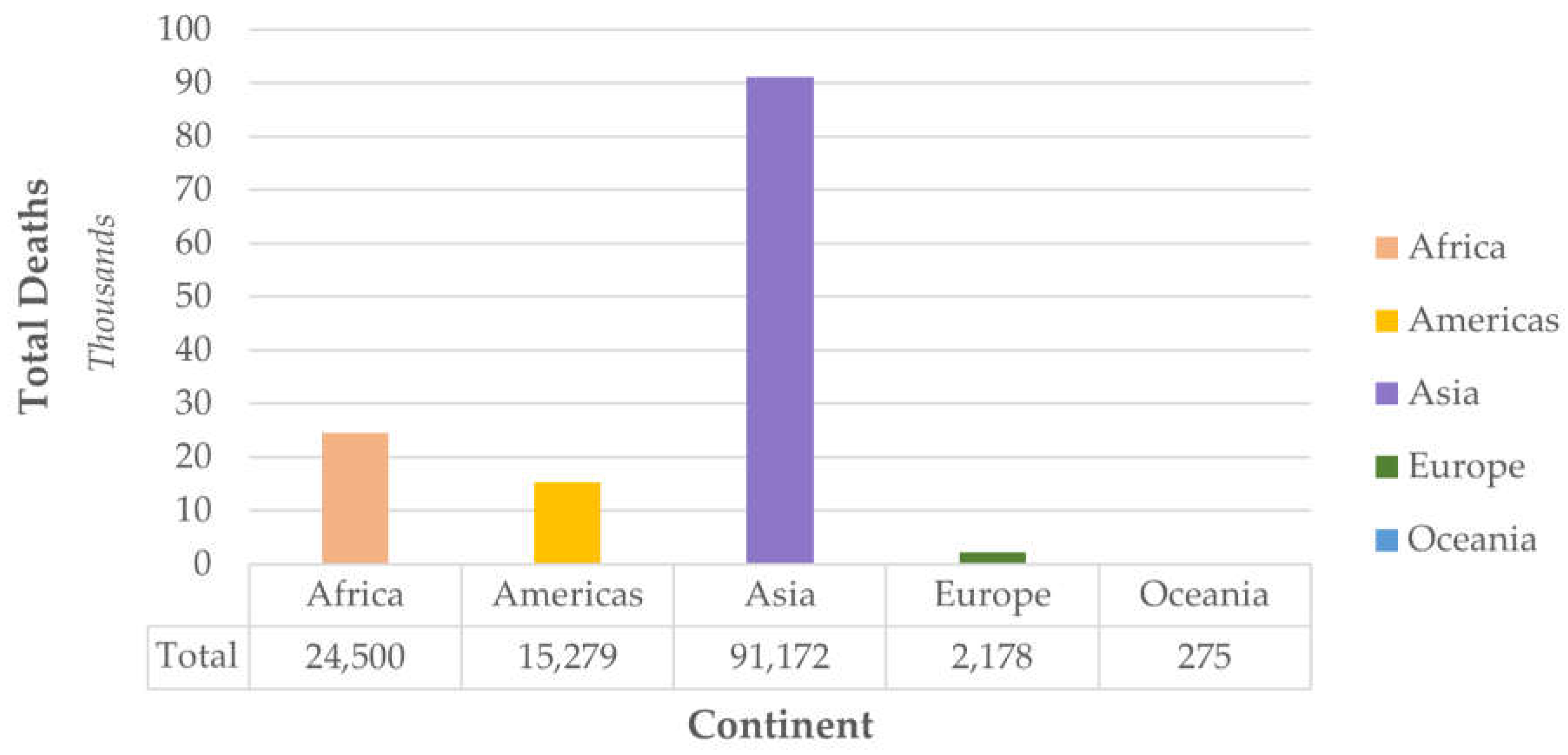
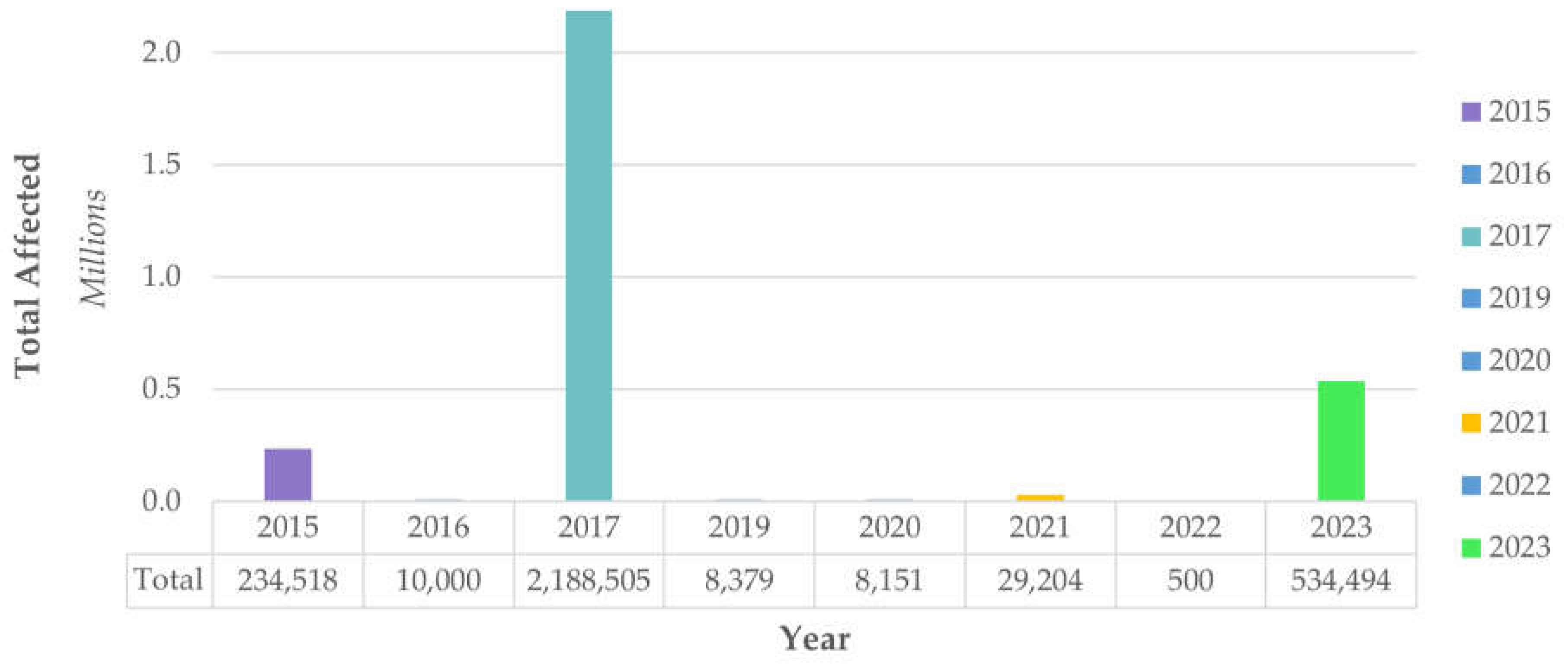
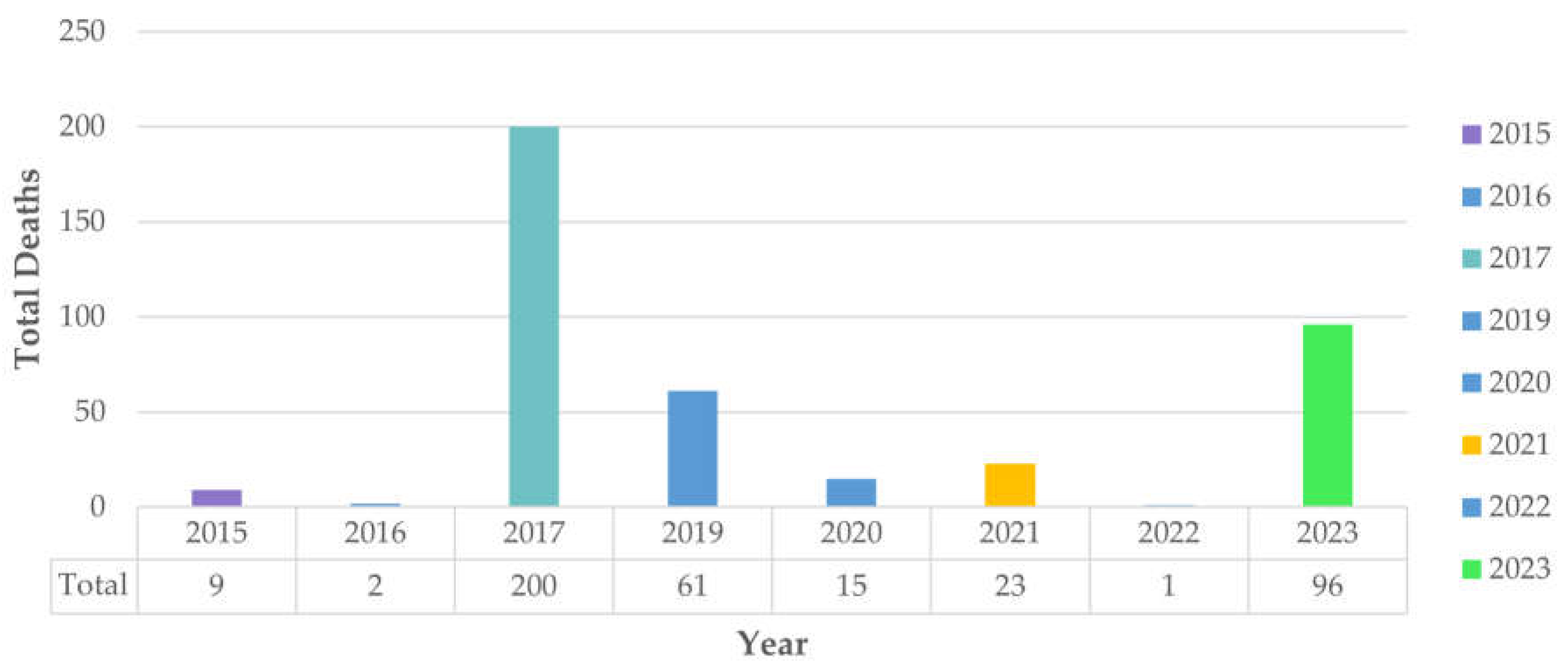
- Espinoza Vigil, A.J.; Booker, J.D. Building national disaster resilience: assessment of ENSO-driven disasters in Peru. International Journal of Disaster Resilience in the Built Environment 2023, 14, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielen, D.R.; Ramoni-Perazzi, P.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Puche, M.L.; Marquez, M.; Quintero, J.I.; Rojas, W.; Quintero, A.; Bianchi, G.; Soto-Werschitz, I.A.; et al. Effect of extreme El Niño events on the precipitation of Ecuador. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 23, 1507–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, W.; Vojinovic, Z.; Price, R.; Solomatine, D. Multiobjective Evolutionary Approach to Rehabilitation of Urban Drainage Systems. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management 2010, 136, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondera, K.; Brelot, E.; Fontanel, F.; Cherqui, F.; Ellerbæk Nielsen, J.; Brüggemann, T.; Naismith, I.; Goerke, M.; Suárez López, J.; Rieckermann, J.; et al. European stakeholders’ visions and needs for stormwater in future urban drainage systems. Urban Water J. 2023, 20, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Cerpa, G.; Russo, B.; Martínez-Puentes, M.; Bladé, E.; Sanz-Ramos, M. “SUDS-linear” to reduce flood risk considering Climate Change scenarios. Ingeniería del agua 2022, 26, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.; O’Donnell, E.; Johnson, M.; Slater, L.; Thorne, C.; Zheng, S.; Stirling, R.; Chan, F.; Li, L.; Boothroyd, R. Green infrastructure: The future of urban flood risk management? WIREs Water 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivtsov, V.; Ahilan, S.; Arthur, S.; Birkinshaw, S.; Dawson, D.; Everett, G.; Glenis, V.; Kapetas, L.; Kilsby, C.; Lamond, J.; et al. Blue-Green Cities: Achieving Urban Flood Resilience, Water Security, and Biodiversity. 2023; pp. 1–8.
- Alves, A.; Sanchez, A.; Vojinovic, Z.; Seyoum, S.; Babel, M.; Brdjanovic, D. Evolutionary and holistic assessment of green-grey infrastructure for CSO reduction. Water (Switzerland) 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Lv, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, N. Performance assessment for the integrated green-gray-blue infrastructure under extreme rainfall scenarios. Front. ecol. evol. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, M.È.; Morin, C.; Duchesne, S.; Pelletier, G.; Pleau, M. Optimization of Real-Time Control With Green and Gray Infrastructure Design for a Cost-Effective Mitigation of Combined Sewer Overflows. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Vojinovic, Z.; Kapelan, Z.; Sanchez, A.; Gersonius, B. Exploring trade-offs among the multiple benefits of green-blue-grey infrastructure for urban flood mitigation. Science of the Total Environment 2020, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega Sandoval, A.D.; Sörensen, J.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Bharati, L. Hydrologic-hydraulic assessment of SUDS control capacity using different modeling approaches: a case study in Bogotá, Colombia. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 3124–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liquete, C.; Udias, A.; Conte, G.; Grizzetti, B.; Masi, F. Integrated valuation of a nature-based solution for water pollution control. Highlighting hidden benefits. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 22, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, C.; Sakurai, M.; Latinos, V.; Majchrzak, T.A. Co-creating communication approaches for resilient cities in Europe: The case of the EU project smart mature resilience. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the International ISCRAM Conference, 2017; pp. 353–362.
- Rusman, A.; Diniatik; Pujiharto. Pelatihan Tatalaksana Pemijahan Ikan Gurami (Osphronemus gouramy) Menggunakan Green Water System (GWS). JURNAL INOVASI DAN PENGABDIAN MASYARAKAT INDONESIA 2023, 2, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardo, M.; Cozzi, A.; Cardani, R.; Renna, L.; Pomati, F.; Asmundo, L.; Di Leo, G.; Sardanelli, F. Reducing contrast agent residuals in hospital wastewater: the GREENWATER study protocol. European Radiology Experimental 2023, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abellán García, A.I.; Cruz Pérez, N.; Santamarta, J.C. Sustainable urban drainage systems in spain: Analysis of the research on SUDS based on climatology. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIRIA. The SuDS Manual (C753). 2015, 968.
- EEAB. NS-166 Criterio para diseño y construcción de sistemas urbanos de drenaje sostenible (SuDS). 2018.
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. A tale of two databases: the use of Web of Science and Scopus in academic papers. Scientometrics 2020, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Martín, A.; Orduna-Malea, E.; Thelwall, M.; Delgado López-Cózar, E. Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Scopus: A systematic comparison of citations in 252 subject categories. Journal of Informetrics 2018, 12, 1160–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadad, M.; Aguilar-Barajas, I.; Khan, A.Z. Green Infrastructure for Urban Flood Resilience: A Review of Recent Literature on Bibliometrics, Methodologies, and Typologies. Water 2023, 15, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, F.; Morshedi, V.; Mozanzadeh, M.T.; Hamedi, S.; Bahabadi, M.N.; Jafari, F.; Azodi, M.; Agh, N. Enrichment of live foods with arachidonic acid enhanced stress resistance, digestive enzyme activity, and total antioxidant capacity in yellowfin seabream (Acanthopagrus latus) larvae. Aquaculture International 2024, 32, 3747–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshedi, V.; Hamedi, S.; Pourkhazaei, F.; Torfi Mozanzadeh, M.; Tamadoni, R.; Ebadi, M.; Esmaili, A.; Azodi, M.; Gisbert, E. Larval rearing and ontogeny of digestive enzyme activities in yellowfin seabream (Acanthopagrus latus, Houttuyn 1782). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2021, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuraj, A.; Suresh Babu, P.P.; Loka, J.; Ignatius, B.; Santhosh, B.; Ramudu, K.R.; Sonali, S.M.; Srinivas Rao, K.; Dube, P.; Kumbhar, N.; et al. Induced breeding and larval rearing of vermiculated spinefoot, Siganus vermiculatus (Valenciennes, 1835) in indoor conditions. Aquaculture 2021, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Kailasam, M.; Rekha, M.U.; Jani Angel, R.; Sukumaran, K.; Sivaramakrishnan, T.; Raja Babu, D.; Subburaj, R.; Thiagarajan, G.; Vijayan, K.K. Captive maturation, breeding and seed production of the brackishwater ornamental fish silver moony, Monodactylus argenteus (Linnaeus, 1758). Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4713–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil, M.K.; Gomathi, P.; Sugi, V.V.; Raheem, P.K.; Raju, B.; Gop, A.P.; Santhosh, B.; Philipose, K.K.; Gopakumar, G.; Gopalakrishnan, A. Captive maturation, breeding and seed production of Pink ear emperor, Lethrinus lentjan (Lacepede, 1802) (Family: Lethrinidae) in recirculating aquaculture system (RAS). Aquaculture 2019, 503, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Megarajan, S.; Xavier, B.; Ghosh, S.; Santhosh, B.; Gopalakrishnan, A. Broodstock development, induced breeding and larval rearing of Indian pompano, Trachinotus mookalee, (Cuvier, 1832) – A new candidate species for aquaculture. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandroulakis, N.; Divanach, P.; Anastasiadis, P.; Kentouri, M. The pseudo-green water technique for intensive rearing of sea bream (Sparus aurata) larvae. Aquaculture International 2001, 9, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Pena, M.R. Use of juvenile instar diaphanosoma celebensis (stingelin) in hatchery rearing of Asian sea bass lates calcarifer (bloch). Isr. J. Aquacult. Bamidgeh 2001, 53, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavioli, I.L.; de Ortiz, D.O.; Bersano, J.G.F.; Vidal, E.A.G. Connecting polarized light and water turbidity with feeding rates in Octopus americanus paralarvae. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2022, 53, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Q.M.; Fotedar, R.; Ho, T.T.T. Impact of different rearing systems on survival, growth and quality of mud crab (Scylla paramamosain) megalopae reared from early zoeae. Aquaculture International 2019, 27, 1673–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, N.K.; Khoa, T.N.D.; Zainathan, S.C.; Musa, N.; Musa, N.; Shaharom-Harrison, F. Development of mud crab crablet, the identification of ciliates and the bioefficacy of leaf extract of Rhizophora apiculata as anti-protozoal agent. J. Sustainability Sci. Manage. 2017, 12, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, K.; Chakraborty, R.D.; Radhakrishnan, E.V.; Vijayan, K.K. Fatty acid profiles of spiny lobster (Panulirus homarus) phyllosoma fed enriched Artemia. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, e393–e403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.T.; Hai, T.N.; Hien, T.T.T.; Bui, T.V.; Huong, D.T.T.; Son, V.N.; Morooka, Y.; Fukuda, Y.; Wilder, M.N. Current status of freshwater prawn culture in Vietnam and the development and transfer of seed production technology. Fish. Sci. 2006, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roustaian, P.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Omar, H.; Saad, C.R.; Ahmad, M.H. Changes in fatty acid profile during larval development of freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man). Aquac. Res. 1999, 30, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.; Dahl, S.; Teichert-Coddington, D.; Kelly, A.M.; Creel, J.D.; Beck, B.H.; Butts, I.A.E.; Roy, L.A. Cohabitation of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) and Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) cultured in low salinity water. Aquacult. Rep. 2024, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.; Weldon, A.; Ito, P.; Stites, W.; Rhodes, M.; Davis, D.A. Automated feeding systems for shrimp: Effects of feeding schedules and passive feedback feeding systems. Aquaculture 2021, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotto, M.R.; Argenta, N.; Forte, J.M.; Hostins, B.; Menezes, F.G.R.; Maggioni, R.; de Sousa, O.V.; Wasielesky, W.; Rosa, R.D.; Perazzolo, L.M. Environmental rearing conditions are key determinants of changes in immune gene expression patterns in shrimp midgut. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Huang, Y.; Salze, G.; Roy, L.A.; Davis, D.A. Use of plant-based protein concentrates as replacement for fishmeal in practical diets for the Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) reared under high stocking density and low salinity conditions. Aquacult. Nutr. 2020, 26, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, J.M.; Nogueira, L.F.F.; dos Santos Rocha, R.; Maggioni, R.; de Sousa, O.V. Multienzymatic capacity of cultivable intestinal bacteria from captive Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) shrimp reared in green water. Aquaculture International 2019, 27, 1813–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Façanha, F.N.; Oliveira-Neto, A.R.; Figueiredo-Silva, C.; Nunes, A.J.P. Effect of shrimp stocking density and graded levels of dietary methionine over the growth performance of Litopenaeus vannamei reared in a green-water system. Aquaculture 2016, 463, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, D.R.; Fox, J.M.; Gatlin, D.; Lawrence, A.L. Dietary effect of fish oil and soybean lecithin on growth and survival of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei in the presence or absence of phytoplankton in an indoor system. Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 1367–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glencross, B.; Irvin, S.; Arnold, S.; Blyth, D.; Bourne, N.; Preston, N. Effective use of microbial biomass products to facilitate the complete replacement of fishery resources in diets for the black tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture 2014, 431, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, D.R.; Fox, J.M.; Gatlin, D.; Lawrence, A.L. Dietary effect of squid and fish meals on growth and survival of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in the presence or absence of phytoplankton in an indoor tank system. Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil, M.K.; Santhosh, B.; Prasad, B.O.; Rani, M.G. Broodstock development and breeding of black-finned anemone fish Amphiprion nigripes regan, 1908 under captive conditions. Indian J. Fish. 2012, 59, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, S.; Madhusoodana Kurup, B. Standardisation of stocking density in the larviculture of Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man 1879) using modified static green water system. Indian J. Fish. 2011, 58, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ruangrit, K.; Whangchai, N.; Pekkoh, J.; Ruangyuttikarn, W.; Peerapornpisal, Y. First report on microcystins contamination in giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) and Nile tilapia (Tilapia nilotica) cultured in earthen ponds. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2011, 13, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnani, K.K.; Kathiravan, V.; Natarajan, M.; Kailasam, M.; Pillai, S.M. Diversity of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in greenwater system of coastal aquaculture. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, P.S.; Andalecio, M.N.; Bolivar, R.B.; Fitzsimmons, K. Tilapia-shrimp polyculture in Negros Island, Philippines: A review. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2008, 39, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.; Forster, I.; Divakaran, S.; Conquest, L.; Decamp, O.; Tacon, A. Effect of green and clear water and lipid source on survival, growth and biochemical composition of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacult. Nutr. 2006, 12, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, R.; Mélo, R.C.S.; de Moraes, R.M.; da Silva, R.C.S.; Cavalli, R.O.; do Amaral Ferraz Navarro, D.M.; de Souza Santos, L.P. Production and use of a flocculated paste of Nannochloropsis oculata for rearing newborn seahorse Hippocampus reidi. Algal Res. 2016, 17, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.M.; ElBanna, N.I.; Fathi, M. Chlorella in aquaculture: challenges, opportunities, and disease prevention for sustainable development. Aquaculture International 2024, 32, 1559–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.; Pelalak, R.; Pishnamazi, M.; Marjani, A.; Albadarin, A.B.; Sarkar, S.M.; Shirazian, S. A novel and facile green synthesis method to prepare LDH/MOF nanocomposite for removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keys, P.W.; Falkenmark, M. Green water and African sustainability. Food Secur. 2018, 10, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, W.J.; Pruden, A.; Edwards, M.A. Survey of green building water systems reveals elevated water age and water quality concerns. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazeau, R.H.; Edwards, M.A. Water and energy savings from on-demand and hot water recirculating systems. J. Green Build. 2013, 8, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaręba, A.; Krzemińska, A.; Adynkiewicz-Piragas, M.; Widawski, K.; van der Horst, D.; Grijalva, F.; Monreal, R. Water Oriented City—A ‘5 Scales’ System of Blue and Green Infrastructure in Sponge Cities Supporting the Retention of the Urban Fabric. Water (Switzerland) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, D.; Du, G.; Yuan, S.; Yu, C.; Zhao, M.; Fang, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H. Planning of Water-Saving Green Space System Based on GIS Technology and Archydrodata Model. Water Resour. 2022, 49, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Tang, J.; Liu, M. Sponge city planning of Dalian based on functional division of natural ecological environment. Ekoloji 2019, 28, 3557–3567. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, P.; Peng, K. Green-energy, water-autonomous greenhouse system: An alternative-technology approach towards sustainable smart-green vertical greening in smart cities. Int. Rev. Spatial Plan. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 5, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadat Foomani, M.; Malekmohammadi, B. Site selection of sustainable urban drainage systems using fuzzy logic and multi-criteria decision-making. Water and Environment Journal 2020, 34, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, S.; Tamaddun, K.A.; Stephen, H.; Ahmad, S. Urban runoff and pollutant reduction by retrofitting green infrastructure in storm water management system. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2019: Water, Wastewater, and Stormwater; Urban Water Resources; and Municipal Water Infrastructure - Selected Papers from the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2019, 2019. 93–104.
- Webber, J.L.; Fu, G.; Butler, D. Rapid surface water intervention performance comparison for urban planning. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 2084–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justin, M.G.; Bergen, J.M.; Emmanuel, M.S.; Roderick, K.G. Mapping the gap of water and erosion control measures in the rapidly urbanizing Mbezi River catchment of Dar es Salaam. Water (Switzerland) 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombes, P.J. Status of transforming stormwater drainage to a systems approach to urban water cycle management–moving beyond green pilots. Aust. J. Water Resour. 2018, 22, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gersberg, R.M.; Ng, W.J.; Tan, S.K. Conventional and decentralized urban stormwater management: A comparison through case studies of Singapore and Berlin, Germany. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, A. Transition Towards Green Water Economies: Surrounding Issues and Needed Capacity Development. Global Environment 2014, 7, 352–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.X.; Shen, S.B.; Hu, X.B.; Tan, S.M.; Wu, H. Effect of baffled water-holding garden system on disposal of rainwater for green building residential districts. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 2717–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Cardin, M.A.; Babovic, V.; Santhanakrishnan, D.; Schmitter, P.; Meshgi, A. Valuing flexibilities in the design of urban water management systems. Water Research 2013, 47, 7162–7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, H.X.; Wei, Y.H.; Xu, H.Y.; He, Q. Water conservation: Construction and operation of management and technology systems for green campus. Environ. Eng. Manage. J. 2011, 10, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.H.; Nile, B.K.; Kadhim, Z.K. Effect of climate change on the flooding of storm water networks under extreme rainfall events using SWMM simulations: a case study. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 10, 4129–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Burian, S.J. Evaluating real-time control of stormwater drainage network and green stormwater infrastructure for enhancing flooding resilience under future rainfall projections. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, F.S.; da Silva, G.J.A.; da Silveira, J.A.R.; Barros Filho, M.N.M. Hydrological simulation of bioretention: analysis of the efficiency of compensatory techniques to mitigate impacts of urbanization. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2022, 27, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.P.; Li, Z.X.; Fu, G. The effects of low impact development on urban flooding under different rainfall characteristics. Journal of Environmental Management 2013, 129, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, S.; Yoshida, K.; Yabe, K. Perceptions of urban stream corridors within the greenway system of Sapporo, Japan. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2004, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, P.; Ursino, N. On the Reason to Implement a Sustainable Urban Drainage Nature-Based Solution to Decrease Flood Threat: A Survey. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlmutter, D.; Pucher, B.; Calheiros, C.S.C.; Hoffmann, K.A.; Aicher, A.; Pinho, P.; Stracqualursi, A.; Korolova, A.; Pobric, A.; Galvão, A.; et al. Closing water cycles in the built environment through nature-based solutions: The contribution of vertical greening systems and green roofs. Water (Switzerland) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugume, S.N.; Kibibi, H.; Sorensen, J.; Butler, D. Can Blue-Green Infrastructure enhance resilience in urban drainage systems during failure conditions? Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 89, 915–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, G. Evaluating the response and adaptation of urban stormwater systems to changed rainfall with the CMIP6 projections. Journal of Environmental Management 2023, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ambrosio, R.; Longobardi, A. Adapting drainage networks to the urban development: An assessment of different integrated approach alternatives for a sustainable flood risk mitigation in Northern Italy. Sustainable Cities and Society 2023, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Lancia, M.; Tian, Y.; Viaroli, S.; Andrews, C.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C. The Role of Aquifers in Sustaining the Sponge City Concept in Chinese High-Density Housing. Water (Switzerland) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Song, K.; Chon, J. Key coastal landscape patterns for reducing flood vulnerability. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClymont, K.; Fernandes Cunha, D.G.; Maidment, C.; Ashagre, B.; Vasconcelos, A.F.; Batalini de Macedo, M.; Nóbrega dos Santos, M.F.; Gomes Júnior, M.N.; Mendiondo, E.M.; Barbassa, A.P.; et al. Towards urban resilience through Sustainable Drainage Systems: A multi-objective optimisation problem. Journal of Environmental Management 2020, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casal-Campos, A.; Sadr, S.M.K.; Fu, G.; Butler, D. Reliable, Resilient and Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems: An Analysis of Robustness under Deep Uncertainty. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9008–9021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende-Prieto, C.; Méndez-Fernández, B.I.; Sañudo-Fontaneda, L.A.; Charlesworth, S.M. Development of a geospatial data-based methodology for stormwater management in urban areas using freely-available software. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldrum, A.; Mickovski, S.B. Development of an independent hydrology audit methodology to support flood risk assessment in the planning process in Scotland. Water and Environment Journal 2017, 31, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Guo, H.; Zeng, S. Enhancing future resilience in urban drainage system: Green versus grey infrastructure. Water Research 2017, 124, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.L.; Peng, J.J.; Ho, M.C.; Liao, W.J.; Chern, S.J. Evaluation of water efficiency in green building in Taiwan. Water (Switzerland) 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, J.; Berthier, E.; Gromaire, M.C. Stormwater Management Criteria for On-Site Pollution Control: A Comparative Assessment of International Practices. Environ. Manage. 2015, 56, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vleeschauwer, K.; Weustenraad, J.; Nolf, C.; Wolfs, V.; De Meulder, B.; Shannon, K.; Willems, P. Green-blue water in the city: Quantification of impact of source control versus end-of-pipe solutions on sewer and river floods. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 1825–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Panduro, T.E.; Thorsen, B.J.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K. Adaption to extreme rainfall with open urban drainage system: An integrated hydrological cost-benefit analysis. Environ. Manage. 2013, 51, 586–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, G.; Xue, K.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, C. Evaluation of rainwater runoff storage by urban green spaces in Beijing. Shengtai Xuebao Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 3839–3845. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Deng, J.; She, L. Research on Sustainable Evaluation Model of Sponge City Based on Emergy Analysis. Water (Switzerland) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Ciais, P.; Wada, Y. Global Water Scarcity Assessment Incorporating Green Water in Crop Production. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Paschalis, A.; Mijic, A. Planning London’s green spaces in an integrated water management approach to enhance future resilience in urban stormwater control. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, K.; Zhuo, L.; Yang, X.; Yue, Z.; Zhao, D.; Wu, P. Emergy analysis of the blue and green water resources in crop production systems. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatikopoulou, I.; Sylla, M.; Zoumides, C. Economic evaluation of green water in cereal crop production: A production function approach. Water Resour. Econ. 2020, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, G.X.; Oh, K.S.; Yoon, L.W.; Tee, L.H. Lake Water Treatment Using Green Wall System: Effects of Filter Media Ratio and Lake Water Flow Rate on Treatment Performance. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2020, 5, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, E.; Agajo, J.; Osanaiye, O.A.; Oyinbo, A.M. Design of a green iot based water monitoring system for metropolitan city. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Conference on Electronics, Computer and Computation, 2019. ICECCO 2019.
- Tang, Y.T.; Chan, F.K.S.; O’Donnell, E.C.; Griffiths, J.; Lau, L.; Higgitt, D.L.; Thorne, C.R. Aligning ancient and modern approaches to sustainable urban water management in China: Ningbo as a “Blue-Green City” in the “Sponge City” campaign. Journal of Flood Risk Management 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Bae, K.H.; Younos, T. Conceptual framework for decentralized green water-infrastructure systems. Water and Environment Journal 2018, 32, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anom, G.; Sudarno, S. Analysis of Implementation Green Infrastructure of Bregas Regional Water Supply System. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Veettil, A.V.; Mishra, A.K. Water security assessment using blue and green water footprint concepts. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantzis, A.; Thatcher, A.; Sheridan, C. Mental models of a water management system in a green building. Appl. Ergon. 2016, 57, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, C.; Tian, Y.; He, L. Ecological effect of water cyclic utilization in green architecture. In Proceedings of the Advanced Materials Research; 2013; pp. 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Liut, D.A.; Weems, K.M.; Yen, T.G. A quasi-three-dimensional finite-volume shallow water model for green water on deck. J Ship Res 2013, 57, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Ou, D.; Zhang, J.; Fang, S. The construction and application of green residential community water-saving evaluation system. In Proceedings of the Applied Mechanics and Materials; 2011; pp. 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- Aldaya, M.M.; Allan, J.A.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Strategic importance of green water in international crop trade. Ecological Economics 2010, 69, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatibu, N.; Rockström, J. Green-blue water system innovations for upgrading of smallholder farming systems - A policy framework for development. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chun, K.P.; Mijic, A. A meta-model for understanding ‘green-red loop’ social-water interactions at a global scale. Journal of Cleaner Production 2024, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Sudarsan, J.S.; Nithiyanantham, S. Nature-Based Disaster Risk Reduction of Floods in Urban Areas. Water Resour. Manage. 2024, 38, 1847–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, R. Optimization of the integrated green–gray–blue system to deal with urban flood under multi-objective decision-making. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 89, 434–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y. New green development indicator of water resources system based on an improved water resources ecological footprint and its application. Ecological Indicators 2023, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Sun, Y. Scenario-based hydrodynamic simulation of adaptive strategies for urban design to improve flood resilience: A case study of the Mingzhu Bay Region, Guangzhou, Greater Bay Area. River Res. Appl. 2023, 39, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares, P.S.; DePippo, K.; Schofield, R.; Sewell, N. Combining small-scale sustainable drainage systems with real-time control systems. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Civ. Eng. 2023, 177, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Mei, C.; Wang, H.; Lu, J. A multi-objective optimization model for synergistic effect analysis of integrated green-gray-blue drainage system in urban inundation control. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjali, D.; Anjali, S. Mitigation of Urban Flooding using Blue-Green Infrastructure: A Case of Dehradun City, India. Disaster Adv. 2022, 15, 50–61. [Google Scholar]
- Green, D.; O’Donnell, E.; Johnson, M.; Slater, L.; Thorne, C.; Zheng, S.; Stirling, R.; Chan, F.K.S.; Li, L.; Boothroyd, R.J. Green infrastructure: The future of urban flood risk management? WIREs Water 2021, 8, e1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, E.; Thorne, C.; Ahilan, S.; Arthur, S.; Birkinshaw, S.; Butler, D.; Dawson, D.; Everett, G.; Fenner, R.; Glenis, V.; et al. The blue-green path to urban flood resilience. Blue-Green Systems 2020, 2, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Tang, T.; Jia, H.; Xu, M.; Xu, T.; Liu, Z.; Long, Y.; Zhang, R. Benefits of coupled green and grey infrastructure systems: Evidence based on analytic hierarchy process and life cycle costing. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 151, 104478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, M.; Gehrmann, S.; Schramm, E.; Zimmermann, M.; Rudolph-Cleff, A. Chapter 21 - Greening and Cooling the City Using Novel Urban Water Systems: A European Perspective. In Approaches to Water Sensitive Urban Design, Sharma, A.K., Gardner, T., Begbie, D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: 2019; pp. 431–454.
- Haghighatafshar, S.; Yamanee-Nolin, M.; Klinting, A.; Roldin, M.; Gustafsson, L.G.; Aspegren, H.; Jönsson, K. Hydroeconomic optimization of mesoscale blue-green stormwater systems at the city level. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, R.; O’Donnell, E.; Ahilan, S.; Dawson, D.; Kapetas, L.; Krivtsov, V.; Ncube, S.; Vercruysse, K. Achieving urban flood resilience in an uncertain future. Water (Switzerland) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zischg, J.; Zeisl, P.; Winkler, D.; Rauch, W.; Sitzenfrei, R. On the sensitivity of geospatial low impact development locations to the centralized sewer network. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, J.; Chang, N.B.; Harji, R.; Ruppert, T.; Imen, S. Developing a multi-scale modeling system for resilience assessment of green-grey drainage infrastructures under climate change and sea level rise impact. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 90, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aivazidou, E.; Tsolakis, N.; Vlachos, D.P.; Iakovou, E. Water Footprint Mitigation Strategies for Agrifood Products: The Application of System Dynamics in Green Marketing. In Proceedings of the Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics; 2017; pp. 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Mottaghi, M.; Aspegren, H.; Jönsson, K. Integrated urban design and open storm drainage in our urban environments: Merging drainage techniques into our city’s urban spaces. Water Pract. Technol. 2016, 11, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, H.; Falkenmark, M.; Gerten, D.; Gordon, L.; Karlberg, L.; Rockström, J. Greening the global water system. J. Hydrol. 2010, 384, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.L. Evaluating water conservation measures for Green Building in Taiwan. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, P.; Illyes, E.; McCauley, S.; Jackson, D.A.; Michalakos, D.; Ferzoco, I.M.C.; Timms, L.; Murray, R.L.; MacFarlane, Z.S.; Duval, T.P.; et al. Ecosystem functions and services in urban stormwater ponds: Co-producing knowledge for better management. Ecol. Solut. Evid. 2024, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Tian, Z.; Sun, L.; Wen, J.; Liang, Z.; Dong, G.; Liu, J. Synthesized trade-off analysis of flood control solutions under future deep uncertainty: An application to the central business district of Shanghai. Water Research 2019, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lhamidi, K.; El Khattabi, J.; Nguyen, H.D.; Aljer, A. Hydrological Performance Assessment of Low-Impact Development Practices: A Vegetated Swale Case Study. Water (Switzerland) 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedashraf, O.; Bottacin-Busolin, A.; Harou, J.J. A design framework for considering spatial equity in sustainable urban drainage infrastructure. Sustainable Cities and Society 2022, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, J.P.R.; Okumura, C.K.; Guimarães, L.F.; Arruda, R.N.; Becker, B.R.; de Oliveira, A.K.B.; Veról, A.P.; Miguez, M.G. Cost-benefit analysis of sustainable drainage systems considering ecosystems services benefits: case study of canal do mangue watershed in Rio de Janeiro city, Brazil. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2022, 24, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, J. Assessing the performance of gray and green strategies for sustainable urban drainage system development: A multi-criteria decision-making analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirouz, B.; Palermo, S.A.; Turco, M. Improving the efficiency of green roofs using atmospheric water harvesting systems (An innovative design). Water (Switzerland) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertan, S.; Çelik, R.N. The assessment of urbanization effect and sustainable drainage solutions on flood hazard by gis. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2021, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, N.A.L.; Bell, R.A.; Butcher, A.S.; Bricker, S.H. Infiltration efficiency and subsurface water processes of a sustainable drainage system and consequences to flood management. Journal of Flood Risk Management 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Melià, D.; López-Aburto, C.S.; Ballesteros-Pérez, P.; Muñoz-Velasco, P. Viability of green roofs as a flood mitigation element in the central region of Chile. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, R.; Pecnik, G.; Girvan, M.; De La Rosa, T. Delivering integrated water management benefits: The North West Bicester development, UK. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manage. 2018, 171, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, V.; La Rosa, D.; Campisano, A.; La Greca, P. The potential of green infrastructure application in urban runoff control for land use planning: A preliminary evaluation from a southern Italy case study. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loc, H.H.; Duyen, P.M.; Ballatore, T.J.; Lan, N.H.M.; Das Gupta, A. Applicability of sustainable urban drainage systems: an evaluation by multi-criteria analysis. Enviro. Sys. Decis. 2017, 37, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, C.; Cameira, M.D.R.; Valente, F.; Cruz de Carvalho, R.; Paço, T.A. Wet season hydrological performance of green roofs using native species under Mediterranean climate. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitter, P.; Goedbloed, A.; Galelli, S.; Babovic, V. Effect of catchment-scale green roof deployment on stormwater generation and reuse in a tropical city. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management 2016, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graceson, A.; Hare, M.; Monaghan, J.; Hall, N. The water retention capabilities of growing media for green roofs. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.B. Sustainable surface water management and green infrastructure in UK urban catchment planning. J. Environ. Plann. Manage. 2013, 56, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosatto, H.G.; Laureda, D.; Perez, D.; Barrera, D.; Meyer, M.; Gamboa, P.; Villalba, G.; Friedrich, M.; Bargiela, M.; Rodríguez Plaza, L.; et al. Water retention efficiency of green roof systems. 2010, 42, 213–219.
- Schroeder, D.W.; Tsegaye, S.; Singleton, T.L.; Albrecht, K.K. GIS-and ICPR-Based Approach to Sustainable Urban Drainage Practices: Case Study of a Development Site in Florida. Water (Switzerland) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, M.F.N.; Barbassa, A.P.; Vasconcelos, A.F.; Ometto, A.R. Stormwater management for highly urbanized areas in the tropics: Life cycle assessment of low impact development practices. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köppen, W. Das geographische System der Klimate, 1st edition ed.; Gebrüder Borntraeger: Berlín, Germany, 1936; Volume N. [Google Scholar]
- (UNDP), U.N.D.P. Human Development Report 2023: Uncertain Times, Unsettled Lives - Shaping Our Future in a Transforming World N/A; New York, USA, 2023; pp. Full Report (page Numbers depend on the reference, e.g., 20-50 for classifications).
- Environment, O.M.o.t. Stormwater Management Planning and Design Manual. 2003.
- Salvador, C.d.A.y.O.d.P.d.Á.M.d.S. Resumen Ejecutivo de la Guía Técnica para el diseño de SUDS en el AMSS. 2021.
- Ministère de l’Environnement, d.l.L.c.l.c.c. , de la Faune et des Parcs Guide de Gestion des eaux Pluviales. 2024.
- Government of Malasya, D.o.I.a.D. Urban Stormwater Management Manual for Malasya. 2012.
- Ajuntament de Valencia. Guía Básica para el Diseño de Sistemas Urbanos de Drenaje Sostenible en la Ciudad de València. 2021.
- García-Colin, J.C.; Díaz-Delgado, C.; Salinas Tapia, H.; Fonseca Ortiz, C.R.; Esteller Alberich, M.V.; Bâ, K.M.; García Pulido, D. Design of a Bioretention System with Water Reuse for Urban Agriculture through a Daily Water Balance. Water (Switzerland) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saneamiento, M.d.V.C.y. Modificación de la Norma Técnica OS.060 Drenaje Pluvial Urbano a Norma Técnica CE.040 Drenaje Pluvial del Reglamento Nacional de Edificaciones. Resolución Ministerial N° 126-2021-Vivienda, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza Vigil, A.J.; Carhart, N.J. Local infrastructure governance in Peru: a systems thinking appraisal. Infrastructure Asset Management 2024, 11, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Vivienda Construcción y Saneamiento. Norma OS.010: Captación y Conducción de agua para consumo humano. Obras de Saneamiento 2016.
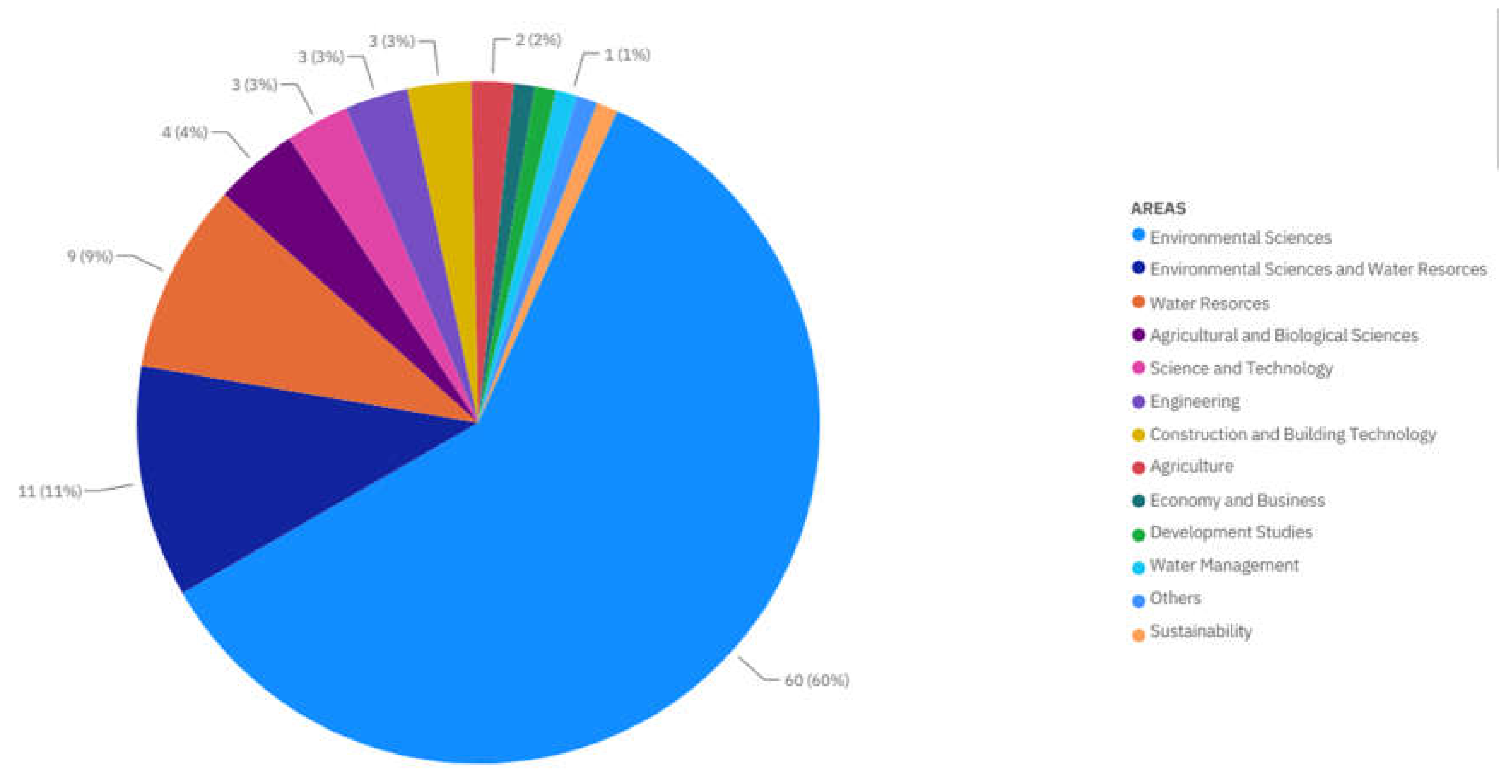
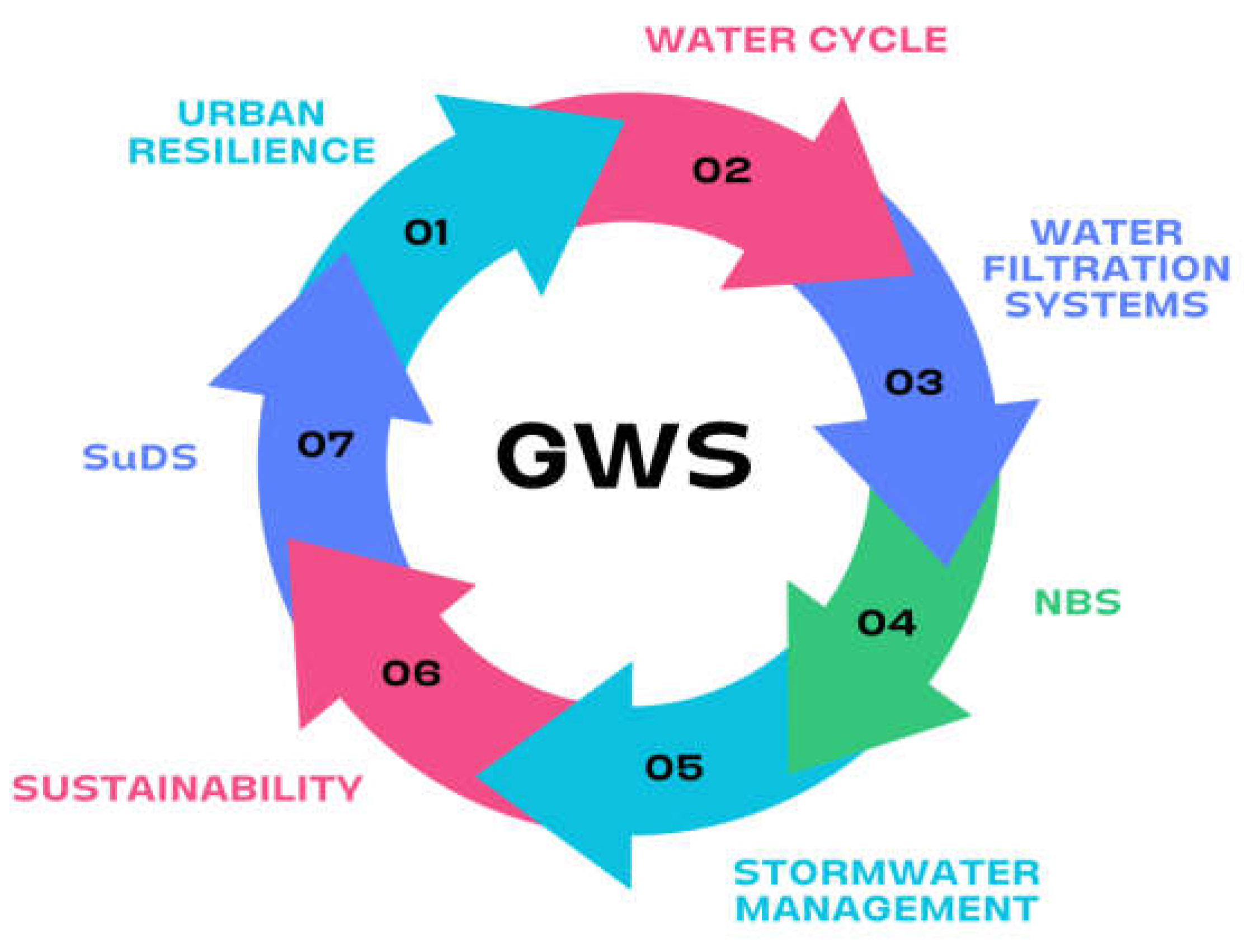
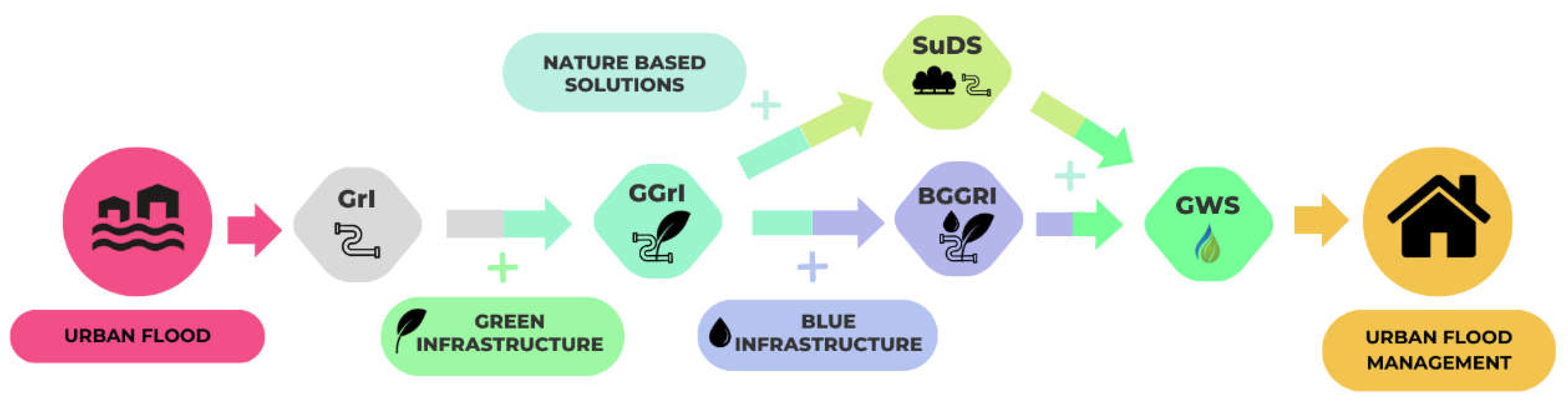
| Country | Documents |
|---|---|
| Australia | 2 |
| Brasil | 5 |
| Egypt | 1 |
| Spain | 1 |
| E.E.U.U. | 6 |
| Philippines | 2 |
| Greece | 1 |
| India | 9 |
| Iran | 3 |
| Malaysia | 3 |
| Peru | 2 |
| Sweden | 1 |
| Thailand | 1 |
| Vietnam | 1 |
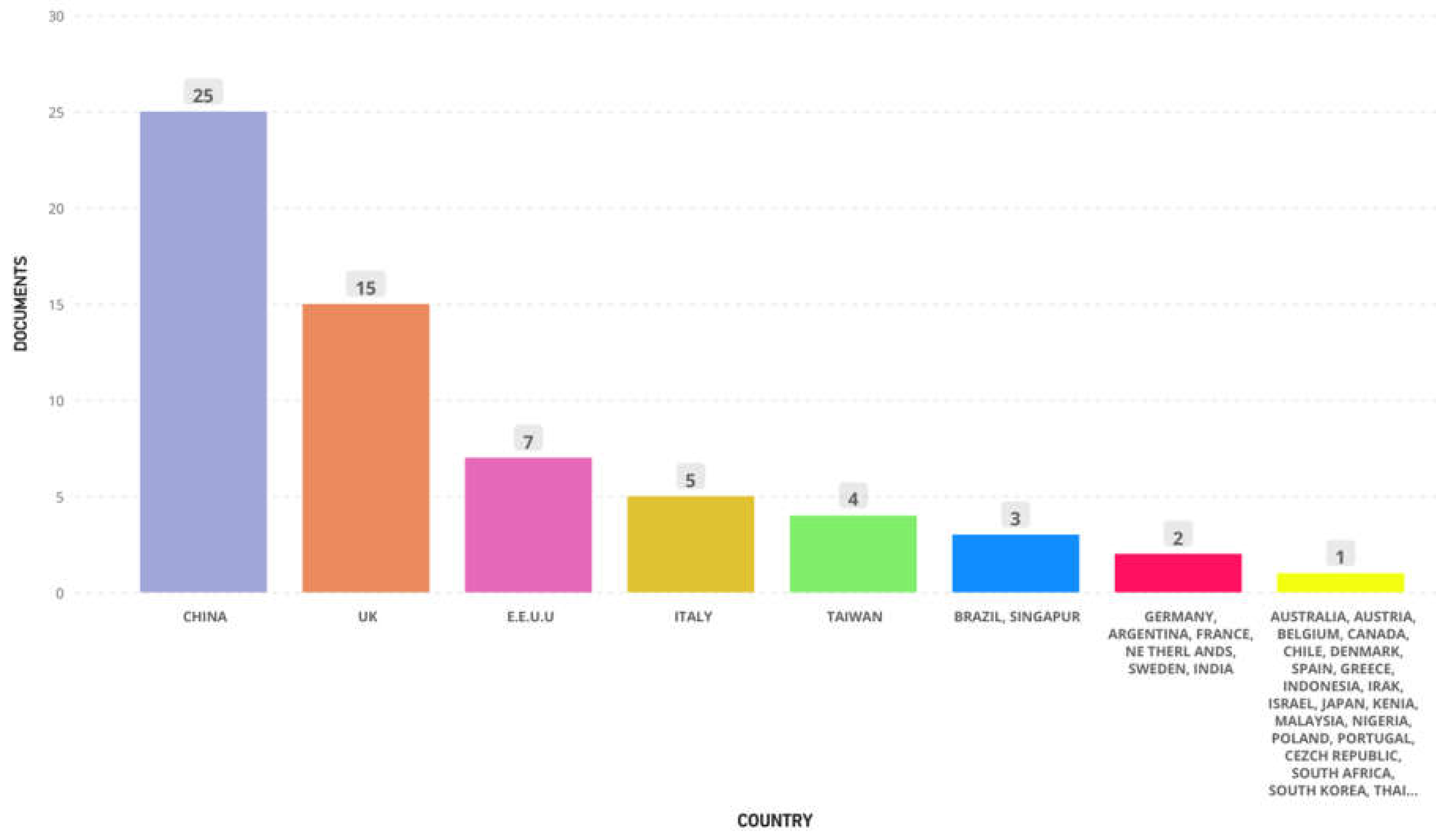
| Total | 38 |
| Scientific Journal | ID | Quartile |
|---|---|---|
| Aquaculture International | R1 | Q2 |
| Algal Research | R2 | Q1 |
| Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology | R3 | Q2 |
| Aquaculture | R4 | Q1 |
| Aquaculture International | R5 | Q2 |
| Aquaculture Nutrition | R6 | Q1 |
| Aquaculture Reports | R7 | Q1 |
| Aquaculture Research | R8 | Q2 |
| Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - Part A: Molecular and Integrative Physiology | R9 | Q1 |
| Developmental and Comparative Immunology | R10 | Q3 |
| Environmental Science: Water Research and Technology | R11 | Q1 |
| Fisheries Science | R12 | Q3 |
| Food Security | R13 | Q1 |
| Indian Journal of Fisheries | R14 | Q4 |
| International Journal of Agriculture and Biology | R15 | Q3 |
| Israeli Journal of Aquaculture - Bamidgeh | R16 | Q3 |
| Journal of Green Building | R17 | Q2 |
| Journal of Sustainability Science and Management | R18 | Q3 |
| Journal of the World Aquaculture Society | R19 | Q3 |
| Scientific Reports | R20 | Q1 |
| Journal of Fish Diseases | R21 | Q1 |
| ID | Aquaculture | Agriculture | Agrotechnology | Marine Science | Chemical Ecology | Pharmacy | Environmental Sustainability | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 2 | 2 | ||||||
| R2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R3 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R4 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 6 | ||||
| R5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||||
| R6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| R7 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R8 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5 | ||||
| R9 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R10 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R11 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R12 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R13 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R14 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| R15 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R16 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R17 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| R18 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R19 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| R20 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| R21 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Total | 16 | 2 | 1 | 13 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 38 |
| Country | Climate [158] | Economy [159] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Maritime | Developed | |
| Canada | Continental | Developed | |
| Colombia | Tropical | Developing | |
| El Salvador | Tropical | Developing | |
| France | Temperate | Developed | |
| Malaysia | Tropical | Developing | |
| Spain | Mediterranean | Developed |
| Types of SuDS | Country | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Canada | Colombia | El Salvador | France | Malaysia | Spain | |
| Green roofs | X | X | X | ||||
| Soakaways | X | X | |||||
| Water butts | X | ||||||
| Rainwater tank | X | X | X | X | |||
| Filter strips | X | X | X | ||||
| Trenches | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Swales | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Bioretention | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Pervious pavement | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Geocellular/modular systems | X | ||||||
| Sand filters | X | X | X | ||||
| Infiltration basins | X | X | X | X | |||
| Detention basins | X | X | |||||
| Ponds | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Stormwater wetlands | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Reduced lot grading | X | ||||||
| Rear year ponding | X | ||||||
| Pervious pipes | X | X | X | ||||
| Oil/grit separators | X | X | |||||
| Filter drains | X | X | X | ||||
| Trees | X | X | X | ||||
| Design parameters | Units | Country | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | El Salvador | France | Malaysia | Spain | |||
| Area | ha | 1 or less | 1 or less | - | |||
| Impervious Surface Area | % | 5 to 10 | 5 to 10 | 5 to 10 | - | - | |
| Slope | % | - | ˂ 10 | ˂ 5 | ˂ 5 | ||
| Distance to the water table | m | 1 | 3 | 1.2 | ˃ 0.6 | 1 | |
| Composted organic material | % | - | 5 a 10 | - | - | - | |
| Time for adequate capacity | hrs | 24 | - | - | - | - | |
| Water Depth | m | ˂ 0.15 | - | - | - | - | |
| System Depth | m | - | - | - | - | ˂ 0.3 | |
| Width | m | - | - | - | - | ˃ 0.6 | |
| Conductivity | mm/hr | - | - | 25 or more | ˃ 13 | 100 - 300 | |
| Planting density | plants/m2 | - | - | - | 6 a 10 | ||
| Velocity | m/s | - | - | - | ˂ 0.5 | - | |
| Design parameters | Units | Proposal | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area | ha | 1 or less | |
| Impervious Surface Area | % | 5 a 10 | |
| Slope | % | ˂ 5 | |
| Distance to the water table | m | ˃ 0.6 | |
| Composted organic material | % | 5 to 10 | |
| Time for adequate capacity | hrs | 24 | |
| Water Depth | m | ˂ 0.15 | |
| System Depth | m | ˂ 0.3 | |
| Width | m | ˃ 0.6 | |
| Conductivity | mm/hr | ˃ 13 | |
| Planting density | plants/m2 | 6 to 10 | |
| Velocity | m/s | ˂ 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





