Submitted:
13 September 2024
Posted:
16 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
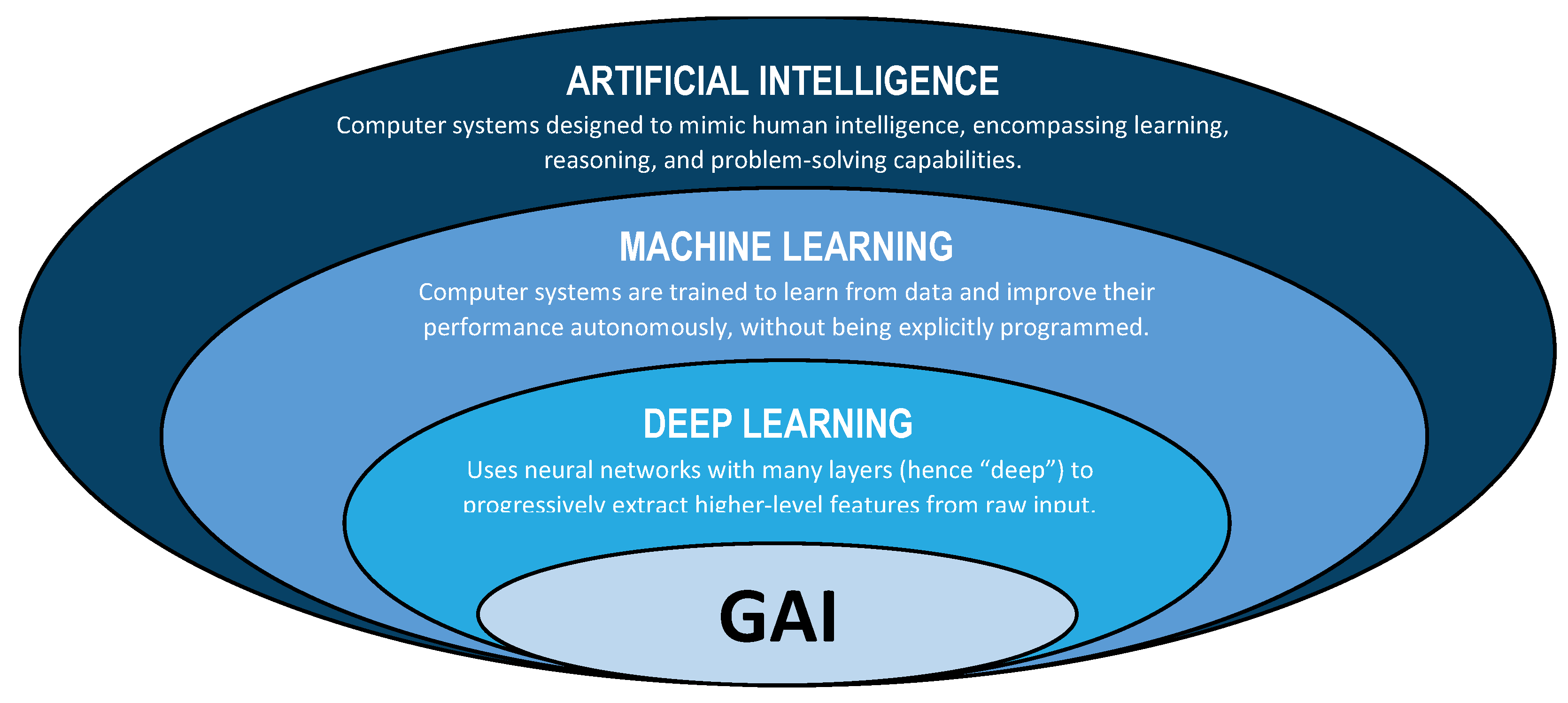
2. GAI Models
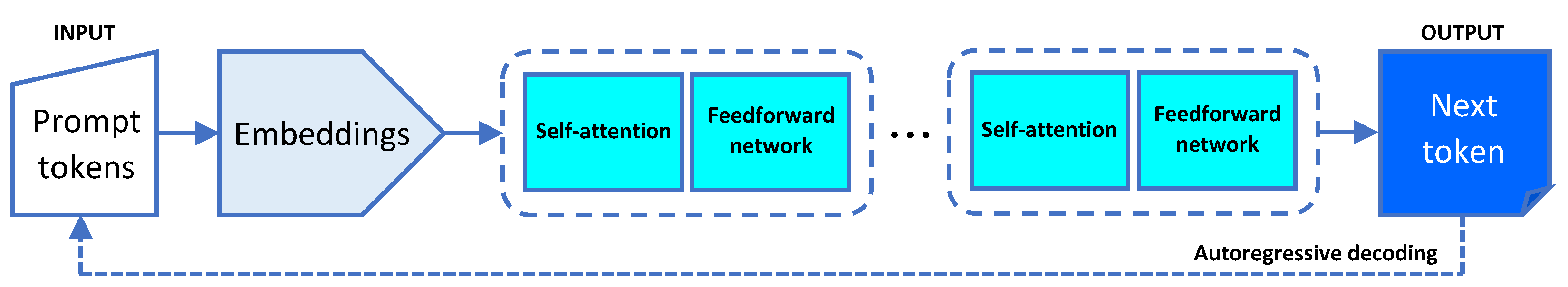
2.1. Transformer Architecture
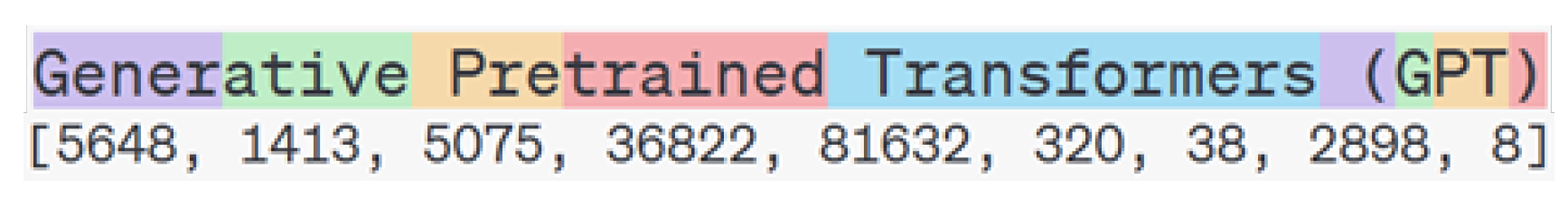
2.1.1. Tokenization
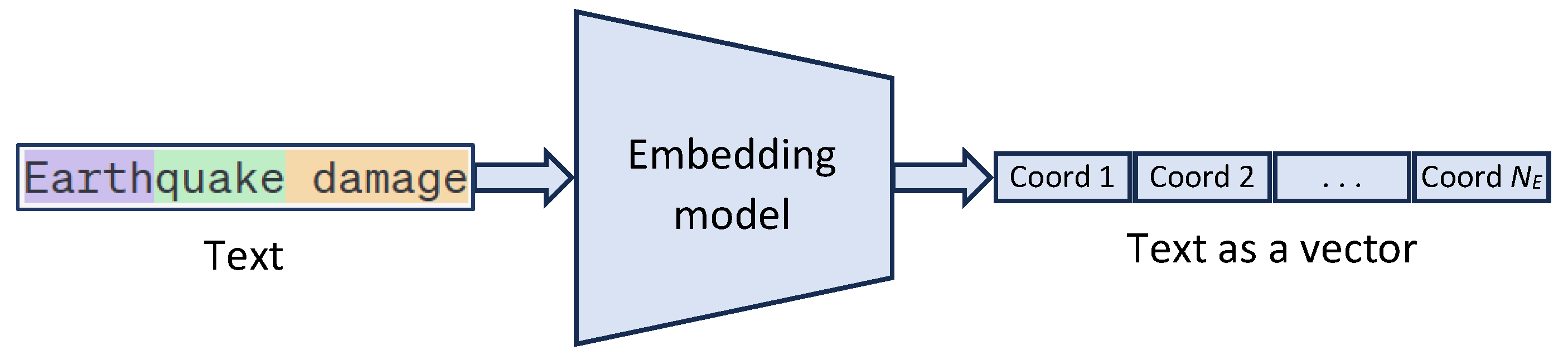
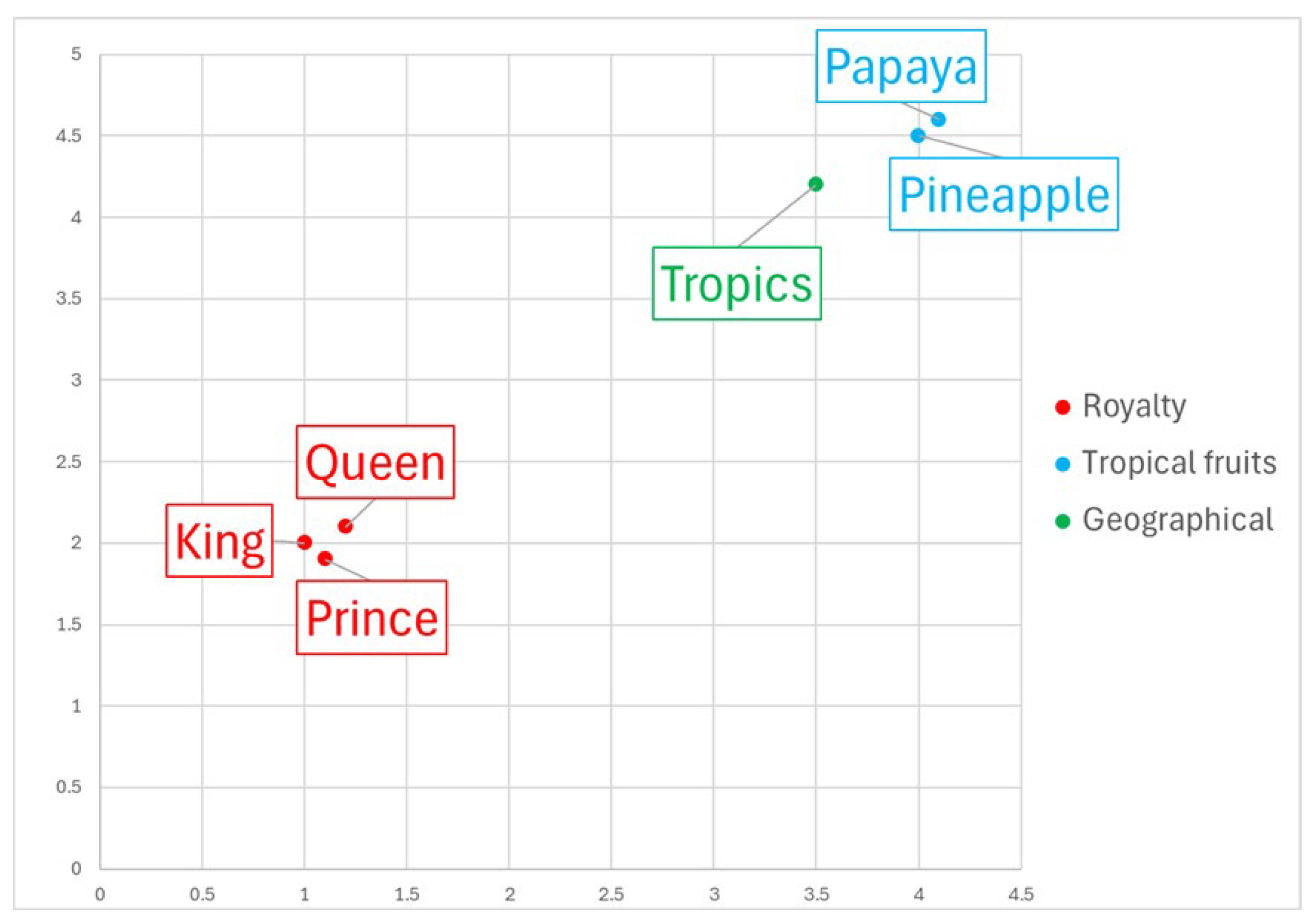
2.1.2. Embedings
2.1.3. Attention Mechanism
2.1.4. Next Token Prediction
2.1.5. Temperature and Top-P
2.2. Prompt Engineering
2.3. Fine-Tuning
2.4. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
3. Tested Approach
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- -
- It is relatively straightforward to create software for the automatic assessment of building damage in post-earthquake scenarios by integrating calls to Generative AI (GAI) models via an API.
- -
- Using recent multimodal GAI models of different sizes, such as GPT-4o, GPT-4o mini, Gemini 1.5 Pro, and Gemini 1.5 Flash, very different results were obtained. The overall average accuracy values were: 68.2% with GPT-4o; 31.8% with Gemini 1.5 Pro; 45.5% with GPT-4o mini; and 50.0% with Gemini 1.5 Flash. GPT-4o demonstrated the lowest average error.
- -
- Although the results are not yet ideal, based on the tests conducted, it is possible to conclude that the use of techniques such as RAG or fine-tuning (which is more demanding) could significantly improve the outcomes. Thus, the future use of GAI models appears to be feasible for preliminary damage assessments of buildings subjected to seismic vibrations.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Estêvão, J.M.C. Modelo computacional de avaliação do risco sísmico de edifícios (Computational model for seismic risk assessment of buildings). MSc thesis, Instituto Superior Técnico, UTL, Lisbon, 1998.
- Klein, D. Neural Networks for Chess. The magic of deep and reinforcement learning revealed; arXiv:2209.01506: 2022. [CrossRef]
- Estêvão, J.M.C. Feasibility of using neural networks to obtain simplified capacity curves for seismic assessment. Buildings 2018, 8, 151. [CrossRef]
- de-Miguel-Rodríguez, J.; Morales-Esteban, A.; Requena-García-Cruz, M.-V.; Zapico-Blanco, B.; Segovia-Verjel, M.-L.; Romero-Sánchez, E.; Estêvão, J.M.C. Fast Seismic Assessment of Built Urban Areas with the Accuracy of Mechanical Methods Using a Feedforward Neural Network. Sustainability 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Estêvão, J.M.C.; Morales-Esteban, A.; Sá, L.F.; Ferreira, M.A.; Tomás, B.; Esteves, C.; Barreto, V.; Carreira, A.; Braga, A.; Requena-Garcia-Cruz, M.-V., et al. Improving the Earthquake Resilience of Primary Schools in the Border Regions of Neighbouring Countries. Sustainability 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation Applied to Handwritten Zip Code Recognition. Neural Computation 1989, 1, 541-551. [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Taha, T.M.; Yakopcic, C.; Westberg, S.; Sidike, P.; Nasrin, M.S.; Esesn, B.C.V.; Awwal, A.A.S.; Asari, V.K. The History Began from AlexNet: A Comprehensive Survey on Deep Learning Approaches. arXiv:1803.01164v2 2018, 1-39. [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Advances in neural information processing systems, 2017; pp. 5998–6008.
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training. Availabe online: https://cdn.openai.com/research-covers/language-unsupervised/language_understanding_paper.pdf (accessed on 10/07/2024).
- Yenduri, G.; Ramalingam, M.; Selvi, G.C.; Supriya, Y.; Srivastava, G.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Raj, G.D.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Prabadevi, B.; Wang, W., et al. GPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) - A Comprehensive Review on Enabling Technologies, Potential Applications, Emerging Challenges, and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 54608-54649. [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, I.; Paul, L.A. From task structures to world models: what do LLMs know? Trends in Cognitive Sciences 2024, 28, 404-415. [CrossRef]
- Matin, S.S.; Pradhan, B. Challenges and limitations of earthquake-induced building damage mapping techniques using remote sensing images-A systematic review. Geocarto International 2022, 37, 6186-6212. [CrossRef]
- Ishiwatari, M. Leveraging Drones for Effective Disaster Management: A Comprehensive Analysis of the 2024 Noto Peninsula Earthquake Case in Japan. Progress in Disaster Science 2024, 10.1016/j.pdisas.2024.100348, 100348. [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Li, P.; Shan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y. Multi-feature driven rapid inspection of earthquake-induced damage on building facades using UAV-derived point cloud. Measurement 2024, 232, 114679. [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Hu, X.; Song, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, X.; Song, X.; Fan, X.; Wang, F. Intelligent assessment of building damage of 2023 Turkey-Syria Earthquake by multiple remote sensing approaches. npj Natural Hazards 2024, 1, 3. [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L. A rapid evaluation method of the seismic damage to buildings based on UAV images. Geomatica 2024, 76, 100006. [CrossRef]
- Albahri, A.S.; Khaleel, Y.L.; Habeeb, M.A.; Ismael, R.D.; Hameed, Q.A.; Deveci, M.; Homod, R.Z.; Albahri, O.S.; Alamoodi, A.H.; Alzubaidi, L. A systematic review of trustworthy artificial intelligence applications in natural disasters. Computers and Electrical Engineering 2024, 118, 109409. [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, S.; Dang, J. Seismic damage prediction of RC buildings using machine learning. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics 2023, 52, 3504-3527. [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, S.; Dang, J. Machine Learning-Based Classification for Rapid Seismic Damage Assessment of Buildings at a Regional Scale. Journal of Earthquake Engineering 2024, 28, 1861-1891. [CrossRef]
- Macchiarulo, V.; Giardina, G.; Milillo, P.; Aktas, Y.D.; Whitworth, M.R.Z. Integrating post-event very high resolution SAR imagery and machine learning for building-level earthquake damage assessment. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering 2024, . [CrossRef]
- Anniballe, R.; Noto, F.; Scalia, T.; Bignami, C.; Stramondo, S.; Chini, M.; Pierdicca, N. Earthquake damage mapping: An overall assessment of ground surveys and VHR image change detection after L’Aquila 2009 earthquake. Remote Sensing of Environment 2018, 210, 166-178. [CrossRef]
- Adriano, B.; Yokoya, N.; Xia, J.; Miura, H.; Liu, W.; Matsuoka, M.; Koshimura, S. Learning from multimodal and multitemporal earth observation data for building damage mapping. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2021, 175, 132-143. [CrossRef]
- Akhyar, A.; Asyraf Zulkifley, M.; Lee, J.; Song, T.; Han, J.; Cho, C.; Hyun, S.; Son, Y.; Hong, B.-W. Deep artificial intelligence applications for natural disaster management systems: A methodological review. Ecological Indicators 2024, 163, 112067. [CrossRef]
- Amanollah, H.; Asghari, A.; Mashayekhi, M.; Zahrai, S.M. Damage detection of structures based on wavelet analysis using improved AlexNet. Structures 2023, 56, 105019. [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Liu, T.; Zou, D.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Q.; zhou, A.; Li, Y. Multi-scale image-based damage recognition and assessment for reinforced concrete structures in post-earthquake emergency response. Engineering Structures 2024, 314, 118402. [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, S.; Dang, J. Multiclass seismic damage detection of buildings using quantum convolutional neural network. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering 2024, 39, 406-423. [CrossRef]
- Braik, A.M.; Koliou, M. Automated building damage assessment and large-scale mapping by integrating satellite imagery, GIS, and deep learning. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering 2024, n/a. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.-Y.; Khasani, R.R.; Citra, R.J. Image-based preliminary emergency assessment of damaged buildings after earthquake: Taiwan case studies. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2023, 126, 107164. [CrossRef]
- Kijewski-Correa, T.; Canales, E.; Hamburger, R.; Lochhead, M.; Mbabazi, A.; Presuma, L. A hybrid model for post-earthquake performance assessments in challenging contexts. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering 2024, 10.1007/s10518-024-01927-8. [CrossRef]
- Matin, S.S.; Pradhan, B. Earthquake-Induced Building-Damage Mapping Using Explainable AI (XAI). Sensors 2021, 21. [CrossRef]
- Ogunjinmi, P.D.; Park, S.-S.; Kim, B.; Lee, D.-E. Rapid Post-Earthquake Structural Damage Assessment Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Transfer Learning. Sensors 2022, 22. [CrossRef]
- Sublime, J.; Kalinicheva, E. Automatic Post-Disaster Damage Mapping Using Deep-Learning Techniques for Change Detection: Case Study of the Tohoku Tsunami. Remote Sensing 2019, 11. [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Wu, J.; Yao, J.; Zhu, H.; Gong, A.; Yang, J.; Hu, L.; Mo, F. A Deep Learning Application for Building Damage Assessment Using Ultra-High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery in Turkey Earthquake. International Journal of Disaster Risk Science 2023, 14, 947-962. [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Dogan, G.; Arslan, M.H.; Ilki, A. Categorization of Post-Earthquake Damages in RC Structural Elements with Deep Learning Approach. Journal of Earthquake Engineering 2024, 28, 2620-2651. [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Liu, W.; Hou, L. Convolutional Neural Networks for Structural Damage Identification in Assembled Buildings. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2022, 2022, 2326903. [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Liu, W.; Maruyama, Y. Damaged Building Extraction Using Modified Mask R-CNN Model Using Post-Event Aerial Images of the 2016 Kumamoto Earthquake. Remote Sensing 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Marano, G.C.; Rosso, M.M.; Aloisio, A.; Cirrincione, G. Generative adversarial networks review in earthquake-related engineering fields. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering 2024, 22, 3511-3562. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.-Y.; Sholeh, M.N.; Kwek, A. Computer vision-based post-earthquake inspections for building safety assessment. Journal of Building Engineering 2024, 94, 109909. [CrossRef]
- Bommasani, R.; Hudson, D.A.; Adeli, E.; Altman, R.; Arora, S.; Arx, S.v.; Bernstein, M.S.; Bohg, J.; Bosselut, A.; Brunskill, E., et al. On the Opportunities and Risks of Foundation Models. arXiv:2108.07258v3 2022. [CrossRef]
- LlamaTeam. The Llama 3 Herd of Models. Availabe online: https://ai.meta.com/research/publications/the-llama-3-herd-of-models/ (accessed on 24/07/2024).
- Eloundou, T.; Manning, S.; Mishkin, P.; Rock, D. GPTs are GPTs: An Early Look at the Labor Market Impact Potential of Large Language Models. arXiv:2303.10130v5 2023, 1-36 . [CrossRef]
- Betker, J.; Goh, G.; Jing, L.; Brooks, T.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Ouyang, L.; Zhuang, J.; Lee, J.; Guo, Y., et al. Improving Image Generation with Better Captions. Availabe online: https://cdn.openai.com/papers/dall-e-3.pdf (accessed on 12/07/2024).
- OpenAI. GPT-4 Technical Report. arXiv:2303.08774v6 2023, 1-100 . [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.P. ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems 2023, 3, 121-154. [CrossRef]
- Ooi, K.-B.; Tan, G.W.-H.; Al-Emran, M.; Al-Sharafi, M.A.; Capatina, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Huang, T.-L.; Kar, A.K.; Lee, V.-H., et al. The Potential of Generative Artificial Intelligence Across Disciplines: Perspectives and Future Directions. Journal of Computer Information Systems 2023, 10.1080/08874417.2023.2261010, 1-32. [CrossRef]
- 3, D.-E. Tokenizer. Availabe online: https://openai.com/index/dall-e-3/ (accessed on September 2024).
- Yao, Y.; Duan, J.; Xu, K.; Cai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y. A survey on large language model (LLM) security and privacy: The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly. High-Confidence Computing 2024, 4, 100211. [CrossRef]
- OpenAI. Tokenizer. Availabe online: https://platform.openai.com/tokenizer (accessed on July 2024).
- ChameleonTeam. Chameleon: Mixed-ModalEarly-FusionFoundation Models. arXiv:2405.09818v1 2024, 1-27. [CrossRef]
- Neelakantan, A.; Xu, T.; Puri, R.; Radford, A.; Han, J.M.; Tworek, J.; Yuan, Q.; Tezak, N.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C., et al. Text and Code Embeddings by Contrastive Pre-Training. arXiv:2201.10005v1 2022, 1-13 . [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, G. But what is a GPT? Visual intro to transformers | Chapter 5, Deep Learning. Availabe online: https://www.3blue1brown.com/lessons/gpt (accessed on 17/07/2024).
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality. arXiv:1310.4546v1 2013, 1-9 . [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Tian, F.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, X.; Chen, E. Word Embedding Revisited: A New Representation Learning and Explicit Matrix Factorization Perspective. In Proceedings of Twenty-Fourth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Buenos Aires, Argentina; pp. 3650-3656.
- Sanderson, G. Visualizing Attention, a Transformer’s Heart | Chapter 6, Deep Learning. Availabe online: https://www.3blue1brown.com/lessons/attention (accessed on 17/07/2024).
- Gemini Team, G. Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context. arXiv:2403.05530v3 2024, 1-154 . [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, A.; Buys, J.; Du, L.; Forbes, M.; Choi, Y. The Curious Case of Neural Text Degeneration. arXiv:1904.09751v2 2020, 1-16 . [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Fu, Q.; Hays, S.; Sandborn, M.; Olea, C.; Gilbert, H.; Elnashar, A.; Spencer-Smith, J.; Schmidt, D.C. A Prompt Pattern Catalog to Enhance Prompt Engineering with ChatGPT. arXiv:2302.11382v1 2023, 1-19 . [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Lee, N.; Frieske, R.; Yu, T.; Su, D.; Xu, Y.; Ishii, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Madotto, A.; Fung, P. Survey of Hallucination in Natural Language Generation. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, Article 248. [CrossRef]
- López Espejel, J.; Ettifouri, E.H.; Yahaya Alassan, M.S.; Chouham, E.M.; Dahhane, W. GPT-3.5, GPT-4, or BARD? Evaluating LLMs reasoning ability in zero-shot setting and performance boosting through prompts. Natural Language Processing Journal 2023, 5, 100032. [CrossRef]
- Lo, L.S. The Art and Science of Prompt Engineering: A New Literacy in the Information Age. Internet Reference Services Quarterly 2023, 10.1080/10875301.2023.2227621, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A., et al. Language models are few-shot learners. In Proceedings of Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada; p. Article 159.
- Yao, S.; Yu, D.; Zhao, J.; Shafran, I.; Griffiths, T.L.; Cao, Y.; Narasimhan, K. Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models. arXiv:2305.10601v2 2023, 1-14 . [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv:1810.04805v2 2019, 1-16 . [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xiong, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, C.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, X.; Kuo, T.-W.; Guan, N., et al. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Natural Language Processing: A Survey. arXiv:2407.13193v2 2023, 1-14 . [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; He, Z.; Qiu, T.; Wu, H.; Yu, B. Customized Retrieval Augmented Generation and Benchmarking for EDA Tool Documentation QA. arXiv:2407.15353v1 2024, 1-9.
- Arasteh, S.T.; Lotfinia, M.; Bressem, K.; Siepmann, R.; Ferber, D.; Kuhl, C.; Kather, J.N.; Nebelung, S.; Truhn, D. RadioRAG: Factual Large Language Models for Enhanced Diagnostics in Radiology Using Dynamic Retrieval Augmented Generation. arXiv:2407.15621v1 2024, 1-32.
- Grünthal, G. European Macroseismic Scale 1998. Volume 15.; Centre Europèen de Géodynamique et de Séismologie: Luxembourg, 1998; pp. 99.
- OpenAI. GPT-4o. Availabe online: https://platform.openai.com/playground/chat?models=gpt-4o (accessed on July 2024).
- Google. Google AI Studio. Availabe online: https://aistudio.google.com/app/prompts/new_chat (accessed on July 2024).
- OpenAI. GPT-4o mini. Availabe online: https://platform.openai.com/playground/chat?models=gpt-4o-mini (accessed on July 2024).
- Chester, D.K.; Chester, O.K. The impact of eighteenth century earthquakes on the Algarve region, southern Portugal. The Geographical Journal 2010, 176, 350–370. [CrossRef]

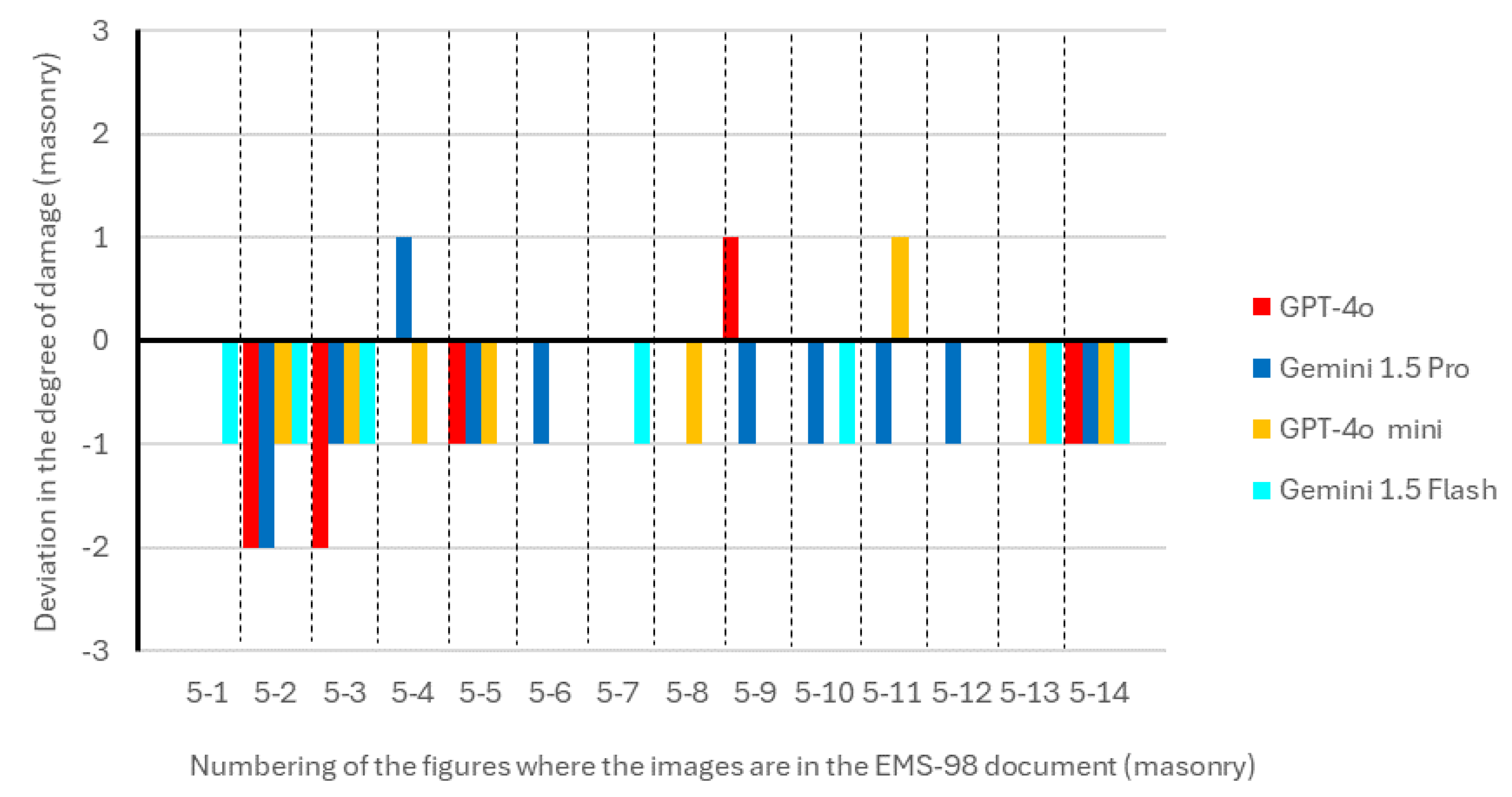
| N. | Figure | EMS-98 document | GPT-4o | Gemini 1.5 Pro | GPT-4o mini | Gemini 1.5 Flash |
| 1 | 5-1 | D3 | Masonry (85%) D3 (80%) 1 |
Masonry (95%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (85%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (100%) D2 (90%) |
| 2 | 5-2 | D4 | Masonry (90%) D2 (80%) |
Masonry (95%) D2 (80%) |
Masonry (85%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (100%) D3 (80%) |
| 3 | 5-3 | D4 | Masonry (95%) D2 (90%) |
Masonry (95%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (85%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (100%) D3 (100%) |
| 4 | 5-4 | D4 | Masonry (90%) D4 (85%) |
Masonry (95%) D5 (95%) |
Masonry (90%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (100%) D4 (90%) |
| 5 | 5-5 | D5 | Masonry (90%) D4 (85%) |
Masonry (95%) D4 (85%) |
Masonry (85%) D4 (90%) |
Masonry (100%) D5 (90%) |
| 6 | 5-6 | D2 | Masonry (90%) D2 (80%) |
Masonry (95%) D1 (70%) |
Masonry (85%) D2 (75%) |
Masonry (100%) D2 (80%) |
| 7 | 5-7 | D3 | Masonry (90%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (100%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (85%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (100%) D2 (90%) |
| 8 | 5-8 | D4 | Masonry (95%) D4 (90%) |
Masonry (95%) D4 (90%) |
Masonry (90%) D3 (85%) |
Masonry (100%) D4 (90%) |
| 9 | 5-9 | D2 | Masonry (90%) D3 (85%) |
Masonry (95%) D1 (75%) |
Masonry (85%) D2 (80%) |
Masonry (100%) D2 (100%) |
| 10 | 5-10 | D2 | Masonry (90%) D2 (80%) |
Masonry (95%) D1 (75%) |
Masonry (90%) D2 (85%) |
Masonry (100%) D1 (90%) |
| 11 | 5-11 | D2 | Masonry (90%) D2 (85%) |
Masonry (90%) D1 (80%) |
Masonry (85%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (100%) D2 (90%) |
| 12 | 5-12 | D2 | Masonry (90%) D2 (85%) |
Masonry (95%) D1 (80%) |
Masonry (85%) D2 (80%) |
Masonry (100%) D2 (80%) |
| 13 | 5-13 | D3 | Masonry (90%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (95%) D3 (85%) |
Masonry (85%) D2 (75%) |
Masonry (100%) D2 (100%) |
| 14 | 5-14 | D4 | Masonry (90%) D3 (85%) |
Masonry (95%) D3 (85%) |
Masonry (85%) D3 (80%) |
Masonry (100%) D3 (90%) |
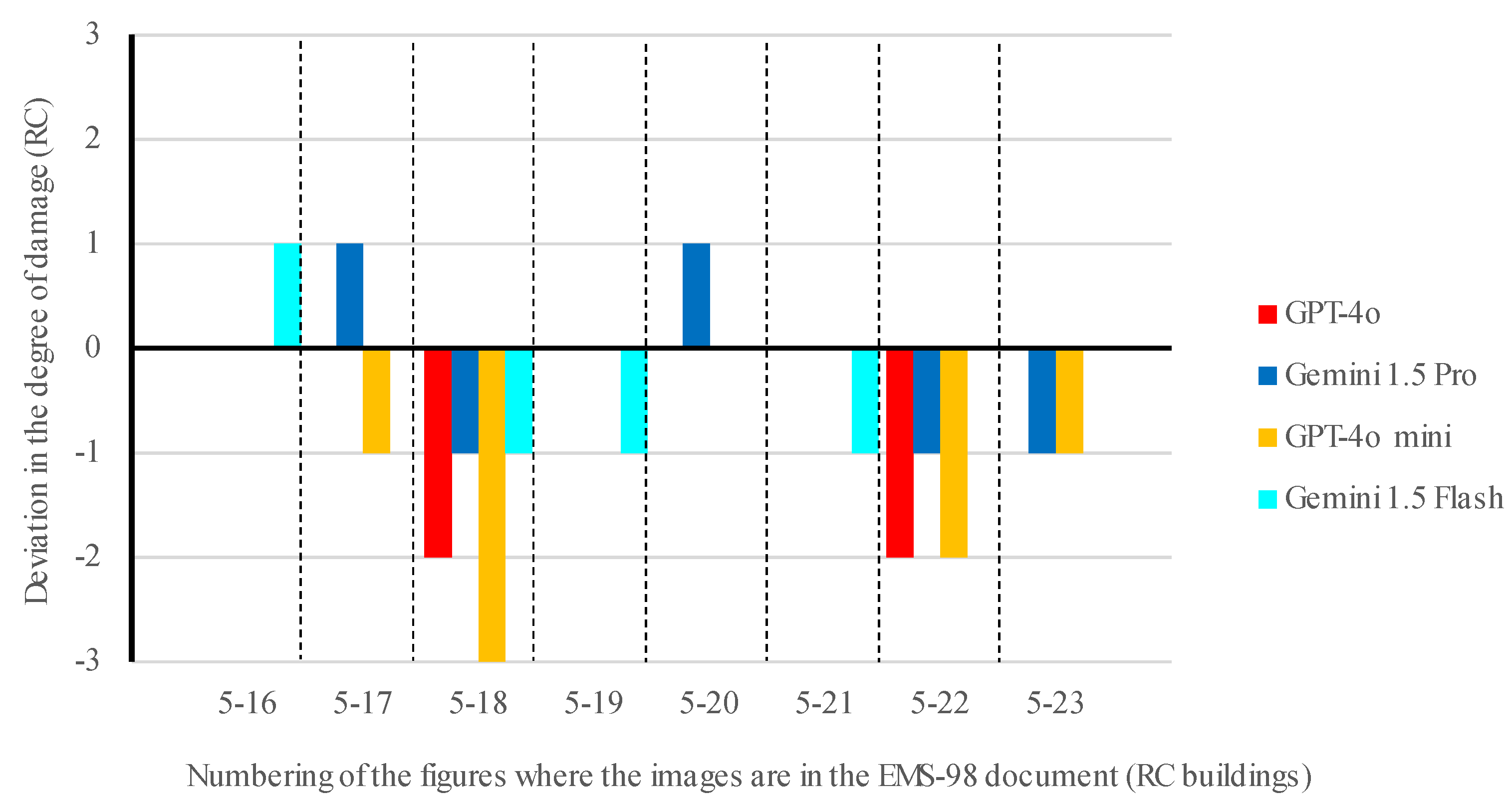
| N. | Figure | EMS-98 document | GPT-4o | Gemini 1.5 Pro | GPT-4o mini | Gemini 1.5 Flash |
| 1 | 5-16 | D3 | RC (90%) D3 (85%) 1 |
RC (95%) D3 (85%) |
RC (90%) D3 (85%) |
RC (100%) D4 (100%) |
| 2 | 5-17 | D4 | RC (90%) D4 (85%) |
RC (95%) D5 (95%) |
Masonry (90%) D3 (85%) |
RC (100%) D4 (90%) |
| 3 | 5-18 | D5 | RC (90%) D3 (85%) |
RC (95%) D4 (85%) |
RC (90%) D2 (85%) |
RC (100%) D4 (90%) |
| 4 | 5-19 | D5 | RC (90%) D5 (95%) |
RC (95%) D5 (90%) |
RC (85%) D5 (90%) |
RC (100%) D4 (90%) |
| 5 | 5-20 | D4 | RC (90%) D4 (85%) |
RC (95%) D5 (90%) |
RC (90%) D4 (85%) |
RC (100%) D4 (90%) |
| 6 | 5-21 | D5 | RC (90%) D5 (95%) |
RC (95%) D5 (99%) |
RC (85%) D5 (90%) |
RC (100%) D4 (100%) |
| 7 | 5-22 | D5 | RC (95%) D3 (90%) |
RC (95%) D4 (85%) |
RC (85%) D3 (80%) |
RC (100%) D5 (100%) |
| 8 | 5-23 | D3 | RC (90%) D3 (85%) |
RC (95%) D2 (80%) |
RC (85%) D2 (80%) |
RC (100%) D3 (90%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





