Submitted:
12 September 2024
Posted:
13 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Fractal-Paradigm and the Fractal Calculus
1.1.1. Basic Research Paradigm
1.2. Brief history of HRV as a ’Hard Problem’
1.3. Outline of Modeing Synthesis Using 4 Models
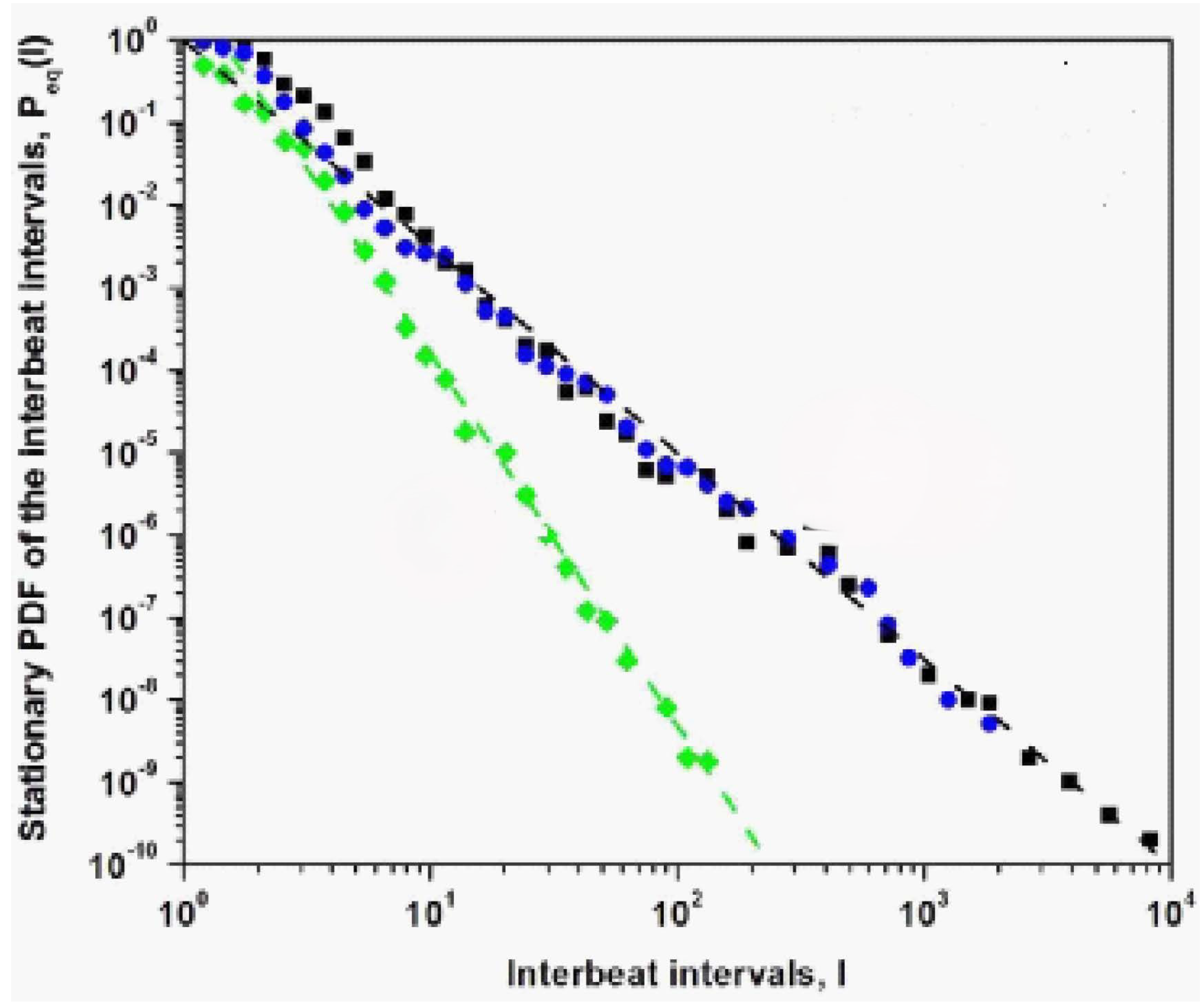
2. Empirical Lévy Statistics for HRV: FOCM-0
3. Theoretical Lévy statistics for HRV: FOCM-1
3.1. FOCM-0 and FOCM-1 Are Both Unacceptable
4. Tempering Fluctuations: FOCM-2
4.1. Why Is FOCM-2 Unacceptable?
5. HRV Control Hypothesis: FOCM-3
5.1. Why is FOCM-3 Acceptable?
6. Discussion and Conclusions
FOCM-0 verified the processing of the empirical HRV time series for the healthy state of variability of the heartbeat intervals as a Lévy PDF but ultimately it is unsatisfactory because the Lévy PDF has an unphysiologic divergence of the second moment. The FOCM-0 is too simple.
FOCM-1 was designed to provide a formal mathematical description of the Lévy PDF empirically observed by [36] in FOCM-0. The natural calculus to obtain this PDF is the FOC but the FOFPE given in Eq.(4) requires additional modifications to incorporate the tempering mechanism in the dynamics and thereby avoid the second moment divergence.
FOMC-2 uses the infinite divisibilty of the PDF to obtain Eq.(6) which has an elegant tempered Lévy PDF solution. However it does not realize the proper control mechanism to supress the heart rate at the extremes, but instead suppresses the extreme flctuations themselves before they can disrupt the HRV time series.
FOCM-3 solved this remaining problem by introducing a nonlinear negative feedback mechanism that is self-regulating and is asymptotically consistent with the hypothesis that “disease is the loss of complexity” made by [17].
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Appendices
Appendix A.1. On Crucial Events (CEs)

Appendix A.2. Scaling Solution to Fractal Kinetic Equation
Steady state solution ;
Appendix A.3. Diffusion Entropy Analysis (DEA)
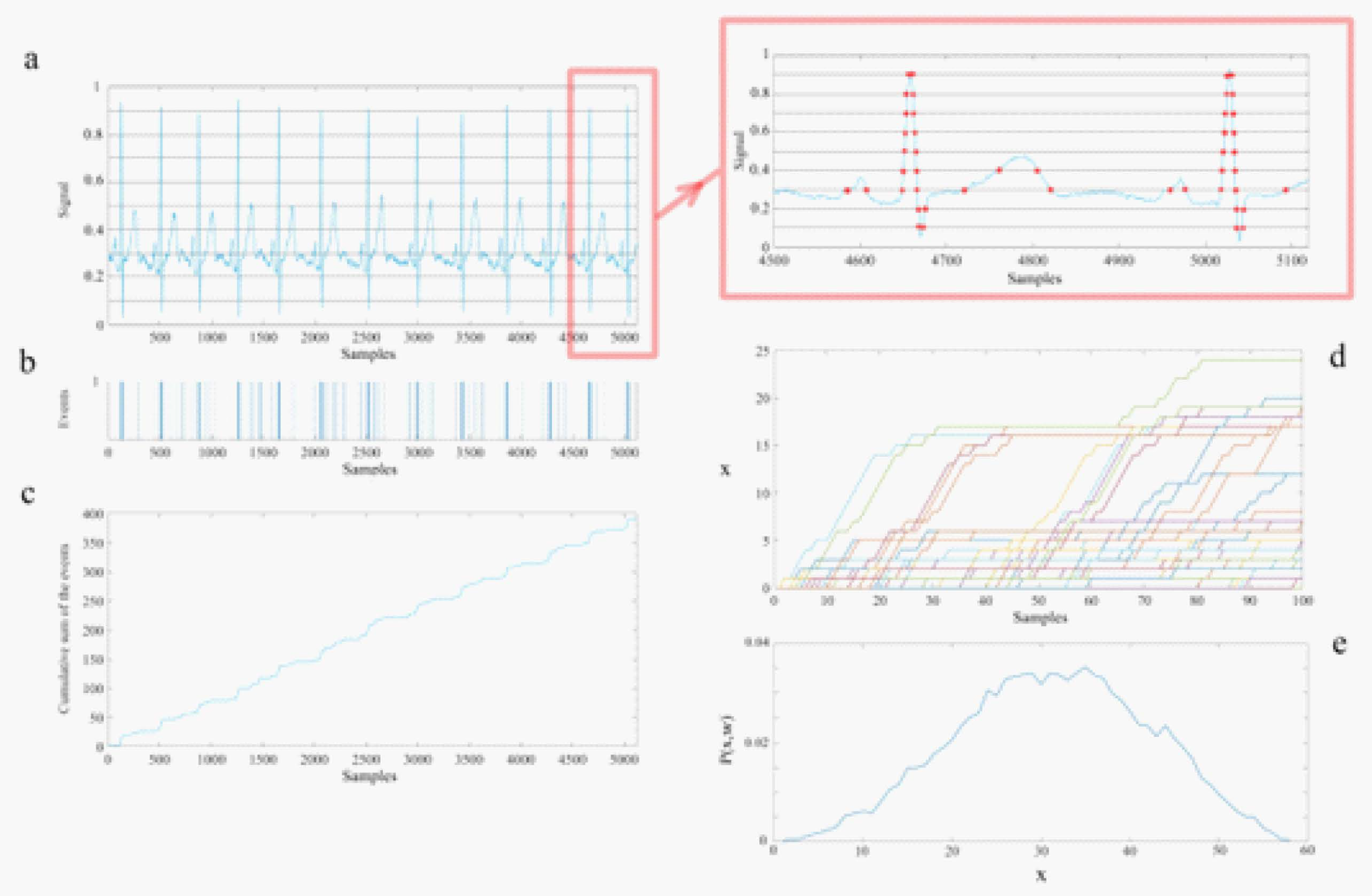
1.) The raw data of each channel is projected onto the interval [0,1] by normalizing each time series by the total time interval of the dataset thereby enabling the processing of each time series to be directly compared.
2.) Divide the normalized data profile into parallel stripes of size of 0.01 (panel (a), ECG data).
3.) Extract events by defining them as unit amplitude pulses if the signal at that time is in a different stripe with respect to its previous value (panel (b)) and zero if it remains in the same stripe.
4.) Create a diffusion trajectory (panel (c)) using the time series of the extracted events from step 3.
5.) Determine the statistics of a single diffusion trajectory by selecting a window size w and partitioning the diffusion trajectory into many pieces, each starting from an event.
6.) Initiating all the trajectories from an event enables their being shifted to start from a common origin (panel (d)).
7.) Finally, we evaluate the ensemble distribution of histograms at a given time (panel (e)) since the events are statistically independent.
Appendix A.4. Non-Gaussian Index
References
- LA Amaral, PC Ivanov, N Aoyagi, I Hidaka, S Tomono, AL Goldberger, et al. "Behavioral-independent features of complex heartbeat dynamics", Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 6026–6029 (2001). [CrossRef]
- F Beckers, B Verheyden and A Aubert. "Aging and nonlinear heart rate control in a healthy population", Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 290, H2560–H2570 (2006). [CrossRef]
- GE Billman, "Heart rate variability – a historical perspective", Front. Physiol.|Clin. & Trans. Physiol.2(86), 1-86 (2011). [CrossRef]
- G Bohara, D Lambert, BJ West and P Grigolini, “Crucial events, randomness, and multifractality,” Physical Review E 96, 062216 (2017).
- G Bohara, BJ West and P Grigolini, “Bridging waves and crucial events in the dynamics of the brain,” Frontier in Physiology 9, 1174 (2018).
- B Castaing, Y Gagne, and F Hopfinger, "Velocity probability density functions of high Reynolds-number turbulence", Phys. D 46, 177–200, (1990). [CrossRef]
- D Chalmers. The Conscious Mind. New York: Oxford University Press. (1996).
- A Chechkin, V Gonchar, J Klafter and R Metzler. "Natural cutoff in Lévy flights caused by dissipative nonlinearity", Phys. Rev. E 72:010101 (2005). [CrossRef]
- S Crowe, K Cresswell, A Robertson, et al. "The case study approach", BMC Med Res Methodol 11, 100 (2011). [CrossRef]
- A Einstein, "Über die von der molekularkinetischen Theorie der Wärme geforderte Bewegung von in ruhenden Flüssigkeiten suspendierten Teilchen",Annalen der Physik 322 (8): 549–560 (1905).
- R Failla, P Grigolini, M Ignaccolo, and A Schwettman, "Random growth of interfaces as a subordination process", Phys. Rev. E 70, 010101 (R) (2004).
- FJ Feder. Fractals, Plenum Press: New York, NY (1988).
- W Feller. An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications, Vol. II, 2nd Printing,John Wiley & Sons. New York, NY (1966).
- AL Goldberger, L Findley, MJ Blackburn and AJ Mandell, “Nonliear dynamics of heart failure: implications of long-wavelength cardiopulmonary osciallations”, Am. Heart J. 107, 612-615 (1984).
- AL Goldberger, V Bhargava, BJ West and AJ Mandell, “On a mechanism of cardiac electrical stability: the fractal hypothesis”, Biophys. J. 48, 525-528 (1985).
- AL Goldberger, D Goldwater, and V Bhargava, “Atrophine unmasks bed-rest deconditioning effect in healthy men: a spectral analysis of cardiac interbeat intervals”, J. Appl. Physiol. 61, 1843-1848 (1986).
- AL Goldberger and BJ West, "Fractals: a contemporary mathematical concept with applications to physiology and medicine", Yale J. Biol. Med. 60, 104–119 (1987).
- AL Goldberger, D Rigney and BJ West, "Chaos and fractals in human physiology", Sci. Am. 262, 42–49 (1990). [CrossRef]
- AL Goldberger. "Giles f. Filley lecture. Complex systems", Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc.3, 467–471 (2006). [CrossRef]
- S Guzzetti, S Mezzetti, R Magatelli, A Porta, G De Angelis, G Rovelli, and A Malliani, "Linear and non-linear 24 h heart rate variability in chronic heart failure",Autonomic Neuroscience 86(1-2), 114-119 (2000). [CrossRef]
- H Hall. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 13th Edn. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier (2016).
- J Hayano, K Kiyono, Z Struzik, Y Yamamoto, E Watanabe, et al. "Increased non-Gaussianity of heart rate variability predicts cardiac mortality after an acute myocardial infraction", Front. Physiol. 2:65. (2011). [CrossRef]
- H Huikuri. "Heart rate variability in coronary artery disease". J. Intern.Med. 237, 349–357 (1995). [CrossRef]
- N Iyengar, C Peng, R Morin, A Goldberger and L Lipsitz,"Age-related alterations in the fractal scaling of cardiac interbeat interval dynamics".Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 271, R1078–R1084 (1996). [CrossRef]
- PC Ivanov, LAN Amaral, AL Goldberger, S Havlin, MG Rosenblum, ZR Struzik and HE Stanley, "Multifractality in human heartbeat dynamics", Nature 399, 461–465 (1999).
- V Kariniemi and P Ammälä, “Short-term variability of fetal heart rate during pregnancies with normal and insufficient placental function”, Am. J. Obster. Gynecol. 139, 33-37 (1981).
- K Kiyono, Z Struzik, N Aoyagi, S Sakata, J Hayano and Y Yamamoto. "Critical scale invariance in a healthy human heart raté", Phys. Rev. Lett. 93:178103 (2004). [CrossRef]
- K Kiyono, Z Struzik, N Aoyagi and Y Yamamoto. "Multiscale probability density function analysis: non-Gaussian and scale-invariant fluctuations of healthy human heart rate", IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.53, 95–102 (2006). [CrossRef]
- R Kleiger, J Miller, J Bigger and A Moss. "Decreased heart rate variability and its association with increased mortality after acute myocardial infarction",Am. J. Cardiol. 59, 256–262 (1987). [CrossRef]
- arXiv:2406.16117v1 (2024).NM MacKay, "Non-equilibrium Noise in V-shaped, Linear Well Profiles", arXiv:2406.16117v1 (2024).
- K Mahmoodi, SE Kerick, P Grigolini, PJ Franaszczuk, and BJ West, ”Complexity synchronization: a measure of interaction between the brain, heart and lungs”, Sci. Rep. 13, 11433 (2023).
- K Mahmoodi, SE Kerick, P Grigolini, PJ Franaszczuk, and BJ West, "Temporal complexity measure of reaction time series: Operational versus event time",Brain and Behavior13(7): e3069 (2023).
- BB Mandelbrot, “1/f noises and the infrared catastrophe”, IEEE Comm. Conv., Boulder, CO (1965).
- GA Myers, GJ Martin, NM Magrid et al. “Power spectral analysis of heart rate variability in sudden cardiac death: comparison to other methods”, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 33, 1149-1156 (1986).
- B Neubauer and HJG Gundersen, “Analysis of heart rate variations in patients with multiple sclerosis. A simple measure of autonomic disturbances using an ordinary ECG”, J. Neurol. Neuosug. Psychiatry41, 417-419 (1978).
- C-K Peng, J Mietus, JM Hausdorff, S Havlin, HE Stanley and AL Goldberger, "Long-range anticorrelations and non-Gaussian behavior of the heartbeat", Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1343-46 (1993).
- M Rahman, "Navigating the landscape of research paradigms: An overview and critique", Inter. J. of Ed. Studies 6(1), 1-18 (2023). [CrossRef]
- LE Reichl, The Transition to Chaos, Springer, New York (1992).
- AI Sachev and GM Zaslavsky, "Fractiomal kinetic equation: Solutions and applications", Chaos7, 753-764 (1997).
- M Shlesinger and BJ West. "Complex fractal dimension of the bronchial tree", Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 2106–2108 (1991). [CrossRef]
- A Smolyak, O Levy, I Vodenska, S Buldyrev and S Havlin. "Mitigation of cascading failures in complex networks", Science Reports/natureresearch10,16124 (2020).
- RE Stake. The art of case study research. Sage Publications Ltd. London. (1995).
- P Stein, P Domitrovich, N Hui, P Rautaharju and J Gottdiener. "Sometimes higher heart rate variability is not better heart rate variability: results of graphical and nonlinear analyses". J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol.16,954–959 (2005). [CrossRef]
- Z Struzik, K Kiyono,J Hayano, E Watanabe and Y Yamamoto. "Increased heteroscedasticity of heart rate in fatal heart failure". EPL82:28005 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. "Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use". Circulation 93,1043–1065 (1996). [CrossRef]
- LD Valdez, L Shekhtman, CE La Rocca, X Zhang, SV Buldyrev, PA Trunfio, LA Braunstein, S Havlin. "Cascading Failures in Complex Networks", Journal of Complex Networks8(2),1-25 (2020). [CrossRef]
- JL Waddington, MJ MacCulloch and JE Sambrooks, “Resting heartrate variability in man declines with age”, Experientia 35, 1197-1198 (1979).
- ER Weibel, "Fractal geometry: a design principle for living organisms", American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology261(6): (1991). [CrossRef]
- ER Weibel, Symmorphosis: On Form and Function in Shaping Life, Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA (2000).
- BJ West and V Seshadri. "Linear systems with Lévy fluctuations". Phys. A 113, 203–216 (1982). [CrossRef]
- BJ West and P Grigolini, Complex Webs: Anticipating the Improbable, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, MA (2011).
- BJ West. Fractal Physiology and Chaos in Medicine. Hackensack, NJ:World Scientific (2013).
- BJ West, M Turalska and P Grigolini. Networks of Echoes: Imitation, Innovation and Invisible Leaders. New York, NY: Springer (2013).
- BJ West. "A mathematics for medicine: the network effect". Front. Physiol.| Fractal Physio. 5:456, (2014). [CrossRef]
- BJ West, Fractional Calculus View of Complexity: Tomorrow’s Science, see Section 7.6.1 Truncated Lévy Process, CRC Press, (2016).
- BJ West and M Turalska, "Hypothetical control of heart rate variability", Frontiers in Physiogy|Fractal Physiolgy10:1078,1-9 (2019).
- BJ West, K Mahmoodi, and P Grigolini, Empirical paradox, complexity thinking and generating new kinds of knowledge,Cambridge Scholars Publishing,UK (2019).
- BJ West and P. Grigolini, Crucial Events: Why are Catastrophies Never Expected?,World Scientific, Singapore (2021).
- BJ West, P Grigolini and M. Bologna. Crucial Event Rehabiliation Therapy: Multifractal Medicine, Springer International Pub. (2023).
- BJ West, P Grigolini, SE Kerick, PJ Franaszczuk and K Mahmoodi, "Complexity Synchronization of Organ Networks", Entropy 25, 1393-1412 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Factals in Biology and Medicine: Volume I, TF Nonnenmacher, SA Losa and ER Weibel Eds, Birkhäuser, Boston(1993); Volume II, SA Losa, D Merlini, TF Nonnenmacher and ER Weibel Eds, Birkhäuser, Boston (1998); Volume III, SA Losa, D Merlini, TF Nonnenmacher and ER Weibel Eds, Birkhäuser, Boston (2002); Volume IV, SA Losa, D Merlini, TF Nonnenmacher and ER Weibel Eds, Birkhäuser, Boston (2005)
- Y Yaniv, A Lyaskov and E Lakatta . "The fractal-like complexity of heart rate variability beyond neurotranmitters and autonomic receptors: signaling.intrinsic to sinoatrial node pacemaker cells". Cardiovasc. Pharm. Open Access.2:111 (2013). [CrossRef]
- GM Zaslavsky, "Chaos, fractional kinetics, and anomalus transport", Phys. Rept.371, 461 (2002).
| 1 | The terminology ’fractal calculus’ is used throughout to emphasize that the fact that the fractal descriptor means that ’fractal geometry’ and ’fractal statistics’ are vastly different from the usual terms of geometry and statisitics. So too is the ’fractal calculus’ (FOC) remarkably different from the integer-order calculus (IOC) and the integer-order differential equations (IODE). |
| 2 | Chalmers [7] coined the term ’hard problem of consciousness’ to distinguish the totality of consciosness from the easy poblems that are amenable to reductive logic . Herein we classify nearly every fundamental problem remaing in science as a ’hard’ problem in the sence that they typically arise out of empirical paradox [57]. |
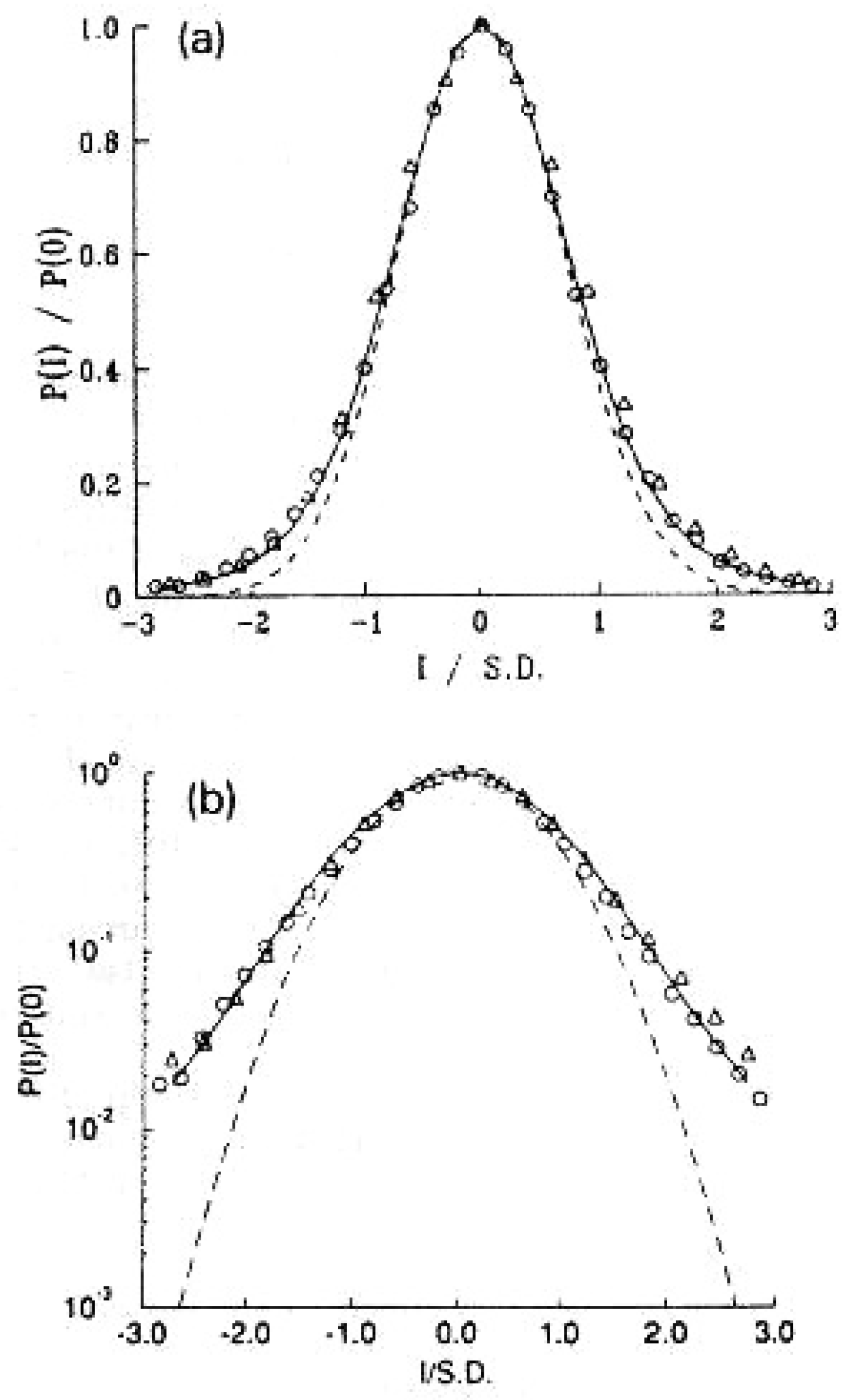
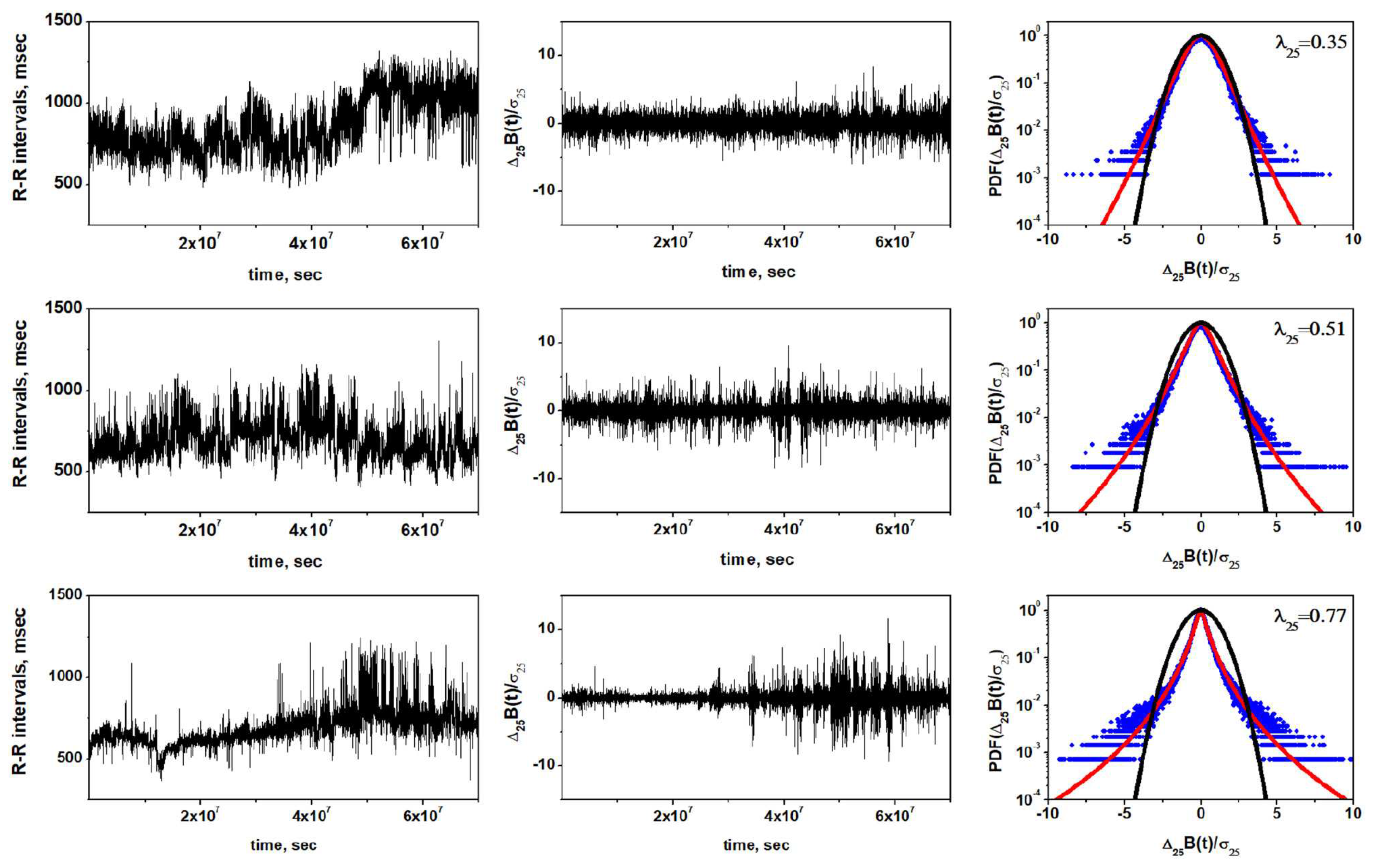
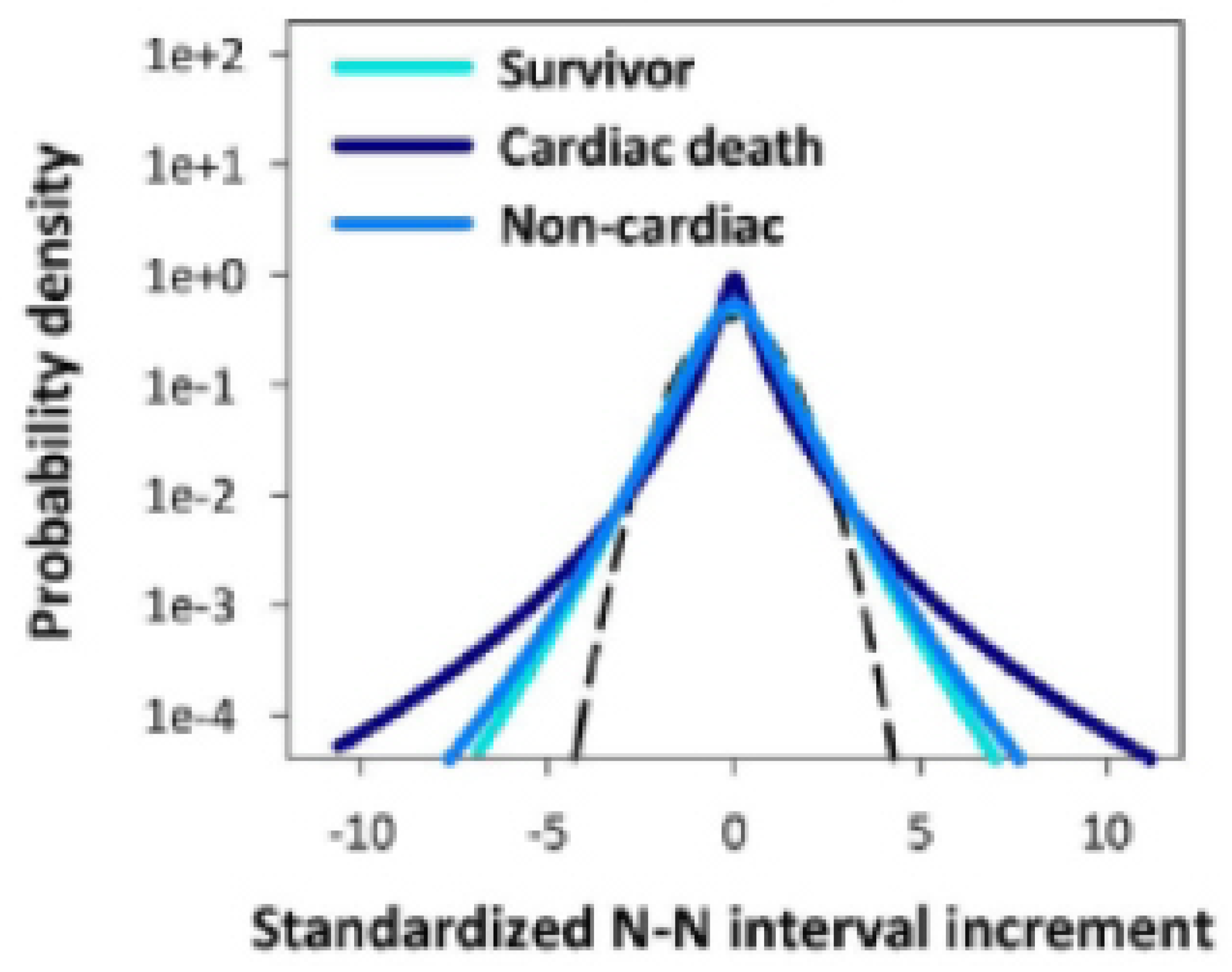
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




