Submitted:
09 September 2024
Posted:
10 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature
3. Materials and Methods
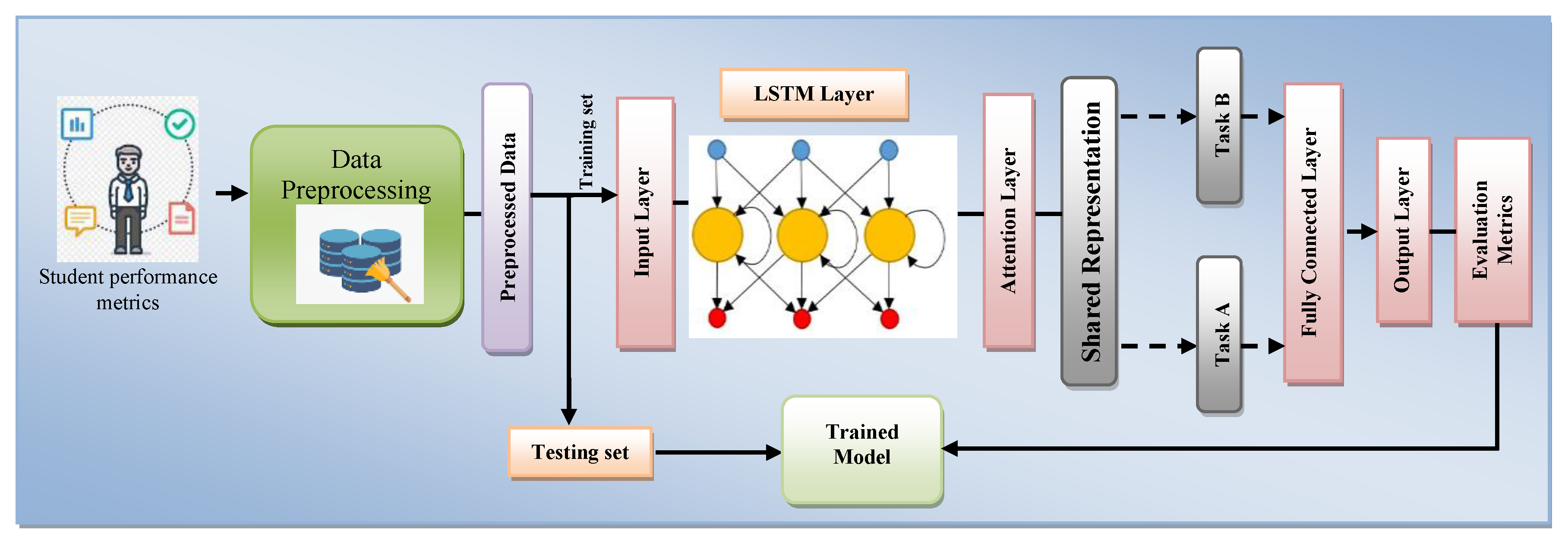
3.1. Proposed Architecture
3.2. Dataset Creation
= 1, 000, 000 x 40
= 40, 000, 000
| Algorithm 1: Pseudocode for data pre-processing |
|
import itertools import csv # Define the range of values for each variable range_values = range(11) # For x1 to x6 range_x7 = range(41) # For x7 # Generate all combinations of the variables combinations = list(itertools.product(range_values, repeat=6)) # For x1 to x6 combinations_with_x7 = [(c + (x7,)) for c in combinations for x7 in range_x7] # Combine with x7 # Calculate total for each combination combinations_with_total = [(c + (sum(c),)) for c in combinations_with_x7] # Specify the file name file_name = "resultPredictionDataset.csv" # Write combinations with sum to CSV file with open(file_name, 'w', newline='') as csvfile: csvwriter = csv.writer(csvfile) # Write header row csvwriter.writerow(["x1", "x2", "x3", "x4", "x5", "x6", "x7", "total"]) # Write data rows csvwriter.writerows(combinations_with_total) print(f"Final Dataset Generated Successfully to {file_name}") # total_rows = 5**6 * 70 # print("Total number of rows:", total_rows) |
3.2.1. Dataset Description
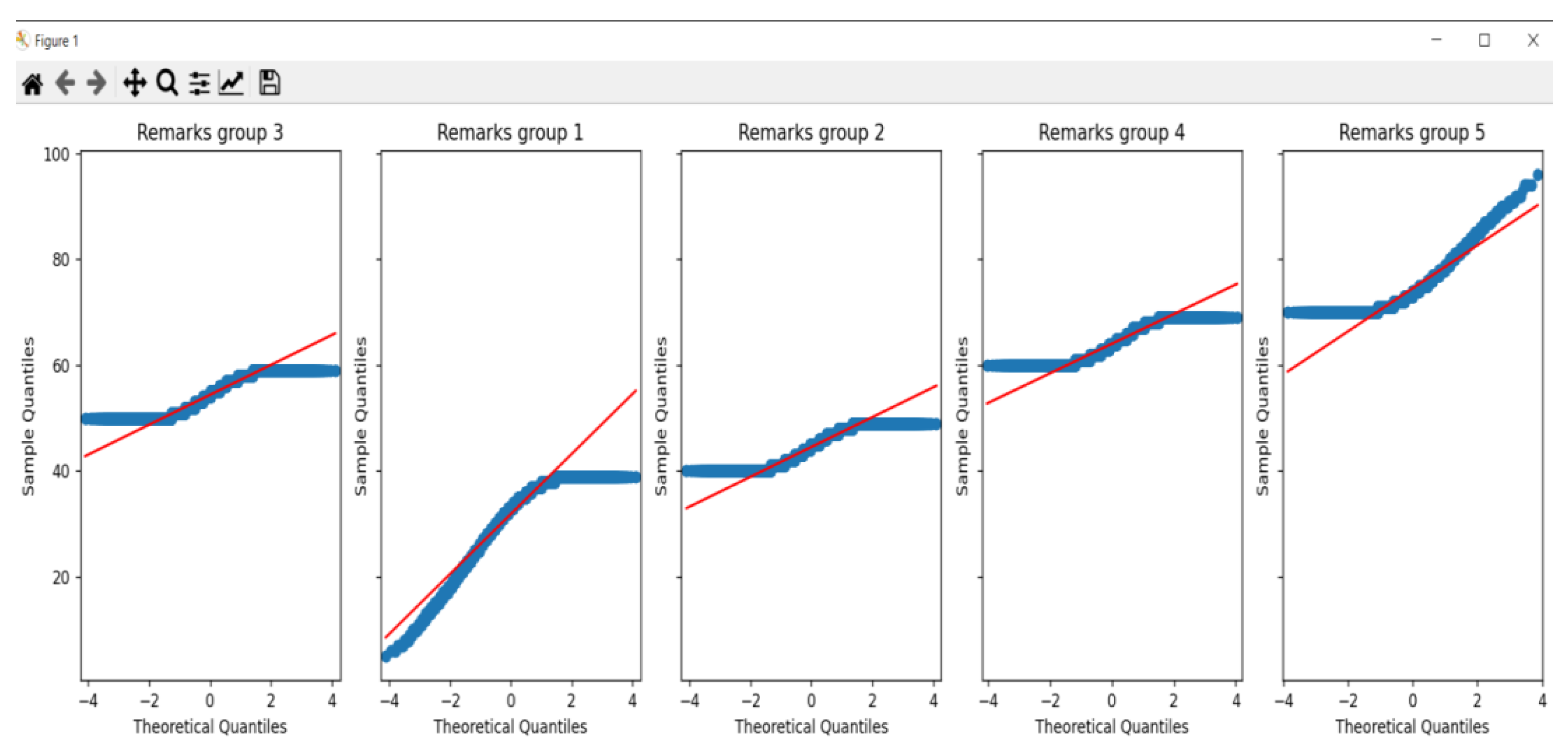
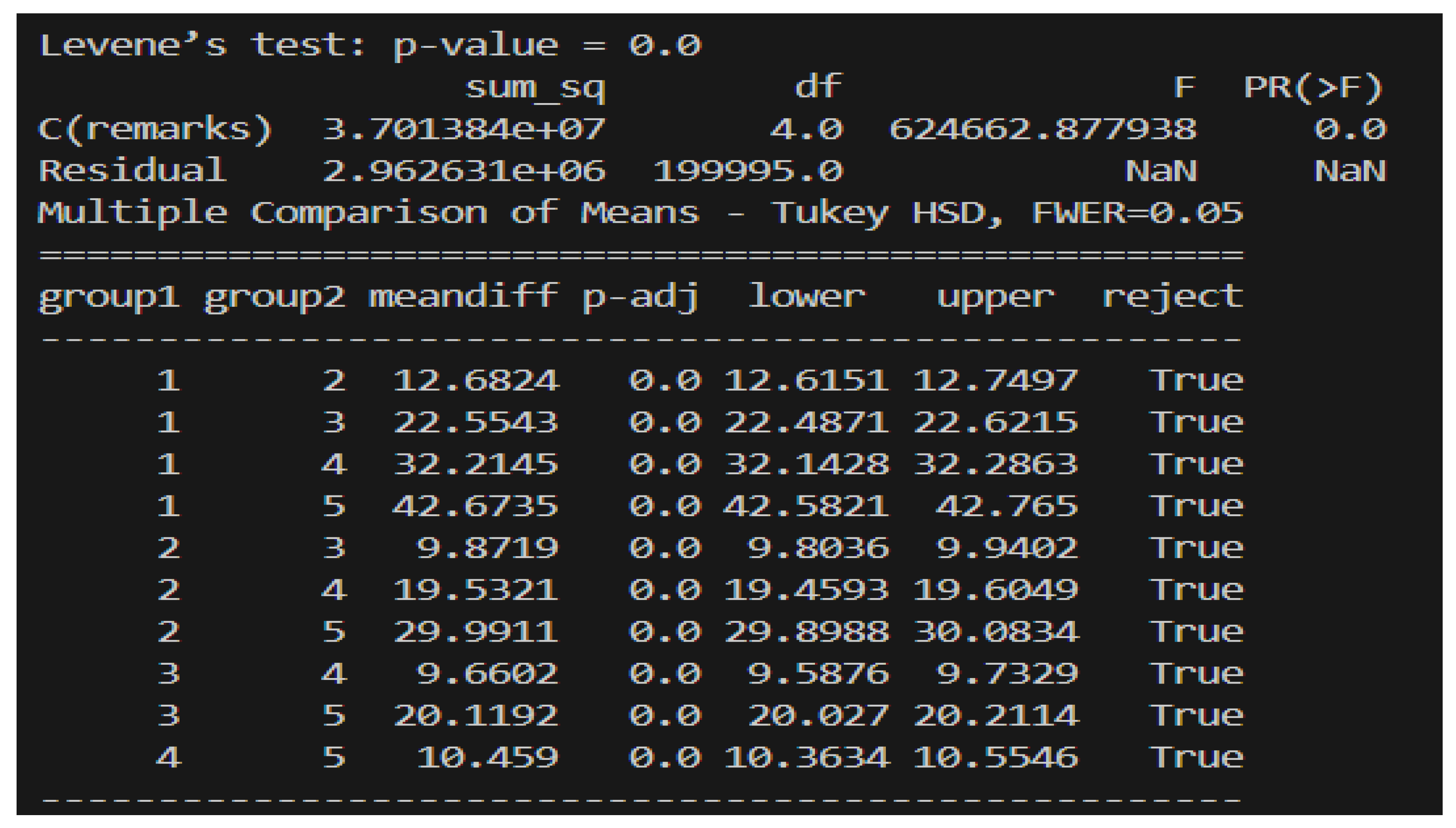
3.2.2. Data Analysis
3.2.3. Data Preprocessing
| Algorithm 2: Data Preprocessing |
| dataPreprocessing(dataset) |
| Load the dataset from the CSV file |
| Extract features as X and target variables as y_total and y_remarks |
| Adjust y_remarks for zero-based indexing by subtracting 1 |
| Reshape X to fit the LSTM input format (samples, timesteps, features) |
| Split the dataset into training and testing sets: |
| X_train, X_test |
| y_total_train, y_total_test |
| y_remarks_train, y_remarks_test |
| Define the input shape for the LSTM network based on the reshaped data |
| end dataPreprocessing |
3.2.4. The Model
4. Results and Discussions
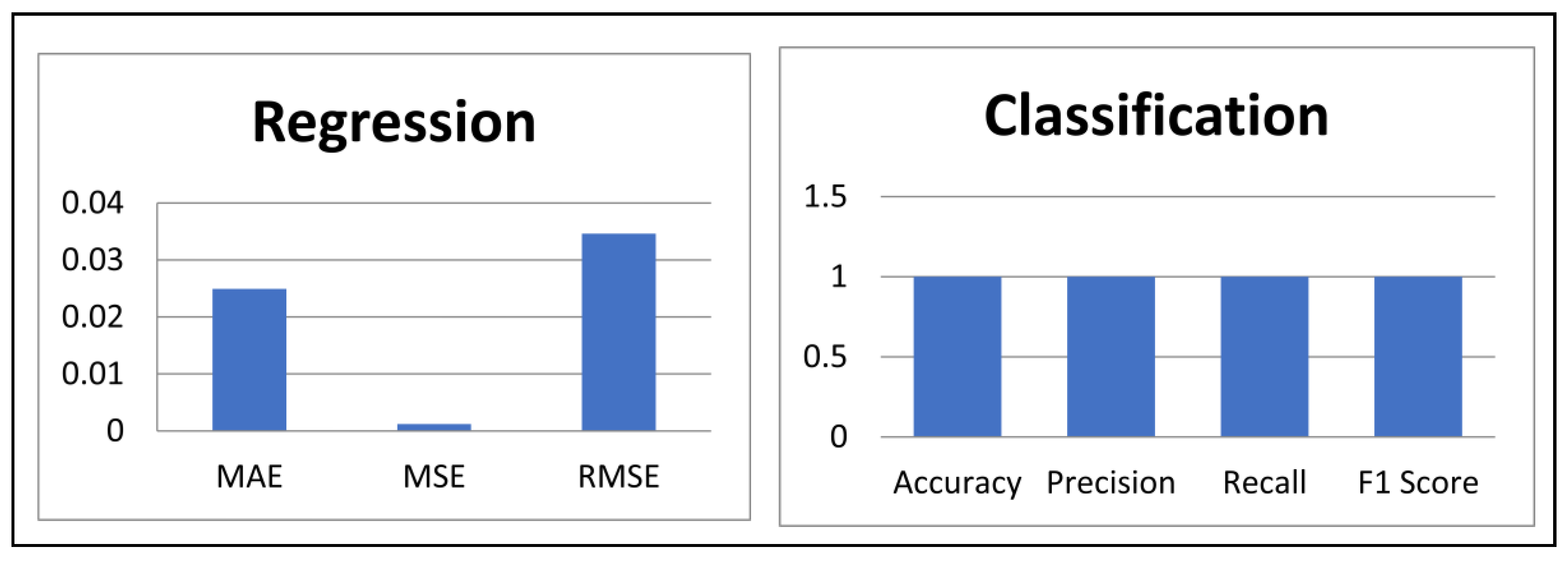
4.1. Performance Evaluation Metrics
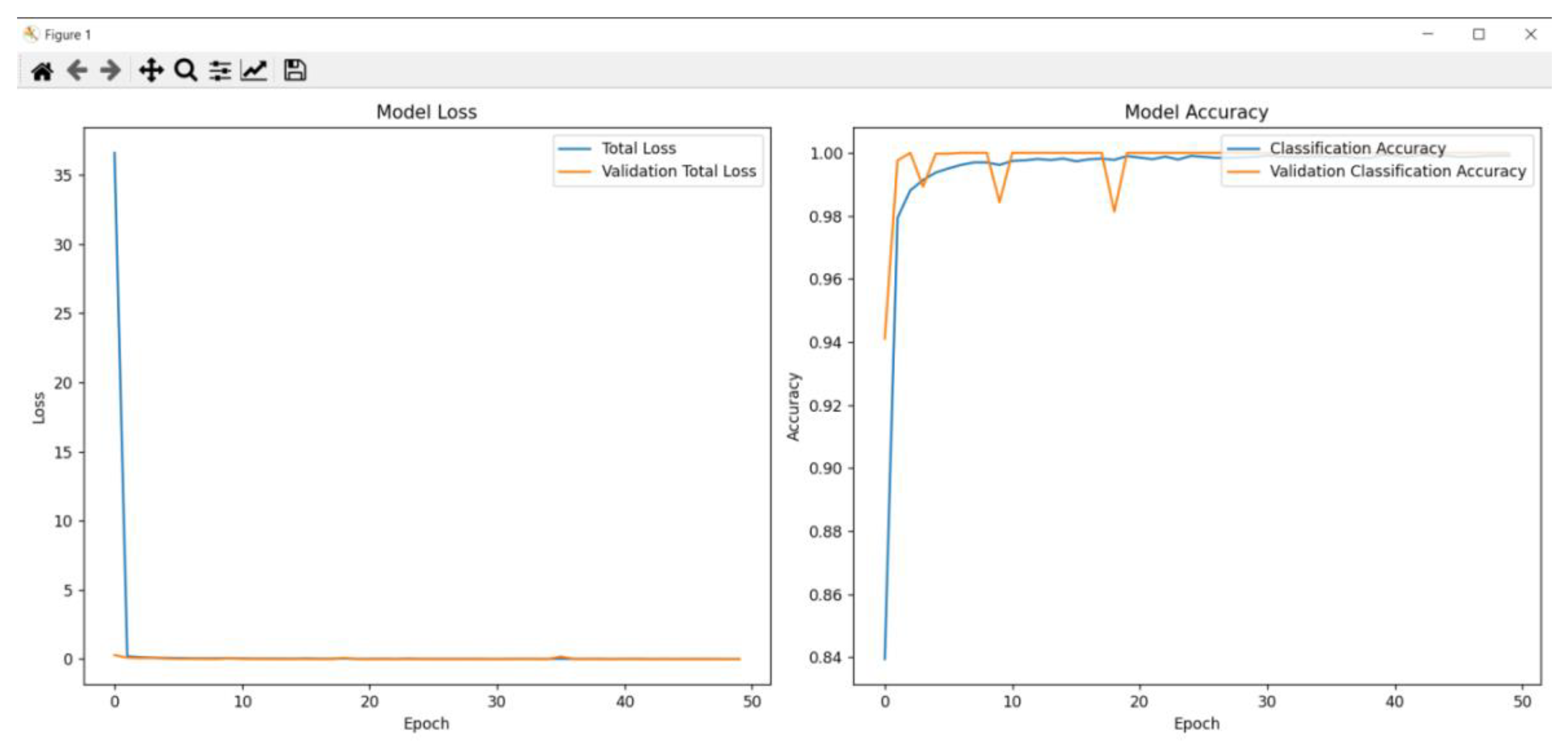
4.2. Training and Evaluation Results
4.3. Comparative Analysis
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Suskie: L. (2018). Assessing student learning: A common sense guide. John Wiley & Sons.
- Scully, D. (2019). Constructing multiple-choice items to measure higher-order thinking. Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation, 22(1), 4.
- Morley, J., Floridi, L., Kinsey, L., & Elhalal, A. (2020). From what to how: an initial review of publicly available AI ethics tools, methods and research to translate principles into practices. Science and engineering ethics, 26(4), 2141-2168. [CrossRef]
- Wei, L. (2024). Transformative pedagogy for inclusion and social justice through translanguaging, co-learning, and transpositioning. Language Teaching, 57(2), 203-214.
- Say, R., Visentin, D., Saunders, A., Atherton, I., Carr, A., & King, C. (2024). Where less is more: Limited feedback in formative online multiple-choice tests improves student self-regulation. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 40(1), 89-103. [CrossRef]
- Li, S., Zhang, X., Li, Y., Gao, W., Xiao, F., & Xu, Y. (2023). A comprehensive review of impact assessment of indoor thermal environment on work and cognitive performance-Combined physiological measurements and machine learning. Journal of Building Engineering, 106417. [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, M. C., & Bowling, N. A. (2024). Building a bigger toolbox: The construct validity of existing and proposed measures of careless responding to cognitive ability tests. Organizational Research Methods, 10944281231223127. [CrossRef]
- Maki, P. L. (2023). Assessing for learning: Building a sustainable commitment across the institution. Routledge.
- Geletu, G. M., & Mihiretie, D. M. (2023). Professional accountability and responsibility of learning communities of practice in professional development versus curriculum practice in classrooms: Possibilities and pathways. International Journal of Educational Research Open, 4, 100223. [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R. (2023). Measurement, evaluation and assessment in education. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.
- Yuksel, P., & Bailey, J. (2024). Designing a Holistic Syllabus: A Blueprint for Student Motivation, Learning Efficacy, and Mental Health Engagement. In Innovative Instructional Design Methods and Tools for Improved Teaching (pp. 92-108). IGI Global. [CrossRef]
- Thornhill-Miller, B., Camarda, A., Mercier, M., Burkhardt, J. M., Morisseau, T., Bourgeois-Bougrine, S., ... & Lubart, T. (2023). Creativity, critical thinking, communication, and collaboration: assessment, certification, and promotion of 21st century skills for the future of work and education. Journal of Intelligence, 11(3), 54. [CrossRef]
- Zughoul, O., Momani, F., Almasri, O. H., Zaidan, A. A., Zaidan, B. B., Alsalem, M. A., ... & Hashim, M. (2018). Comprehensive insights into the criteria of student performance in various educational domains. IEEE access, 6, 73245-73264. [CrossRef]
- AlAfnan, M. A., & Dishari, S. (2024). ESD goals and soft skills competencies through constructivist approaches to teaching: an integrative review. Journal of Education and Learning (EduLearn), 18(3), 708-718. [CrossRef]
- Wong, Z. Y., & Liem, G. A. D. (2022). Student engagement: Current state of the construct, conceptual refinement, and future research directions. Educational Psychology Review, 34(1), 107-138. [CrossRef]
- Al-Adwan, A. S., Albelbisi, N. A., Hujran, O., Al-Rahmi, W. M., & Alkhalifah, A. (2021). Developing a holistic success model for sustainable e-learning: A structural equation modeling approach. Sustainability, 13(16), 9453. [CrossRef]
- Zaffar, M., Garg, S., Milford, M., Kooij, J., Flynn, D., McDonald-Maier, K., & Ehsan, S. (2021). Vpr-bench: An open-source visual place recognition evaluation framework with quantifiable viewpoint and appearance change. International Journal of Computer Vision, 129(7), 2136-2174. [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, B., Rouleau, K., Abla, C., Baptiste, K., Gibson, T., & Kimball, M. (2022). The new classroom instruction that works: The best research-based strategies for increasing student achievement. ASCD.
- Sebbaq, H. (2023). MTBERT-Attention: An Explainable BERT Model based on Multi-Task Learning for Cognitive Text Classification. Scientific African, 21, e01799. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H., Zhu, Y., Zang, T., Xu, Y., Yu, J., & Tang, F. (2021). Jointly modeling heterogeneous student behaviors and interactions among multiple prediction tasks. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data (TKDD), 16(1), 1-24. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y. (2021). Student performance prediction via attention-based multi-layer long-short term memory. Journal of Computer and Communications, 9(8), 61-79. [CrossRef]
- He, L., Li, X., Wang, P., Tang, J., & Wang, T. (2023). Integrating fine-grained attention into multi-task learning for knowledge tracing. World Wide Web, 26(5), 3347-3372. [CrossRef]
- Su, Y., Yang, X., Lu, J., Liu, Y., Han, Z., Shen, S., ... & Liu, Q. (2024). Multi-task Information Enhancement Recommendation model for educational Self-Directed Learning System. Expert Systems with Applications, 252, 124073. [CrossRef]
- Ren, X., Yang, W., Jiang, X., Jin, G., & Yu, Y. (2022). A deep learning framework for multimodal course recommendation based on LSTM+ attention. Sustainability, 14(5), 2907. [CrossRef]
| x1 | x2 | x3 | x4 | x5 | x6 | x7 | total | remarks |
| 7 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 22 | 46 | 2 |
| 7 | 2 | 5 | 9 | 6 | 8 | 39 | 76 | 5 |
| 7 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 7 | 30 | 62 | 4 |
| 5 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 22 | 49 | 2 |
| 5 | 4 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 14 | 46 | 2 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 35 | 55 | 3 |
| 5 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 6 | 39 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 35 | 61 | 4 |
| 3 | 10 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 10 | 26 | 63 | 4 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 25 | 1 |
| 8 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 43 | 2 |
| 8 | 7 | 10 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 35 | 75 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 20 | 55 | 3 |
| 5 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 9 | 9 | 41 | 2 |
| 2 | 8 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 41 | 2 |
| 2 | 8 | 9 | 6 | 8 | 3 | 34 | 70 | 5 |
| 2 | 9 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 26 | 1 |
| Author | Focus Area | Techniques Used | Metrics | Gaps | Proposed Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu et al. (2021) | Prediction of student behavior | LSTM with soft-attention mechanism | Effective in predicting student behaviors and improving academic outcomes | Does not consider holistic student performance, limited to behavior prediction | Uses LSTM with multi-task learning for both regression and classification |
| Xie (2021) | Predicting student performance | Attention-based Multi-layer LSTM (AML) | Improved prediction accuracy and F1 score using demographic and clickstream data | Limited to performance prediction, lacks comprehensive metric integration | Combines various metrics for a complete evaluation of student performance |
| Ren et al. (2022) | Course recommendation | Deep course recommendation model with LSTM and Attention | Higher AUC scores in course recommendations | Focuses on course recommendations, lacks integration of diverse metrics | Integrates multimodal data for comprehensive student performance evaluation |
| He et al. (2023) | Knowledge Tracing (KT) | Multi-task Attentive Knowledge Tracing (MAKT) | Improved prediction accuracy in KT tasks | Focuses on KT, does not address real-time feedback or holistic evaluation | Provides real-time feedback, integrates multiple metrics for holistic evaluation |
| Sebbaq (2023) | Cognitive classification of text | Multi-task BERT (MTBERT-Attention) with co-attention mechanism | Superior performance and explainability in text classification | Focuses on text classification only, lacks holistic student evaluation | Integrates multiple performance metrics, captures complex relationships |
| Su et al. (2024) | Cross-type recommendation in SDLS | Multi-task Information Enhancement Recommendation (MIER) Model with attention and knowledge graph | Superior performance in concept prediction and exercise recommendation | Limited to recommendation systems, does not provide holistic student evaluation | Utilizes attention mechanisms for comprehensive evaluation of multiple student metrics |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





