Submitted:
07 September 2024
Posted:
09 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
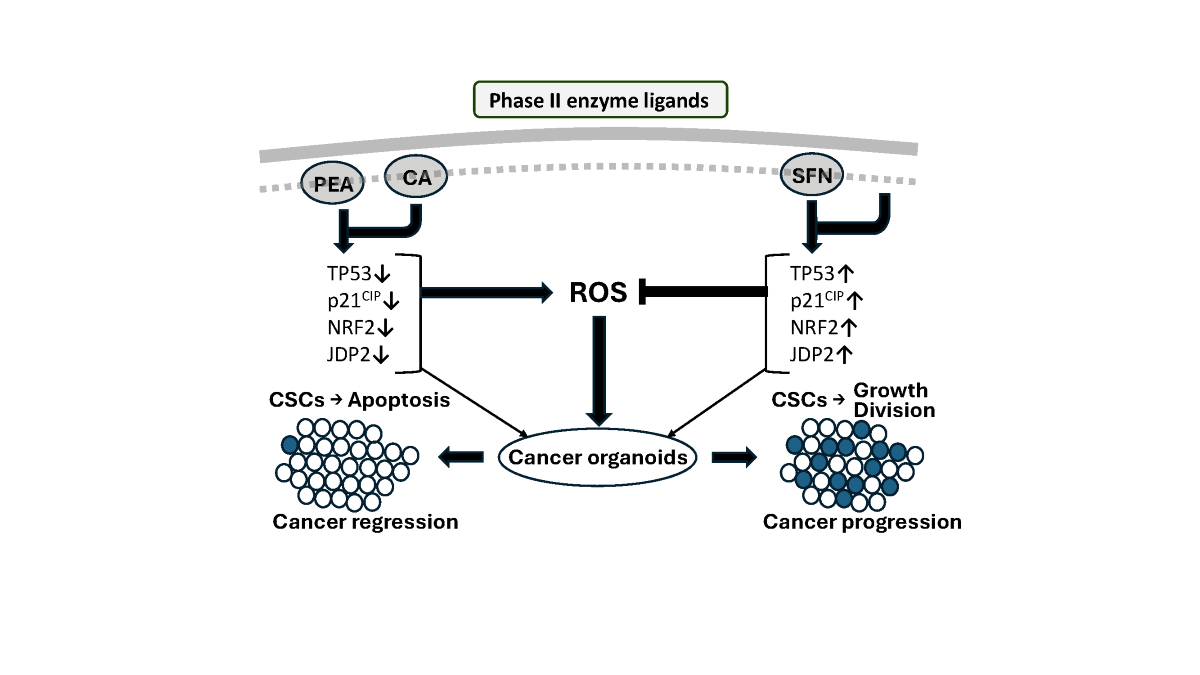
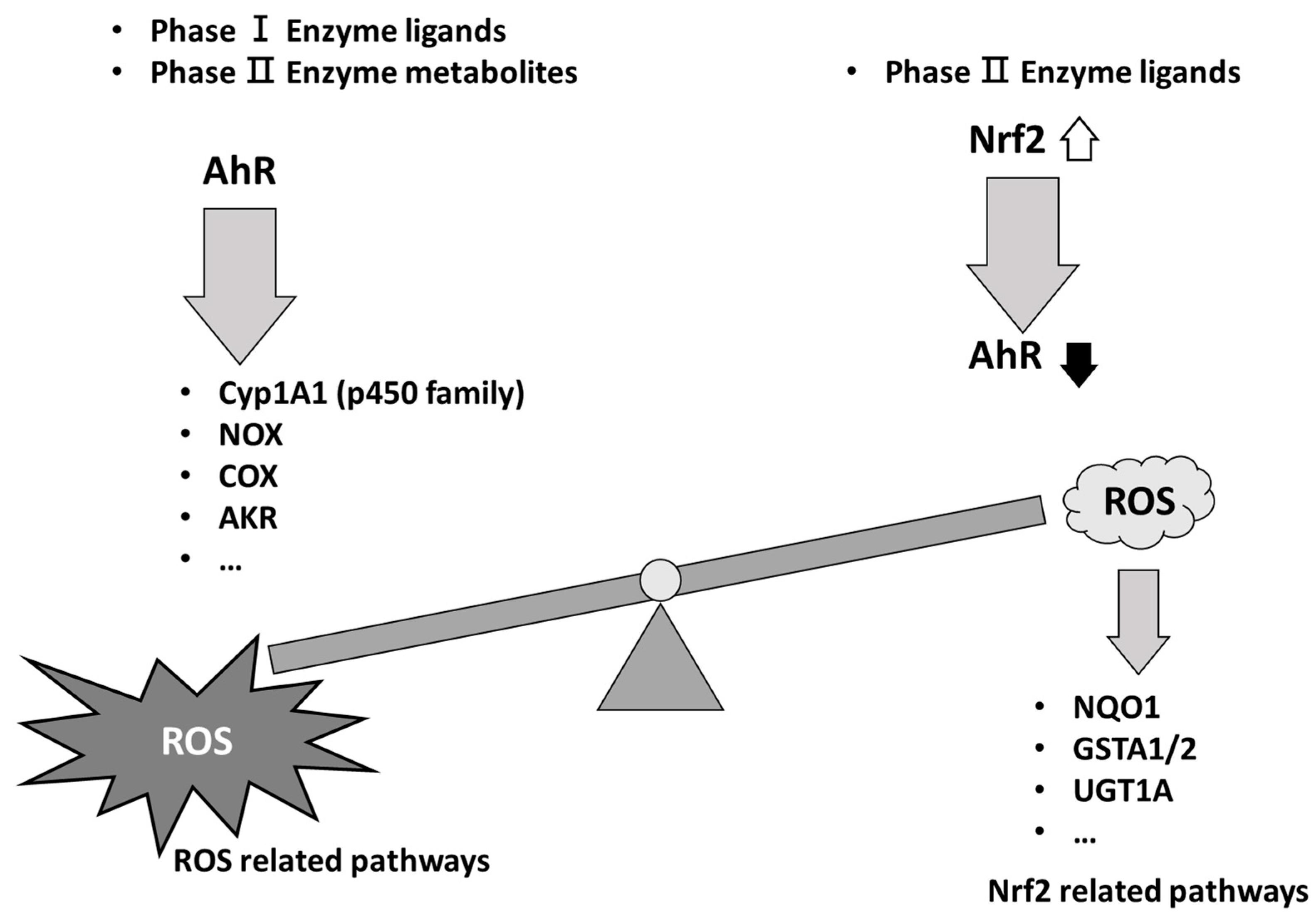
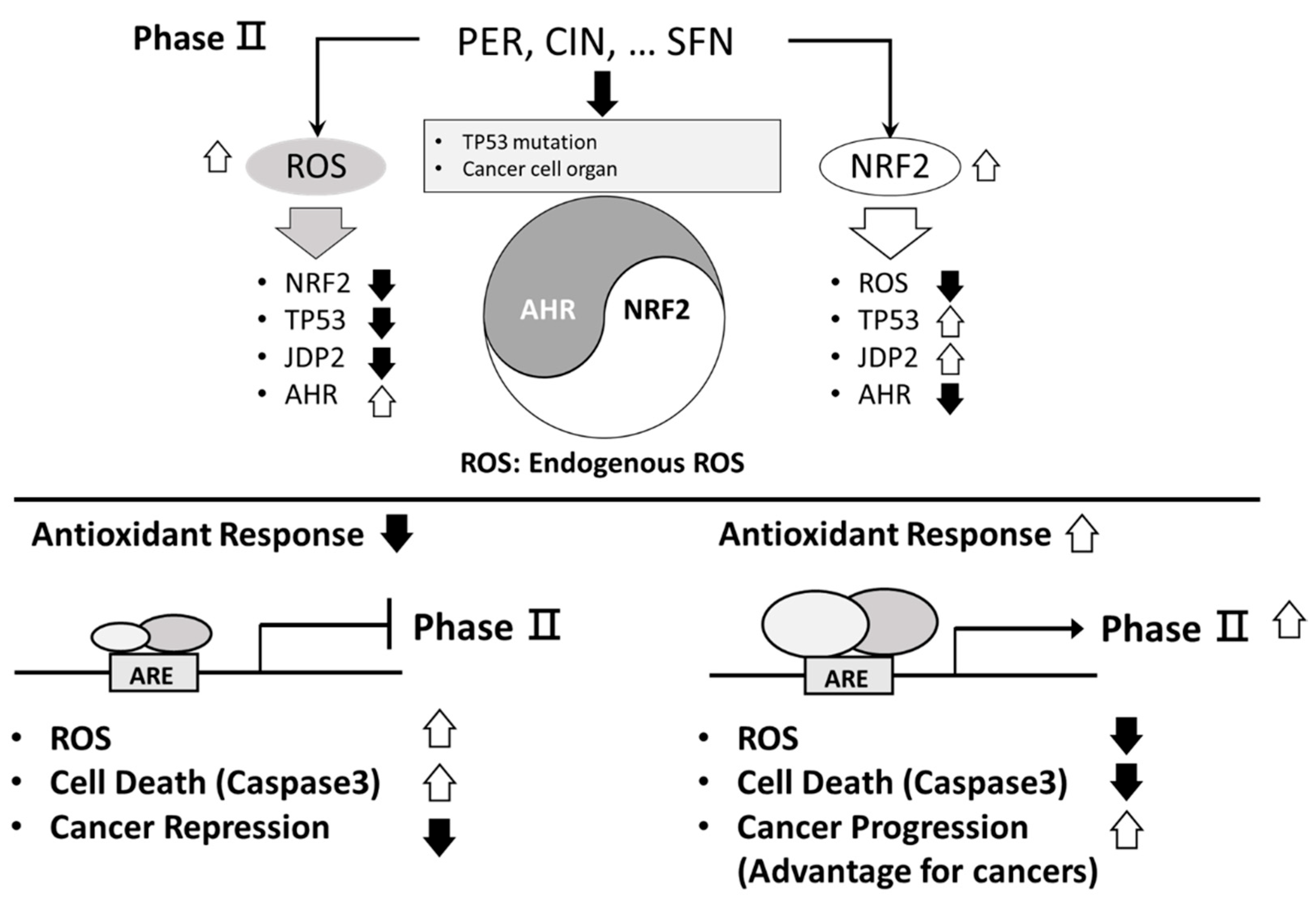
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. ROS in Cancer Cells
3. NRF2 Has Dual Roles in Tumorigenesis
3.1. Tumor Suppressive Actions of NRF2
3.2. Oncogenic Functions of NRF2
4. NRF2-Tragetted Drugs in Cancer Prevention
Heterogeneity of Antioxidation Drugs against Cancer
5. Phase I Drugs in Clinical Trials
6. Phase II Drugs in Clinical Trials
7. Discussion
Funding
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
Data Availability
Acknowledgments
Abbreviations
| AhR | aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| AP-1 | Activation protein-1 |
| ARE | antioxidant response element |
| BAX | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
| BCL2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| BCRP | breast cancer-resistant protein |
| BRCA1 | breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 |
| CBP | CREB binding protein |
| CDKN1A | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 |
| CE | cinnamaldehyde |
| COX2 | cyclooxygenase 2 |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| CREB | cyclic AMP response element binding protein |
| CSCs | cancer stem cells |
| DPx2 | glutathione peroxidase 2 |
| DSS | dextran sodium sulfate |
| EMT | epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| ERBB2 | Erb-B2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 2 |
| GC | gastric cancer |
| GLUTs | glucose transporters |
| G6PD | glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GPR78 | glucose-regulated protein 78 |
| GSH | glutathione-SH |
| GSK3 | glycogen synthetase kinase 3 |
| GSSG | glutathione sulfide |
| H2O2 | hydrogen peroxide |
| HIF-1β | hypoxia inducible factor beta |
| HNSCC | head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| HO-1 | heme oxygenase 1 |
| 3-IAld | indole-3-aldehyde |
| ICI | immune checkpoint inhibitor |
| IKK-α:-β | inhibitor of nuclear factor κB kinase subunit-α,-β |
| IPA | Ingenuity pathway analysis |
| iNOS | nitric oxide synthase |
| JDP2 | Jun dimerization protein 2 |
| JNKs | c-Jun N-terminal kinases |
| Keap1 | Kelch like ECH associated protein 1 |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MARCO | macrophage receptor with collagenous structure |
| MDR1 | multidrug resistance protein 1 |
| MRP1-5 | multidrug resistance-associated protein 1-5 |
| MSCs | mesenchymal stem cells |
| NAC | N-acetylcysteine |
| NFkB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| NO | nitrogen oxide |
| NQO1 | NAD(P)H:quinone dehydrogenase 1 |
| NRF2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cance |
| OXPHOS | oxidative phosphorylation |
| PEA | perillaldehyde |
| PGD | phosphoglucomutase dehydrogenase |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| p-PERK | phosphorylated protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase |
| PSMA2 | proteasome 20S alpha 2 |
| PSMC4 | 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 4 |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SFN | sulforaphane |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| SQSRM1 | sequestosome-1 |
| TALDO1 | trans-aldolase |
| TBK1 | TANK-binding kinase 2 |
| TKT | transketolase |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| β-TrCP | β-transduction repeat-containing E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase |
| Trx | thioredoxin |
| TrxR1 | thioredoxin reductase 1 |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| x-CT = SLC7a11 cystine/glutamate transporter | |
References
- C. Gorrini, I.S.; Harris, T.W.; Mak, Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 12 (12) (2013) 931-947. [CrossRef]
- F.; Xing, Q.; Hu, Y.; Qin, J.; Xu, B. Zhang, et al., The Relationship of Redox With Hallmarks of Cancer: The Importance of Homeostasis and Context, Front. Oncol. 12 (2022) 862743. [CrossRef]
- B.; Perillo, M. Di Donato, A.; Pezone, E. Di Zazzo, P. Giovannelli, et al., ROS in cancer therapy: the bright side of the moon, Exp. Mol. Med. 52 (2) (2020) 192-203. [CrossRef]
- D.L.; Kirkpatrick, G.; Powis, Clinically Evaluated Cancer Drugs Inhibiting Redox Signaling, Antioxid. Redox Signal. 26 (6) (2017) 262-273. [CrossRef]
- X.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, K.; Li, S.; Liu, Nanomaterials-Induced Redox Imbalance: Challenged and Opportunities for Nanomaterials in Cancer Therapy, Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11 (16) (2024) e2308632. [CrossRef]
- D.C.; Wu, C.C.; Ku, J.B.; Pan, K.; Wuputra, Y.H. Yang, et al., Heterogeneity of Phase II Enzyme Ligands on Controlling the Progression of Human Gastric Cancer Organoids as Stem Cell Therapy Model, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (21) (2023) 15911. [CrossRef]
- P.; Poprac, K.; Jomova, M.; Simunkova, V.; Kollar, C.J. Rhodes, et al., Targeting Free Radicals in Oxidative Stress-Related Human Diseases, Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 38 (7) (2017) 592-607. [CrossRef]
- S.; Liu, M.; Yue, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S. Luo, et al., Advancing the frontiers of colorectal cancer treatment: harnessing ferroptosis regulation, Apoptosis 29 (1-2) (2024) 86-102. [CrossRef]
- C.J.; Schmidlin, A.; Shakya, M.; Dodson, E.; Chapman, D.D.; Zhang, The intricacies of NRF2 regulation in cancer, Semin. Cancer Biol. 76 (2021) 110-119. [CrossRef]
- M.R.I.; Young, Y.; Xiong, Influence of vitamin D on cancer risk and treatment: Why the variability?, Trends Cancer Res. 13 (2018) 43-53.
- R.; Bakalova, Z.; Zhelev, T.; Miller, I.; Aoki, T.; Higashi, New potential biomarker for stratification of patients for pharmacological vitamin C in adjuvant settings of cancer therapy, Redox Biol. 28 (2020) 101357. [CrossRef]
- F.; Augsburger, A.; Filippova, D.; Rasti, T.; Seredenina, M. Lam, et al., Pharmacological characterization of the seven human NOX isoforms and their inhibitors, Redox Biol. 26 (2019) 101272. [CrossRef]
- S.; Liang, H.Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhong, D.; Dhar, X. Liu, et al., NADPH Oxidase 1 in Liver Macrophages Promotes Inflammation and Tumor Development in Mice, Gastroenterology 156 (4) (2019) 1156-1172.e6. [CrossRef]
- ; Spasojevic, Mn Porphyrin-Based Redox-Active Drugs: Differential Effects as Cancer Therapeutics and Protectors of Normal Tissue Against Oxidative Injury, Antioxid. Redox Signal. 29 (16) (2018) 1691-1724. [CrossRef]
- Z.Y.; Wu, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, I.Y.; Chung, J.S. Kim, et al., Breast Cancer Recurrence in the Nipple-Areola Complex After Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy With Immediate Breast Reconstruction for Invasive Breast Cancer, JAMA Surg. 154 (11) (2019) 1030-1037. [CrossRef]
- J.H.; Wu, G.; Batist, Glutathione and glutathione analogues; therapeutic potentials, Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1830 (5) (2013) 3350-3353. [CrossRef]
- X.; Luo, C.; Cheng, Z.; Tan, N.; Li, M. Tang, et al., Emerging roles of lipid metabolism in cancer metastasis, Mol. Cancer 16 (1) (2017) 76. [CrossRef]
- H.S. Selistre-de-Araujo, B.C.; Pachane, W.F.; Altei, Tumor heterogeneity and the dilemma of antioxidant therapies in cancer, Ann. Transl. Med. 10 (19) (2022) 1074. [CrossRef]
- S.; Wu, H.; Lu, Y.; Bai, Nrf2 in cancers: A double-edged sword, Cancer Med. 8 (5) (2019) 2252-2267. [CrossRef]
- H.; Jiang, J.; Zuo, B.; Li, R.; Chen, K. Luo, et al., Drug-induced oxidative stress in cancer treatments: Angel or devil?, Redox Biol. 63 (2023) 102754. [CrossRef]
- C.; Gorrini, P.S.; Baniasadi, I.S.; Harris, J.; Silvester, S. Inoue, et al., BRCA1 interacts with Nrf2 to regulate antioxidant signaling and cell survival, J. Exp. Med. 210 (8) (2013) 1529-1544. [CrossRef]
- W.; Chen, Z.; Sun, X.J.; Wang, T.; Jiang, Z. Huang, et al., Direct interaction between Nrf2 and p21(Cip1/WAF1) upregulates the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response, Mol. Cell 34 (6) (2009) 663-673. [CrossRef]
- S.K.; Niture, R.; Khatri, A.K.; Jaiswal, Regulation of Nrf2-an update, Free Radic. Biol. Med. 66 (2014) 36-44. [CrossRef]
- D.J. Long, 2nd, R.L.; Waikel, X.J.; Wang, L.; Perlaky, D.R. Roop, et al., NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 deficiency increases susceptibility to benzo(a)pyrene-induced mouse skin carcinogenesis, Cancer Res. 60 (21) (2000) 5913-5915.
- M. Ramos-Gomez, M.K.; Kwak, P.M.; Dolan, K.; Itoh, M. Yamamoto, et al., Sensitivity to carcinogenesis is increased and chemoprotective efficacy of enzyme inducers is lost in nrf2 transcription factor-deficient mice, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98 (6) (2001) 3410-3415. [CrossRef]
- Y.; Kitamura, T.; Umemura, K.; Kanki, Y.; Kodama, S. Kitamoto, et al., Increased susceptibility to hepatocarcinogenicity of Nrf2-deficient mice exposed to 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline, Cancer Sci. 98 (1) (2007) 19-24. [CrossRef]
- K.; Iida, K.; Itoh, J.M.; Maher, Y.; Kumagai, R. Oyasu, et al., Nrf2 and p53 cooperatively protect against BBN-induced urinary bladder carcinogenesis, Carcinogenesis 28 (11) (2007) 2398-2403. [CrossRef]
- N.; Wakabayashi, A.T. Dinkova-Kostova, W.D.; Holtzclaw, M.I.; Kang, A. Kobayashi, et al., Protection against electrophile and oxidant stress by induction of the phase 2 response: fate of cysteines of the Keap1 sensor modified by inducers, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101 (7) (2004) 2040-2045. [CrossRef]
- L. Gamet-Payrastre, P.; Li, S.; Lumeau, G.; Cassar, M.A. Dupont, et al., Sulforaphane, a naturally occurring isothiocyanate, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT29 human colon cancer cells, Cancer Res. 60 (5) (2000) 1426-1433.
- E.; Heiss, C.; Herhaus, K.; Klimo, H.; Bartsch, C.; Gerhauser, Nuclear factor kappa B is a molecular target for sulforaphane-mediated anti-inflammatory mechanisms, J. Biol. Chem. 276 (34) (2001) 32008-32015. [CrossRef]
- S.E.; Dickinson, T.F.; Melton, E.R.; Olson, J.; Zhang, K. Saboda, et al., Inhibition of activator protein-1 by sulforaphane involves interaction with cysteine in the cFos DNA-binding domain: implications for chemoprevention of UVB-induced skin cancer, Cancer Res. 69 (17) (2009) 7103-7110. [CrossRef]
- K.T.; Liby, D.B.; Royce, R.; Risingsong, C.R.; Williams, A. Maitra, et al., Synthetic triterpenoids prolong survival in a transgenic mouse model of pancreatic cancer, Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 3 (11) (2010) 1427-1434. [CrossRef]
- E.H.; Kim, C.; Deng, M.B.; Sporn, D.B.; Royce, R. Risingsong, et al., CDDO-methyl ester delays breast cancer development in BRCA1-mutated mice, Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 5 (1) (2012) 89-97. [CrossRef]
- S.S.; Boyanapalli, X. Paredes-Gonzalez, F.; Fuentes, C.; Zhang, Y. Guo, et al., Nrf2 knockout attenuates the anti-inflammatory effects of phenethyl isothiocyanate and curcumin, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 27 (12) (2014) 2036-2043. [CrossRef]
- E.H.; Kobayashi, T.; Suzuki, R.; Funayama, T.; Nagashima, M. Hayashi, et al., Nrf2 suppresses macrophage inflammatory response by blocking proinflammatory cytokine transcription, Nat. Commun. 7 (2016) 11624. [CrossRef]
- X.; Kong, R.; Thimmulappa, F.; Craciun, C.; Harvey, A. Singh, et al., Enhancing Nrf2 pathway by disruption of Keap1 in myeloid leukocytes protects against sepsis, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 184 (8) (2011) 928-938. [CrossRef]
- X.L.; Chen, G.; Dodd, S.; Thomas, X.; Zhang, M.A. Wasserman, et al., Activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway protects endothelial cells from oxidant injury and inhibits inflammatory gene expression, Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 290 (5) (2006) H1862-1870. [CrossRef]
- J.E.; Kim, D.J.; You, C.; Lee, C.; Ahn, J.Y. Seong, et al., Suppression of NF-kappaB signaling by KEAP1 regulation of IKKbeta activity through autophagic degradation and inhibition of phosphorylation, Cell Signal. 22 (11) (2010) 1645-1654. [CrossRef]
- W.; Gao, L.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S. Xia, et al., Dissecting the Crosstalk Between Nrf2 and NF-kappaB Response Pathways in Drug-Induced Toxicity, Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9 (2021) 809952. [CrossRef]
- Y.C.; Kim, H.; Masutani, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Itoh, M. Yamamoto, et al., Hemin-induced activation of the thioredoxin gene by Nrf2. A differential regulation of the antioxidant responsive element by a switch of its binding factors, J. Biol. Chem. 276 (21) (2001) 18399-18406. [CrossRef]
- N.; Hanada, T.; Takahata, Q.; Zhou, X.; Ye, R. Sun, et al., Methylation of the KEAP1 gene promoter region in human colorectal cancer, BMC Cancer 12 (2012) 66. [CrossRef]
- G.M. DeNicola, F.A.; Karreth, T.J.; Humpton, A.; Gopinathan, C. Wei, et al., Oncogene-induced Nrf2 transcription promotes ROS detoxification and tumorigenesis, Nature 475 (7354) (2011) 106-109. [CrossRef]
- A.I.; Rojo, P.; Rada, M.; Mendiola, A. Ortega-Molina, K. Wojdyla, et al., The PTEN/NRF2 axis promotes human carcinogenesis, Antioxid. Redox Signal. 21 (18) (2014) 2498-2514. [CrossRef]
- Y.; Mitsuishi, K.; Taguchi, Y.; Kawatani, T.; Shibata, T. Nukiwa, et al., Nrf2 redirects glucose and glutamine into anabolic pathways in metabolic reprogramming, Cancer Cell 22 (1) (2012) 66-79. [CrossRef]
- N.R.; Kitteringham, A.; Abdullah, J.; Walsh, L.; Randle, R.E. Jenkins, et al., Proteomic analysis of Nrf2 deficient transgenic mice reveals cellular defence and lipid metabolism as primary Nrf2-dependent pathways in the liver, J. Proteomics 73 (8) (2010) 1612-1631. [CrossRef]
- D.; Malhotra, E. Portales-Casamar, A.; Singh, S.; Srivastava, D. Arenillas, et al., Global mapping of binding sites for Nrf2 identifies novel targets in cell survival response through ChIP-Seq profiling and network analysis, Nucleic Acids Res. 38 (17) (2010) 5718-5734. [CrossRef]
- N.M.; Reddy, S.R.; Kleeberger, J.H.; Bream, P.G.; Fallon, T.W. Kensler, et al., Genetic disruption of the Nrf2 compromises cell-cycle progression by impairing GSH-induced redox signaling, Oncogene 27 (44) (2008) 5821-5832. [CrossRef]
- C.W.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, Y.G.; Tsay, C.L.; Han, Y.J. Chen, et al., ROS-independent ER stress-mediated NRF2 activation promotes warburg effect to maintain stemness-associated properties of cancer-initiating cells, Cell Death Dis. 9 (2) (2018) 194. [CrossRef]
- C.W.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, S.H.; Chou, C.L.; Han, Y.J. Chen, et al., Distinct subpopulations of head and neck cancer cells with different levels of intracellular reactive oxygen species exhibit diverse stemness, proliferation, and chemosensitivity, Cancer Res. 74 (21) (2014) 6291-6305. [CrossRef]
- H.; Kumar, R.M.; Kumar, D.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Somanna, V.; Jain, Role of Nrf2 Signaling Cascade in Breast Cancer: Strategies and Treatment, Front. Pharmacol. 13 (2022) 720076. [CrossRef]
- I.G.; Ryoo, S.H.; Lee, M.K.; Kwak, Redox Modulating NRF2: A Potential Mediator of Cancer Stem Cell Resistance, Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016 (2016) 2428153. [CrossRef]
- A.; Singh, S. Boldin-Adamsky, R.K.; Thimmulappa, S.K.; Rath, H. Ashush, et al., RNAi-mediated silencing of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer inhibits tumor growth and increases efficacy of chemotherapy, Cancer Res. 68 (19) (2008) 7975-7984. [CrossRef]
- T.; Yasuda, T.; Ishimoto, H.; Baba, Conflicting metabolic alterations in cancer stem cells and regulation by the stromal niche, Regen. Ther. 17 (2021) 8-12. [CrossRef]
- L.; Gao, Y.; Morine, S.; Yamada, Y.; Saito, T. Ikemoto, et al., Nrf2 signaling promotes cancer stemness, migration, and expression of ABC transporter genes in sorafenib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cells, PLoS One 16 (9) (2021) e0256755. [CrossRef]
- H.; Kahroba, M.; Shirmohamadi, M.S.; Hejazi, N.; Samadi, The Role of Nrf2 signaling in cancer stem cells: From stemness and self-renewal to tumorigenesis and chemoresistance, Life Sci. 239 (2019) 116986. [CrossRef]
- S.M.; Ridge, F.J.; Sullivan, S.A.; Glynn, Mesenchymal stem cells: key players in cancer progression, Mol. Cancer 16 (1) (2017) 31. [CrossRef]
- M. Mohammadzadeh-Vardin, M. Habibi Roudkenar, A. Jahanian-Najafabadi, Adenovirus-Mediated Over-Expression of Nrf2 Within Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Protected Rats Against Acute Kidney Injury, Adv. Pharm. Bull 5 (2) (2015) 201-208. [CrossRef]
- Z.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W. Liu, et al., NRF2 overexpression in mesenchymal stem cells induces stem-cell marker expression and enhances osteoblastic differentiation, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 491 (1) (2017) 228-235. [CrossRef]
- H.; Kitamura, H.; Motohashi, NRF2 addiction in cancer cells, Cancer Sci. 109 (4) (2018) 900-911. [CrossRef]
- K.; Okazaki, T.; Papagiannakopoulos, H.; Motohashi, Metabolic features of cancer cells in NRF2 addiction status, Biophys. Rev. 12 (2) (2020) 435-441. [CrossRef]
- S.; Zhou, W.; Ye, M.; Zhang, J.; Liang, The effects of nrf2 on tumor angiogenesis: a review of the possible mechanisms of action, Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 22 (2) (2012) 149-160. [CrossRef]
- B.; Bussolati, J.C.; Mason, Dual role of VEGF-induced heme-oxygenase-1 in angiogenesis, Antioxid. Redox Signal. 8 (7-8) (2006) 1153-1163. [CrossRef]
- S.A.; Rushworth, D.J. MacEwan, HO-1 underlies resistance of AML cells to TNF-induced apoptosis, Blood 111 (7) (2008) 3793-3801. [CrossRef]
- S.K.; Niture, A.K.; Jaiswal, Nrf2 protein up-regulates antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 and prevents cellular apoptosis, J. Biol. Chem. 287 (13) (2012) 9873-9886. [CrossRef]
- R.; Elsby, N.R.; Kitteringham, C.E.; Goldring, C.A.; Lovatt, M. Chamberlain, et al., Increased constitutive c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling in mice lacking glutathione S-transferase Pi, J. Biol. Chem. 278 (25) (2003) 22243-22249. [CrossRef]
- A.; Jain, T.; Lamark, E.; Sjottem, K.B.; Larsen, J.A. Awuh, et al., p62/SQSTM1 is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element-driven gene transcription, J. Biol. Chem 285 (29) (2010) 22576-22591. [CrossRef]
- M.; Komatsu, H.; Kurokawa, S.; Waguri, K.; Taguchi, A. Kobayashi, et al., The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1, Nat. Cell Biol. 12 (3) (2010) 213-223. [CrossRef]
- C.G.; Towers, B.E.; Fitzwalter, D.; Regan, A.; Goodspeed, M.J. Morgan, et al., Cancer Cells Upregulate NRF2 Signaling to Adapt to Autophagy Inhibition, Dev. Cell 50 (6) (2019) 690-703 e696. [CrossRef]
- K.; Taguchi, I.; Hirano, T.; Itoh, M.; Tanaka, A. Miyajima, et al., Nrf2 enhances cholangiocyte expansion in Pten-deficient livers, Mol. Cell Biol. 34 (5) (2014) 900-913. [CrossRef]
- K.; Shirasaki, K.; Taguchi, M.; Unno, H.; Motohashi, M.; Yamamoto, NF-E2-related factor 2 promotes compensatory liver hypertrophy after portal vein branch ligation in mice, Hepatology 59 (6) (2014) 2371-2382. [CrossRef]
- T.; Suzuki, S.; Seki, K.; Hiramoto, E.; Naganuma, E.H. Kobayashi, et al., Hyperactivation of Nrf2 in early tubular development induces nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, Nat. Commun. 8 (2017) 14577. [CrossRef]
- S.; Murakami, T.; Suzuki, H.; Harigae, P.H.; Romeo, M. Yamamoto, et al., NRF2 Activation Impairs Quiescence and Bone Marrow Reconstitution Capacity of Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Mol. Cell Biol. 37 (19) (2017) e00086-17. [CrossRef]
- K.; Taguchi, J.M.; Maher, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Kawatani, H. Motohashi, et al., Genetic analysis of cytoprotective functions supported by graded expression of Keap1, Mol. Cell Biol. 30 (12) (2010) 3016-3026. [CrossRef]
- Y.; Jeong, N.T.; Hoang, A.; Lovejoy, H.; Stehr, A.M. Newman, et al., Role of KEAP1/NRF2 and TP53 Mutations in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Development and Radiation Resistance, Cancer Discov. 7 (1) (2017) 86-101. [CrossRef]
- X.; Bai, Y.; Chen, X.; Hou, M.; Huang, J.; Jin, Emerging role of NRF2 in chemoresistance by regulating drug-metabolizing enzymes and efflux transporters, Drug Metab. Rev. 48 (4) (2016) 541-567. [CrossRef]
- I.G.; Ryoo, G.; Kim, B.H.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, M.K.; Kwak, Involvement of NRF2 Signaling in Doxorubicin Resistance of Cancer Stem Cell-Enriched Colonospheres, Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 24 (5) (2016) 482-488. [CrossRef]
- H.; Sasaki, M.; Shitara, K.; Yokota, Y.; Hikosaka, S. Moriyama, et al., MRP3 gene expression correlates with NRF2 mutations in lung squamous cell carcinomas, Mol. Med. Rep. 6 (4) (2012) 705-708. [CrossRef]
- A.M.; Gao, Z.P.; Ke, J.N.; Wang, J.Y.; Yang, S.Y. Chen, et al., Apigenin sensitizes doxorubicin-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7402/ADM cells to doxorubicin via inhibiting PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway, Carcinogenesis 34 (8) (2013) 1806-1814. [CrossRef]
- H.M.; Ahmed, Ethnomedicinal, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Investigations of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt, Molecules 24 (1) (2018). [CrossRef]
- W.W.; Ji, S.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Ma, R.P.; Li, S.S. Li, et al., Effects of perillaldehyde on alternations in serum cytokines and depressive-like behavior in mice after lipopolysaccharide administration, Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 116 (2014) 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Y.; Song, R.; Sun, Z.; Ji, X.; Li, Q. Fu, et al., Perilla aldehyde attenuates CUMS-induced depressive-like behaviors via regulating TXNIP/TRX/NLRP3 pathway in rats, Life Sci. 206 (2018) 117-124. [CrossRef]
- T.; Uemura, T.; Yashiro, R.; Oda, N.; Shioya, T. Nakajima, et al., Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Perillaldehyde, J. Agric. Food Chem. 66 (13) (2018) 3443-3448. [CrossRef]
- Y.; Fuyuno, H.; Uchi, M.; Yasumatsu, S. Morino-Koga, Y. Tanaka, et al., Perillaldehyde Inhibits AHR Signaling and Activates NRF2 Antioxidant Pathway in Human Keratinocytes, Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018 (2018) 9524657. [CrossRef]
- C.M.; Cabello, W.B. Bair, 3rd, S.D.; Lamore, S.; Ley, A.S. Bause, et al., The cinnamon-derived Michael acceptor cinnamic aldehyde impairs melanoma cell proliferation, invasiveness, and tumor growth, Free Radic. Biol. Med. 46 (2) (2009) 220-231. [CrossRef]
- J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Dong, Y.; Wen, X. Zheng, et al., Cinnamaldehyde inhibits inflammation and brain damage in a mouse model of permanent cerebral ischaemia, Br. J. Pharmacol. 172 (20) (2015) 5009-5023. [CrossRef]
- T.W.; Kim, Cinnamaldehyde induces autophagy-mediated cell death through ER stress and epigenetic modification in gastric cancer cells, Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 43 (3) (2022) 712-723. [CrossRef]
- H.; Uchi, M.; Yasumatsu, S. Morino-Koga, C.; Mitoma, M.; Furue, Inhibition of aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling and induction of NRF2-mediated antioxidant activity by cinnamaldehyde in human keratinocytes, J Dermatol. Sci. 85 (1) (2017) 36-43. [CrossRef]
- Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, N.; Dong, X.; Su, M. Duan, et al., Sulforaphane induces S-phase arrest and apoptosis via p53-dependent manner in gastric cancer cells, Sci. Rep. 11 (1) (2021) 2504. [CrossRef]
- Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, N.; Li, M.; Xu, T. Miyamoto, et al., Sulforaphane suppresses metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells by targeting the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, NPJ Breast Cancer 8 (1) (2022) 40. [CrossRef]
- Ostolga-Chavarria, C. Sanchez-Garibay, P. Rojas-Morales, S. Galvan-Arzate, et al., Sulforaphane protects from myocardial ischemia-reperfusion damage through the balanced activation of Nrf2/AhR, Free Radic. Biol. Med. 143 (2019) 331-340. [CrossRef]
- S.; Cao, S.; Hu, P.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L. Li, et al., Effects of sulforaphane on breast cancer based on metabolome and microbiome, Food Sci. Nutr. 11 (5) (2023) 2277-2287. [CrossRef]
- R.L.; Yeager, S.A.; Reisman, L.M.; Aleksunes, C.D.; Klaassen, Introducing the "TCDD-inducible AhR-Nrf2 gene battery", Toxicol. Sci. 111 (2) (2009) 238-246. [CrossRef]
- K.; Wuputra, M.H.; Tsai, K.; Kato, C.C.; Ku, J.B. Pan, et al., Jdp2 is a spatiotemporal transcriptional activator of the AhR via the Nrf2 gene battery, Inflamm. Regen. 43 (1) (2023) 42. [CrossRef]
- K. McGovern, A.C.; Castro, J.; Cavanaugh, S.; Coma, M. Walsh, et al., Discovery and Characterization of a Novel Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Inhibitor, IK-175, and Its Inhibitory Activity on Tumor Immune Suppression, Mol. Cancer Ther. 21 (8) (2022) 1261-1272. [CrossRef]
- F. D'Onofrio, G.; Renga, M.; Puccetti, M.; Pariano, M.M. Bellet, et al., Indole-3-Carboxaldehyde Restores Gut Mucosal Integrity and Protects from Liver Fibrosis in Murine Sclerosing Cholangitis, Cells 10 (7) (2021). [CrossRef]
- M.; Puccetti, G.; Paolicelli, V.; Oikonomou, A. De Luca, G. Renga, et al., Towards Targeting the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Cystic Fibrosis, Mediators Inflamm. 2018 (2018) 1601486. [CrossRef]
- G.; Renga, E.; Nunzi, M.; Pariano, M.; Puccetti, M.M. Bellet, et al., Optimizing therapeutic outcomes of immune checkpoint blockade by a microbial tryptophan metabolite, J. Immunother. Cancer 10 (3) (2022). [CrossRef]
- C.; Kober, J.; Roewe, N.; Schmees, L.; Roese, U. Roehn, et al., Targeting the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) with BAY 2416964: a selective small molecule inhibitor for cancer immunotherapy, J. Immunother. Cancer 11 (11) (2023). [CrossRef]
- S.V.; Singh, S.K.; Srivastava, S.; Choi, K.L.; Lew, J. Antosiewicz, et al., Sulforaphane-induced cell death in human prostate cancer cells is initiated by reactive oxygen species, J. Biol. Chem. 280 (20) (2005) 19911-19924. [CrossRef]
- L.L.; Atwell, Z.; Zhang, M.; Mori, P.; Farris, J.T. Vetto, et al., Sulforaphane Bioavailability and Chemopreventive Activity in Women Scheduled for Breast Biopsy, Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 8 (12) (2015) 1184-1191. [CrossRef]
- M.; Ge, L.; Zhang, L.; Cao, C.; Xie, X. Li, et al., Sulforaphane inhibits gastric cancer stem cells via suppressing sonic hedgehog pathway, Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 70 (5) (2019) 570-578. [CrossRef]
- S.; Li, P.N.; Khoi, H.; Yin, D.K.; Sah, N.H. Kim, et al., Sulforaphane Suppresses the Nicotine-Induced Expression of the Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 via Inhibiting ROS-Mediated AP-1 and NF-kappaB Signaling in Human Gastric Cancer Cells, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (9) (2022) 5172. [CrossRef]
- M.; Honma, M.; Yamada, M.; Yasui, K.; Horibata, K.I. Sugiyama, et al., In vivo and in vitro mutagenicity of perillaldehyde and cinnamaldehyde, Genes Environ. 43 (1) (2021) 30. [CrossRef]
- J.; Puschhof, C. Pleguezuelos-Manzano, A. Martinez-Silgado, N.; Akkerman, A. Saftien, et al., Intestinal organoid cocultures with microbes, Nat. Protoc. 16 (10) (2021) 4633-4649. [CrossRef]
- K.; Murai, S.; Dentro, S.H.; Ong, R.; Sood, D. Fernandez-Antoran, et al., p53 mutation in normal esophagus promotes multiple stages of carcinogenesis but is constrained by clonal competition, Nat. Commun. 13 (1) (2022) 6206. [CrossRef]
- K.; Sabapathy, D.P.; Lane, Therapeutic targeting of p53: all mutants are equal, but some mutants are more equal than others, Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15 (1) (2018) 13-30. [CrossRef]
- K.; Liu, W.; Chen, S.; Lei, L.; Xiong, H. Zhao, et al., Wild-type and mutant p53 differentially modulate miR-124/iASPP feedback following pohotodynamic therapy in human colon cancer cell line, Cell Death Dis. 8 (10) (2017) e3096. [CrossRef]
- K.; Lisek, E.; Campaner, Y.; Ciani, D.; Walerych, G. Del Sal, Mutant p53 tunes the NRF2-dependent antioxidant response to support survival of cancer cells, Oncotarget 9 (29) (2018) 20508-20523. [CrossRef]
- D.; Walerych, K.; Lisek, R.; Sommaggio, S.; Piazza, Y. Ciani, et al., Proteasome machinery is instrumental in a common gain-of-function program of the p53 missense mutants in cancer, Nat. Cell Biol. 18 (8) (2016) 897-909. [CrossRef]
- M.C.; Tung, P.L.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, T.Y.; He, M.C. Lee, et al., Mutant p53 confers chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer by upregulating Nrf2, Oncotarget 6 (39) (2015) 41692-41705. [CrossRef]
- S.A.; Rushworth, L.; Zaitseva, M.Y.; Murray, N.M.; Shah, K.M. Bowles, et al., The high Nrf2 expression in human acute myeloid leukemia is driven by NF-kappaB and underlies its chemo-resistance, Blood 120 (26) (2012) 5188-5198. [CrossRef]
- G.; Asher, J.; Lotem, R.; Kama, L.; Sachs, Y.; Shaul, NQO1 stabilizes p53 through a distinct pathway, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 (5) (2002) 3099-3104. [CrossRef]
- G.; Asher, J.; Lotem, P.; Tsvetkov, V.; Reiss, L. Sachs, et al., P53 hot-spot mutants are resistant to ubiquitin-independent degradation by increased binding to NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100 (25) (2003) 15065-15070. [CrossRef]
- E.; Kalo, I. Kogan-Sakin, H.; Solomon, E. Bar-Nathan, M. Shay, et al., Mutant p53R273H attenuates the expression of phase 2 detoxifying enzymes and promotes the survival of cells with high levels of reactive oxygen species, J. Cell Sci. 125 (Pt 22) (2012) 5578-5586. [CrossRef]
- A.S.; Gomes, H.; Ramos, J.; Soares, L. Saraiva, p53 and glucose metabolism: an orchestra to be directed in cancer therapy, Pharmacol. Res. 131 (2018) 75-86. [CrossRef]
- V.J.N.; Bykov, S.E.; Eriksson, J.; Bianchi, K.G.; Wiman, Targeting mutant p53 for efficient cancer therapy, Nat. Rev. Cancer 18 (2) (2018) 89-102. [CrossRef]
- X.; Peng, M.Q.; Zhang, F.; Conserva, G.; Hosny, G. Selivanova, et al., APR-246/PRIMA-1MET inhibits thioredoxin reductase 1 and converts the enzyme to a dedicated NADPH oxidase, Cell Death Dis. 4 (10) (2013) e881. [CrossRef]
- L.; Haffo, J.; Lu, V.J.N.; Bykov, S.S.; Martin, X. Ren, et al., Inhibition of the glutaredoxin and thioredoxin systems and ribonucleotide reductase by mutant p53-targeting compound APR-246, Sci. Rep. 8 (1) (2018) 12671. [CrossRef]
- B.; Tessoulin, G.; Descamps, P.; Moreau, S.; Maiga, L. Lode, et al., PRIMA-1Met induces myeloma cell death independent of p53 by impairing the GSH/ROS balance, Blood 124 (10) (2014) 1626-1636. [CrossRef]
- N.; Mohell, J.; Alfredsson, A.; Fransson, M.; Uustalu, S. Bystrom, et al., APR-246 overcomes resistance to cisplatin and doxorubicin in ovarian cancer cells, Cell Death Dis. 6 (6) (2015) e1794. [CrossRef]
- Z.; Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Heitink, K.; Rogers, Y. You, et al., The anti-cancer agent APR-246 can activate several programmed cell death processes to kill malignant cells, Cell Death Differ. 30 (4) (2023) 1033-1046. [CrossRef]
- R.; Faraonio, P.; Vergara, D. Di Marzo, M.G.; Pierantoni, M. Napolitano, et al., p53 suppresses the Nrf2-dependent transcription of antioxidant response genes, J. Biol. Chem. 281 (52) (2006) 39776-39784. [CrossRef]
- Y.; Liang, J.; Liu, Z.; Feng, The regulation of cellular metabolism by tumor suppressor p53, Cell Biosci. 3 (1) (2013) 9. [CrossRef]
- T.; Li, N.; Kon, L.; Jiang, M.; Tan, T. Ludwig, et al., Tumor suppression in the absence of p53-mediated cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis, and senescence, Cell 149 (6) (2012) 1269-1283. [CrossRef]
- H.; Yang, S.; Xiang, A.; Kazi, S.M.; Sebti, The GTPase KRAS suppresses the p53 tumor suppressor by activating the NRF2-regulated antioxidant defense system in cancer cells, J. Biol. Chem. 295 (10) (2020) 3055-3063. [CrossRef]
- C.P.; Kung, J.D.; Weber, It's Getting Complicated-A Fresh Look at p53-MDM2-ARF Triangle in Tumorigenesis and Cancer Therapy, Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10 (2022) 818744. [CrossRef]
- Y.; Xu, C.; Jin, Z.; Liu, J.; Pan, H. Li, et al., Cloning and characterization of the mouse JDP2 gene promoter reveal negative regulation by p53, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 450 (4) (2014) 1531-1536. [CrossRef]
- S.; Tanigawa, C.H.; Lee, C.S.; Lin, C.C.; Ku, H. Hasegawa, et al., Jun dimerization protein 2 is a critical component of the Nrf2/MafK complex regulating the response to ROS homeostasis, Cell Death Dis. 4 (11) (2013) e921. [CrossRef]
- C.; Jin, K.; Kato, T.; Chimura, T.; Yamasaki, K. Nakade, et al., Regulation of histone acetylation and nucleosome assembly by transcription factor JDP2, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13 (4) (2006) 331-338. [CrossRef]
- J.; Pan, K. Nakade, Y.C. Huang, Z.W. Zhu, S. Masuzaki, et al., Suppression of cell-cycle progression by Jun dimerization protein-2 (JDP2) involves downregulation of cyclin-A2, Oncogene 29 (47) (2010) 6245-6256. [CrossRef]
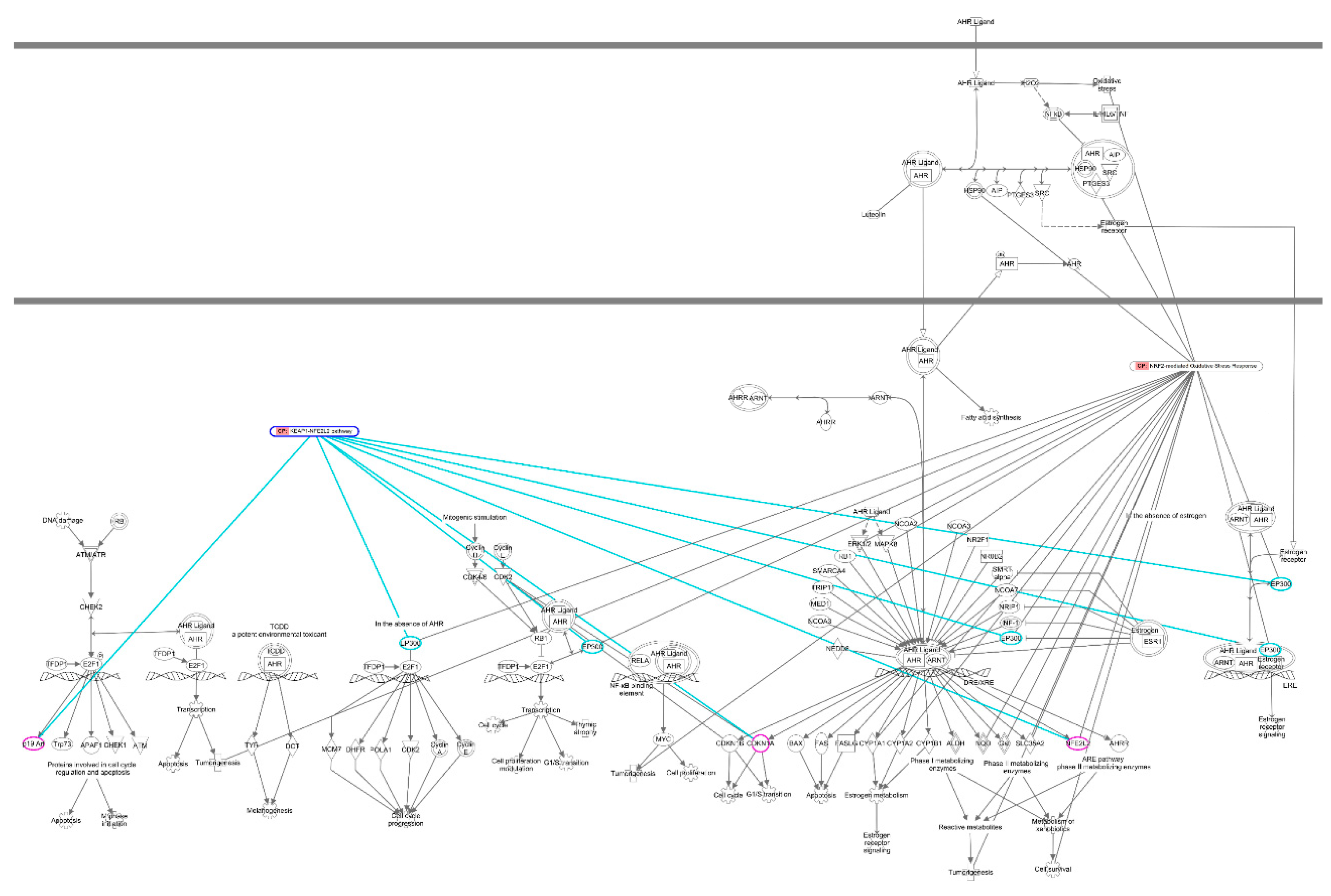
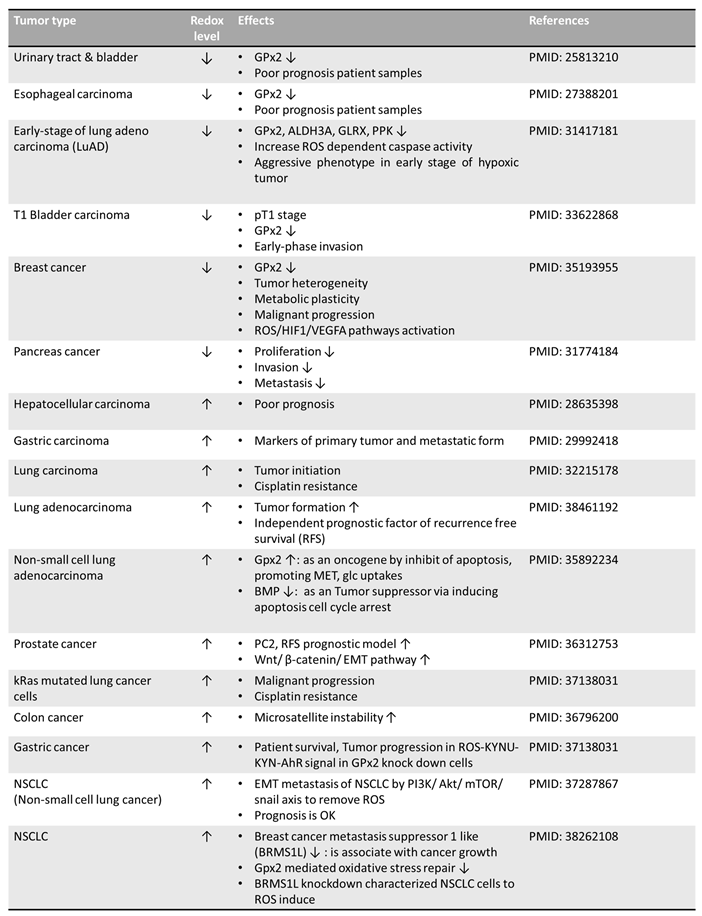 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





