Submitted:
06 September 2024
Posted:
06 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Patients and Methods
Population and Study Period
Methodology
Measures
Assessment of Blood Pressure and Hypertension
Cardiovascular Risk Level Stratification [30]
Statistical Analysis
Ethics
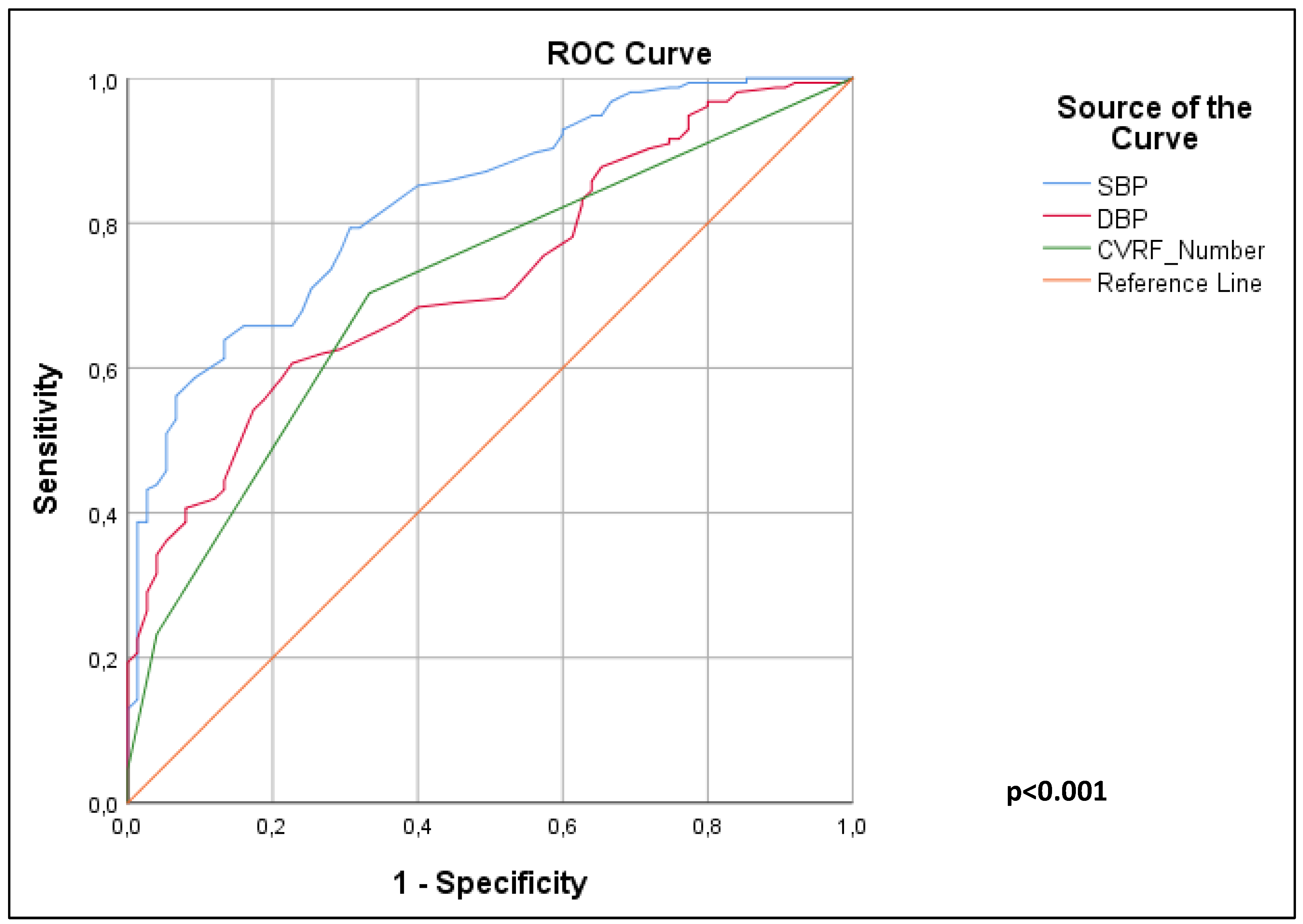
Results
Discussion
Epidemiology and Prevalence of Obesity-Related Hypertension
The Pathophysiology of Obesity-Related Hypertension [6,12,36]
Joint Effects of Obesity and Hypertension on Cardiovascular Risk
Therapeutic Implications
Hygieno-Dietary Measures [6]
Pharmacological Means
Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akpa OM, Made F, Ojo A, Ovbiagele B, Adu D, Motala AA, Mayosi BM, Adebamowo SN, Engel ME, Tayo B, Rotimi C, Salako B, Akinyemi R, Gebregziabher M, Sarfo F, Wahab K, Agongo G , Alberts M, Ali SA, Asiki G, Boua RP, Gómez-Olivé FX, Mashinya F, Micklesfield L, Mohamed SF, Nonterah EA, Norris SA, Sorgho H, Tollman S, Parekh RS, Chishala C, Ekoru K, Waddy SP , Peprah E, Mensah GA, Wiley K, Troyer J, Ramsay M, Owolabi MO; as members of the CVD Working Group of the H3Africa Consortium. Regional Patterns and Association between Obesity and Hypertension in Africa: Evidence from the H3Africa CHAIR Study. Hypertension. 2020; 75:1167-78. [CrossRef]
- El Meouchy P, Wahoud M, Allam S, Chedid R, Karam W, Karam S. Hypertension Related to Obesity: Pathogenesis, Characteristics and Factors for Control. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23:12305. [CrossRef]
- Fahed G, Aoun L, Bou Zerdan M, Allam S, Bou Zerdan M, Bouferraa Y, Assi HI Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J.Mol. Science. 2022; 23:786. [CrossRef]
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005; 365:217–23. [CrossRef]
- Kelly T, Yang W, Chen CS, Reynolds K, He J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008; 32:1431-7. [CrossRef]
- Landsberg L, Aronne LJ, Beilin LJ, Burke V, Igel LI, Lloyd-Jones D, Sowers J. Obesity-related hypertension: pathogenesis, cardiovascular risk, and treatment: a position paper of The Obesity Society and the American Society of Hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2013; 15:14-33. [CrossRef]
- Dalichaouch-Benchaoui, Souhaila, and Noureddine Abadi. “Variables of adiposity related to obesity and morbid states of a population of eastern Algeria.” Metabolic Disease Medicine 15.8.2021:809-17.
- Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J; IDF Epidemiology Task Force Consensus Group. The metabolic syndrome--a new worldwide definition. Lancet. 2005;366:1059-62. [CrossRef]
- El Rhazia, K., et al. “Prevalence of obesity and the main socio-demographic factors associated in Morocco.” Papers 57.2009: S3-S59.
- Pathak, A., Rouet, P., Despas, F., Jourdan, G., Verwaerde, P., Galinier, M., & Senard, JM Obesity and arterial hypertension: epidemiology, pathophysiology and management. mt cardio.2007; 3 :169-177. [CrossRef]
- Clinical Guidelines on the Identification. Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults--The Evidence Report.National Institutes of Health.Obes Res.1998; 62: 51S-209S.
- Seravalle G, Grassi G. Obesity and hypertension. Pharmacol Res. 2017; 122:1-7. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Zhang WQ, Tang WW, Zhang WY, Liu JX, Xu RH, Wang TD, Huang XB. The prevalence of obesity-related hypertension among middle-aged and older adults in China. Front Public Health. 2022; 10:865870. [CrossRef]
- Okosun IS, Prewitt TE, Cooper RS. Abdominal obesity in the United States: prevalence and attributable risk of hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 1999; 13:425–30. [CrossRef]
- Hebebrand J, Holm JC, Woodward E, Baker JL, Blaak E, Durrer Schutz D, Farpour-Lambert NJ, Frühbeck G, Halford JGC, Lissner L, Micic D, Mullerova D, Roman G, Schindler K, Toplak H, Visscher TLS , Yumuk V. A Proposal of the European Association for the Study of Obesity to Improve the ICD-11 Diagnostic Criteria for Obesity Based on the Three Dimensions Etiology, Degree of Adiposity and Health Risk. Obese Facts. 2017; 10:284-307. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. Report of a WHO Consultation (WHO Technical Report Series 894). 2000. www.who.int/nutrition/publications/obesity/WHO_TRS_894/en/ (last accessed on August 10, 2023).
- Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1 (last accessed on August 10, 2023).
- Lauby-Secretan B, Dossus L, Marant-Micallef C, His M. Obésité et cancer [Obesity and Cancer]. Bull Cancer. 2019; 106:635-46. [CrossRef]
- El Meouchy P, Wahoud M, Allam S, Chedid R, Karam W, Karam S. Hypertension Related to Obesity: Pathogenesis, Characteristics and Factors for Control. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23:12305. [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.; Neeland, IJ; Yamashita, S.; Shai, I.; Seidell, J.; Magni, P.; Santos, RD; Arsenault, B.; Cuevas, A.; Hu, FB; et al. Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: A Consensus Statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020; 16: 177–18. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Beydoun MA, Min J, Xue H, Kaminsky LA, Cheskin LJ. Has the prevalence of overweight, obesity and central obesity leveled off in the United States? Trends, patterns, disparities, and future projections for the obesity epidemic. Int J Epidemiol. 2020; 49:810-23. [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Heart L, and Blood Institute’s (NHLBI) North American Association for the Study of Obesity (NAASO). The practical guide: identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults In. National Institutes of Health , 2000. Vol Publication no. 00-4084. Rockville, MD.
- Köchli S, Endes K, Steiner R, Engler L, Infanger D, Schmidt-Trucksäss A, Zahner L, Hanssen H. Obesity, High Blood Pressure, and Physical Activity Determine Vascular Phenotype in Young Children. Hypertension. 2019; 73:153-61. [CrossRef]
- Ma S, Xi B, Yang L, Sun J, Zhao M, Bovet P. Trends in the prevalence of overweight, obesity, and abdominal obesity among Chinese adults between 1993 and 2015. Int J Obes. 2021; 45:427–37. [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, MM Body mass index and quality of life in a survey of primary care patients. J.Fam. Practice 2000; 49:734–37. [PubMed]
- Fujioka, S.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Tokunaga, K.; Tarui, S. Contribution of intra-abdominal fat accumulation to the impairment of glucose and lipid metabolism in human obesity. Metabolism. 1987; 36:54–59. [CrossRef]
- CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/basic/adult-defining.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https%3A%2%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Fobesity%2Fadult%2Fdefining.html (last accessed on 4 July 2023).
- Cheung AK, Whelton PK, Muntner P, Schutte AE, Moran AE, Williams B, Sarafidis P, Chang TI, Daskalopoulou SS, Flack JM, Jennings G, Juraschek SP, Kreutz R, Mancia G, Nesbitt S, Ordunez P, Padwal R , Persu A, Rabi D, Schlaich MP, Stergiou GS, Tobe SW, Tomaszewski M, Williams KA Sr, Mann JFE. International Consensus on Standardized Clinic Blood Pressure Measurement - A Call to Action. Am J Med. 2023; 136:438-45. [CrossRef]
- Flack JM, Adekola B. Blood pressure and the new ACC/AHA hypertension guidelines. Trends Cardiovascular Med. 2020; 30:160-64. [CrossRef]
- Mancia Chairperson G, Kreutz Co-Chair R, Brunström M, Burnier M, Grassi G, Januszewicz A, Muiesan ML, Tsioufis K, Agabiti-Rosei E, Algharably EAE, Azizi M, Benetos A, Borghi C, Hitij JB, Cifkova R , Coca A, Cornelissen V, Cruickshank K, Cunha PG, Danser AHJ, de Pinho RM, Delles C, Dominiczak AF, Dorobantu M, Doumas M, Fernández-Alfonso MS, Halimi JM, Járai Z, Jelaković B, Jordan J, Kuznetsova T, Laurent S, Lovic D, Lurbe E, Mahfoud F, Manolis A, Miglinas M, Narkiewicz K, Niiranen T, Palatini P, Parati G, Pathak A, Persu A, Polonia J, Redon J, Sarafidis P, Schmieder R, Spronck B, Stabouli S, Stergiou G, Taddei S, Thomopoulos C, Tomaszewski M, Van de Borne P, Wanner C, Weber T, Williams B, Zhang ZY, Kjeldsen SE; Authors/Task Force Members:. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension Endorsed by the European Renal Association (ERA) and the International Society of Hypertension (ISH). J Hypertens. 2023 Jun 21. Epub ahead of print. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan H, Wang Y, Xiang Q, Fang S, Chen Y, Chen C, Zhang W, Zhang H, Xia F, Wang N, Lu Y. Associations between abdominal obesity indices and diabetic complications: Chinese visceral adiposity index and neck circumference. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020; 19:118. [CrossRef]
- Múzquiz-Barberá P, Ruiz-Cortés M, Herrero R, Vara MD, Escrivá-Martínez T, Baños RM, Rodilla E, Lisón JF. “Own doctor” presence in a web-based lifestyle intervention for adults with obesity and hypertension: A randomized controlled trial. Front Public Health. 2023; 11:1115711. [CrossRef]
- Leggio M, Lombardi M, Caldarone E, Severi P, D’Emidio S, Armeni M, Bravi V, Bendini MG, Mazza A. The relationship between obesity and hypertension: an updated comprehensive overview on vicious twins. Hypertens Res. 2017; 40:947-63. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Wang QJ. The prevalence of prehypertension and hypertension among US adults according to the new joint national committee guidelines: new challenges of the old problem. Arch Intern Med. 2004; 164:2126-34. [CrossRef]
- Kannel WB, Brand N, Skinner JJ Jr, Dawber TR, McNamara PM. The relation of adiposity to blood pressure and development of hypertension. The Framingham study. Ann InternMed. 1967; 67:48-59. [CrossRef]
- DeMarco VG, Aroor AR, Sowers JR. The pathophysiology of hypertension in patients with obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014; 10:364-76. [CrossRef]
- Stamler J, Dyer AR, Shekelle RB, Neaton J, Stamler R. Relationship of baseline major risk factors to coronary and all-cause mortality, and to longevity: findings from long-term follow-up of Chicago cohorts. Cardiology. 1993; 82:191-222. [CrossRef]
- Haffner SM, Lehto S, Rönnemaa T, Pyörälä K, Laakso M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:229-34. [CrossRef]
- Juutilainen A, Lehto S, Rönnemaa T, Pyörälä K, Laakso M. Type 2 diabetes as a “coronary heart disease equivalent”: an 18-year prospective population-based study in Finnish subjects. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:2901-7. [CrossRef]
- Chi JH, Lee BJ. Association of myocardial infarction and angina pectoris with obesity and biochemical indices in the South Korean population. Sci Rep. 2022; 12:13769. [CrossRef]
- Wilson PW, Bozeman SR, Burton TM, Hoaglin DC, Ben-Joseph R, Pashos CL. Prediction of first events of coronary heart disease and stroke with consideration of adiposity. Traffic. 2008; 118 :124–30. [CrossRef]
- Huxley R, Mendis S, Zheleznyakov E, Reddy S, Chan J. Body mass index, waist circumference and waist:hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular risk--a review of the literature. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010; 64:16-22. [CrossRef]
- Staiano AE, Reeder BA, Elliott S, Joffres MR, Pahwa P, Kirkland SA, Paradis G, Katzmarzyk PT. Body mass index versus waist circumference as predictors of mortality in Canadian adults. Int J Obes (Lond). 2012; 36:1450-4. [CrossRef]
- Ashwell M, Gunn P, Gibson S. Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2012; 13:275-86. [CrossRef]
- Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Ross R. Waist circumference and not body mass index explains obesity-related health risk. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004; 79:379-84. [CrossRef]
| Variables | Average values (N=230) |
Class 1 obesity (n=170) | Class 2 obesity (n=43) | Class 3 obesity (n=17) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 52.5 ± 12.05 [Extremes: 24-85] | 51 | 50 | 56.5 | 0.77 |
| Sex Male Female |
75(32.61%) 155 (67.39%) |
67(39.4%) 103 (60.6%) |
6(14%) 37 (86%) |
2(11.8%) 15 (88.2%) |
0.001 |
| Origin rural Urban |
93(40.4%) 137(59.6%) |
74(43.5%) 96(56.5%) |
13(30.2%) 30(69.8%) |
06(35.3%) 11(64.7%) |
0.25 |
| CVRF | 2.8±0.81 [Extremes:2-6] | 2.6 | 2.8 | 3 | 0.82 |
| Type 2 diabetes | 28 (12.2%) | 17 (10%) | 6 (14%) | 5 (29.4%) | 0.048 |
| Dyslipidemia Active smoking |
37(16.1%) 10(4.3%) |
26(15.3%) 7(4.11%) |
6(14%) 3(6.97%) |
5(29.4%) 00(0%) |
0.29 0.506 |
| Angina Pain Dyspnea |
17(7.4%) 29(12.60) |
12(7.1%) 16(9.41) |
1(2.3%) 7(16.27) |
4 (23.5%) 3(17.64) |
0.017 0.577 |
| Arterial hypertension Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 |
123(53.5%) 47(20.4%) 60(26.1%) |
91(53%) 33(19.4%) 46(27.1%) |
22(51.2%) 10(23.3%) 11(25.6%) |
10(58.8%) 4(23.5%) 3(17.6%) |
0.913 |
| BMI, Kg/m² | 33.59± 4.20 [Extremes: 30-53.99] | - | - | - | - |
| Abdominal perimeter, cm Abdominal Obesity |
103.71± 10.66[Extremes: 69-150] 189(82.17) |
- - |
- - |
- - |
- - |
| CKF | 5 (2.2%) | 2 (1.2%) | 1 (2.3%) | 2 (11.8%) | 0.035 |
| HVG Stroke Heart failure Cancer |
18(7.82%) 18(7.82%) 19(8.26%) 02(0.86%) |
13(7.6%) 15(8.82) 15(8.82%) 2(1.17%) |
4(9.3%) 3(6.97) 2(4.65%) 0(00%) |
1(5.9%) 0(0%) 2(11.76%) 0(00%) |
0.90 0.63 0.54 0.99 |
| Variables | Average values (N=230) |
Grade 1 obesity (n=170) |
Grade 3 obesity (n=17) |
odds ratio | 95% CI | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Abdominal Obesity Type 2 diabetes |
189(82.17) 28 (12.2%) |
132(77.64%) 17(10%) |
16(94.11%) 5 (29.4%) |
0.135 |
0.034–0.541 |
0.005 |
| Dyslipidemia | 37 (16.1%) | 26(15.3%) | 5 (29.4%) | 0.458 | 0.052-4.063 |
0.48 |
| Angina Pain | 17 (7.4%) | 12(7.1%) | 4 (23.5%) | 0.084 | 0.009–0.790 |
0.030 |
|
Arterial hypertension Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 |
123(53.5%) 47 (20.4%) 60 (26.1%) |
91(53%) 33(19.4%) 46(27.1%) |
10(58.8%) 4(23.5%) 3(17.6%) |
0.602 | 0.157–2.305 | 0.45 |
|
Chronic Kidney Failure |
5 (2.2%) | 2 (1.2%) | 2 (11.8%) | 2,416 | 1.471–85.268 | 0.020 |
|
LVH |
18 (7.8%) | 13 (7.6%) | 1(5.9%) | 1,255 | 0.152–10.389 | 0.83 |
| LVH: Left ventricular hypertrophy. | ||||||
| Variables | Average values (N=230) |
Grade 1 obesity (n=170) | Grade 2 obesity (n=43) | Grade 3 obesity (n=17) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Risk Stratification | 0.32 | ||||
| Low Risk | 28(12.2) | 20(11.76%) | 5(11.62) | 3(17.64) | |
| Moderate Risk | 50(21.7) | 41(24.11%)) | 9(20.93) | 0(0%) | |
| High Risk | 103(44.8) | 73(42.94%) | 20(46.51) | 10(58.82) | |
| Very High Risk | 49(21.3) | 36(21.17%) | 9(20.93) | 4(23.52) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





