Submitted:
04 September 2024
Posted:
05 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
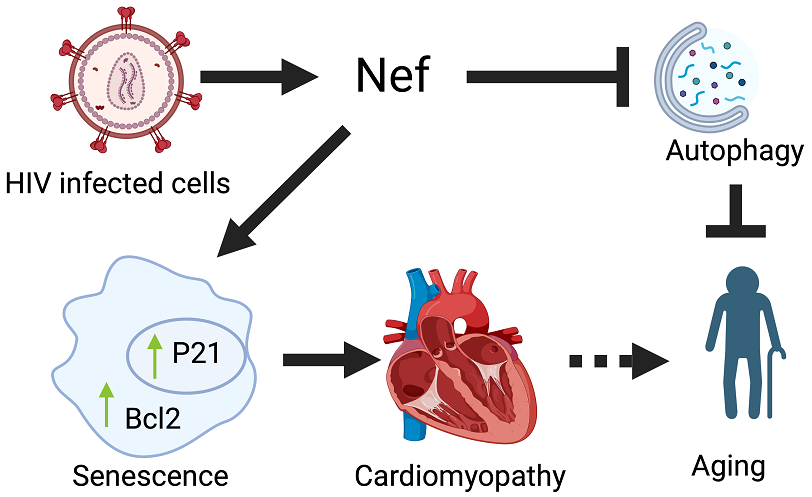
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Cell Culture and Plasmid Transfection
Animal Model and Ethics
Heart Function Analysis by Echocardiography
Western Blot Assay
Histology
Autophagy Assay
Determination of Lipofuscin
SA-βgal Staining
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Nef Transgenic Mouse Was Generated to Express Nef Protein in an Organ-Specific Manner:
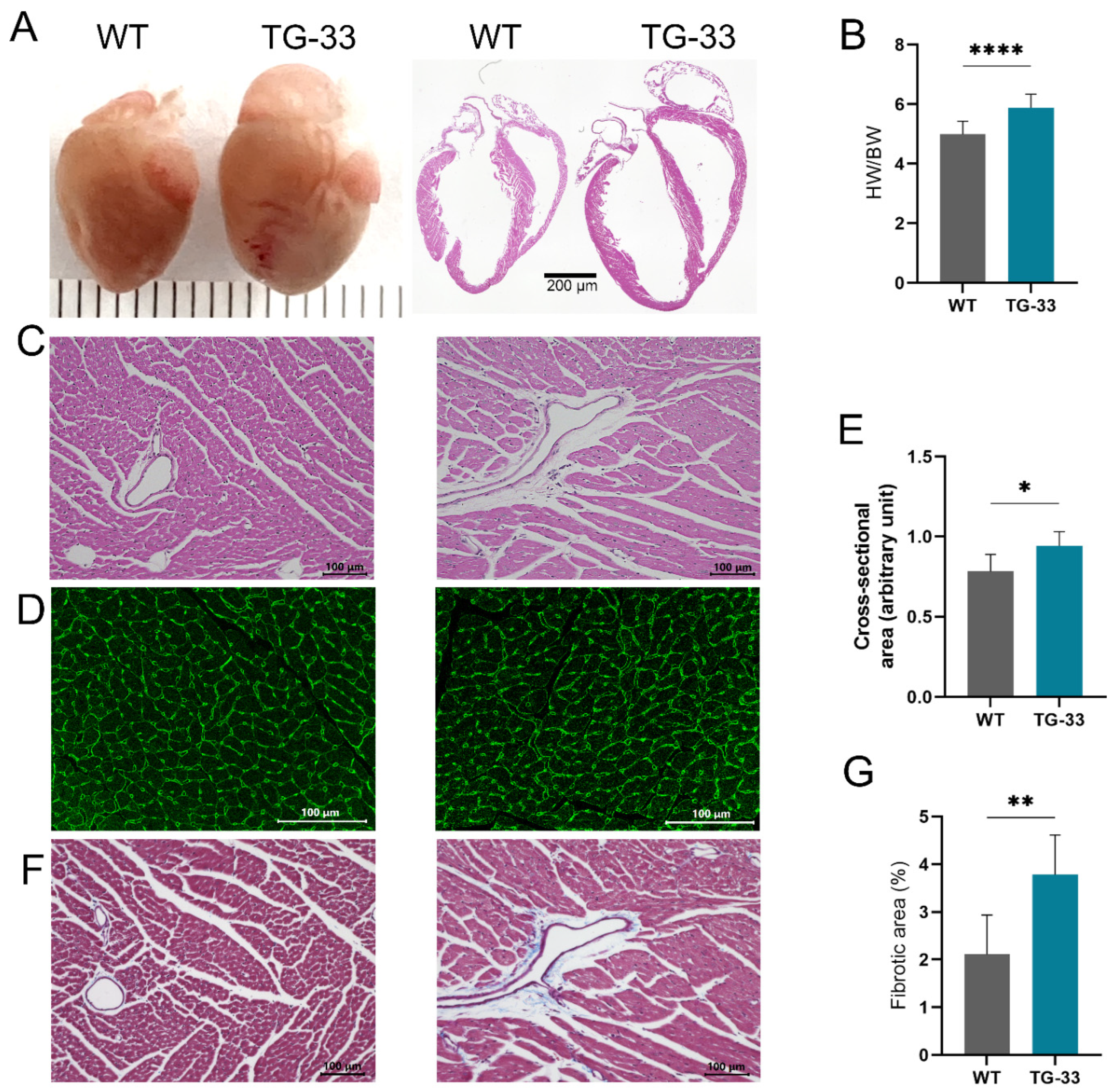
Nef Transgenic Mice Develop Cardiac Abnormality and Fibrosis:
Nef Protein Expression Compromises Heart Function:
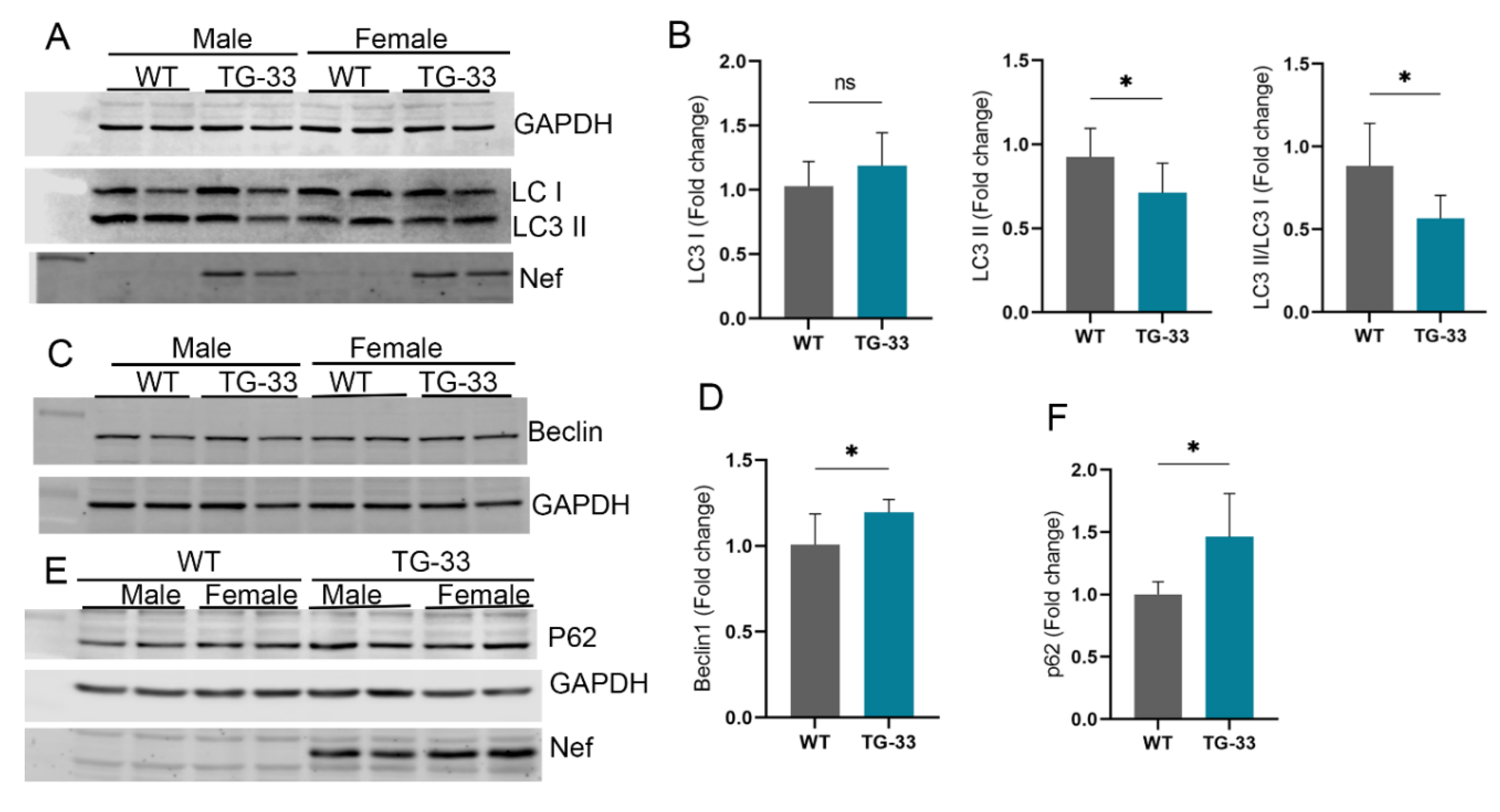
Nef Protein Expression Dysregulates Autophagy in Cardiac Tissue:
Nef Protein Dysregulates Autophagy through Increased Stability of Bcl2:
Nef Protein Induces Senescence-Associated Gene Expression:
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Abbreviations
References
- World Health Organization. Global HIV/AIDS statistics Fact Sheet. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids (accessed on 30th July, 2024).
- Hsue, P. Y.; Waters, D. D., Time to Recognize HIV Infection as a Major Cardiovascular Risk Factor. Circulation 2018, 138, (11), 1113-1115. [CrossRef]
- Ntsekhe, M.; Baker, J. V., Cardiovascular Disease Among Persons Living With HIV: New Insights Into Pathogenesis and Clinical Manifestations in a Global Context. Circulation 2023, 147, (1), 83-100. [CrossRef]
- Volberding, P. A.; Deeks, S. G., Antiretroviral therapy and management of HIV infection. Lancet 2010, 376, (9734), 49-62. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Green, L. A.; Gupta, S. K.; Amet, T.; Byrd, D. J.; Yu, Q.; Twigg, H. L., 3rd; Clauss, M., Intracellular Nef detected in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from HIV patients. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 2015, 31, (2), 217-20.
- Cheney, L.; Guzik, H.; Macaluso, F. P.; Macian, F.; Cuervo, A. M.; Berman, J. W., HIV Nef and Antiretroviral Therapy Have an Inhibitory Effect on Autophagy in Human Astrocytes that May Contribute to HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders. Cells 2020, 9, (6). [CrossRef]
- Ferdin, J.; Goricar, K.; Dolzan, V.; Plemenitas, A.; Martin, J. N.; Peterlin, B. M.; Deeks, S. G.; Lenassi, M., Viral protein Nef is detected in plasma of half of HIV-infected adults with undetectable plasma HIV RNA. PLoS One 2018, 13, (1), e0191613. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M. K.; Kaminski, R.; Mullen, B.; Gordon, J.; Burdo, T. H.; Cheung, J. Y.; Feldman, A. M.; Madesh, M.; Khalili, K., HIV-1 Nef-induced cardiotoxicity through dysregulation of autophagy. Sci Rep 2017, 7, (1), 8572. [CrossRef]
- Twu, C.; Liu, N. Q.; Popik, W.; Bukrinsky, M.; Sayre, J.; Roberts, J.; Rania, S.; Bramhandam, V.; Roos, K. P.; MacLellan, W. R.; Fiala, M., Cardiomyocytes undergo apoptosis in human immunodeficiency virus cardiomyopathy through mitochondrion- and death receptor-controlled pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99, (22), 14386-91. [CrossRef]
- Geyer, M.; Fackler, O. T.; Peterlin, B. M., Structure--function relationships in HIV-1 Nef. EMBO Rep 2001, 2, (7), 580-5.
- Frankel, A. D.; Young, J. A., HIV-1: fifteen proteins and an RNA. Annu Rev Biochem 1998, 67, 1-25. [CrossRef]
- Trillo-Pazos, G.; McFarlane-Abdulla, E.; Campbell, I. C.; Pilkington, G. J.; Everall, I. P., Recombinant nef HIV-IIIB protein is toxic to human neurons in culture. Brain Res 2000, 864, (2), 315-26. [CrossRef]
- Kyei, G. B.; Dinkins, C.; Davis, A. S.; Roberts, E.; Singh, S. B.; Dong, C.; Wu, L.; Kominami, E.; Ueno, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Federico, M.; Panganiban, A.; Vergne, I.; Deretic, V., Autophagy pathway intersects with HIV-1 biosynthesis and regulates viral yields in macrophages. J Cell Biol 2009, 186, (2), 255-68.
- Castro-Gonzalez, S.; Shi, Y.; Colomer-Lluch, M.; Song, Y.; Mowery, K.; Almodovar, S.; Bansal, A.; Kirchhoff, F.; Sparrer, K.; Liang, C.; Serra-Moreno, R., HIV-1 Nef counteracts autophagy restriction by enhancing the association between BECN1 and its inhibitor BCL2 in a PRKN-dependent manner. Autophagy 2021, 17, (2), 553-577. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Gulick, J.; Pratt, R.; Robbins, J., Noonan syndrome is associated with enhanced pERK activity, the repression of which can prevent craniofacial malformations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, (36), 15436-41. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M. K.; McLendon, P. M.; Gulick, J.; James, J.; Khalili, K.; Robbins, J., UBC9-Mediated Sumoylation Favorably Impacts Cardiac Function in Compromised Hearts. Circ Res 2016, 118, (12), 1894-905. [CrossRef]
- Halade, G. V.; Kain, V.; Ingle, K. A., Heart functional and structural compendium of cardiosplenic and cardiorenal networks in acute and chronic heart failure pathology. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2018, 314, (2), H255-H267.
- Kashyap, S.; Mukker, A.; Gupta, D.; Datta, P. K.; Rappaport, J.; Jacobson, J. M.; Ebert, S. N.; Gupta, M. K., Antiretroviral Drugs Regulate Epigenetic Modification of Cardiac Cells Through Modulation of H3K9 and H3K27 Acetylation. Front Cardiovasc Med 2021, 8, 634774. [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, M. Y.; Rappaport, J.; Gupta, M. K., Activation of Immune System May Cause Pathophysiological Changes in the Myocardium of SARS-CoV-2 Infected Monkey Model. Cells 2022, 11, (4).
- Takemura, G.; Kanamori, H.; Goto, K.; Maruyama, R.; Tsujimoto, A.; Fujiwara, H.; Seishima, M.; Minatoguchi, S., Autophagy maintains cardiac function in the starved adult. Autophagy 2009, 5, (7), 1034-6. [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M. S.; Pattison, J. S.; Osinska, H.; James, J.; Gulick, J.; McLendon, P. M.; Hill, J. A.; Sadoshima, J.; Robbins, J., Enhanced autophagy ameliorates cardiac proteinopathy. J Clin Invest 2013, 123, (12), 5284-97. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Torres, C., HIV-associated cellular senescence: A contributor to accelerated aging. Ageing Res Rev 2017, 36, 117-124. [CrossRef]
- Kakimoto, Y.; Okada, C.; Kawabe, N.; Sasaki, A.; Tsukamoto, H.; Nagao, R.; Osawa, M., Myocardial lipofuscin accumulation in ageing and sudden cardiac death. Sci Rep 2019, 9, (1), 3304. [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, M. J., HIV and Cardiovascular Disease: From Insights to Interventions. Top Antivir Med 2021, 29, (4), 407-411.
- Nanditha, N. G. A.; Paiero, A.; Tafessu, H. M.; St-Jean, M.; McLinden, T.; Justice, A. C.; Kopec, J.; Montaner, J. S. G.; Hogg, R. S.; Lima, V. D., Excess burden of age-associated comorbidities among people living with HIV in British Columbia, Canada: a population-based cohort study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, (1), e041734. [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Barnes, A. E.; Guest, J. L.; Shah, A.; Shao, I. Y.; Marconi, V., HIV Infection and Incidence of Cardiovascular Diseases: An Analysis of a Large Healthcare Database. J Am Heart Assoc 2019, 8, (14), e012241. [CrossRef]
- Guaraldi, G.; Orlando, G.; Zona, S.; Menozzi, M.; Carli, F.; Garlassi, E.; Berti, A.; Rossi, E.; Roverato, A.; Palella, F., Premature age-related comorbidities among HIV-infected persons compared with the general population. Clin Infect Dis 2011, 53, (11), 1120-6. [CrossRef]
- Trickey, A.; Sabin, C. A.; Burkholder, G.; Crane, H.; d'Arminio Monforte, A.; Egger, M.; Gill, M. J.; Grabar, S.; Guest, J. L.; Jarrin, I.; Lampe, F. C.; Obel, N.; Reyes, J. M.; Stephan, C.; Sterling, T. R.; Teira, R.; Touloumi, G.; Wasmuth, J. C.; Wit, F.; Wittkop, L.; Zangerle, R.; Silverberg, M. J.; Justice, A.; Sterne, J. A. C., Life expectancy after 2015 of adults with HIV on long-term antiretroviral therapy in Europe and North America: a collaborative analysis of cohort studies. Lancet HIV 2023, 10, (5), e295-e307. [CrossRef]
- Montano, M.; Oursler, K. K.; Xu, K.; Sun, Y. V.; Marconi, V. C., Biological ageing with HIV infection: evaluating the geroscience hypothesis. Lancet Healthy Longev 2022, 3, (3), e194-e205. [CrossRef]
- Dash, P. K.; Alomar, F. A.; Hackfort, B. T.; Su, H.; Conaway, A.; Poluektova, L. Y.; Gendelman, H. E.; Gorantla, S.; Bidasee, K. R., HIV-1-Associated Left Ventricular Cardiac Dysfunction in Humanized Mice. Sci Rep 2020, 10, (1), 9746. [CrossRef]
- Dickie, P.; Felser, J.; Eckhaus, M.; Bryant, J.; Silver, J.; Marinos, N.; Notkins, A. L., HIV-associated nephropathy in transgenic mice expressing HIV-1 genes. Virology 1991, 185, (1), 109-19. [CrossRef]
- Mandell, C. P.; Reyes, R. A.; Cho, K.; Sawai, E. T.; Fang, A. L.; Schmidt, K. A.; Luciw, P. A., SIV/HIV Nef recombinant virus (SHIVnef) produces simian AIDS in rhesus macaques. Virology 1999, 265, (2), 235-51. [CrossRef]
- Watkins, R. L.; Zou, W.; Denton, P. W.; Krisko, J. F.; Foster, J. L.; Garcia, J. V., In vivo analysis of highly conserved Nef activities in HIV-1 replication and pathogenesis. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 125. [CrossRef]
- Chowers, M. Y.; Spina, C. A.; Kwoh, T. J.; Fitch, N. J.; Richman, D. D.; Guatelli, J. C., Optimal infectivity in vitro of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 requires an intact nef gene. J Virol 1994, 68, (5), 2906-14. [CrossRef]
- Chelvanambi, S.; Bogatcheva, N. V.; Bednorz, M.; Agarwal, S.; Maier, B.; Alves, N. J.; Li, W.; Syed, F.; Saber, M. M.; Dahl, N.; Lu, H.; Day, R. B.; Smith, P.; Jolicoeur, P.; Yu, Q.; Dhillon, N. K.; Weissmann, N.; Twigg Iii, H. L.; Clauss, M., HIV-Nef Protein Persists in the Lungs of Aviremic Patients with HIV and Induces Endothelial Cell Death. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2019, 60, (3), 357-366. [CrossRef]
- Yarandi, S. S.; Robinson, J. A.; Vakili, S.; Donadoni, M.; Burdo, T. H.; Sariyer, I. K., Characterization of Nef expression in different brain regions of SIV-infected macaques. PLoS One 2020, 15, (11), e0241667. [CrossRef]
- Markle, T. J.; Philip, M.; Brockman, M. A., HIV-1 Nef and T-cell activation: a history of contradictions. Future Virol 2013, 8, (4). [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Zhang, L., Mouse Models for Studies of In Vivo Functions of HIV-1 Nef. AIDS Rev 2016, 18, (3), 158-165.
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Im, S. K.; Fang, S., Mouse Cre-LoxP system: general principles to determine tissue-specific roles of target genes. Lab Anim Res 2018, 34, (4), 147-159.
- Duffy, P.; Wang, X.; Lin, P. H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C., HIV Nef protein causes endothelial dysfunction in porcine pulmonary arteries and human pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Surg Res 2009, 156, (2), 257-64.
- Chelvanambi, S.; Gupta, S. K.; Chen, X.; Ellis, B. W.; Maier, B. F.; Colbert, T. M.; Kuriakose, J.; Zorlutuna, P.; Jolicoeur, P.; Obukhov, A. G.; Clauss, M., HIV-Nef Protein Transfer to Endothelial Cells Requires Rac1 Activation and Leads to Endothelial Dysfunction Implications for Statin Treatment in HIV Patients. Circ Res 2019, 125, (9), 805-820. [CrossRef]
- Marecki, J. C.; Cool, C. D.; Parr, J. E.; Beckey, V. E.; Luciw, P. A.; Tarantal, A. F.; Carville, A.; Shannon, R. P.; Cota-Gomez, A.; Tuder, R. M.; Voelkel, N. F.; Flores, S. C., HIV-1 Nef is associated with complex pulmonary vascular lesions in SHIV-nef-infected macaques. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006, 174, (4), 437-45. [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Z. H.; Hsue, P. Y.; Moffatt, E., Sudden Cardiac Death and Myocardial Fibrosis in Persons with HIV. Reply. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, (15), e50.
- Teer, E.; Dominick, L.; Mukonowenzou, N. C.; Essop, M. F., HIV-Related Myocardial Fibrosis: Inflammatory Hypothesis and Crucial Role of Immune Cells Dysregulation. Cells 2022, 11, (18). [CrossRef]
- Saribas, A. S.; Khalili, K.; Sariyer, I. K., Dysregulation of autophagy by HIV-1 Nef in human astrocytes. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, (18), 2899-904. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lin, X.; Li, G.; Shen, X.; Niu, D.; Lu, G.; Fu, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, M.; Bai, Y., Knockout of Eva1a leads to rapid development of heart failure by impairing autophagy. Cell Death Dis 2017, 8, (2), e2586. [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, O.; Marechal, V.; Danos, O.; Heard, J. M., Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef increases the efficiency of reverse transcription in the infected cell. J Virol 1995, 69, (7), 4053-9. [CrossRef]
- Regamey, N.; Harr, T.; Battegay, M.; Erb, P., Downregulation of Bcl-2, but not of Bax or Bcl-x, is associated with T lymphocyte apoptosis in HIV infection and restored by antiretroviral therapy or by interleukin 2. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 1999, 15, (9), 803-10. [CrossRef]
- Fevrier, M.; Dorgham, K.; Rebollo, A., CD4+ T cell depletion in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection: role of apoptosis. Viruses 2011, 3, (5), 586-612. [CrossRef]
- Airo, P.; Torti, C.; Uccelli, M. C.; Malacarne, F.; Palvarini, L.; Carosi, G.; Castelli, F., Naive CD4+ T lymphocytes express high levels of Bcl-2 after highly active antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 2000, 16, (17), 1805-7. [CrossRef]
- Dillon, S. M.; Friedlander, L. J.; Rogers, L. M.; Meditz, A. L.; Folkvord, J. M.; Connick, E.; McCarter, M. D.; Wilson, C. C., Blood myeloid dendritic cells from HIV-1-infected individuals display a proapoptotic profile characterized by decreased Bcl-2 levels and by caspase-3+ frequencies that are associated with levels of plasma viremia and T cell activation in an exploratory study. J Virol 2011, 85, (1), 397-409. [CrossRef]
- Veenhuis, R. T.; Abreu, C. M.; Costa, P. A. G.; Ferreira, E. A.; Ratliff, J.; Pohlenz, L.; Shirk, E. N.; Rubin, L. H.; Blankson, J. N.; Gama, L.; Clements, J. E., Monocyte-derived macrophages contain persistent latent HIV reservoirs. Nat Microbiol 2023, 8, (5), 833-844. [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, A. P.; Cummins, N. W.; Badley, A. D., The Role of the BCL-2 Family of Proteins in HIV-1 Pathogenesis and Persistence. Clin Microbiol Rev 2019, 33, (1). [CrossRef]
- Valle-Casuso, J. C.; Allouch, A.; David, A.; Lenzi, G. M.; Studdard, L.; Barre-Sinoussi, F.; Muller-Trutwin, M.; Kim, B.; Pancino, G.; Saez-Cirion, A., p21 Restricts HIV-1 in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells through the Reduction of Deoxynucleoside Triphosphate Biosynthesis and Regulation of SAMHD1 Antiviral Activity. J Virol 2017, 91, (23). [CrossRef]
- Chen, N. C.; Partridge, A. T.; Tuzer, F.; Cohen, J.; Nacarelli, T.; Navas-Martin, S.; Sell, C.; Torres, C.; Martin-Garcia, J., Induction of a Senescence-Like Phenotype in Cultured Human Fetal Microglia During HIV-1 Infection. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2018, 73, (9), 1187-1196. [CrossRef]
- Yosef, R.; Pilpel, N.; Papismadov, N.; Gal, H.; Ovadya, Y.; Vadai, E.; Miller, S.; Porat, Z.; Ben-Dor, S.; Krizhanovsky, V., p21 maintains senescent cell viability under persistent DNA damage response by restraining JNK and caspase signaling. EMBO J 2017, 36, (15), 2280-2295. [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhu, B.; Xiong, K.; Sun, Y.; Shi, D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xue, L., Senescence as a novel mechanism involved in beta-adrenergic receptor mediated cardiac hypertrophy. PLoS One 2017, 12, (8), e0182668.
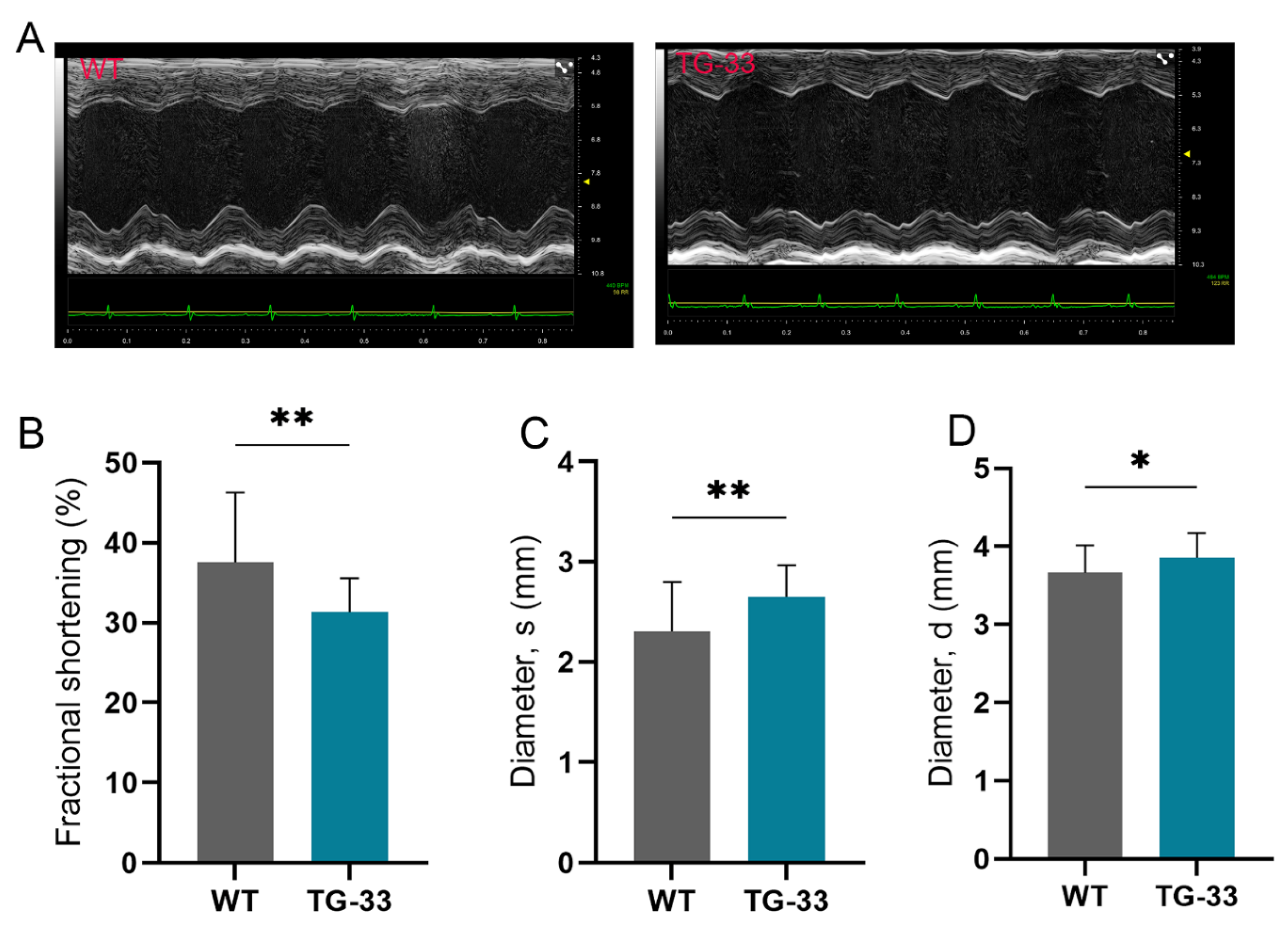
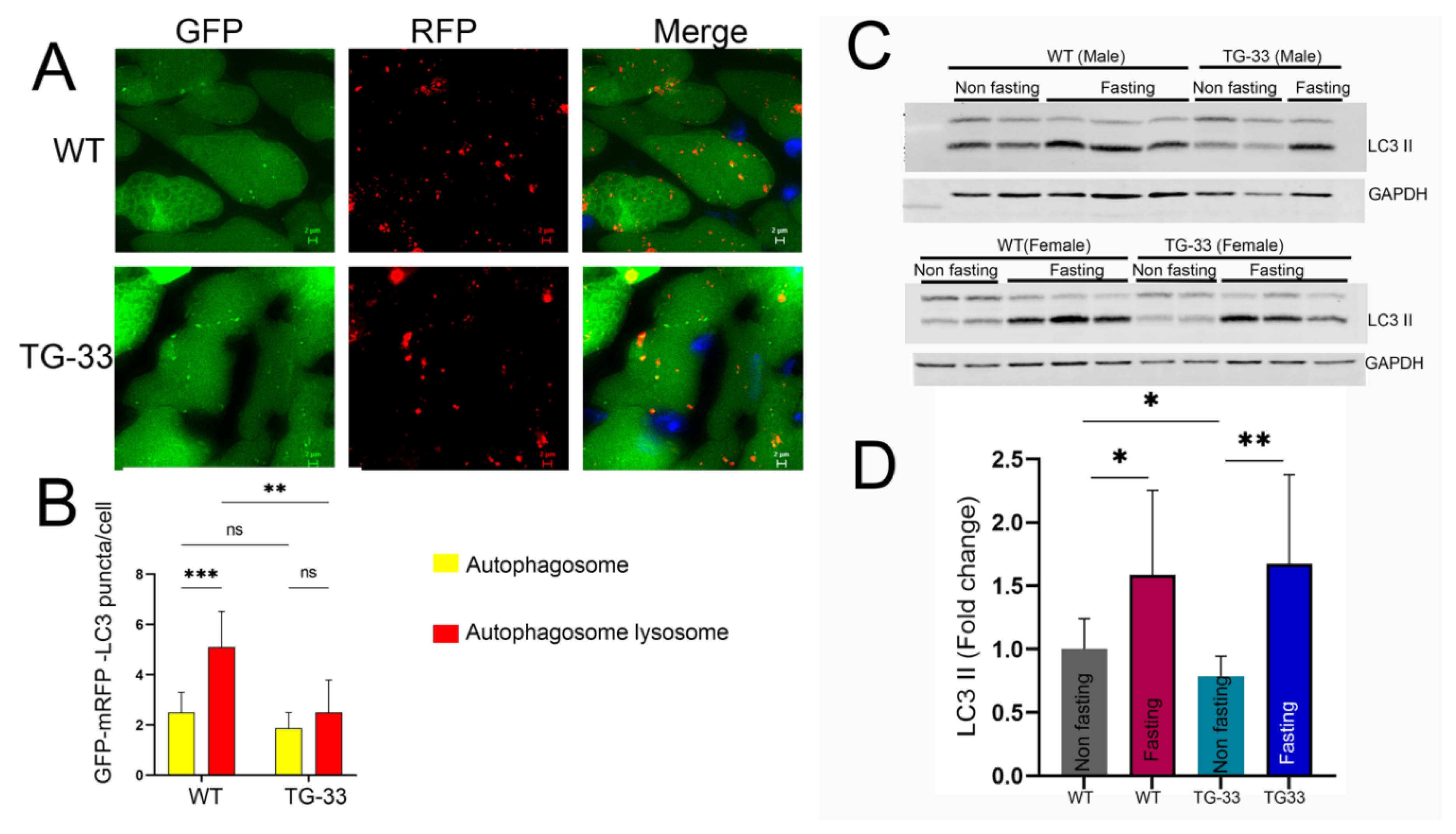
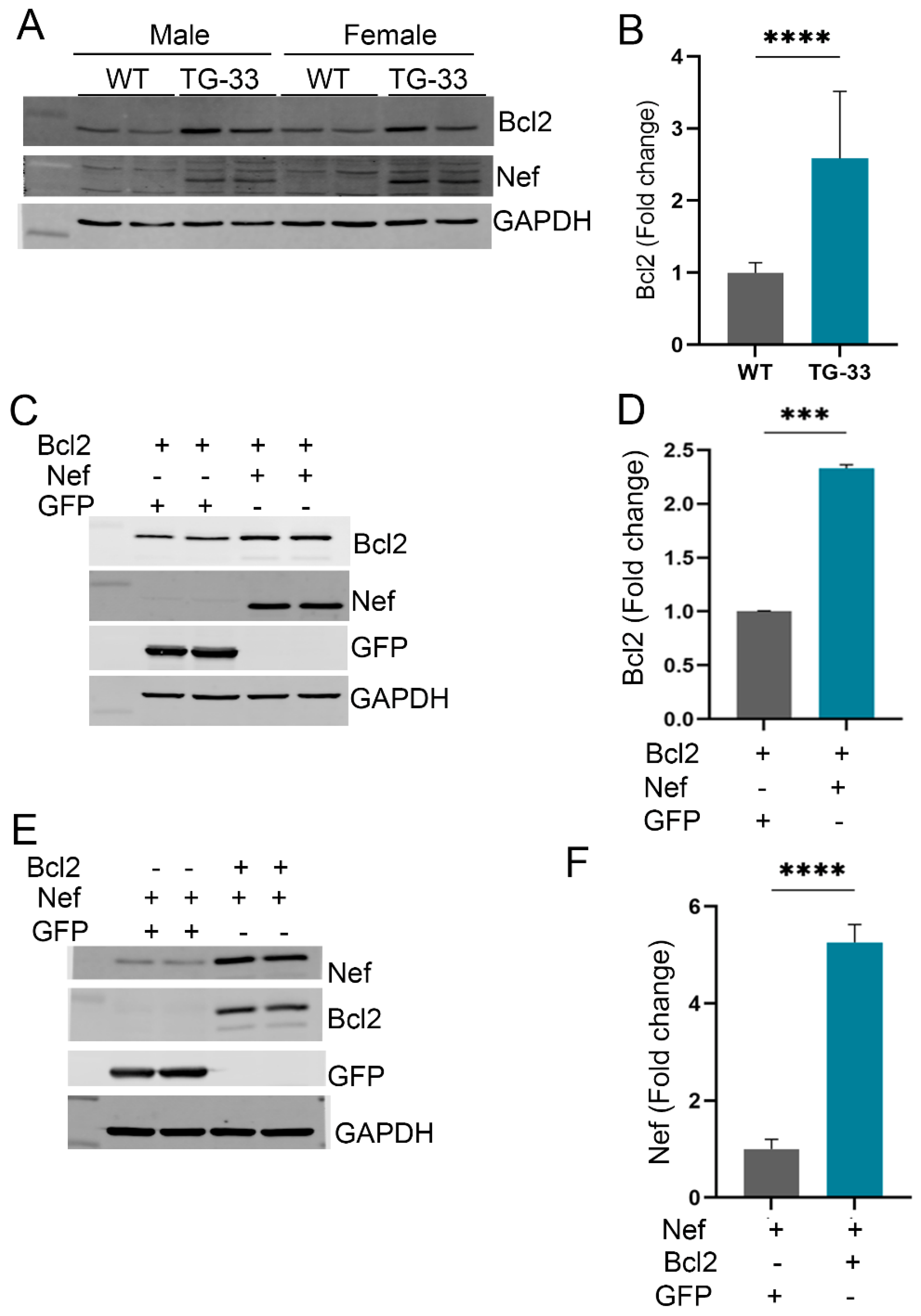
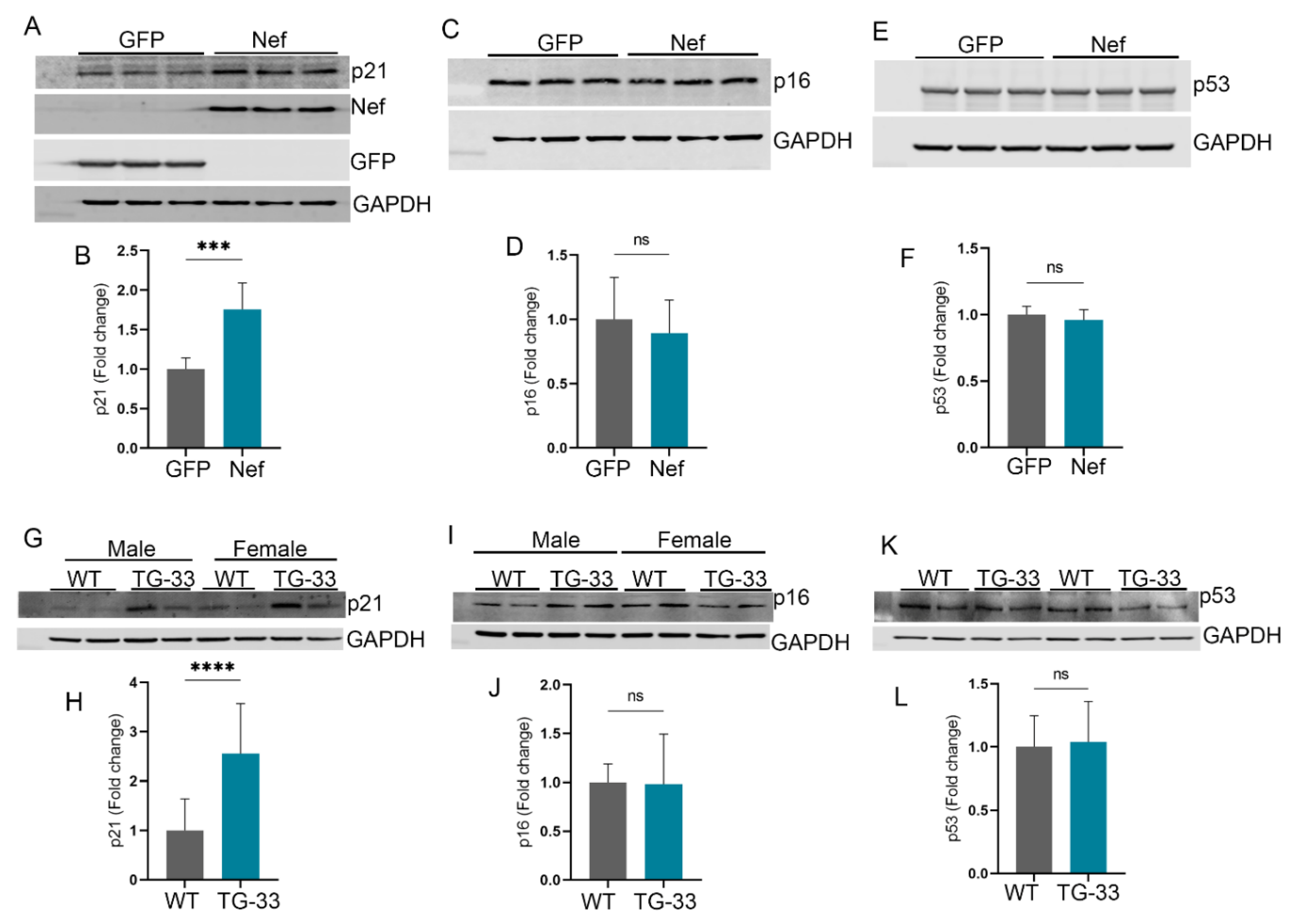
| WT (12-Week-Old) (n=32) | TG-33 (12-Week-Old) (n=24) | WT (24-Week-Old) (n=30) | TG-33 (24-Week-Old) (n=15) | WT (48-Week-Old) (n=9) | TG-33 (48-Week-Old) (n=11) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LV DIAMs (mm) | 2.306 ± 0.4971 | 2.653 ± 0.3155** | 2.846 ± 0.4455 | 3.129 ± 0.4737 | 3.056 ± 0.444 | 4.634 ± 0.9447*** |
| LV DIAMd | 3.66 ± 0.3538 | 3.857 ± 0.3135* | 3.964 ± 0.3477 | 4.088 ± 0.4108 | 4.122 ± 0.31.56 | 5.133 ± 0.7494** |
| LV VOLs (μl) | 19.71 ± 9.932 | 26.49 ± 8.082** | 31.99 ± 11.91 | 40.15 ± 14.42* | 37.79 ± 14.47 | 104.5 ± 50.28** |
| LV VOLd (μl) | 57.45 ± 13.11 | 64.84 ± 12.7* | 69.29 ± 14.05 | 74.77 ± 17.65 | 75.76 ± 14.05 | 129.2 ± 46.03** |
| SV (ul) | 37.74 ± 6.044 | 42.75 ± 10.73* | 37.3 ± 6.426 | 34.62 ± 4.637 | 37.98 ± 8.226 | 24.71 ± 9.025** |
| EF (%) | 67.45 ± 10.93 | 59.6 ± 6.322** | 55.08 ± 9.748 | 47.7 ± 7.655* | 51.02 ± 10.71 | 22.03 ± 12.49**** |
| FS (%) | 37.58 ± 8.712 | 31.32 ± 4.239** | 28.54 ± 6.21 | 23.8 ± 4.505* | 26.04 ± 6.528 | 10.32 ± 6.198**** |
| CO (ml/min) | 16.32 ± 2.956 | 17.29 ± 3.29 | 16.98 ± 3.183 | 15.41 ± 2.299 | 18.06 ± 3.676 | 11.31 ± 4.315** |
| LV mass (mg) | 118.1 ± 22.49 | 123.6 ± 27.6 | 136.1 ± 29.2 | 137.6 ± 24.48 | 147.2 ± 14.46 | 197.8 ± 44.18** |
| LVAWs (mm) | 1.406 ± 0.182 | 1.319 ± 0.2129 | 1.36 ± 0.155 | 1.269 ± 0.2072 | 1.343 ± 0.1427 | 1.15 ± 0.2266* |
| LVAWd (mm) | 0.9511 ± 0.1362 | 0.9037 ± 0.1623 | 0.966 ± 0.1217 | 0.9168 ± 0.1335 | 0.9776 ± 0.08788 | 0.9325 ± 0.1545 |
| LVPWs (mm) | 1.279 ± 0.2415 | 1.126 ± 0.1454** | 1.144 ± 0.1769 | 1.068 ± 0.1257 | 1.161 ± 0.2137 | 0.8678 ± 0.1551** |
| LVPWd (mm) | 0.8287 ± 0.1877 | 0.816 ± 0.0982 | 0.8208 ± 0.1386 | 0.8278 ± 0.1008 | 0.8435 ± 0.1178 | 0.7925 ± 0.1315 |
| HR (bpm) | 432 ± 29.98 | 451.8 ± 29.6* | 454.4 ± 18.41 | 445.8 ± 36.76 | 577.4 ± 37.72 | 456 ± 46.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




