Submitted:
27 August 2024
Posted:
28 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Research Method
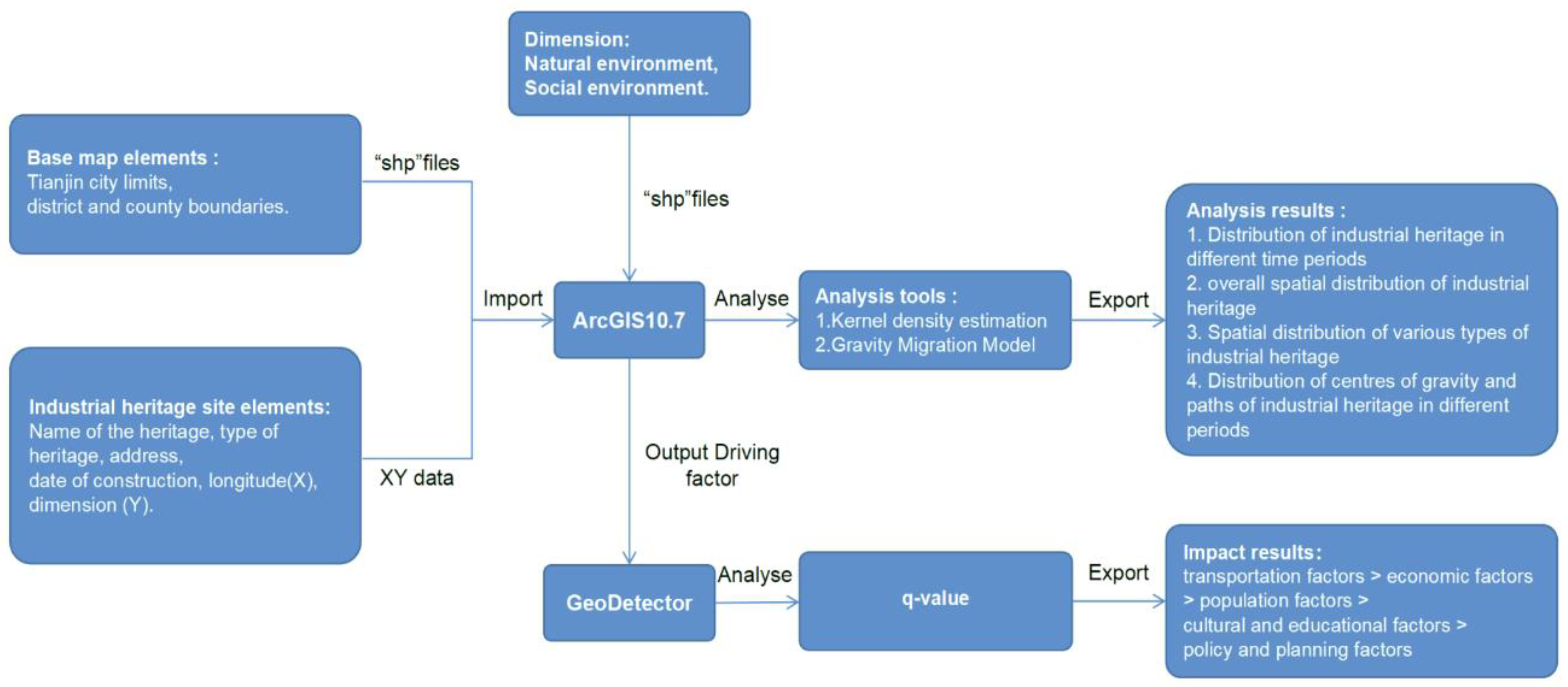
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Research Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Time Situation
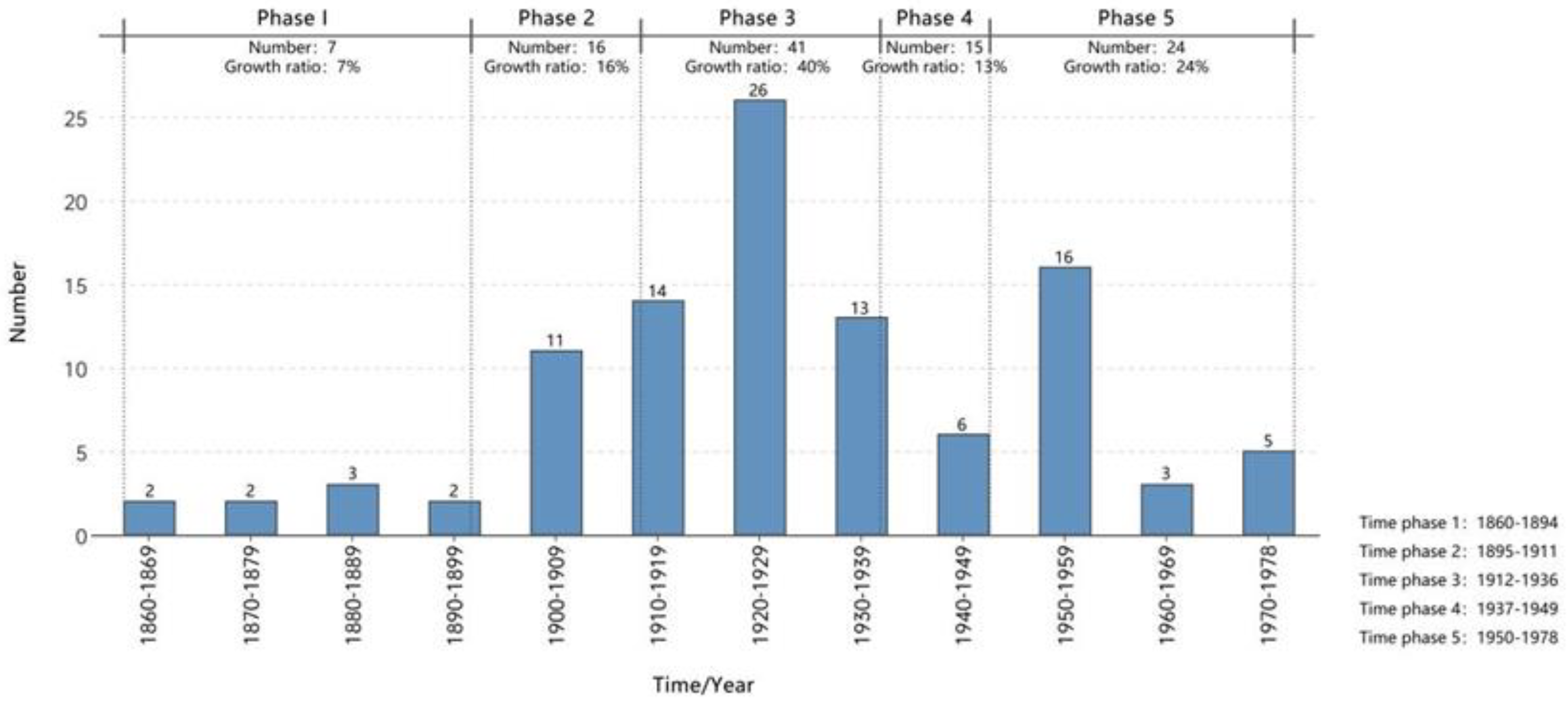
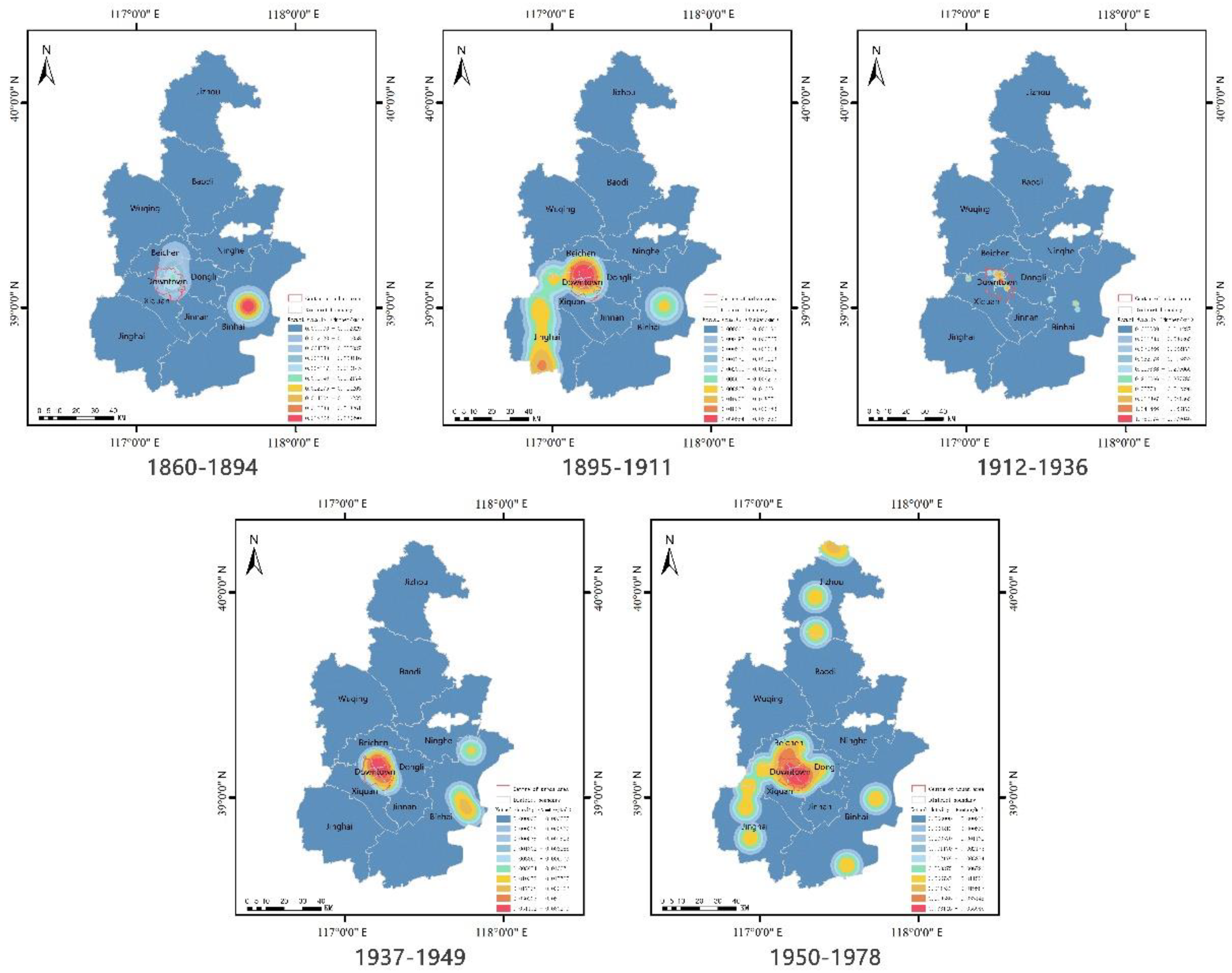
3.1.1. Distribution of Industrial Heritage in Various Historical Periods
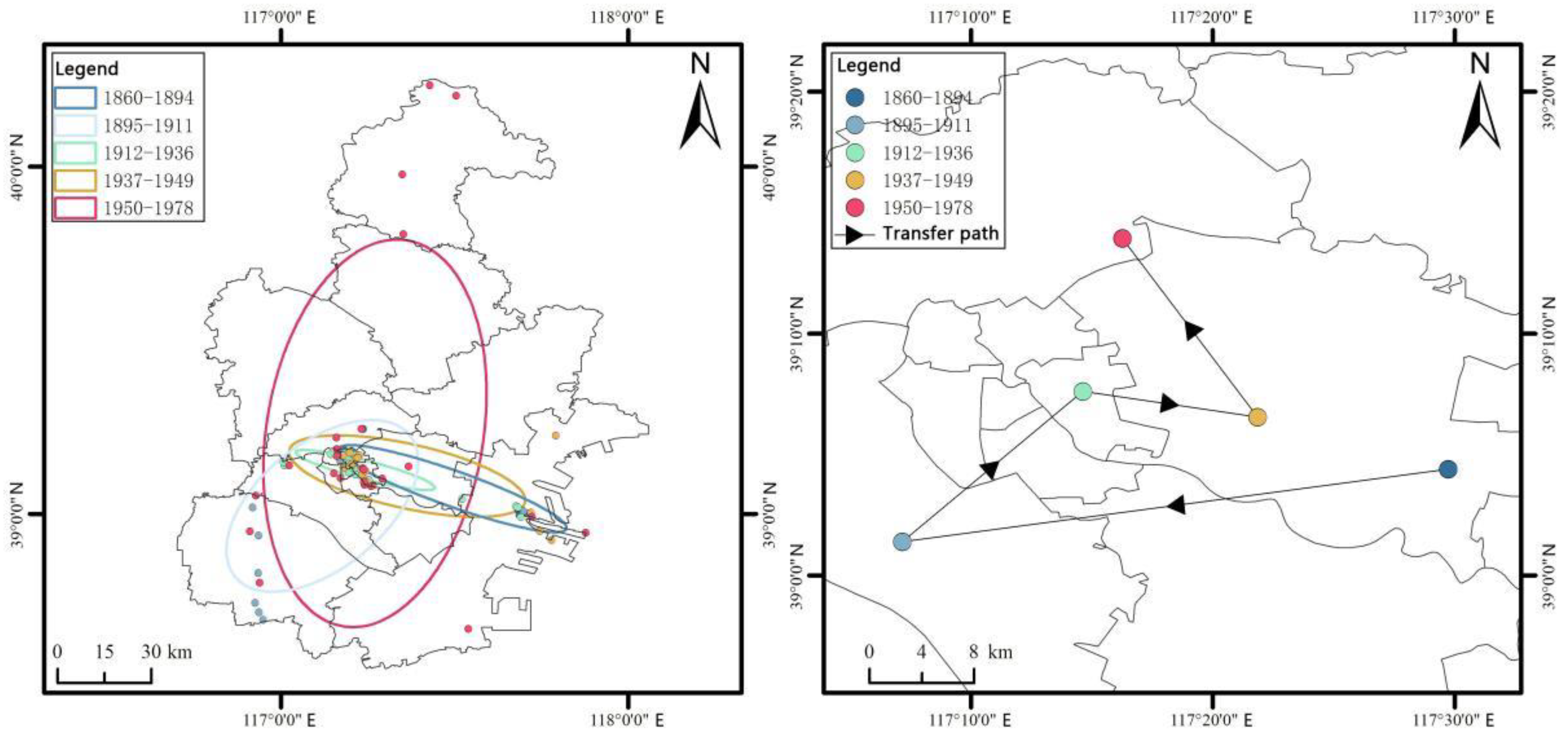
3.1.2. Distribution Center of Gravity and Migration Path
3.2. Space Situation
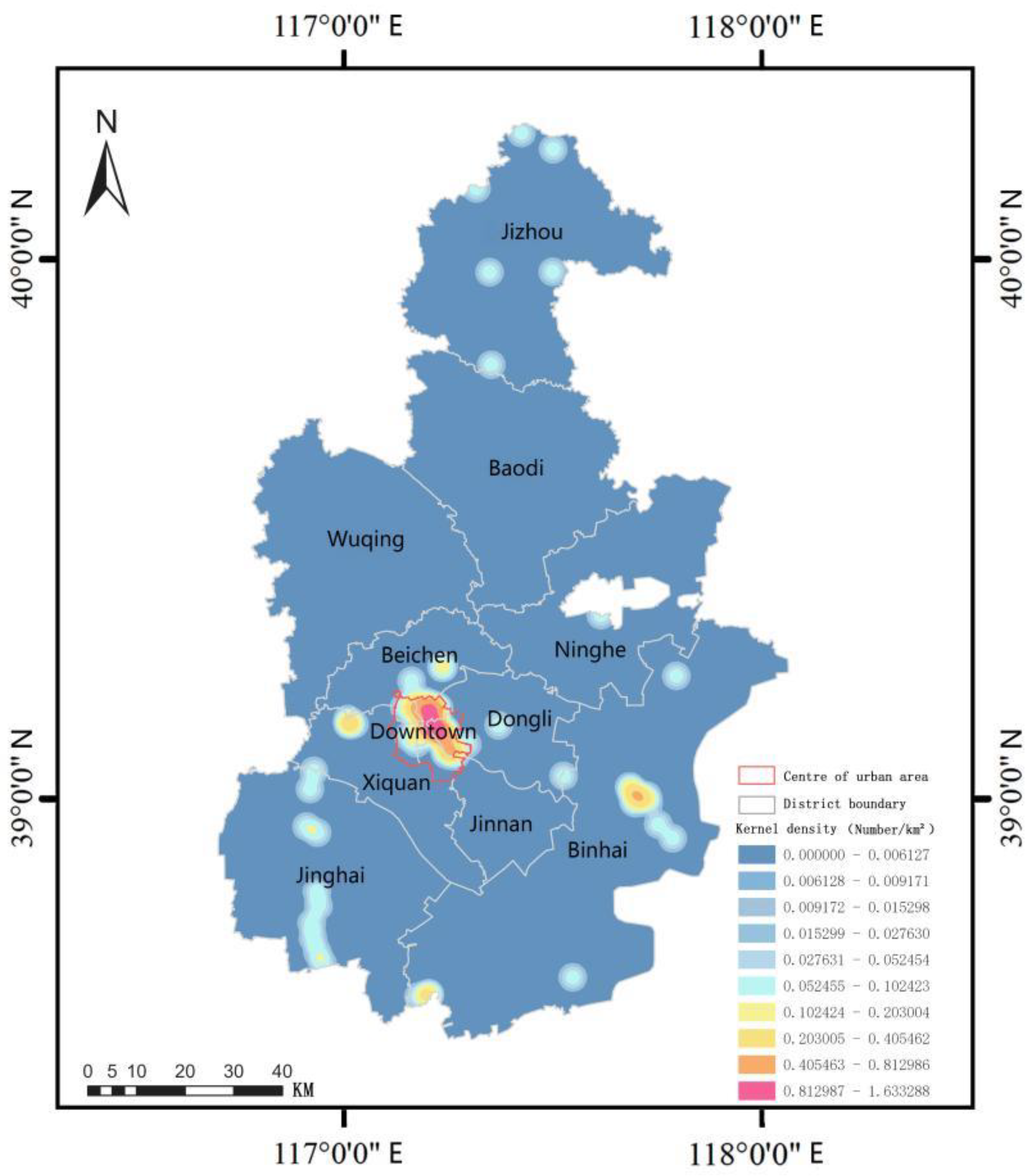
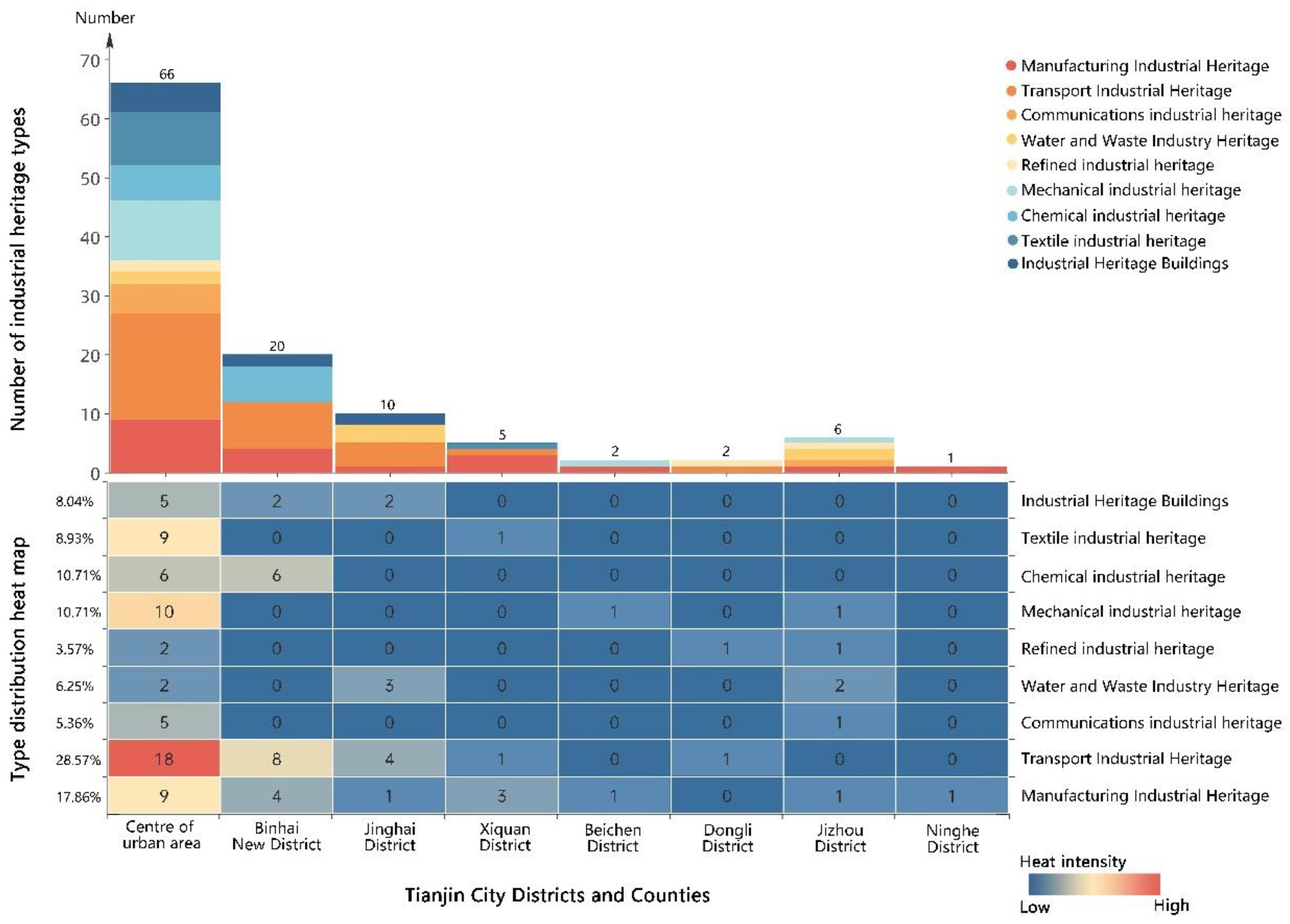
3.2.1. The Spatial Distribution of Industrial Heritage Resources in Tianjin
3.2.2. The relationship between the spatial distribution of industrial heritage and the spatial structure of the water systems.
3.3. Type Characteristics
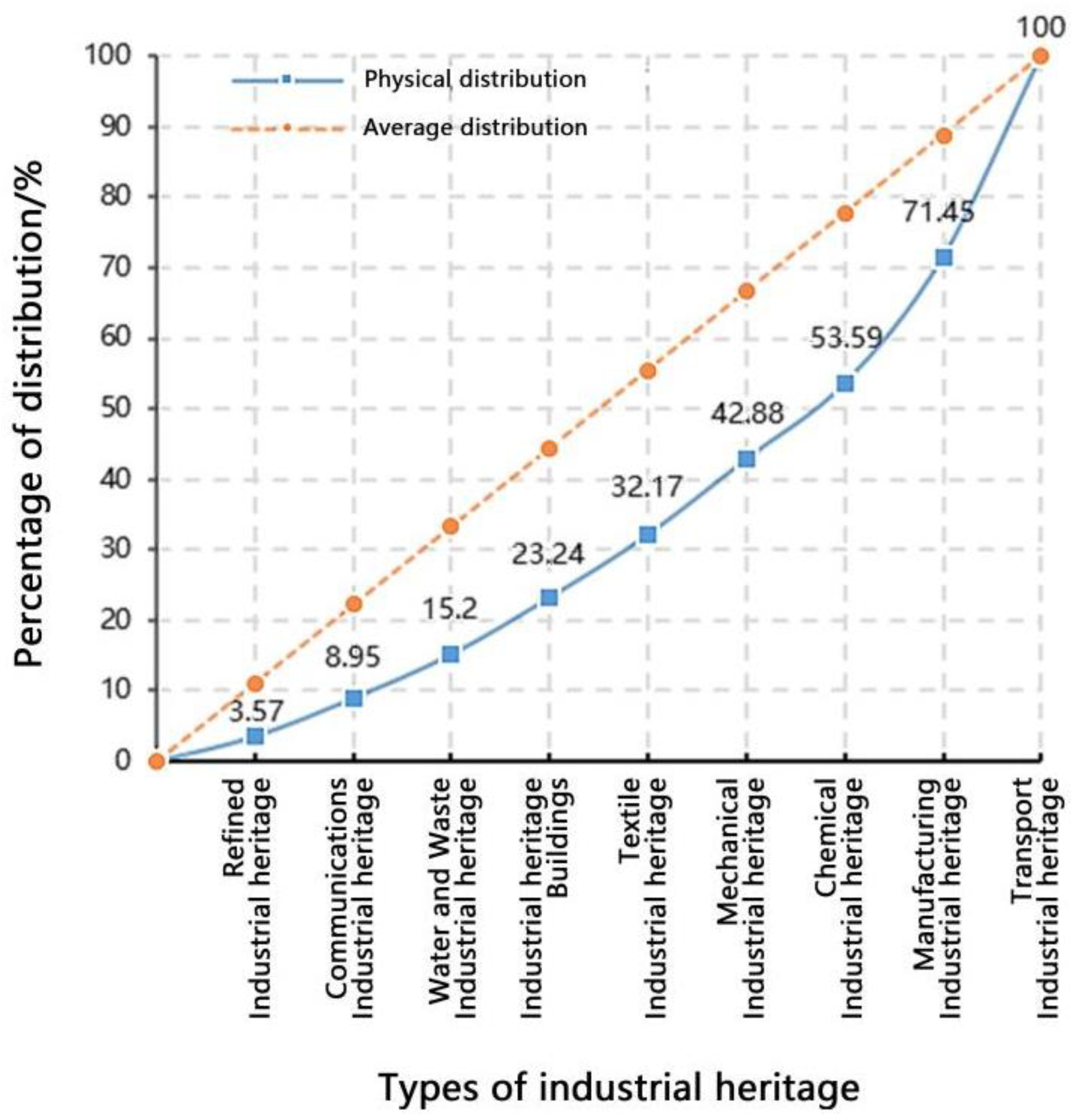
3.3.1. Structured distribution characteristics of industrial heritage types
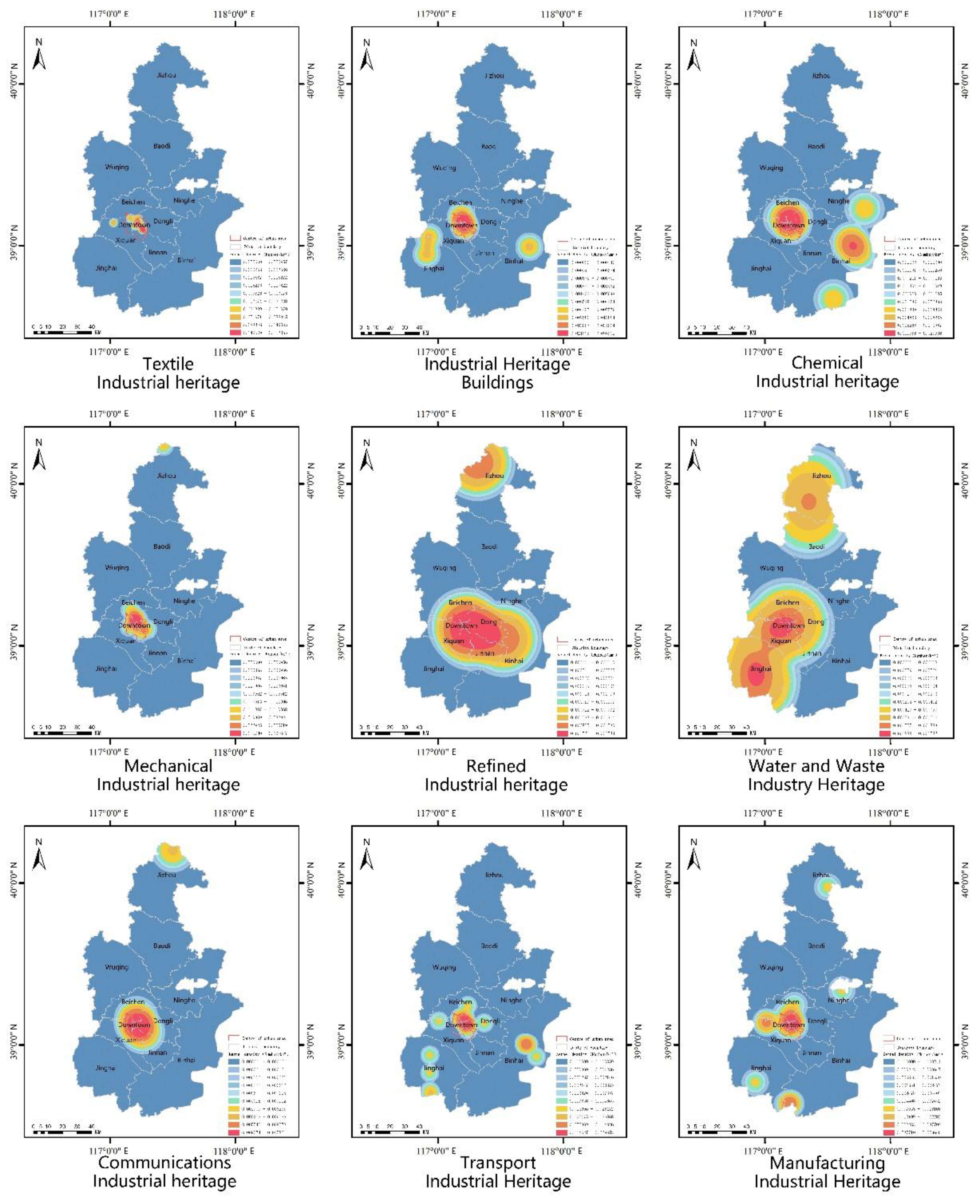
3.3.2. Industrial Type Distribution
3.4. Influencing Factors and Explanatory Power of Distributional Differences
4. Conclusions
4.1. Objective Law
4.2. Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Development and Reform Commission. National old industrial base adjustment and transformation plan. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2013/content_2441018.htm (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Luo, S. Leading Early Modern Civilisation: Tianjin Witnesses to 100 Years of China; Tianjin People Press: Tianjin, China, 2005; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- China.gov.cn. Circular of the National Development and Reform Commission and other departments on the issuance of the "14th Five-Year Plan" to support the high-quality development of demonstration zones for industrial transformation and upgrading in old industrial cities and resource cities. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-12/01/content_5655185.htm (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Ren, B.B.; Wang, J.S.; Xiao, S.Y.; Li, J.H.; Li, H.X. Research on the Vitality of Industrial Heritage in Central Urban Area of Tianjin Based on Multi-Source Data. Modern Urban Research 2023, 5, 59–67+75. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, N.; Yan, F.; Xu, S.B.; Ji, H. Composition and Characteristics of Industrial Heritage Cluster in Tianjin. Architectural Journal 2014, S2, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.X.; Cai, L.W.; Yu, Z.R. Study on the spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of industrial land in old industrial cities in China--Tianjin as an example. Planners 2021, 00, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.L.; Guo, L.J. Exploration and Practice of Protection and Utilization of industrial Heritage in Tianjin. Urban Studies 2018, 10, 140–143+155. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.B.; Zhang, J.H.; Aoki, N.; Wu, C. Construction of GIS Database for Industrial Heritage in Key Cities:Taking Tianjin as AIV Example.Journal of Industrial Architecture. Industrial Construction 2015, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Aoki, N.; Xu, S.B. Grading Protection of Industrial Heritage of Tianjin Soda Plant Based on Value Evaluation. Industrial Construction 2015, 5, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Chen, Y. On the Legal Protection of Industrial Heritage. China Anc. City 2018, 3, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Industrial Heritage Preservation Method Integrating with Urban Development: The Case of Chongqing. New Archit. 2016, 3, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B. A Review of Industrial Architecture Heritage Research in China. New Archit. 2012, 2, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Cenci, J.; Becue, V.; Koutra, S.; Loakimidis, C.S. Recent Evolution of Research on Industrial Heritage in Western Europe and China Based on Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 13, 5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Distribution situation and Attribution of cultural Heritage in Yangtze River Economic Belt:A Case Study on National Key Cultural Relics Protection Units. Nanjing Journal of Social Sciences 2022, 7, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Cen, C.J.; Becue, V.; Koutra, S. Analysis of spatial structure and influencing factors of the distribution of national industrial heritage sites in China based on mathematical calculations. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2022, 3, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Yang, Z.; Han, F.; Shi, T.; Li, D. Assessing landscape ecological risk for a world natural heritage site: a case study of Bayanbulak in China. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies 2015, 3, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, L. Spatial distribution of traditional Chinese villages andfactors affecting their distribution. Journal of Landscape Research 2019, 1, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xia, J.; Zuo, Y.; Cui, J.; Qiu, Q.; Liu, X.; Zeng, H. Spatiotemporal evolution patterns and driving factors of synergistic development of culture,sports,and tourism industries:the case study of China. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2021, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.D.; Zhang, Y.K.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Lin, F.Y. Spatial–temporal distribution and evolution of the socialist built heritage in China, 1949–1978. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.S. Modern Tianjin and Northern Economic Development. Journal of ZhengZhou University 2007, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Lv, Q.A. Study on The History of Tianjin Early-Modern City Planning (1860–1949). Urban Plan. Forum 2005, 5, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P. Eariy-Modern Tianjin City Planning Illustration; Tianjin Urban Construction Archives: Tianjin, China, 2012; pp. 120–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.T. Yuan Shikai and Tian Jin's Early Pursuit of Modernity. Historical Review 2017, 6, 18–26+218. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H. The study on the evolution of the industrial configuration and current protect situation of industrial heritage in Tianjin. Journal of Fuzhou University(Natural Science Edition) 2014, 3, 439–444. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.H. Tianjin Shipping during the Period of War of Resistance against Japan. Urban History Research 2015, 2, 56–65+289–290. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.Y. Courageous Expansion and Brilliance--Tianjin's Economic Construction and Historical Experience in the First Five-Year Plan Period. Journal of CPC Tianjin Party School 1999, 4, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J. History of Urban Construction in China, 3rd ed.; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, X. The Impact of the Third line Construction on China's Industrial Economy and Urbanization. Contemp. China Hist. Stud. 2015, 22, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.L. Tianjin Industry in the Republican Period. Tianjin Economy 2004, 5, 77–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H. Inestigation on Tianjin's Modern Autonomous Industrial Heritage. Tianjin University 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F. Study on The Industrial Heritage conservation and the Reuse Pattern Pedigree: From the Scalehierarchy Perspective. City Plan. Rev. 2016, 40, 84–96+112. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, M. Relocation and Agglomeration of Chinese Industry. Econ. Res. J. 2004, 2, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, J.; Cui, X. Research on the Practice and Theory of Regional Economic Policy since the Founding of New China. Reg. Econ. Rev. 2019, 4, 8–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.K.; Zhao, X.X. A Renewal Strategy for an Old Industrial Community in an Urban Fringe Area: A Case Study of the Nanjing Jiangnan Cement Factory-affiliated Community. South Architecture 2022, 7, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Tianjin Local Records Revision Committee. Tianjin Tongjian (first volume); China Youth Publishing House, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, R. Tianjin's Leading Role in the Economic Development of Northern China in the Modern Times. Journal of Chinese Historical Geography 2006, 2, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.H.; He, J.; Han, F.W. The Basic Features and Cultural Connotation of Modern Industrial Heritage in Northeast China, Analyzed as Historical and Cultural Units Under Government Protection. Economic Geography 2016, 1, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Tianjin government website. Municipal Bureau of Culture and Tourism showcases cultural features, creates new world of industrial tours. Available online: https://www.tj.gov.cn/sy/zwdt/bmdt/202302/t20230228_6122888.html (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Guo, H.; Ma, Y. Protection and Utilization of Riverside Industrial Heritage Under the Mode of Industrial Heritage Corridor: Taking the Pearl River in Guangzhou as an Example. Industrial Construction 2022, 5, 9–15+76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, F. A Literature Review of Linear Heritage. Southeast Cult. 2016, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, H.; Cao, X. Review of Heritage Corridor Research in China. Urban Dev. Stud. 2016, 23, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Loren-Mendez, M.; Mata-Olmo, R.; Ruiz, R.; Pinzon-Ayala, D. An Interdisciplinary Methodology for the Characterization and Visualization of the Heritage of Roadway Corridors. Geogr. Rev. 2016, 106, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Duan, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Tan, X.; Li, G. Geo-Informatics in Resource Management and Sustainable Ecosystem, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.; Lu, C. The City-oriented Industrial Heritage Protection—With the Industrial Heritage Protection of Nanjing as the Example. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2013, 29, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Tianjin government affairs website. Tianjin Natural Resources Protection and Utilization "14th Five-Year Plan". Available online: https://www.tj.gov.cn/zwgk/szfwj/tjsrmzfbgt/202107/t20210705_5496394.html (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- TianjinGovernment.com. Notice of the Tianjin Municipal People's Government on the Issuance of the Outline of the Fourteenth Five-Year Plan for the National Economic and Social Development of Tianjin and the Visionary Goals for the 2035 Years. Available online: https://www.tj.gov.cn/zwgk/szfwj/tjsrmzf/202102/t20210208_5353467.html (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Liu, B.Y. Different Types of the Renewal of Urban Industrial Sites. Architectural Journal 2006, 8, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.B.; Aoki, N.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.Y.; Chang, J.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.C.; Zuo, Y.; Cao, Y.K.; Zhou, L.; Chen, C. Discussion: Turning "the Rusty" into "Beauty" -the New ldeas and New Development of the Preservation and Reuse Trend of Industrial Heritage. China Cultural Heritage 2022, 3, 4–18. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.H.; He, J. Traumatic memory of industrial heritage and its mechanism for community cultural identity: A case study of Tiexi District, Shenyang. Journal of Chinese Ecotourism 2023, 2, 316–328. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Research on the Construction of Industrial Heritage Information Collection and Management System in China. Ph.D. Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, H.; Ran, H.; Zhang, D. Value of Industrial Heritage and Its Conservation. J. Northeast. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2007, 1, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. A Research on the Protection of Equipment for Industrial Services in the Industrial Heritage. Master's Thesis, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Liu, S.D. The Importance of Management and Reuse of Industrial Cultural Heritage for Urban Renewal--A Review of Industrial Cultural Heritage: Value System, Educational Inheritance and Industrial Tourism. Leadership Science 2022, 12, 147. [Google Scholar]
| Water system |
Center of urban area | Binhai New District | Jinghai district | Xiquan district | Beichen district | Dongli district | Ji Zhou district | Ninghe district | Percentage share% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main stream of the Haihe River | 34 | 14 | 1 | 51.58 | |||||
| South and North Canals | 6 | 10 | 5 | 1 | 23.16 | ||||
| Other water systems | 22 | 2 | 25.26 |
| Dimension | Targets | Evaluation indicators | q-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural environment | Topography and geomorphology | Topography, geomorphology, elevation data | 0.004 |
| Green space and water system | Rivers, lakes, length of waterways, distribution of green spaces | 0.018 | |
| Climatological | Annual precipitation, average annual temperature | 0.034 | |
| Social environment | Transportation factors | Roads, metro, transit, shipping | 0.702 |
| Economic factors | GDP per capita | 0.422 | |
| Demographic factors | Total population, residential distribution | 0.325 | |
| Cultural and educational factors | Science, education, and culture | 0.257 | |
| Policy planning factors | Land use, construction land use classification | 0.031 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





