Submitted:
22 August 2024
Posted:
23 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
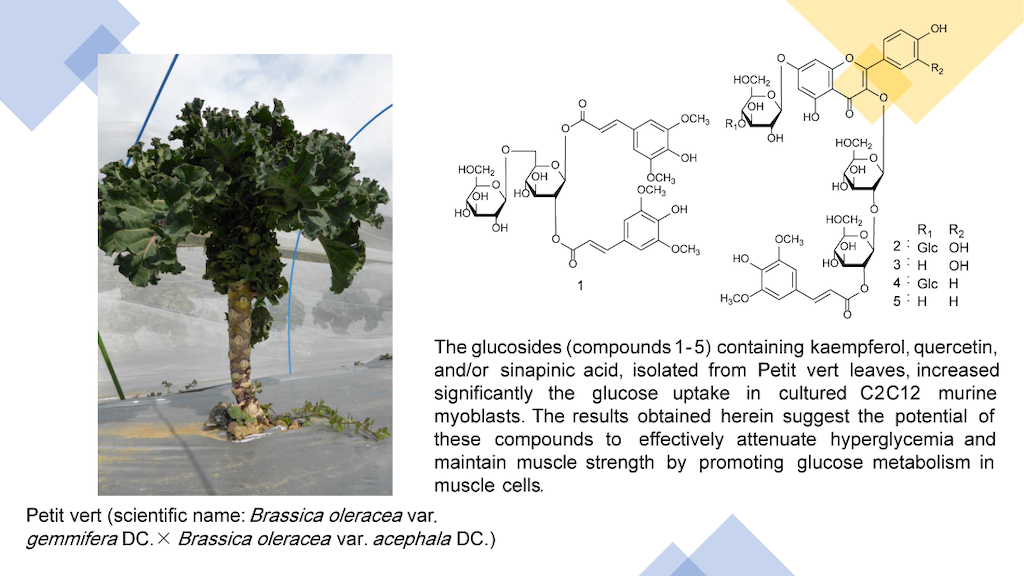
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction and Isolation
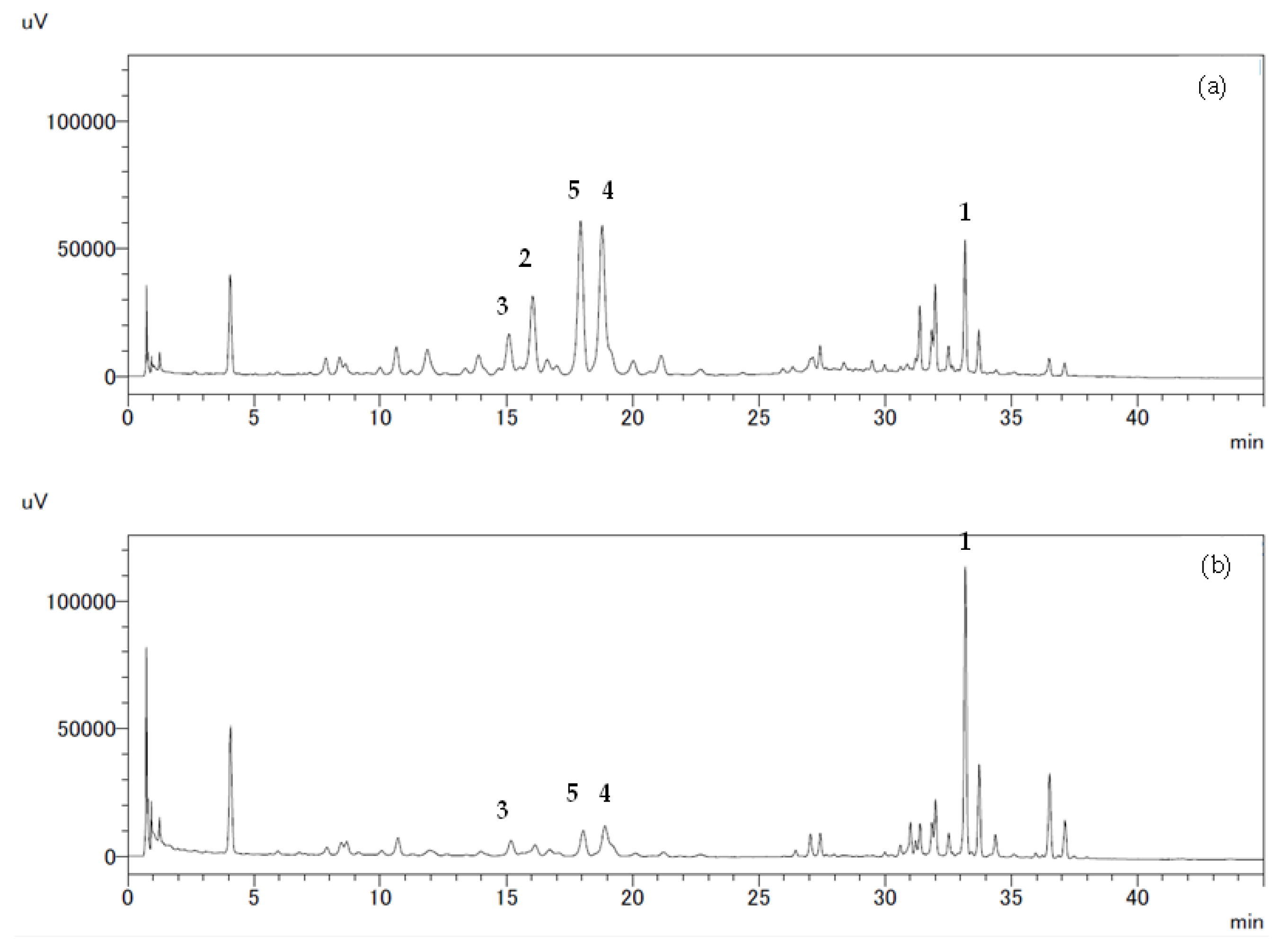
2.3. Identification of Phenolic Compounds by HPLC
2.4. Structural Elucidation of Phenolic Compounds by NMR and MS
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.7. Assay of Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Mouse Myoblast Cells
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
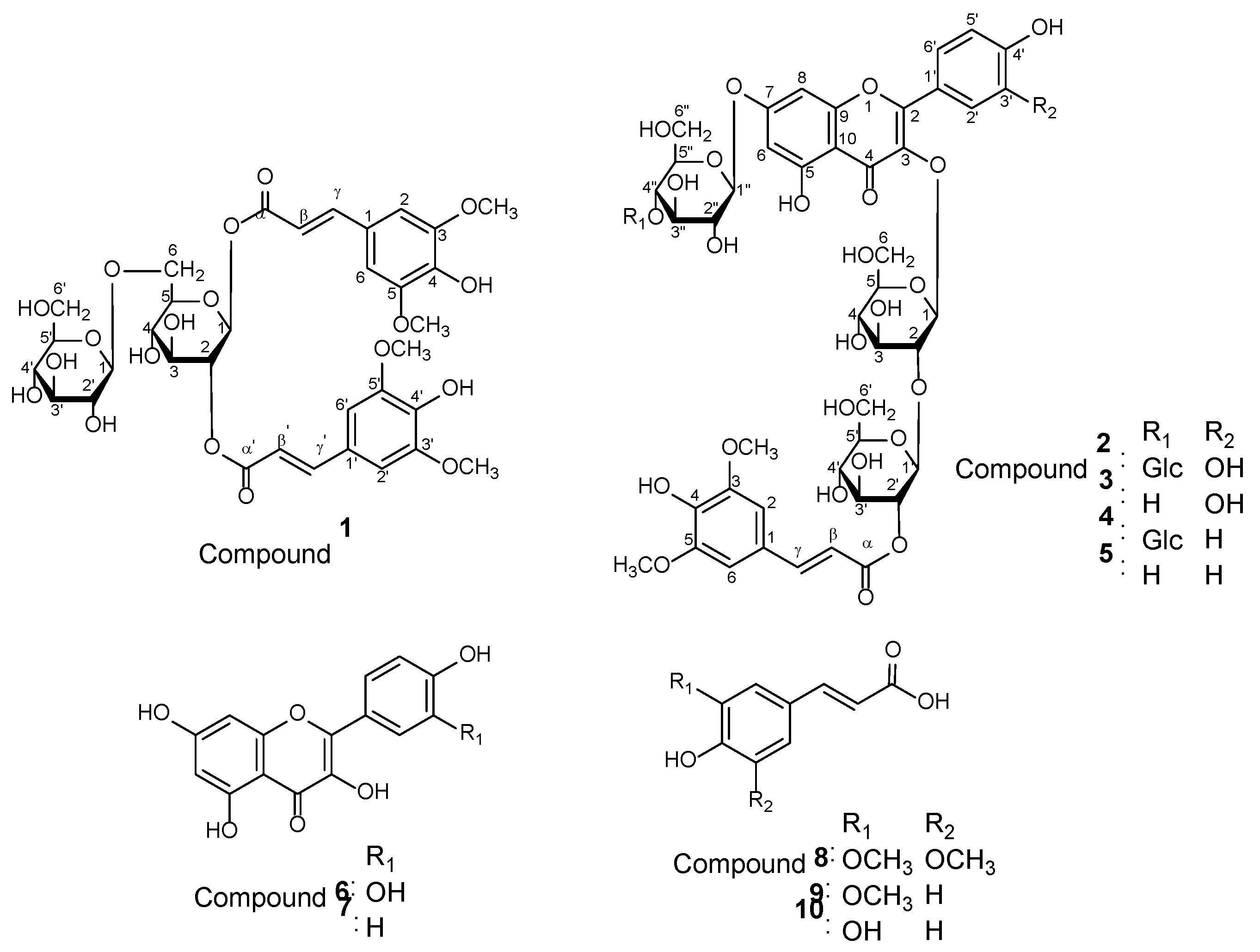
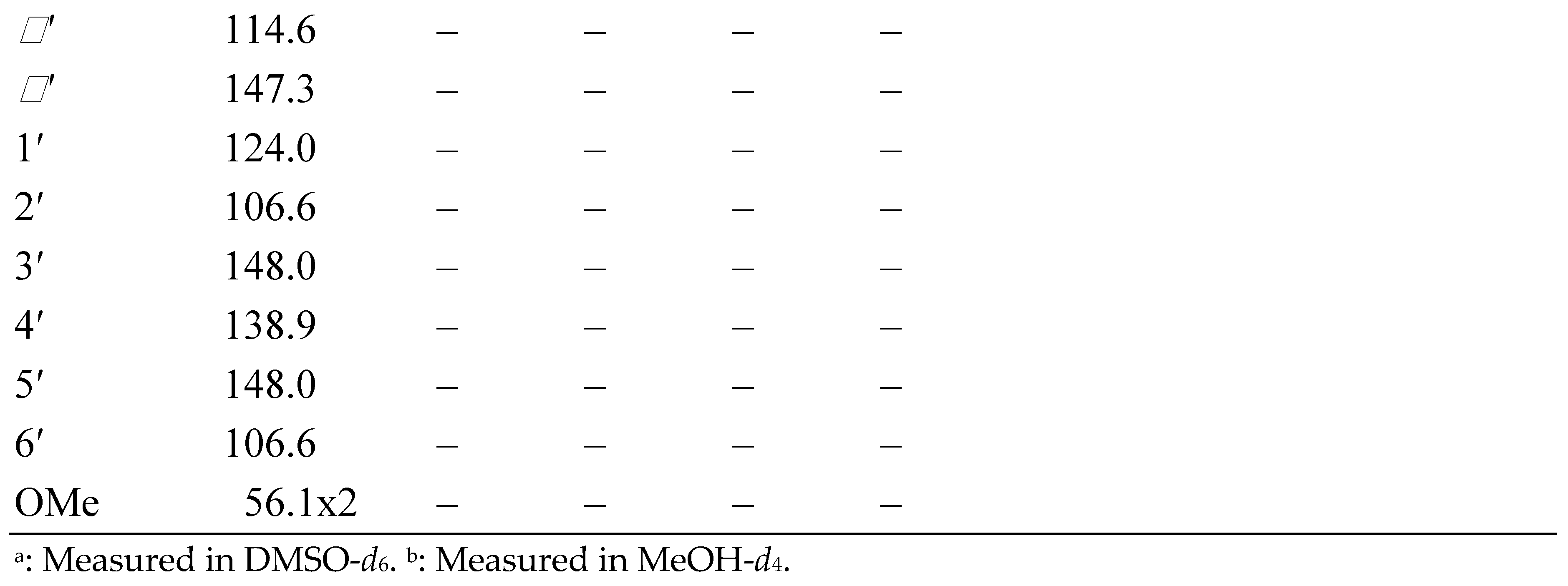
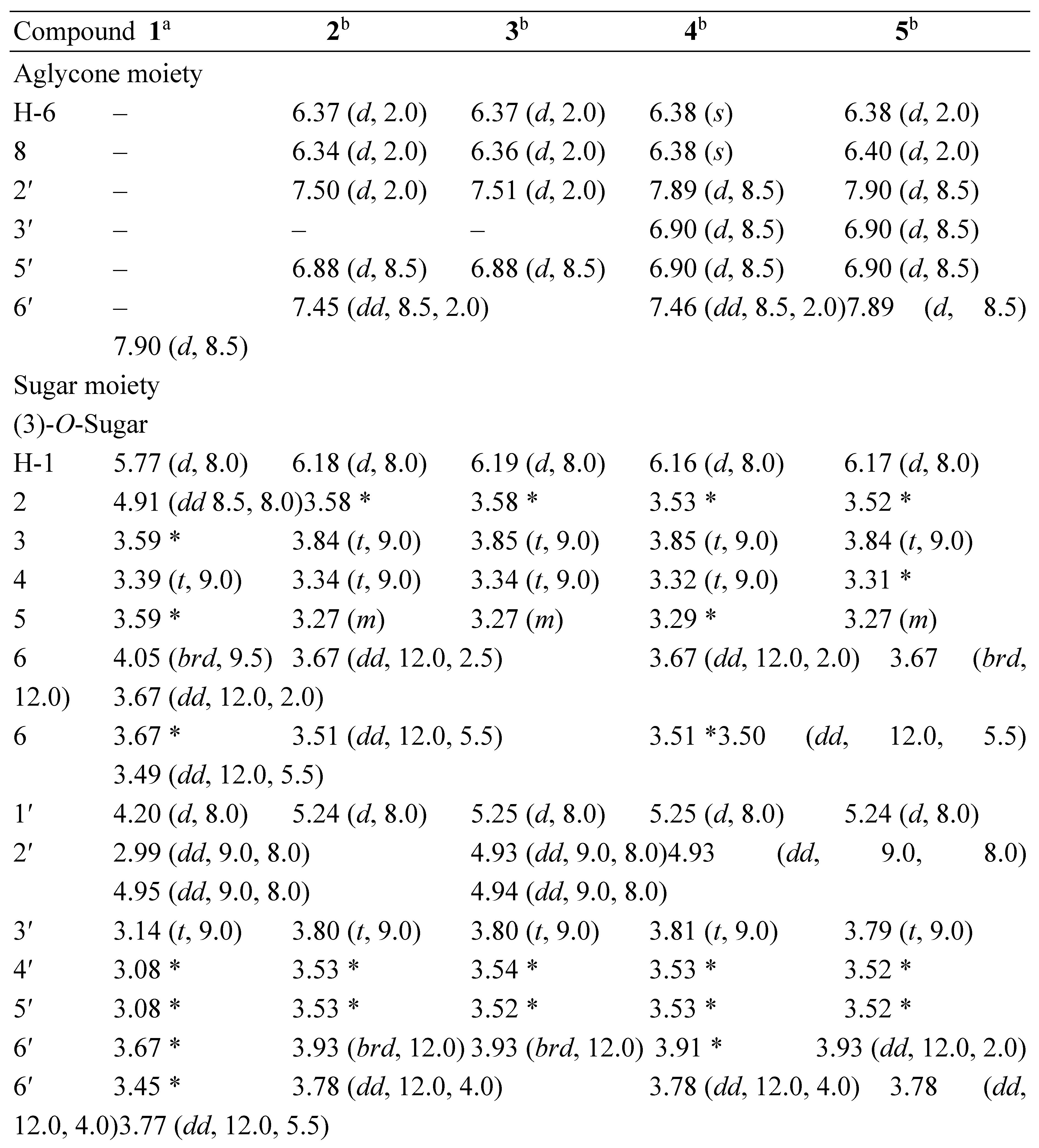
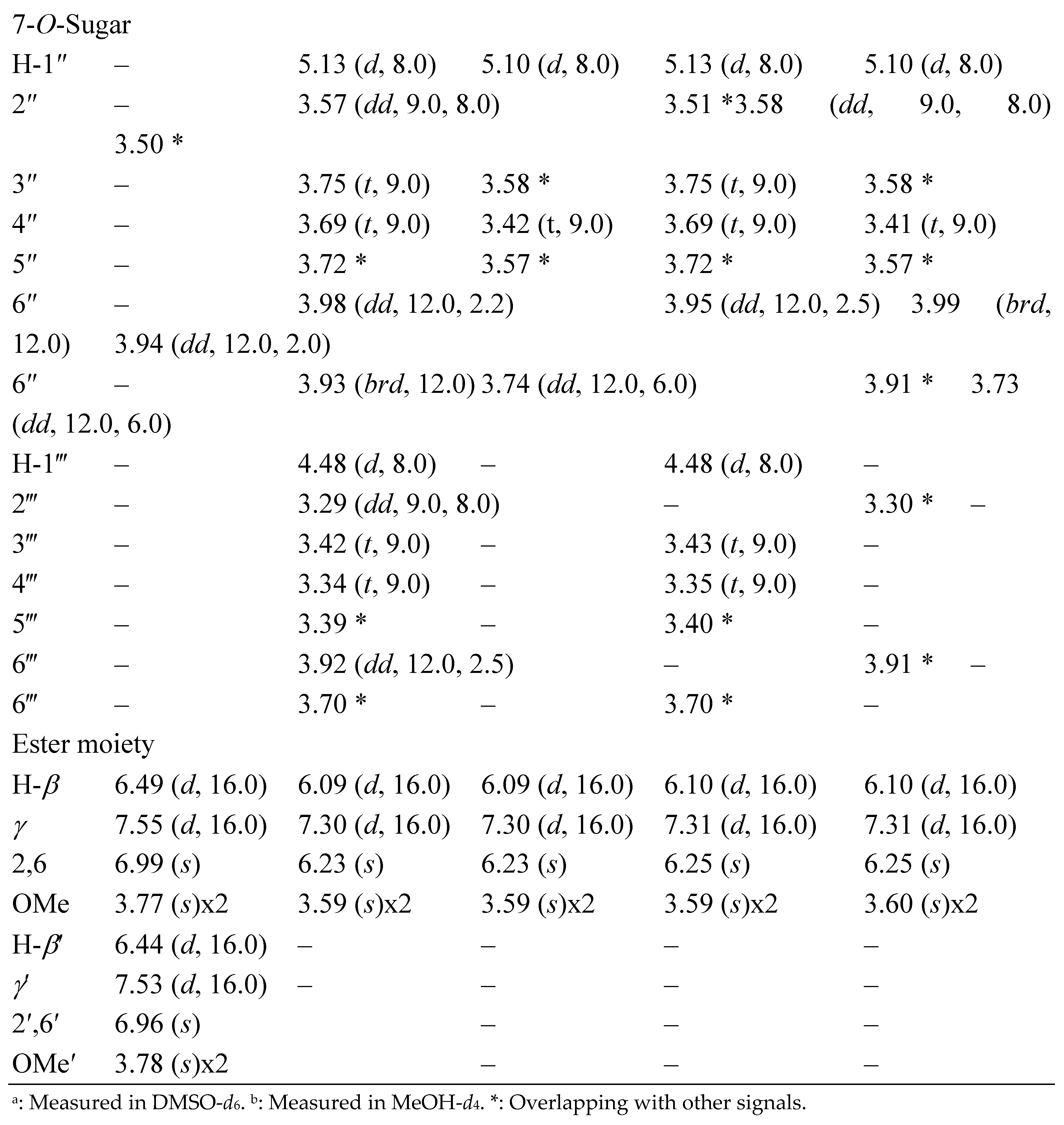
3.1. Structural Elucidation of Phenolic Compounds by NMR
3.2. Effects on Glucose Uptake in Cultured C2C12 Murine Myoblasts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Authorship Contributions
Declaration of Interest
Data availability Statement
References
- Ou, S.; Kwok, K.C. Ferulic acid: Pharmaceutical functions, preparation and applications in foods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 1261–1269. [CrossRef]
- Fresco, P.; Borges, F.; Diniz, C.; Marques, M. New insights on the anticancer properties of dietary polyphenols. Med. Res. Rev. 2006, 26, 747–766. [CrossRef]
- Darvesh, A.S.; Carroll, R.T.; Bishayee, A.; Geldenhuys, W.J.; Van der Schyf, C.J. Oxidative stress and Alzheimer’s diseases: Dietary polyphenols as potential therapeutic agents. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2010, 10, 729–745. [CrossRef]
- Niciforovic, N.; Abramovic, H. Sinapic acid and its derivatives: Natural sources and bioactivity. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 34–51. [CrossRef]
- Karakida, F.; Ikeya, Y.; Tsunakawa, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ikarashi, Y.; Takeda, S.; Aburada, M. Cerebral protective and cognition-improving effects of sinapic acid in rodents. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 514–519. [CrossRef]
- Lee, I-S.; Choi, G-Y.; Sreelatha, I.; Yoon, J-W.; Youn, S-H.; Maeng, S.; Park, J-H. Effect of sinapic acid on scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairment in SD rats. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 427. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.E.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, Y.W.; Jung, J.M.; Lee, C.H.; Hong, J.G.; Liu, X.; Cai, M.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of sinapic acid in a mouse model of amyloid 1-42 protein-induced Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 103, 260–266. [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Singh, D.; Kh, R. Sinapic acid alleviates oxidative stress and neuro- inflammatory changes in sporadic model of Alzheimer’s disease in rats. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 923. [CrossRef]
- Zare, K.; Eidi, A.; Roghani, J.; Rohani, A.H. The neuroprotective potential of sinapic acid in the 6-hydroxydopamine-induced hemi-parkinsonian rat. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 205–213. 10.1007/s11011-014-9604-6.
- Nishida, H.; Kuriyama, Y.; Kawakami, K.; Takei, Y.; Chiba, T.; Masuda, H.; Kazama, K.; Ohtsuka, A.; Sato, S.; Konishi, T. Anti-obesitic effect of petit vert on mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Jpn. Soc. Nutr. Food Sci. 2011, 64, 169–175. (in Japanese. [CrossRef]
- Price, K. R.; Casuscelli F.; Colquhoun, I. J.; Rhodes M. J. C. Hydroxycinnamic acid esters from broccoli florets. Phytochemistry, 1997, 45, 1683–1687. [CrossRef]
- Fiol M.; Adermann S.; Neugart S.; Rohn S.; Mügge C.; Schreiner M.; Krumberin A.; Kroh L. W. Highly glycosylated and acylated flavonols from kale (Brassica oleracea var. sabellica) - Structure-antioxidant activity relationship. Food Res. Int., 2012,47, 80–89. [CrossRef]
- Olsson, L. C.; Veit M.; Weissenböck G.; Bornman J. F. Differential flavonoid response to enhanced UV-B radiation in Brassica napus. Phytochemistry, 1998, 49, 1021–1028. [CrossRef]
- Nielsen J. K., Olesen C. E. L., Petersen M. K. Acylated flavonol glycosides from cabbage leaves. Phytochemistry, 1993, 34, 539–544. [CrossRef]
- Nielsen J. K.; Nørbæk R.; Olsen C. E. Kaempferol tetraglucosides from Cabbage leaves. Phytochemistry, 1998, 49, 2171–2176. [CrossRef]
- Ranilla, L.G.; Kwon, Y.-I.; Apostolidis, E.; Shetty, K. Phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity and in vitro inhibitory potential against key enzymes relevant for hyperglycemia and hypertension of commonly used medicinal plants, herbs and spices in Latin America. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4676–4689. [CrossRef]
- Cory, H.; Passarellim S.; Szeto, J.; Tamez, M.; Mattei, J. The role of polyphenols in human health and food systems: A mini-review. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, D. Flavonol kaempferol improves chronic hyperglycemia-impaired pancreatic beta-cell viability and insulin secretory function. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 325–332. [CrossRef]
- Pandi, A.; Kalappan, V.M. Pharmacological and therapeutic applications of sinaptic acid-an updated review. Mol. Biol. Reports. 2021, 48, 3733–3745. 10.1007/s11033-021-06367-0.
- Cherng, Y.G.; Tsai, C.C.; Chung, H.H.; Lai, Y.W.; Kuo, S.C.; Cheng, J.T. Antihyperglycemic action of sinapic acid in diabetic rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 12053–12059. [CrossRef]
- Dubie, J.; Stancik, A.; Morra, M.; Nindo, C. Antioxidant extraction from mustard (Brassica juncea) seed meal using high-intensity ultrasound. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, F542-E548. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, J.; Ding, X.; Xuan, J.; Hu, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhu, X.; Feng, Z.; Ni, W.; Wu, A. The protective effect of sinapic acid in osteoarthritis: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 1940–1950. [CrossRef]
- Balaji, D.; Muthukumaran, J.; Nalini, N. Chemopreventive effect of sinapic acid on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced experimental rat colon carcinogenesis. Hum.Exp. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 1253–1268. [CrossRef]
- Shin D.S.; Kim, K.W.; Chung, H.Y.; Yoon, S.; Moon, J.O. Effect of sinapic acid against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic injury in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 626–633. 10.1007/s12272-013-0050-5.
- Roy, S.J.; Mainzen Prince, P.S. Protective effects of sinapic acid on cardiac hypertrophy, dyslipidaemia and altered electrocardiogram in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarcted rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 699, 213–218. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Raish, M.; Ahmad, A.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Ahmad, S.F.; Attia, S.M.; Alsaad, A.M.S.; Bakheel, S.A. Sinapic acid ameliorate cadmiun-induced nephrotoxicity: In vivo possible involvement of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation via NF-kaB NF-κB downregulation. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 51, 100–107. [CrossRef]
- Kanchana, G.; Shyni, W.J.; Rajadurai, M.; Periasamy, R. Evaluation of anti-hyperglycemic effect of sinapic acid in normal and streptozocin (STZ)-induced diabetic diabetes in albino rats. Global J. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 33–39. chromeextension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://idosi.org/gjp/5(1)11/7.
- Tesaki, S.; Tanabe, S.; Ono, H.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J.; Watanabe, M. 4-Hydroky-3-nitrophenylacetic and sinapic acid as antibacterial compounds from Mustard seed. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 998–1000. [CrossRef]
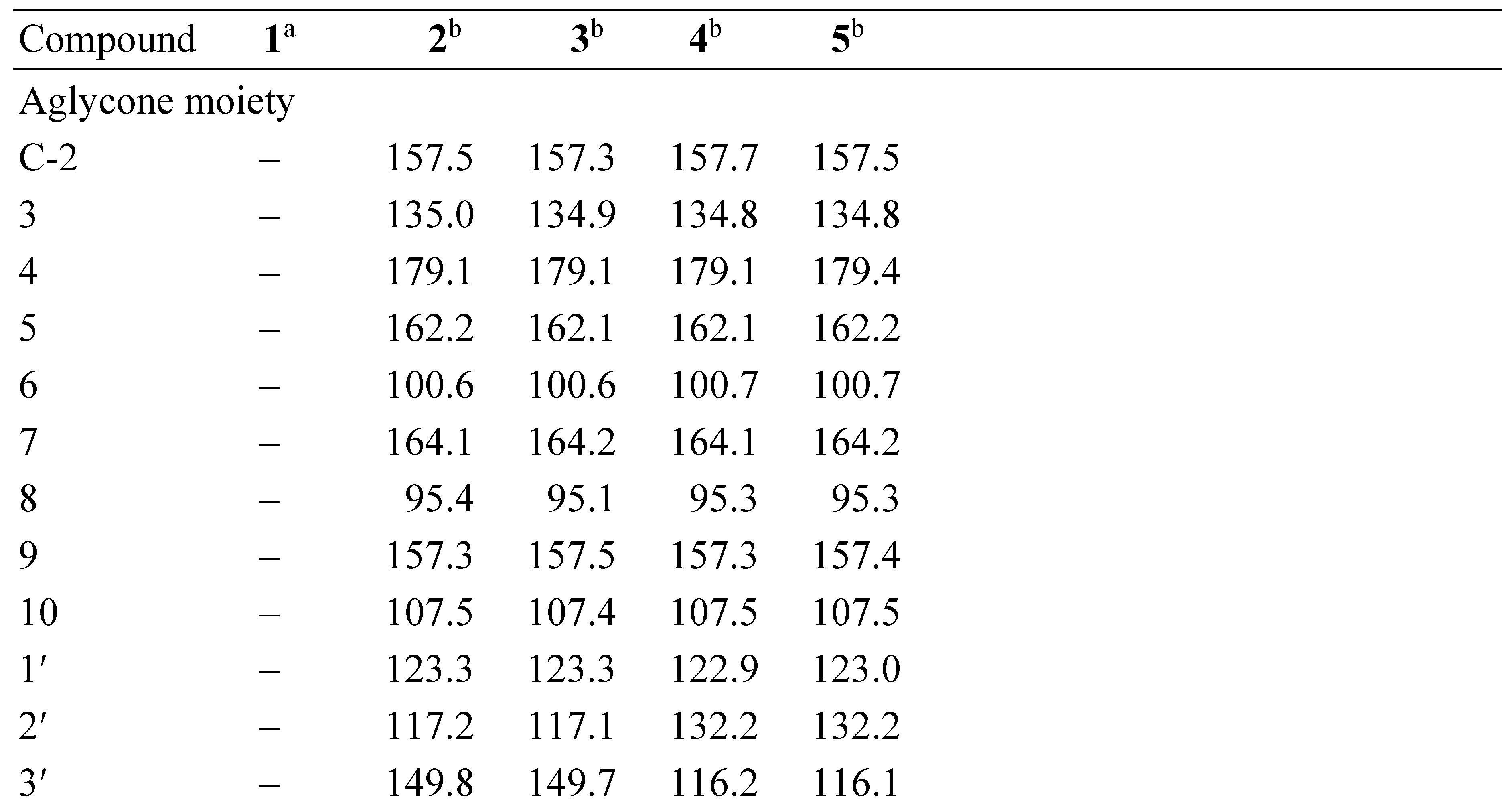
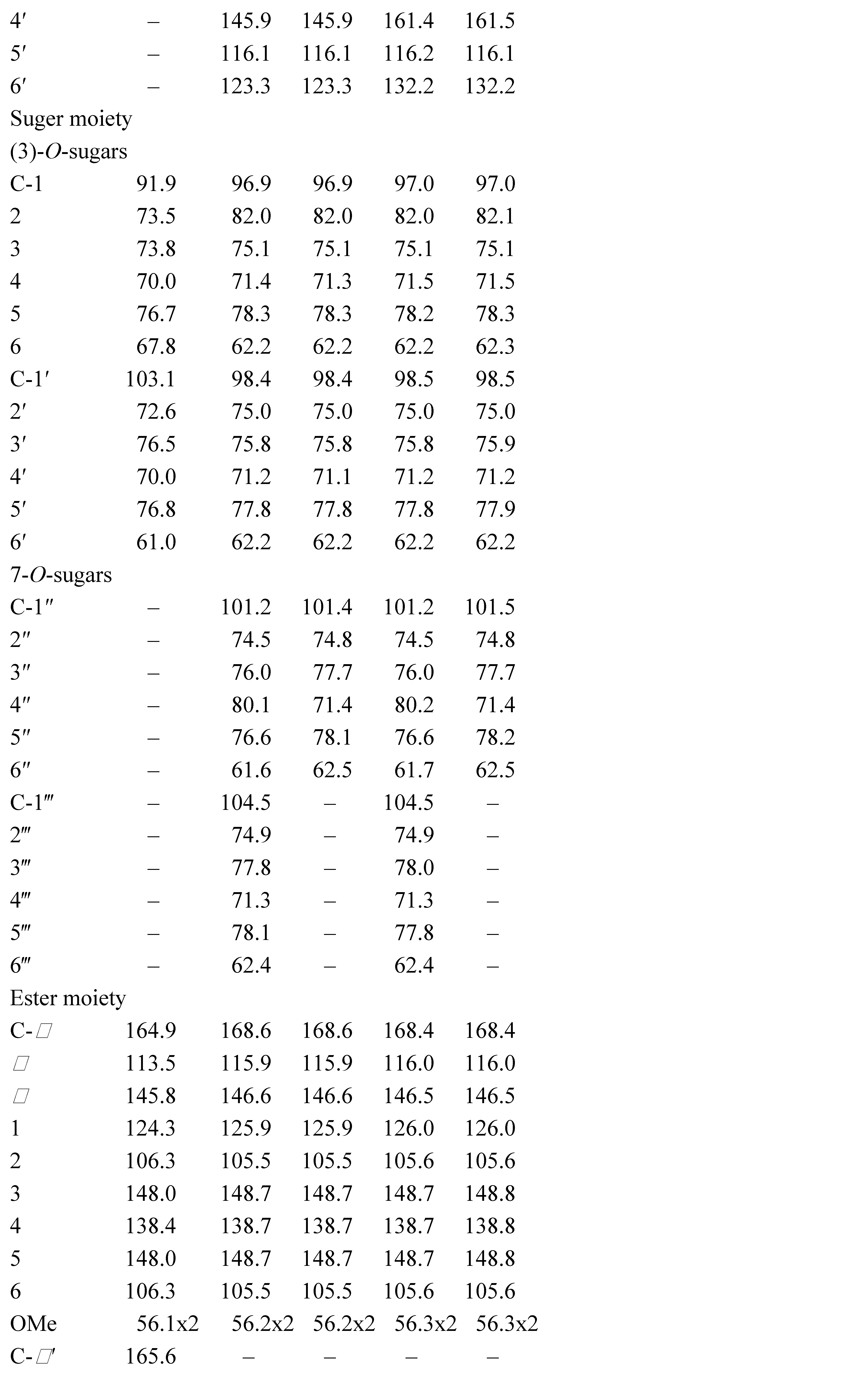
| Test substance | Control | 1 | 10 (µM) |
100 |
| Viable cell rate (% of control) | ||||
| 1 | 100.0 ± 0.9 | 105.0 ± 1.6 | 101.4 ± 1.1 | 103.1 ± 0.7 |
| 2 | 100.0 ± 0.6 | 96.0 ± 0.9 | 94.9 ± 1.1 | 96.1 ± 1.0 |
| 3 | 100.0 ± 0.9 | 97.9 ± 0.4 | 98.9 ± 1.1 | 103.8 ± 1.1 |
| 4 | 100.0 ± 1.1 | 88.6 ± 0.8 | 93.5 ± 1.8 | 91.6 ± 0.7 |
| 5 | 100.0 ± 0.2 | 98.5 ± 2.5 | 102.0 ± 1.1 | 99.5 ± 0.8 |
| Quercetin (6) | 100.0 ± 0.6 | 102.0 ± 0.4 | 98.0 ± 1.1 | 76.6 ± 1.2* |
| Kaempferol (7) | 100.0 ± 1.2 | 105.7 ± 2.5 | 111.1 ± 1.7 | 66.6 ± 1.0* |
| Sinapic acid (8) | 100.0 ± 1.4 | 110.0 ± 1.4 | 107.0 ± 0.9 | 119.1 ± 2.4 |
| Ferulic acid (9) | 100.0 ± 0.6 | 102.4 ± 1.2 | 108.4 ± 1.3 | 111.5 ± 0.3 |
| Caffeic acid (10) | 100.0 ± 0.1 | 107.0 ± 1.7 | 107.8 ± 1.6 | 101.0 ± 2.4 |
- Each value represents the mean ± S.E. for 3 determinations.
- *P<0.05, significantly different from the control (0.1%DMSO).
| Test compounds | Control | 1 | 10 (µM) |
100 |
| Uptake (% of control) | ||||
| 1 | 100.0 ± 2.8 | 128.4 ± 5.5** | 125.2 ± 3.2*** | 122.1± 1.4*** |
| 2 | 100.0 ± 2.8 | 130.9 ± 8.0* | 108.7 ± 4.8 | 88.3 ± 1.8* |
| 3 | 100.0 ± 3.6 | 130.7 ± 6.9** | 120.1 ± 1.9** | 100.8 ± 3.7 |
| 4 | 100.0 ± 3.6 | 110.4 ± 5.6 | 127.4 ± 5.0** | 145.5 ± 2.8*** |
| 5 | 100.0 ± 3.7 | 116.8 ± 3.5* | 114.9 ± 2.5* | 103.0 ± 4.7 |
| Quercetin (6) | 100.0 ± 3.7 | 104.1 ± 3.5 | 102.3 ± 2.8 | 25.5 ± 0.7*** |
| Kaempferol (7) | 100.0 ± 4.4 | 135.0 ± 2.4*** | 144.5 ± 9.5** | 39.8 ± 1.4*** |
| Sinapic acid (8) | 100.0 ± 4.4 | 135.8 ± 6.8** | 129.7 ± 4.9** | 127.3 ± 3.7** |
| Ferulic acid (9) | 100.0 ± 3.7 | 105.6 ± 2.4 | 120.5 ± 2.8** | 116.2 ± 1.5** |
| Caffeic acid (10) | 100.0 ± 3.7 | 129.9 ± 11.7 | 111.9 ± 5.0 | 108.6 ± 7.1 |
- After treatment with various compounds at the indicated concentration in the absence of insulin, glucose uptake was measured using Promega Glucose Uptake-Glo™ Assay kit.
- Each value represents the mean ± S.E. for 5 determinations.
- *** P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05, significantly different from the control (0.1%DMSO).
| Test compounds | Control | 1 | 10 (µM) |
100 |
| Uptake (% of control) | ||||
| 1 | 100.0 ± 8.4 | 96.3 ± 4.0 | 92.1 ± 2.9 | 81.8 ± 1.8 |
| 2 | 100.0 ± 8.4 | 84.4 ± 1.9 | 82.2 ± 3.9 | 83.8 ± 5.2 |
| 3 | 100.0 ± 3.1 | 110.6 ± 2.6* | 120.5 ± 7.4 | 81.9 ± 4.6* |
| 4 | 100.0 ± 3.1 | 74.2 ± 2.9*** | 90.5 ± 1.7 | 123.1 ± 9.4* |
| 5 | 100.0 ± 3.5 | 114.5 ± 5.4 | 103.7 ± 5.7 | 81.1 ± 4.4* |
| Quercetin (6) | 100.0 ± 3.5 | 72.9 ± 5.5** | 76.8 ± 3.7** | 20.1 ± 1.8*** |
| Kaempferol (7) | 100.0 ± 4.6 | 148.4 ± 6.8*** | 132.7 ± 2.3*** | 31.7 ± 1.0*** |
| Sinapic acid (8) | 100.0 ± 4.6 | 116.5 ± 1.5* | 119.3 ± 2.7* | 123.0 ± 3.1** |
| Ferulic acid (9) | 100.0 ± 8.6 | 97.0 ± 2.0 | 118.7 ± 7.3 | 94.9 ± 2.2 |
| Caffeic acid (10) | 100.0 ± 8.6 | 94.3 ± 1.9 | 101.7 ± 5.6 | 99.5 ± 0.7 |
- After treatment with various compounds at the indicated concentration in the presence of insulin, glucose uptake was measured using Promega Glucose Uptake-Glo™ Assay kit.
- Each value represents the mean ± S.E. for 5 determinations.
- *** P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05, significantly different from the control (0.1%DMSO).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





