Submitted:
22 August 2024
Posted:
23 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Steel Substrate Preparation
2.3. Thin Film Deposition
2.4. SEM and EDS Analysis
2.5. Mechanical Tests
2.5.1. Nanoindentation Testing
2.5.2. Micro-Scratch Tests
2.6. Tribological Tests
2.7. Corrosion Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SEM and EDS analysis
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.2.1. Nanoindentation Testing Results
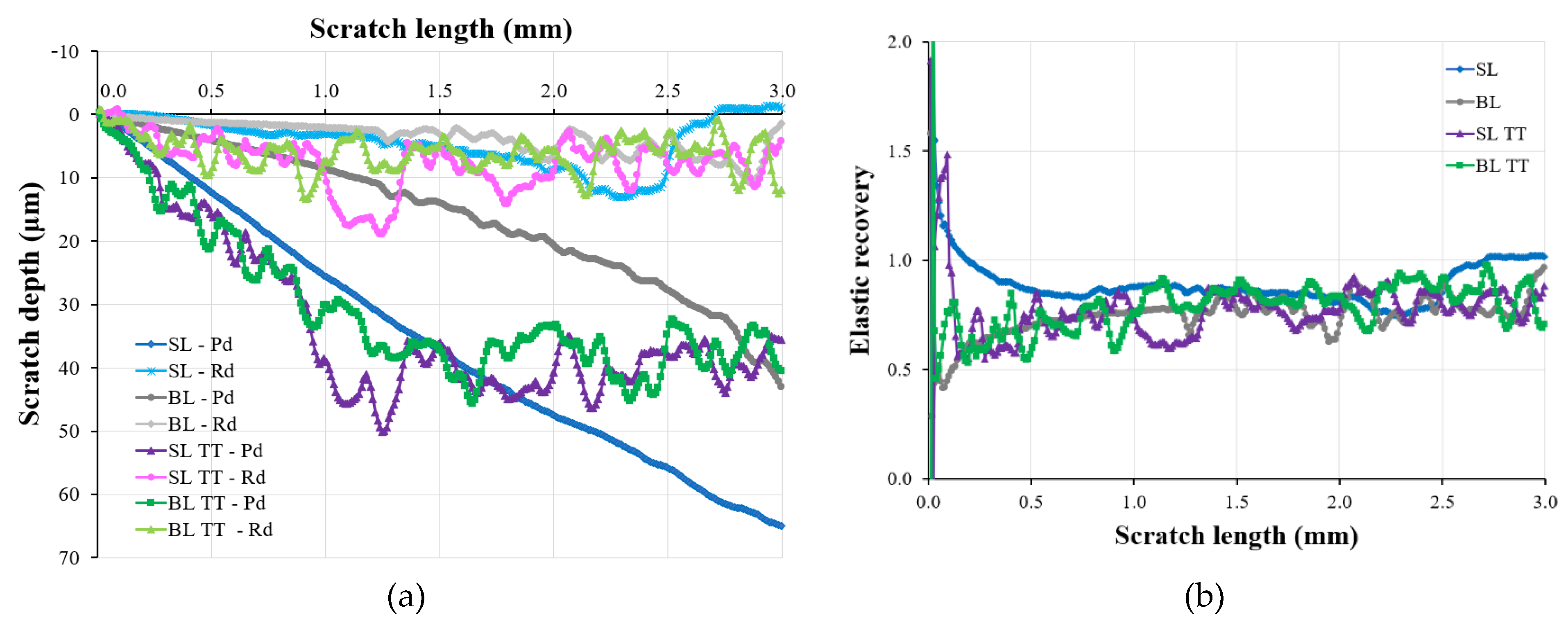
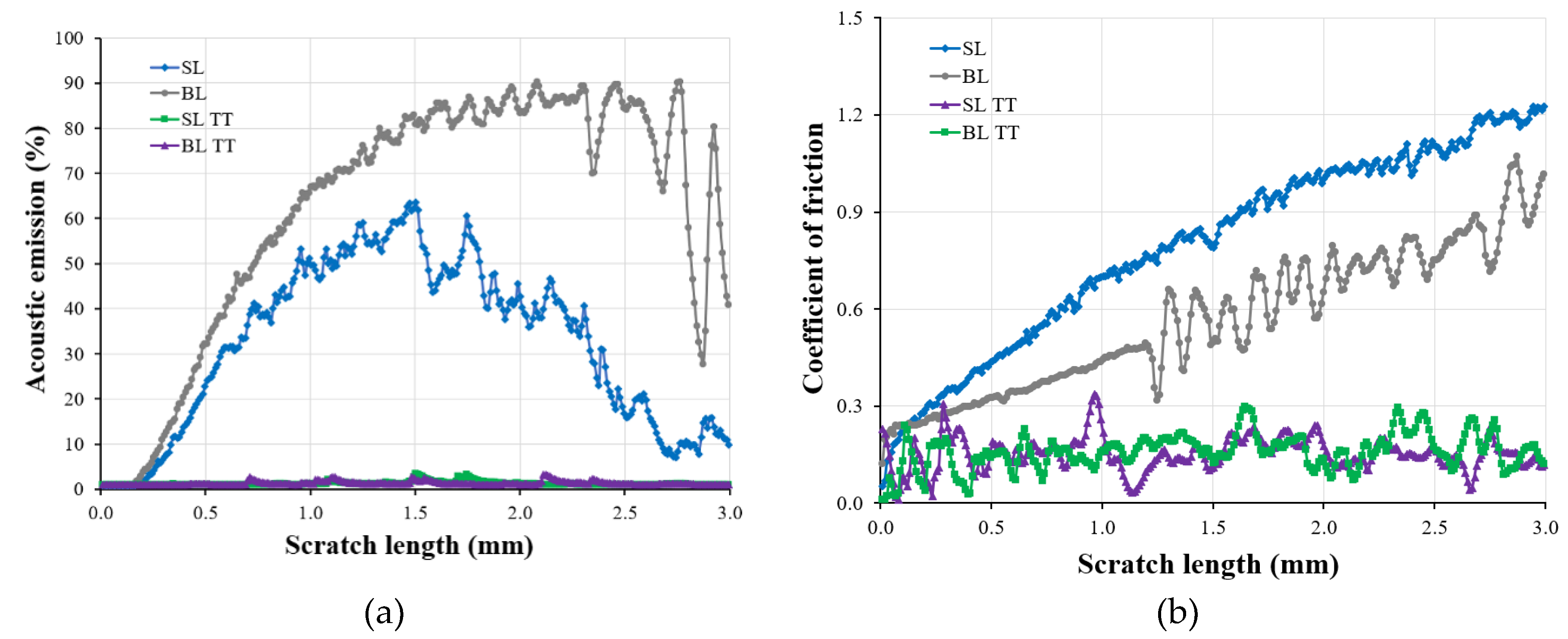
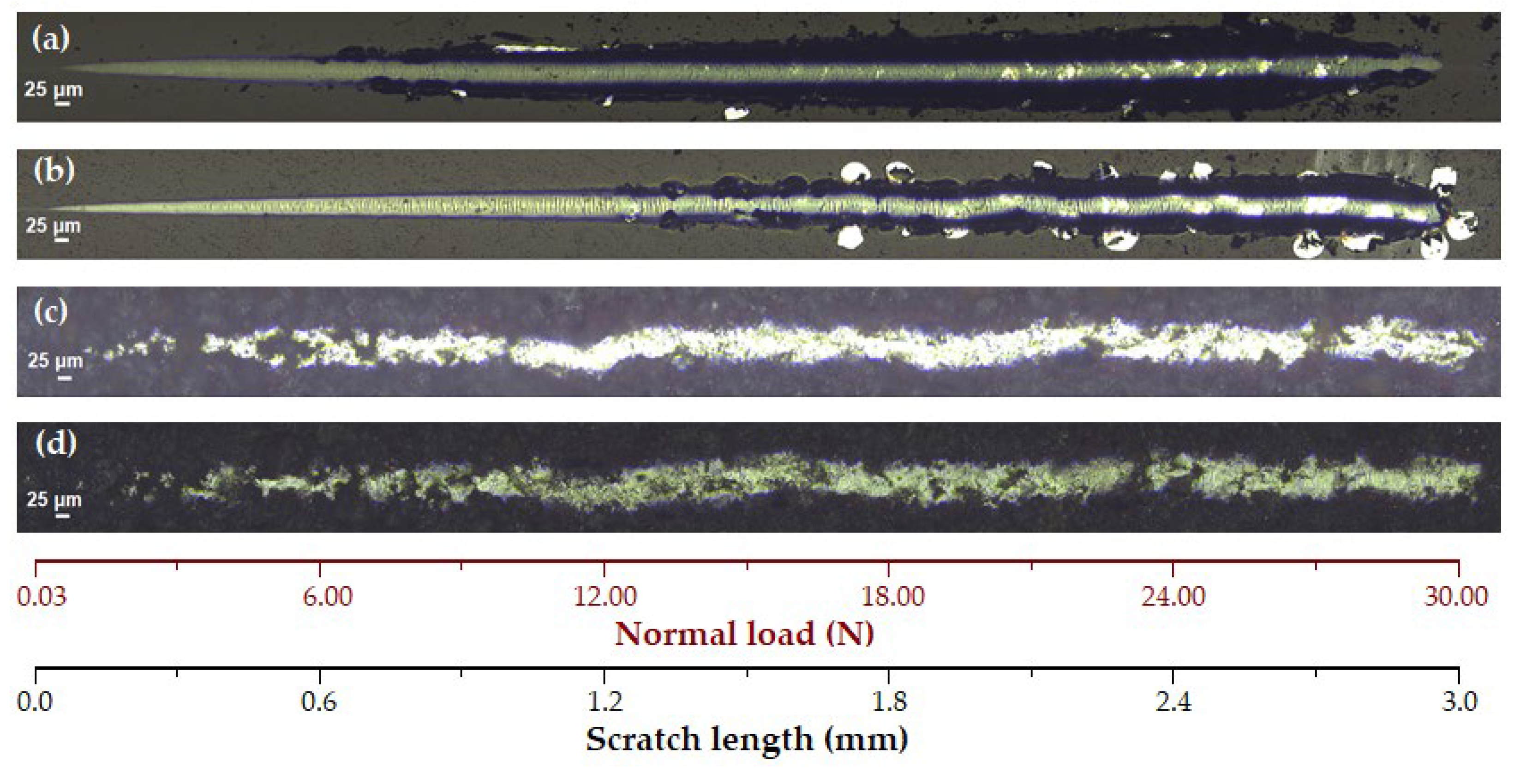
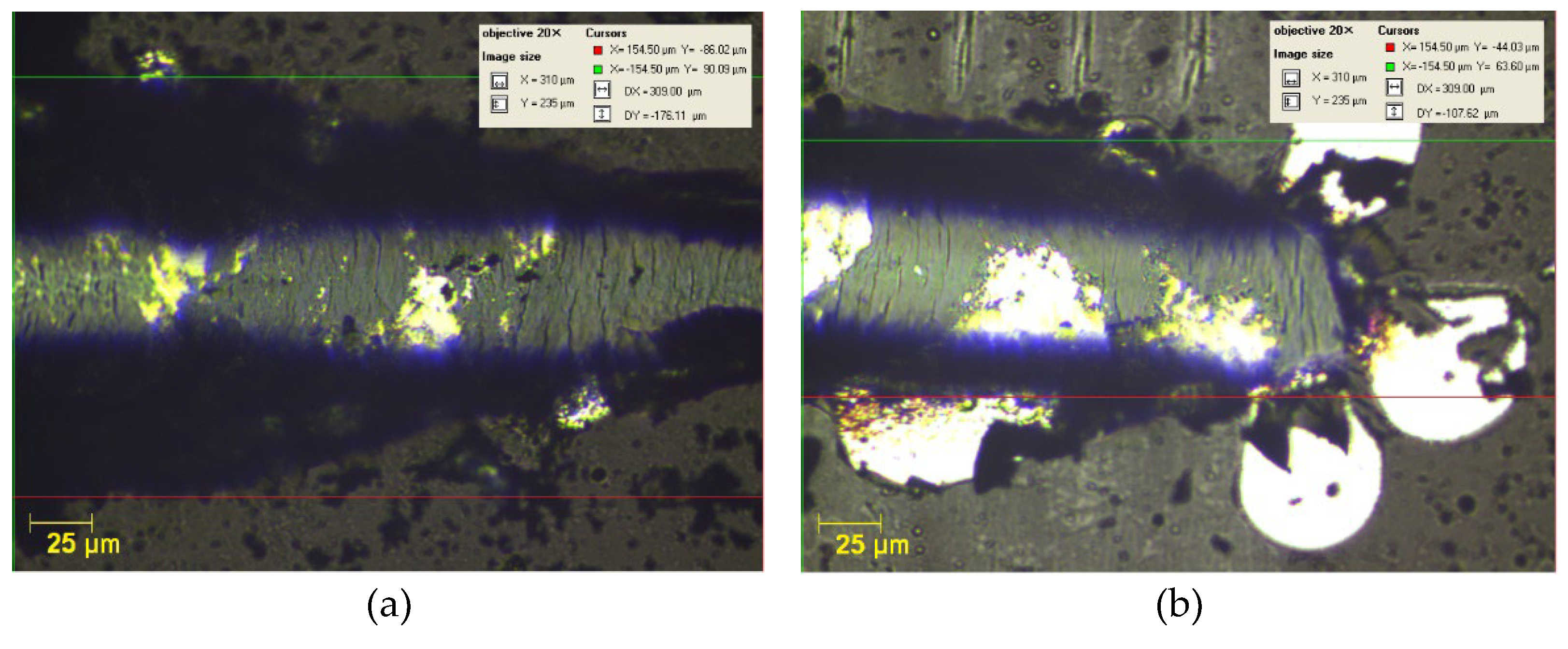
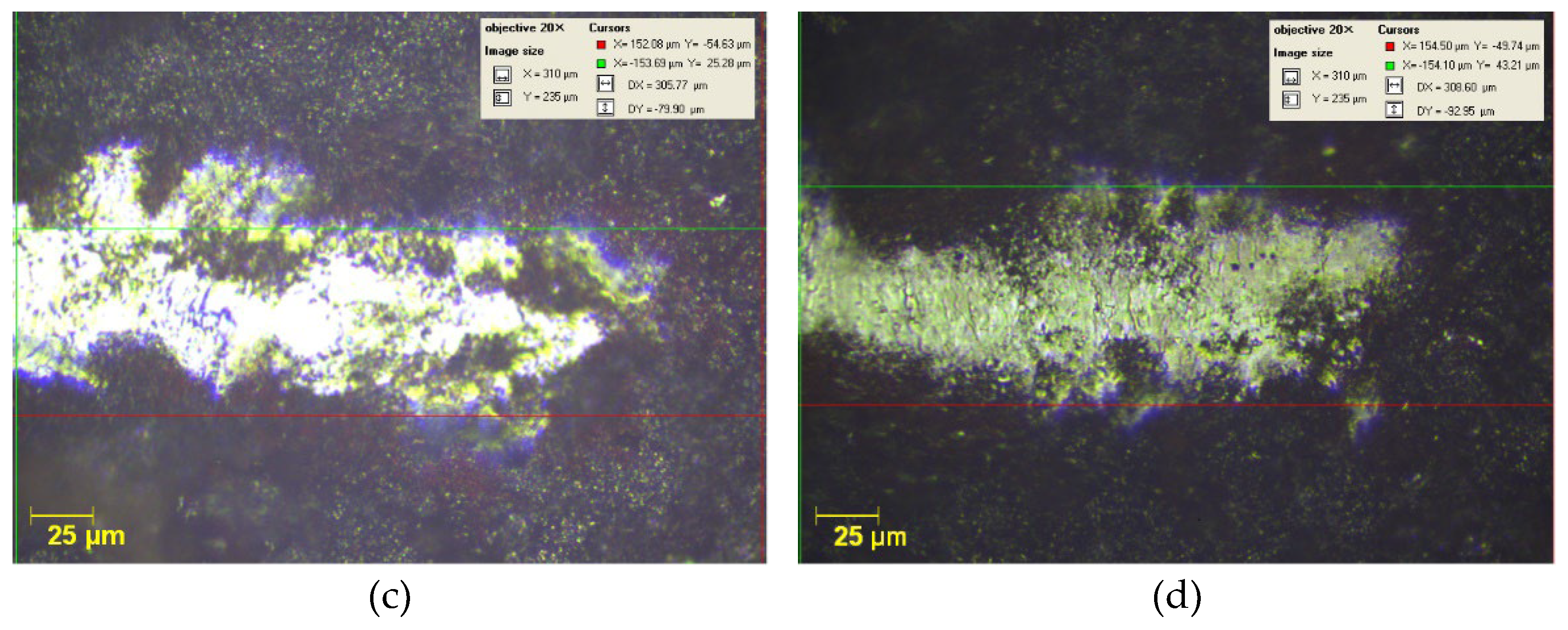
3.2.2. Micro-Scratch Testing Results
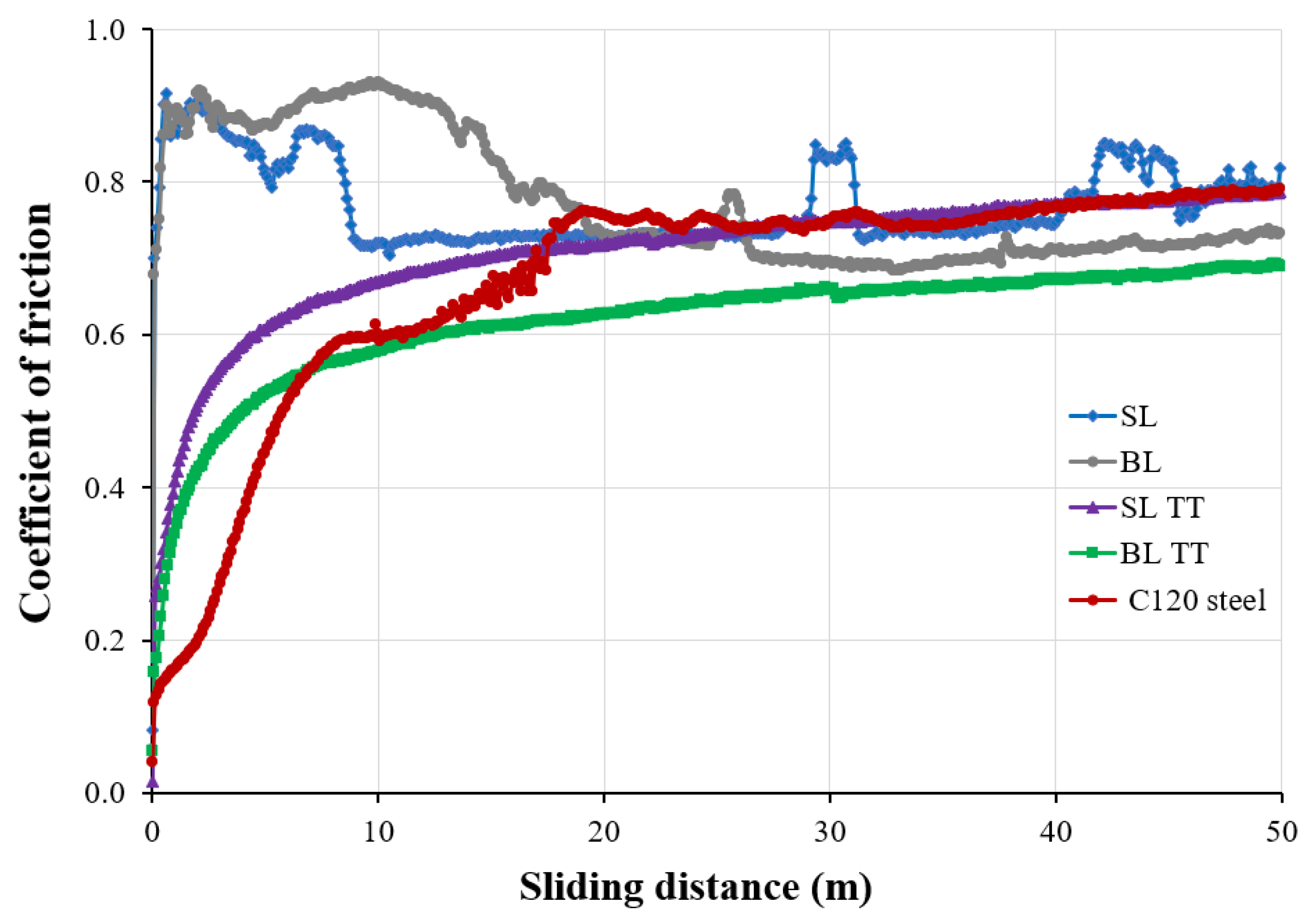
3.3. Tribological Properties
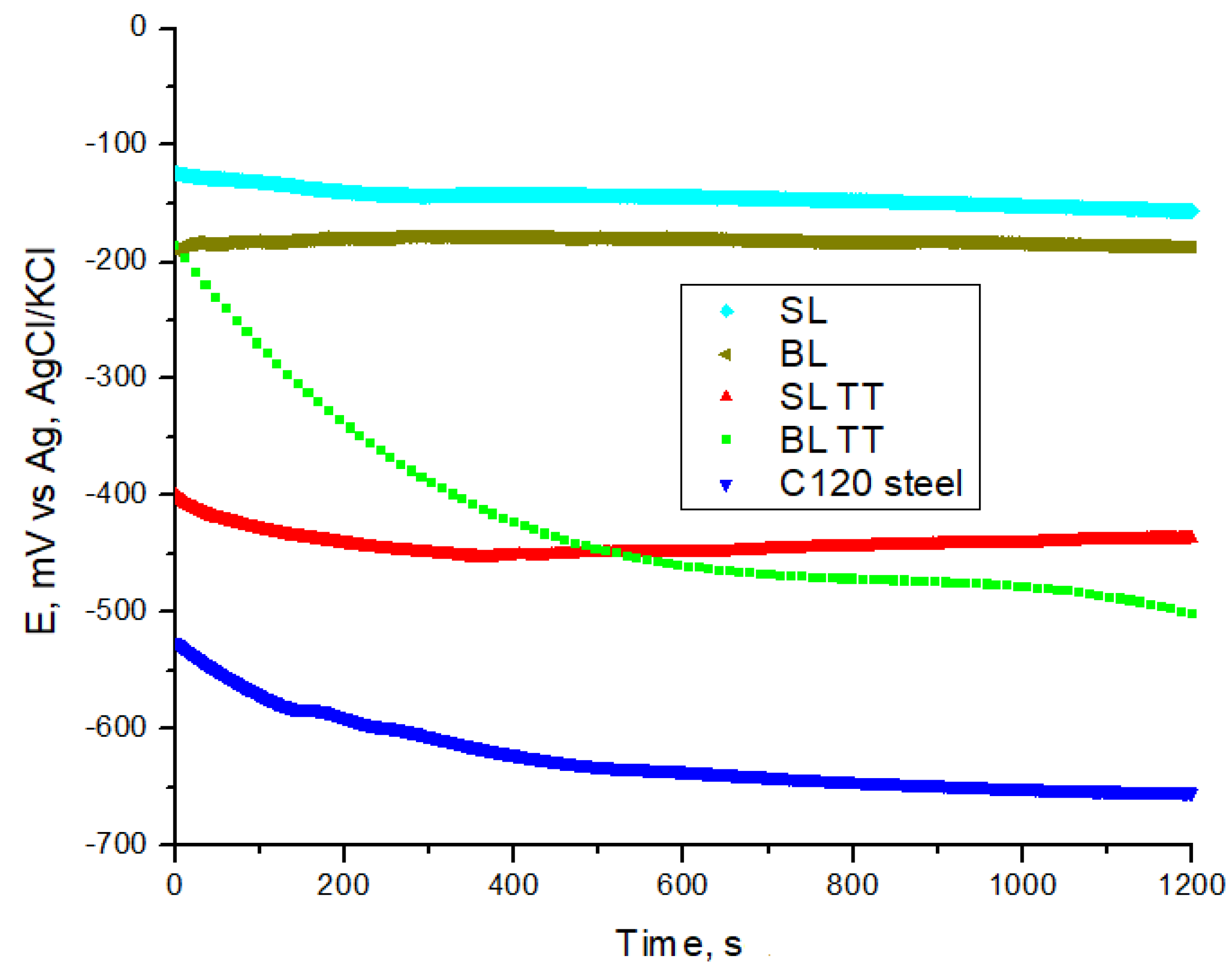
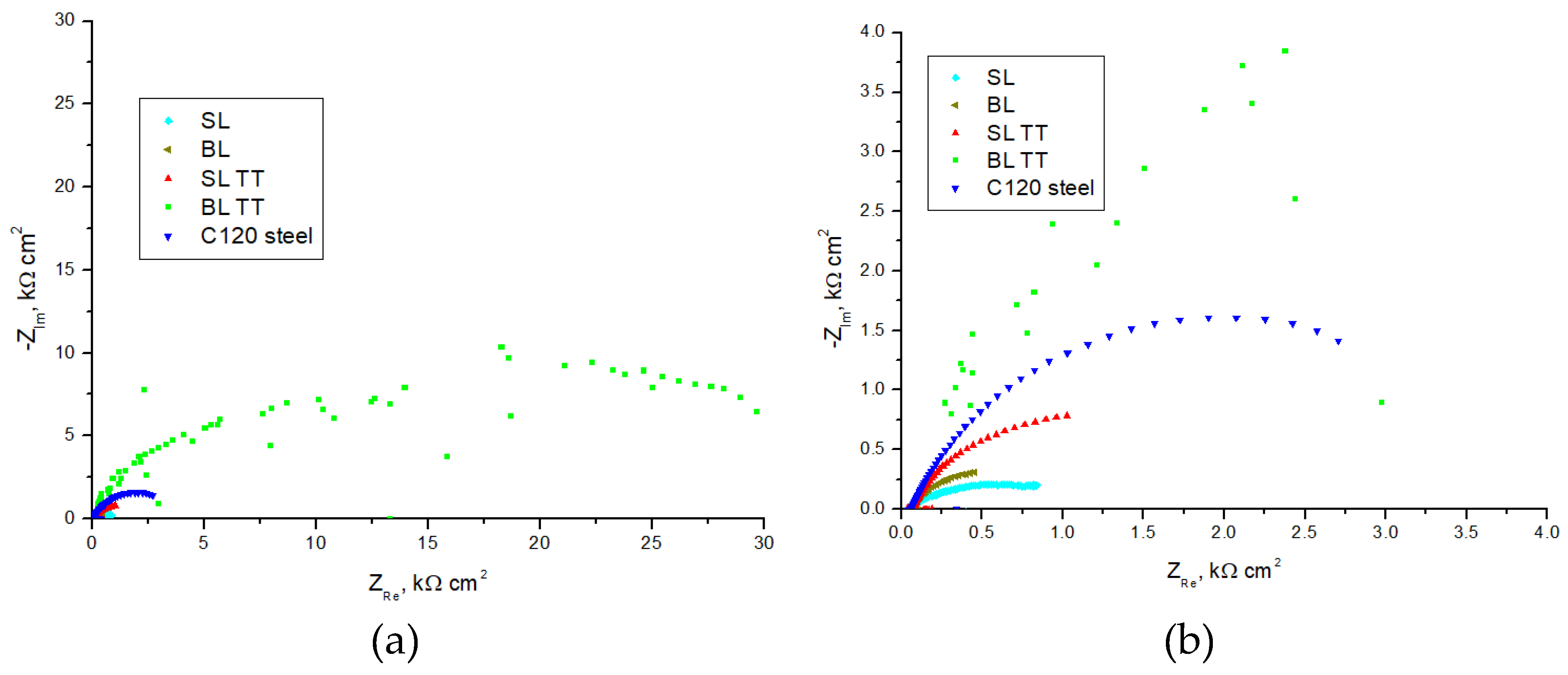
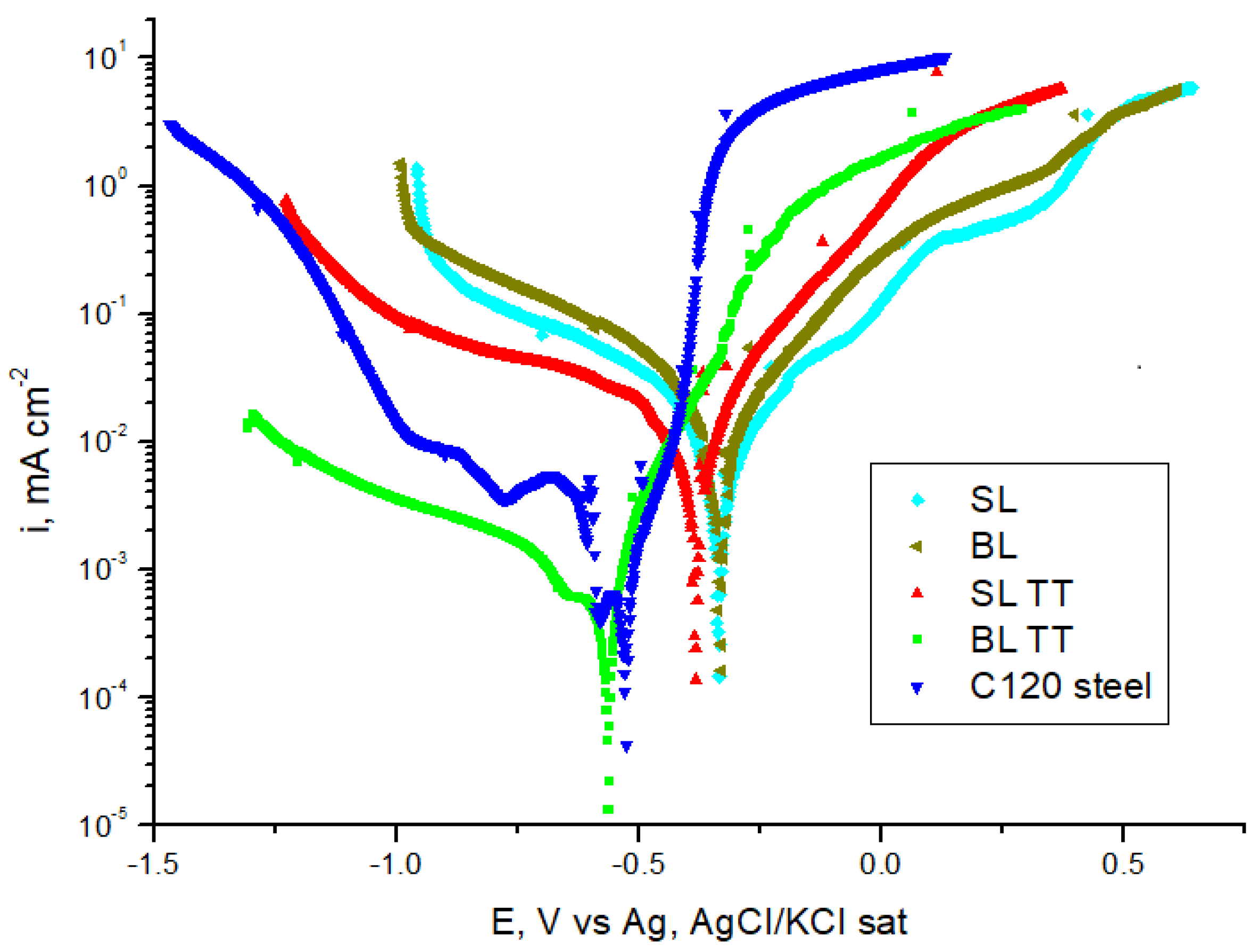
3.4. Electrochemical Properties
4. Conclusions
- -
- Macrographic examination confirmed the uniform and homogeneous nature of the TiAlSiN-based coatings, which were free of defects such as cracks and voids and exhibited good adherence to the base material (C120 tool steel substrate and TiN film/steel).
- -
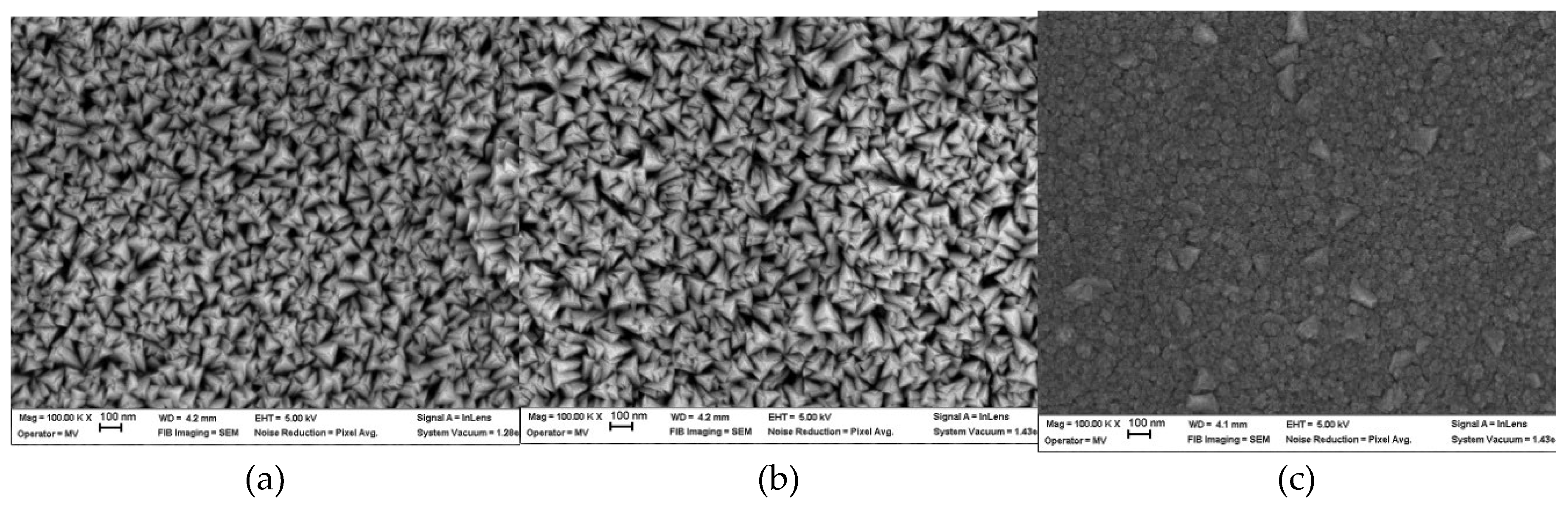
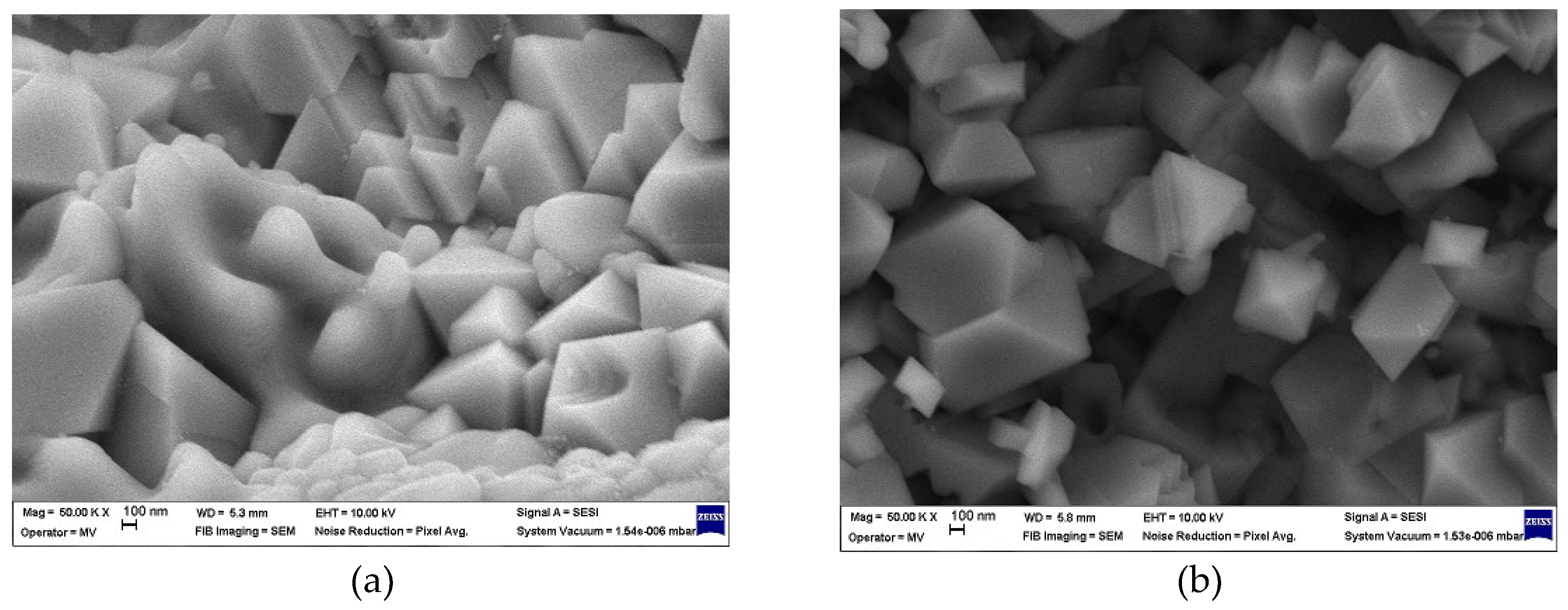
- SEM analysis revealed that the as-deposited SL and BL coatings exhibited a columnar structure with pyramidal-shaped grains measuring several tenths of a nanometer, and no structural defects were observed. The SL TT and BL TT coatings developed a coarser microstructure, featuring a mix of pyramidal and prismatic grains, along with some irregular grains, all ranging in size from a few hundred nanometers.
- -
- EDS analysis confirmed the presence of Ti, Al, Si, and N elements in all TiAlSiN-based coatings. However, oxygen contamination was also detected, indicated by the presence of the O element. Variations in elemental content were observed between the single-layer and bilayer coatings, as well as after thermal treatment.
- -
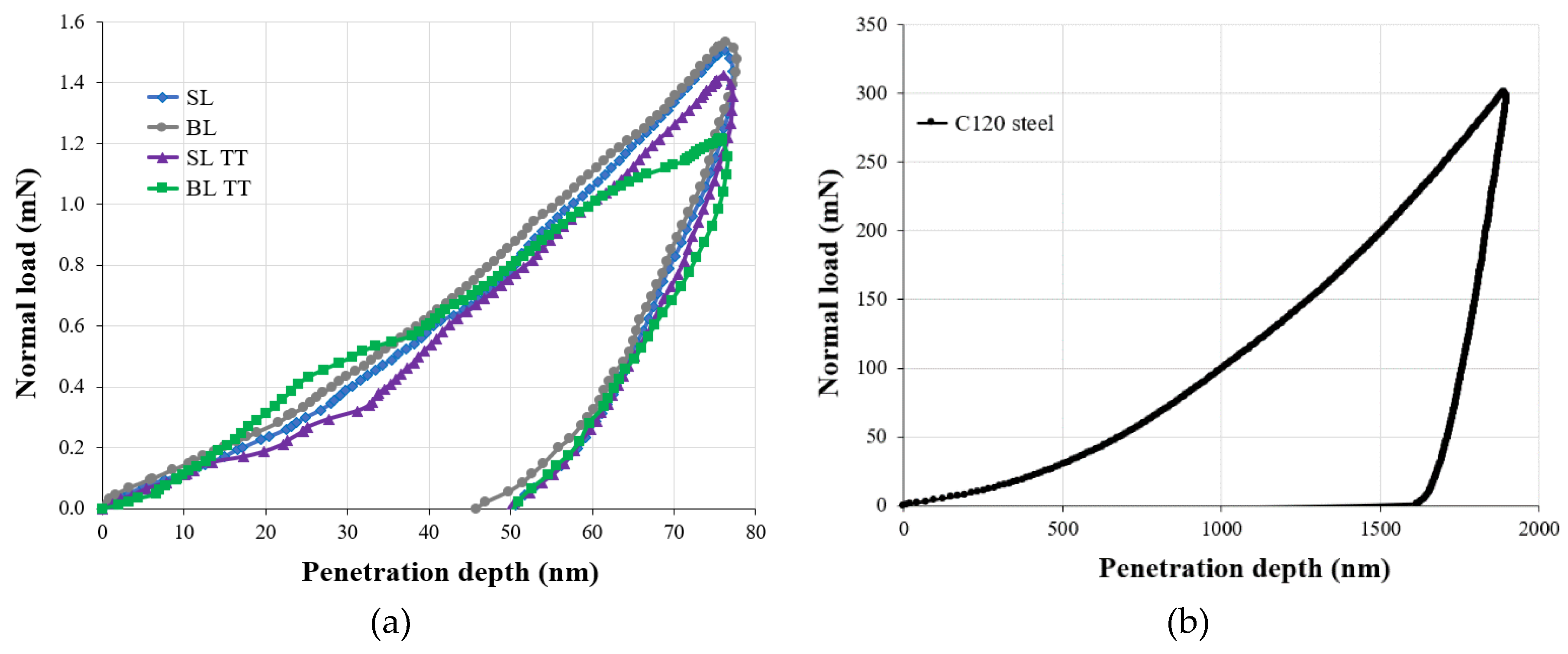
- Mechanical testing by nanoindentation revealed that the BL coating exhibited superior hardness compared to the other coatings and the C120 tool steel substrate. Thermal treatment at 800 °C for 1 hour resulted in a slight decrease in hardness and elastic modulus for the SL TT and BL TT coatings. All the coatings showed higher HIT/EIT and HIT/E* ratios compared to the steel substrate, indicating better resistance to plastic deformation and improved wear resistance. The highest fracture toughness was observed in the BL TT coating (0.0354 GPa), which is 16.4 times greater than that of the steel substrate (0.0022 GPa).
- -
- All TiAlSiN coatings exhibited both plastic and elastic behavior, as indicated by the nanoindentation and micro-scratch results. The SL TT and BL TT coatings demonstrated higher critical loads, improved adhesion, and better scratch resistance compared to the SL and BL coatings. Additionally, the SL TT and BL TT coatings showed stable behavior during scratching, with very low acoustic emission (AE) values (≤ 3.3%) and a reduced coefficient of friction (COF) (≤ 0.35), indicating no exposure of the tool steel substrate. The inclusion of the TiN layer enhanced the scratch performance of the BL and BL TT coatings.
- -
- The TiAlSiN coatings with higher elastic modulus (EIT) and indentation hardness (HIT) exhibited higher Hertzian stress (contact pressure), resulting in a lower wear rate. The BL TT coatings demonstrated the lowest stable COF (0.58–0.69) over a sliding distance of 10–50 m compared to the bare tool steel substrate and the other coatings.
- -
- The variation in COF and wear rate among the TiAlSiN-based coatings can be attributed to changes in elemental content, microstructural features, and mechanical properties resulting from thermal treatment in air at 800 °C for 1 hour.
- -
- All samples subjected to tribological testing showed irreversible plastic deformation on the surface, caused by plowing due to wear particles and the hard asperities of the static partner (Al2O3 ball).
- -
- Electrochemical testing indicated that the BL TT coating provides effective protection against corrosion in a 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. This is evidenced by its lowest corrosion current density (0.1298 µA/cm²), highest polarization resistance (46.34 kΩ·cm²), and lowest corrosion rate (1.51 µm/year) among the tested TiAlSiN-based coatings and C120 tool steel substrate.
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bobzin, K. High-Performance Coatings for Cutting Tools. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Tec. 2017, 18, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Schulz, W.; Joukov, V.; Köhn, F.; Engelhart, W.; Schier, V.; Schubert, T.; Albrecht, J. The Behavior of TiAlN and TiAlCrSiN Films in Abrasive and Adhesive Tribological Contacts. Coatings 2023, 13 (9), 1603. [CrossRef]
- Kolesnikov, V. I.; Novikov, E. S.; Kudryakov, O. V.; Varavka, V. N. The Degradation Mechanisms in Ion-Plasma Nanostructured Coatings under the Conditions of Contact Cyclic Loads. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2019, 1281 (1), 012036. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Hua, J.; Deng, X. Properties and Performance of TiAlSiN and AlCrN Monolayer and Multilayer Coatings for Turning Ti-6Al-4V. Coatings 2023, 13 (7), 1229. [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Laukkanen, A.; Turunen, E.; Laitinen, T. Wear Resistance Optimisation of Composite Coatings by Computational Microstructural Modelling. Surface and Coatings Technology 2014, 247, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, G.; Jiang, X.; Yang, X.; Cheng, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, G. Friction and Wear Properties of TiAlN Coated Tools with Different Levels of Surface Integrity. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48 (4), 4433–4443. [CrossRef]
- Bouzakis, K.-D.; Skordaris, G.; Gerardis, S.; Katirtzoglou, G.; Makrimallakis, S.; Pappa, M.; LilI, E.; M’Saoubi, R. Ambient and Elevated Temperature Properties of TiN, TiAlN and TiSiN PVD Films and Their Impact on the Cutting Performance of Coated Carbide Tools. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 204 (6–7), 1061–1065. [CrossRef]
- Gavrilov, N. V.; Kamenetskikh, A. S.; Chukin, A. V. Analysis of TiAlSiN Coatings Deposited by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering under High-Current Ion Assistance. J. Synch. Investig. 2017, 11 (3), 671–676. [CrossRef]
- PalDey, S.; Deevi, S. C. Single Layer and Multilayer Wear Resistant Coatings of (Ti,Al)N: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 342 (1–2), 58–79. [CrossRef]
- Shugurov, A. R.; Kazachenok, M. S. Mechanical Properties and Tribological Behavior of Magnetron Sputtered TiAlN/TiAl Multilayer Coatings. Surface and Coatings Technology 2018, 353, 254–262. [CrossRef]
- Miletić, A.; Panjan, P.; Škorić, B.; Čekada, M.; Dražič, G.; Kovač, J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Ti–Al–Si–N Coatings Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 241, 105–111. [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Munroe, P.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, Z. Mechanically Robust TiAlSiN Coatings Prepared by Pulsed-DC Magnetron Sputtering System: Scratch Response and Tribological Performance. Thin Solid Films 2018, 645, 222–230. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, J.-F.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Chang, C.-L. Effects of Nitrogen-Argon Flow Ratio on the Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of TiAlSiN/CrN Multilayer Coatings Prepared Using High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A: Vac. Surf. Films 2019, 37 (5), 051501. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Huang, B.; Zhang, E.; Peng, Z.; Chen, Q.; Liang, D. Improving the Mechanical and Tribological Properties of TiAlSiN Coatings by Annealing. Vacuum 2023, 214, 112249. [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Li, G.; Qin, X.; Yu, H.; Zhou, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, Q. Relationship of Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Titanium Cutting Performance of TiAlN/TiAlSiN Composite Coated Tool. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42 (6), 7524–7532. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. K.; Chang, C. L.; Shieh, Y. N.; Tsai, K. J.; Tsai, B. H. Structures and Properties of (TiAlSi)N Films. Procedia Eng. 2012, 36, 335–340. [CrossRef]
- Kengesbekov, A.; Rakhadilov, B.; Sagdoldina, Z.; Buitkenov, D.; Dosymov, Y.; Kylyshkanov, M. Improving the Efficiency of Air Plasma Spraying of Titanium Nitride Powder. Coatings 2022, 12 (11), 1644. [CrossRef]
- Heimann, R. B. The Nature of Plasma Spraying. Coatings 2023, 13 (3), 622. [CrossRef]
- Bouzakis, K.-D.; Michailidis, N.; Skordaris, G.; Bouzakis, E.; Biermann, D.; M’Saoubi, R. Cutting with Coated Tools: Coating Technologies, Characterization Methods and Performance Optimization. CIRP Annals 2012, 61 (2), 703–723. [CrossRef]
- Lungu, M. V. An Insight into TiN, TiAlN and AlTiN Hard Coatings for Cutting Tools. Mat. Sci. Res. India 2020, 17 (2), 87–89. [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y. H.; Le, D. P.; Kim, J. G.; Kim, S. K.; Vinh, P. V. Corrosion Behavior of TiN, TiAlN, TiAlSiN Thin Films Deposited on Tool Steel in the 3.5 Wt.% NaCl Solution. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516 (11), 3544–3548. [CrossRef]
- Yasin, J.; Selvakumar, S.; Mathan Kumar, P.; Sundaresan, R.; Arunraja, K. M. Experimental Study of TiN, TiAlN and TiSiN Coated High Speed Steel Tool. Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 64, 1707–1710. [CrossRef]
- Lü, W.; Li, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, Q. Effect of High Hardness and Adhesion of Gradient TiAlSiN Coating on Cutting Performance of Titanium Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 820, 153137. [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Liu, H.; Huang, C.; Liu, X.; Chu, D.; Liu, Y.; Yao, P. Effect of Arc Deposition Process on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of TiAlSiN Gradient Coatings. Ceram. Int. 2024, S0272884224033297. [CrossRef]
- Philippon, D.; Godinho, V.; Nagy, P. M.; Delplancke-Ogletree, M. P.; Fernández, A. Endurance of TiAlSiN Coatings: Effect of Si and Bias on Wear and Adhesion. Wear 2011, 270 (7–8), 541–549. [CrossRef]
- Münz, W. Titanium Aluminum Nitride Films: A New Alternative to TiN Coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A: Vac. Surf. Films 1986, 4 (6), 2717–2725. [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, G. G.; Almandoz, E.; Pierrugues, R.; Martínez, R.; Rodríguez, R. J.; Caro, J.; Vilaseca, M. High Temperature Tribological Characterisation of TiAlSiN Coatings Produced by Cathodic Arc Evaporation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205 (5), 1368–1373. [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Li, H.; Ji, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J. High Temperature Tribological Properties of TiAlSiN Coatings Produced by Hybrid PVD Technology. Tribol. Int. 2016, 98, 133–143. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. M.; Jiang, Z.-T.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, Z.; Yin, C. Y.; Kabir, H.; Haque, Md. M.; Amri, A.; Mondinos, N.; Altarawneh, M. Effects of Annealing Temperatures on the Morphological, Mechanical, Surface Chemical Bonding, and Solar Selectivity Properties of Sputtered TiAlSiN Thin Films. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 671, 254–266. [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Fehr, A.; Stangier, D.; Dildrop, M. Influences of Substrate Pretreatments and Ti/Cr Interlayers on the Adhesion and Hardness of CrAlSiN and TiAlSiN Films Deposited on Al2O3 and ZrO2-8Y2O3 Thermal Barrier Coatings. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 2206–2212. [CrossRef]
- Sousa, V. F. C.; Silva, F. J. G.; Lopes, H.; Casais, R. C. B.; Baptista, A.; Pinto, G.; Alexandre, R. Wear Behavior and Machining Performance of TiAlSiN-Coated Tools Obtained by Dc MS and HiPIMS: A Comparative Study. Materials 2021, 14 (18), 5122. [CrossRef]
- .
- Lungu, M. V.; Enescu, E.; Tălpeanu, D.; Pătroi, D.; Marinescu, V.; Sobetkii, A.; Stancu, N.; Lucaci, M.; Marin, M.; Manta, E. Enhanced Metallic Targets Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering for Sputtering Deposition of Protective Coatings. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6 (7), 076565. [CrossRef]
- Lungu, M. V.; Tălpeanu, D.; Pătroi, D.; Lucaci, M.; Tsakiris, V.; Marin, M. Sputtering Targets Based on Titanium-Aluminium and Titanium-Silicon for Wear-Resistant Hard Coatings and Process for Preparing the Same, Patent Application Number A/00703 of 05.11.2020 Filed with the State Office for Inventions and Trademarks (OSIM), Romania.
- Oliver, W. C.; Pharr, G. M. An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus Using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7 (6), 1564–1583. [CrossRef]
- 36. ISO/TC 164/SC 3 Committee. ISO 14577-1:2015, Metallic Materials — Instrumented Indentation Test for Hardness and Materials Parameters, Part 1: Test Method, 2015. https://www.iso.org/standard/56626.html.
- ISO/TC 164/SC 3 Committee. ISO 14577-4:2016, Metallic Materials — Instrumented Indentation Test for Hardness and Materials Parameters, Part 4: Test Method for Metallic and Non-Metallic Coatings, 2016. https://www.iso.org/standard/61823.html.
- . [CrossRef]
- ISO/TC 206 Committee. ISO 20502:2005, Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics) — Determination of Adhesion of Ceramic Coatings by Scratch Testing, 2005. https://www.iso.org/standard/34189.html.
- Gil-Flores, L.; Salvador, M. D.; Penaranda-Foix, F. L.; Dalmau, A.; Fernández, A.; Borrell, A. Tribological and Wear Behaviour of Alumina Toughened Zirconia Nanocomposites Obtained by Pressureless Rapid Microwave Sintering. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 101, 103415. [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.; Dandapat, N.; Das, M.; Balla, V. K.; Chakraborty, S.; Saha, R.; Mallik, A. K. Severe Wear Behaviour of Alumina Balls Sliding against Diamond Ceramic Coatings. Bull Mater Sci 2016, 39 (2), 573–586. [CrossRef]
- . [CrossRef]
- T-09-113 – Wear and Friction Analysis of Thin Coatings, Available at: Https://Www.Silcotek.Com/Hs-Fs/Hub/22765/File-341679011-Pdf/Docs/t-09-113_silcotek_tribology_testing_final_report.Pdf, Accessed: 04.07.2024.
- Huang, B.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, E.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Liang, D.-D.; Chen, Q.; An, Q. Effects of Annealing Temperature on the Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of TiAlSiCN Coatings. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50 (11), 20612–20623. [CrossRef]
- Lekatou, A. G.; Emmanouilidou, S.; Dimitriadis, K.; Baikousi, M.; Karakassides, M. A.; Agathopoulos, S. Simulating Porcelain Firing Effect on the Structure, Corrosion and Mechanical Properties of Co–Cr–Mo Dental Alloy Fabricated by Soft Milling. Odontology 2023. [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Guha, S.; Ghadai, R.; Swain, B. P. A Comparative Analysis over Different Properties of TiN, TiAlN and TiAlSiN Thin Film Coatings Grown in Nitrogen Gas Atmosphere. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2021, 258, 123866. [CrossRef]
- Weikert, T.; Wartzack, S.; Baloglu, M. V.; Willner, K.; Gabel, S.; Merle, B.; Pineda, F.; Walczak, M.; Marian, M.; Rosenkranz, A.; Tremmel, S. Evaluation of the Surface Fatigue Behavior of Amorphous Carbon Coatings through Cyclic Nanoindentation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 407, 126769. [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, J.; Song, G.; Ma, G.; Du, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, D. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Reactive Sputtered Nanocrystalline (Ti,Al)N Films. Thin Solid Films 2015, 584, 192–197. [CrossRef]
- Lungu, M. V.; Sobetkii, A.; Sobetkii, A. A.; Pătroi, D.; Prioteasa, P.; Ion, I.; Negrilă, C. C.; Chifiriuc, M. C. Functional Properties Improvement of Ag-ZnO Thin Films Using Inconel 600 Interlayer Produced by Electron Beam Evaporation Technique. Thin Solid Films 2018, 667, 76–87. [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, Y.; Rao, G.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, R.; Chen, Y. Tribological Properties and Cutting Performance of AlTiN Coatings with Various Geometric Structures. Coatings 2023, 13 (2), 402. [CrossRef]
- Zmitrowicz, A. Wear Patterns and Laws of Wear – A Review. J. Theor. App. Mech.-Pol 2006, 44 (2), 219–253.
- Komartin, R. S.; Balanuca, B.; Necolau, M. I.; Cojocaru, A.; Stan, R. Composite Materials from Renewable Resources as Sustainable Corrosion Protection Coatings. Polymers 2021, 13 (21), 3792. [CrossRef]
- Li, R. T.; Murugan, V. K.; Dong, Z. L.; Khor, K. A. Comparative Study on the Corrosion Resistance of Al–Cr–Fe Alloy Containing Quasicrystals and Pure Al. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32 (10), 1054–1058. [CrossRef]
- . [CrossRef]
- Aljibori, H.S.; Alamiery, A.; Kadhum, A.A.H. Advances in Corrosion Protection Coatings: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2023, 12 (4), 1476–1520. [CrossRef]
- Shao, J. The Effect of Sealing Processes On The Corrosion Behaviour Of Al₂O₃-13 WT.%TiO₂ Coating. Ceramics - Silikaty 2019, 185–193. [CrossRef]
| Technical characteristics | TiAlSi 75–20–5 (at.%) target | Ti target |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter × thickness (mm × mm) | 50.8 × 6.3 | 50.8 × 6.3 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 4.093 ± 0.003 | 4.379 ± 0.001 |
| Surface roughness Ra (µm) | ≤ 0.2 | ≤ 0.2 |
| Thermal conductivity at 25 °C (W.m-1.K-1) | 11.93 ± 0.13 | 18.38 ± 0.14 |
| Indentation hardness, HIT (GPa) | 7.88 ± 0.64 | 2.77 ± 0.08 |
| Vickers hardness HV0.02/10 | 730 ± 59 | 256 ± 7 |
| Elastic modulus, EIT (GPa) | 163 ± 6 | 117 ± 6 |
| Measurement conditions in instrumented nanoindentation testing |
TiAlSiN-based coatings | C120 steel substrate |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum indentation load (Fmax) (mN) | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 300 ± 1 |
| Loading type | linear | linear |
| Indenter approach speed to the sample (nm/min) | 1000 | 2000 |
| Loading/unloading rate (nm/min) | 500 | 600 |
| Pause at Fmax (s) | 0 | 0 |
| Data acquisition frequency (Hz) | 10 | 10 |
| Poisson’s ratio (ν) | 0.25 | 0.30 |
| Sample | Elemental content ± SD (wt.%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | Al | Si | N | O | Fe | Cr | Mn | |
| SL | 52.4 ± 0.3 | 11.9 ± 0.1 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 21.2 ± 0.3 | 11.5 ± 0.3 | - | - | - |
| BL | 51.7 ± 0.3 | 12.1 ± 0.1 | 3.6 ± 0.1 | 21.4 ± 0.3 | 11.2 ± 0.3 | - | - | - |
| TiN | 56.6 ± 0.4 | - | - | 5.3 ± 0.2 | 31.1 ± 0.3 | 4.5 ± 0.4 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | - |
| SL TT | 26.7 ± 0.1 | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | - | 27.4 ± 0.1 | 38.0 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| BL TT | 23.4 ± 0.1 | 7.7 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | - | 29.7 ± 0.1 | 34.0 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 3.7 ± 0.1 |
| Sample | HIT (GPa) |
HV | EIT (GPa) |
E* (GPa) |
HIT/EIT | HIT/E* | HIT3/EIT2 (GPa) |
HIT3/E*2 (GPa) |
Welast (pJ) |
Wplast (pJ) |
ηIT (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL | 10.29 ± 0.26 |
953 ± 24 |
216 ± 15 |
231 ± 17 |
0.0476 | 0.0445 | 0.0234 | 0.0204 | 12.59 ± 1.17 |
34.62 ± 2.03 |
26.64 ± 0.67 |
| BL | 10.45 ± 0.32 |
968 ± 29 |
215 ± 16 |
229 ± 18 |
0.0486 | 0.0456 | 0.0247 | 0.0218 | 14.25 ± 0.43 |
36.15 ± 1.58 |
28.28 ± 0.27 |
| SL TT | 9.98 ± 0.18 |
925 ± 16 |
188 ± 5 |
201 ± 5 |
0.0531 | 0.0497 | 0.0281 | 0.0246 | 11.74 ± 0.03 |
31.89 ± 1.84 |
26.93 ± 1.08 |
| BL TT | 9.19 ± 0.09 |
851 ± 8 |
139 ± 5 |
148 ± 6 |
0.0661 | 0.0621 | 0.0402 | 0.0354 | 11.12 ± 3.19 |
34.83 ± 1.24 |
24.08 ± 5.93 |
| C120 steel | 4.45 ± 0.09 |
412 ± 8 |
184 ± 2 |
202 ± 2 |
0.0242 | 0.0220 | 0.0026 | 0.0022 | 29335.52 ± 366.46 |
176769.48 ± 8580.53 |
14.25 ± 0.43 |
| Sample | Optical critical loads | Pd critical load (N) | AE critical load (N) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lc1 (N) | Lc2 (N) | Lc3 (N) | |||
| SL | 2.65 | 6.31 | 14.03 | - | 14.38 |
| BL | 3.28 | 12.26 | 17.28 | - | 20.52 |
| SL TT | 3.89 | 13.63 | - | 12.50 | 15.02 |
| BL TT | 4.72 | 27.82 | - | 16.41 | 21.21 |
| Sample | Coefficient of friction (µ) | Worn track area (µm²) |
Specific wear rate (mm³/N·m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µminimum | µmaximum | µmean ± SD | |||
| SL | 0.083 | 0.916 | 0.770 ± 0.053 | 946.2–1062.4 | (2.14–2.40) × 10-4 |
| BL | 0.056 | 0.931 | 0.773 ± 0.084 | 866.8–986.7 | (1.96–2.23) × 10-4 |
| SL TT | 0.015 | 0.789 | 0.708 ± 0.088 | 1291.3–1891.9 | (2.92–4.28) × 10-4 |
| BL TT | 0.055 | 0.694 | 0.616 ± 0.083 | 1237.2–1683.1 | (2.80–3.80) × 10-4 |
| C120 steel | 0.041 | 0.822 | 0.670± 0.162 | 1173.8–1646.4 | (2.65–3.72) × 10-4 |
| Sample | R1 (Ω cm2) |
R2 (Ω cm2) |
Cdl (µF/cm²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SL | 47.34 | 1057 | 150.4 |
| BL | 66.03 | 854.5 | 1862.0 |
| SL TT | 66.03 | 2184 | 728.7 |
| BL TT | 147.1 | 35550 | 0.159 |
| C120 steel | 68.35 | 4182 | 240.4 |
| Sample | Ecorr (mV vs Ag, AgCl/KCl) |
icorr (µA/cm²) |
Rp (kΩ cm2) |
βa (mV/dec) |
βc (mV/dec) |
CR (µm/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL | -340.9 | 1.1393 | 5.07 | 33.9 | -34.6 | 13.24 |
| BL | -338.9 | 1.2567 | 3.92 | 26.8 | -31.4 | 14.60 |
| SL TT | -384.3 | 1.1658 | 3.06 | 4.2 | -41.5 | 13.55 |
| BL TT | -567.7 | 0.1298 | 46.34 | 25.7 | -45.2 | 1.51 |
| C120 steel | -532.5 | 0.1825 | 28.52 | 22.4 | -36.2 | 2.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





