Submitted:
18 September 2024
Posted:
19 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- We introduce an innovative dynamic task offloading model to optimize EE for a WPMEC network with integration of BackCom and AC communication under user cooperation, taking into account the randomness of task arrival and time-varying wireless channels. Our model effectively balances the trade-off between energy efficiency and system queues stability, while mitigating the double-near-far effect. Additionally, we explore the use of variable data weighting to motivate proximal users to relay data for distant users, enhancing overall network efficiency.
- We propose an online control algorithm to maximize the EE metric of WPMEC network by determining the time fraction allocation, data offloading, transmission power and the Backscatter reflection coefficients at each time slot. To address the complex coupling of user cooperation and control decisions over time, we employ Dinkelbach’s method and the Lyapunov optimization theory to decouple the stochastic fractional optimization problem into deterministic sub-problems for each time slot, and transforms it into a convex problem, ensuring an efficient and optimal solution.
- We present a rigorous mathematical analysis to demonstrate the performance of our proposed algorithm, that achieves a balanced trade-off between energy efficiency and queue stability within the bounds of . Extensive simulation experiments are conducted to verify the algorithm’s effectiveness and practical applicability. We have systematically evaluated the impact of key control parameters, including variable V, bandwidth, communication gap, and task arrival rates, on the algorithm’s performance.
1.1. Related Work
2. System Model
2.1. Energy Harvesting Model
2.2. Dynamic Queues Model
2.3. Local Computing Model
2.4. Task Offloading Model
2.4.1. BackCom Data Transmission
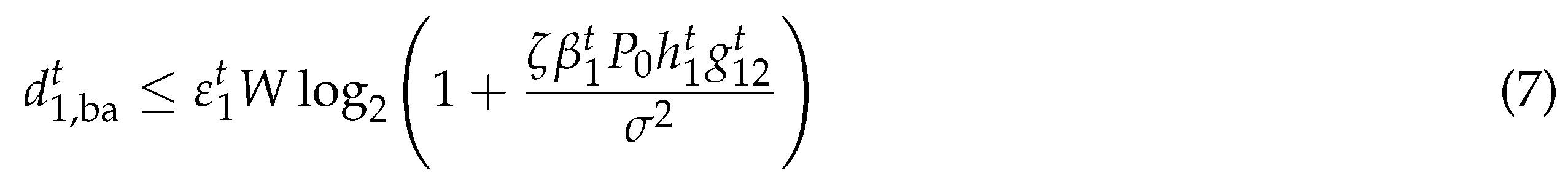 where represents the performance gap reflecting real modulation [11], is the noise power. The corresponding energy consumption by circuit is
where represents the performance gap reflecting real modulation [11], is the noise power. The corresponding energy consumption by circuit is
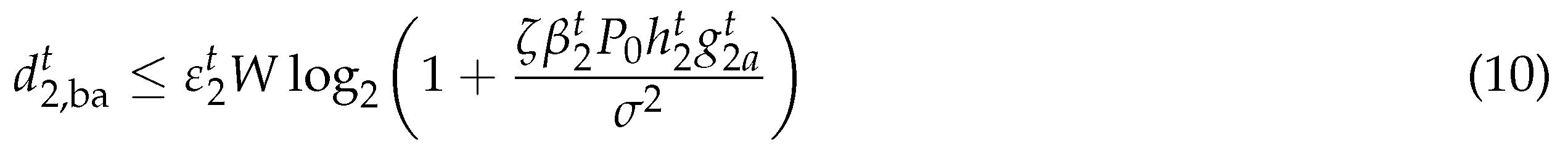 where is the reflection coefficient of the BackCom at . represents the channel gain from the HAP to the at time slot t, and denotes the channel gain from the to the HAP at time slot t. The corresponding energy consumption is
where is the reflection coefficient of the BackCom at . represents the channel gain from the HAP to the at time slot t, and denotes the channel gain from the to the HAP at time slot t. The corresponding energy consumption is
2.4.2. AC Data Transmission
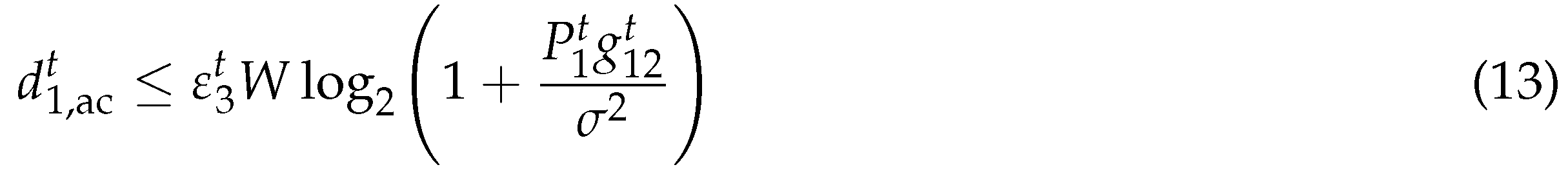 where represents the transmit power allocated to AC at [8], is the noise power and represents the channel gain from and . The corresponding AC offloading energy consumption is
where represents the transmit power allocated to AC at [8], is the noise power and represents the channel gain from and . The corresponding AC offloading energy consumption is
 where
denotes the transmit power of the through AC. Let denote the circuit power of through AC. The energy consumed for task offloading AC at in slot t is
where
denotes the transmit power of the through AC. Let denote the circuit power of through AC. The energy consumed for task offloading AC at in slot t is
2.5. Network Stability and Utility
3. Problem Formulation
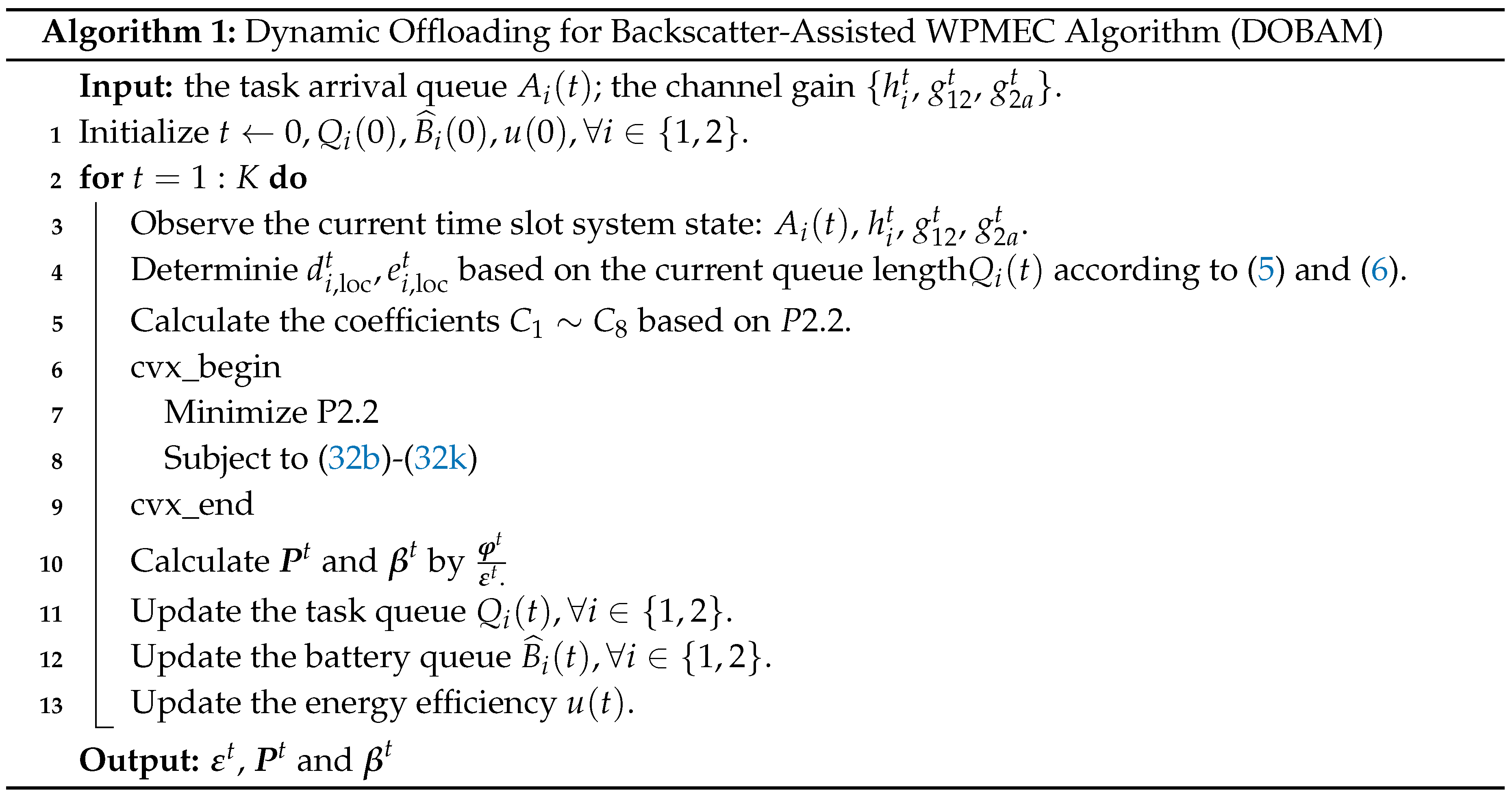
4. Algorithm Design
4.1. Lyapunov Optimization Formulation
 |
4.2. Algorithm Performance Analysis
- 1.
- 2.
- All queues , , are mean rate stable, and thus the constraints are satisfied.
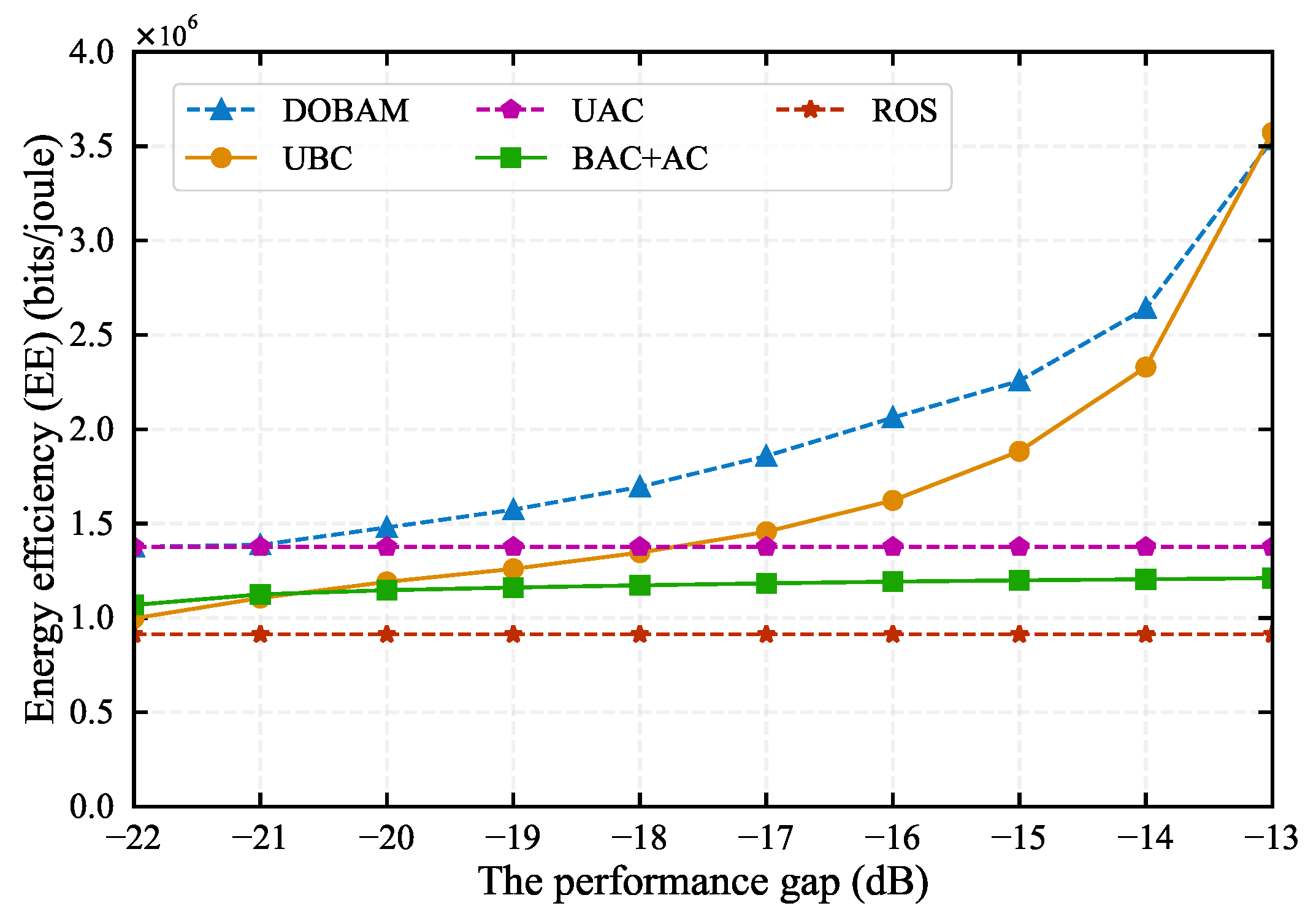
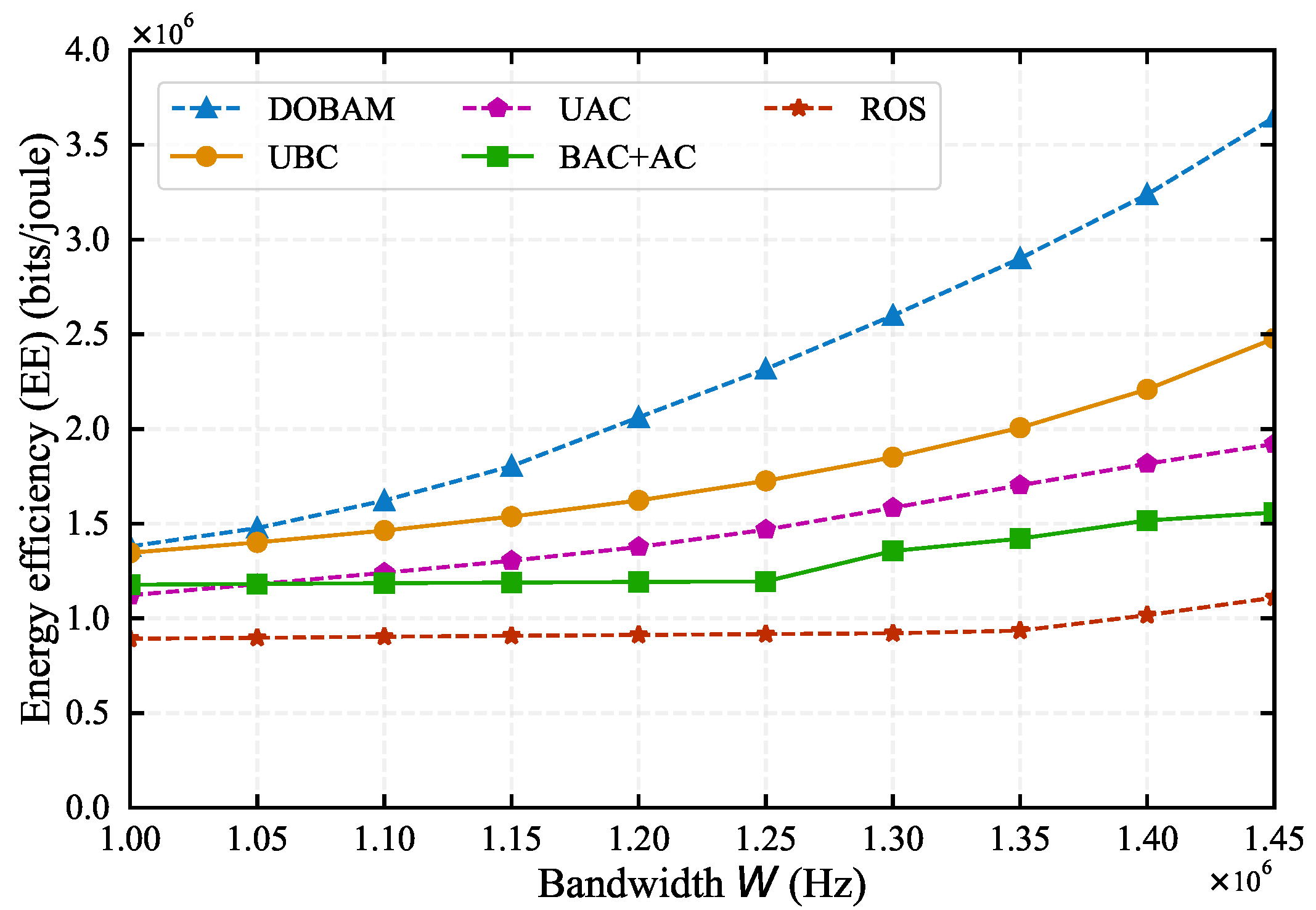
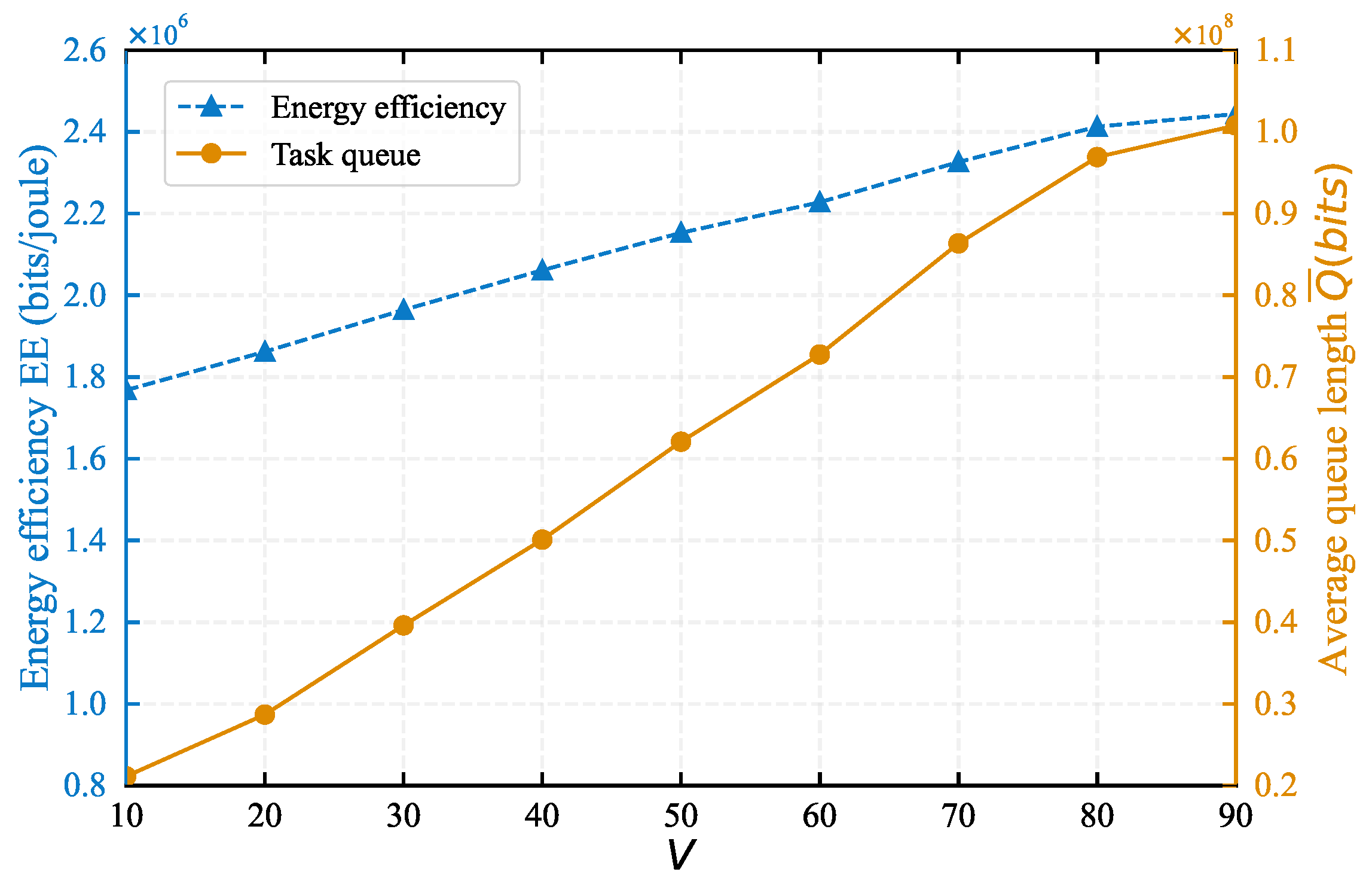
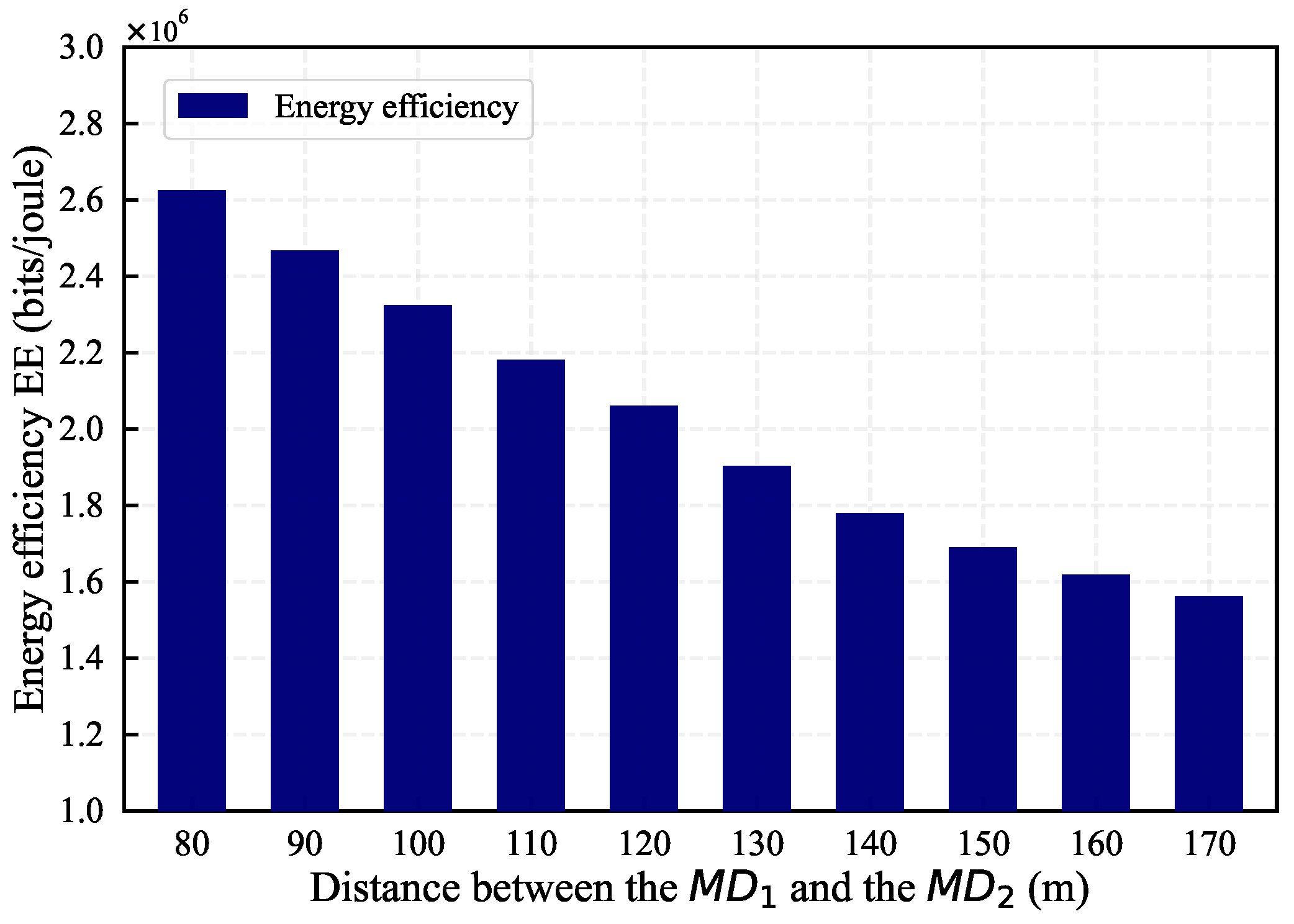
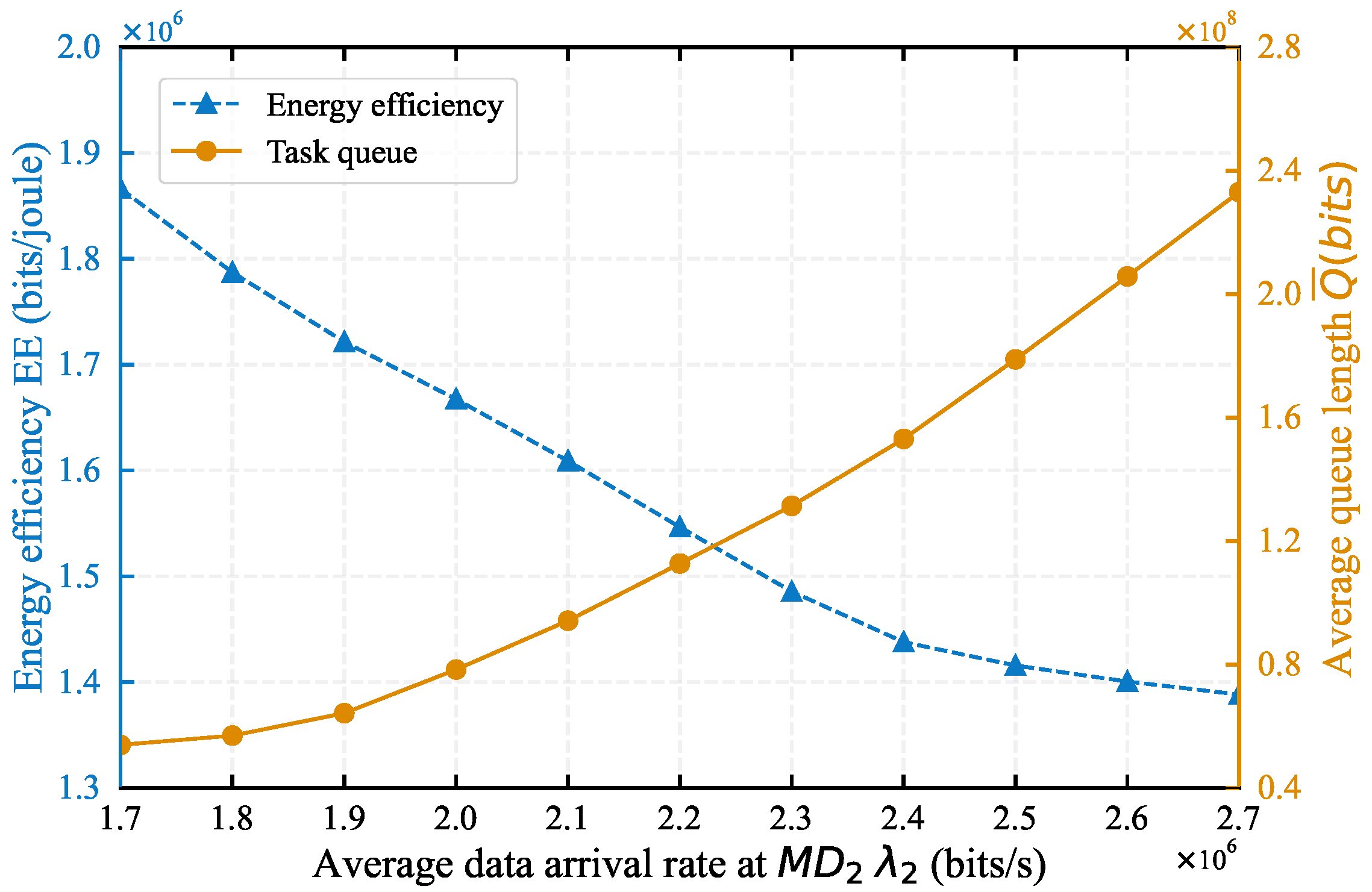
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, R.; Zhu, F.; Tang, M.; He, L. Profit maximization in cache-aided intelligent computing networks. Physical Communication 2023, 58, 102065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Ning, Z.; Song, Q.; Guo, L.; Guo, S.; Obaidat, M.S. Wireless powered mobile edge computing networks: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys 2023, 55, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Cui, S. Optimal energy allocation and task offloading policy for wireless powered mobile edge computing systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2020, 19, 2443–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhang, B.; Lin, S.; Wang, C. A self-oscillation WPT system with high misalignment tolerance. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zeng, M.; Mishra, D.; Hao, L.; Ma, Z.; Dobre, O.A. Latency minimization for IRS-aided NOMA MEC systems with WPT-enabled IoT devices. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023, 10, 12156–12168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Zhang, R. Throughput maximization in wireless powered communication networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2013, 13, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhou, C.; Huang, F.; Shen, H.; Li, S. Energy-Efficient Task Offloading in Wireless-Powered MEC: A Dynamic and Cooperative Approach. Mathematics 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, X.; He, Z.; Guizani, M. Energy efficiency maximization of backscatter-assisted wireless-powered MEC with user cooperation. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2023, 23, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Ni, Q.; Yu, W.; Pervaiz, H. Optimizing computation efficiency for NOMA-assisted mobile edge computing with user cooperation. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking 2021, 5, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Niyato, D.; Wang, P.; Kim, D.I.; Han, Z. Ambient backscatter: A new approach to improve network performance for RF-powered cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications 2017, 65, 3659–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Ye, Y.; Chu, X.; Sun, S.; Lu, G. Energy-efficient resource allocation for backscatter-assisted wireless powered MEC. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2023, 72, 9591–9596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Shi, L.; Chu, X.; Lu, G. Throughput fairness guarantee in wireless powered backscatter communications with HTT. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters 2020, 10, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Shi, L.; Chu, X.; Hu, R.Q.; Lu, G. Resource allocation in backscatter-assisted wireless powered MEC networks with limited MEC computation capacity. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2022, 21, 10678–10694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Guo, S. Energy-efficient cooperative resource allocation in wireless powered mobile edge computing. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2018, 6, 4744–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabella, D.; Vaillant, A.; Kuure, P.; Rauschenbach, U.; Giust, F. Mobile-edge computing architecture: The role of MEC in the Internet of Things. IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine 2016, 5, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Liu, A.; Zhang, S. A cloud–MEC collaborative task offloading scheme with service orchestration. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2019, 7, 5792–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Wang, Z.; Su, H.; Yu, H.; Lei, B.; Guizani, M. Profit Maximization of Independent Task Offloading in MEC-Enabled 5G Internet of Vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024; 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernest, T.Z.H.; Madhukumar, A. Computation offloading in MEC-enabled IoV networks: Average energy efficiency analysis and learning-based maximization. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Bao, S.; Chi, K.; Yu, K.; Mumtaz, S. DRL-based computation rate maximization for wireless powered multi-AP edge computing. IEEE Transactions on Communications 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yan, X.; Yuan, S.; Li, C. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Adaptive Offloading Algorithm for Wireless Power Transfer-Aided Mobile Edge Computing. 2024 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC). IEEE, 2024, pp. 1–6.
- Wang, R.; Chen, J.; He, B.; Lv, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, L. Energy consumption minimization for wireless powered NOMA-MEC with user cooperation. 2021 13th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–5.
- He, B.; Bi, S.; Xing, H.; Lin, X. Collaborative computation offloading in wireless powered mobile-edge computing systems. 2019 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps). IEEE, 2019, pp. 1–7.
- Iwaki, A.; Sanada, K.; Hatano, H.; Mori, K. Performance Analysis of Wireless Powered Communication Networks Based on Harvest-then-Access Scheduling Considering Double-near far Problem. IEICE Technical Report; IEICE Tech. Rep. 2022, 122, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Mao, S. Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Based Joint Caching and Resources Allocation for Cooperative MEC. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2024, 11, 12203–12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, J.; Cui, S. User association and resource allocation for MEC-enabled IoT networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2022, 21, 8051–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; He, H. An Efficient Energy Efficiency Maximization Algorithm for Backscatter-Assisted WP-MEC Network with Relay. Proceedings of the 2024 16th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing; ICMLC ’24; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Shi, L.; Chu, X.; Li, D.; Lu, G. Delay minimization in wireless powered mobile edge computing with hybrid BackCom and AT. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters 2021, 10, 1532–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, R.; Carvalho, N.B.; Kawasaki, S. Continuously power delivering for passive backscatter wireless sensor networks. IEEE transactions on microwave theory and techniques 2016, 64, 3723–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Huang, K. Wirelessly powered backscatter communication networks: Modeling, coverage, and capacity. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2017, 16, 2548–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Guo, H.; Yang, Z.; Gui, G. Throughput maximization for hybrid backscatter assisted cognitive wireless powered radio networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2018, 5, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Ye, Y.; Chu, X.; Lu, G. Computation bits maximization in a backscatter assisted wirelessly powered MEC network. IEEE Communications Letters 2020, 25, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Wang, K.; Wang, T.; Ding, Z. Uplink Data Rate Maximization in Multi-Cell BackCom NOMA Systems. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society 2024, 5, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Shi, L.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, G. Computation EE Fairness for a UAV-Enabled Wireless Powered MEC Network With Hybrid Passive and Active Transmissions. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Zhang, Y.J. Computation rate maximization for wireless powered mobile-edge computing with binary computation offloading. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2018, 17, 4177–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gu, B.; Hu, R.Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, H. Joint computation offloading and radio resource allocation in MEC-based wireless-powered backscatter communication networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2021, 70, 6200–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdu, S. Fifty years of Shannon theory. IEEE Transactions on information theory 1998, 44, 2057–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, M. Stochastic network optimization with application to communication and queueing systems; Springer Nature, 2022.
- Sun, M.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Tao, X.; Zhang, P. Resource management for computation offloading in D2D-aided wireless powered mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 8, 8005–8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkelbach, W. On nonlinear fractional programming. Management science 1967, 13, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, S.; Boyd, S. CVXPY: A Python-embedded modeling language for convex optimization. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2016, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zawawi, Z.B.; Huang, Y.; Clerckx, B. Multiuser wirelessly powered backscatter communications: Nonlinearity, waveform design, and SINR-energy tradeoff. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2018, 18, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; He, H.; Shen, H.; Tian, H. Energy-Efficiency Maximization for Relay-Aided Wireless-Powered Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2024, 11, 18534–18548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhou, C.; Huang, F.; Shen, H.; Li, S. Energy-Efficient Task Offloading in Wireless-Powered MEC: A Dynamic and Cooperative Approach 2024.
- Shi, L.; Ye, Y.; Chu, X.; Lu, G. Computation Bits Maximization in a Backscatter Assisted Wirelessly Powered MEC Network. IEEE Communications Letters 2021, 25, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gui, G. Optimal Resource Allocation for Wireless Powered Multi-Carrier Backscatter Communication Networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters 2020, 9, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Notation | Definition |
|---|---|
| T | The time block |
| The time for WPT at slot t | |
| The time for offloading by BackCom of and at slot t | |
| The time for offloading by AC of and at slot t | |
| The energy harvested by at slot t | |
| The WPT channel gain between and HAP at slot t | |
| , | The offloading channel gain between and , and HAP at slot t |
| ,, | The transmit power by AC at HAP, , at slot t |
| , | The circuit power by BackCom and AC at |
| The amount of tasks processed locally at at slot t | |
| The amount of tasks offloaded by BackCom at at slot t | |
| The amount of tasks offloaded by AC at at slot t | |
| The energy consumed by processing tasks locally at at slot t | |
| The energy consumed by offloading tasks by BackCom at at slot t | |
| The energy consumed by processing tasks at helper at slot t | |
| The energy harvested by WPT at at slot t | |
| The energy harvested by Bakcom at at slot t | |
| The amount of tasks of processed by offloading at slot t | |
| The local CPU frequency at | |
| The CPU cycles required to compute one bit task at | |
| The reflection coefficient of at slot t | |
| The energy conversion efficiency | |
| The computing energy efficiency | |
| W | The channel bandwidth |
| The additive white Gaussian noise |
| Symbol | Value |
|---|---|
| Time slot length | 1 s |
| Maximum battery capacity | 50 J |
| Minimum battery capacity | 0 J |
| Transmit power of the AP | 5 W |
| Noise power | W |
| The circuit consumption of the BackCom and | W |
| The circuit consumption of the AC and | W |
| CPU frequency of | 500 MHz |
| CPU cycles to compute 1 bit task of | 490 cycles/bit |
| CPU frequency of | 480 MHz |
| CPU cycles to compute 1 bit task of | 470 cycles/bit |
| Equal computing efficiency parameter of | |
| Equal computing efficiency parameter of |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





