Submitted:
15 August 2024
Posted:
16 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population, Sample Size and Sampling
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Ethical Considerations
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
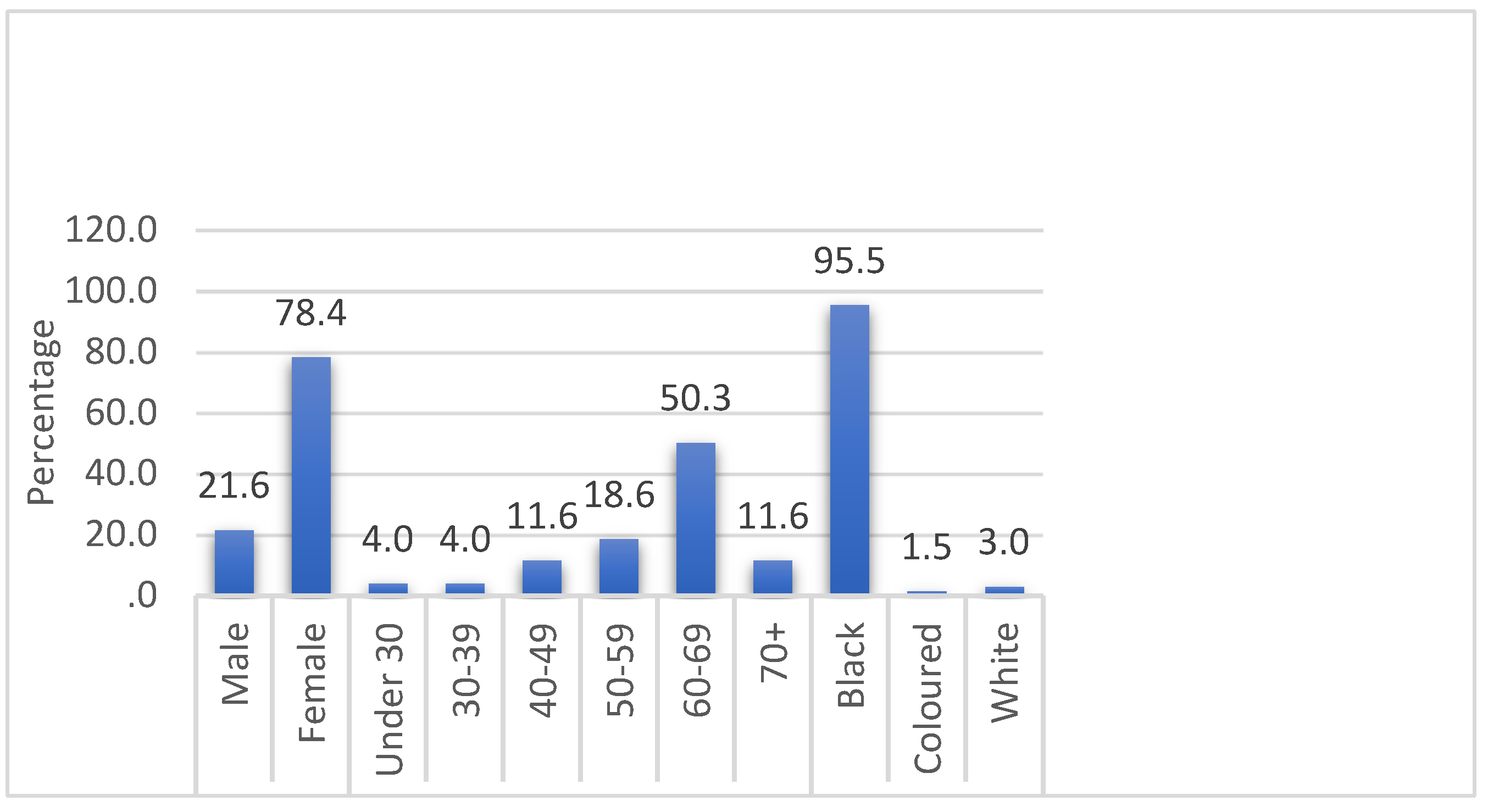
3.1. Demographic Characteristics of the Participants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
References
- Alaofè, H., Hounkpatin, W. A., Djrolo, F., Ehiri, J., & Rosales, C. (2021). Knowledge, attitude, practice and associated factors among patients with type 2 diabetes in Cotonou, Southern Benin. BMC Public Health, 21, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Aljofan, M., Altebainawi, A., & Alrashidi, M. N. (2019). Public knowledge, attitude and practice toward diabetes mellitus in Hail region, Saudi Arabia. International Journal of General Medicine, 255-262. [CrossRef]
- Almousa, A. Y., Hakami, O. A., Qutob, R. A., Alghamdi, A. H., Alaryni, A. A., Alammari, Y. M., & Amlih, M. F. (2023). Knowledge, attitude, and practice toward diabetes mellitus and their association with socioeconomic status among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia. Cureus, 15(5).
- Amiriparsa, T., Attarzadeh Hosseini, S. R., Bijeh, N., & Nia, M. R. H. (2018). The Study of the Effect of a 16-Week Program of Resistance-Aerobic Training on BDNF, Hba1c, Pain, and Michigan Neuropathy Score Among Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy. Journal of Diabetes and Metabolism, 2(124),9.
- Belsti, Y., Akalu, Y., & Animut, Y. (2020). Attitude, practice and its associated factors towards Diabetes complications among type 2 diabetic patients at Addis Zemen District hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Public Health, 20, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, D., Norman, R., Pieterse, D., & Levitt, N. S. (2007). Estimating the burden of disease attributable to diabetes South Africa in 2000. South African Medical Journal, 97(8), 700-706.
- Chetty, L., Govender, N., Govender, G. M., & Reddy, P. (2021). Demographic stratification of Type 2 diabetes and comorbidities in district healthcare in KwaZulu-Natal. South African Family Practice, 63(2). [CrossRef]
- Chiwungwe, F. (2017). Diabetes-related knowledge, attitudes and practices [KAP] of adult patients with type 2 diabetes in Maseru, Lesotho.
- Dessie, G., Mulugeta, H., Amare, D., Negesse, A., Wagnew, F., Getaneh, T., & Lebu, S. (2020). A systematic analysis on prevalence and sub-regional distribution of undiagnosed diabetes mellitus among adults in African countries. Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders, 19, 1931-1941. [CrossRef]
- Egede, L. E., & Ellis, C. (2010). The effects of depression on metabolic control and quality of life in indigent patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes technology & therapeutics, 12(4), 257-262. [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N. A., Aleppo, G., Aroda, V. R., Bannuru, R. R., Brown, F. M., Bruemmer, D., & American Diabetes Association. (2023). 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes—2023. Diabetes care, 46(Supplement_1), S19-S40. [CrossRef]
- Grundlingh, N., Zewotir, T. T., Roberts, D. J., & Manda, S. (2022). Assessment of prevalence and risk factors of diabetes and pre-diabetes in South Africa. Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition, 41(1), 7. [CrossRef]
- Imam, A., & Dharepgol, P. (2023). Exploring knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding diabetes mellitus among the general population: a cross-sectional investigation. Student’s Journal of Health Research Africa, 4(12), 7-7.
- Le Roux, M. (2016). Diabetes-related knowledge, attitude and practices (KAP) of adult patients with type 2 diabetes in the Free State, South Africa (Doctoral dissertation, University of the Free State).
- Manafe, M., Chelule, P. K., & Madiba, S. (2022). The perception of overweight and obesity among South African adults: Implications for intervention strategies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12335. [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S., Karim, N. A., Talib, R. A., & Amani, R. (2015). Knowledge, attitude and practices on diabetes among type 2 diabetic patients in Iran: a cross-sectional study. Science, 3(4), 520-4. [CrossRef]
- Moodley, L. M., & Rambiritch, V. (2007). An assessment of the level of knowledge about diabetes mellitus among diabetic patients in a primary healthcare setting. South African Family Practice, 49(10), 16-16d. [CrossRef]
- Mukeshimana, M. M., & Nkosi, Z. Z. (2014). Communities’ knowledge and perceptions of type two diabetes mellitus in Rwanda: a questionnaire survey. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 23(3-4), 541-549. [CrossRef]
- Mwimo, J. L., Somoka, S., Leyaro, B. J., Amour, C., Mao, E., & Mboya, I. B. (2021). Knowledge, attitude, and practice of physical activity among patients with diabetes in Kilimanjaro region, Northern Tanzania: a descriptive cross-sectional. study. BMJ open, 11(9): 046841. [CrossRef]
- Niroomand, M., Ghasemi, S. N., Karimi-Sari, H., Kazempour-Ardebili, S., Amiri, P., & Khosravi, M. H. (2016). Diabetes knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP) study among Iranian in-patients with type-2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 10(1), S114-S119. [CrossRef]
- Odili, V. U., Isiboge, P. D., & Eregie, A. (2011). Patients’ knowledge of diabetes mellitus in a Nigerian city. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 10(5), 637-642.
- Okolie, V. U., Ehiemere, O. I., Iheanacho, N. P., & Kalu-Igwe, I. N. (2009). Knowledge of diabetes management and control by diabetic patients at Federal Medical Center Umuahia Abia State, Nigeria. International Journal of Medicine and Medical sciences, 1(9), 353-358.
- Owolabi, E. O., Goon, D. T., Ajayi, A. I., & Adeniyi, O. V. (2022). Knowledge of diabetes and associated factors in rural Eastern Cape, South Africa: A cross-sectional study. Plos one, 17(7), e0269811. [CrossRef]
- Peter, P. I., Steinberg, W. J., van Rooyen, C., & Botes, J. (2022). Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients’ knowledge, attitude and practice of lifestyle modifications. Health SA Gesondheid (Online), 27, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Phoosuwan, N., Ongarj, P., & Hjelm, K. (2022). Knowledge on diabetes and its related factors among the people with type 2 diabetes in Thailand: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health, 22(1), 2365. [CrossRef]
- Reid, M., Roux, M. L., Raubenheimer, J., & Walsh, C. (2019). Diabetes-related knowledge, attitude and practices (KAP) of adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Free State province, South Africa. South African Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 32(4), 20-27. [CrossRef]
- Sookan, T., Vaizie, A., Pillay, T., Moodley, S., Naidoo, S., & Naidoo, K. (2022). Exploring the role of the biokinetics in diabetes self-management: a survey of patients’ knowledge, attitudes and perceptions about exercise. Journal of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Diabetes of South Africa, 27(2), 70-74.
- World Health Organization (WHO).2019). Classification of diabetes mellitus, World Health Organization, Geneva, viewed 20 June 2020, from https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/classification-of-diabetes-mellitus.
- Zhao, R., Zhang, X., Wang, S., Zhao, N., Li, D., & Fan, H. (2023). Factors affecting T2DM patients’ behaviors associated with integrated treatment and prevention services in China. International Journal for Equity in Health, 22(1), 223. [CrossRef]
| Item | Frequencies (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Correct | Incorrect | |
| Physical activity & exercise are the same thing? | 36 (18) | 163 (82) |
| People with T2DM can safely perform exercise? | 140 (70) | 59 (30) |
| Exercise can be used in the management/treatment of T2DM. | 138(69) | 61(31) |
| A person with T2DM cannot do strenuous exercise like weightlifting, cycling, or running. | 49(25) | 150(75) |
| I am willing to engage in exercise to improve my health. | 131(66) | 68(34) |
| Type-2 diabetes mellitus management should include both exercise & a healthy diet. | 134(67) | 65(33) |
| A person with T2DM will often have high blood pressure. | 61(31) | 138(69) |
| A person with T2DM using herbs makes that person healthier than if they use Western medication. | 65(33) | 134(67) |
| A person with T2DM using any type of medication be cured of the disease? | 60(30) | 139(70) |
| Type-2 diabetes mellitus medication may cause swelling of the feet. | 57(29) | 142(71) |
| Item | Responses as frequency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| True | False | Unsure | |
| I feel that my regular work is an adequate substitute for exercise. | 158 (79.4) | 37 (18.6) | 4 (2.0) |
| I need someone to keep prompting me to do my exercises | 128 (64.3) | 58 (29.1) | 12 (6.0) |
| I use mild pain or fatigue as an excuse to keep away from my exercises. | 139 (69.8) | 55 (27.6) | 5 (2.5) |
| I will continue my exercises until I improve, regardless of how long it takes | 49 (24.6) | 145 (73,9) | 5 (2.5) |
| I believe I will improve with exercises as I have seen others improving | 59(29.6) | 129(68.4) | 11 (5.5) |
| I look forward to doing my exercises each day | 60 (30.2) | 125 (63.8) | 14 (7.0) |
| I feel that age is an influencing factor in motivating me to do my exercises | 137 (68.8) | 57 (28.6) | 5 (2.5) |
| I feel embarrassed doing exercise in front of others | 128 (69.3) | 63 (31.7) | 8 (4.0) |
| I feel that I have no time of my own and my daily exercises take away my valuable time | 130 (65.3) | 63 (31.7) | 6 (3.0) |
| I give up on exercises owing to the difficulty in sticking to a schedule | 128 (64.3) | 65 (37.7) | 6 (3.0) |
| Item | Responses as frequency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| True | False | Unsure | |
| I do activities that make me sweat as I exercise | 157 (78.9) | 38 (19.1) | 4 (2.0) |
| I find out how I can still adjust my lifestyle to living with T2DM | 141 (70.9) | 46 (23.1) | 12 (6.0) |
| I check my blood pressure monthly | 124 (62.3) | 58 (29.1) | 17(8.5) |
| I check my feet for injuries regularly | 130 (65.3) | 57 (28.6) | 12 (6.0) |
| I find it difficult to lose weight if I become overweight | 133 (66.8) | 57 (28.6) | 9(4.5) |
| I feel that my therapist is making tall claims when he explains to me the benefits of the exercise program | 136 (68.3) | 53 (26.6) | 10 (5.0) |
| I thought of asking my doctor, if there are any medicines available, which will make me better, without doing exercise | 131 (65.8) | 58 (29.1) | 10 (5.0) |
| I keep asking my therapist how perfectly I have learned the exercises or how better I could do it | 133 (66.8) | 55 (27.6) | 11 (5.5) |
| I am prompt in doing my exercises regularly as it keeps me alert and energetic throughout the day | 139 (69.8) | 55 (27.6) | 5 (2.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





