Submitted:
15 August 2024
Posted:
15 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Databases
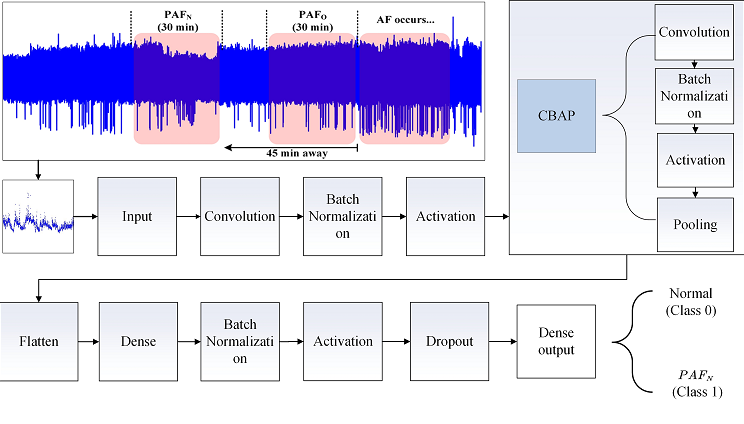
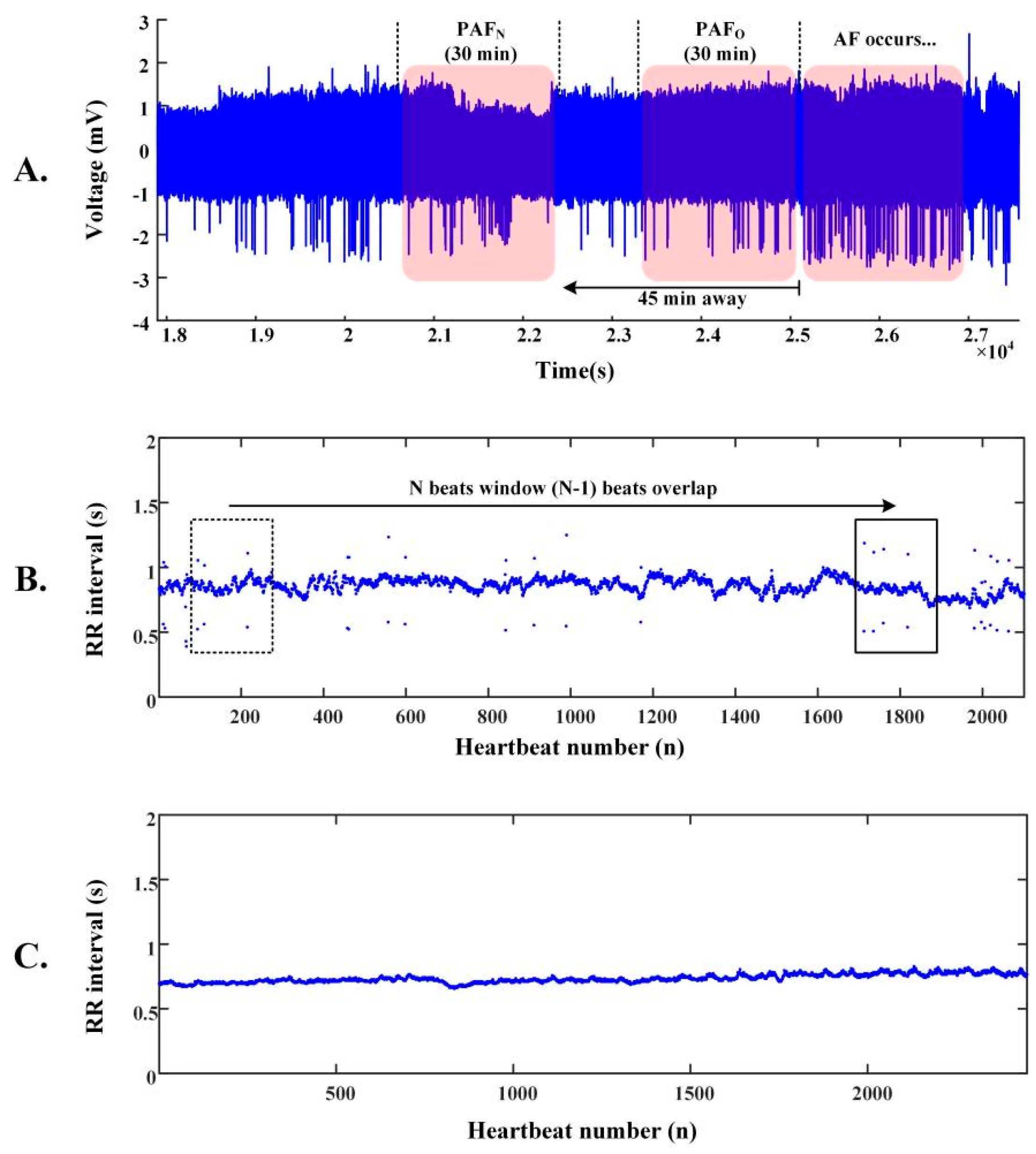
2.2. R-R Intervals of ECG Segments
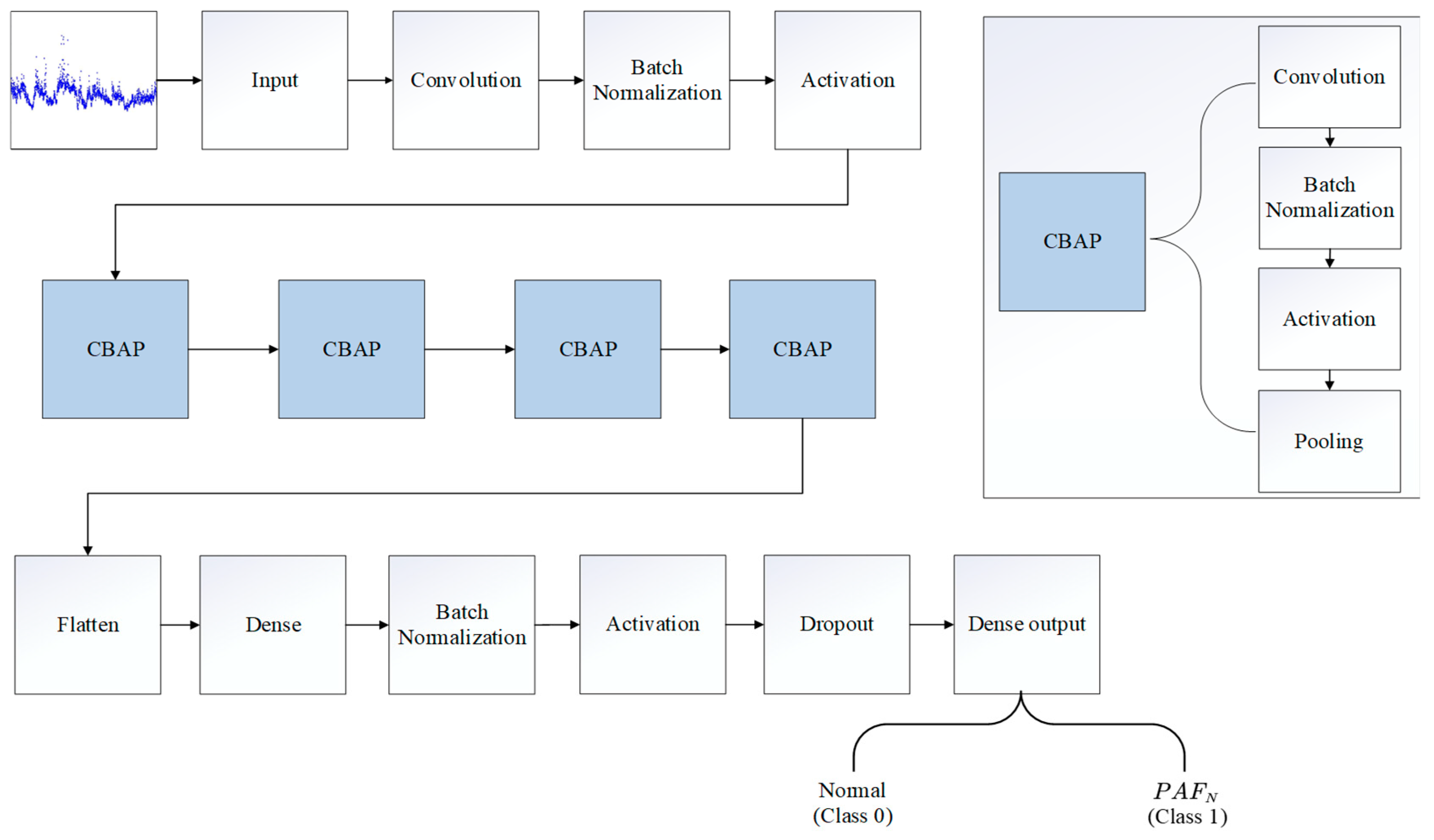
2.3. Architecture of the PAFNet Model
2.4. Training and Optimization of the PAFNet Model
2.4. Evaluation Protocols
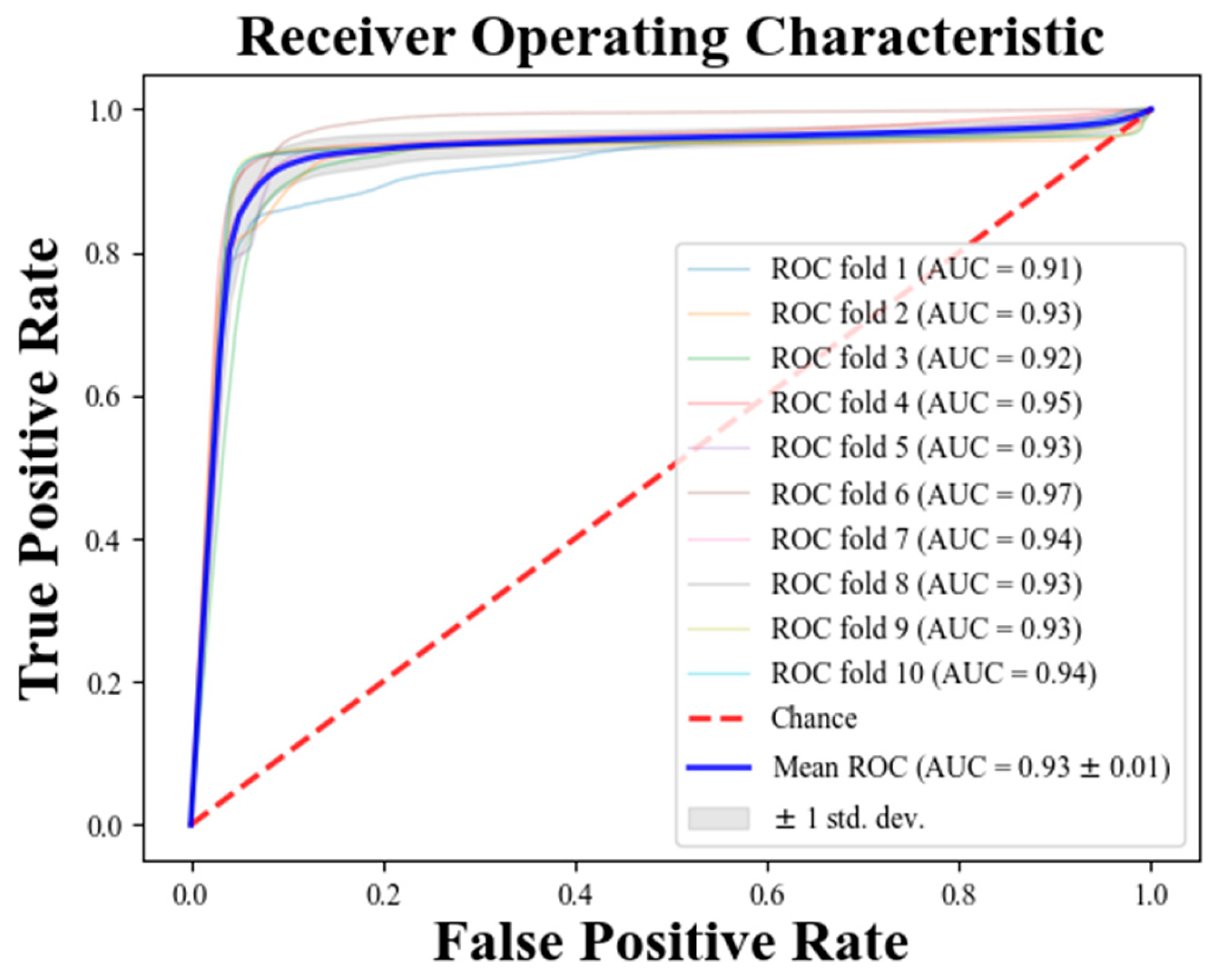
3. Results
4. Discussions
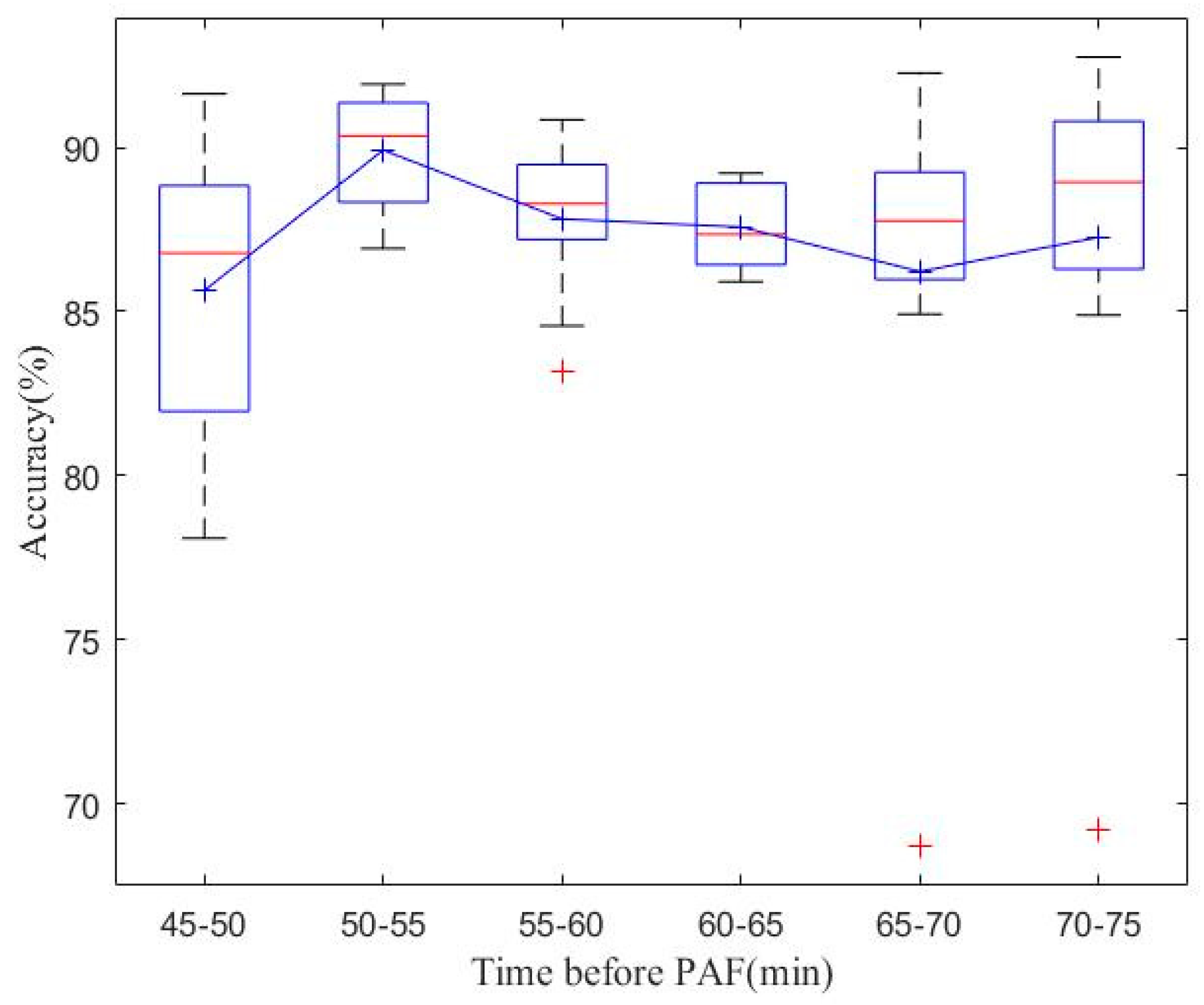
4.1. Real-Time PAF Onset Prediction
4.2. Performance Compared with Other Methods
4.3. Study Limitations and Future Works
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calkins H., Hindricks G., Cappato R., et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, vol. 14, no. 10, pp. e275-e444, 2017.
- Colilla S, Crow A, Petkun W, Singer DE, Simon T, Liu XC, et al. Estimates of Current and Future Incidence and Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation in the US Adult Population. American Journal of Cardiology 2013; 112(8):1142-1147. [CrossRef]
- Boon KH, Khalil-Hani M, Malarvili MB, and Sia CW. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation prediction method with shorter HRV sequences. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2016; 134:187-196. [CrossRef]
- Chiang CE, Okumura K, Zhang S, Chao TF, Siu C, Wei L, et al. 2017 consensus of the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society on stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. Journal of Arrhythmia 2017; 33(4):345-367. [CrossRef]
- Boon KH, Khalil-Hani M, and Malarvili MB. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation prediction based on HRV analysis and non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm III. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2017; 153:171-184. [CrossRef]
- Narin A, Isler Y, Ozer M, and Perc M. Early prediction of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation based on short-term heart rate variability. Physica A 2018;509:56-65. [CrossRef]
- Soliman EZ, Safford MM, Muntner P, Khodneva Y, Dawood FZ, Zakai NA, et al.. Atrial Fibrillation and the Risk of Myocardial Infarction. JAMA Internal Medicine 2014;174(1): E107-E114. [CrossRef]
- Wang LH, Yan ZH, Yang YT, Chen JY, Yang T, Kuo IC, et al. A Classification and Prediction Hybrid Model Construction with the IQPSO-SVM Algorithm for Atrial Fibrillation Arrhythmia. Sensors-Basel 2021; 21(15). [CrossRef]
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). European Heart Journal 2021;42(5):373-498. [CrossRef]
- Chen WS, Gao BR, Chen WQ, Li ZZ, Xu ZY, Zhang YH, et al. Comparison of pharmacological and electrical cardioversion in permanent atrial fibrillation after prosthetic cardiac valve replacement: A prospective randomized trial. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2013;41(4):1067-1073. [CrossRef]
- Gitt AK, Smolka W, Michailov G, Bernhardt A, Pittrow D, Lewalter T, et al. Types and outcomes of cardioversion in patients admitted to hospital for atrial fibrillation: results of the German RHYTHM-AF Study. Clinical Research in Cardiology 2013;102(10):713-723. [CrossRef]
- Moody GB, Goldberger AL, McClennen S, and Swiryn SP. Predicting the onset of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. In: Proc. The Computers in Cardiology Challenge 2001, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2001. [Online]. Available: <Go to ISI>://WOS:000173806400029.
- de Chazal P and Heneghan, C. Automated assessment of atrial fibrillation. In: Proc. The Computers in Cardiology Challenge 2001, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2001. [Online] Available: <Go to ISI>://WOS:000173806400030.
- Lynn KS and Chiang, HD. A two-stage solution algorithm for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation prediction. In: Proc. The Computers in Cardiology Challenge 2001, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2001. [Online] Available: <Go to ISI>://WOS:000173806400103.
- Krstacic G, Gamberger D, Smuc T, and Krstacic A. Some important R-R interval based paroxysmal atrial fibrillation predictors. In: Proc. The Computers in Cardiology Challenge 2001, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2001. [Online] Available: <Go to ISI>://WOS:000173806400104.
- Maier C, Bauch M, and Dickhaus H. Screening and prediction of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation by analysis of heart rate variability parameters. In: Proc. The Computers in Cardiology Challenge 2001, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2001. [Online] Available: <Go to ISI>://WOS:000173806400033.
- Yang ACC and Yin, HW. Prediction of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation by footprint analysis. In: Proc. The Computers in Cardiology Challenge 2001, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2001. [Online] Available: <Go to ISI>://WOS:000173806400102.
- Langley P, di Bernardo D, Allen J, Bowers E, Smith FE, Vecchietti S, et al. Can paroxysmal atrial fibrillation be predicted? In: Proc. The Computers in Cardiology Challenge 2001, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2001. [Online] Available: <Go to ISI>://WOS:000173806400031.
- Zong W, Mukkamala R, and Mark RG. A methodology for predicting paroxysmal atrial fibrillation based on ECG arrhythmia feature analysis. In: Proc. The Computers in Cardiology Challenge 2001, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2001. [Online]. Available: <Go to ISI>://WOS:000173806400032.
- Islam MS, Ammour N, Alajlan N, and Aboalsamh H. Rhythm-based heartbeat duration normalization for atrial fibrillation detection. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2016; 72:160-9. [CrossRef]
- Schreier G, Kastner P, and Marko W. An automatic ECG processing algorithm to identify patients prone to paroxysmal atrial fibrillation In: Proc. The Computers in Cardiology Challenge 2001, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2001. [Online] Available: <Go to ISI>://WOS:000173806400034.
- Sutton JR, Mahajan R, Akbilgic O, and Kamaleswaran R. PhysOnline: An Open Source Machine Learning Pipeline for Real-Time Analysis of Stream Physiological Waveform. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2019; 23(1): 59-65. [CrossRef]
- Acharya UR, Fujita H, Lih OS, Hagiwara Y, Tan JH, Adam M, et al. Automated detection of arrhythmias using different intervals of tachycardia ECG segments with convolutional neural network. Information Sciences 2017; 405: 81-90. [CrossRef]
- Fan X, Yao Q, Cai Y, Miao F, Sun F, Li Y, et al. Multiscaled Fusion of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Screening Atrial Fibrillation From Single Lead Short ECG Recordings. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2018; 22 (60:pp. 1744-1753. [CrossRef]
- Hannun AY, Rajpurkar P, Haghpanahi M, Tison GH, Bourn C, Turakhia MP, et al. Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nature Medicine 2019; 25(1):65-72. [CrossRef]
- Kamaleswaran R, Mahajan R, and Akbilgic O. A robust deep convolutional neural network for the classification of abnormal cardiac rhythm using single lead electrocardiograms of variable length. Physiological Measurement 2018; 39(3):035006. [CrossRef]
- Rubin J, Parvaneh S, Rahman A, Conroy B, and Babaeizadeh S. Densely connected convolutional networks for detection of atrial fibrillation from short single-lead ECG recordings. Journal of Electrocardiology 2018; 51(6):S18-S21. [CrossRef]
- Lian J, Wang L, and Muessig D. A Simple Method to Detect Atrial Fibrillation Using RR Intervals. American Journal of Cardiology 2011; 107(10):1494-1497. [CrossRef]
- Stridh M, Sornmo L, Meurling CJ, and Olsson SB. Sequential characterization of atrial tachyarrhythmias based on ECG time-frequency analysis. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2004; 51(1):100-114. [CrossRef]
- Roonizi EK and Sassi, R. An Extended Bayesian Framework for Atrial and Ventricular Activity Separation in Atrial Fibrillation. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2017; 21(6):1573-1580. [CrossRef]
- Mehta S, Lingayat N, and Sanghvi S. Detection and delineation of P and T waves in 12-lead electrocardiograms. Expert Systems 2009; 26(1):125-143. [CrossRef]
- Ladavich S and Ghoraani, B. Developing An Atrial Activity-Based Algorithm For Detection Of Atrial Fibrillation. In: Proc. the IEEE 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the Ieee Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 2014. [Online] Available: <Go to ISI>://WOS:000350044700014.
- Kennedy A, Finlay DD, Guldenring D, Bond RR, Moran K, McLaughlin J, et al. Automated detection of atrial fibrillation using R-R intervals and multivariate-based classification. Journal of Electrocardiology 2016; 49(6):871-876. [CrossRef]
- Goldberger AL, Amaral LAN, Glass L, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov PC, Mark RG, et al. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet-Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 2000; 101(23):E215-E220. [CrossRef]
- LeCun Y, Bengio Y, and Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature 2015; 521(7553):436-444. [CrossRef]
- Camm AJ, Malik M, Bigger JT, Briethardt G, Cerutti S, Cohen RJ, et al. Heart rate variability-Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Circulation 1996; 93(5):1043-1065. [CrossRef]
| Database | Number of Records (n) | Number of R-R intervals (n) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Training and validation | AFPDB (PAFN) | 25 | 56,381 |
| AFPDB (N) | 25 | 56,900 | |
| Testing | AFDB (PAFN) | 12 | 27,836 |
| NSRDB (N) | 18 | 44,087 | |
| Number | Layer type | Number of feature maps or nodes | Parameters | Number | Layer type | Number of feature maps or nodes | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | input | changing with the size of the sliding window | N | 14 | BN * | - | - |
| 2 | convolutional | 16 | size: N, kernel: 8, padding="same" | 15 | activation | - | ReLU |
| 3 | BN | - | - | 16 | pooling | - | size: 2 |
| 4 | activation | - | ReLU | 17 | convolutional | 256 | size: N/16, kernel: 8, padding="same" |
| 5 | convolutional | 32 | size: N/2, kernel: 8, padding="same" | 18 | BN | - | - |
| 6 | BN | - | - | 19 | activation | - | ReLU |
| 7 | activation | - | ReLU | 20 | pooling | - | size: 2 |
| 8 | pooling | - | size: 2 | 21 | Flatten | - | - |
| 9 | convolutional | 64 | size: N/4, kernel: 8, padding="same" | 22 | Dense | 512 | - |
| 10 | BN | - | - | 23 | BN | - | - |
| 11 | activation | - | ReLU | 24 | activation | - | ReLU |
| 12 | pooling | - | size: 2 | 25 | dropout | - | 0.25 |
| 13 | convolutional | 128 | size: N/8, kernel: 8, padding="same" | 26 | Dense output | 1 | activation function: Sigmoid |
| Model | Input size(n) | Sen (%) | Spe (%) | Acc (%) | Testing time (ms / batch) |
Totalparams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 50 | 85.44 | 92.45 | 89.74 | 13.8 | 878,017 |
| M2 | 100 | 89.92 | 93.24 | 91.96 | 23.1 | 1,271,233 |
| M3 | 200 | 88.17 | 93.47 | 91.42 | 43.0 | 2,057,665 |
| Fold | Training data (rows) | Validation data(rows) | Sen (%) | Spe (%) | Acc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11329-113281 | 1-11328 | 82.11 | 92.09 | 87.16 |
| 2 | 1-11328,22656-113281 | 11328-22656 | 95.34 | 87.84 | 91.63 |
| 3 | 1-22656, 33984-113281 | 22656-33984 | 98.74 | 98.86 | 98.80 |
| 4 | 1-33984, 45312-113281 | 33984-45312 | 99.39 | 99.39 | 99.39 |
| 5 | 1-45312, 56640-113281 | 45312-56640 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 6 | 1-56640, 67968-113281 | 56640-67968 | 98.76 | 99.95 | 99.35 |
| 7 | 1-67968, 79296-113281 | 67968-79296 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 8 | 1-79296, 90624-113281 | 79296-90624 | 98.47 | 100.00 | 99.21 |
| 9 | 1-90624, 101952-113281 | 90624-101952 | 98.43 | 99.54 | 98.98 |
| 10 | 1-101952 | 101952-113281 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Mean | - | - | 97.12 | 97.77 | 97.45 |
| Var * | 0.0030 | 0.0018 | 0.0019 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





