Submitted:
13 August 2024
Posted:
14 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
| Drug class | Subtype | Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Cytotoxic chemotherapy | All breast cancer subtypes | Carboplatin, Docetaxel, Doxorubicin, Epirubicin, Ixabepilone, Liposomal doxorubicin, Nab-paclitaxel, Paclitaxel, Vinorelbine |
| HR+ | No approved agents for only HR+ subtype | |
| HER2+ | Carboplatin | |
| HER2- | No approved agents for only HER2-subtype | |
| TNBC | Cisplatin | |
| Targeted therapy | All breast cancer subtypes | No approved agents targeting all subtypes |
| HR+ | Abemaciclib, Alpelisib, Anastrozole, Capivasertib, Elacestrant, Everolimus, Exemestane, Fulvestrant, Lapatinib, Letrozole, Palbociclib, Ribociclib, Tamoxifen, Toremifene | |
| HER2+ | Lapatinib, Margetuximab, Neratinib, Pertuzumab, Tucatinib, Trastuzumab | |
| HER2- | Abemaciclib, Alpelisib, Bevacizumab, Capivasertib, Elacestrant, Everolimus, Fulvestrant, Olaparib, Palbociclib, Ribociclib, Talazoparib | |
| TNBC | Atezolizumab, Pembrolizumab | |
| Antibody-Drug Conjugates | All breast cancer subtypes | Sacituzumab govitecan |
| HR+ | No approved agents for only HR+ subtype | |
| HER2+ | Ado-trastuzumab emtansine, Trastuzumab deruxtecan | |
| HER2- | No approved agents for only HER2- subtype | |
| TNBC | Trastuzumab deruxtecan (TNBC with low/ultra-low HER2 expression) |
2. Immune Microenvironment of TNBC
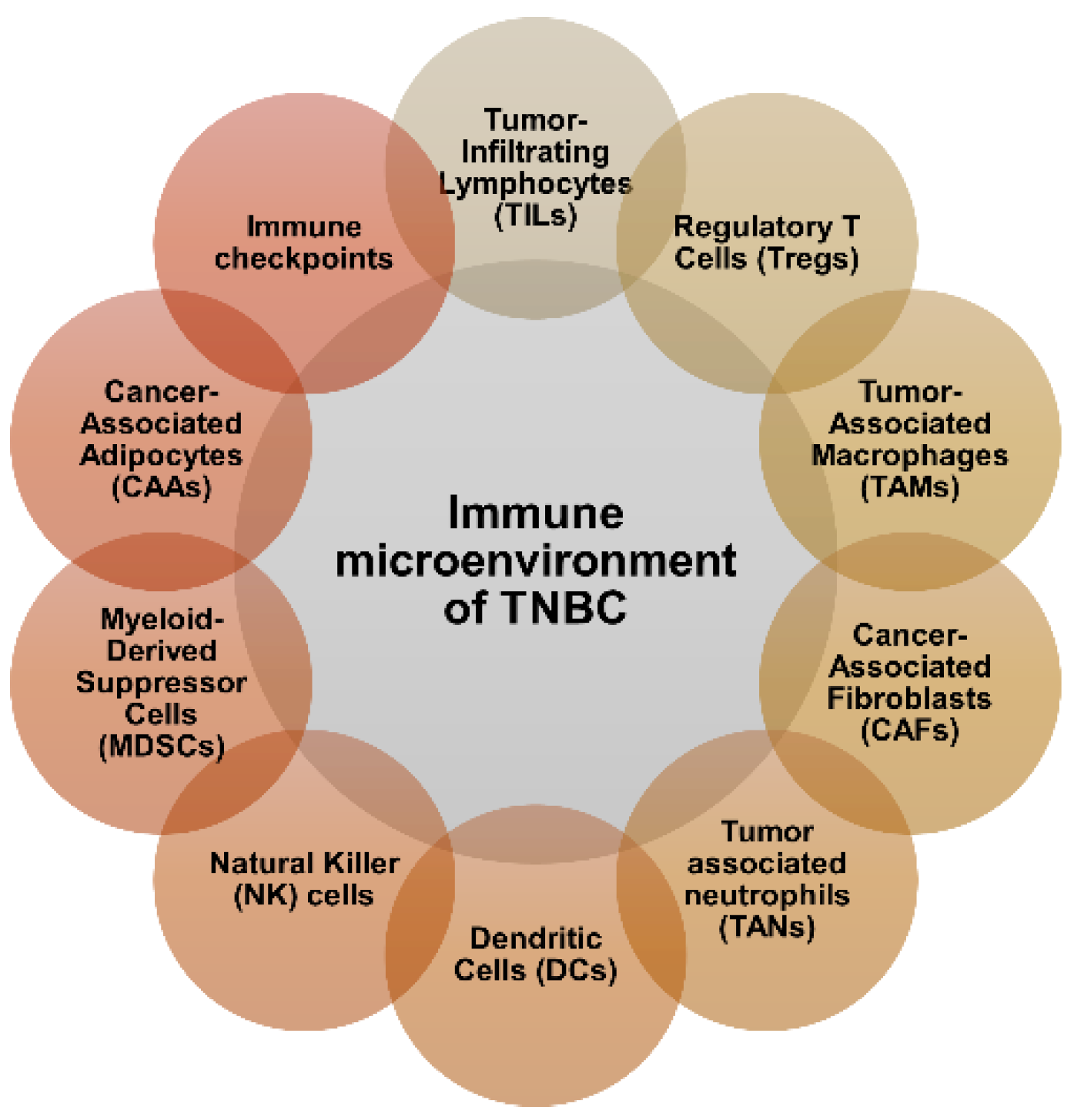
3. Current Clinical Immunotherapy Approaches for TNBC
3.1. Cytokines
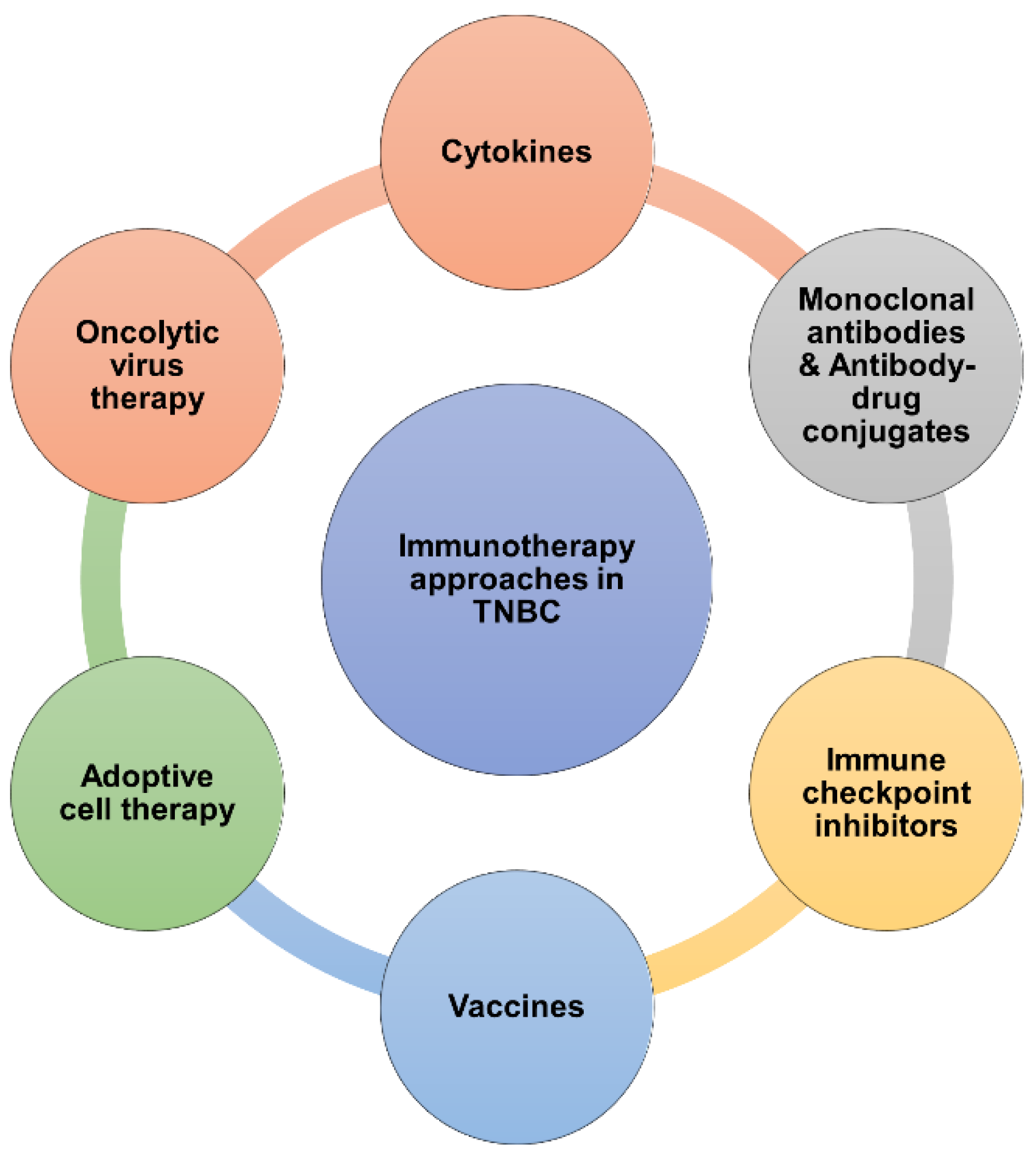
3.2. Monoclonal Antibodies
3.3. Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
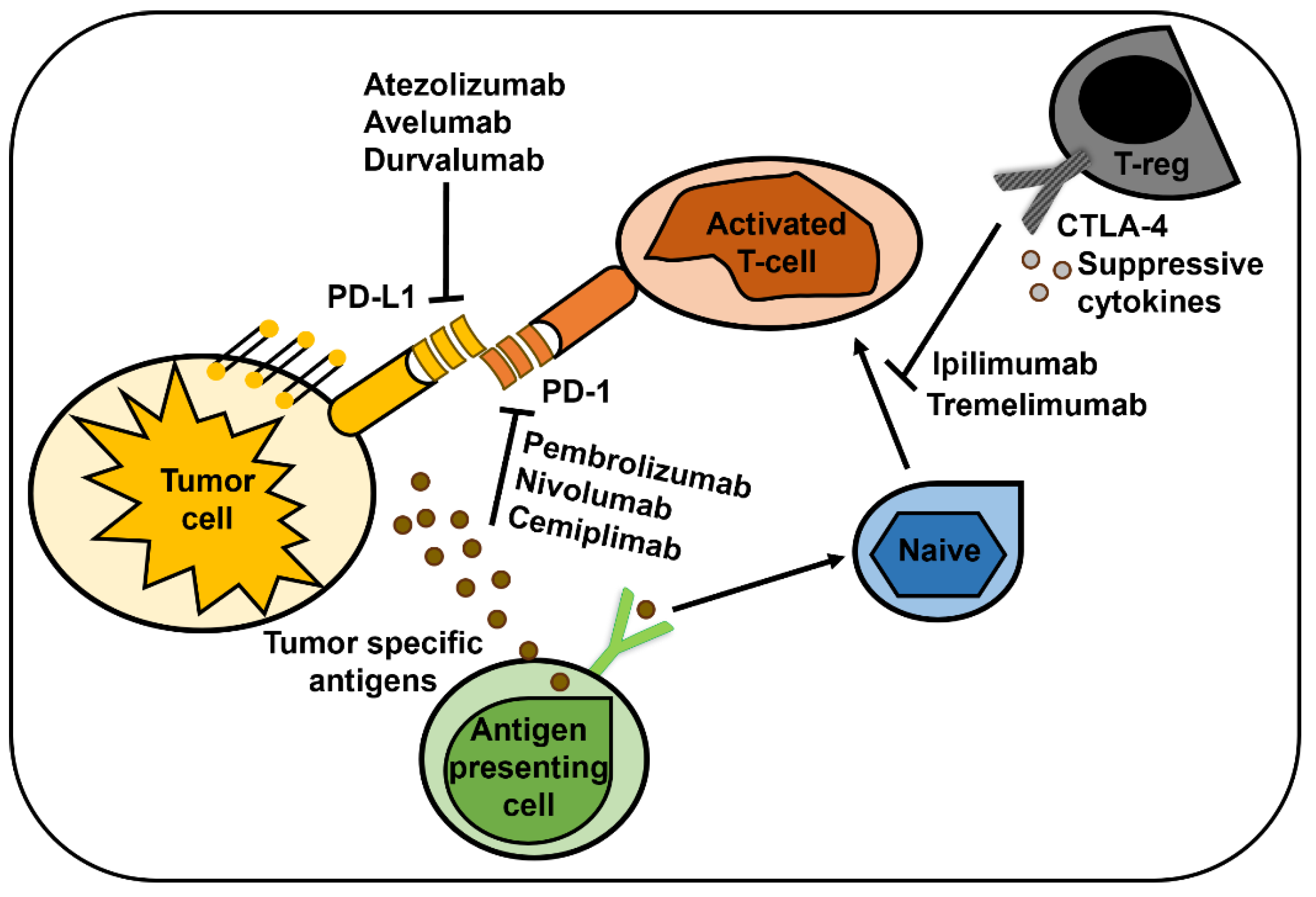
3.4. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
3.5. Vaccines
3.6. Adoptive cell therapy (ACT)
3.7. Oncolytic Virus Therapy
4. Rationale of Combining Immunotherapy with Other Therapies
| Target | Interventions | Clinical status & Identifier | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| PARP and PD-1 | Drug: Niraparib Biological: Pembrolizumab |
Phase I/II NCT02657889 |
Completed |
| PARP and PD-L1 | Drug: Avelumab Phase 1b Drug: Talazoparib Phase 1b Drug: Avelumab Phase 2 Drug: Talazoparib Phase 2 |
Phase Ib/II NCT03330405 |
Completed |
| PD-1 | Biological: Pembrolizumab Drug: Nab-paclitaxel Drug: Paclitaxel Drug: Gemcitabine Drug: Carboplatin Drug: Normal Saline Solution |
Phase III NCT02819518 |
Completed |
| PD-1 | Drug: Eribulin Mesylate Drug: Pembrolizumab |
Phase Ib/II NCT02513472 |
Completed |
| PD-L1 | Drug: Atezolizumab (MPDL3280A), an engineered anti-PDL1 antibody Drug: Nab-Paclitaxel Drug: Placebo |
Phase III NCT02425891 |
Completed |
| PD-L1 | Drug: Atezolizumab Drug: Nab-paclitaxel |
Phase Ib NCT01633970 |
Completed |
| PD-L1 | Drug: Atezolizumab (MPDL3280A), an engineered anti-PDL1 antibody Drug: Atezolizumab Placebo Drug: Paclitaxel |
Phase III NCT03125902 |
Completed |
| PD-1 | Drug: Nivolumab Radiation: Radiation therapy Drug: Low dose doxorubicin Drug: Cyclophosphamide Drug: Cisplatin |
Phase II NCT02499367 |
Ongoing |
| PD-1 | Biological: Pembrolizumab Drug: Nab-paclitaxel Drug: Anthracycline (doxorubicin) Drug: Cyclophosphamide Drug: Carboplatin Drug: Paclitaxel |
Phase I NCT02622074 |
Completed |
| PD-1 | Biological: Pembrolizumab Drug: Carboplatin Drug: Paclitaxel Drug: Doxorubicin Drug: Epirubicin Drug: Cyclophosphamide Drug: Placebo Biological: GM-CSF |
Phase III NCT03036488 |
Ongoing |
| PD-L1 | Drug: MEDI4736 (Durvalumab) Drug: Placebo Drug: Nab-Paclitaxel Drug: Epirubicin Drug: Cyclophosphamide |
Phase II NCT02685059 |
Completed |
| PD-L1 | Drug: Carboplatin Drug: Abraxane Drug: MPDL3280A (Atezolizumab) Procedure: Surgery Drug: Anthra |
Phase III NCT02620280 |
Ongoing |
| PD-L1 | Drug: Atezolizumab (MPDL3280A), an engineered anti-PDL1 antibody Drug: Placebo Drug: Nab-paclitaxel Drug: Doxorubicin Drug: Cyclophosphamide Drug: Filgrastim Drug: Pegfilgrastim |
Phase III NCT03197935 |
Completed |
| PD-1 | Drug: Pembrolizumab Radiation: Radiotherapy |
Phase II NCT02730130 |
Completed |
| PD-L1 | Radiation: SABR Drug: Atezolizumab |
Phase II NCT03464942 |
Completed |
| PD-1 and LIV-1 | Drug: Ladiratuzumab vedotin Drug: Pembrolizumab |
Phase Ib/II NCT03310957 |
Ongoing |
| PD-L1 and AKT | Drug: Atezolizumab Drug: Ipatasertib Drug: Paclitaxel Drug: Placebo for Atezolizumab Drug: Placebo for Ipatasertib |
Phase III NCT04177108 |
Completed |
| PD-1, PARP, and VEGFR-2 | Drug: SHR-1210 + Apatinib +Fluzoparib | Phase I NCT03945604 |
Completed |
| PD-1, VEGFR-2,c-KIT, and PDGFRb | Drug: Camrelizumab in combination with nab-paclitaxel and famitinib | Phase II NCT04129996 |
Completed |
| PD-L1 and CD73 | Drug: Paclitaxel Drug: Carboplatin Drug: MEDI4736 Drug: MEDI9447 |
Phase I/II NCT03616886 |
Ongoing |
| PD-L1 and modified oncolytic herpes virus | Biological: Talimogene Laherparepvec Biological: Atezolizumab |
Phase Ib NCT03256344 |
Ongoing |
| PD-L1 | Avelumab, SBRT, haNK and 15 other interventions/treatments | Phase I/II NCT03387085 |
Completed |
4.1. Combination of Immunotherapy with PARP Inhibitors
4.2. Combination of Immunotherapy with Chemotherapy
4.3. Combination of Immunotherapy with Radiotherapy
4.4. Dual Antibody Combinations and Dual Immunotherapies
5. Conclusion and Future Perspectives
| Target | Interventions | Clinical status & Identifier | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | Drug: Metformin Drug: Erlotinib |
Phase I NCT01650506 |
Completed |
| PI3K | Drug: BKM120 | Phase II NCT01790932 |
Completed |
| PI3K | Drug: BKM120 and Olaparib Drug: BYL719 and Olaparib |
Phase I NCT01623349 |
Completed |
| PI3K | Drug: BYl719 | Phase II NCT02506556 |
Completed |
| AKT | Drug: Ipatasertib Drug: Paclitaxel Drug: Placebo |
Phase II NCT02301988 |
Completed |
| AKT | Drug: Ipatasertib Drug: Paclitaxel Drug: Placebo |
Phase II NCT02162719 |
Completed |
| AKT | Drug: Paclitaxel Drug: AZD5363 Drug: Placebo |
Phase II NCT02423603 |
Unknown |
| AKT | Drug: Capivasertib Drug: Paclitaxel Drug: Placebo |
Phase III NCT03997123 |
On-going |
| AKT | Drug: Capivasertib Other: Laboratory Biomarker Analysis Drug: Olaparib Other: Pharmacological Study Drug: Vistusertib |
Phase Ib NCT02208375 |
On-going |
| AKT | Drug: GSK1120212 Drug: GSK2141795 |
Phase I NCT01138085 |
Completed |
| mTOR | Drug: Doxil Drug: Bevacizumab Drug: Temsirolimus |
Phase I NCT00761644 |
Completed |
| mTOR | Drug: Everolimus | Phase II NCT01931163 |
Completed |
| mTOR | Drug: Everolimus Drug: Eribulin mesylate Other: Pharmacological study Other: Laboratory biomarker analysis |
Phase I NCT02120469 |
Completed |
| mTOR | Drug: Everolimus Drug: Eribulin |
Phase I NCT02616848 |
Completed |
| CDK4/6 | Drug: Trilaciclib Drug: Gemcitabine Drug: Carboplatin |
Phase 2 NCT02978716 |
Completed |
| CDK4/6 | Drug: Trilaciclib Drug: Gemcitabine Drug: Carboplatin |
Phase 2 NCT02978716 |
Completed |
| ATR | Drug: M6620 Drug: Gemcitabine Drug: Cisplatin Drug: Etoposide Drug: Carboplatin Drug: Irinotecan |
Phase I NCT02157792 |
Completed |
| ATR | Drug: Olaparib Drug: Ceralasertib Drug: Adavosertib |
Phase 2 NCT03330847 |
On-going |
| ATR | Procedure: Biopsy Drug: Capivasertib Drug: Ceralasertib Biological: Durvalumab Drug: Olaparib Other: Quality-of-Life Assessment Drug: Selumetinib |
Phase II NCT03801369 |
On-going |
| CHK1 | Drug: LY2606368 | Phase II NCT02203513 |
Completed |
| WEE1 | Drug: Cisplatin Drug: AZD1775 |
Phase II NCT03012477 |
Completed |
| MEK | Drug: GSK1120212 Drug: GSK2141795 |
Phase I NCT01138085 |
Completed |
| MEK | Drug: Akt Inhibitor GSK2141795 Other: Laboratory Biomarker Analysis Drug: Trametinib |
Phase II NCT01964924 |
Completed |
| MEK | Drug: Ipatasertib Drug: Cobimetinib |
Phase I NCT01562275 |
Completed |
| MET, VEGFR2, RET, AXL, FTL3, etc. | Drug: Cabozantinib | Phase II NCT01738438 |
Completed |
| VEGF, PDGFR, HGF, etc. | Drug: Paclitaxel Drug: Carboplatin Drug: Sunitinib |
Phase I/II NCT00887575 |
Completed |
| VEGF, PDGFR, HGF, etc. | Drug: SU011248 Drug: Chemotherapy |
Phase II NCT00246571 |
Completed |
| Aurora-A, VEGFR, FGFR | Drug: ENMD-2076 | Phase II NCT01639248 |
Completed |
| EGFR, HER2 | Drug: Combination of Veliparib + Lapatinib | Phase: N/A NCT02158507 |
On-going |
| PI3K, mTOR | Drug: Prexasertib Drug: Cisplatin Drug: Cetuximab Drug: G-CSF Drug: Pemetrexed Drug: Fluorouracil Drug: LY3023414 Drug: Leucovorin |
Phase I NCT02124148 |
Completed |
| PARP | Drug: Pamiparib | Phase I/II NCT03333915 |
Completed |
| PARP | Drug: Talazoparib | Phase II NCT03499353 |
Completed |
| PARP | Drug: Olaparib | Phase II NCT02681562 |
Completed |
| PARP | Drug: Olaparib Radiation: Radiation therapy |
Phase I NCT03109080 |
Completed |
| PARP | Drug: Iniparib Drug: Gemcitabine Drug: Carboplatin |
Phase II NCT01045304 |
Completed |
| PARP | Drug: Cyclophosphamide Drug: Placebo Drug: Doxorubicin Drug: Paclitaxel Drug: Carboplatin Drug: Veliparib Drug: Placebo |
Phase III NCT02032277 |
Completed |
| HDAC | Drug: Chidamide combined with Cisplatin | Phase II NCT04192903 |
Completed |
| HDAC | Drug: Entinostat | Phase I NCT03361800 |
Terminated |
| HDAC | Drug: Romidepsin Drug: Cisplatin Drug: Nivolumab |
Phase I/II NCT02393794 |
On-going |
| SMO | Drug: LDE225 Drug: Docetaxel |
Phase I NCT02027376 |
Completed |
| XPO1 | Drug: Selinexor | Phase II NCT02402764 |
Completed |
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zagami, P.; Carey, L.A. Triple negative breast cancer: Pitfalls and progress. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litton, J.K.; Rugo, H.S.; Ettl, J.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Gonçalves, A.; Lee, K.-H.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Yerushalmi, R.; Mina, L.A.; Martin, M. Talazoparib in patients with advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation. New England Journal of Medicine 2018, 379, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, M.; Im, S.-A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Domchek, S.M.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Li, W.; Tung, N.; Armstrong, A. Olaparib for metastatic breast cancer in patients with a germline BRCA mutation. New England Journal of Medicine 2017, 377, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, K.R.; Brown, M.; Cress, R.D.; Parise, C.A.; Caggiano, V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: a population-based study from the California cancer Registry. Cancer 2007, 109, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizides, S.; Constantinidou, A. Triple negative breast cancer: Immunogenicity, tumor microenvironment, and immunotherapy. Front Genet 2022, 13, 1095839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, C.; Mazouni, C.; Hess, K.R.; Andre, F.; Tordai, A.; Mejia, J.A.; Symmans, W.F.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Hennessy, B.; Green, M.; et al. Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy and Long-Term Survival in Patients With Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J Clin Oncol 2023, 41, 1809–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blows, F.M.; Driver, K.E.; Schmidt, M.K.; Broeks, A.; van Leeuwen, F.E.; Wesseling, J.; Cheang, M.C.; Gelmon, K.; Nielsen, T.O.; Blomqvist, C.; et al. Subtyping of breast cancer by immunohistochemistry to investigate a relationship between subtype and short and long term survival: a collaborative analysis of data for 10,159 cases from 12 studies. PLoS Med 2010, 7, e1000279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortazar, P.; Zhang, L.; Untch, M.; Mehta, K.; Costantino, J.P.; Wolmark, N.; Bonnefoi, H.; Cameron, D.; Gianni, L.; Valagussa, P.; et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: the CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet 2014, 384, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, M.D.; Tsimelzon, A.; Poage, G.M.; Covington, K.R.; Contreras, A.; Fuqua, S.A.; Savage, M.I.; Osborne, C.K.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Chang, J.C.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis identifies novel subtypes and targets of triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2015, 21, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.J.; Bian, X.W.; Yu, S.C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speers, C.; Tsimelzon, A.; Sexton, K.; Herrick, A.M.; Gutierrez, C.; Culhane, A.; Quackenbush, J.; Hilsenbeck, S.; Chang, J.; Brown, P. Identification of novel kinase targets for the treatment of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2009, 15, 6327–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Jovanovic, B.; Chen, X.; Estrada, M.V.; Johnson, K.N.; Shyr, Y.; Moses, H.L.; Sanders, M.E.; Pietenpol, J.A. Refinement of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes: Implications for Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Selection. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0157368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Adams, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Iwata, H.; Dieras, V.; Hegg, R.; Im, S.A.; Shaw Wright, G.; et al. Atezolizumab and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 2018, 379, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, S.; Krug, D.; Meattini, I.; Matuschek, C.; Bolke, E.; Francolini, G.; Baumann, R.; Figlia, V.; Pazos, M.; Tonetto, F.; et al. Preoperative radiotherapy: A paradigm shift in the treatment of breast cancer? A review of literature. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2019, 141, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Gao, H.F.; Yang, X.; Zhu, T.; Zheng, X.X.; Ji, F.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, C.Q.; Yang, M.; Li, J.Q.; et al. Neoadjuvant therapy in triple-negative breast cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Breast 2022, 66, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; O'Shaughnessy, J.; Untch, M.; Sikov, W.M.; Rugo, H.S.; McKee, M.D.; Huober, J.; Golshan, M.; von Minckwitz, G.; Maag, D.; et al. Addition of the PARP inhibitor veliparib plus carboplatin or carboplatin alone to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer (BrighTNess): a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2018, 19, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, G.A.; Rioja, P.; Morante, Z.; Ruiz, R.; Fuentes, H.; Castaneda, C.A.; Vidaurre, T.; Neciosup, S.; Gomez, H.L. Immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer: A literature review and new advances. World J Clin Oncol 2022, 13, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Z. Immunotherapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Combination Strategies to Improve Outcome. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Osgood, C.L.; Amatya, A.K.; Fiero, M.H.; Pierce, W.F.; Nair, A.; Herz, J.; Robertson, K.J.; Mixter, B.D.; Tang, S.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Pembrolizumab for Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Treatment of Patients with High-Risk Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2022, 28, 5249–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, E.; Savas, P.; Policheni, A.N.; Darcy, P.K.; Vaillant, F.; Mintoff, C.P.; Dushyanthen, S.; Mansour, M.; Pang, J.B.; Fox, S.B.; et al. Combined immune checkpoint blockade as a therapeutic strategy for BRCA1-mutated breast cancer. Sci Transl Med 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safonov, A.; Jiang, T.; Bianchini, G.; Gyorffy, B.; Karn, T.; Hatzis, C.; Pusztai, L. Immune Gene Expression Is Associated with Genomic Aberrations in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res 2017, 77, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; He, S. The Characteristics of Tumor Microenvironment in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Manag Res 2022, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciarka, A.; Piatek, M.; Peksa, R.; Kunc, M.; Senkus, E. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) in Breast Cancer: Prognostic and Predictive Significance across Molecular Subtypes. Biomedicines 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Qu, Q.; Chen, X.; Huang, O.; Wu, J.; Shen, K. The Prognostic Value of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0152500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denkert, C.; von Minckwitz, G.; Darb-Esfahani, S.; Lederer, B.; Heppner, B.I.; Weber, K.E.; Budczies, J.; Huober, J.; Klauschen, F.; Furlanetto, J.; et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: a pooled analysis of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol 2018, 19, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, R.E.; Richardson, E.K.; Toh, H.C. Revisiting the role of CD4(+) T cells in cancer immunotherapy-new insights into old paradigms. Cancer Gene Ther 2021, 28, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanmee, T.; Ontong, P.; Konno, K.; Itano, N. Tumor-associated macrophages as major players in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers (Basel) 2014, 6, 1670–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Guo, W.; Sun, L.; Lin, L. Targeting M2-like tumor-associated macrophages is a potential therapeutic approach to overcome antitumor drug resistance. NPJ Precis Oncol 2024, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, E.; Paul, B.T.; Koziol, J.A.; ElShamy, W.M. The Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in BRCA1-IRIS-Overexpressing TNBC Tumors Is Induced by Bidirectional Interaction with Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cancer Res 2020, 80, 1102–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascard, P.; Tlsty, T.D. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts: orchestrating the composition of malignancy. Genes Dev 2016, 30, 1002–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, K.; Le, A.; Weaver, V.M.; Werb, Z. Targeting the cancer-associated fibroblasts as a treatment in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 82889–82901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraj, S.; Schrum, A.G.; Cho, H.I.; Celis, E.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Mechanism of T cell tolerance induced by myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Immunol 2010, 184, 3106–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queen, M.M.; Ryan, R.E.; Holzer, R.G.; Keller-Peck, C.R.; Jorcyk, C.L. Breast cancer cells stimulate neutrophils to produce oncostatin M: potential implications for tumor progression. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 8896–8904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.W.; Kim, K.D.; Lee, H.K. The role of dendritic cells in tumor microenvironments and their uses as therapeutic targets. BMB Rep 2021, 54, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Dong, J.; He, X.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Cui, J.; Zhou, Z. Impaired function of dendritic cells within the tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1213629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domagala, J.; Lachota, M.; Klopotowska, M.; Graczyk-Jarzynka, A.; Domagala, A.; Zhylko, A.; Soroczynska, K.; Winiarska, M. The Tumor Microenvironment-A Metabolic Obstacle to NK Cells' Activity. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.I.; Gabrilovich, D.I. The biology of myeloid-derived suppressor cells: the blessing and the curse of morphological and functional heterogeneity. Eur J Immunol 2010, 40, 2969–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udumula, M.P.; Sakr, S.; Dar, S.; Alvero, A.B.; Ali-Fehmi, R.; Abdulfatah, E.; Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Tang, A.; Buekers, T.; et al. Ovarian cancer modulates the immunosuppressive function of CD11b(+)Gr1(+) myeloid cells via glutamine metabolism. Mol Metab 2021, 53, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Renz, B.W.; Ilmer, M.; Koch, D.; Yang, Y.; Werner, J.; Bazhin, A.V. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Solid Tumors. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochet, L.; Meulle, A.; Imbert, S.; Salles, B.; Valet, P.; Muller, C. Cancer-associated adipocytes promotes breast tumor radioresistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011, 411, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, R.; Yang, A.G.; Zheng, G. Diversity of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1121285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Dewanjee, S.; Li, Y.; Jha, N.K.; Chen, Z.-S.; Kumar, A.; Vishakha; Behl, T. ; Jha, S.K.; Tang, H. Advancements in clinical aspects of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in breast cancer. Molecular Cancer 2023, 22, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berraondo, P.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Ochoa, M.C.; Etxeberria, I.; Aznar, M.A.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Castañón, E.; Melero, I. Cytokines in clinical cancer immunotherapy. British Journal of Cancer 2019, 120, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Margolin, K. Cytokines in cancer immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel) 2011, 3, 3856–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrina, M.; Martin, J.; Basta, S. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor has come of age: From a vaccine adjuvant to antiviral immunotherapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2021, 59, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckers, J.; Anbergen, T.; Hokke, A.M.; de Dreu, A.; Schrijver, D.P.; de Bruin, K.; Toner, Y.C.; Beldman, T.J.; Spangler, J.B.; de Greef, T.F.A.; et al. Engineering cytokine therapeutics. Nature Reviews Bioengineering 2023, 1, 286–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.G.; Vrabel, M.R.; Mantooth, S.M.; Hopkins, J.J.; Wagner, E.S.; Gabaldon, T.A.; Zaharoff, D.A. Localized Interleukin-12 for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 575597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdou, Y.; Goudarzi, A.; Yu, J.X.; Upadhaya, S.; Vincent, B.; Carey, L.A. Immunotherapy in triple negative breast cancer: beyond checkpoint inhibitors. npj Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.M.; Rolig, A.S.; Charych, D.H.; Hoch, U.; Kasiewicz, M.J.; Rose, D.C.; McNamara, M.J.; Hilgart-Martiszus, I.F.; Redmond, W.L. NKTR-214 immunotherapy synergizes with radiotherapy to stimulate systemic CD8(+) T cell responses capable of curing multi-focal cancer. J Immunother Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavazzoni, A.; Digiacomo, G. Role of Cytokines and Other Soluble Factors in Tumor Development: Rationale for New Therapeutic Strategies. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, K.C.; Miljkovic, M.D.; Waldmann, T.A. Cytokines in the Treatment of Cancer. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2019, 39, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutcher, J.P.; Schwartzentruber, D.J.; Kaufman, H.L.; Agarwala, S.S.; Tarhini, A.A.; Lowder, J.N.; Atkins, M.B. High dose interleukin-2 (Aldesleukin) - expert consensus on best management practices-2014. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer 2014, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, D.B.; Pucilowska, J.; Sanchez, K.G.; Conrad, V.K.; Conlin, A.K.; Acheson, A.K.; Perlewitz, K.S.; Imatani, J.H.; Aliabadi-Wahle, S.; Moxon, N.; et al. A Phase Ib Study of Preoperative, Locoregional IRX-2 Cytokine Immunotherapy to Prime Immune Responses in Patients with Early-Stage Breast Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2020, 26, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, T.A. Cytokines in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesolowski, J.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A.; Pawlak, D. Modern Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmete, J.J.; Mukherji, S.K. Trastuzumab (herceptin). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2011, 32, 1373–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baez Navarro, X.; van den Ender, N.S.; Nguyen, A.; Sinke, R.; Westenend, P.; van Brakel, J.B.; Stobbe, C.; Westerga, J.; van Deurzen, C.H.M. HER2-low and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in triple negative breast cancer: are they mutually connected? European Journal of Cancer 2024, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Hurwitz, H.I.; Sandler, A.B.; Miles, D.; Coleman, R.L.; Deurloo, R.; Chinot, O.L. Bevacizumab (Avastin®) in cancer treatment: A review of 15 years of clinical experience and future outlook. Cancer Treatment Reviews 2020, 86, 102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasich, L.D.; Sukkari, S.R. The US FDAs withdrawal of the breast cancer indication for Avastin (bevacizumab). Saudi Pharm J 2012, 20, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Wang, P.; He, S.; Zhu, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J. Progress and Prospect of Immunotherapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 919072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.L.; Schwettmann, B.; McArthur, H.L.; Chan, I.S. Antibody-drug conjugates in breast cancer: overcoming resistance and boosting immune response. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panowski, S.; Bhakta, S.; Raab, H.; Polakis, P.; Junutula, J.R. Site-specific antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy. MAbs 2014, 6, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonderheide, R.H. CD40 Agonist Antibodies in Cancer Immunotherapy. Annu Rev Med 2020, 71, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, I.; Alkassis, S.; Fukui, J.; Alsawah, F.; Fedak, K.; Al Hallak, M.N.; Sukari, A.; Nagasaka, M. Spotlight on Trastuzumab Deruxtecan (DS-8201,T-DXd) for HER2 Mutation Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer (Auckl) 2021, 12, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, C.; Lee, J.S.; Cui, X.; Yuan, Y. Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Breast Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Jacot, W.; Yamashita, T.; Sohn, J.; Vidal, M.; Tokunaga, E.; Tsurutani, J.; Ueno, N.T.; Prat, A.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Low Advanced Breast Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 2022, 387, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, R.; Berghoff, A.S.; Furtner, J.; Marhold, M.; Bergen, E.S.; Roider-Schur, S.; Starzer, A.M.; Forstner, H.; Rottenmanner, B.; Dieckmann, K.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in HER2-positive breast cancer with brain metastases: a single-arm, phase 2 trial. Nature Medicine 2022, 28, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Shen, P.; Xue, R.; Zhang, M. Disitamab vedotin: a novel antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Drug Deliv 2022, 29, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, K.M.; Kalinsky, K. Sacituzumab govitecan: antibody-drug conjugate in triple-negative breast cancer and other solid tumors. Drugs Today (Barc) 2019, 55, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardia, A.; Rugo, H.S.; Tolaney, S.M.; Loirat, D.; Punie, K.; Oliveira, M.; Brufsky, A.; Kalinsky, K.; Cortés, J.; Shaughnessy, J.O.; et al. Final Results From the Randomized Phase III ASCENT Clinical Trial in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Association of Outcomes by Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 and Trophoblast Cell Surface Antigen 2 Expression. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2024, 42, 1738–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Cusmai, A.; Acquafredda, S.; Rinaldi, L.; Palmiotti, G. Ladiratuzumab vedotin for metastatic triple negative cancer: preliminary results, key challenges, and clinical potential. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2022, 31, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Pusztai, L.; Forero, A.; Mita, M.; Miller, K.; Weise, A.; Krop, I.; Burris, H., III; Kalinsky, K.; Tsai, M.; et al. Abstract PD3-14: Phase 1 study of the antibody-drug conjugate SGN-LIV1A in patients with heavily pretreated triple-negative metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Research 2018, 78, PD3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.; Han, H.S.; Montero, A.J.; Tkaczuk, K.H.; Assad, H.; Pusztai, L.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Wilks, S.T.; Specht, J.M.; Nanda, R.; et al. 259P Weekly ladiratuzumab vedotin monotherapy for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Annals of Oncology 2021, 32, S474–S475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Qiu, F.; Tong, Z.; Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Bai, R.; Zhou, Q.; Xing, X. Preliminary results from a first-in-human study of ESG401, a trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2 (TROP2) antibody drug conjugate (ADC), in patients with locally advanced/metastatic solid tumors. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2023, 41, 1100–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Qiu, F.; Tong, Z.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, A.; et al. ESG401, a trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2 (TROP2) antibody drug conjugate (ADC), for the treatment of first-line metastatic triple negative breast cancer (mTNBC). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2024, 42, e13132–e13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Pusztai, L.; Albain, K.; Ciruelos, E.M.; Im, S.A.; Hershman, D.; Kalinsky, K.; Isaacs, C.; Loirat, D.; Testa, L.; et al. TROPION-Breast03: a randomized phase III global trial of datopotamab deruxtecan ± durvalumab in patients with triple-negative breast cancer and residual invasive disease at surgical resection after neoadjuvant therapy. Ther Adv Med Oncol 2024, 16, 17588359241248336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardia, A.; Krop, I.E.; Kogawa, T.; Juric, D.; Tolcher, A.W.; Hamilton, E.P.; Mukohara, T.; Lisberg, A.; Shimizu, T.; Spira, A.I.; et al. Datopotamab Deruxtecan in Advanced or Metastatic HR+/HER2– and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Results From the Phase I TROPION-PanTumor01 Study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2024, 42, 2281–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, D.J.; Wolchok, J.D.; Rosenberg, L.M.; Girotra, M. Cancer immunotherapy - immune checkpoint blockade and associated endocrinopathies. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2017, 13, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, J.; Yi, J.; Bu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, P.; Gu, X. Correction: Advances in immunotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer. Molecular Cancer 2023, 22, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.S.; Gaule, P.; McGuire, J.; Patel, K.; Blenman, K.; Pusztai, L.; Rimm, D.L. PD-L1 Protein Expression on Both Tumor Cells and Macrophages are Associated with Response to Neoadjuvant Durvalumab with Chemotherapy in Triple-negative Breast Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2020, 26, 5456–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargadon, K.M.; Johnson, C.E.; Williams, C.J. Immune checkpoint blockade therapy for cancer: An overview of FDA-approved immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int Immunopharmacol 2018, 62, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, R.; Chow, L.Q.; Dees, E.C.; Berger, R.; Gupta, S.; Geva, R.; Pusztai, L.; Pathiraja, K.; Aktan, G.; Cheng, J.D.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Patients With Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Phase Ib KEYNOTE-012 Study. J Clin Oncol 2016, 34, 2460–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.; Loi, S.; Toppmeyer, D.; Cescon, D.W.; De Laurentiis, M.; Nanda, R.; Winer, E.P.; Mukai, H.; Tamura, K.; Armstrong, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab monotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-positive, metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: cohort B of the phase II KEYNOTE-086 study. Ann Oncol 2019, 30, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, S.; Gogia, A. Pembrolizumab monotherapy in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. The Lancet Oncology 2021, 22, e224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, S.; Song, H.; Xu, M.; Yao, S.; Jiang, Z. JS001, an anti-PD-1 mAb for advanced triple negative breast cancer patients after multi-line systemic therapy in a phase I trial. Ann Transl Med 2019, 7, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, P.; Cortes, J.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kümmel, S.; Bergh, J.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Hui, R.; Harbeck, N.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.; Cescon, D.W.; Rugo, H.S.; Nowecki, Z.; Im, S.A.; Yusof, M.M.; Gallardo, C.; Lipatov, O.; Barrios, C.H.; Holgado, E.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy for previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (KEYNOTE-355): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 clinical trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emens, L.A.; Cruz, C.; Eder, J.P.; Braiteh, F.; Chung, C.; Tolaney, S.M.; Kuter, I.; Nanda, R.; Cassier, P.A.; Delord, J.P.; et al. Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Biomarker Analyses of Atezolizumab Therapy for Patients With Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Phase 1 Study. JAMA Oncol 2019, 5, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirix, L.Y.; Takacs, I.; Jerusalem, G.; Nikolinakos, P.; Arkenau, H.T.; Forero-Torres, A.; Boccia, R.; Lippman, M.E.; Somer, R.; Smakal, M.; et al. Avelumab, an anti-PD-L1 antibody, in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer: a phase 1b JAVELIN Solid Tumor study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2018, 167, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, F.; Agostinetto, E.; Miggiano, C.; De Sanctis, R.; Zambelli, A.; Santoro, A. Hope and Hype around Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, A.; Gharibi, T.; Marofi, F.; Babaloo, Z.; Baradaran, B. CTLA-4: From mechanism to autoimmune therapy. Int Immunopharmacol 2020, 80, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Su, P.; Yang, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, F.; Yang, B. Identification of CTLA-4 associated with tumor microenvironment and competing interactions in triple negative breast cancer by co-expression network analysis. J Cancer 2020, 11, 6365–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewkangsadan, V.; Verma, C.; Eremin, J.M.; Cowley, G.; Ilyas, M.; Eremin, O. Tumour-draining axillary lymph nodes in patients with large and locally advanced breast cancers undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC): the crucial contribution of immune cells (effector, regulatory) and cytokines (Th1, Th2) to immune-mediated tumour cell death induced by NAC. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sharma, P.K.; Peter Goedegebuure, S.; Gillanders, W.E. Personalized cancer vaccines: Targeting the cancer mutanome. Vaccine 2017, 35, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, E.E.; Kodumudi, K.; Ramamoorthi, G.; Czerniecki, B.J. Vaccine Therapies for Breast Cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 2019, 28, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Ardavanis, A.; Litton, J.K.; Shumway, N.M.; Hale, D.F.; Murray, J.L.; Perez, S.A.; Ponniah, S.; Baxevanis, C.N.; Papamichail, M.; et al. Primary analysis of a prospective, randomized, single-blinded phase II trial evaluating the HER2 peptide GP2 vaccine in breast cancer patients to prevent recurrence. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66192–66201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Clifton, G.T.; Holmes, J.P.; Schneble, E.; van Echo, D.; Ponniah, S.; Peoples, G.E. Final report of the phase I/II clinical trial of the E75 (nelipepimut-S) vaccine with booster inoculations to prevent disease recurrence in high-risk breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol 2014, 25, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalli, K.R.; Block, M.S.; Kasi, P.M.; Erskine, C.L.; Hobday, T.J.; Dietz, A.; Padley, D.; Gustafson, M.P.; Shreeder, B.; Puglisi-Knutson, D.; et al. Folate Receptor Alpha Peptide Vaccine Generates Immunity in Breast and Ovarian Cancer Patients. Clin Cancer Res 2018, 24, 3014–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heery, C.R.; Ibrahim, N.K.; Arlen, P.M.; Mohebtash, M.; Murray, J.L.; Koenig, K.; Madan, R.A.; McMahon, S.; Marté, J.L.; Steinberg, S.M.; et al. Docetaxel Alone or in Combination With a Therapeutic Cancer Vaccine (PANVAC) in Patients With Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol 2015, 1, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebtash, M.; Tsang, K.Y.; Madan, R.A.; Huen, N.Y.; Poole, D.J.; Jochems, C.; Jones, J.; Ferrara, T.; Heery, C.R.; Arlen, P.M.; et al. A pilot study of MUC-1/CEA/TRICOM poxviral-based vaccine in patients with metastatic breast and ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2011, 17, 7164–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svane, I.M.; Pedersen, A.E.; Johansen, J.S.; Johnsen, H.E.; Nielsen, D.; Kamby, C.; Ottesen, S.; Balslev, E.; Gaarsdal, E.; Nikolajsen, K.; et al. Vaccination with p53 peptide-pulsed dendritic cells is associated with disease stabilization in patients with p53 expressing advanced breast cancer; monitoring of serum YKL-40 and IL-6 as response biomarkers. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2007, 56, 1485–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.J.; Ning, Y.L.; Han, Y.S.; Min, H.Y.; Ye, H.; Zhu, Y.L.; Qian, K.Q. Autologous dendritic cell vaccine for estrogen receptor (ER)/progestin receptor (PR) double-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2012, 61, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avigan, D.; Vasir, B.; Gong, J.; Borges, V.; Wu, Z.; Uhl, L.; Atkins, M.; Mier, J.; McDermott, D.; Smith, T.; et al. Fusion cell vaccination of patients with metastatic breast and renal cancer induces immunological and clinical responses. Clin Cancer Res 2004, 10, 4699–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonderheide, R.H.; Glennie, M.J. Agonistic CD40 antibodies and cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 2013, 19, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budd, G.T.; Johnson, J.M.; Rhoades, E.E.; Moore, H.C.F.; Kruse, M.L.; Roesch, E.E.; Abraham, J.; Elliott, B.; Lach, D.; Tuohy, V.K. Phase I trial of an alpha-lactalbumin vaccine in patients with moderate- to high-risk operable triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2022, 40, TPS1125–TPS1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disis, M.; Liu, Y.; Stanton, S.; Gwin, W.; Coveler, A.; Liao, J.; Childs, J.; Cecil, D. 546 A phase I dose escalation study of STEMVAC, a multi-antigen, multi-epitope Th1 selective plasmid-based vaccine, targeting stem cell associated proteins in patients with advanced breast cancer. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer 2022, 10, A571–A571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cao, Y.J. Engineered T Cell Therapy for Cancer in the Clinic. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Palmer, D.C.; Robeson, A.C.; Shou, P.; Bommiasamy, H.; Laurie, S.J.; Willis, C.; Dotti, G.; Vincent, B.G.; Restifo, N.P.; et al. STING agonist promotes CAR T cell trafficking and persistence in breast cancer. J Exp Med 2021, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Levine, B.L.; Zhang, P.J.; Davis, M.M.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Kulikovskaya, I.; Brennan, A.L.; Liu, X.; Lacey, S.F.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Intratumoral Injections of Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cells in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancer Immunol Res 2017, 5, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.R.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Xu, X.E.; Yu, K.D.; Jin, X.; Hu, X.; Zuo, W.J.; Hao, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, G.Y.; et al. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis identifies novel molecular subtypes and subtype-specific RNAs of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 2016, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosn, M.; Cheema, W.; Zhu, A.; Livschitz, J.; Maybody, M.; Boas, F.E.; Santos, E.; Kim, D.; Beattie, J.A.; Offin, M.; et al. Image-guided interventional radiological delivery of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells for pleural malignancies in a phase I/II clinical trial. Lung Cancer 2022, 165, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adusumilli, P.S.; Zauderer, M.G.; Rivière, I.; Solomon, S.B.; Rusch, V.W.; O'Cearbhaill, R.E.; Zhu, A.; Cheema, W.; Chintala, N.K.; Halton, E.; et al. A Phase I Trial of Regional Mesothelin-Targeted CAR T-cell Therapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Disease, in Combination with the Anti-PD-1 Agent Pembrolizumab. Cancer Discov 2021, 11, 2748–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kufe, D.W. MUC1-C oncoprotein as a target in breast cancer: activation of signaling pathways and therapeutic approaches. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamdad, C.C.; Yuan, Y.; Specht, J.M.; Stewart, A.K.; Smagghe, B.J.; Lin, S.C.-M.; Carter, M.G.; Synold, T.W.; Frankel, P.H.; Parekh, V.; et al. Phase I/II first-in-human CAR T–targeting MUC1 transmembrane cleavage product (MUC1*) in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2022, 40, TPS1130–TPS1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaglia, P.; Caldarola, B.; Bussone, R.; Potente, F.; Lauro, D.; Jayme, A.; Caldarola, L. Prognostic value of CEA and ferritin assay in breast cancer: a multivariate analysis. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 1988, 24, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phase Ia/Ib Trial of 2nd Generation Anti-CEA Designer T Cells in Metastatic Breast Cancer. 2008.
- Luen, S.J.; Savas, P.; Fox, S.B.; Salgado, R.; Loi, S. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and the emerging role of immunotherapy in breast cancer. Pathology 2017, 49, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuhara, H.; Ino, Y.; Todo, T. Oncolytic virus therapy: A new era of cancer treatment at dawn. Cancer Sci 2016, 107, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoidingjam, S.; Sriramulu, S.; Freytag, S.; Brown, S.L.; Kim, J.H.; Chetty, I.J.; Siddiqui, F.; Movsas, B.; Nyati, S. Oncolytic virus-based suicide gene therapy for cancer treatment: a perspective of the clinical trials conducted at Henry Ford Health. Transl Med Commun 2023, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Huang, J.; Tong, A.; Yang, H. Oncolytic Viruses for Cancer Therapy: Barriers and Recent Advances. Mol Ther Oncolytics 2019, 15, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, H.L.; Kohlhapp, F.J.; Zloza, A. Oncolytic viruses: a new class of immunotherapy drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2015, 14, 642–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, H.L.; Shalhout, S.Z.; Iodice, G. Talimogene Laherparepvec: Moving From First-In-Class to Best-In-Class. Front Mol Biosci 2022, 9, 834841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, M.; Marx, A.N.; Liu, D.D.; Shen, Y.; Gao, H.; Reuben, J.M.; Whitman, G.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Ross, M.I.; Litton, J.K.; et al. A phase II study of talimogene laherparepvec for patients with inoperable locoregional recurrence of breast cancer. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 22242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokisalmi, P.; Pesonen, S.; Escutenaire, S.; Särkioja, M.; Raki, M.; Cerullo, V.; Laasonen, L.; Alemany, R.; Rojas, J.; Cascallo, M.; et al. Oncolytic adenovirus ICOVIR-7 in patients with advanced and refractory solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2010, 16, 3035–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemminki, O.; Parviainen, S.; Juhila, J.; Turkki, R.; Linder, N.; Lundin, J.; Kankainen, M.; Ristimäki, A.; Koski, A.; Liikanen, I.; et al. Immunological data from cancer patients treated with Ad5/3-E2F-Δ24-GMCSF suggests utility for tumor immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4467–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, M.L.; Idris, O.A.; Essani, K. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Basic Biology and Immuno-Oncolytic Viruses. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, U.M.; Beil, J. Oncolytic viruses: challenges and considerations in an evolving clinical landscape. Future Oncology 2022, 18, 2713–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Peng, K.-W.; Federspiel, M.; Russell, S.; Brunton, B.; Zhou, Y.; Packiriswamy, N.; Hubbard, J.; Loprinzi, C.; Peethambaram, P.; et al. Abstract P6-21-03: Phase I trial of intratumoral (IT) administration of a NIS-expressing derivative manufactured from a genetically engineered strain of measles virus (MV). Cancer Research 2019, 79, P6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanneman, M.; Dranoff, G. Combining immunotherapy and targeted therapies in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer 2012, 12, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, K.P.; Wolfson, B.; Hodge, J.W. From Immunogenic Cell Death to Immunogenic Modulation: Select Chemotherapy Regimens Induce a Spectrum of Immune-Enhancing Activities in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 728018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljković, M.; Damjanović, A. Mechanisms of Chemotherapy Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer-How We Can Rise to the Challenge. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayat Mokhtari, R.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungles, K.M.; Holcomb, E.A.; Pearson, A.N.; Jungles, K.R.; Bishop, C.R.; Pierce, L.J.; Green, M.D.; Speers, C.W. Updates in combined approaches of radiotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of breast cancer. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 1022542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obidiro, O.; Battogtokh, G.; Akala, E.O. Triple Negative Breast Cancer Treatment Options and Limitations: Future Outlook. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragupathi, A.; Singh, M.; Perez, A.M.; Zhang, D. Targeting the BRCA1/2 deficient cancer with PARP inhibitors: Clinical outcomes and mechanistic insights. Front Cell Dev Biol 2023, 11, 1133472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchiesi, G.; Roberto, M.; Verrico, M.; Vici, P.; Tomao, S.; Tomao, F. Emerging Role of PARP Inhibitors in Metastatic Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Current Scenario and Future Perspectives. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 769280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, P.; Perrone, M.; Guarini, C.; Santoro, A.N.; Laface, C.; Carrozzo, D.; Oliva, G.R.; Fedele, P. Early-stage triple negative breast cancer: the therapeutic role of immunotherapy and the prognostic value of pathological complete response. Explor Target Antitumor Ther 2024, 5, 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, M.; Im, S.-A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Domchek, S.M.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Li, W.; Tung, N.; Armstrong, A.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Breast Cancer in Patients with a Germline <i>BRCA</i> Mutation. New England Journal of Medicine 2017, 377, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litton, J.K.; Rugo, H.S.; Ettl, J.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Gonçalves, A.; Lee, K.H.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Yerushalmi, R.; Mina, L.A.; Martin, M.; et al. Talazoparib in Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer and a Germline BRCA Mutation. N Engl J Med 2018, 379, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutt, A.N.J.; Garber, J.E.; Kaufman, B.; Viale, G.; Fumagalli, D.; Rastogi, P.; Gelber, R.D.; Azambuja, E.d.; Fielding, A.; Balmaña, J.; et al. Adjuvant Olaparib for Patients with <i>BRCA1</i>- or <i>BRCA2</i>-Mutated Breast Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 2021, 384, 2394–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.; Purington, N.; Liu, M.; Han, S.; Sledge, G.; Schapira, L.; Kurian, A.W. Incident comorbidities after tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitor therapy in a racially and ethnically diverse cohort of women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2022, 196, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miglietta, F.; Cinquini, M.; Dieci, M.V.; Cortesi, L.; Criscitiello, C.; Montemurro, F.; Del Mastro, L.; Zambelli, A.; Biganzoli, L.; Levaggi, A.; et al. PARP-inhibitors for BRCA1/2-related advanced HER2-negative breast cancer: A meta-analysis and GRADE recommendations by the Italian Association of Medical Oncology. Breast 2022, 66, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayak, S.; Tolaney, S.M.; Schwartzberg, L.S.; Mita, M.M.; McCann, G.A.-L.; Tan, A.R.; Hendrickson, A.E.W.; Forero-Torres, A.; Anders, C.K.; Wulf, G.M.; et al. TOPACIO/Keynote-162: Niraparib + pembrolizumab in patients (pts) with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), a phase 2 trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2018, 36, 1011–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayak, S.; Tolaney, S.M.; Schwartzberg, L.; Mita, M.; McCann, G.; Tan, A.R.; Wahner-Hendrickson, A.E.; Forero, A.; Anders, C.; Wulf, G.M.; et al. Open-label Clinical Trial of Niraparib Combined With Pembrolizumab for Treatment of Advanced or Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncology 2019, 5, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domchek, S.M.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Im, S.A.; Park, Y.H.; Delord, J.P.; Italiano, A.; Alexandre, J.; You, B.; Bastian, S.; Krebs, M.G.; et al. Olaparib and durvalumab in patients with germline BRCA-mutated metastatic breast cancer (MEDIOLA): an open-label, multicentre, phase 1/2, basket study. Lancet Oncol 2020, 21, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, T.A.; Bardia, A.; Dvorkin, M.; Galsky, M.D.; Beck, J.T.; Wise, D.R.; Karyakin, O.; Rubovszky, G.; Kislov, N.; Rohrberg, K.; et al. Avelumab Plus Talazoparib in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors: The JAVELIN PARP Medley Nonrandomized Controlled Trial. JAMA Oncol 2023, 9, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Buqué, A.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunological Effects of Conventional Chemotherapy and Targeted Anticancer Agents. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 690–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitvogel, L.; Tesniere, A.; Kroemer, G. Cancer despite immunosurveillance: immunoselection and immunosubversion. Nat Rev Immunol 2006, 6, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.; Rugo, H.S.; Cescon, D.W.; Im, S.-A.; Yusof, M.M.; Gallardo, C.; Lipatov, O.; Barrios, C.H.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Iwata, H.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 2022, 387, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolaney, S.M.; Kalinsky, K.; Kaklamani, V.G.; D'Adamo, D.R.; Aktan, G.; Tsai, M.L.; O'Regan, R.M.; Kaufman, P.A.; Wilks, S.T.; Andreopoulou, E.; et al. Eribulin Plus Pembrolizumab in Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (ENHANCE 1): A Phase Ib/II Study. Clin Cancer Res 2021, 27, 3061–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.; Gatti-Mays, M.E.; Kalinsky, K.; Korde, L.A.; Sharon, E.; Amiri-Kordestani, L.; Bear, H.; McArthur, H.L.; Frank, E.; Perlmutter, J.; et al. Current Landscape of Immunotherapy in Breast Cancer: A Review. JAMA Oncol 2019, 5, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Rugo, H.S.; Adams, S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Iwata, H.; Diéras, V.; Henschel, V.; Molinero, L.; Chui, S.Y.; et al. Atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel as first-line treatment for unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (IMpassion130): updated efficacy results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2020, 21, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emens, L.A.; Adams, S.; Barrios, C.H.; Diéras, V.; Iwata, H.; Loi, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Winer, E.P.; Patel, S.; et al. First-line atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel for unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: IMpassion130 final overall survival analysis. Ann Oncol 2021, 32, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Turner, N.C.; Barrios, C.H.; Isakoff, S.J.; Kim, S.B.; Sablin, M.P.; Saji, S.; Savas, P.; Vidal, G.A.; Oliveira, M.; et al. First-Line Ipatasertib, Atezolizumab, and Taxane Triplet for Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical and Biomarker Results. Clin Cancer Res 2024, 30, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, D.; Gligorov, J.; André, F.; Cameron, D.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.; Xu, B.; Wardley, A.; Kaen, D.; Andrade, L.; et al. Primary results from IMpassion131, a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised phase III trial of first-line paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab for unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol 2021, 32, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Mo, H.; Hu, X.; Gao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, B.; Niu, L.; Sun, X.; Yu, X.; et al. Single-cell analyses reveal key immune cell subsets associated with response to PD-L1 blockade in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1578–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorwerk, L.; Slagter, M.; Horlings, H.M.; Sikorska, K.; van de Vijver, K.K.; de Maaker, M.; Nederlof, I.; Kluin, R.J.C.; Warren, S.; Ong, S.; et al. Immune induction strategies in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer to enhance the sensitivity to PD-1 blockade: the TONIC trial. Nature Medicine 2019, 25, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, R.; Liu, M.C.; Yau, C.; Shatsky, R.; Pusztai, L.; Wallace, A.; Chien, A.J.; Forero-Torres, A.; Ellis, E.; Han, H.; et al. Effect of Pembrolizumab Plus Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Pathologic Complete Response in Women With Early-Stage Breast Cancer: An Analysis of the Ongoing Phase 2 Adaptively Randomized I-SPY2 Trial. JAMA Oncol 2020, 6, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Cortes, J.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kümmel, S.; Bergh, J.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Hui, R.; Harbeck, N.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 382, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.M.; Rushton, T.; Nsiah, F.; Stone, R.L.; Beavis, A.L.; Gaillard, S.L.; Dobi, A.; Fader, A.N. Long-term disease-free survival with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab in a patient with unmeasurable, advanced stage dedifferentiated endometrial carcinoma. Gynecologic Oncology Reports 2024, 53, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; Untch, M.; Burchardi, N.; Huober, J.; Sinn, B.V.; Blohmer, J.U.; Grischke, E.M.; Furlanetto, J.; Tesch, H.; Hanusch, C.; et al. A randomised phase II study investigating durvalumab in addition to an anthracycline taxane-based neoadjuvant therapy in early triple-negative breast cancer: clinical results and biomarker analysis of GeparNuevo study. Ann Oncol 2019, 30, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianni, L.; Huang, C.S.; Egle, D.; Bermejo, B.; Zamagni, C.; Thill, M.; Anton, A.; Zambelli, S.; Bianchini, G.; Russo, S.; et al. Pathologic complete response (pCR) to neoadjuvant treatment with or without atezolizumab in triple-negative, early high-risk and locally advanced breast cancer: NeoTRIP Michelangelo randomized study. Ann Oncol 2022, 33, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Zhang, H.; Barrios, C.H.; Saji, S.; Jung, K.H.; Hegg, R.; Koehler, A.; Sohn, J.; Iwata, H.; Telli, M.L.; et al. Neoadjuvant atezolizumab in combination with sequential nab-paclitaxel and anthracycline-based chemotherapy versus placebo and chemotherapy in patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (IMpassion031): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. The Lancet 2020, 396, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Adams, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Iwata, H.; Diéras, V.; Hegg, R.; Im, S.-A.; Wright, G.S.; et al. Atezolizumab and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 2018, 379, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, D.; Gligorov, J.; André, F.; Cameron, D.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.; Xu, B.; Wardley, A.; Kaen, D.; Andrade, L. Primary results from IMpassion131, a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised phase III trial of first-line paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab for unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Annals of Oncology 2021, 32, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radiotherapy to regional nodes in early breast cancer: an individual patient data meta-analysis of 14 324 women in 16 trials. Lancet 2023, 402, 1991–2003. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGale, P.; Taylor, C.; Correa, C.; Cutter, D.; Duane, F.; Ewertz, M.; Gray, R.; Mannu, G.; Peto, R.; Whelan, T.; et al. Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet 2014, 383, 2127–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpentier, M.; Spada, S.; Van Nest, S.J.; Demaria, S. Radiation therapy-induced remodeling of the tumor immune microenvironment. Seminars in Cancer Biology 2022, 86, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.Y.; Wright, J.L.; Blitzblau, R.C.; Mutter, R.W.; Duda, D.G.; Norton, L.; Bardia, A.; Spring, L.; Isakoff, S.J.; Chen, J.H.; et al. Optimizing Radiation Therapy to Boost Systemic Immune Responses in Breast Cancer: A Critical Review for Breast Radiation Oncologists. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2020, 108, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArthur, H.L.; Barker, C.A.; Gucalp, A.; Lebron-Zapata, L.; Wen, Y.H.; Phung, A.; Rodine, M.; Arnold, B.; Zhang, Z.; Ho, A. A single-arm, phase II study assessing the efficacy of pembrolizumab (pembro) plus radiotherapy (RT) in metastatic triple negative breast cancer (mTNBC). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2018, 36, 14–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.; Savas, P.; Siva, S.; White, M.; Neeson, M.W.; White, S.; Marx, G.; Cheuk, R.; Grogan, M.; Farrell, M.; et al. Abstract PD10-02: A randomised phase II trial of single fraction or multi-fraction SABR (stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy) with atezolizumab in patients with advanced triple negative breast cancer (AZTEC trial). Cancer Research 2022, 82, PD10–02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sau, S.; Petrovici, A.; Alsaab, H.O.; Bhise, K.; Iyer, A.K. PDL-1 Antibody Drug Conjugate for Selective Chemo-Guided Immune Modulation of Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Nonneville, A.; Finetti, P.; Boudin, L.; Denicolaï, E.; Birnbaum, D.; Mamessier, E.; Bertucci, F. Prognostic and Predictive Value of LIV1 Expression in Early Breast Cancer and by Molecular Subtype. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisel, J.L.; Pluard, T.J.; Vinayak, S.; Stringer-Reasor, E.M.; Brown-Glaberman, U.; Dillon, P.M.; Basho, R.K.; Varadarajan, R.; O'Shaughnessy, J.; Han, H.S.; et al. Phase 1b/2 study of ladiratuzumab vedotin (LV) in combination with pembrolizumab for first-line treatment of triple-negative breast cancer (SGNLVA-002, trial in progress). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2022, 40, TPS1127–TPS1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Chen, X. Vascular endothelial growth factor as an anti-angiogenic target for cancer therapy. Curr Drug Targets 2010, 11, 1000–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Shao, B.; Tong, Z.; Ouyang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, S.; Li, H. A phase Ib study of camrelizumab in combination with apatinib and fuzuloparib in patients with recurrent or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Med 2022, 20, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Fan, L.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhao, S.; Song, X.Q.; Hu, X.; Yang, W.T.; Chai, W.J.; et al. Combined angiogenesis and PD-1 inhibition for immunomodulatory TNBC: concept exploration and biomarker analysis in the FUTURE-C-Plus trial. Mol Cancer 2022, 21, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Mittra, A.; Naqash, A.R.; Takebe, N. A review of mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors and potential strategies for therapy. Cancer Drug Resist 2020, 3, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santa-Maria, C.A.; Kato, T.; Park, J.H.; Kiyotani, K.; Rademaker, A.; Shah, A.N.; Gross, L.; Blanco, L.Z.; Jain, S.; Flaum, L.; et al. A pilot study of durvalumab and tremelimumab and immunogenomic dynamics in metastatic breast cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18985–18996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buisseret, L.; Loirat, D.; Aftimos, P.; Maurer, C.; Punie, K.; Debien, V.; Kristanto, P.; Eiger, D.; Goncalves, A.; Ghiringhelli, F.; et al. Paclitaxel plus carboplatin and durvalumab with or without oleclumab for women with previously untreated locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: the randomized SYNERGY phase I/II trial. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, J.R.; Raman, S.S.; Chan, A.; Kalinsky, K.; Baurain, J.F.; Jimenez, M.M.; Garcia, M.M.; Berger, M.D.; Lauer, U.M.; Khattak, A.; et al. Phase Ib study of talimogene laherparepvec in combination with atezolizumab in patients with triple negative breast cancer and colorectal cancer with liver metastases. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 100884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kistler, M.; Nangia, C.; To, C.; Sender, L.; Lee, J.; Jones, F.; Jafari, O.; Seery, T.; Rabizadeh, S.; Niazi, K.; et al. Abstract P5-04-02: Safety and efficacy from first-in-human immunotherapy combining NK and T cell activation with off-the-shelf high-affinity CD16 NK cell line (haNK) in patients with 2nd-line or greater metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Cancer Research 2020, 80, P5–04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriramulu, S.; Thoidingjam, S.; Brown, S.L.; Siddiqui, F.; Movsas, B.; Nyati, S. Molecular targets that sensitize cancer to radiation killing: From the bench to the bedside. Biomed Pharmacother 2023, 158, 114126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Y.; Wang, M.; Xu, Q.; Sun, B.; Jia, Y. Small molecule agents for triple negative breast cancer: Current status and future prospects. Translational Oncology 2024, 41, 101893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriramulu, S.; Thoidingjam, S.; Chen, W.M.; Hassan, O.; Siddiqui, F.; Brown, S.L.; Movsas, B.; Green, M.D.; Davis, A.J.; Speers, C.; et al. BUB1 regulates non-homologous end joining pathway to mediate radioresistance in triple-negative breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2024, 43, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Holloway, M.P.; Nguyen, K.; McCauley, D.; Landesman, Y.; Kauffman, M.G.; Shacham, S.; Altura, R.A. XPO1 (CRM1) inhibition represses STAT3 activation to drive a survivin-dependent oncogenic switch in triple-negative breast cancer. Molecular cancer therapeutics 2014, 13, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicirò, Y.; Ragusa, D.; Sala, A. Expression of the checkpoint kinase BUB1 is a predictor of response to cancer therapies. Scientific Reports 2024, 14, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriramulu, S.; Thoidingjam, S.; Siddiqui, F.; Brown, S.L.; Movsas, B.; Walker, E.; Nyati, S. BUB1 Inhibition Sensitizes TNBC Cell Lines to Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Luo, X.; Deng, X.; Tang, Y.; Tian, W.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, J.; Zou, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xie, X. Advances in artificial intelligence to predict cancer immunotherapy efficacy. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 1076883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boniolo, F.; Dorigatti, E.; Ohnmacht, A.J.; Saur, D.; Schubert, B.; Menden, M.P. Artificial intelligence in early drug discovery enabling precision medicine. Expert Opin Drug Discov 2021, 16, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrone, O.; La Porta, C.A.M. Artificial Intelligence for Precision Oncology of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Learning from Melanoma. Cancers (Basel) 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Ma, J. Artificial intelligence: opportunities and challenges in the clinical applications of triple-negative breast cancer. Br J Cancer 2023, 128, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, R.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Wu, W.; Li, H.; Luo, P.; Wang, Z.; et al. Artificial intelligence learning landscape of triple-negative breast cancer uncovers new opportunities for enhancing outcomes and immunotherapy responses. Journal of Big Data 2023, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, R.; Irfan, M.; Gondal, T.M.; Khan, S.; Wu, J.; Hadi, M.U.; Heymach, J.; Le, X.; Yan, H.; Alam, T. AI in drug discovery and its clinical relevance. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





