Submitted:
12 August 2024
Posted:
13 August 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.1. Selection of Dairy Cow Samples for Genotyping
2.2. ELISA Test for Identification of β-Casein A1 Dairy Products
2.3. LFIA Test for Identification of A2A2 Genotype
2.4. LFIA Test for Purity Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
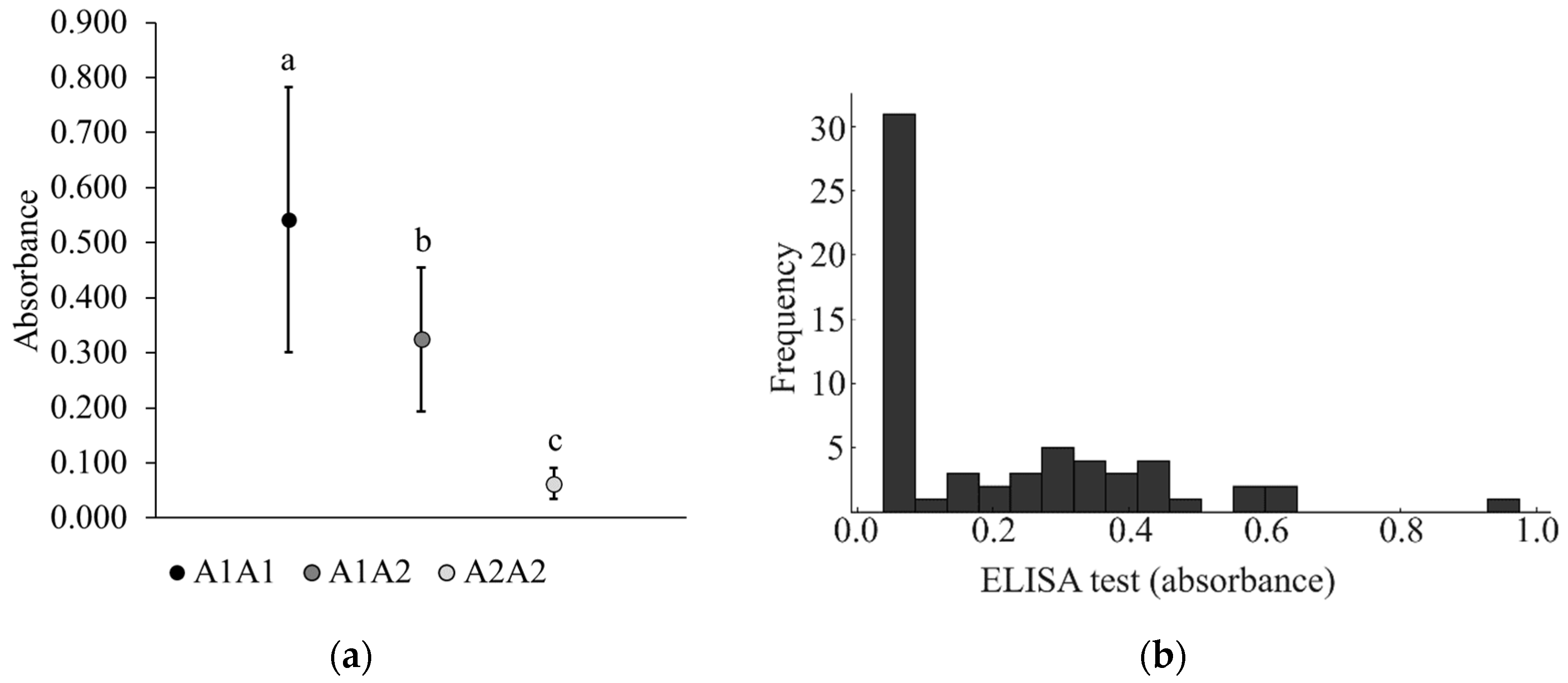
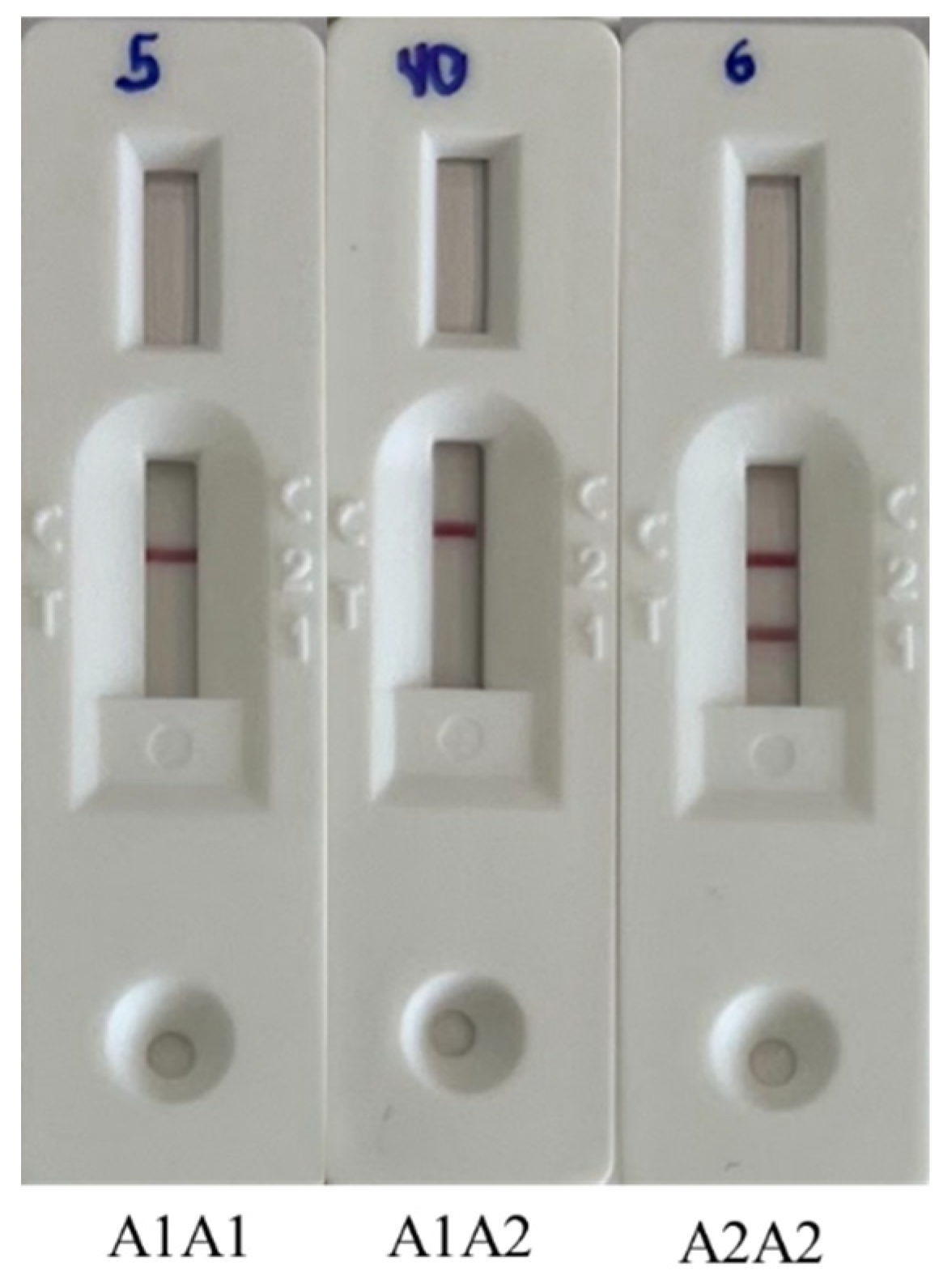
3.1. Identification of β-Casein Phenotypes by ELISA and LFIA Tests
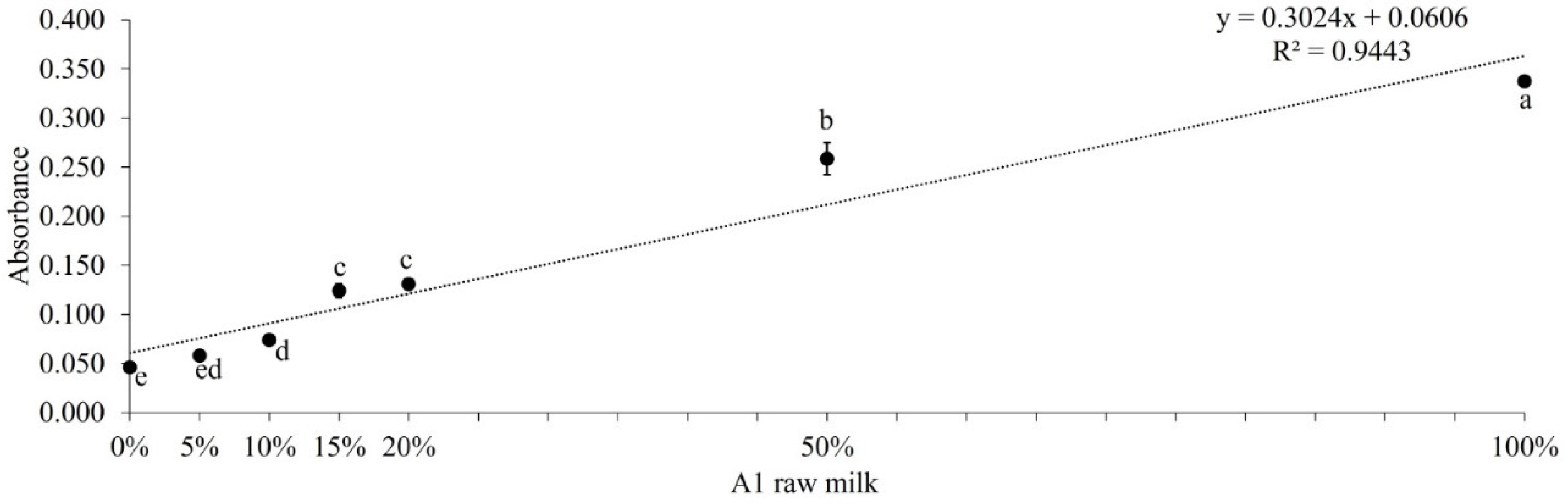
3.2. ELISA and LFIA Tests on Raw Milk Samples to Assess Purity
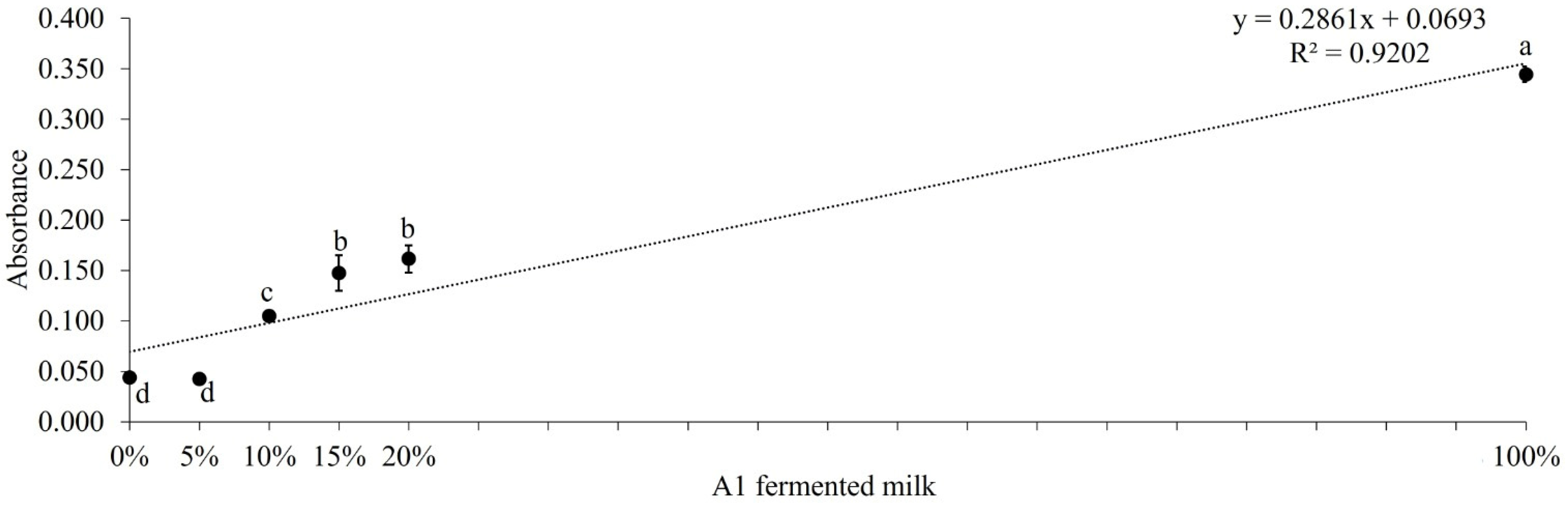
3.3. ELISA and LFIA Tests on Fermented Milk Samples to Assess Purity
4. Discussion
4.1. Importance of Non Invasive ELISA Test and LFIA Test in Detection of A1 β-Casein and Expansion to Other Dairy Products
4.2. Advantages, Limitations, Considerations for Practical Application and Cost-Effectiveness of the ELISA and LFIA Methodologies
4.3. Assessment of Sensitivity and Specificity of ELISA and LFIA Test
5. Conclusions
Data Availability Statement
References
- Kaskous, S. A1- and A2-Milk and Their Effect on Human Health. Journal of Food Engineering and Technology 2020, 9, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardicli, S.; Aldevir, O.; Aksu, E.; Gumen, A. The Variation in the Beta-Casein Genotypes and Its Effect on Milk Yield and Genomic Values in Holstein-Friesian Cows. Anim Biotechnol 2023, 34, 4116–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Park, Y.S.; Yoon, S.S. A2 Milk Consumption and Its Health Benefits: An Update. Food Sci Biotechnol 2024, 33, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, A.; Kumar, H.; Prudencio, E.S.; de Avila, L.B.; Orellana-Palma, P.; Dosoky, N.S.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuča, K.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Verma, R.; et al. An Approach on Detection, Quantification, Technological Properties, and Trends Market of A2 Cow Milk. Food Research International 2023, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Spencer, G.W.K.; Ong, L.; Gras, S.L. Beta Casein Proteins – A Comparison between Caprine and Bovine Milk. Trends Food Sci Technol 2022, 121, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, B.A.P.; Echeverri, L.M.S.; Magalhães, M. de L.B.; Silva, G.F. da Generation and Characterization of Avian IgY Antibodies for Detecting Beta-Casein A1 in Bovine Milk. Anal Biochem 2023, 678, 115283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jann, O.; Ceriotti, G.; Caroli, A.; Erhardt, G. A New Variant in Exon VII of Bovine β-Casein Gene (CSN2) and Its Distribution among European Cattle Breeds. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics 2002, 119, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; De, S.; Dewangan, R.; Tamboli, R.; Gupta, R. Potential Status of A1 and A2 Variants of Bovine Beta-Casein Gene in Milk Samples of Indian Cattle Breeds. Anim Biotechnol 2023, 34, 4878–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borş, A.; Borş, S.I.; Floriștean, V.C. Health-Related Outcomes and Molecular Methods for the Characterization of A1 and A2 Cow’s Milk: Review and Update. Vet Sci 2024, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Fan, Y.; Su, J.; Wang, H.; Luo, X.; Zhang, S. Rapid Identification of A1 and A2 Milk Based on the Combination of Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Food Control 2022, 134, 108659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, N.S.; Albanell, E.; De Marchi, M.; Manuelian, C.L. An Attempt to Identify Milk Protein Fraction Genotypes Using Unsupervised and Supervised Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Methods. Ital J Anim Sci 2024, 23, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giribaldi, M.; Lamberti, C.; Cirrincione, S.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Cavallarin, L. A2 Milk and BCM-7 Peptide as Emerging Parameters of Milk Quality. Front Nutr 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arens, S.C.; Sharpe, K.T.; Schutz, M.M.; Hardie, L.C.; Dechow, C.C.; Heins, B.J. Relationships of Beta-Casein Genetics with Production, Fertility, and Survival of Purebred Organic Holstein Dairy Cows Production, Fertility, and Survival of Purebred Organic Holstein Dairy Cows. JDS Communications 2023, 4, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolat, E.; Eker, F.; Yılmaz, S.; Karav, S.; Oz, E.; Brennan, C.; Proestos, C.; Zeng, M.; Oz, F. BCM-7: Opioid-like Peptide with Potential Role in Disease Mechanisms. Molecules 2024, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, M.; Gourkhede, D.P.; Hb, V.; Shinde, B.; Mishra, B.P.; Wankhade, P.R.; Belore, B.; Lalthanmawii, J.; Koneti, P.B. Delving into the A1/A2 Milk Hypothesis: A Analysis of Milk Proteins and Their on Human Health. International Journal of Veterinary Sciences and Animal Husbandry, -9.
- Morais, A.T. do B.; Morais, S.T.B.; Feitor, J.F.; Santos, W.G.; Gomes da Silva Catunda, L.; Walkling-Ribeiro, M.; Ahrne, L.; Cardoso, D.R. Impact of Physicochemical Modifications in Casein Promoted by UV-C on the Peptide Profile of Gastric Digestion and the Transepithelial Transport of Peptides. J Agric Food Chem 2023, 71, 7495–7507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hiago Bellaver, E.; Eliza Redin, E.; Militão da Costa, I.; Schittler Moroni, L.; Pinto Kempka, A. Food Peptidomic Analysis of Bovine Milk Fermented by Lacticaseibacillus Casei LBC 237: In Silico Prediction of Bioactive Peptides and Anticancer Potential. Food Research International 2024, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, H.K.; Lenz, K.; Halbauer, E.M. “A2 Milk” Authentication Using Isoelectric Focusing and Different PCR Techniques. Food Research International 2021, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brantl, V.; Teschemacher, H.; Bl, J.; Henschen, A.; Lottspeich, F. Opioid Activities of β-Casomorphins. Life Sci 1981, 28, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summer, A.; Frangia, F. Di; Marsan, P.A.; Noni, I. De; Malacarne, M.; Summer, A.; Frangia, F. Di; Marsan, P.A.; Noni, I. De Occurrence, Biological Properties and Potential Effects on Human Health of β -Casomorphin 7: Current Knowledge and Concerns. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2020, 60, 3705–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.W.; Haenlein, G.F.W. A2 Bovine Milk and Caprine Milk as a Means of Remedy for Milk Protein Allergy. Dairy 2021, Vol. 2, Pages 191-201 2021, 2, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, Z.; Gholami, M.; Rahimi, Z.; Yari, K. Evaluation of Beta-Casein Locus for Detection of A1 and A2 Alleles Frequency Using Allele Specific PCR in Native Cattle of Kermanshah, Iran. Biharean Biol 2015, 9, 85–87. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, H.; Ruusunen, A.; Berk, M.; Loughman, A.; Rivera, L.; Pasco, J.A.; Jacka, F.N.; Aslam, H.; Ruusunen, A.; Berk, M.; et al. Unravelled Facets of Milk Derived Opioid Peptides: A Focus on Gut Physiology, Fractures and Obesity. Int J Food Sci Nutr 2020, 71, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Wu, J. Impact of Food-Derived Bioactive Peptides on Gut Function and Health. Food Research International 2021, 147, 110485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-tomé, S.; Martínez-maqueda, D.; Tabernero, M.; Largo, C.; Recio, I.; Miralles, B. Effect of the Long-Term Intake of a Casein Hydrolysate on Mucin Secretion and Gene Expression in the Rat Intestine. 2017, 33, 176–180.
- Barnett, M.P.G.; Mcnabb, W.C.; Roy, N.C.; Woodford, K.B.; Clarke, A.J. Dietary A1 β-Casein Affects Gastrointestinal Transit Time, Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Activity, and Inflammatory Status Relative to A2 β-Casein in Wistar Rats. Int J Food Sci Nutr 2014, 65, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tailford, K.A.; Berry, C.L.; Thomas, A.C.; Campbell, J.H. A Casein Variant in Cow’s Milk Is Atherogenic. Atherosclerosis 2003, 170, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.B.; Harris, D.P.; Hill, J.P.; Bibby, N.J.; Wasmuth, H.E. Type I (Insulin-Dependent) Diabetes Mellitus and Cow Milk: Casein Variant Consumption. Diabetologia 1999, 42, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, O.; Kost, N.; Andreeva, O.; Korneeva, E.; Meshavkin, V.; Tarakanova, Y.; Dadayan, A.; Zolotarev, Y.; Grachev, S.; Mikheeva, I.; et al. Peptides Autistic Children Display Elevated Urine Levels of Bovine Casomorphin-7 Immunoreactivity. Peptides 2014, 56, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, B.A.; Haile-Mariam, M.; MacLeod, I.M.; Xiang, R.; Pryce, J.E. Evaluating the Potential Impact of Selection for the A2 Milk Allele on Inbreeding and Performance in Australian Holstein Cattle. Frontiers in Animal Science 2023, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Kumar, A.; Nimmanapalli, R.; Malik, M.; Aggarwal, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, M. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometer-Based Identification of β-Casein Variant (A2/A1) in the Milk of Indian Holstein Friesian Crossed Cows. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2024, 128, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigolo, V.; Franzoi, M.; Cendron, F.; Salvadore, G.; Penasa, M.; Cassandro, M.; De Marchi, M. Characterization of the Genetic Polymorphism Linked to the β-Casein A1/A2 Alleles Using Different Molecular and Biochemical Methods. J Dairy Sci 2022, 105, 8946–8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.; Kumar, A.; Rai, D.C.; Aggarwal, A.; Malik, M. Identification of β-Casein Phenotypes (A1/A2) in the Milk of the Indian Jersey Crossbreed Bovine Using the High-Resolution Accurate Mass Spectrometer. Int J Food Sci Technol 2023, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Ö.; Boztepe, S. Assessment of A1 and A2 Variants in the CNS2 Gene of Some Cattle Breeds by Using ACRS-PCR Method. Anim Biotechnol 2023, 34, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R.V.; Chauhan, A.; Kumar, A.; Sonwane, A.; K, I.; Singh, R. Investigation of Genetic Polymorphism at β-Casein A1/A2 Loci and Association Analysis with Production & Reproduction Traits in Vrindavani Crossbred Cows. Anim Biotechnol 2022, 33, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sebastiani, C.; Arcangeli, C.; Ciullo, M.; Torricelli, M.; Cinti, G.; Fisichella, S.; Biagetti, M. Frequencies Evaluation of β-Casein Gene Polymorphisms in Dairy Cows Reared in Central Italy. Animals 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz; Suhail, S. M.; Ahmad, I.; Zeb, M.T.; Khan, R.; Ijaz, A.; Ahmad, I.; Riaz, M.H.; Ali, F.; Khan, K.; et al. Detection of A2A2 Genotype of Beta Casein Protein (CSN2) Gene in Local, Exotic and Cross Bred Cattle in Pakistan. Anim Biotechnol 2023, 34, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulos, D.; Vougiouklaki, D.; Laliotis, G.P.; Tsironi, T.; Valasi, I.; Chatzilazarou, A.; Halvatsiotis, P.; Houhoula, D. Identification of Polymorphisms of the CSN2 Gene Encoding β-Casein in Greek Local Breeds of Cattle. Vet Sci 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miluchová, M.; Gábor, M.; Candrák, J. The Effect of the Genotypes of the CSN2 Gene on Test-Day Milk Yields in the Slovak Holstein Cow. Agriculture 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiche, A.-M.; Martín-Hernández, M.C.; Spengler Neff, A.; Bapst, B.; Fleuti, C.; Dohme-Meier, F.; Hess, H.D.; Egger, L.; Portmann, R. The A1/A2 β-Casein Genotype of Cows, but Not Their Horn Status, Influences Peptide Generation during Simulated Digestion of Milk. J Dairy Sci 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giglioti, R.; Gutmanis, G.; Katiki, L.M.; Okino, C.H.; de Sena Oliveira, M.C.; Vercesi Filho, A.E. New High-Sensitive RhAmp Method for A1 Allele Detection in A2 Milk Samples. Food Chem 2020, 313, 126167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulibaba, R.O.; Liashenko, Y.V.; Sakhatskyi, M.I. Polymorphism of CSN2 and TNF-α Genes in the Population of Holstein Cattle Bred in Ukraine. Cytol Genet 2024, 58, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D.; Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T. Past: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontologia Electronica 2001, 4, 178. [Google Scholar]
- Elferink, A.J.W.; Entiriwaa, D.; Bulgarelli, P.; Smits, N.G.E.; Peters, J. Development of a Microsphere-Based Immunoassay Authenticating A2 Milk and Species Purity in the Milk Production Chain. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, A.D.; Cîrîc, A.I.; Begea, M. A Review of Milk Frauds and Adulterations from a Technological Perspective. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 9821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handford, C.E.; Campbell, K.; Elliott, C.T. Impacts of Milk Fraud on Food Safety and Nutrition with Special Emphasis on Developing Countries. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2016, 15, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oglobline, A.N.; Padula, M.P.; Doble, P.A. Quality Control of A1-Free Dairy ☆. Food Control 2022, 135, 108685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Montenegro, L.; Mendizabal, J.A.; Alfonso, L.; Urrutia, O. DNA Extraction Procedures and Validation Parameters of a Real-Time PCR Method to Control Milk Containing Only A2 β-Casein. Food Control 2022, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perestam; Fujisaki, K. K.; Nava, O.; Hellberg, R.S. Comparison of Real-Time PCR and ELISA-Based Methods for the Detection of Beef and Pork in Processed Meat Products. Food Control 2017, 71, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayla, M.E.A. Detection and Validation of A2 Milk Suitable for Consumers Having Milk Intolerance by ELISA Method. Journal of Advanced Research in Natural and Applied Sciences 2023, 9, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Fan, Y.; Su, J.; Wang, H.; Luo, X.; Zhang, S. Rapid Identification of A1 and A2 Milk Based on the Combination of Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Food Control 2022, 134, 108659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minic, R.; Zivkovic, I. Optimization, Validation and Standardization of ELISA. In Norovirus, 1st ed.; Mózsik, G., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 9–27. [Google Scholar]
| Number of cows1 | Genotype – Gene sequencing2 |
ELISA test3 | A2-MiLK TEST®3 | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | A1A1 | No-A2 | No-A2 | 100% | 100% |
| 24 | A1A2 | No-A2 | No-A2 | 100% | 100% |
| 32 | A2A2 | A2 | A2 | 100% | 100% |
| A1A1 (%)1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 50% | 100% | |
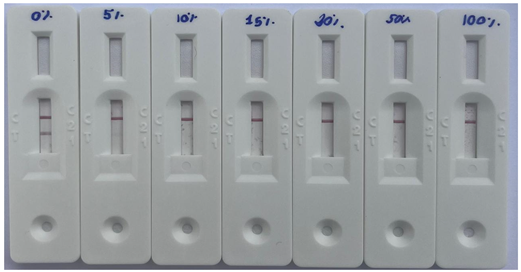 |
|||||||
| Result - Milk A2 presence | Positive | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Positive |
| A1A1 (%)1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 100% | |
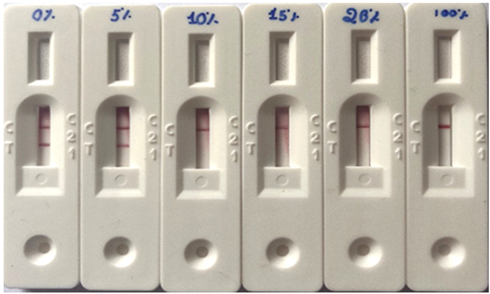 |
||||||
| Result - Milk A2 presence | Positive | Positive | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| Aspect | Traditional genotyping | ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) |
LFIA (Lateral Flow ImmunoAssay) A2 Milk Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Direct DNA analysis | Detection of A1 β-casein using immunological reactions | Detection of milk proteins |
| Process | Use of laboratory techniques to extract and analyze DNA | Use of specific antibodies to detect and quantify A1 β-casein | Point of care testing, no need of lab equipment |
| Result | Identification of genotypes A1A1, A1A2 or A2A2 | Quantification of A1 β-casein concentration in milk | Identification of A2A2 animals and milk mixture purity |
| Precision | High accuracy in determining genotypes | High accuracy in measuring A1 β-casein concentration | 100% A2A2 detection 95% purity detection |
| Application | Genetic studies, heredity analyzes | Milk quality control, selection for human consumption | Milk quality control, heredity analyzes |
| Benefits | Specific and direct; useful for detailed genetic studies | Fast, practical and suitable for quality monitoring | Point of Care, fast, cost-effective, suitable for quality monitoring |
| Disadvantages | Costly and time-consuming; requires specialized equipment and knowledge | Less specific compared to direct genotyping | Does not differentiate among A1A1 and A1A2 genotypes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





