Submitted:
10 August 2024
Posted:
13 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. AI-Enabled Wireless Smart Sensor
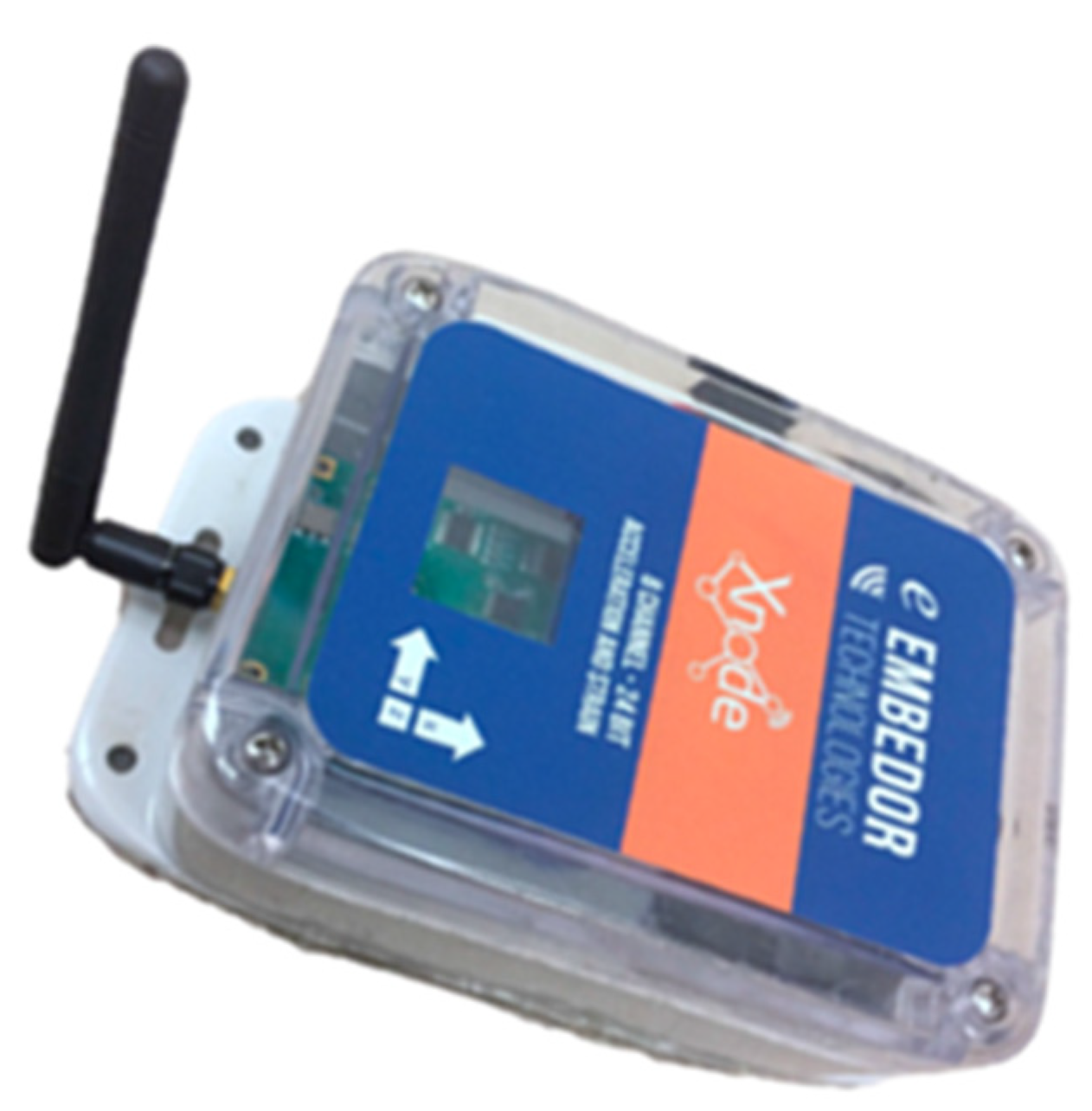
2.1. Xnode
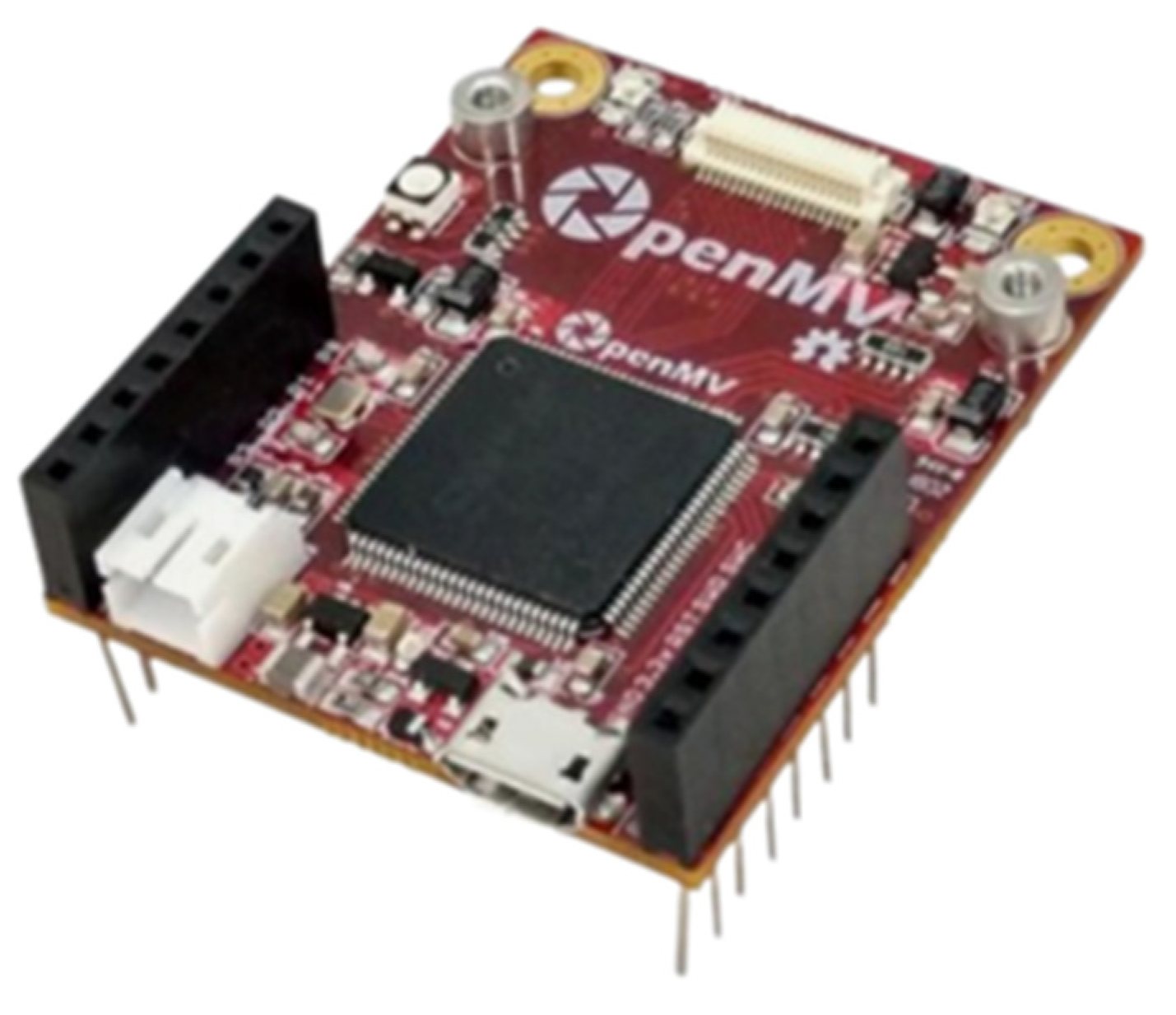
2.2. OpenMV H7 Plus
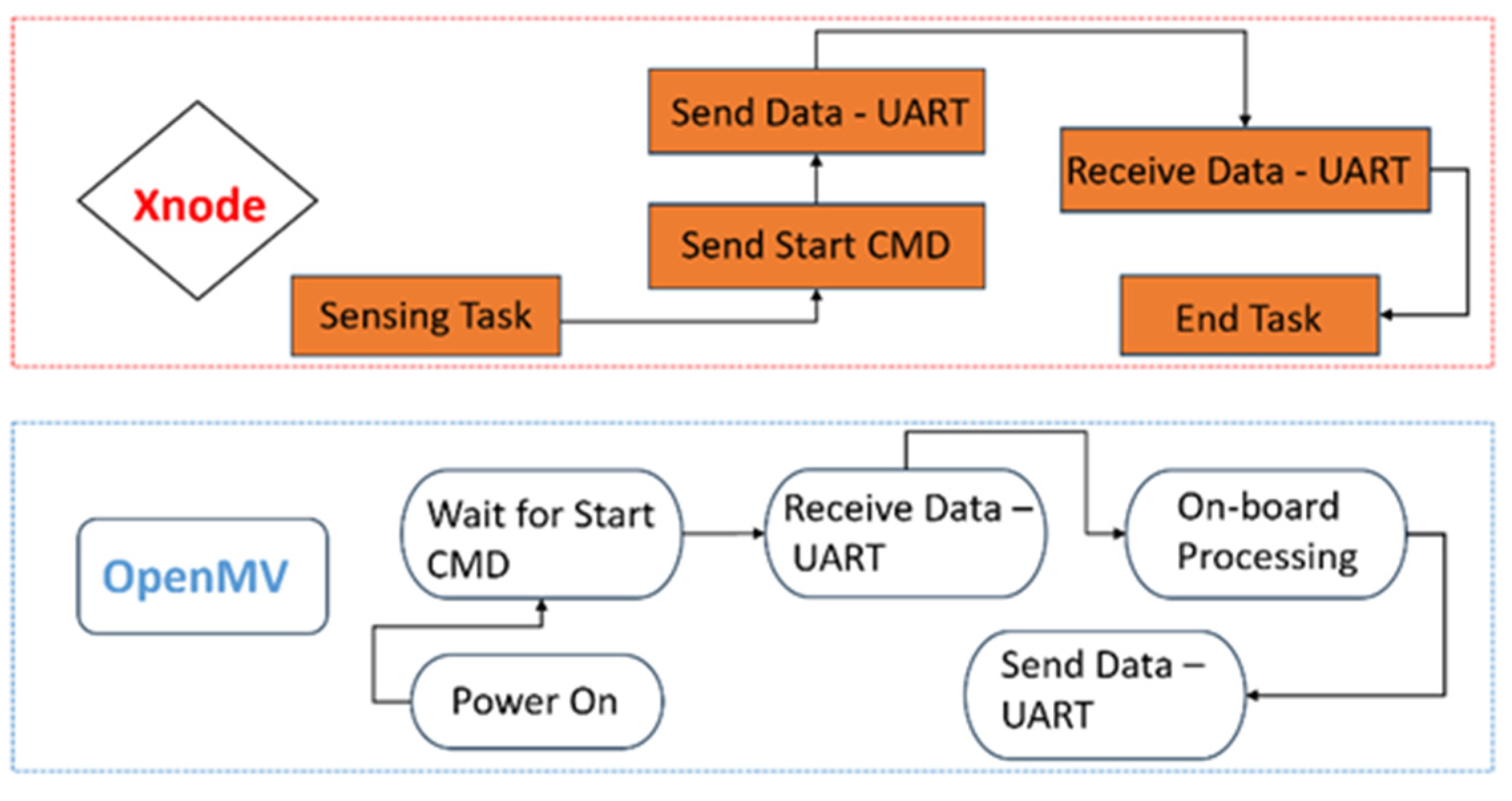
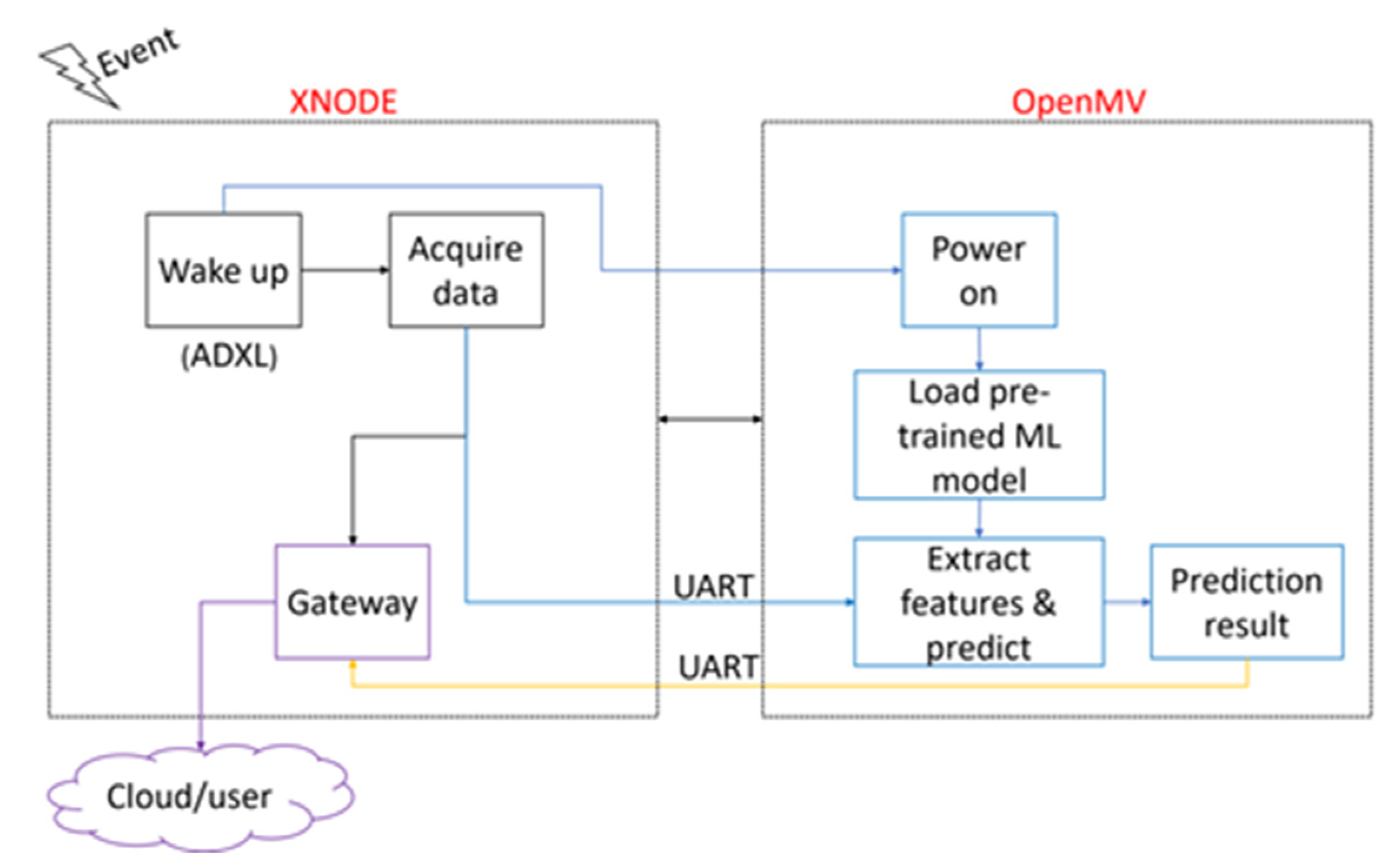
2.3. Framework for AI-Enabled Wireless Smart Sensor
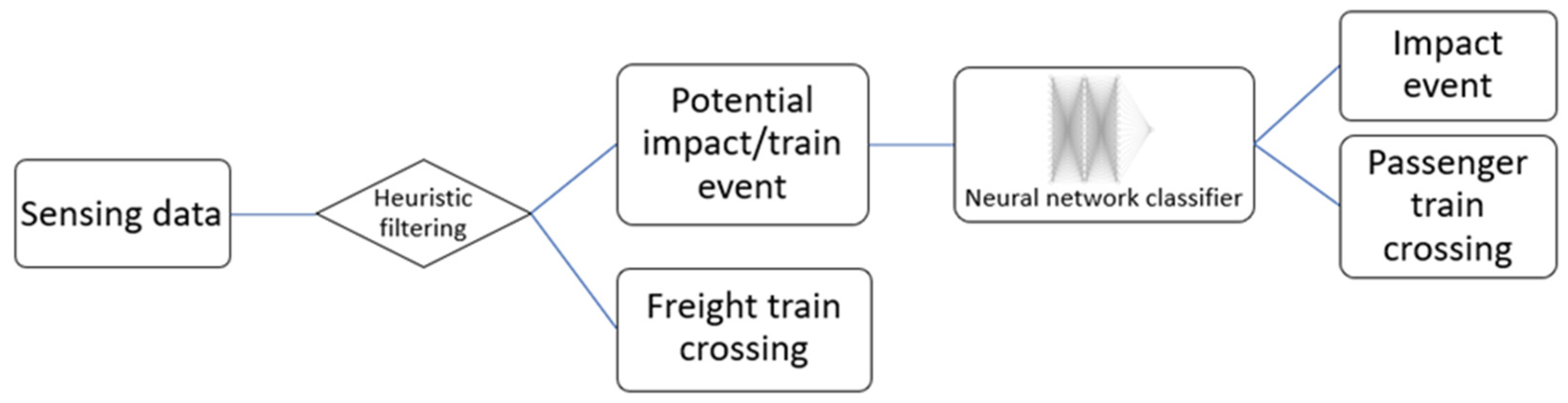
3. Railroad Bridge Impact Detection – Event Classification
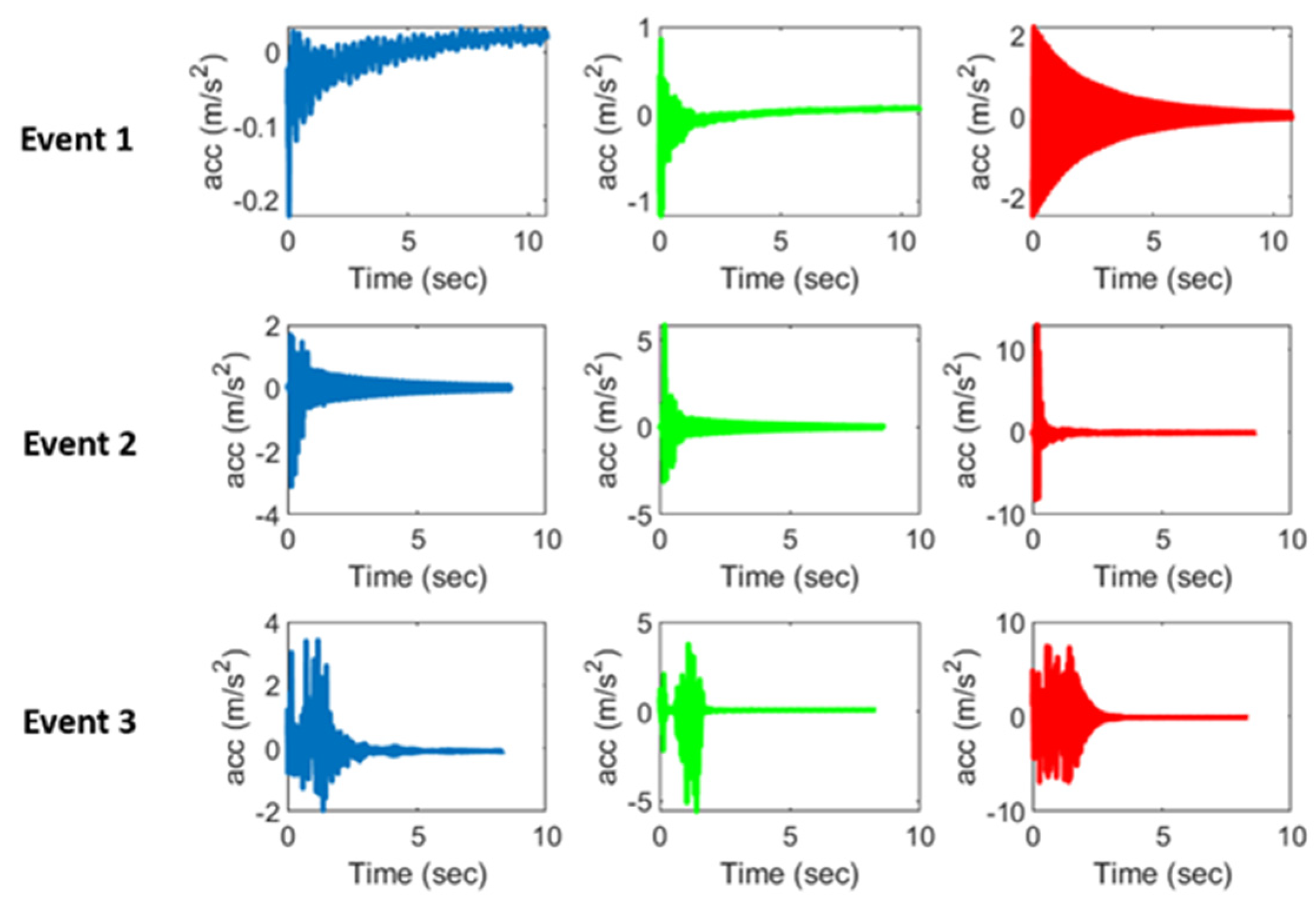
4. Results
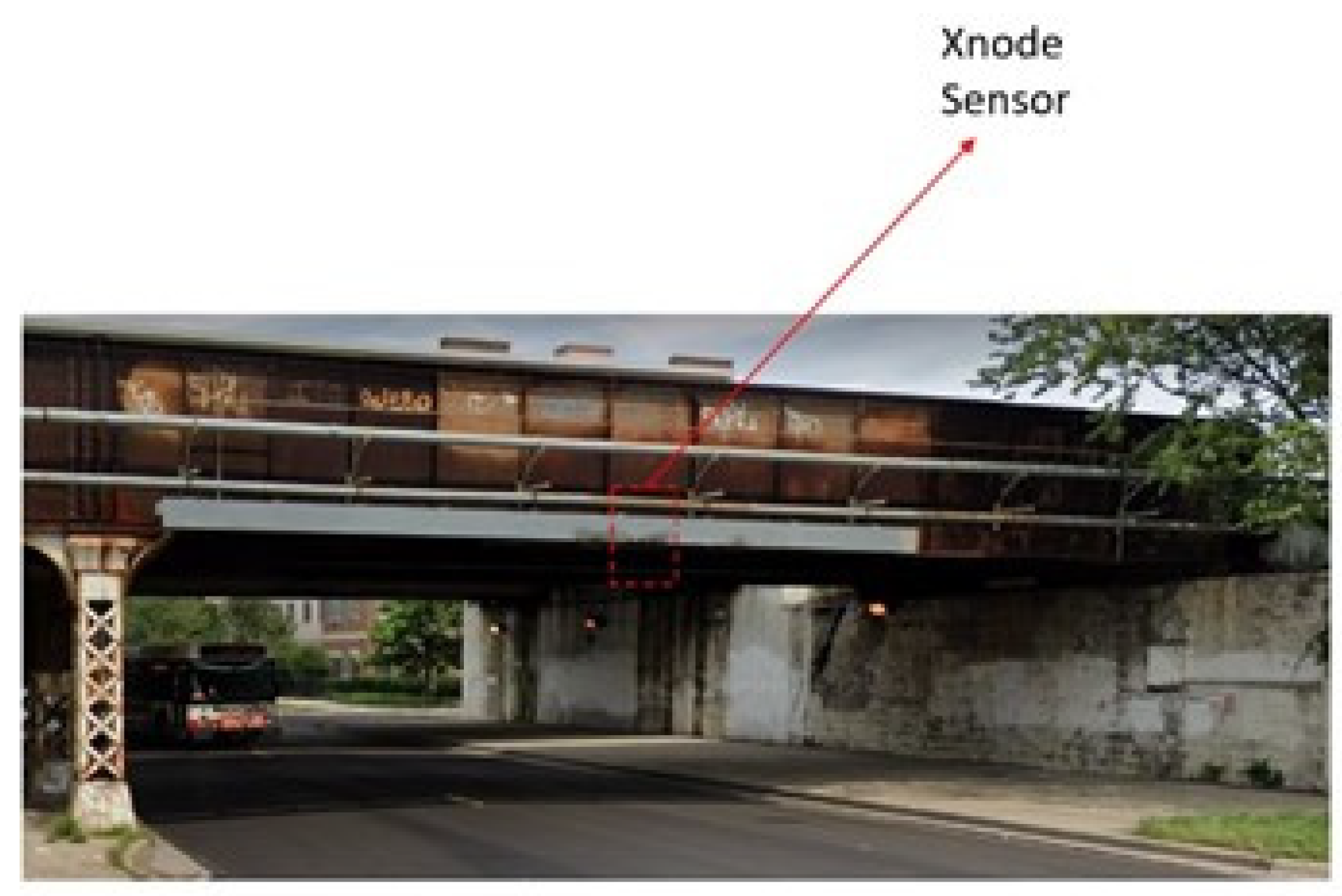
4.1. Railroad Bridge Field Data
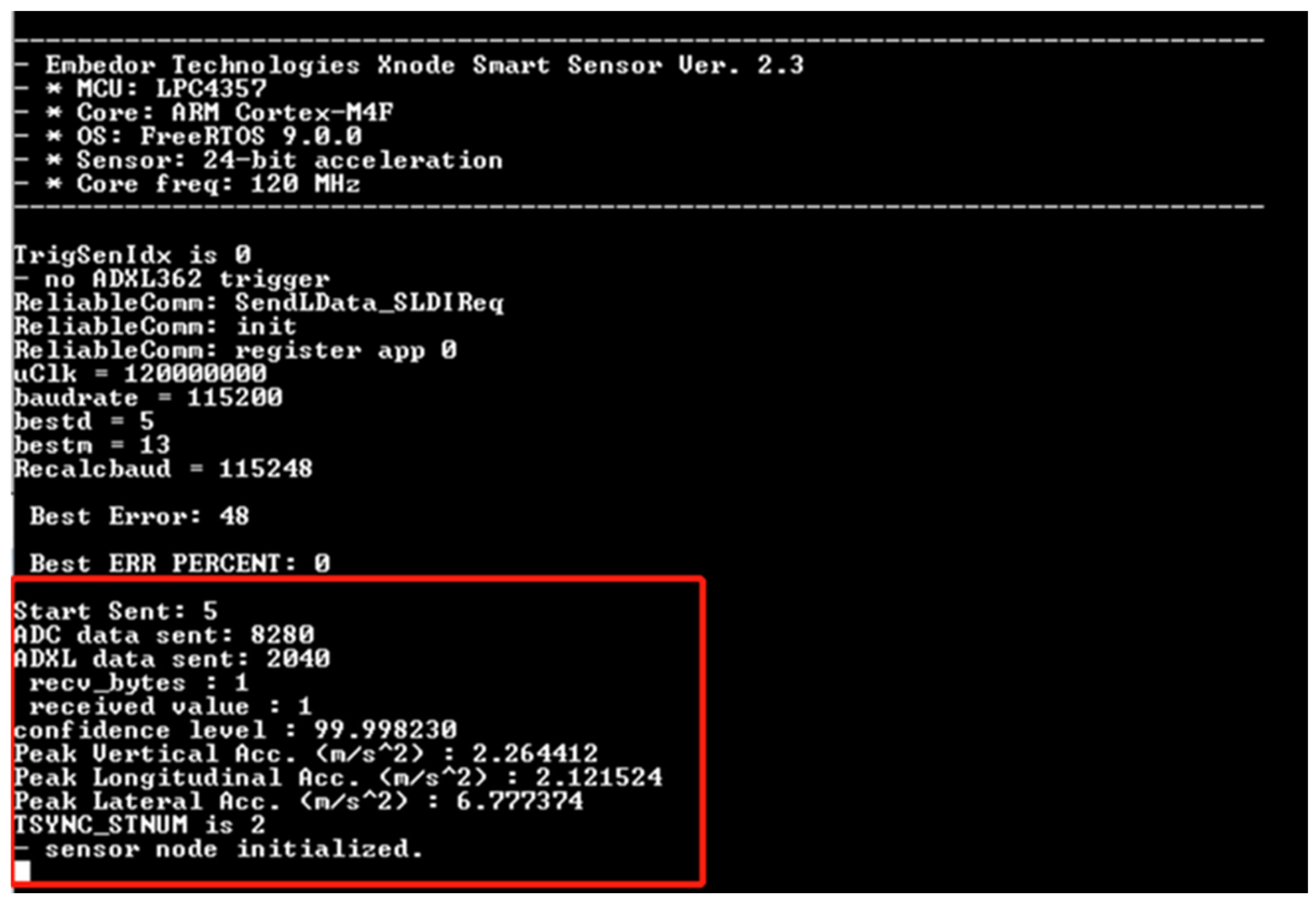
4.2. Neural Network Training and Implementation
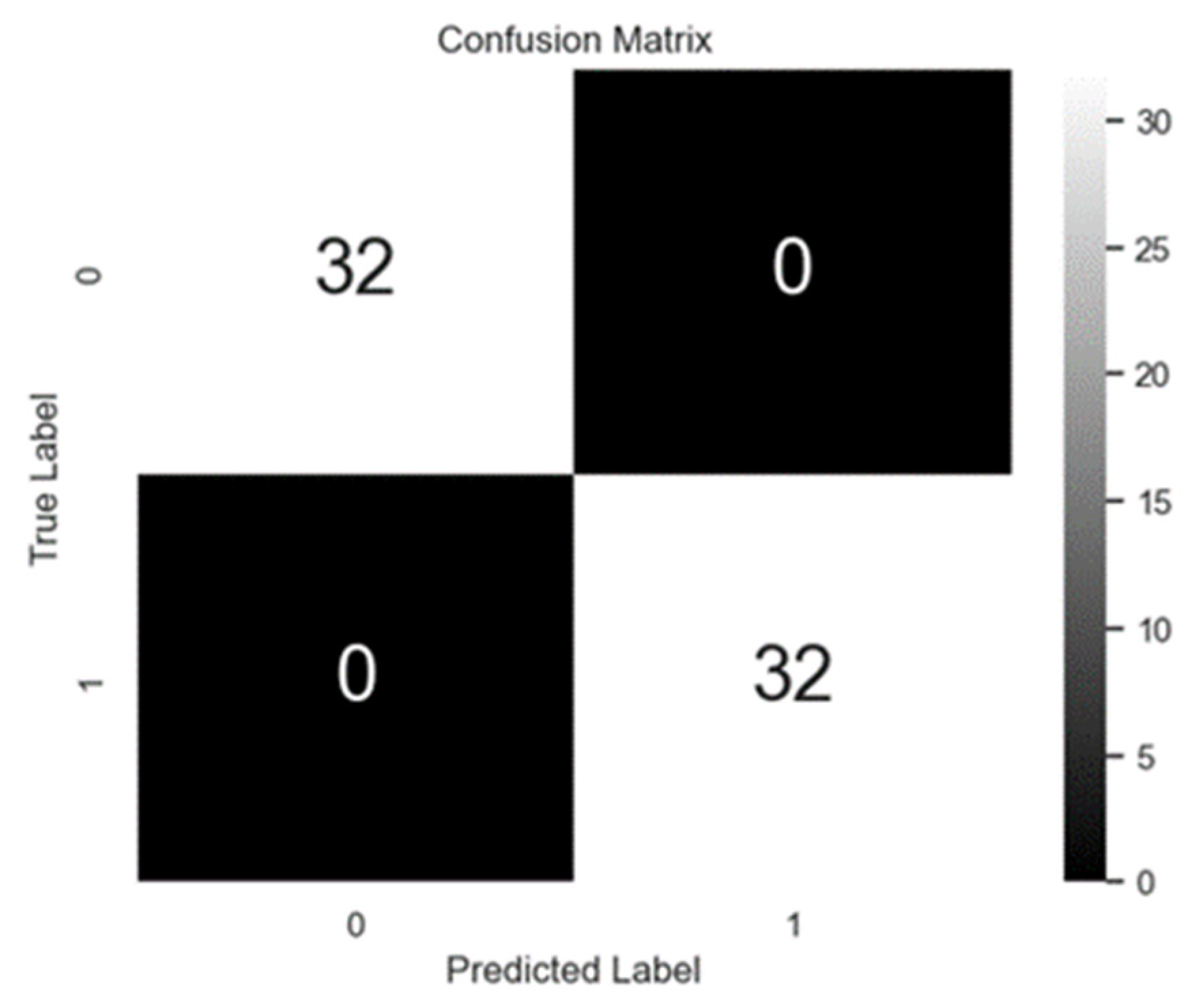
4.3. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
References
- Moving Goods in the United States. Available online: https://data.bts.gov/stories/s/Moving-Goods-in-the-United-States/bcyt-rqmu/ (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Ozdagli, A.I.; Gomez, J.A.; Moreu, F. Real-Time Reference-Free Displacement of Railroad Bridges during Train-Crossing Events. Journal of Bridge Engineering 2017, 22. [CrossRef]
- Rakoczy, A.M. Fatigue Safety Verification of Riveted Steel Railway Bridges Using Probabilistic Method and Standard S-N Curves. Archives of Civil Engineering 2021, 67, 625–642. [CrossRef]
- Sitton, J.D.; Zeinali, Y.; Story, B.A. Design and Field Implementation of an Impact Detection System Using Committees of Neural Networks. Expert Syst Appl 2019, 120, 185–196. [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.K.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z. Bridge Vehicle Impact Assessment (Project # C-07-10). Final Report for New York State Department of Transportation. 2011.
- Joy, R.; Jones, M.; Otter, D.; Maal, L. Characterization of Railroad Bridge Service Interruptions. U.S. Department of Transportation 2013.
- Nguyen, B.; Brilakis, I. Understanding the Problem of Bridge and Tunnel Strikes Caused by Over-Height Vehicles. Transportation Research Procedia 2016, 14, 3915–3924. [CrossRef]
- Connolly, L.; Bernardini, I.; Kakouris, E.; Kelly, J. BRIDGE and Tunnel Strikes by Oversized Vehicles : A PIARC Special Project; ISBN 9782840606758.; PIARC, 2022; ISBN 9782840606758.
- The Risk of Bridge Strikes - Network Rail. Available online: https://www.networkrail.co.uk/running-the-railway/looking-after-the-railway/bridges-tunnels-and-viaducts/the-risk-of-bridge-strikes/ (accessed on 17 July 2022).
- Coleman, L.; Engineer, P.S.; Wheel, M.; Engineer, S.; Dean, A.; Engineer, I.B. Managing Bridge Strikes from Rail to Road Bridges. In Proceedings of the 9h Australian Small Bridges Conference; 2019; pp. 1–8.
- Critchley, J.; Cowell, E. Rail Over Bridge Strikes - Discussion of an Emergency Recovery in a Metro Area Available online: https://na.eventscloud.com/file_uploads/07e9ab4dc5c28687d73704d166a571e6_RAILOVERROADBRIDGESTRIKESDISCUSSIONOFANEMERGENCYRECOVERYINAMETROAREA.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2022).
- Okada, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Saruta, M. Application of Earthquake Early Warning System to Seismic-Isolated Buildings;
- Yamazaki, F.; Motomura, H.; Hamada, T. DAMAGE ASSESSMENT OF EXPRESSWAY NETWORKS IN JAPAN BASED ON SEISMIC MONITORING;
- Çelebi, M. Real-Time Seismic Monitoring of the New Cape Girardeau Bridge and Preliminary Analyses of Recorded Data: An Overview. Earthquake Spectra 2006, 22, 609–630.
- Yun, C.B.; Cho, S.; Park, H.J.; Min, J.; Park, J.W. Smart Wireless Sensing and Assessment for Civil Infrastructure. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering 2014, 10, 534–550. [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.H.; Li, J.; Jo, H.; Park, J.W.; Cho, S.; Spencer, B.F.; Jung, H.J. A Wireless Smart Sensor Network for Automated Monitoring of Cable Tension. Smart Mater Struct 2014, 23. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Hoang, T.; Mechitov, K.; Kim, J.R.; Zhang, D.; Spencer, B.F. Sudden Event Monitoring of Civil Infrastructure Using Demand-Based Wireless Smart Sensors. Sensors (Switzerland) 2018, 18. [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.; Fu, Y.; Mechitov, K.; Sánchez, F.G.; Kim, J.R.; Zhang, D.; Spencer, B.F. Autonomous End-to-End Wireless Monitoring System for Railroad Bridges. Advances in Bridge Engineering 2020, 1. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hoang, T.; Mechitov, K.; Spencer, B.F. XImpact : Intelligent Wireless System for Cost-Effective Rapid Condition Assessment of Bridges under Impacts. 2022.
- Sitton, J.D.; Story, B.A.; Zeinali, Y. Bridge Impact Detection and Classification Using Artificial Neural Networks. Structural Health Monitoring 2017: Real-Time Material State Awareness and Data-Driven Safety Assurance - Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring, IWSHM 2017 2017, 1, 1261–1267. [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.; Shaik, S.A.; Mechitov, K.; Spencer, B.F. An Event-Classification Neural Network Approach for Rapid Railroad Bridge Impact Detection. Sensors 2023, 23. [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Tatipamula, M.; Nguyen, H.X. Cloud-Based Digital Twinning for Structural Health Monitoring Using Deep Learning. IEEE Trans Industr Inform 2022, 18, 3820–3830. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ran, X. Deep Learning With Edge Computing: A Review. Proceedings of the IEEE 2019. [CrossRef]
- Mondal, T.G.; Chou, J.-Y.; Fu, Y.; Jianxiao, M. A Hybrid Deep Neural Network Compression Approach Enabling Edge Intelligence for Data Anomaly Detection in Smart Structural Health Monitoring Systems. Smart Struct Syst 2023, 32, 179–193.
- Fu, Y.; Mechitov, K.; Hoang, T.; Kim, J.R.; Memon, S.A.; Spencer, B.F. Efficient and High-Precision Time Synchronization for Wireless Monitoring of Civil Infrastructure Subjected to Sudden Events. Struct Control Health Monit 2021, 28. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Mechitov, K.; Hoang, T.; Kim, J.R.; Lee, D.H.; Spencer, B.F. Development and Full-Scale Validation of High-Fidelity Data Acquisition on a next-Generation Wireless Smart Sensor Platform. Advances in Structural Engineering 2019, 22, 3512–3533. [CrossRef]
- Shajihan, S.A.V.; Chow, R.; Mechitov, K.; Fu, Y.; Hoang, T.; Spencer, B.F. Development of Synchronized High-Sensitivity Wireless Accelerometer for Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors (Switzerland) 2020, 20, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Spencer, B.F.; Park, J.W.; Mechitov, K.A.; Jo, H.; Agha, G. Next Generation Wireless Smart Sensors Toward Sustainable Civil Infrastructure. In Proceedings of the Procedia Engineering; Elsevier Ltd., 2017; Vol. 171, pp. 5–13.
- V. Shajihan, S.A.; Hoang, T.; Mechitov, K.; Spencer, B.F. Wireless SmartVision System for Synchronized Displacement Monitoring of Railroad Bridges. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering 2022. [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, I.; El-Sonbaty, Y.; El-Habrouk, M. OPENMV: A PYTHON POWERED, EXTENSIBLE MACHINE VISION CAMERA; 2017;
- Structural Health Monitoring at the University of Illinois. Available online: http://shm.cs.illinois.edu/ (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Lawal, O.; Najafi, A.; Hoang, T.; Shajihan, S.A. V.; Mechitov, K.; Spencer, B.F. Development and Validation of a Framework for Smart Wireless Strain and Acceleration Sensing. Sensors 2022, 22. [CrossRef]
- Active Mass Damper for Buildings and Bridges | TESolution. Available online: http://www.tesolution.com/structural-health-monitoring.html (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Zhu, L.; Fu, Y.; Chow, R.; Spencer, B.F.; Park, J.W.; Mechitov, K. Development of a High-Sensitivitywireless Accelerometer for Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors (Switzerland) 2018, 18. [CrossRef]
- Bell, C. MicroPython for the Internet of Things; Apress, 2017;
- OpenMV Cam H7. Available online: https://openmv.io/products/openmv-cam-h7 (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- TensorFlow Lite. Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/guide#2_convert_the_model (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- A Gentle Introduction to K-Fold Cross-Validation. Available online: https://machinelearningmastery.com/k-fold-cross-validation/ (accessed on 30 July 2022).


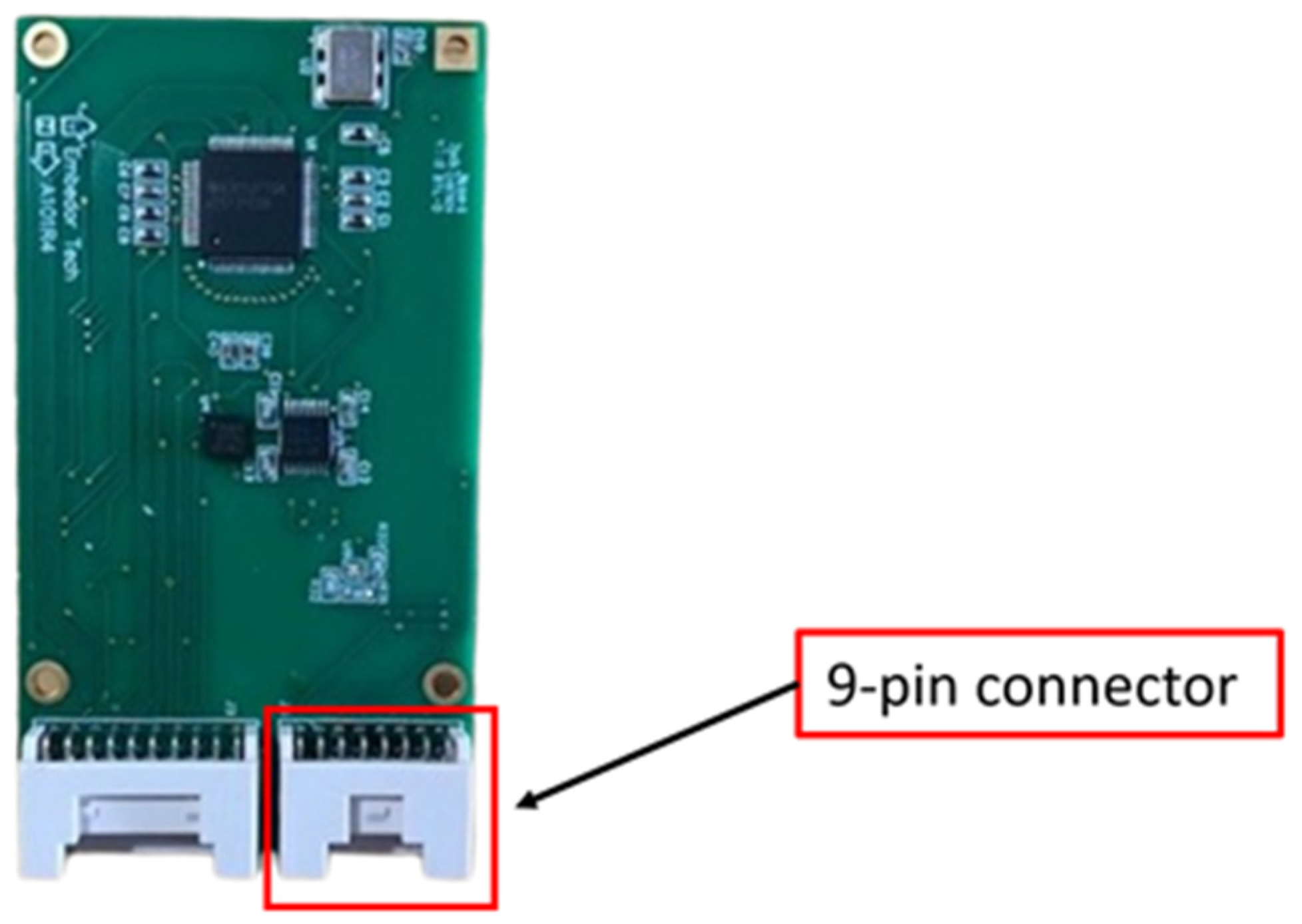
| Specification | OpenMV H7 Plus |
| Power | 240 mA @ 3.3 V |
| Microprocessor | Arm Cortex-M7 |
| Clock speed | 480 MHz |
| RAM | 32 MB |
| Programming | Micropython |
| Open source | Yes |
| Commercially available | Yes |
| Event Number | Peak Longitudinal Acceleration (m/s2) | Peak Vertical Acceleration (m/s2) | Peak Lateral Acceleration (m/s2) | Classification Result |
| 1 | 2.1215 | 2.2644 | 6.7773 | Impact |
| 2 | 0.6733 | 0.8783 | 1.9868 | Impact |
| 3 | 2.267 | 8.1734 | 9.6672 | Impact |
| 4 | 15.1512 | 19.7129 | 30.8948 | Impact |
| 5 | 0.169 | 1.7734 | 1.664 | Train |
| 6 | 20.4395 | 29.67 | 33.1432 | Impact |
| 7 | 0.4972 | 4.4067 | 3.7558 | Train |
| 8 | 0.629 | 5.4063 | 3.0172 | Train |
| 9 | 2.3407 | 9.5216 | 6.1671 | Train |
| 10 | 0.5296 | 4.8359 | 3.7874 | Train |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





