Submitted:
06 August 2024
Posted:
07 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1.0. Introduction
1.1. Problem Statement
2.0. Literature Review
2.1. Theoretical Prespectives
2.2. Organizational Performance
2.3. Review of Case Studies
2.4. Conceptual Framework
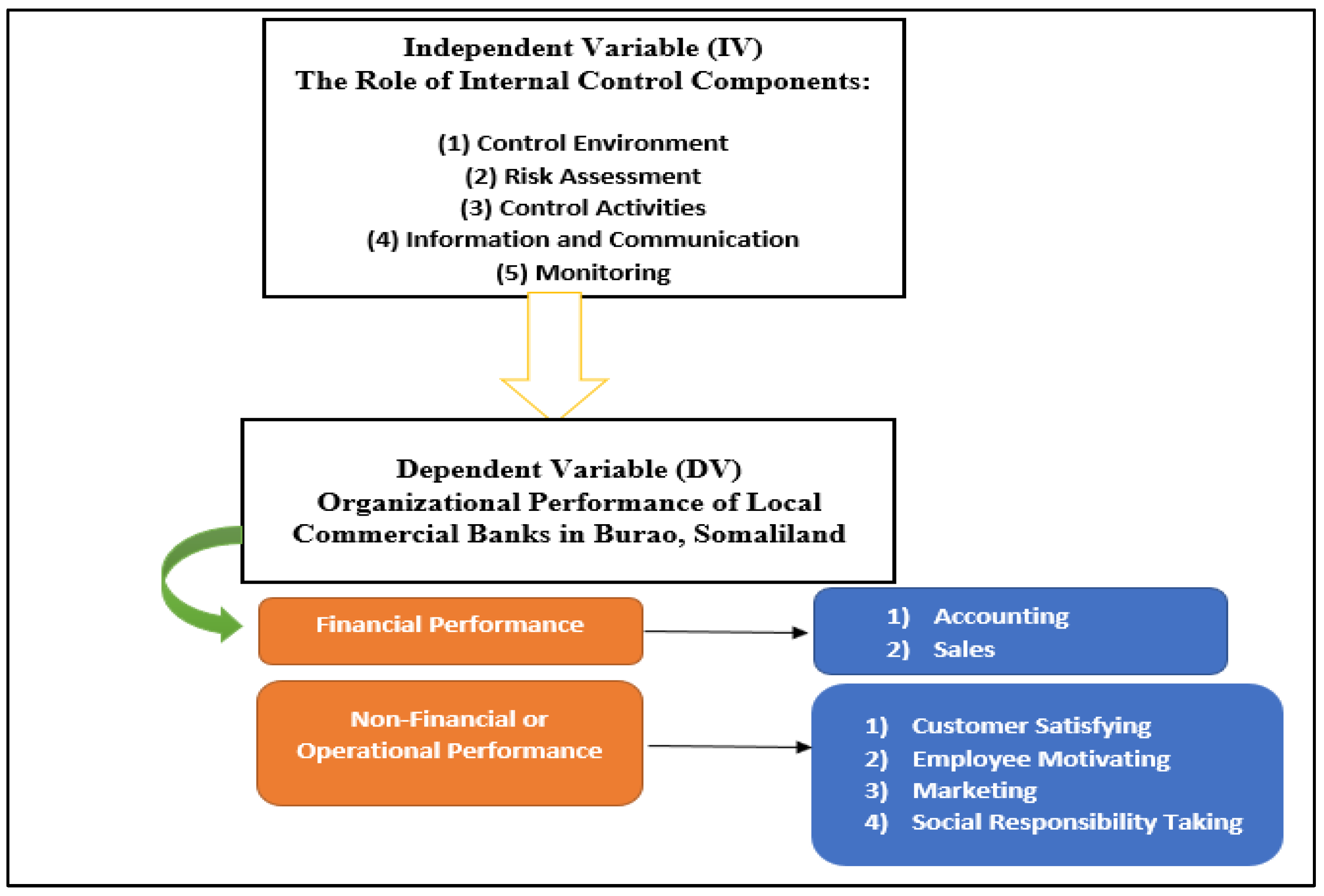
3.0. Methodologies
3.1. Summary
4.0. Data Presentation, Analysis, and Interpretation
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
| Frequency | Percent | ||
| Valid | Male | 30 | 60.0 |
| Female | 20 | 40.0 | |
| Total | 50 | 100.0 | |
| Frequency | Percent | ||
| Valid | 30-39 | 21 | 42.0 |
| 40-59 | 23 | 46.0 | |
| 60 and above | 6 | 12.0 | |
| Total | 50 | 100.0 | |
| Frequency | Percent | ||
| Valid | Diploma | 7 | 14.0 |
| Bachelors | 35 | 70.0 | |
| Masters | 8 | 16.0 | |
| Total | 50 | 100.0 | |
4.2. Variable Tests
4.2.1. Reliability Test:
4.2.3. Correlation Tests:
| Internal Control Systems | Organizational Performance in Local Commercial Banks | ||
| Internal Control Systems | Pearson Correlation | 1 | 558** |
| Sig. (2 tailed) | 0.01 | ||
| N | 50 | 50 | |
| Organizational Performance in Local Commercial Banks | Pearson Correlation | 558** | 1 |
| Sig. (2 tailed) | 0.01 | ||
| N | 50 | 50 |
5.0. Conclusion and Recommendations
5.1. Conclusion
5.2. Recommendations
References
- Wikipedia. (2022, January 1). Retrieved from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Organizational_performance.
- Wikipedia. (2022, june 24). Retrieved from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bank.
- A runa, S. (2019). the impact of internal control on job satisfaction of female workers. international Journal of research in engineering, 1-8.
- Angie, M. (2019, January 28). Small Business Chron. Retrieved from Small Business Chron: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/audit-procedures-sales-collection-cycle-49846.html.
- Audit-Board. (2018, April 17). Audit Board. Retrieved from Audit Board: https://www.auditboard.com/blog/7-reasons-to-maintain-your-internal-controls-compliance-program/.
- Ayneshet, A. A. (2020). The Effect of Internal Control on Organization Performance in. International Journal of Research in Business Studies and Management, 1-10.
- Bhasin Hitesh. (2019). Internal Control: Meaning, Types, Components and objectives. marketing91.
- BPP, M. a. (1988). ICAN Study Test on Auditing and Investigation. oxford: Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Brown, S. P. (Brown, S. P. ). A meta-analysis and review of organizational research on job involvement. Psychological Bulletin, 120(2),, 235–255.
- CFI Team. (2022, February 27). CFI. Retrieved from Corporate Finance Institute: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/financial-performance/.
- Cornelius Kipkemboi Lagat¹, C. A. (2016). EFFECT OF INTERNAL CONTROL SYSTEMS ON FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT. Journal of Economics,, 162-186.
- Danielle, S. (2018, november 16). Retrieved from biz-fluent: www.bizfluent.com/about.
- Dr. Annette, T. (2020, may 30). Retrieved from ckju.net for management skills: www. ckju.net.
- Drupal. (2015).
- Esther, S. (2021). effect of internal control on organizational performance in the T.I in south and southeast Nigeria. International Journal of Social Science, 1-20.
- Forecast Academy team. (2021, August 20). Forecast. Retrieved from Forecast Platform: https://www.forecast.app/blog/operational-performance#:~:text=improve%20operational%20performance-,What%20is%20operational%20performance%3F,to%20accomplish%20specific%20business%20goals.
- Furlong, M. (January 25, 2019). What Are the Types of Internal Controls? bizfluent.
- Hackett, W. a. (1976). An auditing perspective of the Historical development of. Florida Agricultural and Mechanical University, 003-009.
- Henri, J. (2004). "Performance measurement and organizational effectiveness: bridging the gap". Québec City: 93-123.
- Ian Palmer, R. D. (1996). Reframing and organizational action: The unexplored link. Journal of Organizational Change, 12-25.
- James, A. H. (2008). Accounting information system. Mason, Ohio: Cengage Learning Academic Resource Center.
- Jamshidi-Navid, B. a. (2009). A Clear Look at Internal Controls: Theory and Concepts. Hamed: Social Science Research Network.
- Jason, G. (2022, April 07). the business Professor. Retrieved from the business Professor: https://thebusinessprofessor.com/en_US/accounting-taxation-and-reporting-managerial-amp-financial-accounting-amp-reporting/internal-controls-definition.
- Jonathan Duchac, J. M. (2007). financial accounting An Integrated Statements Approach. 0-324-37443-7: Cengage Learning.
- Julia Kagan. (2021, October 06). Investopedia. Retrieved from Investopedia: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/commercialbank.asp#toc-significance-of-commercial-banks.
- Katushabe, P. (2016). INTERNAL CONTROLS AND ORGANISATIONAL PERFORMANCE OF UNITED NATIONS ORGANISATION STABILISATION MISSION IN THE DEMOCRATIC, REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO, ENTEBBE BASE. Uganda management institute, 1-102.
- Kendra, C. (2022, January 26). Retrieved from verywell-mind: www.verywellmind.com.
- Kenton, W. (2019). Principles of Auditing & Other Assurance Services,. Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX).
- Margaret, Scott A., Sott L., and David. (2009). effectof preventive and defective controls on employee performance and motivation. Research-gate, 1-39.
- Martin. (1994). reports of tax cases. Northern Ireland: LNUK.
- Mohamed, A. M. (2016). EFFECTS OF INTERNAL CONTROL SYSTEM ON THE ORGANIZATOINAL PERFORMANCE OF REMITTANCE COMPANIES IN MODADISHU-SOMALIA. Journal of Business Management , 1-15.
- Noorbakhsh, F. a. (2001). Human Capital and FDI Inflows in Developing Countries: New Empirical Evidence. Journal of World Development, 1539-1610.
- Oladele, J. (2010). The Effect of Internal Control System on Nigerian Banks. International Journal of Accounting, 123-129.
- Oxford-Languages. (n.d.). Oxford University Press. Retrieved from Oxford Languages: https://languages.oup.com/google-dictionar-en/.
- Plamen. (2019). Pro-Quest Scholarly Journal. Control and Audit in Marketing, 1-5.
- Poff, D. C. (2018). Fraud triangle: Cressey's fraud triangle and alternative fraud theories. Springer, Cham, Switerland.: https://link.springer.com/referencework/10.1007/978-3-319-23514-1.
- Qasim, A. (2021). the effect of internal control on employee performance of SMS enterprises in Jordan. Jornal of Asian finance, economies, and Business, 1-9.
- Rae, K. a. (2008). Quality of internal control procedures : antecedents and moderating effect on organisational justice and employee fraud. Managerial auditing journal,, 104-124.
- Rae, Kirsten; Sands, John; and Subramaniam, Nava. (2017). Associations among the Five Components within COSO Internal Control-Integrated Framework as the Underpinning of Quality. Australasian Accounting, Business and Finance, 28-54.
- Richard, Pierre, Devinney, Timothy,Yip, George,Johnson, and Gerry. (2009). Measuring Organizational Performance: Towards Methodological Best Practice. Journal of Management, 35.
- Rynes, S. L. (1990). Applicant attraction strategies: An organizational perspective. Academy of Management Review, 286-310.
- Salah, S. (2012).
- Subramaniam, K. R. (2008). Quality of internal control procedures: Antecedents and moderating effect onorganisational justice and employee fraud. Managerial Auditing Journal, 104 - 124.
- Ting, Xiaotao, Chi and Yakun. (2021). Customer satisfaction and Internal Control. College of Management Journal, 1-53.
- Tipgos, M. A. (2002). Why Management Fraud Is Unstoppable. The CPA journal., 34-41.
- Uganda, B. o. (2011). BANK OF UGANDA FINANCIAL CONSUMER PROTECTION. Bank of Uganda, 1-18.
- Veyrat-Durebex, C. C. (2016). Disruption of TCA Cycle and Glutamate Metabolism Identified by Metabolomics in an In Vitro Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Molecular Neurobiology, 6910–6924.
- Wang and Guan. (2017). Research on the relationship between internal control and financial performance. Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research Journal (Press Atlants), 1-6.
- Wikipedia. (2022, July O6). Retrieved from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Commercial_bank#Role.
- Wikipedia. (2022, April). Wikipedia. Retrieved from Wikipedia: https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internal-control.
- Xio, Zheng, Liu and Mohammed. (2018). the effectiveness of Internal Control and Corporate Social Responsibility. MDPI Journal, 1-18.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




