Submitted:
03 August 2024
Posted:
05 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting and Population
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Contribution Statement
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Abbreviations
|
CHF ‒ congestive heart failure PE ‒ pleural effusion PEs ‒ pleural effusions LDH ‒ lactate dehydrogenase MPE ‒ malignant pleural effusion COPD – Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease CVA ‒ cerebrovascular accident CRF – chronic renal failure |
References
- Puchalski, J.T.; Argento, A.C.; Murphy, T.E.; Araujo, K.L.; Oliva, I.B.; Rubinowitz, A.N.; Pisani, M.A. Etiologies of bilateral pleural effusions. Resp. Med. 2013, 107, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, R.; Maskell, N. The modern diagnosis and management of pleural effusions. BMJ 2015, 351, h4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcel, J.M.; Light, R.W. Diagnostic approach to pleural effusion in adults. Am. Fam. Phys. 2006, 73, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Jany, B.; Welte, T. Pleural effusion in adults—etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019, 116, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijayaratne, T.; Yousuf, A.; Panchal, R. Cardiac related pleural effusions: a narrative review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2014, 16, 1674–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korczyński, P.; Górska, K.; Konopka, D.; Al-Haj, D.; Filipiak, K.J.; Krenke, R. Significance of congestive heart failure as a cause of pleural effusion: Pilot data from a large multidisciplinary teaching hospital. Cardiol. J. 2020, 27, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBiasi, E.M.; Pisani, M.A.; Murphy, T.E.; Araujo, K.; Kookoolis, A.; Argento, A.C.; Puchalski, J. Mortality among patients with pleural effusion undergoing thoracentesis. Eur. Resp. J. 2015, 46, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Light, R.W. Pleural effusions. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 95, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcel, J. Pleural effusions from congestive heart failure. Sem. Respir. Crit. Care Med 2011, 31, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.P.; Morley, A.J.; Stadon, L.; De Fonseka, D.; Arnold, D.T.; Medford., A.R.L.; Maskell, N.A. Nonmalignant pleural effusions: A prospective study of 356 consecutive unselected patients. Chest 2017, 151, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtomäki, A.; Nevalainen, R.; Ukkonen, M.; Nieminen, J.; Laurikka, J.; Khan, J. Trends in the incidence, etiology, treatment, and outcomes of pleural infections in adults over a decade in a Finnish University Hospital. Scand. J. Surg. 2020, 109, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, R.; Antoine, M.H.; Rudrappa, M.. Pleural Effusion. [Updated 2023 Mar 18]. In StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL). StatPearls Publishing, 2024. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448189/.
- Ermin, S.; Özdoğan, Y.; Batum, O.; Yılmaz, U. The role of LENT and PROMISE scores in predicting survival in malignant pleural effusion. Lung India 2022, 39, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera Lara, S.; Fernández-Fabrellas, E.; Juan Samper, G.; Marco Buades, J.; Andreu Lapiedra, R.; Pinilla Moreno, A.; Morales Suárez-Varela, M. Predicting malignant and paramalignant pleural effusions by combining clinical, radiological and pleural fluid analytical parameters. Lung 2017, 195, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laisaar, T.; Palmiste, V.; Vooder, T.; Umbleja, T. Life expectancy of patients with malignant pleural effusion treated with video-assisted thoracoscopic talc pleurodesis. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 5, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, O.; Fux, D.; Bartsikhovsky, T.; Vosko, S.; Tishler, M.; Copel, L. Clinical relevance of bilateral pleural effusion in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Inter. Med. J 2020, 50, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
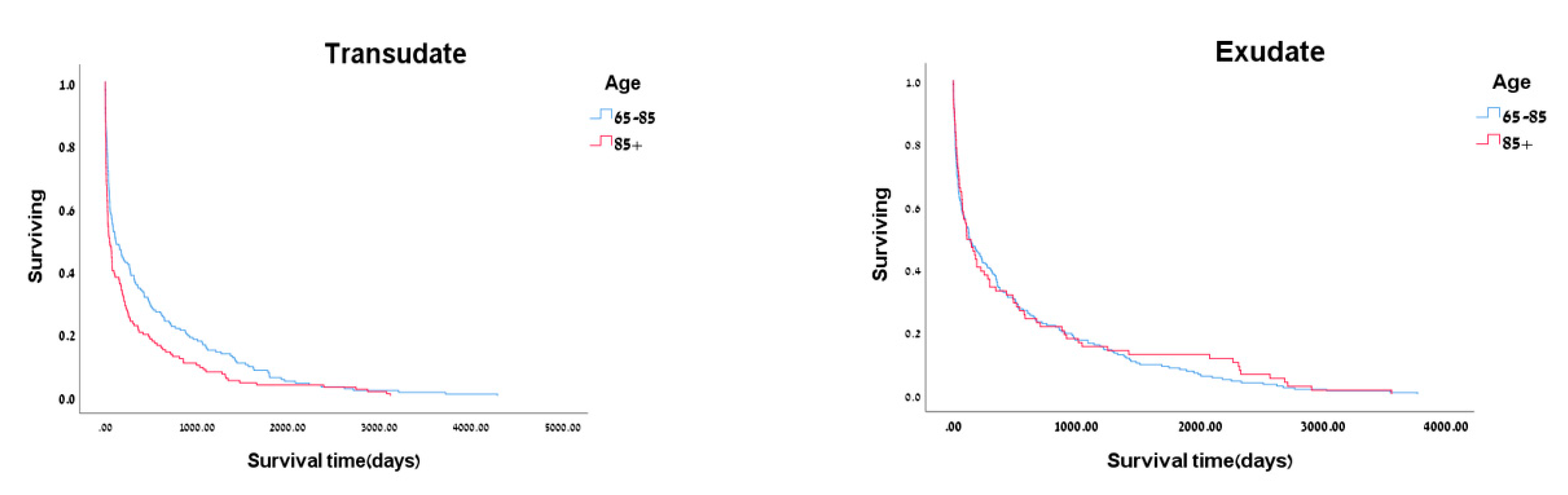
| Characteristic | Exudate n=304 |
p-value | Transudate n=331 |
p-value | ||
| 65-85 | >85 | 65-85 | .>85 | |||
| n=216 | n=88 | n=184 | n=147 | |||
| Age, mean ± SD | 76.13±5.52 | 88.89±10.38 | <0.001 | 77.94±4.86 | 89.59±3.72 | <0.001 |
| Female, n% | 96(44.4) | 44(50.0) | 0.378 | 94(51.1) | 68(46.3) | 0.383 |
| Smoking, n(%) | 45(20.8) | 6(6.8) | 0.003 | 25(13.6) | 9(6.1) | 0.026 |
| Length of hospital stay, mean ± SD | 10.47±12.79 | 10.48±8.91 | 0.250 | 18.56±73.11 | 11.07±10.38 | 0.811 |
| In-hospital mortality | 32(14.8) | 11(12.5) | 0.377 | 40(21.7) | 38(25.9) | 0.381 |
| Comorbidities, n(%) | ||||||
| Ischemic heart Disease | 67(31.0) | 25(28.4) | 0.653 | 64(34.8) | 58(39.5) | 0.381 |
| CHF | 33(15.3) | 26(29.5) | 0.004 | 71(38.6) | 62(42.2) | 0.508 |
| COPD | 44(20.4) | 17(19.3) | 0.835 | 39(21.2) | 35(23.8) | 0.571 |
| Dyslipidemia | 90(41.7) | 25(28.4) | 0.031 | 80(43.5) | 33(22.4) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 99(45.8) | 21(23.9) | <0.001 | 93(50.5) | 46(31.3) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 146(67.6) | 73(83.0) | 0.007 | 139(75.5) | 117(79.6) | 0.372 |
| CVA | 40(18.5) | 12(13.6) | 0.305 | 37(20.1) | 38(25.9) | 0.215 |
| CRF | 57(26.4) | 22(25.0) | 0.802 | 60(32.6) | 45(30.6) | 0.698) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 34(15.7) | 26(29.5) | 0.006 | 66(35.9) | 64(43.5) | 0.156 |
| Dementia | 17(7.9) | 17(19.3) | 0.004 | 18(9.8) | 32(21.8) | 0.002 |
| Parkinson | 13(6.0) | 4(4.5) | 0.612 | 9(4.9) | 12(8.2) | 0.225 |
| History of carcinoma | 89(41.2) | 27(30.7) | 0.087 | 44(23.9) | 41(27.9) | 0.410 |
| Effusion side | ||||||
| Right | 77(35.6) | 34(38.6) | 0.841 | 62(33.7) | 45(30.6) | 0.794 |
| Left | 68(31.5) | 25(28.4) | 0.841 | 23(12.5) | 21(14.3) | 0.794 |
| Bilateral | 71(32.9) | 29(33.0) | 0.841 | 99(53.8) | 81(55.1) | 0.794 |
| Laboratory tests | ||||||
| Urea | 65.22±52.61 | 70.96±52.48 | 0.078 | 81.91±54.34 | 84.96±50.25 | 0.211 |
| Creatinine | 1.36±1.32 | 1.25±0.96 | 0.538 | 1.53±1.22 | 1.45±0.95 | 0.402 |
| Albumin | 3.11±0.64 | 3.04±0.54 | 0.276 | 3.05±0.60 | 3.05±0.57 | 0.885 |
| Cholesterol | 148.15±44.44 | 141.94±41.73 | 0.288 | 132.39±33.69 | 137.42±35.51 | 0.204 |
| LDH | 568.85±368.10 | 514.11±242.56 | 0.467 | 606.49±318.48 | 580.78±295.06 | 0.416 |
| L-side | R-side | p-value | |
| Parameters | Mean (STD) | ||
| Age | 80.59±9.13 | 82.16±8.71 | 0.019 |
| Urea | 66.32±45.64 | 79.72±54.76 | 0.017 |
| Creatinine | 1.24±0.95 | 1.5±1.25 | 0.141 |
| Albumin | 3.09±0.56 | 3.06±0.61 | 0.001 |
| Cholesterol | 140.80±38.94 | 139.78±40.28 | 0.684 |
| LDH | 548.38±288.25 | 599.23±348.84 | 0.682 |
| Length of hospital stay | 9.83±10.36 | 14.52±49.58 | 0.001 |
| Days to death | 520.24±785.88 | 415.89±695.62 | 0.038 |
| L/R-side | Bilateral | p-value | |
| Parameters | Mean ± SD | ||
| Age | 81.54±8.90 | 79.32±8.48 | 0.276 |
| Urea | 74.42±51.73 | 94.45±67.10 | 0.094 |
| Creatinine | 1.40±115 | 1.53±1.07 | 0.359 |
| Albumin | 3.07±0.59 | 2.54±0.75 | 0.002 |
| Cholesterol | 140.19±39.72 | 135.11±45.60 | 0.710 |
| LDH | 579.06±326.88 | 570.55±311.98 | 0.872 |
| Length of hospital stay | 12.66±39.14 | 24.60±24.77 | 0.005 |
| Days to death | 455.87±732.67 | 179.37±408.64 | 0.058 |
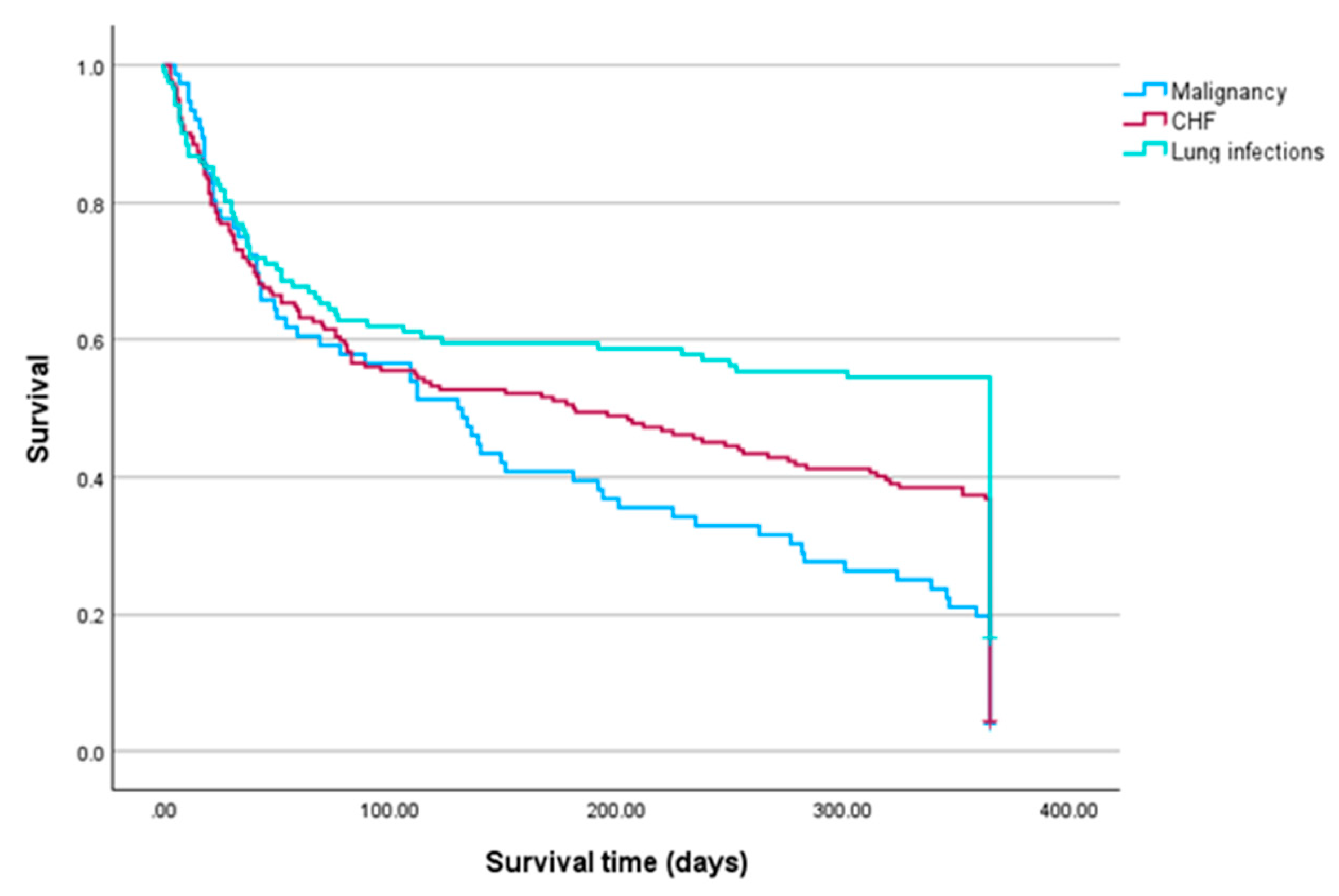
| Diseases | Died n(%) |
| Malignancy, n = 76 | 61(80.3) |
| Lung infections, n = 161 | 71(43.5) |
| CHF, n = 192 | 122(63.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




