Submitted:
01 August 2024
Posted:
06 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Techniques for Studying Protein Dynamics
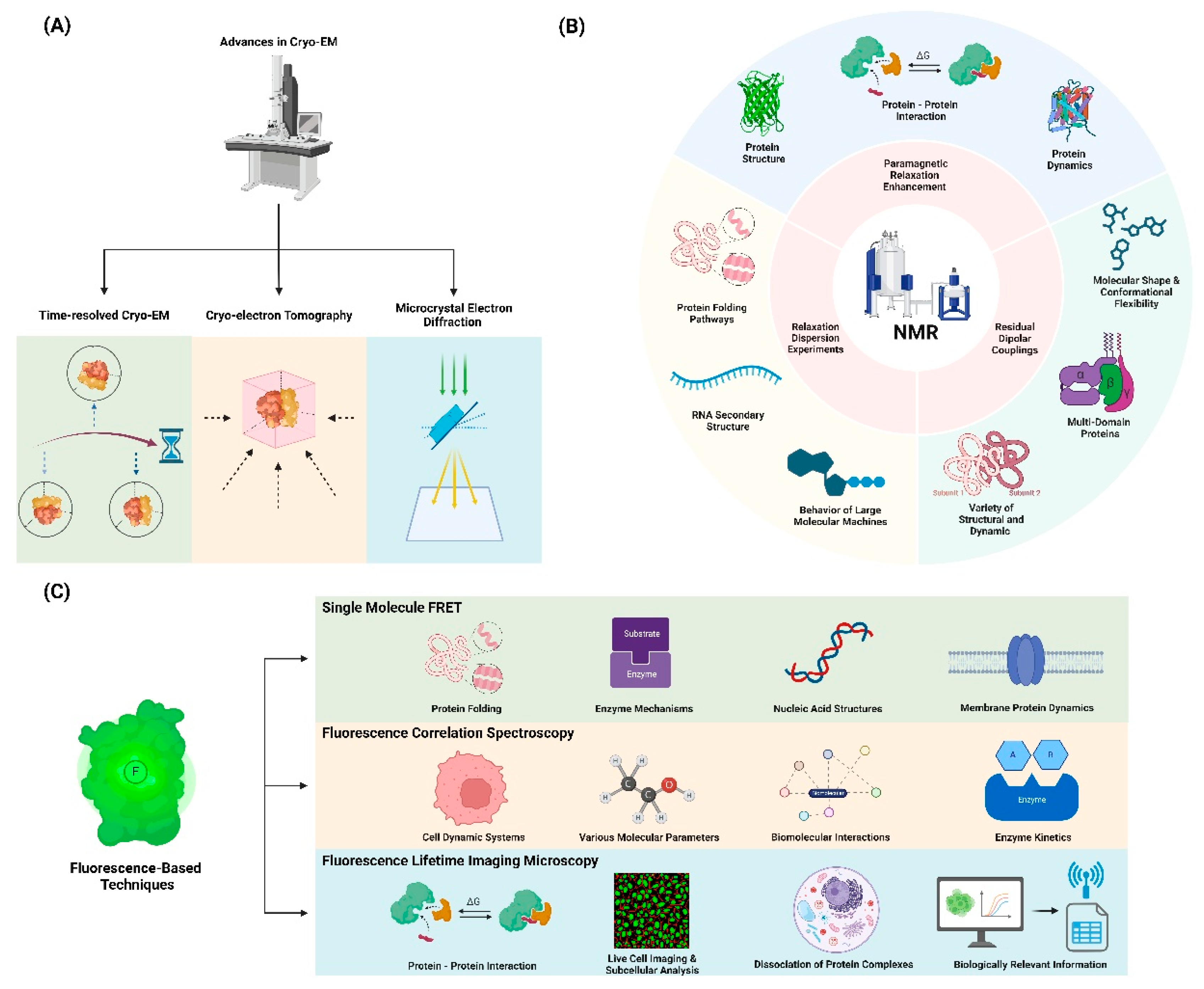
2.1. Advances in Cryo-EM for Dynamics Studies:
2.1.1. Time-resolved cryo-EM: Capturing protein motions at different time points
2.1.2. Cryo-electron tomography: Visualizing proteins in their cellular context
2.1.3. Microcrystal electron diffraction (MicroED): Studying small molecule dynamics
2.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
2.2.1. Relaxation dispersion experiments: Detecting and characterizing excited states
2.2.2. Paramagnetic relaxation enhancement (PRE): Probing long-range interactions
2.2.3. Residual dipolar couplings (RDCs): Characterizing domain orientations and flexibility
2.3. Fluorescence-Based Techniques
2.3.1. Single-molecule FRET: Probing conformational changes in individual molecules
2.3.2. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS): Analyzing diffusion and binding kinetics
2.3.3. Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM): Mapping protein interactions in cells
3. Computational Approaches to Protein Dynamics
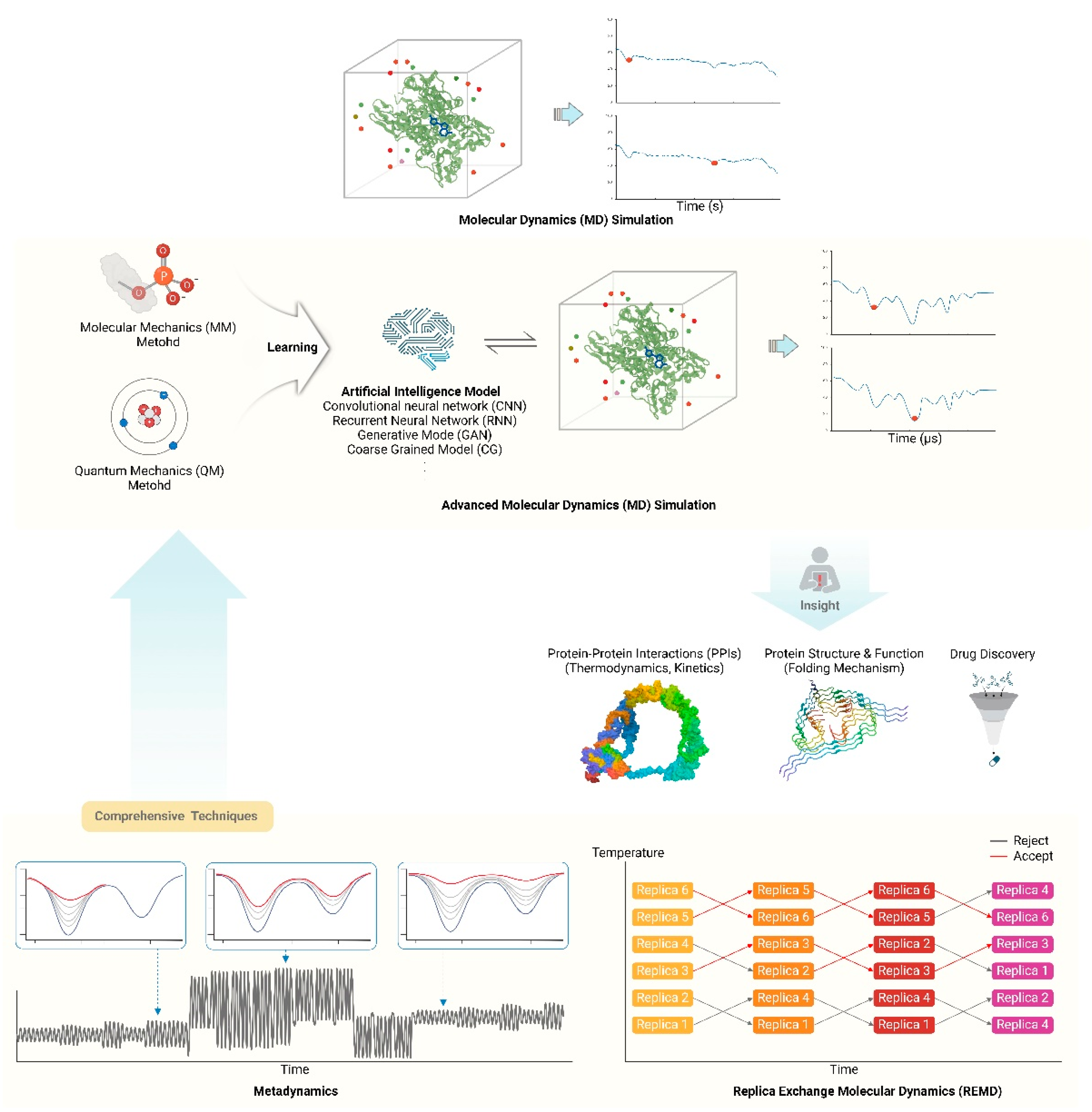
3.1. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3.1.1. Long-timescale simulations: Accessing biologically relevant timescales (ms-s)
3.1.2. Enhanced sampling techniques: Exploring rare events and conformational transitions
3.1.3. Coarse-grained models: Simulating large systems and complex assemblies
3.2. Machine Learning and AI in Protein Dynamics
3.2.1. Deep learning for feature extraction: Identifying relevant collective variables
3.2.2. Generative models: Predicting protein conformations and dynamics
3.2.3. Reinforcement learning: Optimizing sampling strategies in MD simulations
4. Applications and Insights from Protein Dynamics Studies
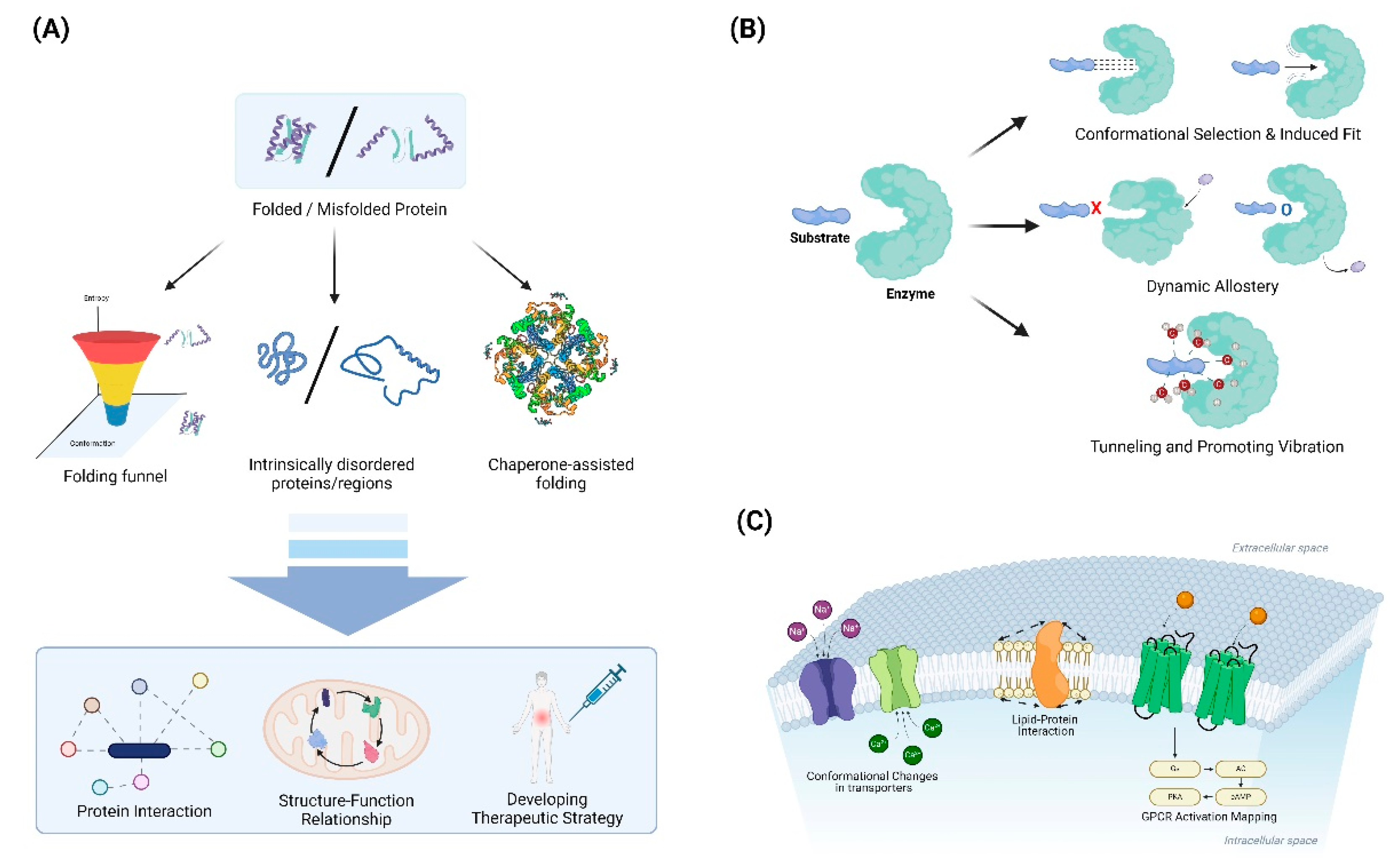
4.1. Protein Folding and Misfolding
4.1.1. Folding funnels and energy landscapes: Characterizing the thermodynamics and kinetics of folding
4.1.2. Intrinsically disordered proteins: Recognizing the functional importance of structural flexibility
4.1.3. Chaperone-assisted folding: Elucidating the role of cellular machinery in protein folding
4.2. Enzyme Catalysis and Allostery
4.2.1. Conformational selection vs. induced fit: Understanding substrate binding mechanisms
4.2.2. Dynamic allostery: Recognizing the importance of entropy in allosteric regulation
4.2.3. Tunneling and promoting vibrations: Exploring quantum effects in enzyme catalysis
4.3. Membrane Protein Dynamics
4.3.1. Lipid-protein interactions: Characterizing the influence of the membrane environment
4.3.2. Conformational changes in transporters: Elucidating alternating access mechanisms
4.3.3. GPCR activation: Mapping the energy landscape of receptor activation
5. Future Directions and Challenges
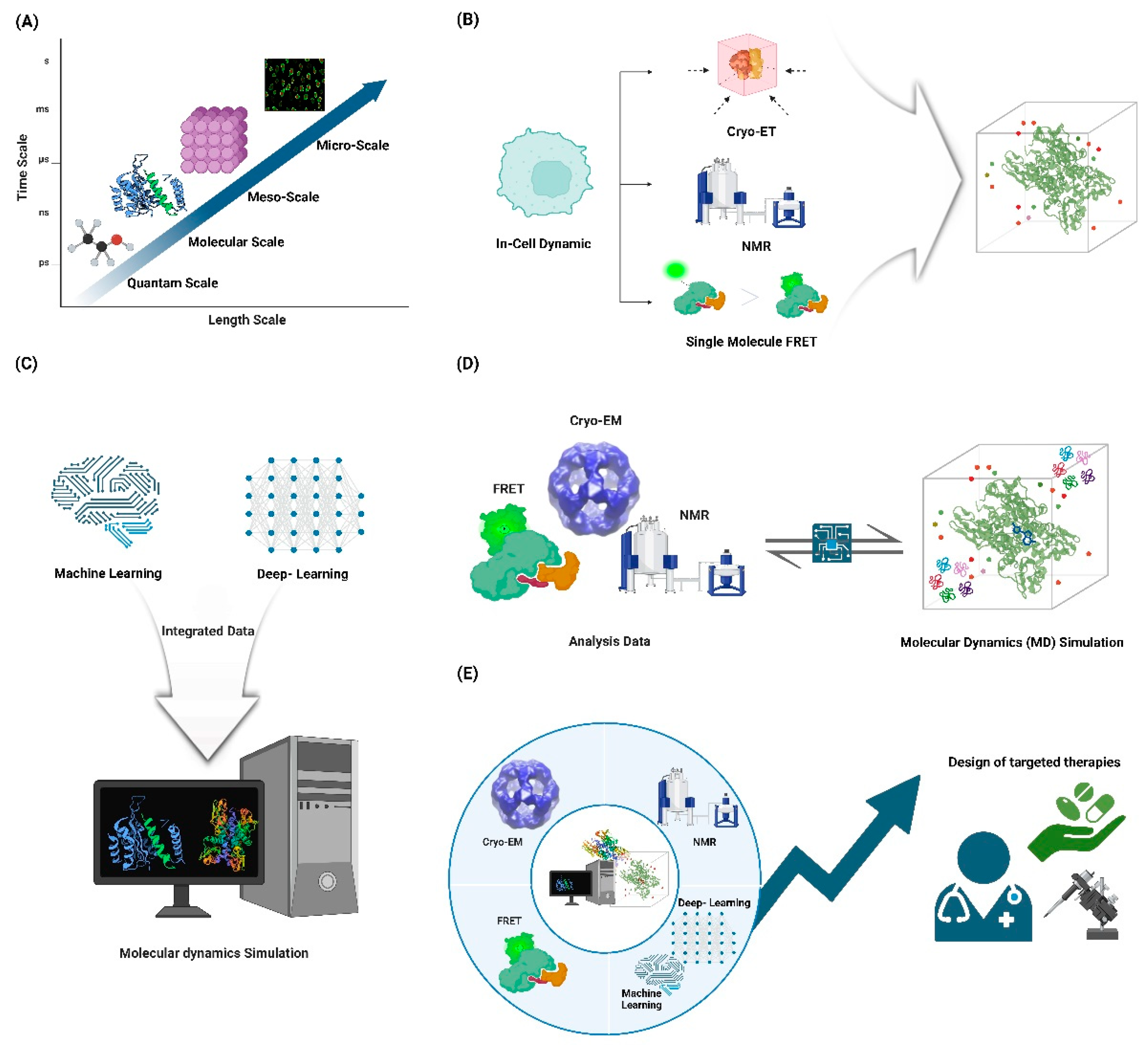
5.1. Integration of multi-scale approaches: Combining atomistic simulations with coarse-grained models and experimental data to bridge timescales and length scales.
5.2. In-cell dynamics: Developing methods to study protein motions in their native cellular environment.
5.3. AI-driven discovery: Leveraging machine learning to predict functional motions and design proteins with specific dynamic properties.
5.4. Dynamics in complex assemblies: Extending our understanding to large macromolecular complexes and cellular machines.
5.5. Linking dynamics to function: Developing quantitative frameworks to relate protein motions to biological function and disease states.
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nam, K.; Wolf-Watz, M. Protein dynamics: The future is bright and complicated! Struct Dyn 2023, 10, 014301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraman, V.; Toledo-Patino, S.; Noda-Garcia, L.; Laurino, P. Mechanisms of protein evolution. Protein Sci 2022, 31, e4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henzler-Wildman, K.A.; Lei, M.; Thai, V.; Kerns, S.J.; Karplus, M.; Kern, D. A hierarchy of timescales in protein dynamics is linked to enzyme catalysis. Nature 2007, 450, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klyshko, E.; Kim, J.S.; McGough, L.; Valeeva, V.; Lee, E.; Ranganathan, R.; Rauscher, S. Functional protein dynamics in a crystal. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca-Martinez, J.; Lazar, T.; Gavalda-Garcia, J.; Bickel, D.; Pancsa, R.; Dixit, B.; Tzavella, K.; Ramasamy, P.; Sanchez-Fornaris, M.; Grau, I.; et al. Challenges in describing the conformation and dynamics of proteins with ambiguous behavior. Front Mol Biosci 2022, 9, 959956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Biswas, A.; Radhakrishna, M. Advanced computational approaches to understand protein aggregation. Biophys Rev (Melville) 2024, 5, 021302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.G. , 3rd. NMR characterization of the dynamics of biomacromolecules. Chem Rev 2004, 104, 3623–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror, R.O.; Dirks, R.M.; Grossman, J.P.; Xu, H.; Shaw, D.E. Biomolecular simulation: a computational microscope for molecular biology. Annu Rev Biophys 2012, 41, 429–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo, P.A.; Balanay, M.P. Recent Advances in Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Tau Fibrils and Oligomers. Membranes (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grutsch, S.; Bruschweiler, S.; Tollinger, M. NMR Methods to Study Dynamic Allostery. PLoS Comput Biol 2016, 12, e1004620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzeng, S.R.; Kalodimos, C.G. Protein dynamics and allostery: an NMR view. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2011, 21, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, H.X. Protein Allostery and Conformational Dynamics. Chem Rev 2016, 116, 6503–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, S.D. Protein Dynamics and Enzymatic Catalysis. J Phys Chem B 2023, 127, 2649–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohen, A. Role of dynamics in enzyme catalysis: substantial versus semantic controversies. Acc Chem Res 2015, 48, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeagh, J.D.; Ranaghan, K.E.; Mulholland, A.J. Protein dynamics and enzyme catalysis: insights from simulations. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011, 1814, 1077–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, R.; Liu, L.; Kenner, L.R.; Clarkson, M.W.; Mavor, D.; Tawfik, D.S.; Kern, D.; Fraser, J.S. Rescue of conformational dynamics in enzyme catalysis by directed evolution. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warshel, A.; Bora, R.P. Perspective: Defining and quantifying the role of dynamics in enzyme catalysis. J Chem Phys 2016, 144, 180901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Bedem, H.; Fraser, J.S. Integrative, dynamic structural biology at atomic resolution--it's about time. Nat Methods 2015, 12, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnley, B.T.; Afonine, P.V.; Adams, P.D.; Gros, P. Modelling dynamics in protein crystal structures by ensemble refinement. Elife 2012, 1, e00311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, M.P.; Sali, A. Principles for Integrative Structural Biology Studies. Cell 2019, 177, 1384–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehr, D.D.; Nussinov, R.; Wright, P.E. The role of dynamic conformational ensembles in biomolecular recognition. Nat Chem Biol 2009, 5, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, P.E.; Dyson, H.J. Intrinsically disordered proteins in cellular signalling and regulation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2015, 16, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, M.M. The contribution of intrinsically disordered regions to protein function, cellular complexity, and human disease. Biochem Soc Trans 2016, 44, 1185–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naudi-Fabra, S.; Blackledge, M.; Milles, S. Synergies of Single Molecule Fluorescence and NMR for the Study of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Biomolecules 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, E.; Cordes, T.; Ingargiola, A.; Alhadid, Y.; Chung, S.; Michalet, X.; Weiss, S. Toward dynamic structural biology: Two decades of single-molecule Forster resonance energy transfer. Science 2018, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellenkamp, B.; Schmid, S.; Doroshenko, O.; Opanasyuk, O.; Kuhnemuth, R.; Rezaei Adariani, S.; Ambrose, B.; Aznauryan, M.; Barth, A.; Birkedal, V.; et al. Precision and accuracy of single-molecule FRET measurements-a multi-laboratory benchmark study. Nat Methods 2018, 15, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T. High-speed atomic force microscopy and its future prospects. Biophys Rev 2018, 10, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhivker, G.M.; Agajanian, S.; Hu, G.; Tao, P. Allosteric Regulation at the Crossroads of New Technologies: Multiscale Modeling, Networks, and Machine Learning. Front Mol Biosci 2020, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, R.G.; Thangapandian, S.; Schauperl, M.; Denny, R.A.; Diller, D.J. Recent applications of computational methods to allosteric drug discovery. Front Mol Biosci 2022, 9, 1070328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Doruker, P.; Li, H.; Demet Akten, E. Editorial: Understanding Protein Dynamics, Binding and Allostery for Drug Design. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 681364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeots, M.E.; Enchev, R.I. Structural dynamics: review of time-resolved cryo-EM. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 2022, 78, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, O.F.; Barrass, S.V.; Drabbels, M.; Lorenz, U.J. Fast viral dynamics revealed by microsecond time-resolved cryo-EM. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, S.J.; Keihsler, D.; Bodrug, T.; Brown, N.G.; Haselbach, D. Frozen in time: analyzing molecular dynamics with time-resolved cryo-EM. Structure 2023, 31, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebl, D.P.; Aspinall, L.; Muench, S.P. Time resolved applications for Cryo-EM; approaches, challenges and future directions. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2023, 83, 102696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeister, W. Cryo-electron tomography: A long journey to the inner space of cells. Cell 2022, 185, 2649–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucic, V.; Rigort, A.; Baumeister, W. Cryo-electron tomography: the challenge of doing structural biology in situ. J Cell Biol 2013, 202, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, C.G.; Lamboo, L.L.; Beniac, D.R.; Booth, T.F. The scanning electron microscope in microbiology and diagnosis of infectious disease. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 26516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauerlein, F.J.B.; Baumeister, W. Towards Visual Proteomics at High Resolution. J Mol Biol 2021, 433, 167187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guaita, M.; Watters, S.C.; Loerch, S. Recent advances and current trends in cryo-electron microscopy. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2022, 77, 102484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, M.; Baumeister, W. The promise and the challenges of cryo-electron tomography. FEBS Lett 2020, 594, 3243–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danelius, E.; Halaby, S.; van der Donk, W.A.; Gonen, T. MicroED in natural product and small molecule research. Nat Prod Rep 2021, 38, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.G.; Martynowycz, M.W.; Hattne, J.; Fulton, T.J.; Stoltz, B.M.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Nelson, H.M.; Gonen, T. The CryoEM Method MicroED as a Powerful Tool for Small Molecule Structure Determination. ACS Cent Sci 2018, 4, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danelius, E.; Patel, K.; Gonzalez, B.; Gonen, T. MicroED in drug discovery. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2023, 79, 102549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, L.J.; Bu, G.; Nannenga, B.L.; Gonen, T. MicroED for the study of protein-ligand interactions and the potential for drug discovery. Nat Rev Chem 2021, 5, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walinda, E.; Morimoto, D.; Sugase, K. Overview of Relaxation Dispersion NMR Spectroscopy to Study Protein Dynamics and Protein-Ligand Interactions. Curr Protoc Protein Sci 2018, 92, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clore, G.M. NMR spectroscopy, excited states and relevance to problems in cell biology - transient pre-nucleation tetramerization of huntingtin and insights into Huntington's disease. J Cell Sci 2022, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neudecker, P.; Lundstrom, P.; Kay, L.E. Relaxation dispersion NMR spectroscopy as a tool for detailed studies of protein folding. Biophys J 2009, 96, 2045–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreydoppel, M.; Lichtenecker, R.J.; Akke, M.; Weininger, U. (1)H R(1rho) relaxation dispersion experiments in aromatic side chains. J Biomol NMR 2021, 75, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeck, J.H.; Kremer, W.; Sprangers, R. A suite of (19)F based relaxation dispersion experiments to assess biomolecular motions. J Biomol NMR 2020, 74, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Kellogg, D.; Kimsey, I.J.; Sathyamoorthy, B.; Stein, Z.W.; McBrairty, M.; Al-Hashimi, H.M. Characterizing RNA Excited States Using NMR Relaxation Dispersion. Methods Enzymol 2015, 558, 39–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallurupalli, P.; Hansen, D.F.; Kay, L.E. Structures of invisible, excited protein states by relaxation dispersion NMR spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105, 11766–11771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clore, G.M.; Iwahara, J. Theory, practice, and applications of paramagnetic relaxation enhancement for the characterization of transient low-population states of biological macromolecules and their complexes. Chem Rev 2009, 109, 4108–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clore, G.M. Practical Aspects of Paramagnetic Relaxation Enhancement in Biological Macromolecules. Methods Enzymol 2015, 564, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocman, V.; Di Mauro, G.M.; Veglia, G.; Ramamoorthy, A. Use of paramagnetic systems to speed-up NMR data acquisition and for structural and dynamic studies. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson 2019, 102, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenard, A.J.; Mulder, F.A.A.; Madl, T. Solvent paramagnetic relaxation enhancement as a versatile method for studying structure and dynamics of biomolecular systems. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 2022, 132-133, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlagnitweit, J.; Tang, M.; Baias, M.; Richardson, S.; Schantz, S.; Emsley, L. Nanostructure of Materials Determined by Relayed Paramagnetic Relaxation Enhancement. J Am Chem Soc 2015, 137, 12482–12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bara-Estaun, A.; Harder, M.C.; Lyall, C.L.; Lowe, J.P.; Suturina, E.; Hintermair, U. Paramagnetic Relaxation Agents for Enhancing Temporal Resolution and Sensitivity in Multinuclear FlowNMR Spectroscopy. Chemistry 2023, 29, e202300215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swartjes, A.; White, P.B.; Bruekers, J.P.J.; Elemans, J.; Nolte, R.J.M. Paramagnetic relaxation enhancement NMR as a tool to probe guest binding and exchange in metallohosts. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Tjandra, N. The use of residual dipolar coupling in studying proteins by NMR. Top Curr Chem 2012, 326, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, A.; Henen, M.A.; Nichols, P.J.; Vogeli, B. On the use of residual dipolar couplings in multi-state structure calculation of two-domain proteins. Magn Reson Lett 2022, 2, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemak, A.; Wu, B.; Yee, A.; Houliston, S.; Lee, H.W.; Gutmanas, A.; Fang, X.; Garcia, M.; Semesi, A.; Wang, Y.X.; et al. Structural characterization of a flexible two-domain protein in solution using small angle X-ray scattering and NMR data. Structure 2014, 22, 1862–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Traaseth, N.J.; Verardi, R.; Gustavsson, M.; Gao, J.; Veglia, G. Paramagnetic-based NMR restraints lift residual dipolar coupling degeneracy in multidomain detergent-solubilized membrane proteins. J Am Chem Soc 2011, 133, 2232–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, A.; Fittolani, G.; Seeberger, P.H.; Delbianco, M.; Jimenez-Barbero, J. The Flexibility of Oligosaccharides Unveiled Through Residual Dipolar Coupling Analysis. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 784318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, D.K.; Pulido, L.E.; Kasal, S.; Huang, J. Single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer in molecular biology. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 19928–19944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Hohng, S.; Ha, T. A practical guide to single-molecule FRET. Nat Methods 2008, 5, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazal, H.; Haran, G. Single-molecule FRET methods to study the dynamics of proteins at work. Curr Opin Biomed Eng 2019, 12, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meszaros, J.; Geggier, P.; Manning, J.J.; Asher, W.B.; Javitch, J.A. Methods for automating the analysis of live-cell single-molecule FRET data. Front Cell Dev Biol 2023, 11, 1184077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agam, G.; Gebhardt, C.; Popara, M.; Machtel, R.; Folz, J.; Ambrose, B.; Chamachi, N.; Chung, S.Y.; Craggs, T.D.; de Boer, M.; et al. Reliability and accuracy of single-molecule FRET studies for characterization of structural dynamics and distances in proteins. Nat Methods 2023, 20, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Lei, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, M.; Zheng, J.; Dan, D.; Gao, P. A Comprehensive Review of Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy. Frontiers in Physics 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elson, E.L. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy: past, present, future. Biophys J 2011, 101, 2855–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jian, L.; Ding, B.; Huang, K.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, S. Principles of fluorescence correlation spectroscopy applied to studies of biomolecular liquid-liquid phase separation. Biophys Rep 2022, 8, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazani, S.; Sgouralis, I.; Shafraz, O.M.; Levitus, M.; Sivasankar, S.; Presse, S. An alternative framework for fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, R.; Heaster, T.M.; Sharick, J.T.; Gillette, A.A.; Skala, M.C. Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy: fundamentals and advances in instrumentation, analysis, and applications. J Biomed Opt 2020, 25, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, T.; Herbert, S.; Hackl, B.; Besold, J.M.; Schramek, C.; Gotzmann, J.; Elsayad, K.; Slade, D. Direct measurement of protein-protein interactions by FLIM-FRET at UV laser-induced DNA damage sites in living cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, R.; Gillette, A.; Stefely, M.; Skala, M.C. Recent innovations in fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy for biology and medicine. J Biomed Opt 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrant, J.D.; McCammon, J.A. Molecular dynamics simulations and drug discovery. BMC Biol 2011, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazim, R.; Suh, D.; Choi, S. Advances in Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Enhanced Sampling Methods for the Study of Protein Systems. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospital, A.; Goni, J.R.; Orozco, M.; Gelpi, J.L. Molecular dynamics simulations: advances and applications. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem 2015, 8, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouvet, F.; Villard, J.; Bolnykh, V.; Rothlisberger, U. Recent Advances in First-Principles Based Molecular Dynamics. Acc Chem Res 2022, 55, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhati, A.P.; Hoti, A.; Potterton, A.; Bieniek, M.K.; Coveney, P.V. Long Time Scale Ensemble Methods in Molecular Dynamics: Ligand-Protein Interactions and Allostery in SARS-CoV-2 Targets. J Chem Theory Comput 2023, 19, 3359–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkelman, G.; Jónsson, H.; Lelièvre, T.; Mousseau, N.; Voter, A.F. Long-Timescale Simulations: Challenges, Pitfalls, Best Practices, for Development and Applications. In Handbook of Materials Modeling; 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.I.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Gao, Y.Q. Enhanced sampling in molecular dynamics. J Chem Phys 2019, 151, 070902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, C.; Banisch, R.; Sarich, M.; Badowski, T.; Schütte, C. Characterization of Rare Events in Molecular Dynamics. Entropy 2013, 16, 350–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, R.C.; Melo, M.C.R.; Schulten, K. Enhanced sampling techniques in molecular dynamics simulations of biological systems. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015, 1850, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi, V.; Aureli, S.; Ansari, N.; Gervasio, F.L. OneOPES, a Combined Enhanced Sampling Method to Rule Them All. J Chem Theory Comput 2023, 19, 5731–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, M.; Perez, A.; Tholke, P.; Doerr, S.; Charron, N.E.; Giorgino, T.; Husic, B.E.; Clementi, C.; Noe, F.; De Fabritiis, G. Machine learning coarse-grained potentials of protein thermodynamics. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gómez-Bombarelli, R. Coarse-graining auto-encoders for molecular dynamics. npj Computational Materials 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Li, W. Recent Advances in Coarse-Grained Models for Biomolecules and Their Applications. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmiecik, S.; Gront, D.; Kolinski, M.; Wieteska, L.; Dawid, A.E.; Kolinski, A. Coarse-Grained Protein Models and Their Applications. Chem Rev 2016, 116, 7898–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noid, W.G. Perspective: Coarse-grained models for biomolecular systems. J Chem Phys 2013, 139, 090901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liwo, A.; Czaplewski, C.; Sieradzan, A.K.; Lipska, A.G.; Samsonov, S.A.; Murarka, R.K. Theory and Practice of Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics of Biologically Important Systems. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, M.G.; Voth, G.A. Coarse-graining methods for computational biology. Annu Rev Biophys 2013, 42, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M. Recent Advances in Deep Learning for Protein-Protein Interaction Analysis: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakat, S. Collective variable discovery in the age of machine learning: reality, hype and everything in between. RSC Adv 2022, 12, 25010–25024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, G.; Valdes-Garcia, G.; Heo, L.; Feig, M. Direct generation of protein conformational ensembles via machine learning. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharkhiz, S.; Mostafavi, M.; Birashk, A.; Karimian, S.; Khalilollah, S.; Jaferian, S.; Yazdani, Y.; Alipourfard, I.; Huh, Y.S.; Farani, M.R.; et al. The State-of-the-Art Overview to Application of Deep Learning in Accurate Protein Design and Structure Prediction. Top Curr Chem (Cham) 2024, 382, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia Venanzi, N.A.; Basciu, A.; Vargiu, A.V.; Kiparissides, A.; Dalby, P.A.; Dikicioglu, D. Machine Learning Integrating Protein Structure, Sequence, and Dynamics to Predict the Enzyme Activity of Bovine Enterokinase Variants. J Chem Inf Model 2024, 64, 2681–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, C.J. Generative models of conformational dynamics. Adv Exp Med Biol 2014, 805, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Tong, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wei, T.; Chen, H.F. Phanto-IDP: compact model for precise intrinsically disordered protein backbone generation and enhanced sampling. Brief Bioinform 2023, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Akin, H.; Rao, R.; Hie, B.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, W.; Smetanin, N.; Verkuil, R.; Kabeli, O.; Shmueli, Y.; et al. Evolutionary-scale prediction of atomic-level protein structure with a language model. Science 2023, 379, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.; Tran, D.P.; Takemura, K.; Kitao, A.; Terayama, K.; Tsuda, K. Enhancing Biomolecular Sampling with Reinforcement Learning: A Tree Search Molecular Dynamics Simulation Method. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 13853–13862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noe, F.; De Fabritiis, G.; Clementi, C. Machine learning for protein folding and dynamics. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2020, 60, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; E, W. Reinforced dynamics for enhanced sampling in large atomic and molecular systems. J Chem Phys 2018, 148, 124113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdi, S.; Smith, Z.; Herron, L.; Zou, Z.; Tiwary, P. Enhanced Sampling with Machine Learning. Annu Rev Phys Chem 2024, 75, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Sidky, H.; Ferguson, A.L. Nonlinear discovery of slow molecular modes using state-free reversible VAMPnets. J Chem Phys 2019, 150, 214114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, W.A. Modern Kinetics and Mechanism of Protein Folding: A Retrospective. J Phys Chem B 2021, 125, 3452–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, S.H.; Ham, S. Folding Free Energy Landscape of Ordered and Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 14927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolynes, P.G. Evolution, energy landscapes and the paradoxes of protein folding. Biochimie 2015, 119, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nymeyer, H.; Garcia, A.E.; Onuchic, J.N. Folding funnels and frustration in off-lattice minimalist protein landscapes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95, 5921–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Kumar, S.; Tsai, C.J.; Nussinov, R. Folding funnels and binding mechanisms. Protein Eng 1999, 12, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. Folding and binding cascades: shifts in energy landscapes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999, 96, 9970–9972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryngelson, J.D.; Onuchic, J.N.; Socci, N.D.; Wolynes, P.G. Funnels, pathways, and the energy landscape of protein folding: a synthesis. Proteins 1995, 21, 167–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, R.; Nagarajaram, H.A. Intrinsically Disordered Proteins: An Overview. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeForte, S.; Uversky, V.N. Not an exception to the rule: the functional significance of intrinsically disordered protein regions in enzymes. Mol Biosyst 2017, 13, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holehouse, A.S.; Kragelund, B.B. The molecular basis for cellular function of intrinsically disordered protein regions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2024, 25, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.; Brangwynne, C.P. Liquid phase condensation in cell physiology and disease. Science 2017, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancsa, R.; Tompa, P. Structural disorder in eukaryotes. PLoS One 2012, 7, e34687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, B.; Soranno, A.; Hofmann, H.; Nettels, D. Single-Molecule FRET Spectroscopy and the Polymer Physics of Unfolded and Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Annu Rev Biophys 2016, 45, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Their “Mysterious” (Meta)Physics. Frontiers in Physics 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, F.U.; Hayer-Hartl, M. Converging concepts of protein folding in vitro and in vivo. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2009, 16, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberek, K.; Lewandowska, A.; Zietkiewicz, S. Chaperones in control of protein disaggregation. EMBO J 2008, 27, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, N.R.; Paudel, B.P.; van Oijen, A.M.; Ecroyd, H. Real-time single-molecule observation of chaperone-assisted protein folding. Sci Adv 2022, 8, eadd0922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, S.; Salmon, L.; Koldewey, P.; Ahlstrom, L.S.; Martin, R.; Quan, S.; Afonine, P.V.; van den Bedem, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, Q.; et al. Visualizing chaperone-assisted protein folding. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2016, 23, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, Z.; Cheng, K.J.; Shukla, D. Reinforcement Learning Based Adaptive Sampling: REAPing Rewards by Exploring Protein Conformational Landscapes. J Phys Chem B 2018, 122, 8386–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balchin, D.; Hayer-Hartl, M.; Hartl, F.U. In vivo aspects of protein folding and quality control. Science 2016, 353, aac4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukau, B.; Weissman, J.; Horwich, A. Molecular chaperones and protein quality control. Cell 2006, 125, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsui, Y.; Wintrode, P.L. Hydrogen/deuterium exchange-mass spectrometry: a powerful tool for probing protein structure, dynamics and interactions. Curr Med Chem 2007, 14, 2344–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, F.U. Molecular chaperones in cellular protein folding. Nature 1996, 381, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussinov, R.; Ma, B.; Tsai, C.J. Multiple conformational selection and induced fit events take place in allosteric propagation. Biophys Chem 2014, 186, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, F.; Weikl, T.R. How to Distinguish Conformational Selection and Induced Fit Based on Chemical Relaxation Rates. PLoS Comput Biol 2016, 12, e1005067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morando, M.A.; Saladino, G.; D'Amelio, N.; Pucheta-Martinez, E.; Lovera, S.; Lelli, M.; Lopez-Mendez, B.; Marenchino, M.; Campos-Olivas, R.; Gervasio, F.L. Conformational Selection and Induced Fit Mechanisms in the Binding of an Anticancer Drug to the c-Src Kinase. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 24439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.; Shao, Y.; Major, D.T.; Wolf-Watz, M. Perspectives on Computational Enzyme Modeling: From Mechanisms to Design and Drug Development. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 7393–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wlodarski, T.; Zagrovic, B. Conformational selection and induced fit mechanism underlie specificity in noncovalent interactions with ubiquitin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 19346–19351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henzler-Wildman, K.; Kern, D. Dynamic personalities of proteins. Nature 2007, 450, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motlagh, H.N.; Wrabl, J.O.; Li, J.; Hilser, V.J. The ensemble nature of allostery. Nature 2014, 508, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussinov, R.; Tsai, C.J. Allostery in disease and in drug discovery. Cell 2013, 153, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, D.; Zuiderweg, E.R. The role of dynamics in allosteric regulation. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2003, 13, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.; Nussinov, R. A unified view of "how allostery works". PLoS Comput Biol 2014, 10, e1003394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinman, J.P.; Kohen, A. Hydrogen tunneling links protein dynamics to enzyme catalysis. Annu Rev Biochem 2013, 82, 471–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, V.L.; Schwartz, S.D. Promoting Vibrations and the Function of Enzymes. Emerging Theoretical and Experimental Convergence. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 3299–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalopin, Y.; Piazza, F.; Mayboroda, S.; Weisbuch, C.; Filoche, M. Universality of fold-encoded localized vibrations in enzymes. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutcliffe, M.J.; Scrutton, N.S. Enzymology takes a quantum leap forward. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci 2000, 358, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Mehmood, R.; Wang, M.; Qi, H.W.; Steeves, A.H.; Kulik, H.J. Revealing quantum mechanical effects in enzyme catalysis with large-scale electronic structure simulation. React Chem Eng 2019, 4, 298–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradi, V.; Sejdiu, B.I.; Mesa-Galloso, H.; Abdizadeh, H.; Noskov, S.Y.; Marrink, S.J.; Tieleman, D.P. Emerging Diversity in Lipid-Protein Interactions. Chem Rev 2019, 119, 5775–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieleman, D.P.; Sejdiu, B.I.; Cino, E.A.; Smith, P.; Barreto-Ojeda, E.; Khan, H.M.; Corradi, V. Insights into lipid-protein interactions from computer simulations. Biophys Rev 2021, 13, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Thienpont, B.; Sapuru, V.; Hite, R.K.; Dittman, J.S.; Sturgis, J.N.; Scheuring, S. Membrane-mediated protein interactions drive membrane protein organization. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.P.; Jiang, T.; Sun, C.; Lihan, M.; Pant, S.; Mahinthichaichan, P.; Trifan, A.; Tajkhorshid, E. Characterization of Lipid-Protein Interactions and Lipid-Mediated Modulation of Membrane Protein Function through Molecular Simulation. Chem Rev 2019, 119, 6086–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, R.X.; de Groot, B.L. Lipid-protein interactions modulate the conformational equilibrium of a potassium channel. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, F.; Faraldo-Gomez, J.D. Conformational free-energy landscapes of a Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger explain its alternating-access mechanism and functional specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2024, 121, e2318009121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyand, S.; Shimamura, T.; Beckstein, O.; Sansom, M.S.; Iwata, S.; Henderson, P.J.; Cameron, A.D. The alternating access mechanism of transport as observed in the sodium-hydantoin transporter Mhp1. J Synchrotron Radiat 2011, 18, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Alamo, D.; Sala, D.; McHaourab, H.S.; Meiler, J. Sampling alternative conformational states of transporters and receptors with AlphaFold2. Elife 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badiee, S.A.; Isu, U.H.; Khodadadi, E.; Moradi, M. The Alternating Access Mechanism in Mammalian Multidrug Resistance Transporters and Their Bacterial Homologs. Membranes (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deupi, X.; Kobilka, B.K. Energy landscapes as a tool to integrate GPCR structure, dynamics, and function. Physiology (Bethesda) 2010, 25, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; He, X.; Yang, Z.; Chai, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Rehman, A.U.; Ni, D.; Pu, J.; Sun, J.; et al. Activation pathway of a G protein-coupled receptor uncovers conformational intermediates as targets for allosteric drug design. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, D.; Wu, M.; Guo, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhong, L.; Cai, X.; Dai, A.; Jang, W.; Shakhnovich, E.I.; et al. Common activation mechanism of class A GPCRs. Elife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenghat, F.J.; Golan, D.E. Membrane protein dynamics and functional implications in mammalian cells. Curr Top Membr 2013, 72, 89–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, A.S.; Kooistra, A.J.; Munk, C.; Heydenreich, F.M.; Veprintsev, D.B.; Bouvier, M.; Babu, M.M.; Gloriam, D.E. GPCR activation mechanisms across classes and macro/microscales. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2021, 28, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleetwood, O.; Matricon, P.; Carlsson, J.; Delemotte, L. Energy Landscapes Reveal Agonist Control of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Activation via Microswitches. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, H.; Wales, D.J.; Leitner, D.M. Vibrational Energy Landscapes and Energy Flow in GPCRs. J Phys Chem B 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.; Pool, R.; van Dijk, E.; Bijlard, J.; Abeln, S.; Heringa, J.; Feenstra, K.A. Coarse-grained versus atomistic simulations: realistic interaction free energies for real proteins. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kamp, M.W.; Shaw, K.E.; Woods, C.J.; Mulholland, A.J. Biomolecular simulation and modelling: status, progress and prospects. J R Soc Interface 2008, 5 Suppl 3, S173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapatas, V.; Stefanidakis, M.; Jimenez, R.C.; Via, A.; Schneider, M.V. Data integration in biological research: an overview. J Biol Res (Thessalon) 2015, 22, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walpole, J.; Papin, J.A.; Peirce, S.M. Multiscale computational models of complex biological systems. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2013, 15, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Snapp, E.; Kenworthy, A. Studying protein dynamics in living cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001, 2, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalejski, J.; Sun, J.; Sharma, A. Unravelling the Mystery inside Cells by Using Single-Molecule Fluorescence Imaging. J Imaging 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Gruebele, M.; Davis, C.M. Quantifying protein dynamics and stability in a living organism. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.E.; Barethiya, S.; Nordquist, E.; Chen, J. Machine Learning Generation of Dynamic Protein Conformational Ensembles. Molecules 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audagnotto, M.; Czechtizky, W.; De Maria, L.; Kack, H.; Papoian, G.; Tornberg, L.; Tyrchan, C.; Ulander, J. Machine learning/molecular dynamic protein structure prediction approach to investigate the protein conformational ensemble. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficner, R. Highlight: integrative structural biology of dynamic macromolecular assemblies. Biol Chem 2023, 404, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, A.J.; Voth, G.A. Advances in coarse-grained modeling of macromolecular complexes. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2018, 52, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monachino, E.; Spenkelink, L.M.; van Oijen, A.M. Watching cellular machinery in action, one molecule at a time. J Cell Biol 2017, 216, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabantu, V.M.; Naveenkumar, N.; Srinivasan, N. Influence of Disease-Causing Mutations on Protein Structural Networks. Front Mol Biosci 2020, 7, 620554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.Q.; Sang, P.; Tao, Y.; Fu, Y.X.; Zhang, K.Q.; Xie, Y.H.; Liu, S.Q. Protein dynamics and motions in relation to their functions: several case studies and the underlying mechanisms. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2014, 32, 372–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacini, L.; Dorantes-Gilardi, R.; Vuillon, L.; Lesieur, C. Mapping Function from Dynamics: Future Challenges for Network-Based Models of Protein Structures. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 744646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.; Zitnik, M.; Leskovec, J. Identification of disease treatment mechanisms through the multiscale interactome. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




