Submitted:
02 August 2024
Posted:
05 August 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. INTRODUCTION
2. OVERVIEW OF KLOTHO STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND REGULATION
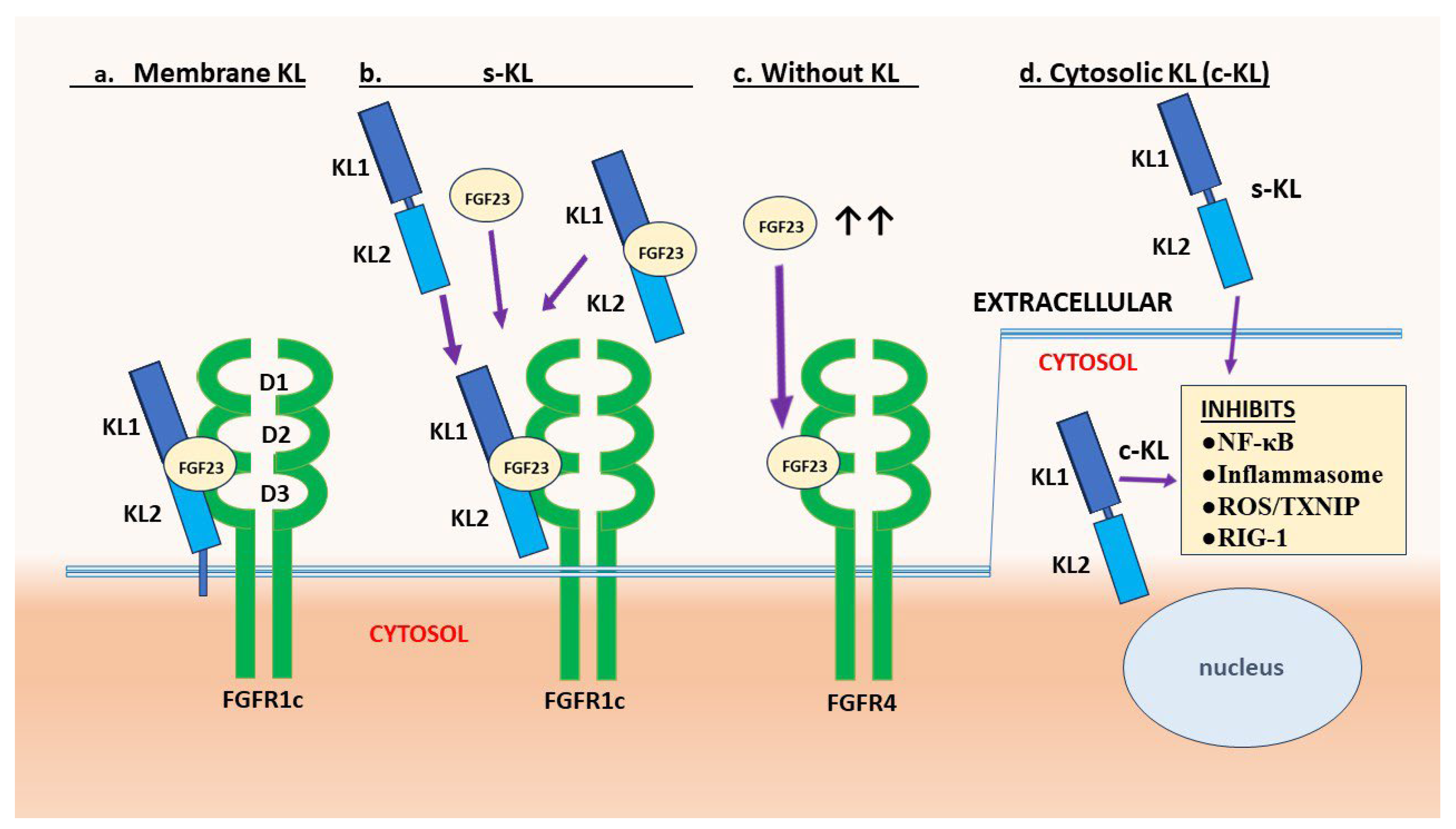
2.1. Membrane-Bound and Soluble Klotho
2.2. KL1 versus KL2 Domain Functions
2.3. Evidence of cytosolic Klotho Action
2.4. Organs and Cells that Produce Klotho
2.5. Physiological Regulators of Klotho Expression
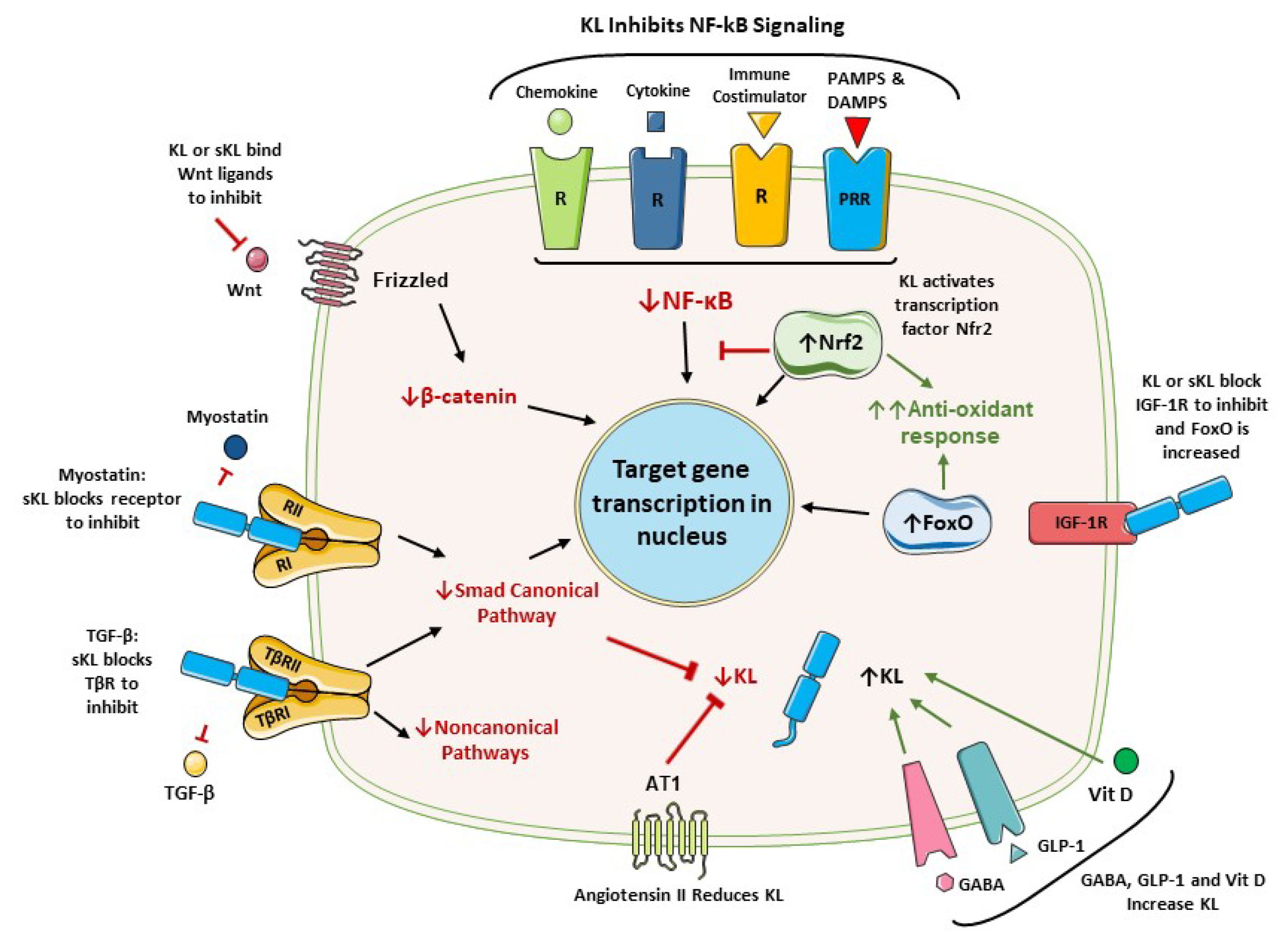
3. Anti-inflammatory Activities of Klotho
3.1. Klotho Inhibits NF-κB
| Klotho treatment Mechanisms or Organ or cells in vivo and/or concurrent events (disease) Reference in vitro |
|---|
| NF-κB↓ TLR4↓ heart (aging) [85] |
| heart (cardiotoxicity) [84] |
| intervertebral disk (degeneration) [83] |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| Nrf2↑ heart (cardiomyopathy) [82] |
| kidney (diabetes) [80] |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| Blocked NF-κB endothelial cells (+ TNFα) [79] |
| p65 nuclear endothelial cells (+ uremic toxins) [48] |
| translocation pancreatic β cells (in culture) [47] |
| alveolar mϕ (cigarette smoke ext.) [42] |
| glomerular cells (+ IFNγ; AG) |
| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| NLRP3 M2 microglial brain (Alzheimer-like disease [80] |
| inflammasome↓ differentiation↑, Aβ↓ mutant mouse) |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| TXNIP↓ brain, choroid plexus [109] |
| brain (neuroinflammation) [113] |
| heart (cardiomyopathy) [111] |
| cartilage (osteoarthritis) [110] |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Nrf2↑ brain (temporal lobe epilepsy) [115] |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| NF-κB↓ kidney (diabetes) [114] |
| testes (dioxin exposure) [108] |
| kidney (contrast-induced injury) [116] |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| NF-κB↓ endothelial-cell dysfunction [107] |
| Blocked IL-1β |
| auto-stimulation loop |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| neuronal brain (ischemic tolerance model) [117] |
| pyroptosis↓ |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Sirtuin-1↑ Nrf2↑ A549 human cell line (LPS-treated [106] |
| apoptosis↓ IL-1β↓ in vitro) |
| TNFα↓ IL-6↓ |
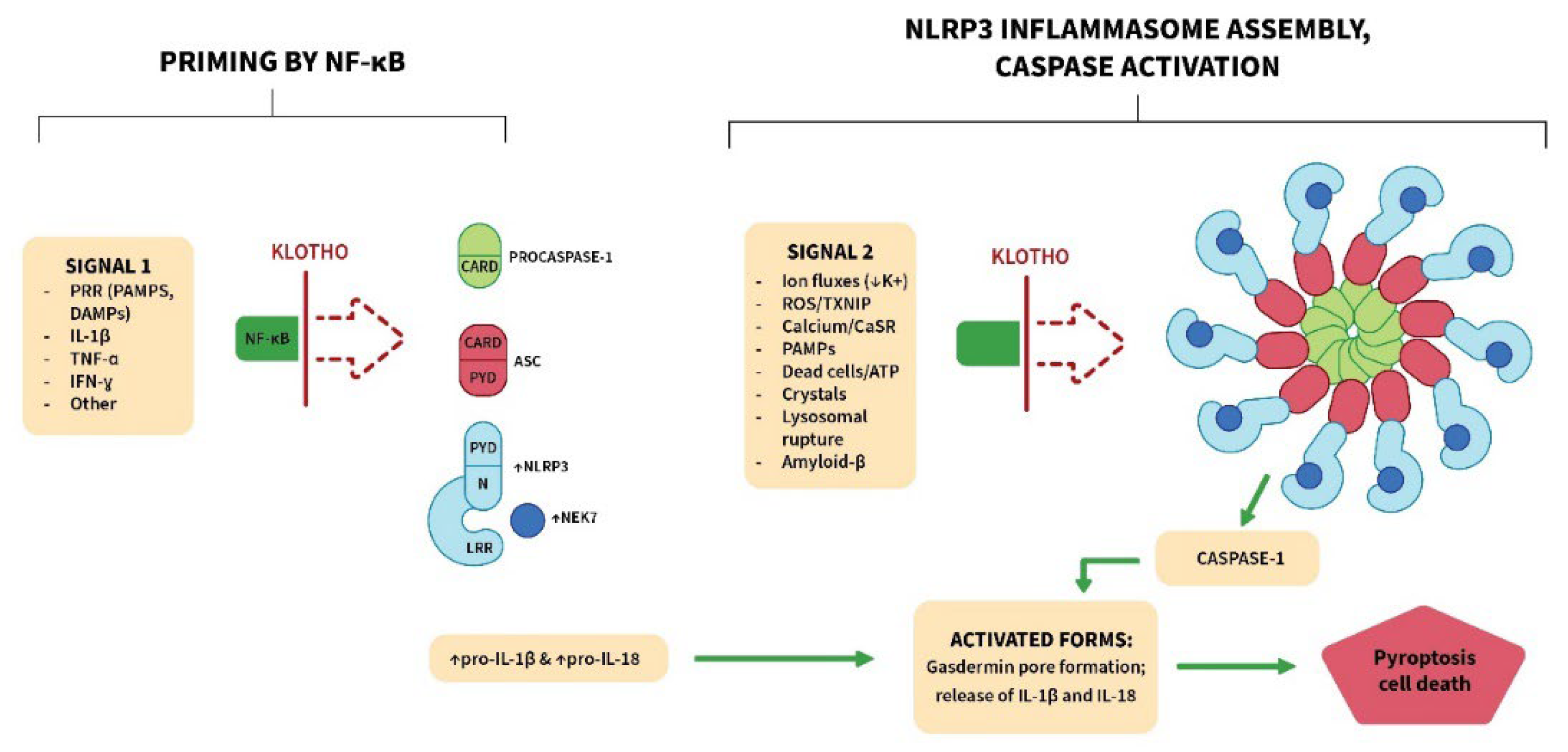
3.2. Klotho Inhibits the NLRP3 (NOD-Like Receptor Pyrin Domain Containing 3) Inflammasome
4. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress and Oxidative Stress
4.1. ER Stress
4.2. Oxidative Stress and Klotho’s Antioxidant Functions
5. Early Vascular Aging
6. Blockade of TGF-β Cytokine Family Members
6.1. Signaling TGF-β Receptors are Blocked
6.2. Klotho Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Fibrosis
6.3. Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EndMT)
6.4. Inhibition of Myostatin and Treatment of Sarcopenia
7. Role of Klotho in Diabetes
7.1. Protection against β-Cell Injury
7.2. Advanced Glycation End Products
7.3. Diabetic Retinopathy and Age-Related Macular Degeneration
8. Protection against Neurodegenerative Pathologies
8.1. Klotho production in the brain
| Species/disease Sample Techniques Main findings Reference |
|---|
| Human/AD Serum & ELISA KL serum and CSF levels [224] |
| CSF positively correlated with cognition, |
| negatively correlated with dementia |
| rating (apoE4 positive or not). |
| Human Serum ELISA KL serum levels positively [226] |
| correlated with cognition |
| (60-79 year old subjects). |
| Human/AD Serum & ELISA KL-VS variant carriers had [222] |
| CSF higher KL levels than noncarriers. |
| Human/AD Brain PET KL-VShet associated with (in vivo) lower tau, better memory. |
| Human/AD CSF & ELISA KL lower in CSF of AD; high KL [223] |
| plasma in CSF associated with improved |
| tau and Aβ biomarkers in CSF. |
| Human/AD Blood qPCR KL was lower in cells [228] |
| & FTD mononuclear from AD and FTD; no |
| cells KL-VS effect. |
| Human / Plasma ELISA, Higher KL levels associated [217] |
| cerebrovascular cerebral with lesser cerebral small |
| disease (stroke) imaging vessel disease. |
| Human Brain In vitro KL inhibited neuronal [221] |
| organoids culture senescence. |
| Human neural In vitro KL increased neuronal [218] |
| hippocampal culture differentiation and reduced |
| progenitors cell death by apoptosis. |
| Nonhuman Serum KL s.c., KL injection improved [225] cognitive performance in cognitive tests. |
| Human N/A N/A KL functions in the brain. [216,219,229] |
8.2 Neuropathologic Findings and the Role of Neuroinflammation
8.3. Evidence that Klotho Counters Neurodegenerative Diseases
9. Therapy with Klotho
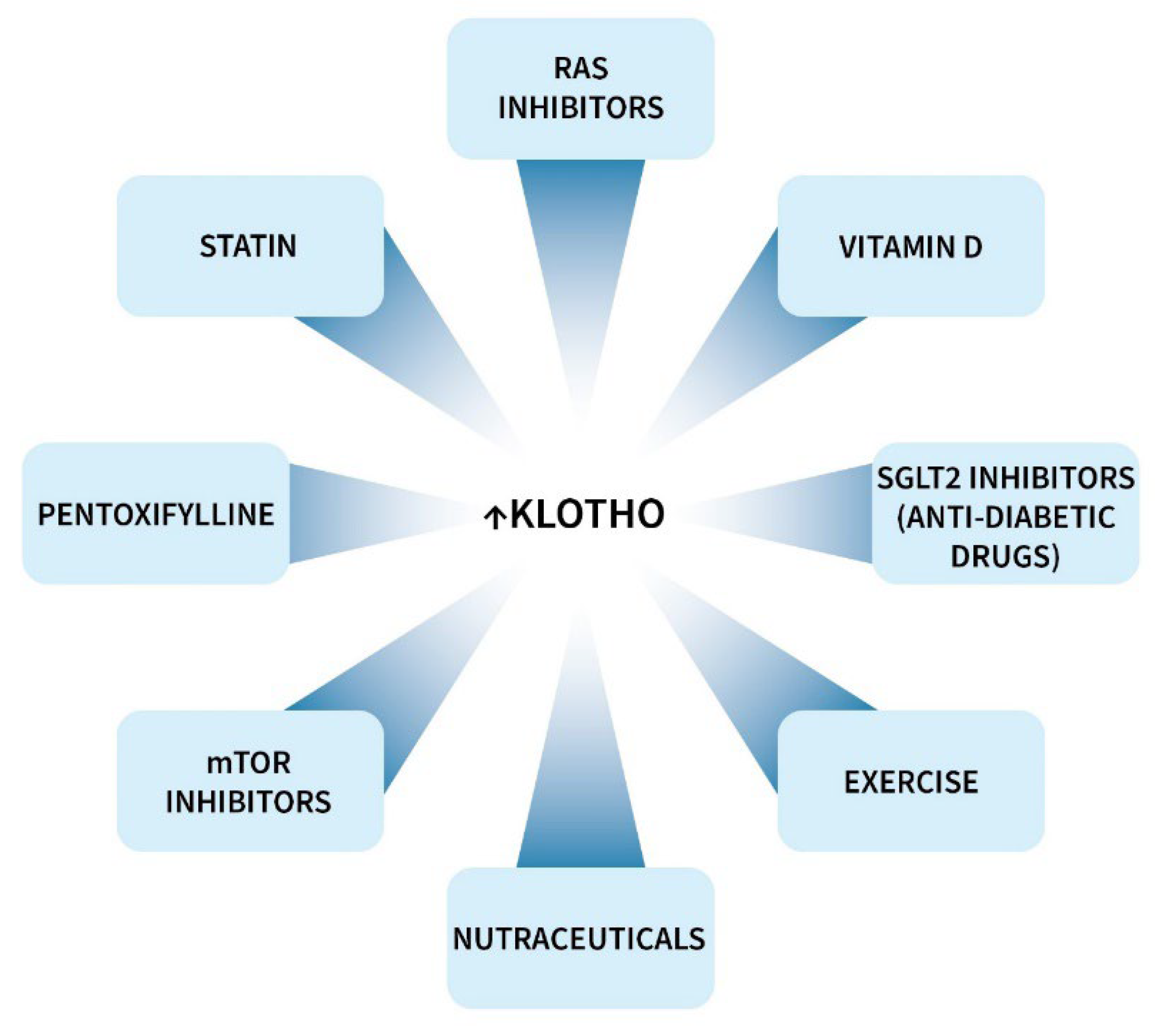
9.1. Klotho-Enhancing Strategies
9.2. Non-linear Klotho Responses
10. CONCLUSION
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M. Kuro-o, The Klotho proteins in health and disease, Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 15(1) (2019) 27-44. [PMID: 30455427]. [CrossRef]
- K. Lim, A. Halim, T.S., et al., 2019. Klotho: A Major Shareholder in Vascular Aging Enterprises. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20(18):4637. [PMID: 31546756]. [CrossRef]
- S. Buchanan, E. Combet, P. Stenvinkel, et al., 2020. Klotho, Aging, and the Failing Kidney. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 11:560. [PMID: 32982966]. [CrossRef]
- M. Typiak, A. Piwkowska A, 2021. Antiinflammatory Actions of Klotho: Implications for Therapy of Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22(2):956. [PMID: 33478014]. [CrossRef]
- G.J. Prud'homme, M. Kurt, Q. Wang, 2022. Pathobiology of the Klotho Antiaging Protein and Therapeutic Considerations. Front. Aging. 3:931331. [PMID: 35903083]. [CrossRef]
- D. Edmonston, A. Grabner, M. Wolf M, 2023. FGF23 and klotho at the intersection of kidney and cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. Online ahead of print. [PMID: 37443358]. [CrossRef]
- M. Kanbay, S. Copur, L. Ozbek L, et al., 2023. Klotho: a potential therapeutic target in aging and neurodegeneration beyond chronic kidney disease-a comprehensive review from the ERA CKD-MBD working group. Clin. Kidney J. 17(1):sfad276. [PMID: 38213484]. [CrossRef]
- A. Tang, Y. Zhang, L. Wu L, et al., 2023. Klotho's impact on diabetic nephropathy and its emerging connection to diabetic retinopathy. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 14:1180169. [PMID: 37143722]. [CrossRef]
- M. Kuro-o, Y. Matsumura, H. Aizawa, et al., Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing, Nature. 390(6655) (1997) 45-51. [PMID: 9363890]. [CrossRef]
- H. Kurosu, M. Yamamoto, J.D. Clark JD, et al., Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho, Science. 309(5742) (2005) 1829-1833. [PMID: 16123266]. [CrossRef]
- M.C. Hu, M. Kuro-o, O.W. Moe, Klotho and chronic kidney disease, Contrib. Nephrol. 180 (2013) 47-63. [PMID: 23652549]. [CrossRef]
- M.C. Hu, M. Shi, J. Zhang J, et al., Renal Production, Uptake, and Handling of Circulating alphaKlotho, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 27(1) (2016) 79-90. [PMID: 25977312]. [CrossRef]
- M.C. Hu, M. Shi, N. Gillings, et al., Recombinant alpha-Klotho may be prophylactic and therapeutic for acute to chronic kidney disease progression and uremic cardiomyopathy. Kidney Int. 91(5) (2017) 1104-1114. [PMID: 28131398]. [CrossRef]
- M. Kuro-o, Klotho in health and disease, Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 21(4) (2012) 362-368. [PMID: 22660551]. [CrossRef]
- R.G. Erben, O. Andrukhova, FGF23-Klotho signaling axis in the kidney, Bone. 100 (2017) 62-68. [PMID: 27622885]. [CrossRef]
- Abraham CR, Li A., 2022. Aging-suppressor Klotho: Prospects in diagnostics and therapeutics. Ageing Res. Rev. 82:101766. [PMID: 36283617]. [CrossRef]
- Z. Wen, X. Liu, T. Zhang, 2024, L-shaped association of systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) with serum soluble alpha-Klotho in the prospective cohort study from the NHANES database. Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 8;14(1):13189. [PMID: 38851827]. [CrossRef]
- Luo K., 2017. Signaling Cross Talk between TGF-beta/Smad and Other Signaling Pathways. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 9(1):a022137. [PMID: 27836834]. [CrossRef]
- A.C. Mullen, J. L. Wrana JL., 2017. TGF-beta Family Signaling in Embryonic and Somatic Stem-Cell Renewal and Differentiation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 9(7):a022186. [PMID: 28108485]. [CrossRef]
- R. Derynck, E.H. Budi, 2019. Specificity, versatility, and control of TGF-β family signaling. Sci. Signal. 12(570):eaav5183. [PMID: 30808818]. [CrossRef]
- Q. Guo, Y. Jin, X. Chen, et al., 2024. NF-kB in biology and targeted therapy: new insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 9(1):53. [PMID: 38433280]. [CrossRef]
- M. Sopjani, M. Rinnerthaler, J. Kruja , M. Dermaku-Sopjani, 2015. Intracellular signaling of the aging suppressor protein Klotho. Curr. Mol. Med. 15(1):27-37. [PMID: 25601466]. [CrossRef]
- T. Rubinek, I. Wolf, 2016. The Role of Alpha-Klotho as a Universal Tumor Suppressor. Vitam. Horm. 101:197-214. [PMID: 27125743]. [CrossRef]
- F. Ewendt, M. Feger, M. Föller, 2021. Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) and αKlotho in Cancer. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 8:601006. [PMID: 33520985]. [CrossRef]
- R.G. Erben, 2018. Physiological Actions of Fibroblast Growth Factor-23. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 9:267. [PMID: 29892265]. [CrossRef]
- G. Chen, Y. Liu, R. Goetz, et al., α-Klotho is a non-enzymatic molecular scaffold for FGF23 hormone signalling, Nature 553(7689) (2018) 461-466. [PMID: 29342138]. [CrossRef]
- D. Zou, W. Wu, Y. He Y, et al., (2018). The role of klotho in chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 19(1):285. [PMID: 30348110]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Suzuki, E. Kuzina, S.J. An, et al., 2020. FGF23 contains two distinct high-affinity binding sites enabling bivalent interactions with α-Klotho. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 117(50):31800-31807. [PMID: 33257569]. [CrossRef]
- J.A. Neyra, M.C. Hu, O.W. Moe OW, Klotho in Clinical Nephrology: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications, Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16(1) (2021) 162-176. [PMID: 32699047]. [CrossRef]
- V. Saar-Kovrov, M.M.P.C. Donners, E.P.C. van der Vorst EPC, 2021. Shedding of Klotho: Functional Implications in Chronic Kidney Disease and Associated Vascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 7:617842. [PMID: 33585584]. [CrossRef]
- F. Sun, P. Liang, B. Wang, W. Liu, 2023. The fibroblast growth factor-Klotho axis at molecular level. Open Life Sci. 18(1):20220655. [PMID: 37941788]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Xu, Z. Sun, Molecular basis of Klotho: from gene to function in aging, Endocr. Rev. 36(2) (2015) 174-193. [PMID: 25695404]. [CrossRef]
- G.D. Dalton, J. Xie, S.W. An, C.L. Huang, 2017. New Insights into the Mechanism of Action of Soluble Klotho. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 8:323. [PMID: 29250031]. [CrossRef]
- R. Mencke, G. Harms, J. Moser, et al., 2017. Human alternative Klotho mRNA is a nonsense-mediated mRNA decay target inefficiently spliced in renal disease. JCI Insight. 2(20):e94375. [PMID: 29046474]. [CrossRef]
- L. Chen, L. Fu, J. Sun, et al., Structural basis for FGF hormone signalling. Nature. 618(7966) (2023) 862-870. [PMID: 37286607]. [CrossRef]
- Urakawa, Y. Yamazaki, T. Shimada , et al., Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for FGF23. Nature. 444(7120) (2006) 770-774. [PMID: 17086194]. [CrossRef]
- E.R. Smith, S.G. Holt, T.D. Hewitson, 76αKlotho-FGF23 interactions and their role in kidney disease: a molecular insight, Cell Mol. Life. Sci. (23) (2019) 4705-4724. [PMID: 31350618]. [CrossRef]
- Yanucil C, Kentrup D, Campos I, et al., Soluble alpha-klotho and heparin modulate the pathologic cardiac actions of fibroblast growth factor 23 in chronic kidney disease, Kidney Int.102(2) (2022) 261-279. [PMID: 35513125]. [CrossRef]
- S.M. Thomas, Q. Li, C. Faul, Fibroblast growth factor 23, klotho and heparin. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 32(4) (2023) 313-323. [PMID: 37195242]. [CrossRef]
- B.B. Ho, C. Bergwitz, FGF23 signalling and physiology, J. Mol. Endocrinol. 66(2) (2021) R23-R32. [PMID: 33338030]. [CrossRef]
- T. Nakano, H. Kishimoto, M. Tokumoto, 2023. Direct and indirect effects of fibroblast growth factor 23 on the heart. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne).14:1059179. [PMID: 36909314]. [CrossRef]
- L. Li, Y. Wang, W. Gao W, et al., Klotho Reduction in Alveolar Macrophages Contributes to Cigarette Smoke Extract-induced Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, J. Biol. Chem. 290(46) (2015) 27890-27900. [PMID: 26385922]. [CrossRef]
- J. Hu, B. Su, X. Li, et al., 2021. Klotho overexpression suppresses apoptosis by regulating the Hsp70/Akt/Bad pathway in H9c2(2-1) cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 21(5):486. [PMID: 33790995]. [CrossRef]
- F. Liu, S. Wu, H. Ren, J. Gu, Klotho suppresses RIG-I-mediated senescence-associated inflammation, Nat. Cell Biol. 13(3) (2011) 254-262. [PMID: 21336305]. [CrossRef]
- S. Nakayama, J. Sun, Y. Horikoshi, et al., Klotho protects chromosomal DNA from radiation-induced damage, J. Biochem. 173(5) (2023) 375-382. [PMID: 36634373]. [CrossRef]
- D.C. German, I. Khobahy, J. Pastor, et al., Nuclear localization of Klotho in brain: an anti-aging protein, Neurobiol. Aging. 33(7) (2012) 1483.e25-30. [PMID: 22245317]. [CrossRef]
- G.J. Prud'homme, Y. Glinka, M. Kurt, W. Liu, Q. Wang, The anti-aging protein Klotho is induced by GABA therapy and exerts protective and stimulatory effects on pancreatic β cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 493(4) (2017) 1542-1547. [PMID: 2899319]. [CrossRef]
- Buendía P, Carracedo J, Soriano S, et al., (2015) α-Klotho Prevents NFκB Translocation and Protects Endothelial Cell From Senescence Induced by Uremia. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 70(10):1198-209. [PMID: 25246106]. [CrossRef]
- P. Buendía, R. Ramírez, P. Aljama, J. Carracedo, α-Klotho Prevents Translocation of NFκB, Vitam. Horm. 101 (2016) 119-50. [PMID: 27125740]. [CrossRef]
- T. He, J. Xiong, Y. Huang, et al., 2019. Klotho restrain RIG-1/NF-κB signaling activation and monocyte inflammatory factor release under uremic condition. Life Sci. 231:116570. [PMID: 31207307]. [CrossRef]
- M. Azubel, S.D. Carter, J. Weiszmann J, et al., 2019). FGF21 trafficking in intact human cells revealed by cryo-electron tomography with gold nanoparticles. Elife. 8:e43146. [PMID: 30688648]. [CrossRef]
- M. Zakrzewska, V. Sørensen, Y. Jin, et al., Translocation of exogenous FGF1 into cytosol and nucleus is a periodic event independent of receptor kinase activity, Exp. Cell Res. 317(7) (2011) 1005-1015. [PMID: 21223966]. [CrossRef]
- M. Pozniak, A. Sokolowska-Wedzina, K. Jastrzebski, et al., FGFR1 clustering with engineered tetravalent antibody improves the efficiency and modifies the mechanism of receptor internalization, Mol. Oncol. 14(9) (2020) 1998-2021. [PMID: 32511887]. [CrossRef]
- K. Lim, A. Groen, G. Molostvov, et al., alpha-Klotho Expression in Human Tissues, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100(10) (2015) E1308-1318. [PMID: 26280509]. [CrossRef]
- B. Richter, J. Haller, D. Haffner, et al., Klotho modulates FGF23-mediated NO synthesis and oxidative stress in human coronary artery endothelial cells, Pflugers Arch. 468(9) (2016) 1621-1635. [PMID: 27448998]. [CrossRef]
- R. Mencke, J.L. Hillebrands, NIGRAM consortium, The role of the anti-ageing protein Klotho in vascular physiology and pathophysiology, Ageing Res. Rev. 35 (2017) 124-146. [PMID: 27693241]. [CrossRef]
- J. Donate-Correa, E. Martín-Núñez, A. Martin-Olivera, et al., 2023. Klotho inversely relates with carotid intima- media thickness in atherosclerotic patients with normal renal function (eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73m2): a proof-of-concept study. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 14:1146012. [PMID: 37274332]. [CrossRef]
- C.P. Chung, Y.C. Chang, Y. Ding, et al., 2017. α-Klotho expression determines nitric oxide synthesis in response to FGF-23 in human aortic endothelial cells. PLoS One. 12(5):e0176817. [PMID: 28463984]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Saito, T. Yamagishi, T. Nakamura, et al., Klotho protein protects against endothelial dysfunction, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 248(2) (1998) 324-9. [PMID: 9675134]. [CrossRef]
- T. Nagai, K. Yamada, H.C. Kim, et al., Cognition impairment in the genetic model of aging klotho gene mutant mice: a role of oxidative stress, FASEB J. 17(1) (2003) 50-52. [PMID: 12475907]. [CrossRef]
- R.D. Thurston, C.B. Larmonier, P.M. Majewski, et al., Tumor necrosis factor and interferon-gamma down-regulate Klotho in mice with colitis, Gastroenterology. 138(4) (2010) 1384-1394, 1394.e1-2. [PMID: 20004202]. [CrossRef]
- S.E. Wu, W.L. Chen, Soluble klotho as an effective biomarker to characterize inflammatory states, Ann. Med. 54(1) (2022) 1520-1529. [PMID: 35603960]. [CrossRef]
- Q. Zhou, S. Lin, R. Tang, et al., Role of Fosinopril and Valsartan on Klotho Gene Expression Induced by Angiotensin II in Rat Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells, Kidney Blood Press Res. 33(3) (2010) 186-192. [PMID: 20571281]. [CrossRef]
- N. Kuwahara, S. Sasaki, M. Kobara, et al., HMG-CoA reductase inhibition improves anti-aging klotho protein expression and arteriosclerosis in rats with chronic inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis, Int. J. Cardiol. 123(2) (2008) 84-90. [PMID: 17434618]. [CrossRef]
- H. Narumiya, S. Sasaki, N. Kuwahara, et al., HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors up-regulate anti-aging klotho mRNA via RhoA inactivation in IMCD3 cells, Cardiovasc. Res. 64(2) (2004) 331-336. [PMID: 15485693]. [CrossRef]
- R. Marsell, T. Krajisnik, H. Göransson, et al., Gene expression analysis of kidneys from transgenic mice expressing fibroblast growth factor-23, Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 23(3) (2008) 827-833. [PMID: 17911089]. [CrossRef]
- P. Kuczera, M. Adamczak, A. Wiecek, 2016. Fibroblast Growth Factor-23-A Potential Uremic Toxin. Toxins (Basel). 8(12):369. [PMID: 27941640]. [CrossRef]
- S. Rausch, M. Föller, The regulation of FGF23 under physiological and pathophysiological conditions, Pflugers Arch. 474(3) (2022) 281-292. [PMID: 35084563]. [CrossRef]
- H. Sugiura, T. Yoshida, S. Shiohira, et al., 2012. Reduced Klotho expression level in kidney aggravates renal interstitial fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 302(10):F1252-64. [PMID: 22338084]. [CrossRef]
- S.S. Li, M.J. Sheng , Z.Y. Sun, et al., 2023. Upstream and downstream regulators of Klotho expression in chronic kidney disease. Metabolism. 142:155530. [PMID: 36868370]. [CrossRef]
- A.J.P.O. de Almeida, M.S. de Almeida Rezende, S.H. Dantas, et al., 2020. Unveiling the Role of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress on Age-Related Cardiovascular Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020:1954398. [PMID: 32454933]. [CrossRef]
- T. Fulop, A. Larbi, G. Pawelec, et al., 2021. Immunology of Aging: the Birth of Inflammaging. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 1-14. [PMID: 34536213]. [CrossRef]
- J.J. Baechle, N. Chen, P. Makhijani, et al., 2023. Chronic inflammation and the hallmarks of aging. Mol. Metab. 74:101755. [PMID: 37329949]. [CrossRef]
- X. Li, C. Li, W. Zhang, et al., 2023. Inflammation and aging: signaling pathways and intervention therapies. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8(1):239. [PMID: 37291105]. [CrossRef]
- M. Haga, M. Okada, Systems approaches to investigate the role of NF-kappaB signaling in aging, Biochem. J. 479(2) (2022) 161-183. [PMID: 35098992]. [CrossRef]
- M. Khalid, G. Petroianu, A. Adem, 2022. Advanced Glycation End Products and Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Biomolecules. 12(4):542. [PMID: 35454131]. [CrossRef]
- A. Roberti, L.E. Chaffey, D.R. Greaves, 2022. NF-κB Signaling and Inflammation-Drug Repurposing to Treat Inflammatory Disorders? Biology (Basel). 11(3):372. [PMID: 35336746]. [CrossRef]
- J. Zindel, P. Kubes, DAMPs, PAMPs, and LAMPs in Immunity and Sterile Inflammation, Annu. Rev. Pathol. 15 (2020) 493-518. [PMID: 31675482]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Maekawa, K. Ishikawa, O. Yasuda O, et al., Klotho suppresses TNF-alpha-induced expression of adhesion molecules in the endothelium and attenuates NF-kappaB activation, Endocrine. 35(3) (2009) 341-6. [PMID: 19367378]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhao, C.Y. Zeng, X.H. Li, et al., 2020. Klotho overexpression improves amyloid-β clearance and cognition in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Aging Cell. 19(10):e13239. [PMID: 32964663]. [CrossRef]
- K. Yang, C. Du, X. Wang, et al., Indoxyl sulfate induces platelet hyperactivity and contributes to chronic kidney disease-associated thrombosis in mice, Blood. 129(19) (2017) 2667-2679. [PMID: 28264799]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Guo, X. Zhuang, Z. Huang, et al., Klotho protects the heart from hyperglycemia-induced injury by inactivating ROS and NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation both in vitro and in vivo, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1864(1) (2018) 238-251. [PMID: 28982613]. [CrossRef]
- F. Bi, W. Liu, Z. Wu, et al., 2020. Antiaging Factor Klotho Retards the Progress of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration through the Toll-Like Receptor 4-NF-κB Pathway. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2020:8319516. [PMID: 32256598. [CrossRef]
- S. Yu, H. Yang, X. Guo, Y. Sun, Klotho attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiotoxicity through suppression of necroptosis and oxidative stress, Mol. Med. Rep. 23(1) (2021) 66. [PMID: 33215215]. [CrossRef]
- 85] Y. Wang, K. Wang, Y. Bao, et al., 2022. The serum soluble Klotho alleviates cardiac aging and regulates M2a/M2c macrophage polarization via inhibiting TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB pathway. Tissue Cell. 76:101812. [PMID: 35597178]. [CrossRef]
- K.D. Tsai, Y.C. Lee, B.Y. Chen, et al., Recombinant Klotho attenuates IFNγ receptor signaling and SAMHD1 expression through blocking NF-κB translocation in glomerular mesangial cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 20(6) (2023) 810-817. [PMID: 37213666]. [CrossRef]
- J.A. Moreno, M.C. Izquierdo, M.D. Sanchez-Niño, et al., The inflammatory cytokines TWEAK and TNFα reduce renal klotho expression through NFκB, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 22(7) (2011) 1315-1325. [PMID: 21719790]. [CrossRef]
- O. Paerewijck, M. Lamkanfi, 2022. The human inflammasomes. Mol. Aspects Med. 88:101100. [PMID: 35696786]. [CrossRef]
- T. Accogli, C. Hibos, F. Vegran, Canonical and non-canonical functions of NLRP3, J. Adv. Res. 53 (2023) 137-151. [PMID: 36610670]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Dai, J. Zhou, C. Shi. 2023. Inflammasome: structure, biological functions, and therapeutic targets. MedComm (2020). 4(5):e391. [PMID: 37817895]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Jiang, S. Gao, Z. Chen, et al., 2023. Pyroptosis in septic lung injury: Interactions with other types of cell death. Biomed. Pharmacother. 31;169:115914. [PMID: 38000360]. [CrossRef]
- S. Oh, J. Lee, J. Oh, et al., 2023. Integrated NLRP3, AIM2, NLRC4, Pyrin inflammasome activation and assembly drive PANoptosis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 20(12):1513-1526. [PMID: 38008850]. [CrossRef]
- D. Li, M. Wu, 2021. Pattern recognition receptors in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 6(1):291. [PMID: 34344870]. [CrossRef]
- C. Moltrasio, M. Romagnuolo, A.V. Marzano, 2022. NLRP3 inflammasome and NLRP3-related autoinflammatory diseases: From cryopyrin function to targeted therapies. Front. Immunol. 13:1007705. [PMID: 36275641]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Chen, X. Ye, G. Escames, et al., 2023. The NLRP3 inflammasome: contributions to inflammation-related diseases. Cell, Mol, Biol, Lett. 28(1):51. [PMID: 37370025]. [CrossRef]
- H. Cheng, L. Chen, M. Huang, et al., 2022. Hunting down NLRP3 inflammasome: An executioner of radiation-induced injury. Front. Immunol. 13:967989. [PMID: 36353625]. [CrossRef]
- S.K. Kim, The Mechanism of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Pathogenic Implication in the Pathogenesis of Gout, J Rheum Dis. 29(3) (2022) 140-153. [PMID: 37475970. [CrossRef]
- Z. Yuan, D. Yu, T. Gou, et al., 2023. Research progress of NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors with aging diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 957:175931. [PMID: 37495038]. [CrossRef]
- N. Zhao, C.C. Li, B. Di, L.L. Xu, 2020. Recent advances in the NEK7-licensed NLRP3 inflammasome activation: Mechanisms, role in diseases and related inhibitors. J. Autoimmun. 113:102515. [PMID: 32703754]. [CrossRef]
- J. Fu, K. Schroder, H. Wu, 2024. Mechanistic insights from inflammasome structures. Nat. Rev. Immunol. [PMID: 38374299]. [CrossRef]
- X. Yu, R.E. Matico, R. Miller, et al., 2024. Structural basis for the oligomerization-facilitated NLRP3 activation. Nat. Commun. 15(1):1164. [PMID: 38326375]. [CrossRef]
- K.V. Swanson, M. Deng, J.P. Ting JP, The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 19(8) (2019) 477-489. [PMID: 31036962]. [CrossRef]
- M. Groslambert, B.F. Py, Spotlight on the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway, J. Inflamm. Res. 11 (2018) 359-374. [PMID: 30288079]. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, S. Chen, M. Liu, et al., NEK7: a new target for the treatment of multiple tumors and chronic inflammatory diseases, Inflammopharmacology. 30(4) (2022) 1179-1187. [PMID: 35829941. [CrossRef]
- L. Vande Walle, M. Lamkanfi, 2023. Drugging the NLRP3 inflammasome: from signalling mechanisms to therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023 Nov 29. [PMID: 38030687]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zeng, G. Xu, C. Feng, et al., Klotho inhibits the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome to alleviate lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury in A549 cells and restore mitochondrial function through SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway, Chin. J. Physiol. 66(5) (2023) 335-344. [PMID: 37929344]. [CrossRef]
- A. Romero, P. Dongil, I. Valencia, et al., Pharmacological Blockade of NLRP3 Inflammasome/IL-1β-Positive Loop Mitigates Endothelial Cell Senescence and Dysfunction, Aging Dis. 13(1) (2022) 84-297. [PMID: 35111374]. [CrossRef]
- M. Jin, J. Lou, H. Yu, et al., Exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin promotes inflammation in mouse testes: The critical role of Klotho in Sertoli cells, Toxicol. Lett. 295(2018) 134-143. [PMID: 29885354]. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhu, L.R. Stein, D. Kim D, et al., Klotho controls the brain-immune system interface in the choroid plexus, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 115(48) (2018) E11388-E11396. [PMID: 30413620]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Gu, K. Ren, C. Jiang, et al., Regulation of cartilage damage caused by lack of Klotho with thioredoxin/peroxiredoxin (Trx/Prx) system and succedent NLRP3 activation in osteoarthritis mice, Am. J. Transl. Res. 11(12) (2019) 7338-7350. [PMID: 31934282].
- X. Li, Z. Li, B. Li, X. Zhu, X. Lai, 2019. Klotho improves diabetic cardiomyopathy by suppressing the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Life Sci. 234:116773. [PMID: 31422095]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhao, S. Banerjee, N. Dey, et al., Klotho depletion contributes to increased inflammation in kidney of the db/db mouse model of diabetes via RelA (serine)536 phosphorylation, Diabetes. 60(7) (2011) 1907-16. [PMID: 21593200]. [CrossRef]
- S. Ismael, S. Nasoohi, L. Li, et al., 2021. Thioredoxin interacting protein regulates age-associated neuroinflammation. Neurobiol. Dis. 156:105399. [PMID: 34029695]. [CrossRef]
- J. He, J. Cui, Y. Shi, et al., 2023. Astragaloside IV Attenuates High-Glucose-Induced Impairment in Diabetic Nephropathy by Increasing Klotho Expression via the NF-κB/NLRP3 Axis. J. Diabetes Res. 2023:7423661. [PMID: 37261217]. [CrossRef]
- T. Xiang, X. Luo, L. Ye, et al., 2022. Klotho alleviates NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation in a temporal lobe epilepsy rat model by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Epilepsy Behav. 128:108509. [PMID: 35104732]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Fu, J. Cao, X, Wei, et al., 2023. Klotho alleviates contrast-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing oxidative stress, inflammation, and NF-KappaB/NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 118:110105. [PMID: 37018977]. [CrossRef]
- X.Y. Liu, L.Y. Zhang, X.Y. Wang, et al.,(2023. STAT4-Mediated Klotho Up-Regulation Contributes to the Brain Ischemic Tolerance by Cerebral Ischemic Preconditioning via Inhibiting Neuronal Pyroptosis. Mol. Neurobiol. [PMID: 37875707]. [CrossRef]
- M. Duan, L. Sun, X. He, et al., 2023. Medicinal chemistry strategies targeting NLRP3 inflammasome pathway: A recent update from 2019 to mid-2023. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 260:115750. [PMID: 37639823]. [CrossRef]
- X. Zhang, Z. Wang, Y. Zheng, et al. 2023. Inhibitors of the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway as promising therapeutic candidates for inflammatory diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 51(4):35. [PMID: 36960868]. [CrossRef]
- P.C. Robinson, R. Terkeltaub, M.H. Pillinger, et al., Consensus Statement Regarding the Efficacy and Safety of Long-Term Low-Dose Colchicine in Gout and Cardiovascular Disease, Am. J. Med. 135(1) (2022) 32-38. [PMID: 34416165]. [CrossRef]
- L. Gonzalez, J.F. Bulnes, M.P. Orellana, et al., 2022. The Role of Colchicine in Atherosclerosis: From Bench to Bedside. Pharmaceutics. 14(7):1395. [PMID: 35890291]. [CrossRef]
- T. Zhuang, S. Li, X. Yi, et al., 2020. Tranilast Directly Targets NLRP3 to Protect Melanocytes From Keratinocyte-Derived IL-1β Under Oxidative Stress. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8:588. [PMID: 32754591]. [CrossRef]
- G.J. Prud'homme, Pathobiology of transforming growth factor beta in cancer, fibrosis and immunologic disease, and therapeutic considerations, Lab. Invest. 87(11) (2007) 1077-91. [PMID: 17724448]. [CrossRef]
- G.J. Prud'homme, Cancer stem cells and novel targets for antitumor strategies, Curr. Pharm. Des. 18(19) (2012) 2838-49. [PMID: 22390767]. [CrossRef]
- G.J. Prud'homme, Y. Glinka, A. Toulina, et al., 2010. Breast cancer stem-like cells are inhibited by a non-toxic aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist. PLoS One. 5(11):e13831. [PMID: 21072210]. [CrossRef]
- S. Darakhshan, A.B. Pour, Tranilast: a review of its therapeutic applications, Pharmacol. Res. 91 (2015) 15-28. [PMID: 25447595]. [CrossRef]
- X. Chen, C. Shi, M. He, et al., 2023. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: molecular mechanism and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8(1):352. [PMID: 37709773]. [CrossRef]
- M. Gebert, J. Sławski, L. Kalinowski, et al., 2023. The Unfolded Protein Response: A Double-Edged Sword for Brain Health. Antioxidants (Basel). 12(8):1648. [PMID: 37627643]. [CrossRef]
- S. Banerjee, Y. Zhao, P.S. Sarkar, et al., Klotho ameliorates chemically induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress signaling, Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 31(4-5) (2013) 659-672. [PMID: 23711492]. [CrossRef]
- S. Song, P. Gao, H. Xiao, et al., 2013. Klotho suppresses cardiomyocyte apoptosis in mice with stress-induced cardiac injury via downregulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress. PLoS One. 8(12):e82968. [PMID: 24340070]. [CrossRef]
- J. Mytych, Actions of Klotho on hippocampal neuronal cells, Vitam. Horm. 118 (2022) 223-246. [PMID: 35180928]. [CrossRef]
- J. Suk Kang , S.S. Son, J.H. Lee, et al., 2021. Protective effects of klotho on palmitate-induced podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy. PLoS One. 16(4):e0250666. [PMID: 33891667]. [CrossRef]
- J. Donate-Correa, B. Martín-Carro, J.B. Cannata-Andía, et al., 2023. Klotho, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Damage in Kidney Disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 12(2):239. [PMID: 36829798]. [CrossRef]
- G. Maltese, P.M. Psefteli, B. Rizzo, et al., The anti-ageing hormone klotho induces Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defences in human aortic smooth muscle cells, J. Cell. Mol. Med. 21(3) (2017) 621-627. [PMID: 27696667]. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhu, Y. Gao, S. Zhu, et al., Klotho Improves Cardiac Function by Suppressing Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Mediated Apoptosis by Modulating Mapks/Nrf2 Signaling in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity Med. Sci. Monit. 23 (2017) 5283-5293. [PMID: 29107939]. [CrossRef]
- L. Xing, H. Guo, S. Meng, et al., Klotho ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by activating Nrf2 signaling pathway in podocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 534 (2021) 450-456. [PMID: 33256980]. [CrossRef]
- W. Gao, L. Guo, Y. Yang, et al., 2022. Dissecting the Crosstalk Between Nrf2 and NF-kappaB Response Pathways in Drug-Induced Toxicity. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 9:809952. [PMID: 35186957]. [CrossRef]
- W. Li, T.O. Khor, C. Xu, et al., Activation of Nrf2-antioxidant signaling attenuates NFkappaB-inflammatory response and elicits apoptosis, Biochem. Pharmacol. 76(11) (2008) 1485-1489. [PMID: 18694732]. [CrossRef]
- A. Minelli, S. Grottelli, A. Mierla, et al., Cyclo(His-Pro) exerts anti-inflammatory effects by modulating NF-κB and Nrf2 signalling, Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 44(3) (2012) 525-35. [PMID: 22185821]. [CrossRef]
- S.W. Kim, H.K. Lee, J.H. Shin, J.K. Lee, Up-down regulation of HO-1 and iNOS gene expressions by ethyl pyruvate via recruiting p300 to Nrf2 and depriving It from p65., Free Radic. Biol. Med. 65 (2013) 468-476. [PMID: 23891677]. [CrossRef]
- S. Grottelli, I. Ferrari, G. Pietrini, et al., 2016. The Role of Cyclo(His-Pro) in Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17(8):1332. [PMID: 27529240]. [CrossRef]
- B.F. Santos, I. Grenho, P.J. Martel, et al., 2023. FOXO family isoforms. Cell Death Dis. 14(10):702. [PMID: 37891184]. [CrossRef]
- A. Olejnik, A. Radajewska, A. Krzywonos-Zawadzka, I. Bil-Lula, 2023. Klotho inhibits IGF1R/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway and protects the heart from oxidative stress during ischemia/reperfusion injury. Sci. Rep.13(1):20312. [PMID: 37985893]. [CrossRef]
- C.D.K. Wungu, H. Susilo, M.Y. Alsagaff, et al., 2024. Role of klotho and fibroblast growth factor 23 in arterial calcification, thickness, and stiffness: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Sci. Rep. 14(1):5712. [PMID: 38459119]. [CrossRef]
- M. Kuro-o, Klotho and calciprotein particles as therapeutic targets against accelerated ageing, Clin. Sci. (Lond). 135(15) (2021) 1915-1927. [PMID: 34374422]. [CrossRef]
- L.E. Werner, U. Wagner, 2023. Calcium-sensing receptor-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in rheumatoid arthritis and autoinflammation. Front. Physiol. 13:1078569. [PMID: 36685206]. [CrossRef]
- K.J. Rocha-Singh, T. Zeller, M.R. Jaff, 2014. Peripheral arterial calcification: prevalence, mechanism, detection, and clinical implications. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 83(6):E212-20. [PMID: 24402839]. [CrossRef]
- T.M. Doherty, L.A. Fitzpatrick, D. Inoue, et al., Molecular, endocrine, and genetic mechanisms of arterial calcification, Endocr. Rev. 25(4) (2004) 629-72. [PMID: 15294885]. [CrossRef]
- D. Lu, H. Jiang, T. Zou, et al., (2023). Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition: New insights into vascular calcification. Biochem. Pharmacol. 213:115579. [PMID: 37589048]. [CrossRef]
- A. Yan, A.I. Gotlieb, 2023. The microenvironment of the atheroma expresses phenotypes of plaque instability. Cardiovas. Pathol. 67:107572. [PMID: 37595697]. [CrossRef]
- A. Olejnik, A. Franczak, A. Krzywonos-Zawadzka, et al., 2018. The Biological Role of Klotho Protein in the Development of Cardiovascular Diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018:5171945. [PMID: 30671457]. [CrossRef]
- N. Akhiyat, I. Ozcan, R. Gulati R, et al., 2024. Patients With Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction Have Less Circulating α-Klotho. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 13(9):e031972. [PMID: 38639380]. [CrossRef]
- A. Gonzalez-Moro, I. Valencia, L. Shamoon, et al., 2022. NLRP3 Inflammasome in Vascular Disease: A Recurrent Villain to Combat Pharmacologically. Antioxidants (Basel). 11(2):269. [PMID: 35204152]. [CrossRef]
- X.D. Xu, J.X. Chen, L. Zhu, et al., (2022). The emerging role of pyroptosis-related inflammasome pathway in atherosclerosis. Mol. Med. 28(1):160. [PMID: 36544112]. [CrossRef]
- I.N. Tyurenkov, V.N. Perfilova, A.A. Nesterova, Y. Glinka, Klotho Protein and Cardio-Vascular System, Biochemistry (Mosc). 86(2) (2021) 132-145. [PMID: 33832412]. [CrossRef]
- C. Tanriover, S. Copur, A. Mutlu, et al., Early aging and premature vascular aging in chronic kidney disease, Clin. Kidney J. 16(11) (2023) 1751-1765. [PMID: 37915901]. [CrossRef]
- S. Doi, Y. Zou, O. Togao, et al., Klotho inhibits transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) signaling and suppresses renal fibrosis and cancer metastasis in mice, J. Biol. Chem. 286(10) (2011) 8655-8665. [PMID: 21209102]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ohsawa, H. Ohtsubo, A. Munekane, et al., Circulating α-Klotho Counteracts Transforming Growth Factor-β-Induced Sarcopenia, Am. J. Pathol. 193(5) (2023) 591-607. [PMID: 36773783]. [CrossRef]
- H. Pratsinis, E. Mavrogonatou, D. Kletsas, TGF-beta in development and aging, in S. I. S. Rattan (Ed), Hormones in Ageing and Longevity, Gewerbestrasse 11, 6330 Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing AG), 2017, pp. 127-148. [CrossRef]
- G.J. Prud’homme, Y. Glinka, P.N. Matkar, H. Leong-Poi, The role of neuropilins in TGF-beta signaling and cancer biology, in G. Neufeld and O. Kessler (Eds.), The Neuropilins: Role and Function in Health and Disease, Gewerbestrasse 11, 6330 Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing AG, 2017, pp. 187-212. [CrossRef]
- J. Mikuła-Pietrasik, S. Rutecki, K. Książek, 2022. The functional multipotency of transforming growth factor beta signaling at the intersection of senescence and cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 79(4):196. [PMID: 35305149]. [CrossRef]
- L.L. Ren, H. Miao, Y.N. Wang, et al., TGF-β as A Master Regulator of Aging-Associated Tissue Fibrosis, Aging Dis. 14(5) (2023) 1633-1650. [PMID: 37196129. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li, F. Hu, M. Xue, et al., Klotho down-regulates Egr-1 by inhibiting TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling in high glucose treated human mesangial cells, Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 487(2) (2017) 216-222. [PMID: 28411025]. [CrossRef]
- S. Hadpech, V. Thongboonkerd, 2023. Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in kidney fibrosis. Genesis. 2023 Jun 22:e23529. [PMID: 37345818]. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, P.J.A. Eichhorn, J.P. Thiery, TGF-β, EMT, and resistance to anti-cancer treatment, Semin. Cancer Biol. 97(2023) 1-11. [PMID: 37944215]. [CrossRef]
- G.J. Prud'homme, Y. Glinka, Neuropilins are multifunctional coreceptors involved in tumor initiation, growth, metastasis and immunity, Oncotarget. 3(9) (2012) 921-939. [PMID: 22948112]. [CrossRef]
- B.R. Varun, P. Ramani, I. Arya, et al., Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer stem cells: Therapeutic implications, J. Oral. Maxillofac. Pathol. 27(2) (2023) 359-363. [PMID: 37854925]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li, M. Xue, F. Hu, et al., 2021. Klotho prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Egr-1 downregulation in diabetic kidney disease. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care. 9(1):e002038. [PMID: 34099438]. [CrossRef]
- X. Li, P. Lu, X.F. Shao, et al., 2021. Klotho Regulates Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition In Vitro via Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway and Attenuates Chronic Allog-raft Dysfunction in a Rat Renal Transplant Model. Ann. Transplant. 26:e930066. [PMID: 33737505]. [CrossRef]
- H.Y. Jang, S.J. Kim, K.S. Park, J.H. Kim, 2023. Klotho prevents transforming growth factor-β2-induced senescent-like morphological changes in the retinal pigment epithelium. Cell Death Dis. 14(5):334. [PMID: 37210384]. [CrossRef]
- Q. Yuan, Q. Ren, L. Li, et al., 2022. A Klotho-derived peptide protects against kidney fibrosis by targeting TGF-beta signaling. Nat. Commun. 13(1):438. [PMID: 35064106]. [CrossRef]
- X. Chen, H. Tan, J. Xu, et al., Klotho-derived peptide 6 ameliorates diabetic kidney disease by targeting Wnt/β-catenin signaling, Kidney Int. 102(3) (2022) 506-520. [PMID: 35644285]. [CrossRef]
- M. Abboud, K. Merenbakh-Lamin, H. Volkov, et al., 2023. Oncogene Revealing the tumor suppressive sequence within KL1 domain of the hormone Klotho. 2023 Dec 1. [PMID: 38040805]. [CrossRef]
- P.Y. Chen, M.A. Schwartz, M. Simons, 2020. Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition, Vascular Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 7:53. [PMID: 32478094]. [CrossRef]
- Q. Peng, D. Shan, K. Cui, et al., 2022. The Role of Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Cardiovascular Disease. Cells. 11(11):1834. [PMID: 35681530]. [CrossRef]
- P.Y. Chen, L. Qin, N. Baeyens, et al., Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition drives atherosclerosis progression, J. Clin. Invest. 125(12) (2015) 4514-28. [PMID: 26517696]. [CrossRef]
- S. Li, L. Yu, A. He, Q. Liu, 2019. Klotho Inhibits Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction-Induced Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via TGF-β1/Smad2/Snail1 Signaling in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 10:348. [PMID: 31024315]. [CrossRef]
- Q. Yao, E. The, Y. Zhai, et al., 2022. Klotho Suppresses Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in the Aorta of Mice With Chronic Kidney Disease by Inhibition of Endothelial Senescent Activity. Circulation. 146:A13254. [CrossRef]
- M.R. Cho, S. Lee, S.K. Song, 2022. A Review of Sarcopenia Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment and Future Direction. J Korean Med Sci. 37(18):e146. [PMID: 35535373]. [CrossRef]
- S.J. Lee, Myostatin: A Skeletal Muscle Chalone, Annu Rev Physiol. 85 (2023) 269-291. [PMID: 36266260]. [CrossRef]
- B.D. Rodgers, C.W. Ward, Myostatin/Activin Receptor Ligands in Muscle and the Development Status of Attenuating Drugs, Endocr. Rev. 43(2) (2022) 329-365. [PMID: 34520530]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Xie, K. Huang, H. Li, et al., 2024. High serum klotho levels are inversely associated with the risk of low muscle mass in middle-aged adults: results from a cross-sectional study. Front. Nutr. 11:1390517. [PMID: 38854159]. [CrossRef]
- A. Sahu, H. Mamiya, S.N. Shinde, et al., 2018. Age-related declines in α-Klotho drive progenitor cell mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired muscle regeneration. Nat. Commun. 9(1):4859. [PMID: 30451844]. [CrossRef]
- R. Elsurer Afsar, B. Afsar, T.A. Ikizler, Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Muscle Wasting: A Metabolic Point of View, Kidney Int. Rep. 8(7) (2023) 1301-1314. [PMID: 37441473]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Lin, Z. Sun, In vivo pancreatic β-cell-specific expression of antiaging gene α-Klotho: a novel approach for preserving β-cells in type 2 diabetes, Diabetes. 64(4) (2015) 1444-58. [PMID: 25377875]. [CrossRef]
- N. Keles, B. Dogan, M. Kalcik, et al., Is serum α-Klotho protective against atherosclerosis in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus?, J. Diabetes Complications. 30(1) (2016) 126-32. [PMID: 26601789]. [CrossRef]
- F. Nie, D. Wu, H. Du, et al., Serum klotho protein levels and their correlations with the progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus, J. Diabetes Complications. 31(3) (2017) 594-598. [PMID: 27916483]. [CrossRef]
- N. Fountoulakis, G. Maltese, L. Gnudi, J. Karalliedde, Reduced Levels of Anti-Ageing Hormone Klotho Predict Renal Function Decline in Type 2 Diabetes, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 103(5) (2018) 2026-2032. [PMID: 29509906]. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhang, T. Liu, Clinical implication of alterations in serum Klotho levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications, J. Diabetes Complications. 32(10) (2018) 922-930. [PMID: 30042059]. [CrossRef]
- F. Tarhani, G. Heidari, A. Nezami, Evaluation of α-klotho level in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) children J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 33(6) (2020) 761-765. [PMID: 32469333]. [CrossRef]
- A. Zubkiewicz-Kucharska, B. Wikiera, A. Noczyńska, 2021. Soluble Klotho Is Decreased in Children With Type 1 Diabetes and Correlated With Metabolic Control. Front. Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12:709564. [PMID: 34603200]. [CrossRef]
- R.F. Lefta, E.A. Hassan, 2023. Serum soluble α-Klotho levels in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2023 Aug 26. [PMID: 37626257]. [CrossRef]
- T. Takenaka, H. Kobori, T. Miyazaki, et al., 2019. Klotho protein supplementation reduces blood pressure and renal hypertrophy in db/db mice, a model of type 2 diabetes. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 225(2):e13190. [PMID: 30251773]. [CrossRef]
- G.J. Prud’homme, Y. Glinka, M. Kurt, W. Liu, Q. Wang, Systemic Klotho therapy protects against insulitis and enhances beta-cell mass in NOD mice, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 525(3) (2020) 693-698. [PMID: 32139120]. [CrossRef]
- M.S. Razzaque, 2012. The role of Klotho in energy metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 8(10):579-87. [PMID: 22641000]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Lin, Z. Sun, Antiaging Gene α-Klotho Attenuates Pancreatic β-Cell Apoptosis in Type 1 Diabetes, Diabetes. 64(12) (2015) 4298-4311. [PMID: 26340932]. [CrossRef]
- W. Liu, D.O. Son, H.K. Lau, Y. Zhou, G.J. Prud'homme, T. Jin, Q. Wang, 2017. Combined Oral Administration of GABA and DPP-4 Inhibitor Prevents Β Cell Damage and Promotes Β Cell Regeneration in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 8:362. [PMID: 28676760]. [CrossRef]
- D.O. Son, W. Liu, X. Li, G.J. Prud'homme, Q. Wang, Combined effect of GABA and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist on cytokine-induced apoptosis in pancreatic β-cell line and isolated human islets, J. Diabetes. 11(7) (2019) 563-572. [PMID: 30520247]. [CrossRef]
- Q. Wang Q, L. Ren, Y. Wan, G.J. Prud'homme, GABAergic regulation of pancreatic islet cells: Physiology and antidiabetic effects, J. Cell. Physiol. 234 (9) (2019) 14432-14444.. [PMID: 30693506]. [CrossRef]
- W. Liu, H.K. Lau, D.O. Son, T. Jin, Y. Yang, Z. Zhang, Y. Li, G.J. Prud'homme, Q. Wang, Combined use of GABA and sitagliptin promotes human β-cell proliferation and reduces apoptosis, J. Endocrinol. 248(2) (2021) 133-143. [PMID: 33258801]. [CrossRef]
- A.W. Hart, N. Baeza, A. Apelqvist, H. Edlund, Attenuation of FGF signalling in mouse β-cells leads to diabetes, Nature. 408(6814) (2000) 864-8. [PMID: 11130726]. [CrossRef]
- M.K. Prasad, S. Mohandas, K.M. Ramkumar, Dysfunctions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic strategies of pancreatic β-cells in diabetes. Apoptosis, 28(7-8) (2023) 958-976. [PMID: 37273039]. [CrossRef]
- S. Dalle, A. Abderrahmani, 2023. Renard E. Pharmacological inhibitors of β-cell dysfunction and death as therapeutics for diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 14:1076343. [PMID: 37008937]. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Borowiec, A. Właszczuk, E. Olakowska, J. Lewin-Kowalik, TXNIP inhibition in the treatment of diabetes. Verapamil as a novel therapeutic modality in diabetic patients, Med Pharm Rep. 95(3) (2022).:243-250. [PMID: 36060506]. [CrossRef]
- E.H. Choi, S.J. Park, TXNIP: A key protein in the cellular stress response pathway and a potential therapeutic target, Exp. Mol. Med. 55(7) (2023) 1348-1356. [PMID: 37394581]. [CrossRef]
- K. Zgutka, M. Tkacz, P. Tomasiak, M. Tarnowski, 2023. A Role for Advanced Glycation End Products in Molecular Ageing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24(12):9881. [PMID: 37373042]. [CrossRef]
- K. Taguchi, K. Fukami, 2023. RAGE signaling regulates the progression of diabetic complications. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1128872. [PMID: 37007029]. [CrossRef]
- M.I. Khan, F. Ashfaq, A.A. Alsayegh, et al., Advanced glycation end product signaling and metabolic complications: Dietary approach, World J. Diabetes. 14(7) (2023) 995-1012. [PMID: 37547584]. [CrossRef]
- W. Yu, M. Tao, Y. Zhao, et al., 4'-Methoxyresveratrol Alleviated AGE-Induced Inflammation via RAGE-Mediated NF-κB and NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway, Molecules. 23(6) (2018) 1447. [PMID: 29903983]. [CrossRef]
- X. Deng, W. Huang, J. Peng, et al., Irisin Alleviates Advanced Glycation End Products-Induced Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction via Inhibiting ROS-NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling, Inflammation. 41(1) (2018) 260-275. [PMID: 29098483]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Song, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, et al., Advanced glycation end products regulate anabolic and catabolic activities via NLRP3-inflammasome activation in human nucleus pulposus cells, J. Cell. Mol. Med. 21(7) (2017) 1373-1387. [PMID: 28224704]. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhou, X. Chen, M. Lu, et al., Wnt/β-catenin links oxidative stress to podocyte injury and proteinuria, Kidney Int. 95(4) (2019) 830-845. [PMID: 30770219]. [CrossRef]
- W.C. Kan, J.Y. Hwang, L.Y. Chuang, et al., Effect of osthole on advanced glycation end products-induced renal tubular hypertrophy and role of klotho in its mechanism of action, Phytomedicine. 53(2019) 205-212. [PMID: 30668400]. [CrossRef]
- A. Puddu, D.C. Maggi, Klotho: A new therapeutic target in diabetic retinopathy?, World J. Diabetes. 14(7) (2023) 1027-1036. [PMID: 37547589]. [CrossRef]
- N.J. Reish, A. Maltare, A.S. McKeown, et al., The age-regulating protein klotho is vital to sustain retinal function, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 54(10) (2013) 6675-6685. [PMID: 24045987]. [CrossRef]
- C.R. Abraham, P.C. Mullen, T. Tucker-Zhou, et al., 2016. Is a Neuroprotective and Cognition-Enhancing Protein. Vitam. Horm.;101:215-38. [PMID: 27125744]. [CrossRef]
- H. Woo, Y. Chang, D.R. Ryu, T.J. Song, 2019. Plasma Klotho concentration is associated with the presence, burden and progression of cerebral small vessel disease in patients with acute ischaemic stroke. PLoS One. 14(8):e0220796. [PMID: 31398214]. [CrossRef]
- G.P. Dias, T. Murphy, D. Stangl, et al., Intermittent fasting enhances long-term memory consolidation, adult hippocampal neurogenesis, and expression of longevity gene Klotho, Mol. Psychiatry 26(11) (2021) 6365-6379. [PMID: 34031536]. [CrossRef]
- K. Hanson, K. Fisher, N.M. Hooper, 2021. Exploiting the neuroprotective effects of alpha-klotho to tackle ageing- and neurodegeneration-related cognitive dysfunction. Neuronal. Signal. 5(2):NS20200101. [PMID: 34194816]. [CrossRef]
- J. Neitzel, N. Franzmeier, A. Rubinski, et al., 2021. KL-VS heterozygosity is associated with lower amyloid-dependent tau accumulation and memory impairment in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), Malik R, Ewers M. Nat. Commun. 12(1):3825. [PMID: 34158479]. [CrossRef]
- M.R. Shaker, J. Aguado, H.K. Chaggar, E.J. Wolvetang, 2021. Klotho inhibits neuronal senescence in human brain organoids. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 7(1):18. [PMID: 34341344]. [CrossRef]
- J.M. Gaitán, S. Asthana, C.M. Carlsson, et al., Circulating Klotho Is Higher in Cerebrospinal Fluid than Serum and Elevated Among Klotho Heterozygotes in a Cohort with Risk for Alzheimer's Disease, J. Alzheimers Dis. 90(4) (2022) 1557-1569. [PMID: 36314202]. [CrossRef]
- G.R. Grontvedt, S.B. Sando, C. Lauridsen, et al., 2022. Association of Klotho Protein Levels and KL-VS Heterozygosity With Alzheimer Disease and Amyloid and Tau Burden. JAMA Netw. Open. 5(11):e2243232. [PMID: 36413367]. [CrossRef]
- P. Kundu, B. Zimmerman, J.F. Quinn, et al., 2022. Serum Levels of alpha-Klotho Are Correlated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels and Predict Measures of Cognitive Function. J. Alzheimers Dis. [PMID: 35213382]. [CrossRef]
- S.A. Castner, S. Gupta, D. Wang, et al., Longevity factor klotho enhances cognition in aged nonhuman primates, Nat. Aging. 3(8) (2023) 931-937. [PMID: 37400721]. [CrossRef]
- D. Linghui, Y. Simin, Z. Zilong, et al., 2023. The relationship between serum klotho and cognitive performance in a nationally representative sample of US adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15:1053390. [PMID: 36819720]. [CrossRef]
- P. Panczyszyn-Trzewik, E. Czechowska, K. Stachowicz, M. Sowa-Kucma, 2023. The Importance of α-Klotho in Depression and Cognitive Impairment and Its Connection to Glutamate Neurotransmission-An Up-to-Date Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24(20):15268. [PMID: 37894946]. [CrossRef]
- F. Sorrentino, C. Fenoglio, L. Sacchi, et al., Klotho Gene Expression Is Decreased in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 94(3) (2023) 1225-1231. [PMID: 37393504]. [CrossRef]
- S.M. Clinton, M.E. Glover, A. Maltare, et al., Expression of klotho mRNA and protein in rat brain parenchyma from early postnatal development into adulthood, Brain Res. 1527 (2013) 1-14. [PMID: 23838326]. [CrossRef]
- M.M. Cararo-Lopes, C.H.Y. Mazucanti, C. Scavone, et al., The relevance of α-KLOTHO to the central nervous system: Some key questions, Ageing Res. Rev. 36 (2017) 137-148. [PMID: 28323064]. [CrossRef]
- T.Y. Fung, A. Iyaswamy, S.G. Sreenivasmurthy, et al., 2022. Klotho an Autophagy Stimulator as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer's Disease: A Review. Biomedicines. 10(3):705. [PMID: 35327507]. [CrossRef]
- A. Gholami, 2023. Alzheimer's disease: The role of proteins in formation, mechanisms, and new therapeutic approaches. Neurosci. Lett. 817:137532. [PMID: 37866702]. [CrossRef]
- S. Chowdhury, N.S. Chowdhury, 2023. Novel anti-amyloid-beta (Aβ) monoclonal antibody lecanemab for Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 37:3946320231209839. [PMID: 37902139]. [CrossRef]
- G. Yadollahikhales, J.C. Rojas, Anti-Amyloid Immunotherapies for Alzheimer's Disease: A 2023 Clinical Update. Neurotherapeutics. 20(4) (2023) 914-931. [PMID: 37490245]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Huang, X. Li, G. Luo, et al., 2022. Pyroptosis as a candidate therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 14:996646. [PMID: 36185484]. [CrossRef]
- S. Jose, N.J. Groves, K.E. Roper, R. Gordon, 2022. Mechanisms of NLRP3 activation and pathology during neurodegeneration. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 151:106273. [PMID: 35926782]. [CrossRef]
- Y.H. Han, X.D. Liu, M.H. Jin, et al., Role of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuronal pyroptosis and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases, Inflamm. Res. 72(9) (2023) 1839-1859. [PMID: 37725102]. [CrossRef]
- C. Ju Hwang, D.Y. Choi, et al., NF-κB as a Key Mediator of Brain Inflammation in Alzheimer's Disease, CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets. 18(1):3-10. (2019) [PMID: 28782486]. [CrossRef]
- S. Moonen, M.J. Koper, E. Van Schoor, et al., Pyroptosis in Alzheimer's disease: cell type-specific activation in microglia, astrocytes and neurons, Acta Neuropathol. 145(2) (2023) 175-195. [PMID: 36481964]. [CrossRef]
- J. Singh, M.L. Habean, N. Panicker, Inflammasome assembly in neurodegenerative diseases, Trends Neurosci. 46(10) (2023) 814-831. [PMID: 37633753]. [CrossRef]
- J. Yao, Z. Wang, W. Song, Y. Zhang, 2023. Targeting NLRP3 inflammasome for neurodegenerative disorders. Mol. Psychiatry. 2023 Sep 5. [PMID: 37670126]. [CrossRef]
- C. Ising, C. Venegas, S. Zhang, et al., NLRP3 inflammasome activation drives tau pathology, Nature. 575(7784) (2019) 669-673. [PMID: 31748742]. [CrossRef]
- A. Chiarini, U. Armato, P. Hu, I. Dal Para, 2020. Danger-Sensing/Patten Recognition Receptors and Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21(23):9036. [PMID: 33261147]. [CrossRef]
- Chiarini, L. Gui, C. Viviani, et al., 2023. NLRP3 Inflammasome's Activation in Acute and Chronic Brain Diseases-An Update on Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives with Respect to Other Inflammasomes. Biomedicines. 11(4):999. [PMID: 37189617]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu, Y. Dai, Q. Li, et al., 2020. Beta-amyloid activates NLRP3 inflammasome via TLR4 in mouse microglia. Neurosci. Lett. 736:135279. [PMID: 32726591]. [CrossRef]
- S. Koerich, G.M. Parreira, D.L. de Almeida, et al., Receptors for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE): Promising Targets Aiming at the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Conditions, Curr. Neuropharmacol. 21(2) (2023) 219-234. [PMID: 36154605]. [CrossRef]
- I.M. Veselov, D.V. Vinogradova, A.V. Maltsev, et al., 2023. Mitochondria and Oxidative Stress as a Link between Alzheimer's Disease and Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24(19):14450. [PMID: 37833898]. [CrossRef]
- C.D. Chen, J.A. Sloane, H. Li, et al., The antiaging protein Klotho enhances oligodendrocyte maturation and myelination of the CNS, J. Neurosci. 33(5) (2013) 1927-39. [PMID: 23365232]. [CrossRef]
- D.B. Dubal, L. Zhu, P.E. Sanchez, et al., Life extension factor klotho prevents mortality and enhances cognition in hAPP transgenic mice, J. Neurosci. 35(6) (2015) 2358-2371. [PMID: 25673831]. [CrossRef]
- C.Y. Zeng, T.T. Yang, H.J. Zhou, et al., Lentiviral vector-mediated overexpression of Klotho in the brain improves Alzheimer's disease-like pathology and cognitive deficits in mice, Neurobiol. Aging. 78 (2019) 18-28. [PMID: 30851437]. [CrossRef]
- S. Gupta, A.J. Moreno, D. Wang, et al., 2022. vKL1 domain of longevity factor klotho mimics the metabolome of cognitive stimulation and enhances cognition in young and aging mice. J. Neurosci. JN-RM-2458-21. [PMID: 35428698]. [CrossRef]
- S. Dubnov, N. Yayon, O. Yakov, et al., 2023. Knockout of the longevity gene Klotho perturbs aging- and Alzheimer's disease-linked brain microRNAs and tRNA fragments. bioRxiv. Sep 12:2023.09.10.557032. [PMID: 37745362]. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Orellana, C.H. Mazucanti, L.P. Dos Anjos, et al., (2023). Klotho increases antioxidant defenses in astrocytes and ubiquitin-proteasome activity in neurons. Sci. Rep. 13(1):15080. [PMID: 37699938]. [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, Y. Ma, C.L. Gallagher, et al., Age-Related Tau Burden and Cognitive Deficits Are Attenuated in KLOTHO KL-VS Heterozygotes, J. Alzheimers Dis. 82(3) (2021) 1369-1370. [PMID: 34250957]. [CrossRef]
- H. Poursistany, S.T. Azar, M.T. Azar, S. Raeisi, 2023. The current and emerging Klotho-enhancement strategies. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 693:149357. [PMID: 38091839]. [CrossRef]
- Mora-Fernández, M.D. Sánchez-Niño, J. Donate-Correa, et al., 2022. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors increase Klotho in patients with diabetic kidney disease: A clinical and experimental study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022 Oct;154:113677. [PMID: 36942605]. [CrossRef]
- Martín-González, F. Gómez-Bernal, J.C. Quevedo-Abeledo, et al., Alpha-Klotho protein in systemic lupus erythematosus, Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 41(1) (2023) 41-47. [PMID: 35349421]. [CrossRef]
- D.L. Russell, J.C. Oates, M. Markiewicz, Association Between the Anti-Aging Gene Klotho and Selected Rheumatologic Autoimmune Diseases, Am. J. Med. Sci. 361(2) (2021) 169-175. [PMID: 33349438]. [CrossRef]
- F.J. Amaro-Gahete, A. de-la-O, L. Jurado-Fasoli, et al., Role of Exercise on S-Klotho Protein Regulation: A Systematic Review, Curr. Aging Sci. 11(2) (2018) 100-107. [PMID: 29962352]. [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, A.D. Troutman, R.N. Moorthi, et al., (2022). Klotho: An Emerging Factor With Ergogenic Potential. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2:807123. [PMID: 36188832]. [CrossRef]
- H.L. Correa, A.T.O. Raab, T.M. Araújo, et al., 2022. A systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrating Klotho as an emerging exerkine. Sci Rep. 12(1):17587. [PMID: 36266389]. [CrossRef]
- K.G. Avin, P.M. Coen, W. Huang, et al., 2014. Skeletal muscle as a regulator of the longevity protein, Klotho. Front. Physiol. 5:189. [PMID: 24987372]. [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, C.A. Leber, H.N. Burney, et al., 2023. Relationship between klotho and physical function in healthy aging. Sci. Rep. 13(1):21158. [PMID: 38036596]. [CrossRef]
- K. Wang, Y. Mao, M. Lu, et al., 2022. Association between serum Klotho levels and the prevalence of diabetes among adults in the United States. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne).13:1005553. [PMID: 36440221]. [CrossRef]
- S. Yan, W. Luo, L. Lei, et al., 2023. Association between serum Klotho concentration and hyperlipidemia in adults: a cross-sectional study from NHANES 2007-2016. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 10;14:1280873. [PMID: 38027194]. [CrossRef]
- J. Bi, M. Zheng, K. Li, et al., 2024. Relationships of serum FGF23 and alpha-klotho with atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 23(1):128. [PMID: 38622690]. [CrossRef]
- K. Kadier, P. Liu, D. Dilixiati, et al., 2024. Maintaining ideal cardiovascular health is associated with higher serum anti-aging protein klotho in the middle-aged and older populations. J. Nutr. Health Aging. 28(6):100224. [PMID: 38582034]. [CrossRef]
- J. Liu, H. Wang, Q. Liu, et al., 2024. Klotho exerts protection in chronic kidney disease associated with regulating inflammatory response and lipid metabolism. Cell. Biosci. 14(1):46. [PMID: 38584258]. [CrossRef]
- H. Luo, Z. Zheng, H. Hu, C. Sun, 2024. Serum klotho levels and mortality patterns in frail individuals: unraveling the u-shaped association. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 36(1):92. [PMID: 38602574]. [CrossRef]
- Z. Yang, Y. Ma, Y. Wang, et al., 2024. The prognostic value of serum alpha-klotho in age-related diseases among the US population: A prospective population-based cohort study. Prev. Med. Rep. 42:102730. [PMID: 38689889]. [CrossRef]
- L. Chen, X. Yin, Y. Zhao, et al., Biological ageing and the risks of all-cause and cause-specific mortality among people with diabetes: a prospective cohort study, J. Epidemiol. Community Health. 76(9) (2022) 771-778. [PMID: 35738895]. [CrossRef]
- J.A. Neyra, O.W. Moe, J. Pastor, et al., Performance of soluble Klotho assays in clinical samples of kidney disease, Clin. Kidney J. 13(2) (2020) 235-244. [PMID: 32297879]. [CrossRef]
- R. Mencke, H. Olauson, J.L. Hillebrands, Effects of Klotho on fibrosis and cancer: A renal focus on mechanisms and therapeutic strategies, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 121 (2017) 85-100. [PMID: 28709936]. [CrossRef]
- C.A. Brownstein, F. Adler, C. Nelson-Williams C, et al., A translocation causing increased alpha-klotho level results in hypophosphatemic rickets and hyperparathyroidism, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA.105(9) (2008) 3455-3460. [PMID: 18308935]. [CrossRef]
- J.S. Paquette, C. Rhéaume, P. Cordeau, et al., 2023. The Longevity Protein Klotho: A Promising Tool to Monitor Lifestyle Improvements. Metabolites. 13(11):1157. [PMID: 37999253]. [CrossRef]
|
Disease model Methods Main findings Reference |
|---|
| Klotho hypomorphic Phenotypic Markedly impaired cognition; [60] |
| mouse (Klkl/kl) analysis ↑ oxidative stress; ↑ neuronal cell |
| death in hippocampus. Countered |
| by an antioxidant. |
| Klotho knockout RNA species Altered expression of long RNAs, [252] |
| mouse (Kl-/-) brain analysis microRNAs and tRFs similar to AD. |
| AD (APP/PS1 KL lentivirus KL overexpression: Improved cognition; [80,250] |
| mouse) vector (i.c.v.) ↑ autophagy; ↓Aβ; ↓ CAA; |
| ↓ NLRP3 inflammasome activation. |
| AD (human KL overexpression KL reduced premature mortality and loss [249] |
| APP-J20 mutant (transgenic) of NMDA receptors in hippocampus; |
| mouse) ↑ synaptic function and memory. |
| Knockout of KL KL knockout KL knockout: ↑ inflammatory mediators [109] |
| in choroid plexus in vivo; and ↑ mϕ in CP; ↑ microglial activation |
| (CP), mouse mϕ + LPS + KL in hippocampus. KL in vitro (mϕ): ↓TXNIP |
| in vitro and ↓ NLRP3 inflammasome activation. |
| Mouse (aging) KL s.c. injection. KL (or KL1 domain only): ↑ cognition [251] and ↑ synaptic plasticity in hippocampus. |
| Mouse (postnatal Cultures of neurons In astrocytes, KL ↑ FOXO3a and [253] |
| or embryo) or astrocytes, with protected against oxidative stress. In |
| or without glucose neurons, KL ↑ proteasomal activity. |
| Rat temporal Induced TLE. KL countered cognitive deficit, and was [115] |
| lobe epilepsy KL vector injected neuroprotective. It suppressed ROS. |
| (TLE) into hippocampus It prevented cell death by ferroptosis. |
| Rat cells and In vitro culture, KL enhanced oligodendrocyte maturation [248] |
| KL deficient mice brain tissue analysis and myelination, in vitro and in vivo. |
| Hippocampal Multiple KL KL protects by regulating ROS, [131] |
| neurons actions (review) DNA damage, inflammation, autophagy, |
| ER stress and cell death. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




