Submitted:
30 July 2024
Posted:
31 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
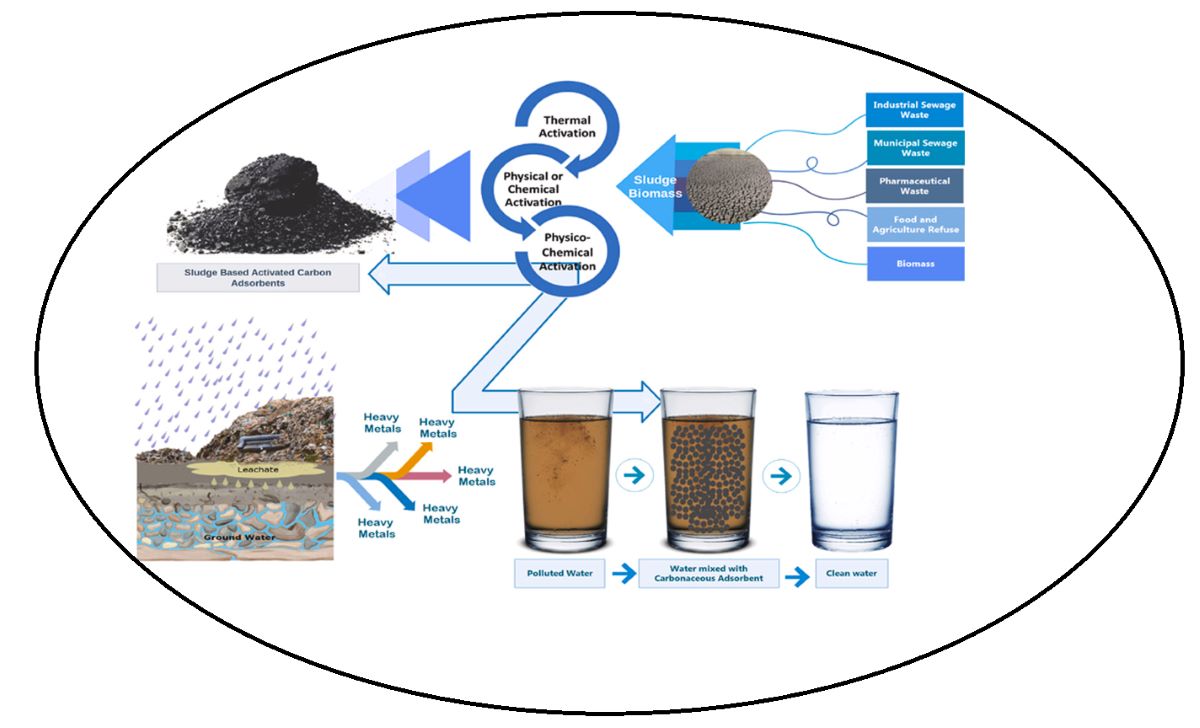
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Fabrication of Activated Carbon
2.4. Adsorption Studies
2.4.1. Adsorption Procedures of Cd+2 and Pb+2
2.4.2. Adsorption Isotherms
2.4.3. Adsorption Kinetics
2.5. Environmental and Industrial Wastewater Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Ultimate Analysis of Activated Carbon
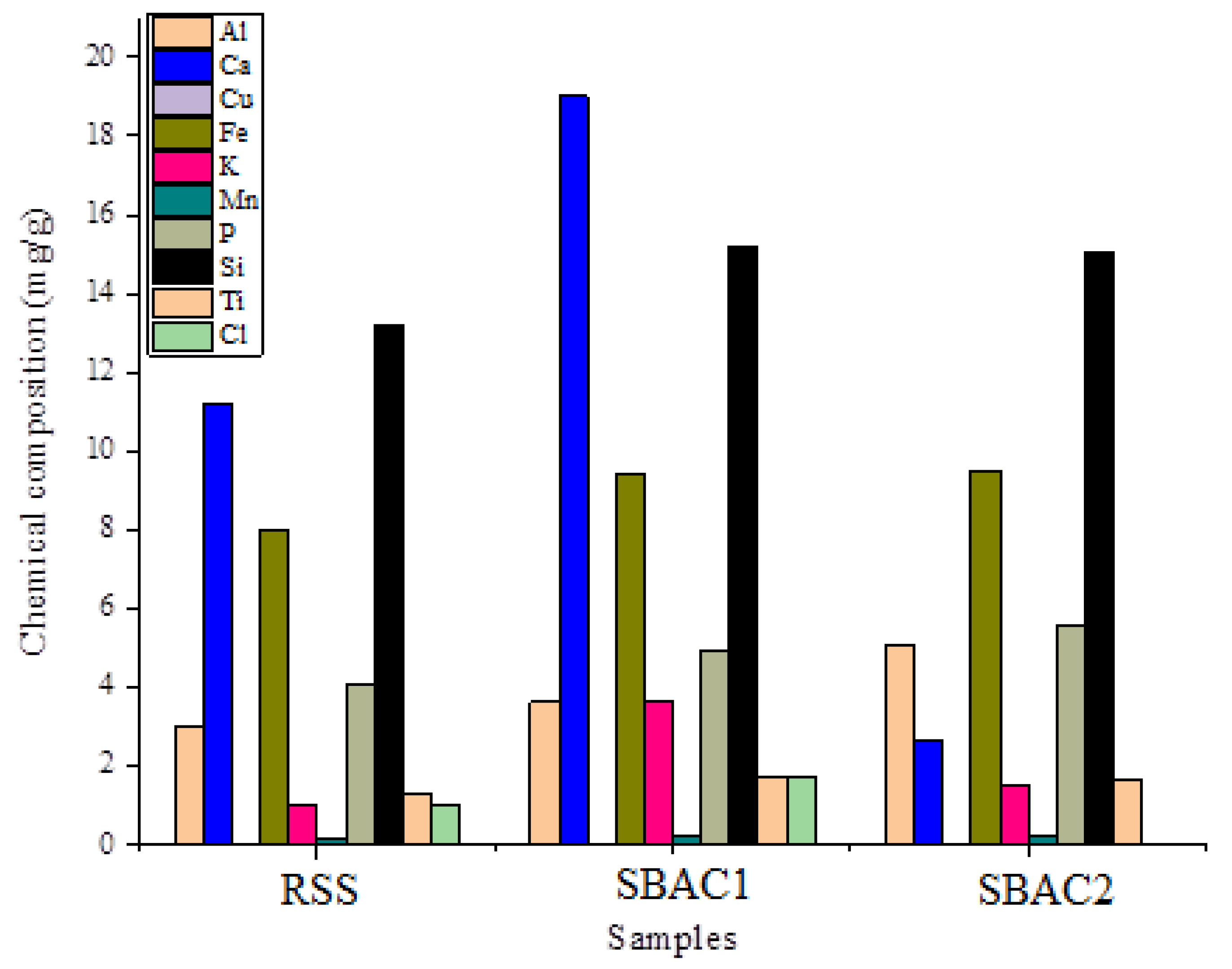
3.2. X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) Analysis
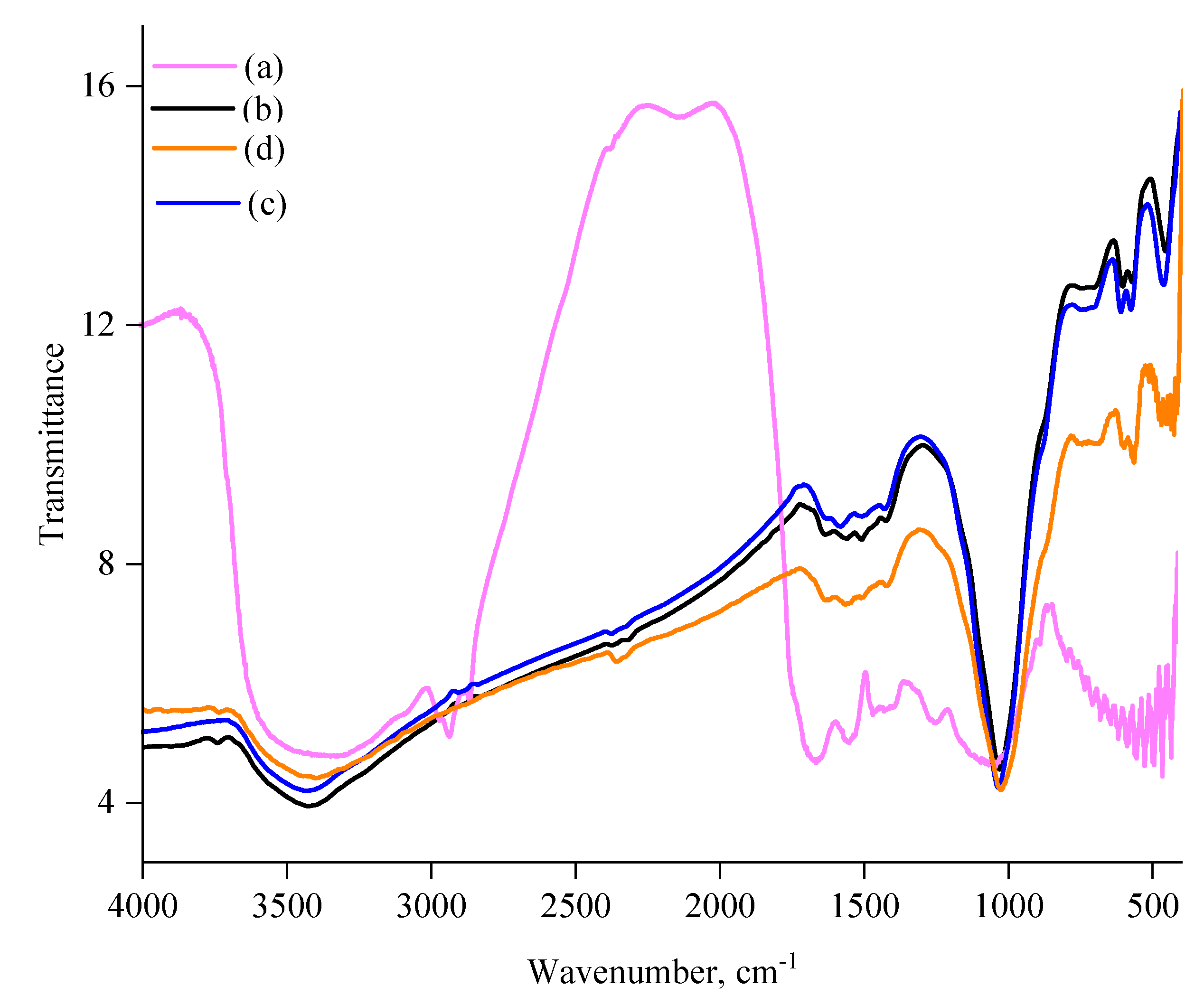
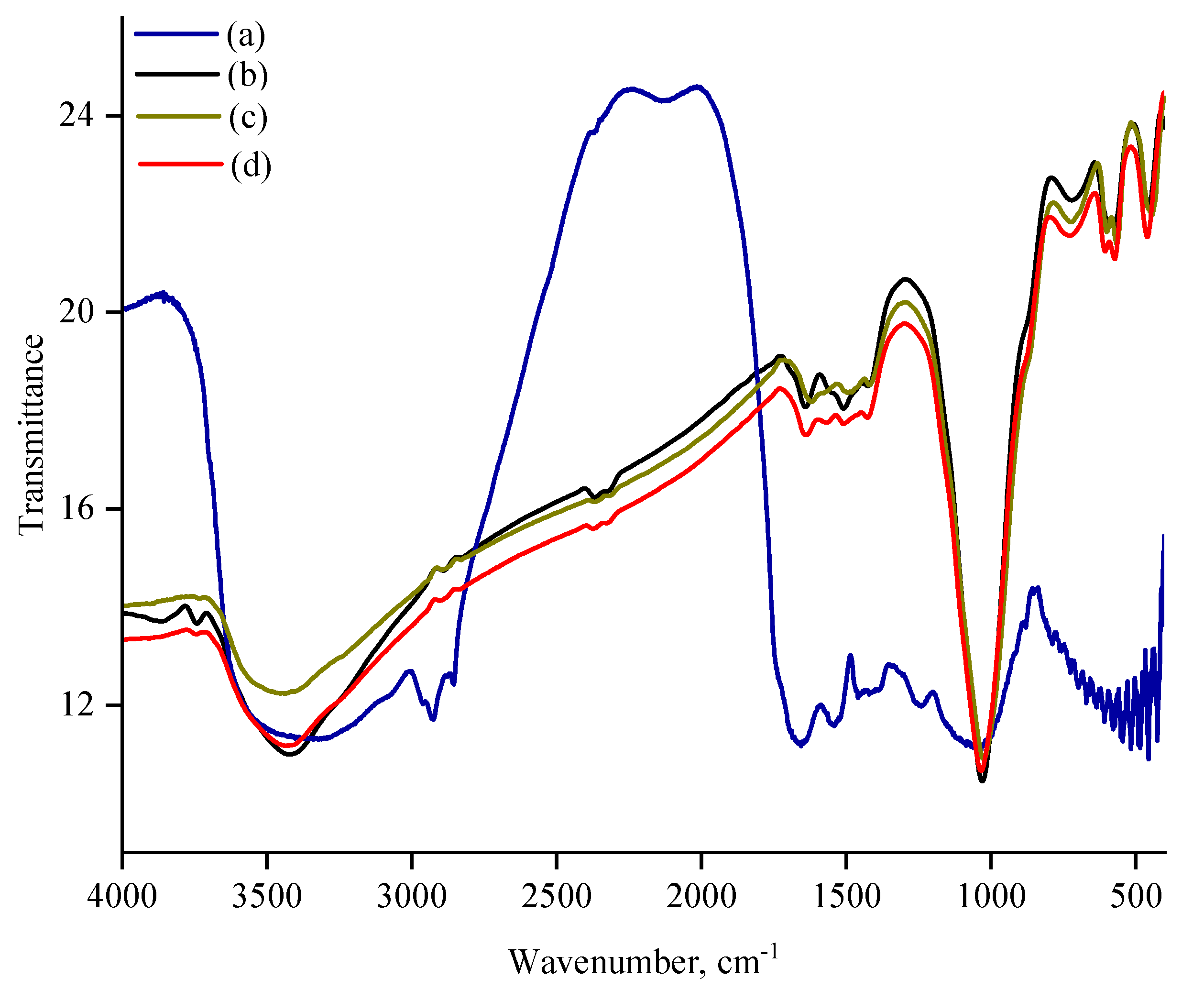
3.3. FT-IR Analysis
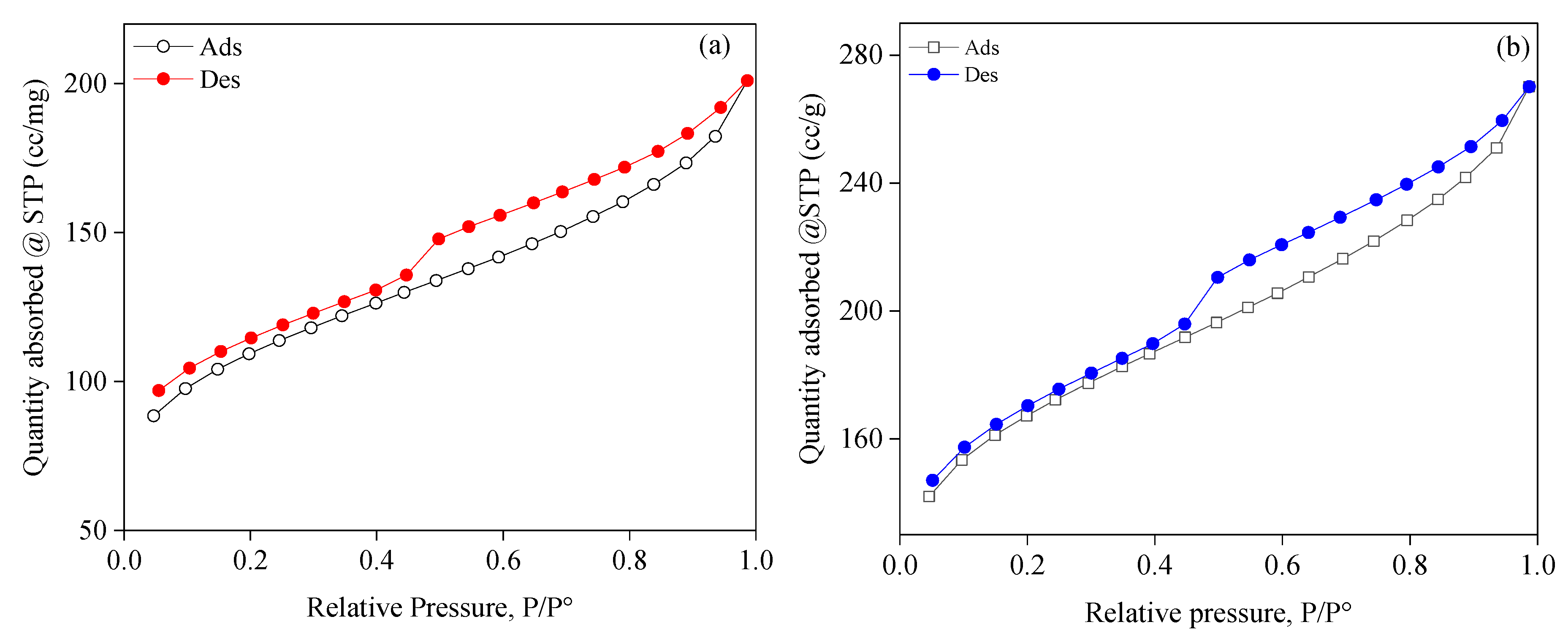
3.4. Characteristics of the Porous Structure
3.5. Zeta Potential Results
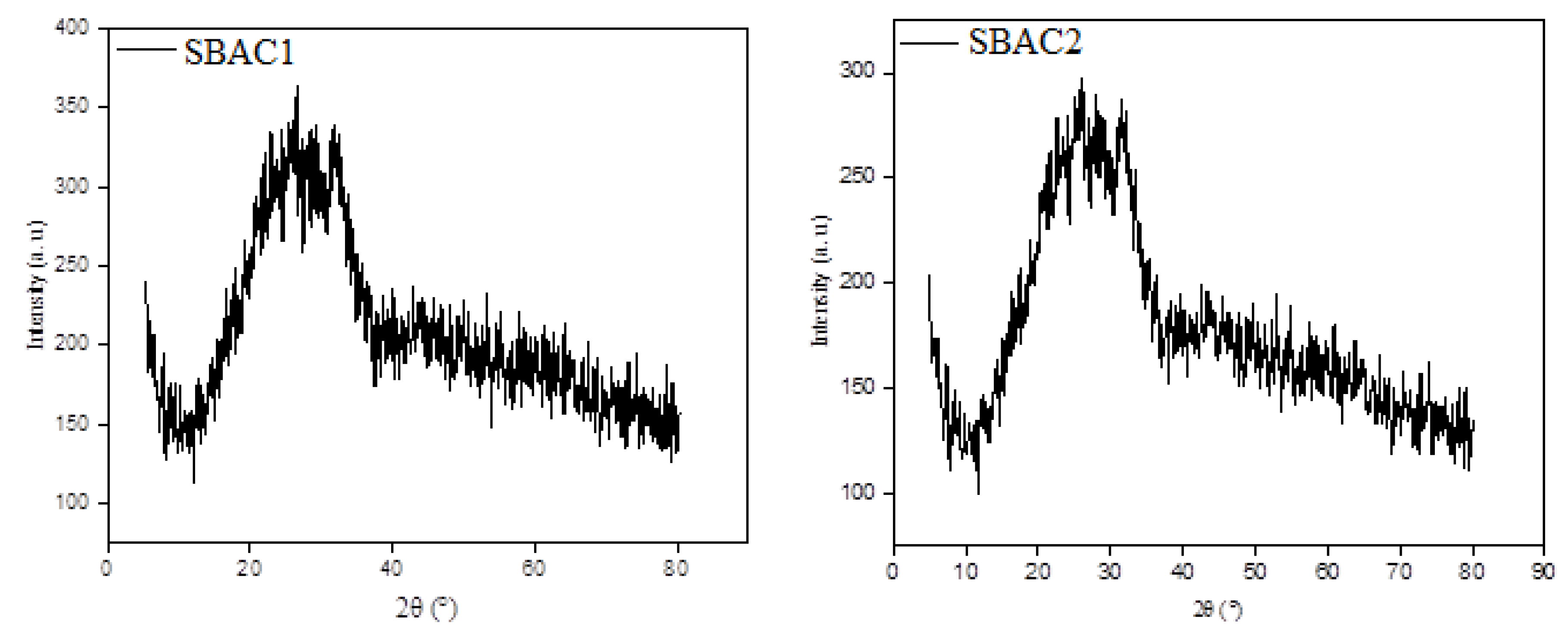
3.6. Powder X-ray Diffraction Spectroscopy
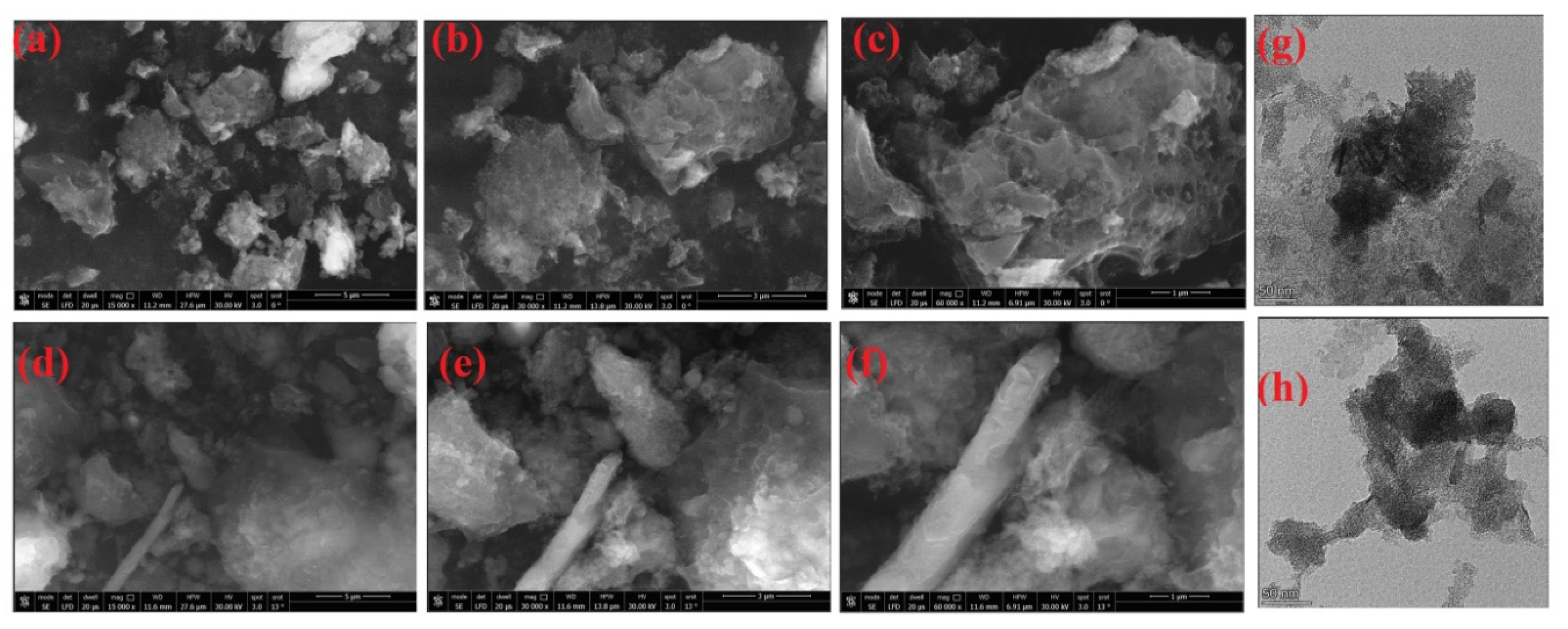
3.7. Microstructure Activated Carbon
3.8. Adsorption Study
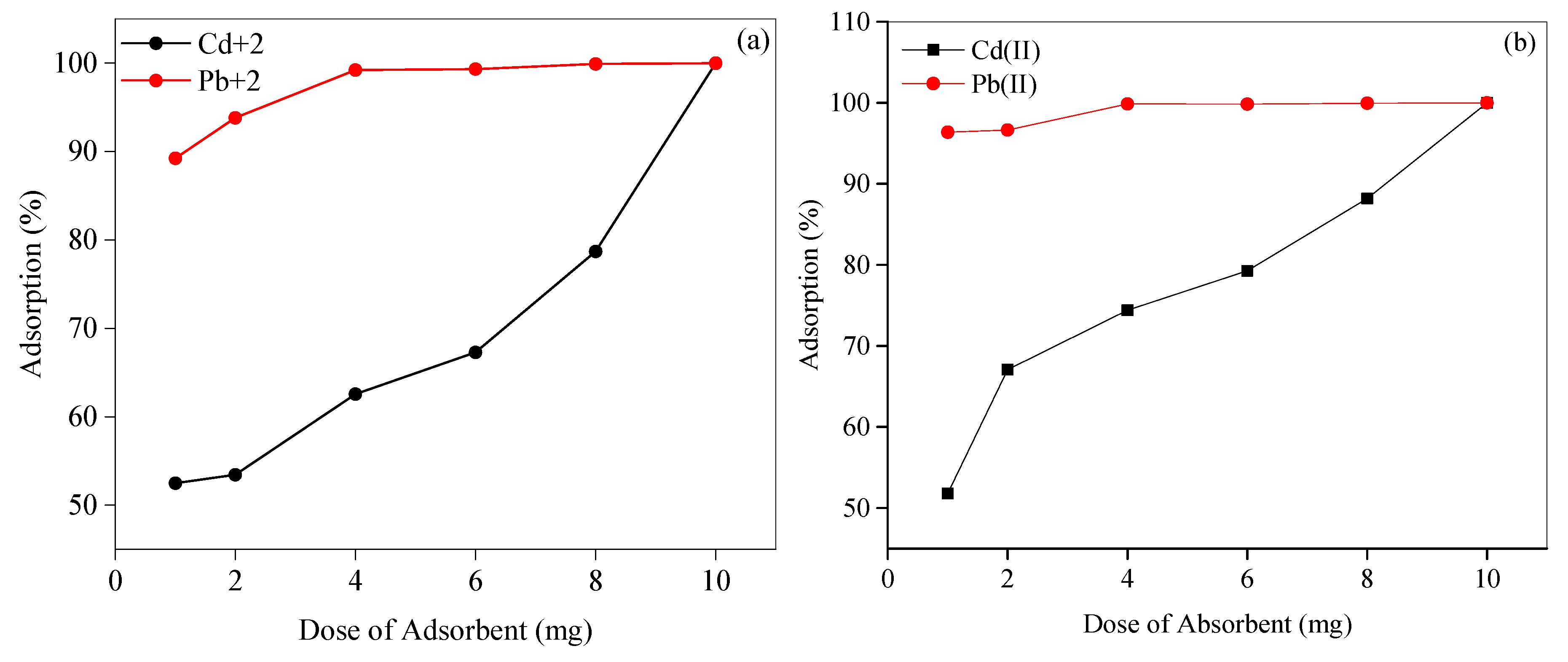
3.8.1. Influence of the SBAC1 and SBAC2 Dosage
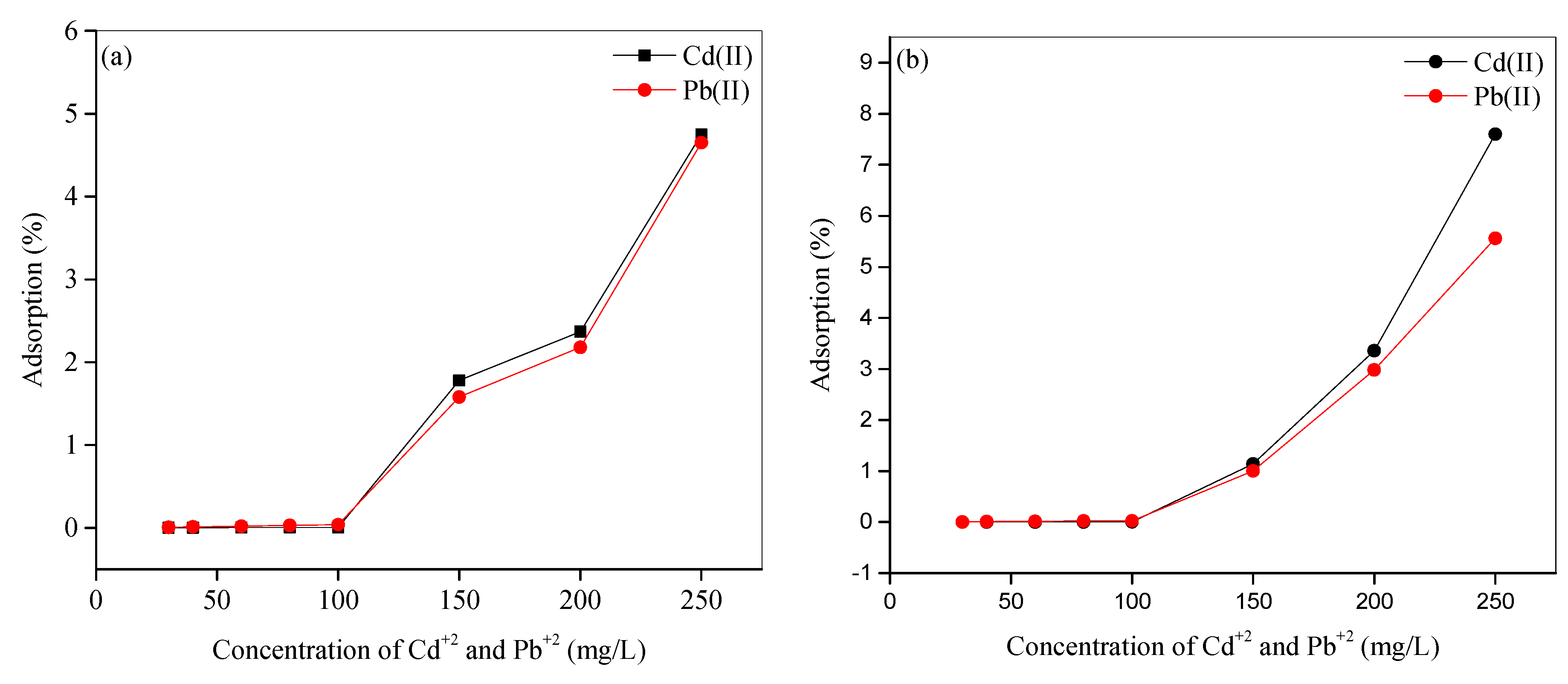
3.8.2. Influence of the of Metal Ion Concentration
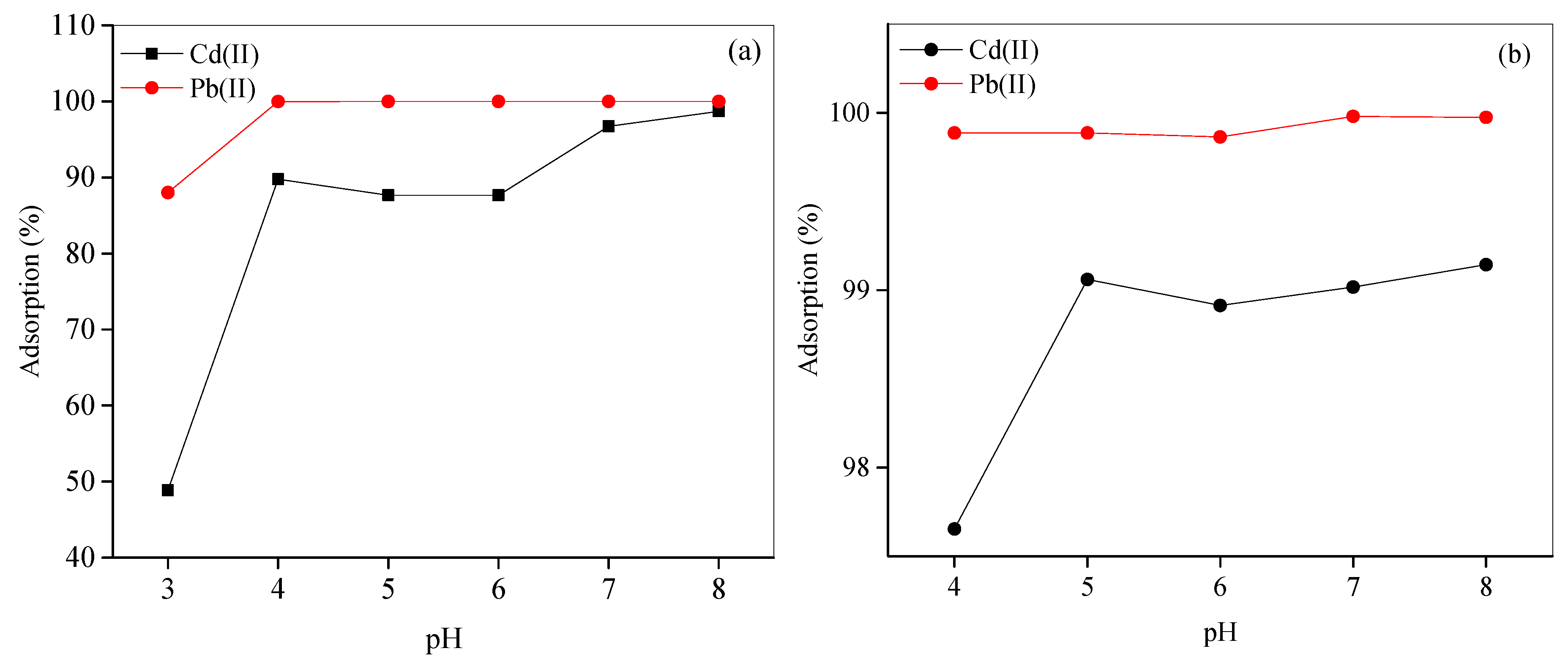
3.8.3. Influence of pH
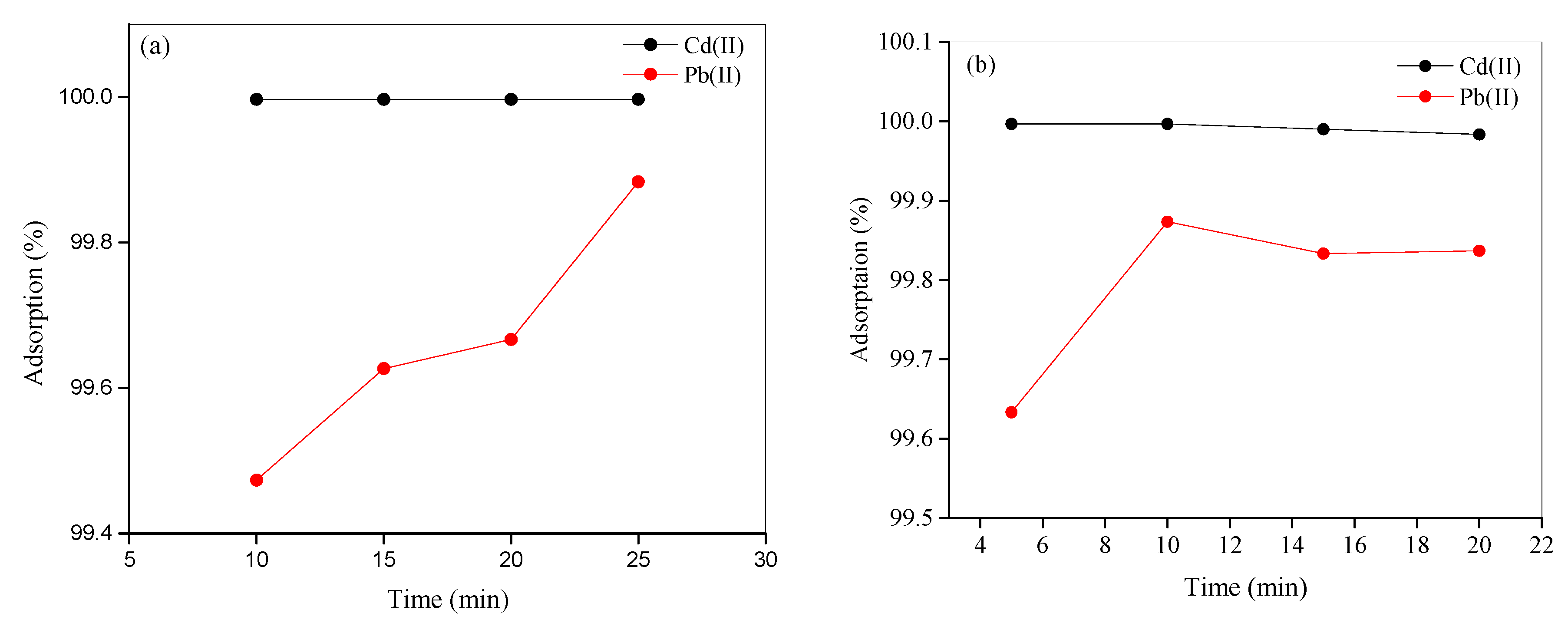
3.8.4. Influence of Time
3.8.5. Influence of Temperature
| Temperature (K) |
lnKc | ∆Go (kJmol-1) |
∆Ho (kJmol-1) |
∆So (kJmol-1) |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBAC1 | SBAC2 | SBAC1 | SBAC2 | SBAC1 | SBAC2 | SBAC1 | SBAC2 | |||||||||
| Cd+2 | Pb+2 | Cd+2 | Pb+2 | Cd+2 | Pb+2 | Cd+2 | Pb+2 | Cd+2 | Pb+2 | Cd+2 | Pb+2 | Cd+2 | Pb+2 | Cd+2 | Pb+2 | |
| 313 | 4.25 | 11.35 | 5.95 | 9.39 | -11.06 | -29.55 | -15.5 | -24.44 | 61.24 | 85.17 | 47.64 | 0 | 0.230 | -0.177 | -0.102 | 0.078 |
| 323 | 4.81 | 10.36 | 5.43 | 9.39 | -0.012 | -0.027 | -0.014 | -0.025 | ||||||||
| 333 | 5.63 | 9.39 | 4.85 | 9.39 | -0.015 | -0.026 | -0.013 | -0.026 | ||||||||
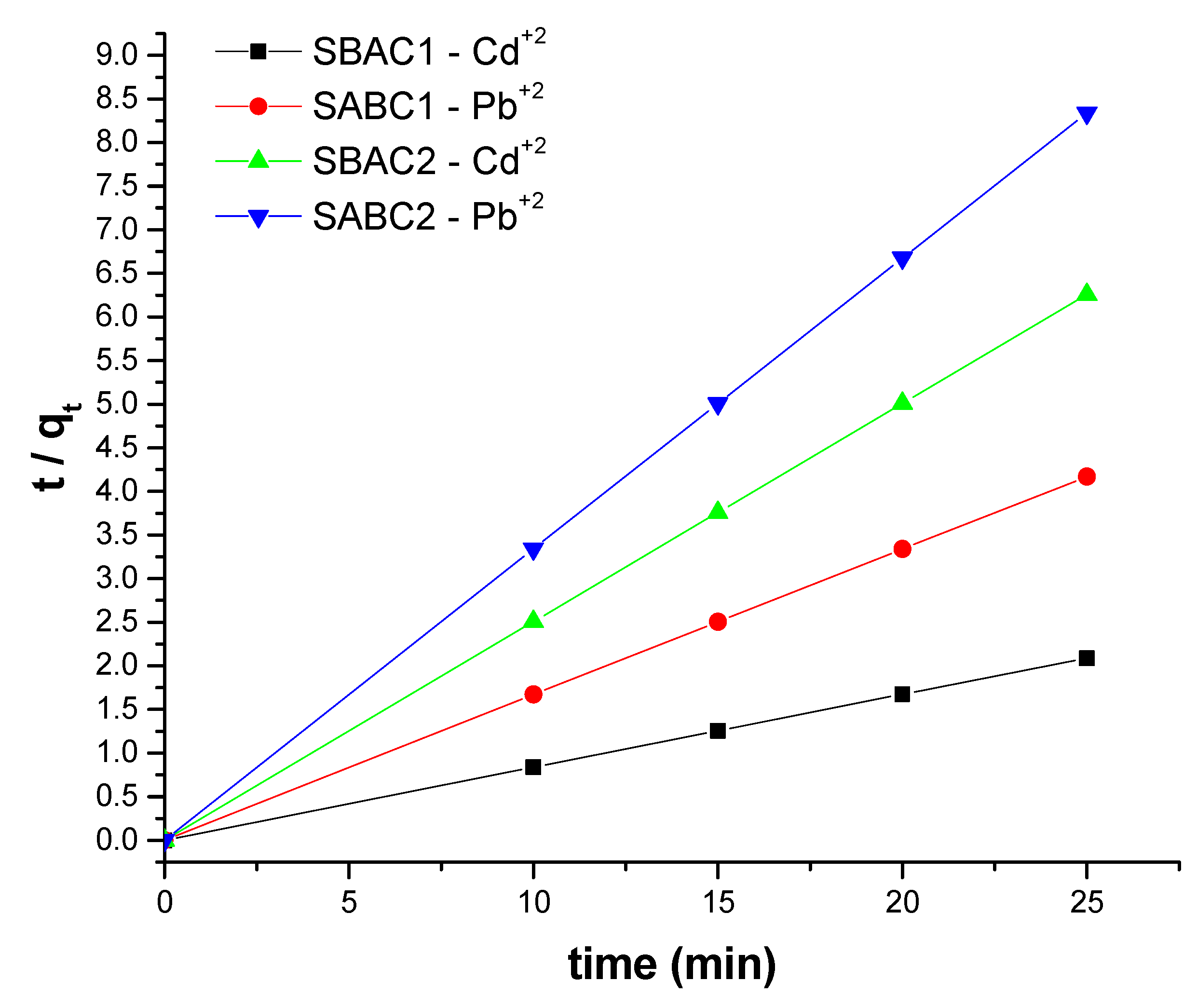
3.9. Adsorption Kinetics
| Kinetics models | Variables | SBAC1 | SBAC2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb+2 | Cd+2 | Pb+2 | Cd+2 | ||
| Pseudo-first order | k1 (min-1) | 0.00032 | 0.00085 | 0.0009 | 0.0009 |
| qe(cal) (mg g-1 ) | 12.00 | 11.937 | 12.00 | 11.9848 | |
| R12 | 0.500 | 0.1529 | 0.6621 | 0.6619 | |
| qe(exp) (mg g-1 ) | 1.7716 | 1.249 | 1.471 | 1.4720 | |
| Pseudo-second order | k2 [g mg-1 min-1] | 6.94 | 4.3556 | -110.1 | 13.527 |
| qe(cal) (mg g-1) | 11.999 | 11.936 | 11.998 | 11.9848 | |
| R22 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| qe(exp) (mg g-1) | 11.999 | 11.978 | 11.998 | 11.9817 | |
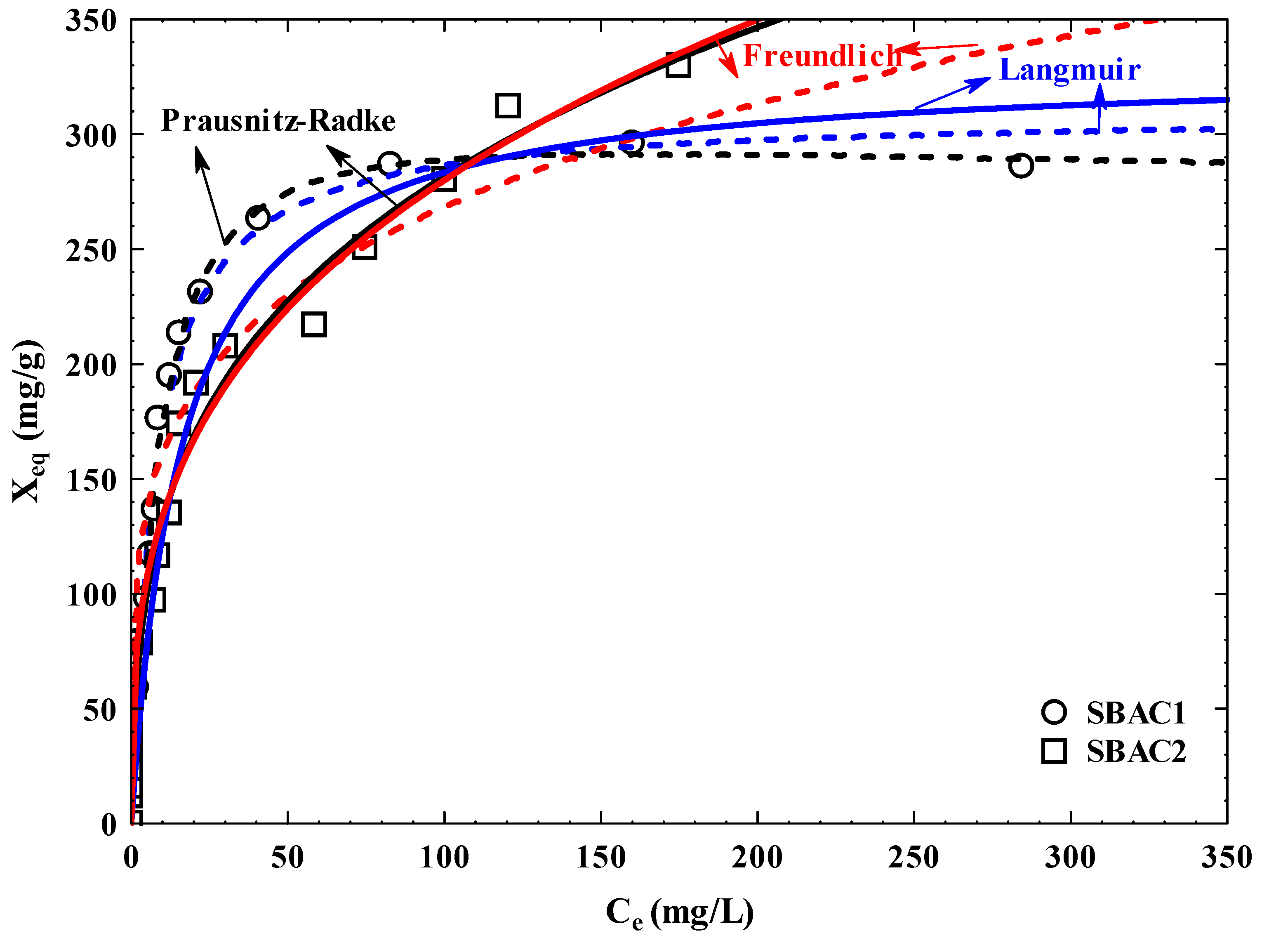
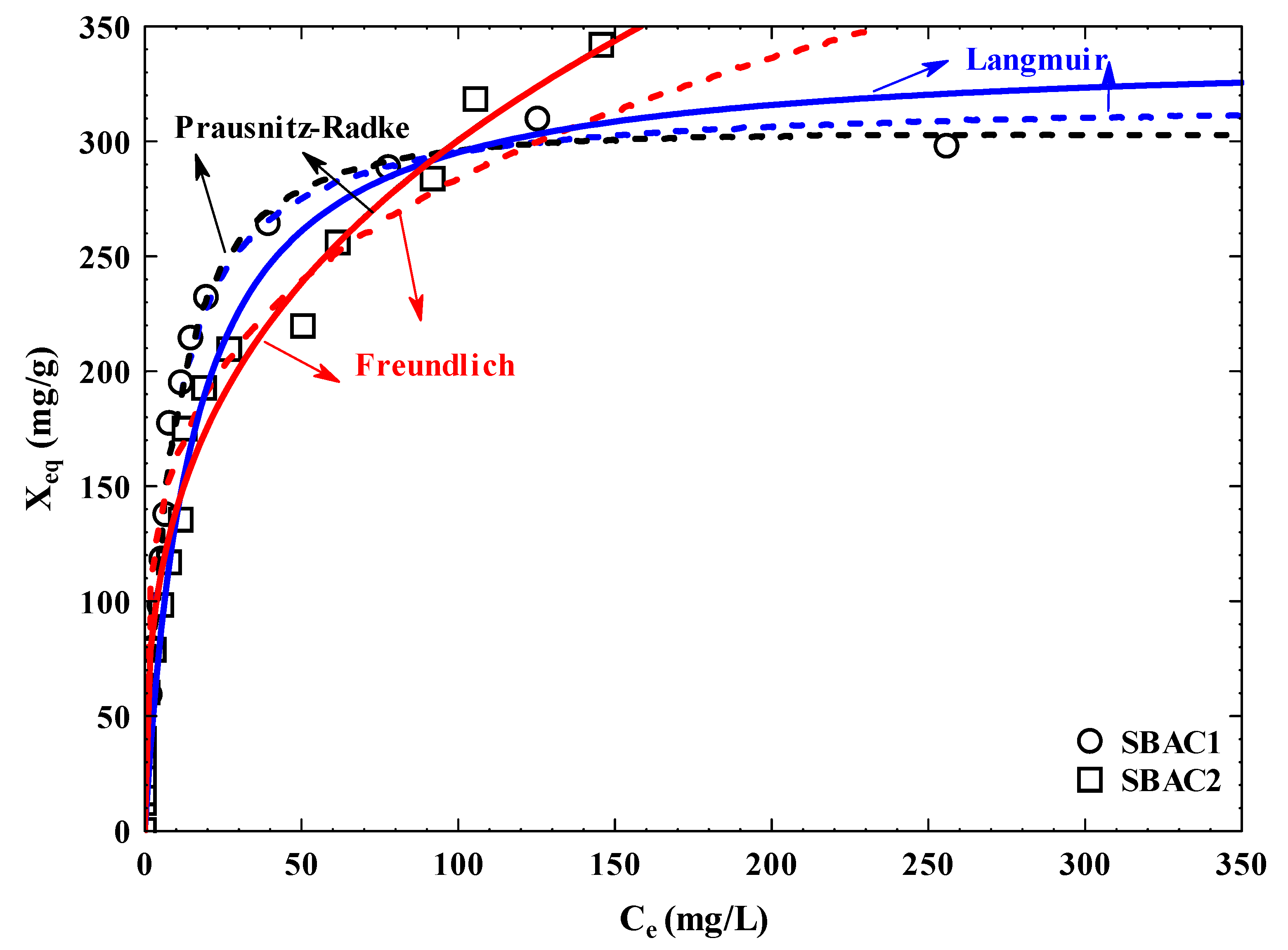
3.10. Adsorption Isotherm
| AC | Pollutant | Langmuir | Freundlich | Prausnitz–Radke | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xm(a) (mg/g) |
B (b) (L/mg) |
BXm (c) (L/g) |
X′m × 10−4 (mg/m2/g) |
%D | KF (d) (L/g) |
1/nF (e) | %D | a (f) (L/g) |
b (g) (Lβ/mgβ) |
β (h) | %D | ||
| SBAC 1 | Cd+2 | 309.24 | 0.13 | 40.20 | 0.92 | 5.94 | 96.07 | 0.22 | 23.51 | 33.37 | 0.08 | 1.06 | 5.80 |
| SBAC 2 | 329.62 | 0.06 | 19.78 | 0.66 | 12.84 | 63.79 | 0.32 | 9.41 | 109.99 | 1.42 | 0.71 | 8.41 | |
| SBAC 1 | Pb+2 | 318.46 | 0.13 | 41.40 | 0.95 | 6.67 | 91.66 | 0.25 | 21.70 | 37.06 | 0.10 | 1.03 | 6.66 |
| SBAC 2 | 339.61 | 0.07 | 23.77 | 0.68 | 13.19 | 64.79 | 0.33 | 8.49 | 1.52x107 | 2.34x105 | 0.67 | 8.50 | |
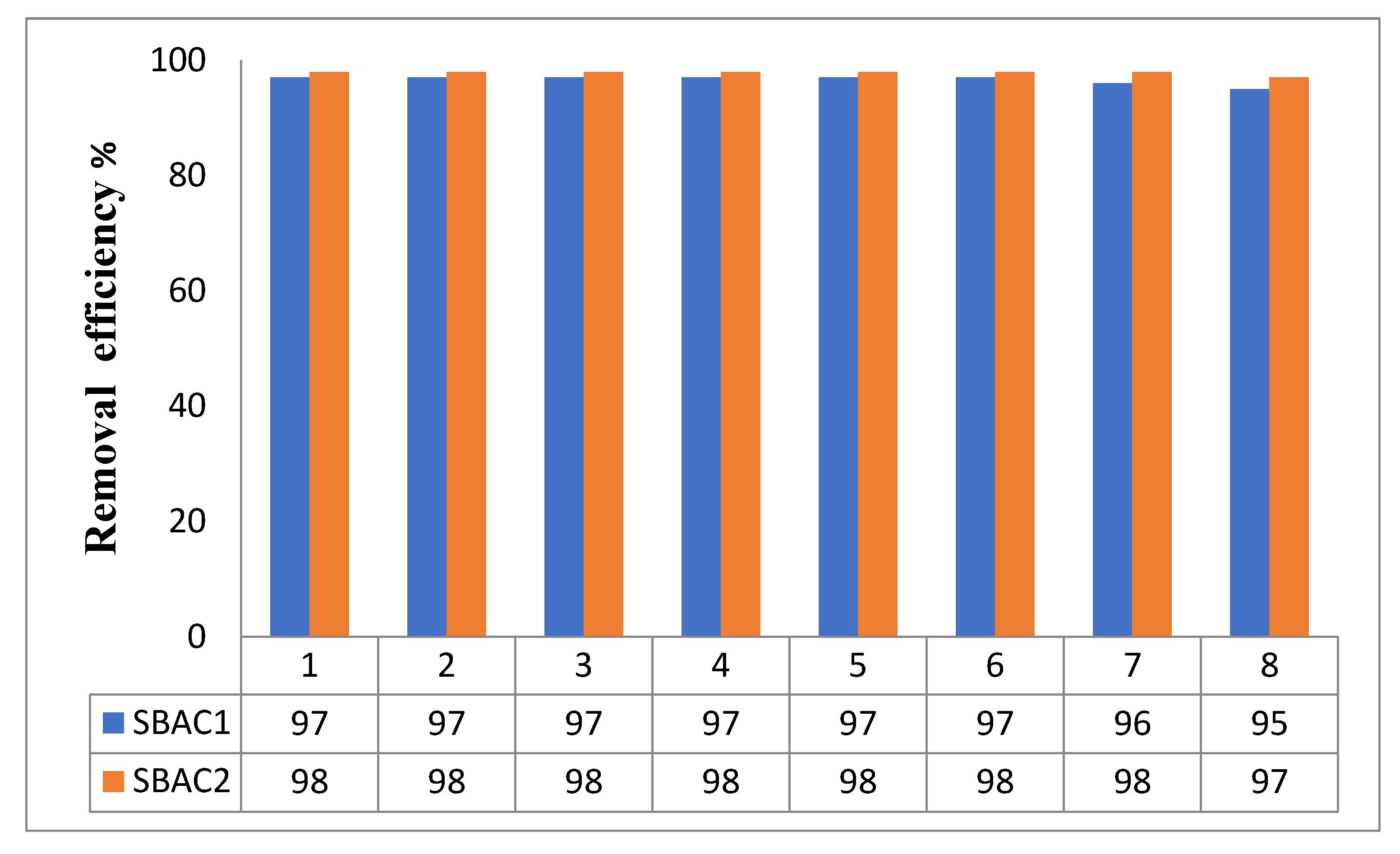
3.11. Analysis of Real Wastewater
| Sample | Metal ions | % Adsorption | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBAC1 | SBAC2 | ||
| TW | Cd+2 | 99.00 | 99.44 |
| Pb+2 | 99.03 | 99.80 | |
| GW | Cd+2 | 98.02 | 99.60 |
| Pb+2 | 98.53 | 98.73 | |
| RSW | Cd+2 | 98.33 | 98.58 |
| Pb+2 | 98.58 | 98.88 | |
| BTW | Cd+2 | 97.00 | 98.00 |
| Pb+2 | 97.19 | 98.50 | |
| WW1 | Cd+2 | 97.33 | 98.44 |
| Pb+2 | 97.96 | 98.77 | |
| WW2 | Cd+2 | 97.60 | 97.74 |
| Pb+2 | 97.54 | 97.88 | |
3.12. Recovery and Recyclability SBAC1 and SBAC2
3.13. Comparison with Another Method
| Adsorbent | Adsorbent dosage | Metal ions | Lower/upper concentration(mg/L) | pH | Time | qm(mg/g) | reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite | 0.3gm/50ml 0,005gm |
Pb+2 Cd+2 |
5-20 |
6 4 |
24h 20min. |
56.82 50.2 |
[61] [62] |
| MWCNTs | 0.03gm/50ml 0.05gm/50ml |
Pb+2 Cd+2 |
3-250 50-150 |
4 8 |
1.5h 1h |
200 200 |
[61] [63] |
| SBAC1 | 0.02gm/50ml | Pb+2 Cd+2 |
30-250 30-250 |
7 7 |
30 min 30 min |
318.46 309.24 |
This work |
| SBAC2 | 0.02gm/50ml | Pb+2 Cd+2 |
30-250 30-250 |
7 7 |
30 min 30 min |
339.61 329.62 |
This work |
4. Conclusions
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kacprzak, M.; Neczaj, E.; Fijałkowski, K.; Grobelak, A.; Grosser, A.; Worwag, M.; Rorat, A.; Brattebo, H.; Almås, Å.; Singh, B. R. , Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development. Environmental Research 2017, 156, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almahbashi, N. M. Y.; Kutty, S. R. M.; Ayoub, M.; Noor, A.; Salihi, I. U.; Al-Nini, A.; Jagaba, A. H.; Aldhawi, B. N. S.; Ghaleb, A. A. S. , Optimization of Preparation Conditions of Sewage sludge based Activated Carbon. Ain Shams Engineering Journal 2021, 12(2), 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinosa, L.; Ayol, A.; Baudez, J.-C.; Canziani, R.; Jenicek, P.; Leonard, A.; Rulkens, W.; Xu, G.; Van Dijk, L. , Sustainable and Innovative Solutions for Sewage Sludge Management. In Water, 2011; Vol. 3, pp 702-717. [CrossRef]
- Bibby, K.; Peccia, J., Identification of Viral Pathogen Diversity in Sewage Sludge by Metagenome Analysis. Environmental Science & Technology 2013, 47, (4), 1945-1951. [CrossRef]
- Nnorom, M.-A.; Saroj, D.; Avery, L.; Hough, R.; Guo, B. , A review of the impact of conductive materials on antibiotic resistance genes during the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge and animal manure. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2023, 446, 130628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samolada, M. C.; Zabaniotou, A. A. , Comparative assessment of municipal sewage sludge incineration, gasification and pyrolysis for a sustainable sludge-to-energy management in Greece. Waste Management 2014, 34(2), 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma. del Rosario Moreno, V.; Omar Francisco González, V.; Virginia Hernández, M.; Rigoberto Tovar, G., Removal of Heavy Metals Using Adsorption Processes Subject to an External Magnetic Field. In Heavy Metals, Hosam El-Din, M. S.; Refaat, F. A., Eds. IntechOpen: Rijeka, 2018; p Ch. 15.
- Senthilkumar, T. S.; Chattopadhyay, S. K.; Miranda, L. R., Optimization of Activated Carbon Preparation from Pomegranate Peel (Punica granatum Peel) Using RSM. Chemical Engineering Communications 2017, 204, 238 - 248. [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Li, C.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; Chen, L.; Zeng, G.; Shu, X.; Zhao, Y. , Study on activated carbon derived from sewage sludge for adsorption of gaseous formaldehyde. Bioresource Technology 2011, 102(2), 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, U.-S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S. H.; Lee, S. m.; Lee, B.-R.; Peck, D.-H.; Jung, D.-H. , Preparation of activated carbon from needle coke via two-stage steam activation process. Materials Letters 2019, 237, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, N. S.; Hashim, R.; Mohamad Amini, M. H.; Danish, M.; Sulaiman, O. , Optimization of activated carbon preparation from cassava stem using response surface methodology on surface area and yield. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 198, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jeyaseelan, S.; Graham, N., Physical and chemical properties study of the activated carbon made from sewage sludge. Waste management (New York, N.Y.) 2002, 22, (7), 755-60. [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Saroha, A. K. , Utilization of sludge based adsorbents for the removal of various pollutants: A review. The Science of the total environment 2017, 578, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björklund, K.; Li, L. Y. , Adsorption of organic stormwater pollutants onto activated carbon from sewage sludge. Journal of environmental management 2017, 197, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’goran, K. P. D. A.; Diabaté, D.; Yao, K. M.; Kouassi, N. G. L. B.; Gnonsoro, U. P.; Kinimo, K. C.; Trokourey, A. , Lead and cadmium removal from natural freshwater using mixed activated carbons from cashew and shea nut shells. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 2018, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavand, M.; Eslami, P.; Razeh, L. , The adsorption of cadmium and lead ions from the synthesis wastewater with the activated carbon: Optimization of the single and binary systems. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2020, 34, 101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerçel, Ö.; Gerçel, H. F. , Adsorption of lead(II) ions from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from biomass plant material of Euphorbia rigida. Chemical Engineering Journal 2007, 132(1), 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, I.; Butler, D.; Docx, P.; Hession, M.; Makropoulos, C.; McMullen, M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Pitman, A.; Rautiu, R.; Sawyer, R. , Pollutants in urban waste water and sewage sludge. Final report prepared for European Commission Directorate-General Environment, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Asuquo, E.; Martin, A.; Nzerem, P.; Siperstein, F.; Fan, X. , Adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions using mesoporous activated carbon adsorbent: Equilibrium, kinetics and characterisation studies. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2017, 5(1), 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzul Erosa, M. S.; Saucedo Medina, T. I.; Navarro Mendoza, R.; Avila Rodriguez, M.; Guibal, E. , Cadmium sorption on chitosan sorbents: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 61(3), 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Díaz, J. D.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Bautista-Toledo, I., Adsorption/bioadsorption of phthalic acid, an organic micropollutant present in landfill leachates, on activated carbons. Journal of colloid and interface science 2012, 369, (1), 358-365. [CrossRef]
- Karnib, M.; Kabbani, A.; Holail, H.; Olama, Z. , Heavy Metals Removal Using Activated Carbon, Silica and Silica Activated Carbon Composite. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Nazir, R.; Khan, M.; Khan, W.; Shah, M.; Afridi, S. G.; Zada, A. , The effective removal of heavy metals from water by activated carbon adsorbents of Albizia lebbeck and Melia azedarach seed shells. Soil and Water Research 2019, 15(No. 1), 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N., Soil water monitoring devices. In Soil Water and Ground Water Sampling, CRC Press: 2020; pp 15-30.
- Adam, A. M.; Saad, H. A.; Atta, A. A.; Alsawat, M.; Hegab, M. S.; Altalhi, T. A.; Refat, M. S. , An Environmentally Friendly Method for Removing Hg(II), Pb(II), Cd(II) and Sn(II) Heavy Metals from Wastewater Using Novel Metal–Carbon-Based Composites. Crystals 2021, 11(8), 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shwiniy, W. H.; El-Desoky, S. I.; Alrabie, A.; Abd El-wahaab, B. , Spectrophotometric determination of Zr(IV), Hg(II) and U(VI) in solution with their analytical applications: Structural characterization and molecular docking of the solid complexes. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2022, 279, 121400. [CrossRef]
- Gascó, G.; Lobo, M. C. , Composition of a Spanish sewage sludge and effects on treated soil and olive trees. Waste Management 2007, 27(11), 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascó, G.; Blanco, C. G.; Guerrero, F.; Méndez Lázaro, A. M. , The influence of organic matter on sewage sludge pyrolysis. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis 2005, 74(1), 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J. P.; Xiao, X. B.; Zhang, S. Y.; Zhao, X. Y.; Sato, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Wei, X. Y.; Takarada, T. , Preparation and characterization of bio-oils from internally circulating fluidized-bed pyrolyses of municipal, livestock, and wood waste. Bioresour Technol 2011, 102(2), 2009–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Hu, M.; Cui, B.; Liu, S.; Guo, D.; Xiao, B. , The effect of bioleaching on sewage sludge pyrolysis. Waste Management 2016, 48, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Kim, S.; Yoom, H.; Son, H. , Evaluation of organics reduction performance of the GAC filtration with regenerated carbons using the long-term operational data of drinking water treatment facilities. AQUA - Water Infrastructure, Ecosystems and Society, 2022, 71, (10), 1219-1228.
- Park, J. E.; Lee, G. B.; Hong, B. U.; Hwang, S. Y. , Regeneration of Activated Carbons Spent by Waste Water Treatment Using KOH Chemical Activation. In Applied Sciences, 2019; Vol. 9. [CrossRef]
- Reig, F. B.; Adelantado, J. G.; Moreno, M. M. , FTIR quantitative analysis of calcium carbonate (calcite) and silica (quartz) mixtures using the constant ratio method. Application to geological samples. Talanta 2002, 58(4), 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenne Diffo, B.; Elimbi, A.; Cyr, M.; Dika Manga, J.; Tchakoute Kouamo, H. , Effect of the rate of calcination of kaolin on the properties of metakaolin-based geopolymers. Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies 2015, 3(1), 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. , Biochar prepared from co-pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge and tea waste for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and mechanism. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2016, 220, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang Bing, Y. B.; Liu YuCheng, L. Y.; Liang QingLing, L. Q.; Chen MingYan, C. M.; Ma LiLi, M. L.; Li LingLi, L. L.; Liu Qian, L. Q.; Tu WenWen, T. W.; Lan DaWei, L. D.; Chen YuanYuan, C. Y. , Evaluation of activated carbon synthesized by one-stage and two-stage co-pyrolysis from sludge and coconut shell. 2019.
- Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Q.; Chen, M.; Ma, L.; Li, L.; Liu, Q.; Tu, W.; Lan, D.; Chen, Y. , Evaluation of activated carbon synthesized by one-stage and two-stage co-pyrolysis from sludge and coconut shell. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety 2019, 170, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Ma, L.; Yang, B.; Li, L.; Liu, Q. , Optimized preparation of activated carbon from coconut shell and municipal sludge. Materials Chemistry and Physics 2020, 241, 122327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herselman, J.; Snyman, H. , Guidelines for the utilisation and disposal of wastewater sludge. Water Research Commission 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Malack, M. H.; Dauda, M. , Competitive adsorption of cadmium and phenol on activated carbon produced from municipal sludge. Journal of environmental chemical engineering 2017, 5(3), 2718–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Idris, A. , Preparation and characterization of activated carbons derived from bio-solid: a review. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2014, 52, (25-27), 4848-4862. [CrossRef]
- Jindarom, C.; Meeyoo, V.; Kitiyanan, B.; Rirksomboon, T.; Rangsunvigit, P. , Surface characterization and dye adsorptive capacities of char obtained from pyrolysis/gasification of sewage sludge. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2007, 133, (1-3), 239-246. [CrossRef]
- Boehm, H. P. , Surface oxides on carbon and their analysis: a critical assessment. Carbon 2002, 40(2), 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Deming, L. S.; Deming, W. E.; Teller, E. , On a Theory of the van der Waals Adsorption of Gases. Journal of the American Chemical Society 1940, 62, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, D. H.; Stone, F. S. , The structure and properties of porous materials. Butterworths: 1958; Vol. 10.
- Rengaraj, S.; Moon, S.-H. , Kinetics of adsorption of Co (II) removal from water and wastewater by ion exchange resins. Water research 2002, 36(7), 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsehly, E.; Chechenin, N.; Makunin, A.; Vorobyeva, E.; Motaweh, H. , Oxidized carbon nanotubes filters for iron removal from aqueous solutions. Int. J. New Technol. Sci. Eng 2015, 2, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, E. A.; Abou El-Nour, K. M.; Awad, A. A.; Orabi, A. S. , Carbon nanotubes modified with 5, 7-dinitro-8-quinolinol as potentially applicable tool for efficient removal of industrial wastewater pollutants. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2020, 13(1), 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosa, S. A.; Al-Zhrani, G.; Salam, M. A. , Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified with 8-hydroxyquinoline. Chemical Engineering Journal 2012, 181, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzombak, D. A.; Morel, F. M. , Surface complexation modeling: hydrous ferric oxide. John Wiley & Sons: 1991.
- Mushtaq, S.; Jamil, F.; Hussain, M.; Inayat, A.; Majeed, K.; Akhter, P.; Khurram, M. S.; Shanableh, A.; Kim, Y. M.; Park, Y.-K. , Utilizing sludge-based activated carbon for targeted leachate mitigation in wastewater treatment. Environmental Research 2024, 249, 118326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J. , Glycine-assisted hydrothermal synthesis and adsorption properties of crosslinked porous α-Fe2O3 nanomaterials for p-nitrophenol. Chemical engineering journal 2012, 211, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Tian, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, L.; Yan, S. , Manganese dioxide/iron oxide/acid oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotube magnetic nanocomposite for enhanced hexavalent chromium removal. Chemical Engineering Journal 2013, 234, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M. Y.; Ahmed, I. S.; Mohamed, T. Y.; Khatab, M. , A controlled, template-free, and hydrothermal synthesis route to sphere-like α-Fe2O3 nanostructures for textile dye removal. RSC Advances 2016, 6(24), 20001–20013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C. , Magnetic Fe3O4/MnO2 core–shell nano-composite for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. SN Applied Sciences 2020, 2(8), 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C. H.; Smith, D.; Huitson, A. , A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm. I. Theoretical. Journal of colloid and interface science 1974, 47(3), 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrowais, R.; Said, N.; Bashir, M. T.; Ghazy, A.; Alwushayh, B.; Daiem, M. M. A. , Adsorption of Diphenolic Acid from Contaminated Water onto Commercial and Prepared Activated Carbons from Wheat Straw. Water 2023, 15(3), 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrowais, R.; Bashir, M. T.; Khan, A. A.; Bashir, M.; Abbas, I.; Abdel Daiem, M. M. , Adsorption and Kinetics Modelling for Chromium (Cr6+) Uptake from Contaminated Water by Quaternized Date Palm Waste. Water 2024, 16(2), 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrowais, R.; Abdel Daiem, M. M.; Nasef, B. M.; Said, N. , Activated Carbon Fabricated from Biomass for Adsorption/Bio-Adsorption of 2, 4-D and MCPA: Kinetics, Isotherms, and Artificial Neural Network Modeling. Sustainability 2023, 16(1), 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaymon, A. H.; Mohammed, A. A.; Al-Musawi, T. J. , Competitive biosorption of lead, cadmium, copper, and arsenic ions using algae. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2013, 20, 3011–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Salam, E. T.; Abou El-Nour, K. M.; Awad, A. A.; Orabi, A. S. , Carbon nanotubes modified with 5,7-dinitro-8-quinolinol as potentially applicable tool for efficient removal of industrial wastewater pollutants. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2020, 13(1), 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, S.; Shalmani, M. M.; Zakaria, S. A. In Removal of heavy metals from Tehran south agricultural water by Zeolite N. P. / PEG / GO nanocomposite, 2019; 2019.
- Obayomi, K.; Bello, J.; Yahya, M. D.; Chukwunedum, E.; Adeoye, J., Statistical analyses on effective removal of cadmium and hexavalent chromium ions by multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). Heliyon 2020, 6, (6). [CrossRef]

| Samples | Yield % | C(wt. %)a | H(wt. %)a | O(wt. %)b | N(wt. %) | H/C | O/C | N/C | Ash % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSS | 67.7 | 9.2 | 14.3 | 9.3 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 13.9 | |
| SBAC1 | 83 | 90.8 | 4.2 | 5.1 | 1.6 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 7.4 |
| SBAC1 | 85 | 93.1 | 5.5 | 4.9 | 2.1 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 2.7 |
| Component | Elements (wt %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RSS | SBAC1 | SBAC2 | |
| Al | 3.00 | 3.65 | 5.08 |
| Ca | 11.21 | 19.01 | 20.67 |
| Cu | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| Fe | 8.02 | 9.44 | 9.52 |
| K | 1.03 | 3.69 | 1.56 |
| Mn | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.22 |
| Nb | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Ni | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| P | 4.08 | 4.93 | 5.56 |
| Si | 13.20 | 15.20 | 15.05 |
| Ti | 1.34 | 1.76 | 1.68 |
| Sr | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.22 |
| Zn | 0.35 | 0.59 | 0.45 |
| Zr | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Co | 0.04 | 0.06 | ــــــــ |
| Cl | 1.01 | 1.73 | ـــــــ |
| Mo | 0.02 | 0.04 | ـــــــ |
| Samples | SBET(m2 g-1) | VT (cm3 g-1) | VBJH (cm3 g-1) | ζ(mV) |
| SBAC1 | 336.339 | 0.268858 | 1.59873 | -11.50 |
| SBAC2 | 498.386 | 0.374884 | 1.5026 | -8.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





