Submitted:
30 July 2024
Posted:
31 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
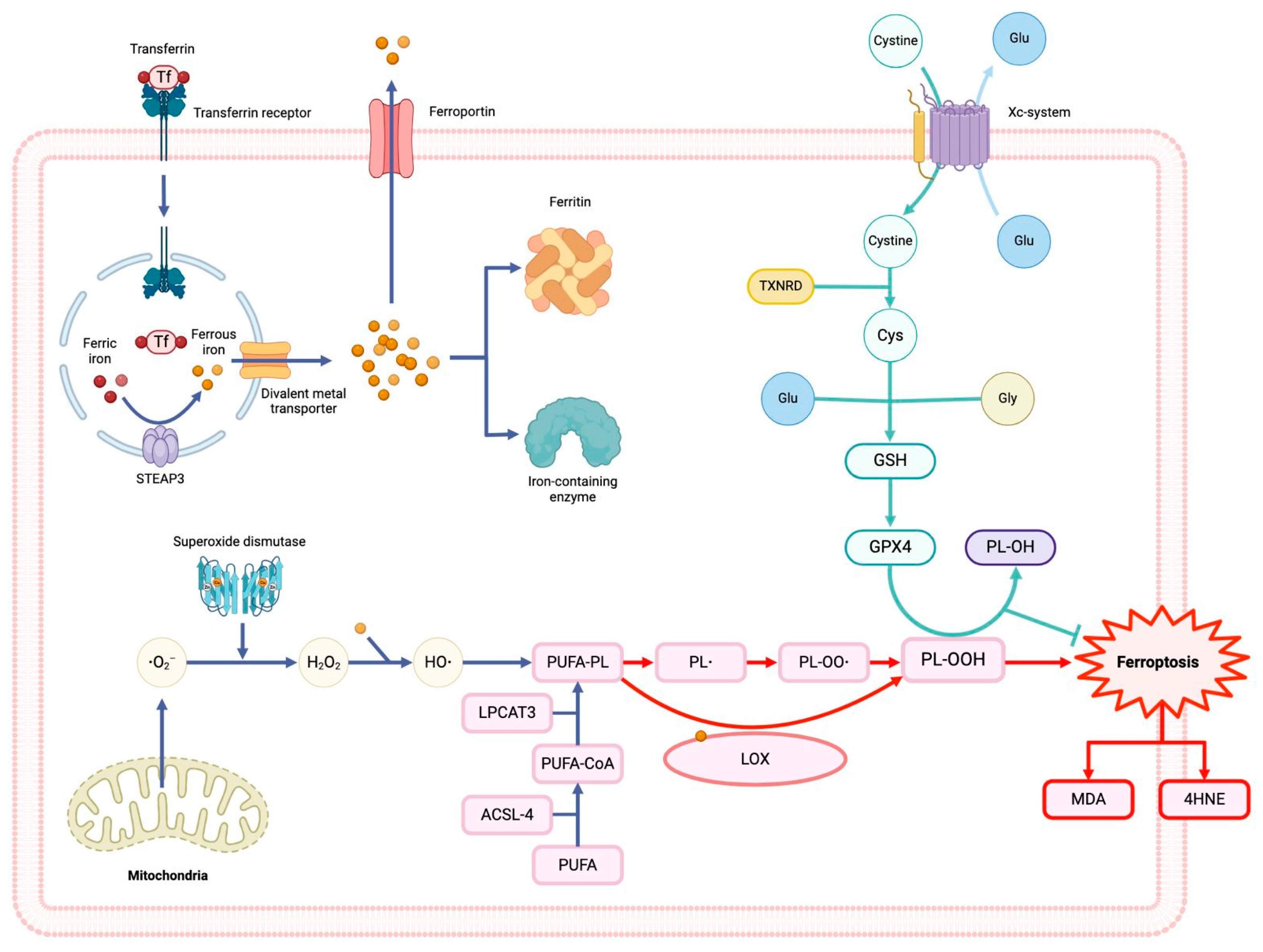
2. Ferroptosis and CVDs
3. Inflammation and Ferroptosis
4. Macrophages and Ferroptosis
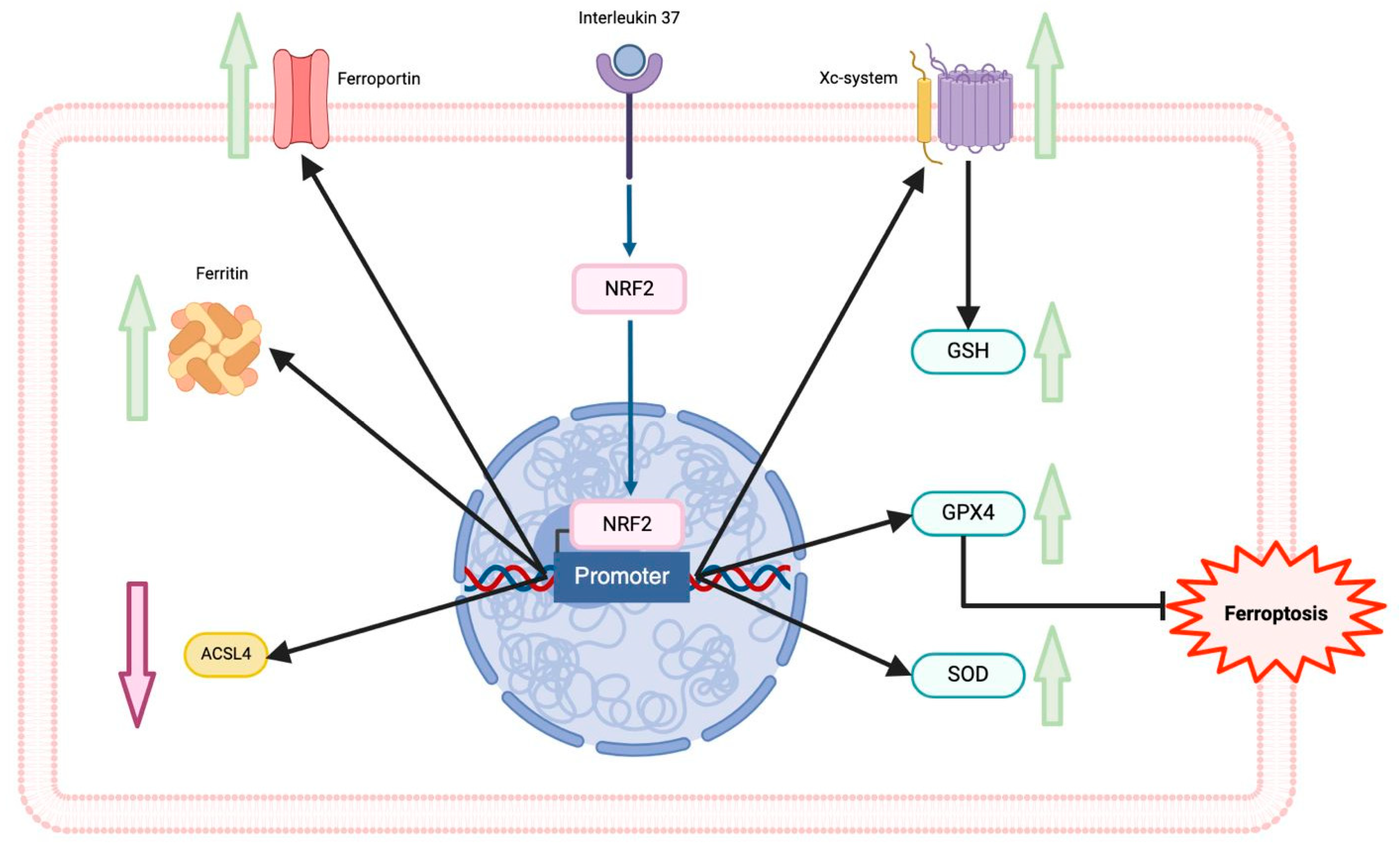
5. Protective Role of Interleukin-37 in Cardiovascular Diseases
5. Interleukin-37 and Ferroptosis in Cardiovascular Diseases
6. Conclusions and Conclusion Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, L.-H.; Fefelova, N.; Pamarthi, S.H.; Gwathmey, J.K. Molecular Mechanisms of Ferroptosis and Relevance to Cardiovascular Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Miao, R.; Zhong, J. Targeting Iron Metabolism and Ferroptosis as Novel Therapeutic Approaches in Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, H.; Wang, S.; Tang, G.; Zhai, C.; Shen, L. Ferroptosis: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 688605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, A.C.B.; Zeng, H.; Chen, J.-X. The therapeutic potential of targeting ferroptosis in the treatment of mitochondrial cardiomyopathies and heart failure. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2023, 83, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Ye, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Yao, C. Construction of a Novel Ferroptosis-Related Gene Signature of Atherosclerosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 800833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Ardehali, H.; Min, J.; Wang, F. The molecular and metabolic landscape of iron and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nold, M.F.; A Nold-Petry, C.; A Zepp, J.; E Palmer, B.; Bufler, P.; A Dinarello, C. IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Camarillo, G.; Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K. Interleukin 35 (IL-35) and IL-37: Intestinal and peripheral expression by T and B regulatory cells in patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cytokine 2015, 75, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.C.; Puranik, R.; Fan, J.; Fei, J.; Hambly, B.D.; Bao, S. Clinical Implications of IL-32, IL-34 and IL-37 in Atherosclerosis: Speculative Role in Cardiovascular Manifestations of COVID-19. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 630767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Han, X.; Xia, N.; Zhao, Q.; Cheng, Z. IL-37 suppresses macrophage ferroptosis to attenuate diabetic atherosclerosis via the NRF2 pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An Iron-Dependent Form of Nonapoptotic Cell Death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassannia, B.; Vandenabeele, P.; Berghe, T.V. Targeting Ferroptosis to Iron Out Cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 830–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrera, L.; Espiritu, R.A.; Ros, U.; Weber, J.; Schmitt, A.; Stroh, J.; Hailfinger, S.; von Karstedt, S.; García-Sáez, A.J. Ferroptotic pores induce Ca2+ fluxes and ESCRT-III activation to modulate cell death kinetics. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1644–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, S.; Conrad, M. Iron and ferroptosis: A still ill-defined liaison. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Ouyang, S.; Xie, Z.; Zhi, C.; Yu, J.; Tan, X.; Li, P.; Lin, X.; Ma, W.; Liu, Z.; et al. The suppression of hyperlipid diet-induced ferroptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells protests against atherosclerosis independent of p53/SCL7A11/GPX4 axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2023, 238, 1891–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Ferroptosis: Death by Lipid Peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfay, L.; Paul, B.T.; Konstorum, A.; Deng, Z.; Cox, A.O.; Lee, J.; Furdui, C.M.; Hegde, P.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V. Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 Protects Ovarian Cancer Cells from Ferroptotic Cell Death. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5355–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Lv, G.; Wang, H. Ferroptosis as a therapeutic target for inflammation-related intestinal diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1095366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocansey, D.K.W.; Yuan, J.; Wei, Z.; Mao, F.; Zhang, Z. Role of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis and as a therapeutic target of inflammatory bowel disease (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 51, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioranelli, M.; Roccia, M.G.; Flavin, D.; Cota, L. Regulation of Inflammatory Reaction in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, R.; Xi, Q.; Wu, H.; Shi, T.; Chen, W. Astragalus polysaccharide prevents ferroptosis in a murine model of experimental colitis and human Caco-2 cells via inhibiting NRF2/HO-1 pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 911, 174518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, J. Ferroptosis: A Double-Edged Sword in Gastrointestinal Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Kim, J.-W.; Zhou, Z.; Lim, C.-W.; Kim, B. Ferroptosis Affects the Progression of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis via the Modulation of Lipid Peroxidation–Mediated Cell Death in Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 190, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, T.; Liu, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, R. DAMP-sensing receptors in sterile inflammation and inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 20, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. The mechanism of HMGB1 secretion and release. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agborbesong, E.; Li, L.X.; Li, L.; Li, X. Molecular Mechanisms of Epigenetic Regulation, Inflammation, and Cell Death in ADPKD. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 922428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Bayir, H.; Bush, A.I.; Conrad, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Gascón, S.; Hatzios, S.K.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 2017, 171, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, M.; Cotella, D.; Santoro, C.; Corà, D.; Barlev, N.A.; Piacentini, M.; Corazzari, M. Aldo-keto reductases protect metastatic melanoma from ER stress-independent ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-S.; Wang, S.-F.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Yin, P.-H.; Yeh, T.-S.; Lee, H.-C.; Tseng, L.-M. CHAC1 degradation of glutathione enhances cystine-starvation-induced necroptosis and ferroptosis in human triple negative breast cancer cells via the GCN2-eIF2α-ATF4 pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 114588–114602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Tao, J.; Yang, Y.; Tan, S.; Liu, H.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, F.; Wu, B. Ferroptosis involves in intestinal epithelial cell death in ulcerative colitis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çolakoğlu, M.; Tunçer, S.; Banerjee, S. Emerging cellular functions of the lipid metabolizing enzyme 15-Lipoxygenase-1. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uauy, R.; Mena, P.; Rojas, C. Essential fatty acid metabolism in the micropremie. Clin. Perinatol. 2000, 27, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- I Sperling, R.; I Benincaso, A.; Knoell, C.T.; Larkin, J.K.; Austen, K.F.; Robinson, D.R. Dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids inhibit phosphoinositide formation and chemotaxis in neutrophils. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- H.W. de Jonge, D.H. Dekkers, J.M. Lamers, Polyunsaturated fatty acids and signalling via phospholipase C-beta and A2 in myocardium, Mol. Cell. Biochem. 157, (1996) 199–210.
- Zhang Z, Tang J, Song J, Xie M, Liu Y, Dong Z, Liu X, Li X, Zhang M, Chen Y, Shi H, Zhong J. Elabela alleviates ferroptosis, myocardial remodeling, fibrosis and heart dysfunction in hypertensive mice by modulating the IL-6/STAT3/GPX4 signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022; 181:130–42.
- Ren F, Yang Y, Wu K, Zhao T, Shi Y, Song M, et al. The effects of dandelion polysaccharides on iron me-tabolism by regulating hepcidin via JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021:7184760.
- Alam Z, Devalaraja S, Li M, To TKJ, Folkert IW, MitchellVelasquez E, Dang MT, Young P, Wilbur CJ, Sil-verman MA, Li X, Chen YH, Hernandez PT, Bhattacharyya A, Bhattacharya M, Levine MH, Haldar M. Counter regulation of spic by NF-κB and STAT signaling controls inflammation and iron metabolism in macrophages. Cell Rep. 2020;31: 107825.
- Liu N, Liang Y, Wei T, Zou L, Huang X, Kong L, et al. The role of ferroptosis mediated by NRF2/ERK-regulated ferritinophagy in CdTe QDs induced inflammation in macrophage. J Hazard Mater. 2022;436:129043.
- Sanz-Ezquerro, J.J.; Cuenda, A. p38 Signalling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ma, T. Function and inhibition of P38 MAP kinase signaling: Targeting multiple inflammation diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 220, 115973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Franczyk, B.; Rysz-Górzyńska, M.; Ławiński, J.; Rysz, J. Emerging Anti-Atherosclerotic Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.-L.; Jin, X.-K.; Zhang, S.-M.; Huang, Q.-X.; Ji, P.; Deng, X.-C.; Cheng, S.-X.; Chen, W.-H.; Zhang, X.-Z. Specific activation of cGAS-STING pathway by nanotherapeutics-mediated ferroptosis evoked endogenous signaling for boosting systemic tumor immunotherapy. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li C, Liu J, Hou W, Kang R, Tang D. STING1 promotes ferroptosis through MFN1/ 2-dependent mitochondrial fusion. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:698679–698679.
- Couillin, I.; Riteau, N. STING Signaling and Sterile Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.; Qin, D.; Zhao, C.; Chai, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, W.; Tong, L.; Lv, L.; Wang, Y.; Rehwinkel, J.; et al. Redox homeostasis maintained by GPX4 facilitates STING activation. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeney, V.; Eaton, J.W.; Balla, G.; Balla, J. Natural History of the Bruise: Formation, Elimination, and Biological Effects of Oxidized Hemoglobin. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, M.P.; Bozza, M.T. Red alert: labile heme is an alarmin. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 38, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Pitzer, A.L.; Li, X.; Li, P.-L.; Zhang, Y. Contribution of redox-dependent activation of endothelial Nlrp3 inflammasomes to hyperglycemia-induced endothelial dysfunction. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdei, J.; Tóth, A.; Balogh, E.; Nyakundi, B.B.; Bányai, E.; Ryffel, B.; Paragh, G.; Cordero, M.D.; Jeney, V. Induction of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Heme in Human Endothelial Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4310816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillemans, M.; Karampini, E.; Kat, M.; Bierings, R. Exocytosis of Weibel–Palade bodies: how to unpack a vascular emergency kit. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belcher, J.D.; Chen, C.; Nguyen, J.; Milbauer, L.; Abdulla, F.; Alayash, A.I.; Smith, A.; Nath, K.A.; Hebbel, R.P.; Vercellotti, G.M. Heme triggers TLR4 signaling leading to endothelial cell activation and vaso-occlusion in murine sickle cell disease. Blood 2014, 123, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.; Knapp, S. Heme and hemolysis in innate immunity: adding insult to injury. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 50, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fang, Z.-M.; Yi, X.; Wei, X.; Jiang, D.-S. The interaction between ferroptosis and inflammatory signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapralov, A.A.; Yang, Q.; Dar, H.H.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Anthonymuthu, T.S.; Kim, R.; St Croix, C.M.; Mikulska-Ruminska, K.; Liu, B.; Shrivastava, I.H.; et al. Redox lipid reprogramming commands susceptibility of macrophages and microglia to ferroptotic death. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, L.; Negre-Salvayre, A.; Costa, L.; Canonne-Hergaux, F. Iron gene expression profile in atherogenic Mox macrophages. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Tian, J.; Shen, W. The Role of Macrophage Iron Overload and Ferroptosis in Atherosclerosis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, A.; Guo, L.; Sakamoto, A.; Virmani, R.; Finn, A.V. New insights into the role of iron in inflammation and atherosclerosis. EBioMedicine 2019, 47, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Luo, G.; Guo, X.; Jiang, C.; Zeng, H.; Zhou, F.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Yao, P. Macrophage iron retention aggravates atherosclerosis: Evidence for the role of autocrine formation of hepcidin in plaque macrophages. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1865, 158531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai Y, Dong C: Therapeutic antibodies that target inflammatory cytokines in autoimmune diseases. Int Immunol, 2016; 28: 181–88.
- Dinarello CA, Nold-Petry C, Nold M et al: Suppression of innate inflammation and immunity by interleukin-37. Eur J Immunol, 2016; 46: 1067–81.
- Xu, W.-D.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Insights into IL-37, the role in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirk, S.; Agrawal, D.K. Immunobiology of IL-37: mechanism of action and clinical perspectives. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar S, Hanning CR, Brigham-Burke MR, Rieman DJ, Lehr R, Khandekar S, et al. Interleukin-1F7B (IL-1H4/IL-1 F7) is processed by caspase-1 and mature IL-1F7B binds to the IL-18 receptor but does not induce IFN-gamma production. Cytokine, 2002;18:61–71.
- Tetè, S.; Tripodi, D.; Rosati, M.; Conti, F.; Maccauro, G.; Saggini, A.; Cianchetti, E.; Caraffa, A.; Antinolfi, P.; Toniato, E.; et al. IL-37 (IL-1F7) the Newest Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Which Suppresses Immune Responses and Inflammation. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2012, 25, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, S.; Bozza, S.; Oikonomou, V.; Renga, G.; Casagrande, A.; Iannitti, R.G.; Puccetti, M.; Garlanda, C.; Kim, S.; Li, S.; et al. IL-37 Inhibits Inflammasome Activation and Disease Severity in Murine Aspergillosis. PLOS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, R.; Agrawal, D.K.; Thankam, F.G. Treg cells in atherosclerosis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 4897–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, H.; Moaaz, M.; Moaaz, M. The novel role of IL-37 to enhance the anti-inflammatory response of regulatory T cells in patients with peripheral atherosclerosis. Vascular 2020, 28, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lu, Z.; Meng, K.; Wu, B.; Yu, K.; Chai, M.; et al. Elevated Plasma IL-37, IL-18, and IL-18BP Concentrations in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 165742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, M.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, G.; Liu, W.; Han, W.; Yang, L.; et al. The Protective Effect of Interleukin-37 on Vascular Calcification and Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice with Diabetes. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2015, 35, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, R.O.; Chin, V.K.; Isnadi, M.F.A.R.; Majid, R.A.; Abdullah, M.A.; Lee, T.Y.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Hussain, M.K.; Basir, R. The Role, Involvement and Function(s) of Interleukin-35 and Interleukin-37 in Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Min, X.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, L.; Peng, Y.; Meng, K.; Li, D.; Ji, Q.; et al. Increased IL-37 concentrations in patients with arterial calcification. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 461, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bautista, F.; Posadas-Sánchez, R.; Vázquez-Vázquez, C.; Fragoso, J.M.; Rodríguez-Pérez, J.M.; Vargas-Alarcón, G. IL-37 Gene and Cholesterol Metabolism: Association of Polymorphisms with the Presence of Hypercholesterolemia and Cardiovascular Risk Factors. The GEA Mexican Study. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Naji, D.H.; Xia, Y.; Li, S.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Genomic Variant in IL-37 Confers A Significant Risk of Coronary Artery Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D., Wang A., Jiang F., Hu J., Zhang X. Effects of interleukin-37 on cardiac function after myocardial infarction in mice. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015;8:5247–5251.
- Wu, B.; Meng, K.; Ji, Q.; Cheng, M.; Yu, K.; Zhao, X.; Tony, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, C.; et al. Interleukin-37 ameliorates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 176, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.C.; Puranik, R.; Fan, J.; Fei, J.; Hambly, B.D.; Bao, S. Clinical Implications of IL-32, IL-34 and IL-37 in Atherosclerosis: Speculative Role in Cardiovascular Manifestations of COVID-19. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 630767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Leng, Y.; Tao, J.; Li, L.; Qiu, Z.; Xia, Z. Activation of NRF2/FPN1 pathway attenuates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by regulating iron homeostasis and ferroptosis. Cell Stress Chaperon- 2022, 27, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Linghu, M.; Luo, X.; Lv, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Isorhamnetin alleviates ferroptosis-mediated colitis by activating the NRF2/HO-1 pathway and chelating iron. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 135, 112318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Chu, W.; Zhang, H.; Peng, Y. Nrf2 and Ferroptosis: A New Research Direction for Ischemic Stroke. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 3885–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




