Submitted:
25 July 2024
Posted:
26 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Basic PN Terminology
1.2. Structure of the Article
2. Preliminaries
4. Elements in the support of each minimal T-semiflow can be fired sequentially.
3. Control of ES3PR
- Ni = (PSi ∪ {p0i} ∪ PRi, Ti, Fi, Wi), i ∈ Im
-
P = Ps ∪ P0 ∪ PR is a partition such that
- PS = ∪ i ∈ Im PSi, PSi ≠ ∅ and PSi ∩ PSj = ∅, ∀i ≠ j (i, j ∈ Im)
- PR = ∪ i ∈ Im PRi = {r1, r2, …, rn}, n > 0
- P0 = ∪ i ∈ Im {p0i}
- The elements in P0, PS, and PR are called idle, operation, and resource places, respectively
- The output transitions of an idle place are called source transitions.
- T = ∪ i ∈ Im Ti, Ti ≠ ∅, Ti ∩ Tj = ∅ for all i ≠ j.
- ∀i ∈ Im the subset Ni generated by PSi ∪ {p0i} ∪ Ti is a strongly connected state machine such that every cycle contains p0i
- ∀r ∈ PR, there exists a unique minimal P-semiflow Ir ∈ IN|P| (here IN = {0, 1, 2, …}) such that {r} = ||Ir|| ∩ PR, P0 ∩ ||Ir|| = ∅, PS ∩ ||Ir|| ≠ ∅ and Ir(r) = 1
- PS = ∪ r ∈ PR (||Ir||\{r})
- N is a strongly connected net.
3.1. Siphons in Petri Nets Control
3.2. Procedure of Setting the Supervisor for ES3PR
3.3. Illustrative Example of ES3PR—Siphons and P-Invariants
4. Controllability of Siphons in Generalized Petri Nets
4.1. Controllability of Elementary Siphons
4.2. Controllability of Dependent Siphons
4.3. Illustrative Example of ES3PR—Control
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Čapkovič, F. Petri Net Based S3PR Models of Automated Manufacturing Systems with Resources and Their Deadlock Prevention. Acta Polytechnica Hungarica, Vol. 20, No. 6, 2023, pp. 79-96. [CrossRef]
- Čapkovič, F. Modeling and Control of Discrete-Event Systems with Partial Non-Deteminism Using Petri Nets. Acta Polytechnica Hungarica, Vol. 17, No. 4, 2020, pp.
- Čapkovič, F. Control of Deadlocked Discrete-Event Systems Using Petri Nets. Acta Polytechnica Hungarica, Vol. 19, No. 2, 2022, pp.
- Čapkovič, F. Modeling and Control of Resource Allocation Systems within Discrete-Event Systems by Means of Petri Nets—Part 1: Invariants, Siphons and Traps in Deadlock Avoidance. Computing and Informatics, Vol. 40, No. 3, 2021, pp. 648-689.
- Li, Z.W.; Zhou, M.C. Deadlock Resolution in Automated Manufacturing Systems. A Novel Petri Net Approach. London, Springer Press, 2009.
- Li, Z.W.; Uzam, M.; Zhou, M.C.: Deadlock Control of Concurrent Manufacturing Process Sharing Finite Resources. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 38, 2008, pp. 787-800. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M. Liveness-Enforcing Supervisor Design for a Class of Generalized Petri Net Models of Flexible Manufacturing Systems. IET Control Theory & Applications, Vol. 1, No. 4, 2007, pp. 955–967. [CrossRef]
- Barkaoui, K.; Abdallah, I.B. A Deadlock Prevention Method for a Class of FMS. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Vancouver, Canada, 1995, pp. 4119–4124.
- Barkaoui, K.; Pradat-Peyre, J.F. On Liveness and Controlled Siphons in Petri Nets. In: Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Application and Theory of Petri Nets, Osaka, Japan, June 24–28, 1996, LNCS, Vol. 1091. New York, Springer, pp. 57–72.
- Tricas, F.; García-Vallès, F.; Colom, J.M.; Ezpeleta, J. A Partial Approach to the Problem of Deadlocks in Processes with Resources, Technical Report, GISI-RR-97–05, University of Zaragoza, Spain, 1997.
- Abdallah, I.B. El Maraghy, H.A. Deadlock Prevention and Avoidance in FMS: A Petri Net Based Approach. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 14, 1998, pp. 704–715.
- Li, Z.W.; Zhou, M.C. Elementary Siphons of Petri Nets and Their Application to Deadlock Prevention in Flexible Manufacturing Systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics—Part A: Systems and Humans, Vol. 34, No. 1, 2004, pp. 38–51.
- Davidrajuh, R. GPenSIM, General Purpose Petri Net Simulator for MATLAB Platform. Available: http://www.davidrajuh.
- Davidrajuh, R. General Purpose Petri Net Simulator GPenSIM v. 9.0, 2014, Available: http://www.davidrajuh.net/gpensim/v9/GPenSIM_v9_User_Manual.pdf.
- . Davidrajuh, R. Modeling Discrete-Event Systems with GPenSIM. Springer, 2018. ISBN-13: 978-3-319-73101-8. Available: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-319-73102-5.
- Li, Z.W.; Zhou, M.C. Clarifications on the Definitions of Elementary Siphons of Petri Nets. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics Cybernetics—Part A: Systems and Humans, Vol. 36, No. 6, 2006, pp. 1227–1229.
- Petri, C.A. Communication with Automata. Ph.D. Thesis. Technical University of Darmstadt, 1962, 128 pages (in German).
- Peterson, J.L. Petri Net Theory and the Modeling of Systems. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1981.
- Murata, T. Petri Nets: Properties, Analysis and Applications, Proceedings of the IEEE, Vol. 77, No. 4, 1989, pp. 541-580.
- Desel, J.; Reisig, W. Place/Transition Petri Nets. In: W. Reisig, G. Rozenberg (Eds.): Advances of Petri Nets, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 1491, Springer, Heidelberg, 1998, pp. 122-173.
- Hou,Y. F.; Barkaoui, K. Deadlock Analysis and Control Based on Petri Nets: A Siphon Approach Review. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 9, No. 5, 2017, pp. 1- 30. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Barkaoui, K. Necessary and Sufficient Liveness Condition of GS3PR Petri Nets. International Journal of Systems Science, Vol. 46, No. 7, 2015, pp. 1147-1160.
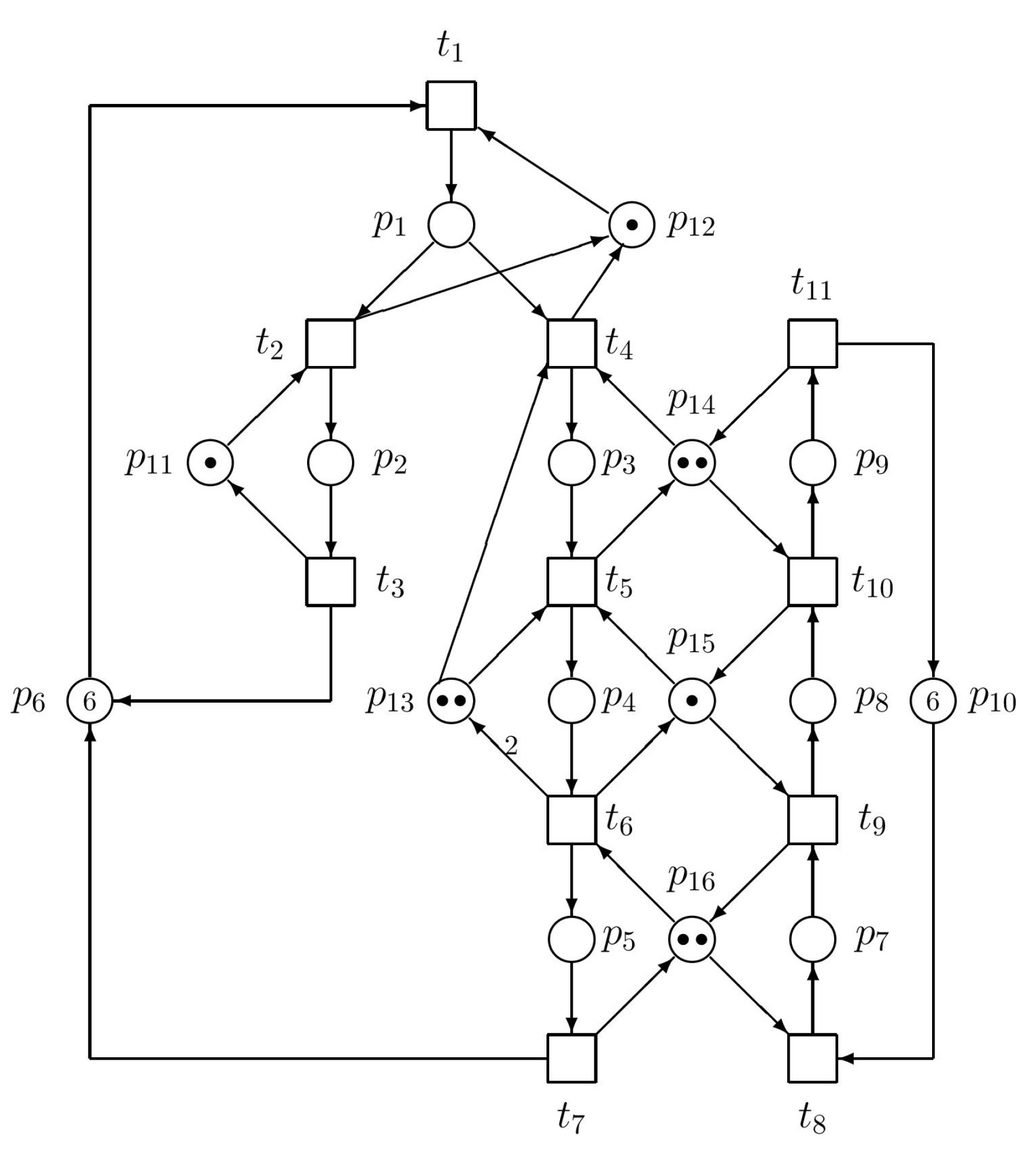
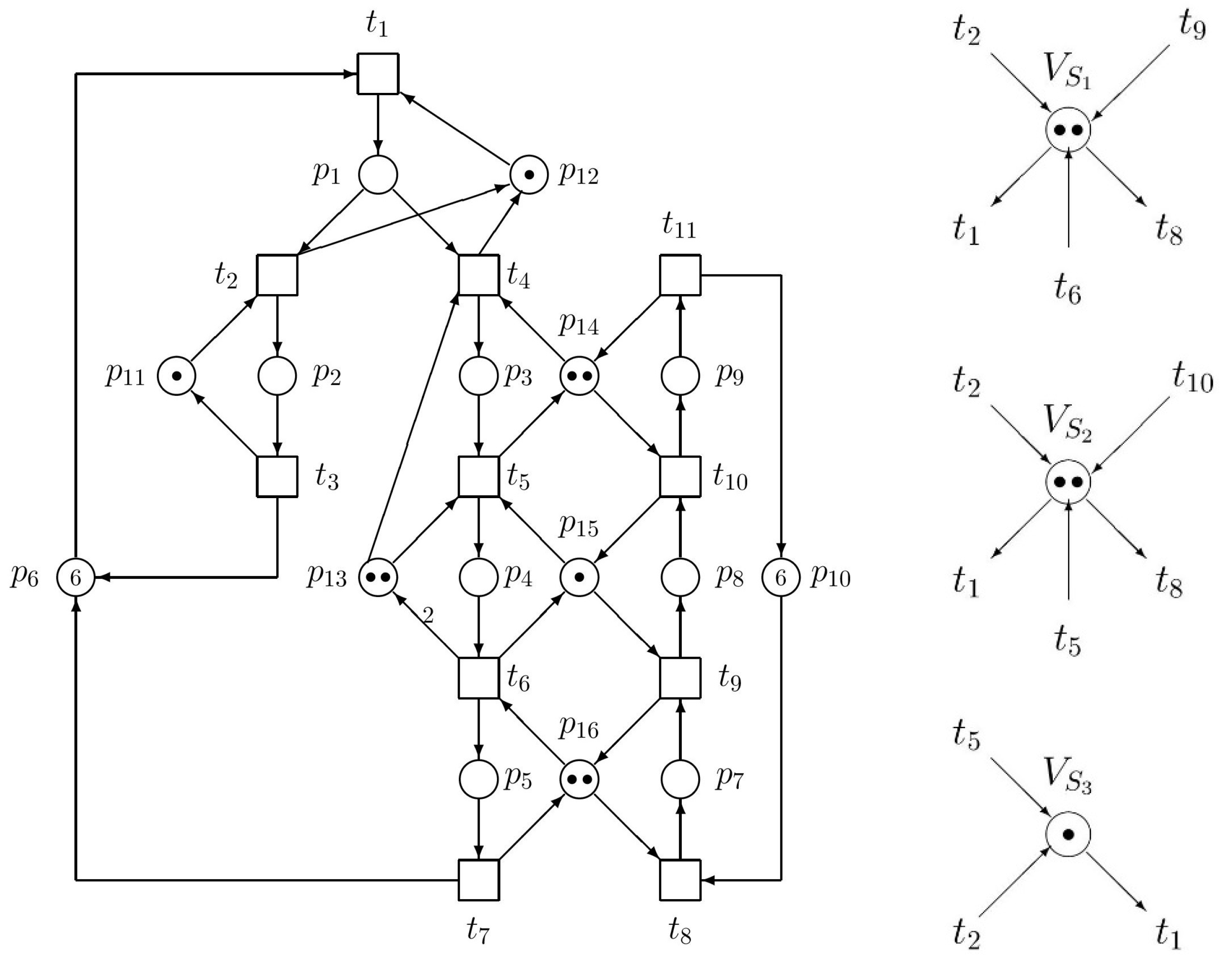
| No. | Siphons | Traps | Notice |
| 1. |
S1 = {p1, p12} |
Tr1 = {p1, p12} | Eliminate S1, because S1 = Tr1 |
| 2. | S2 = {p2, p11} | Tr2 = {p2, p11} | Eliminate S2 because S2 = Tr2 |
| 3. | S3 = {p4, p13} | Tr3 = {p3, p4, p13} | |
| 4. | S4 = {p5, p7, p16} | Tr4 = {p5, p7, p16} | Eliminate S4 because S4 = Tr4 |
| 5. | S5 = {p4, p8, p15} | Tr5 = {p4, p8, p15} | Eliminate S5 because S5 = Tr5 |
| 6. | S6 = {p3, p9, p14} | Tr6 = {p3, p9, p14} | Eliminate S6 because S6 = Tr6 |
| 7. | S7 = {p5, p8, p15, p16} | Tr7 = {p4, p7, p15, p16} | |
| 8. | S8 = {p4, p9, p14, p15} | Tr8 = {p3, p8, p14, p15} | |
| 9. | S9 = {p7, p8, p9, p10} | Tr9 = {p7, p8, p9, p10} | Eliminate S9 because S9 = Tr9 |
| 10. | S10 = {p5, p9, p14, p15, p16} | Tr10 = {p3, p7, p14, p15, p16} | |
| 11. | S11 = {p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6} | Tr11 = {p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6} | Eliminate S11 because S11 = Tr11 |
| p1 | p2 | p3 | p4 | p5 | p6 | p7 | p8 | p9 | p10 | p11 | p12 | p13 | p14 | p15 | p16 | |
| I1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| I2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| I3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| I4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| I5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| I6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| I7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| I8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




