Submitted:
24 July 2024
Posted:
25 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Study Period and Location
2.3. Cells and Chemicals
2.4. Cell Culture and Assays
2.5. Determination of Apoptotic-Related Gene Expression
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
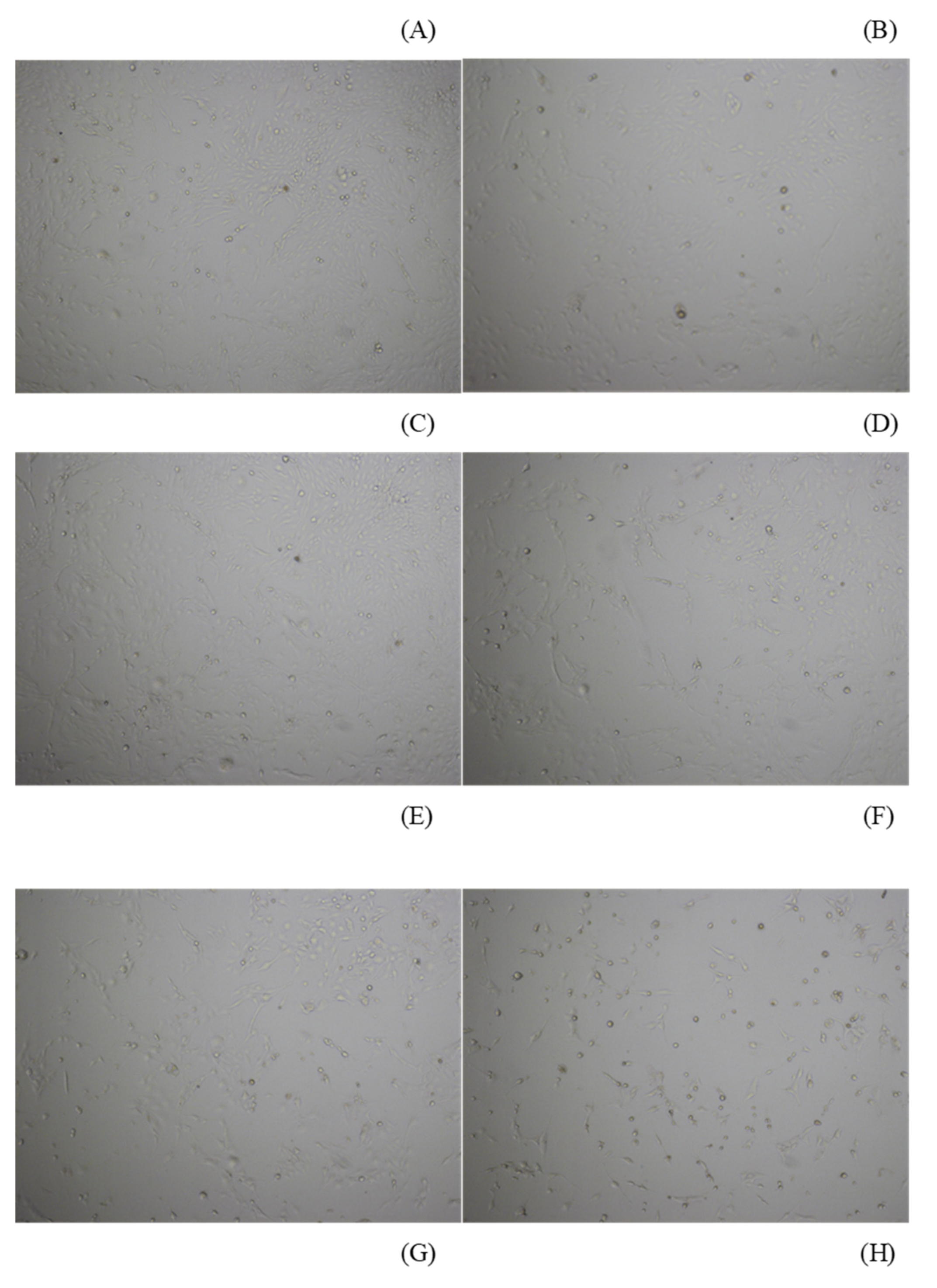
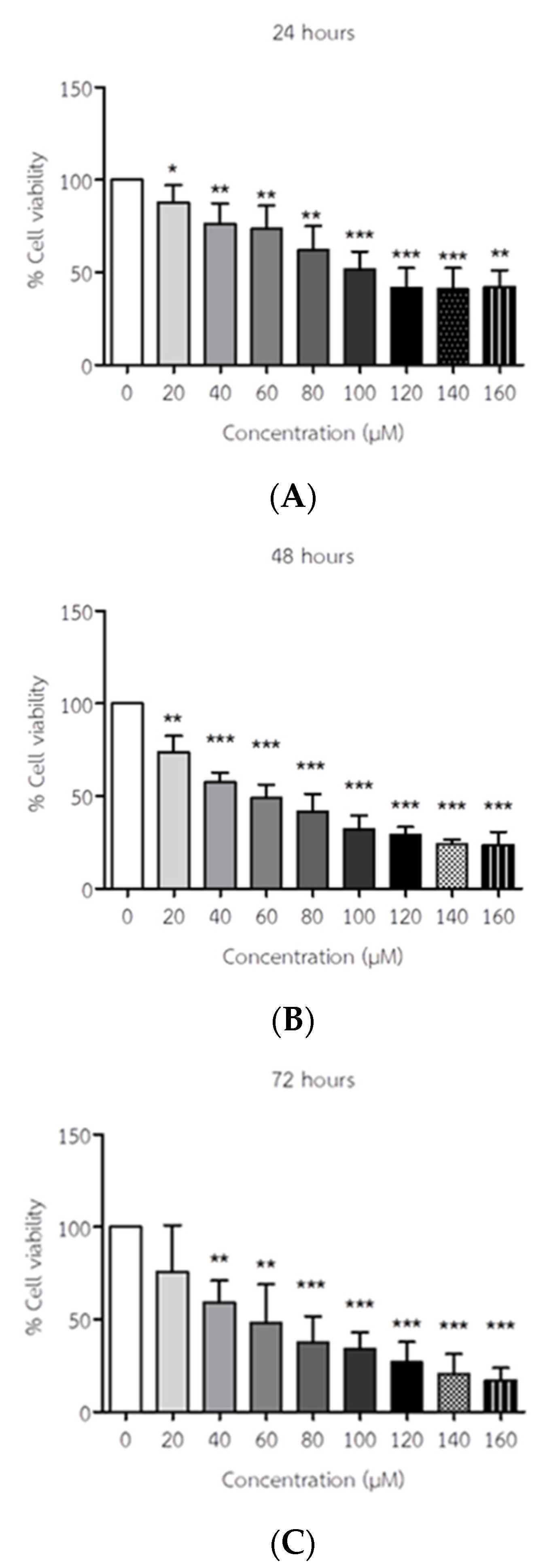
3.1. API Decreased the Viability of ELT3 Cells
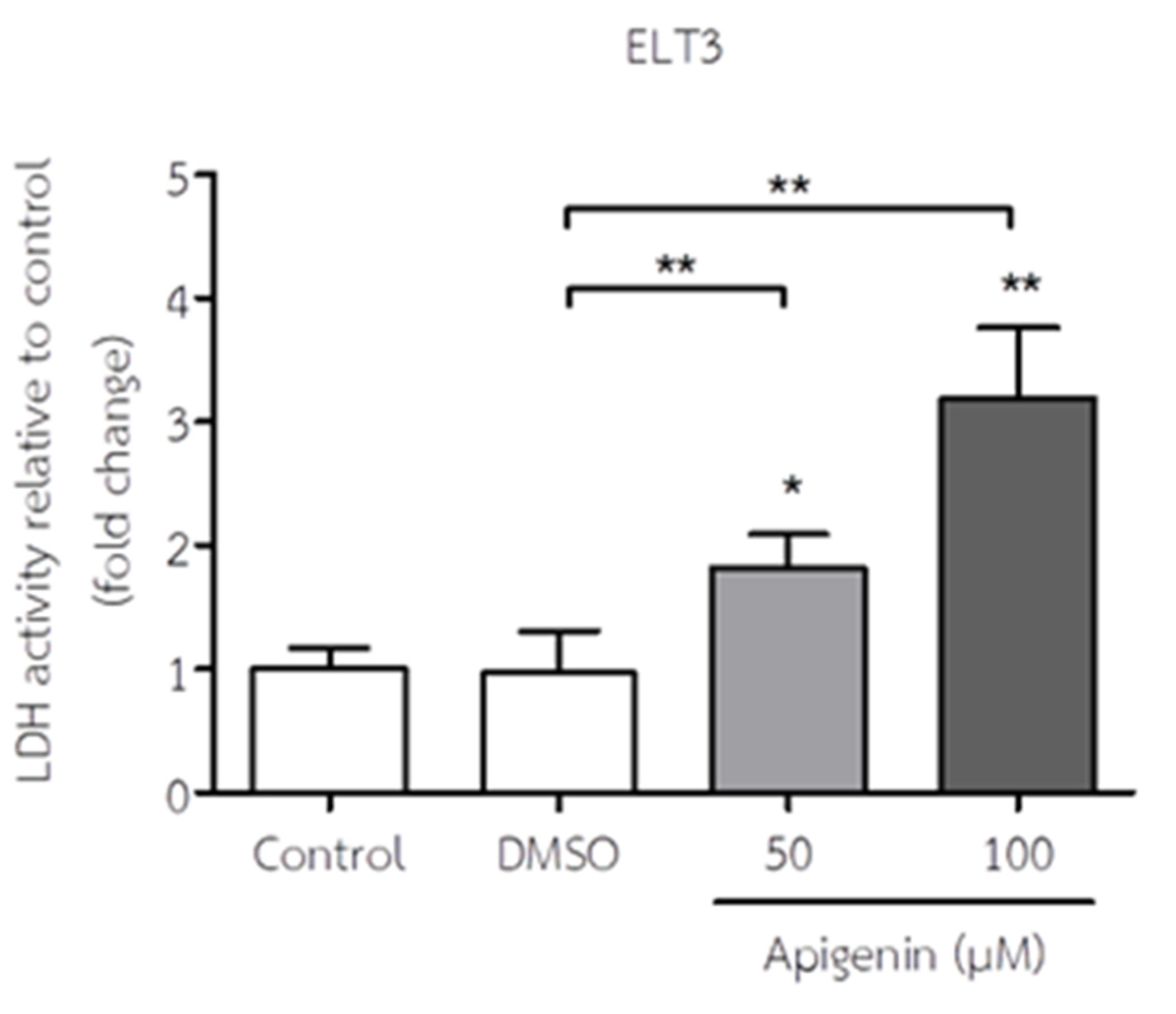
3.2. API Increased LDH Activity of ELT3 Cells
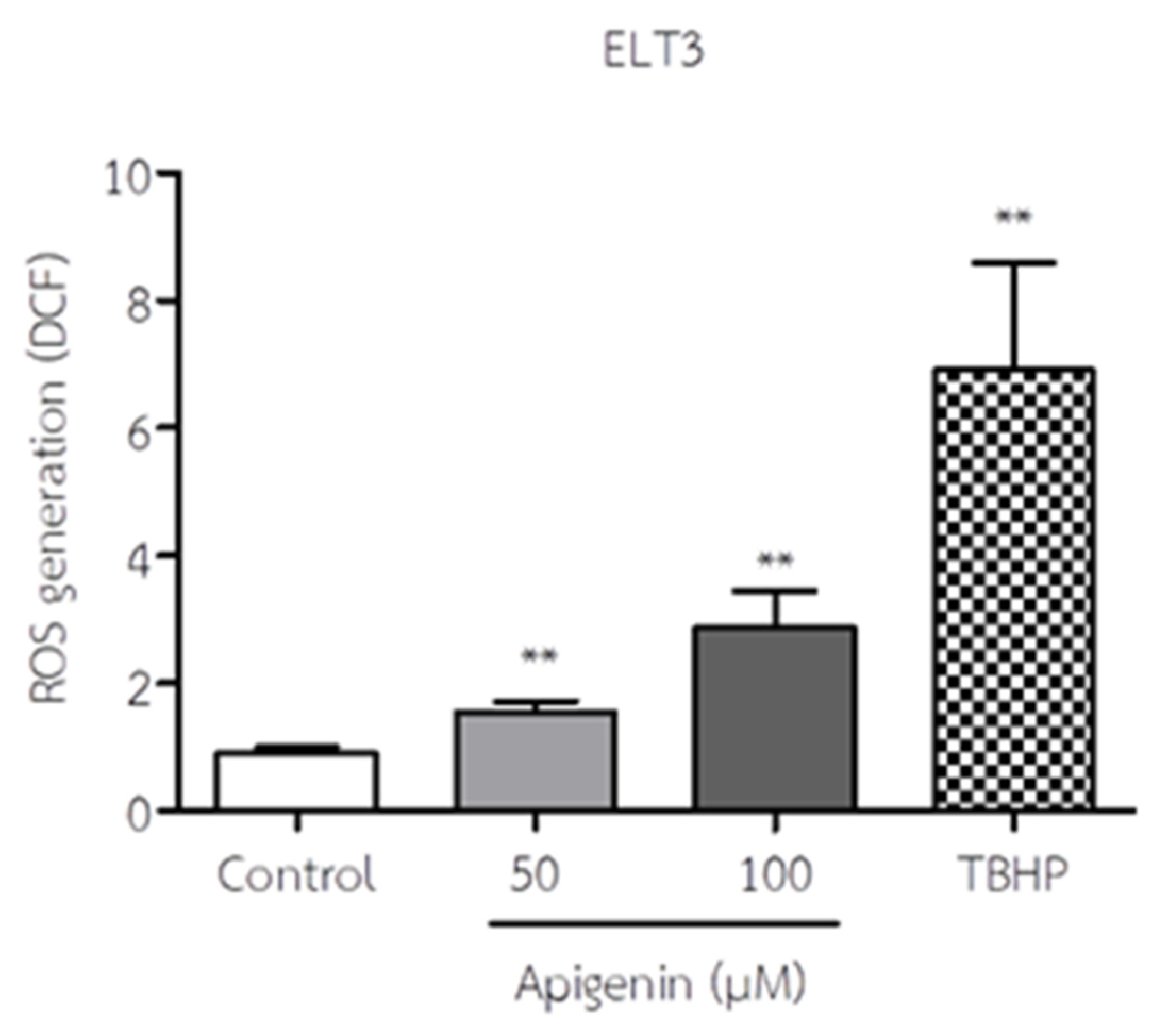
3.3. API Increased ROS Production of ELT3 Cells
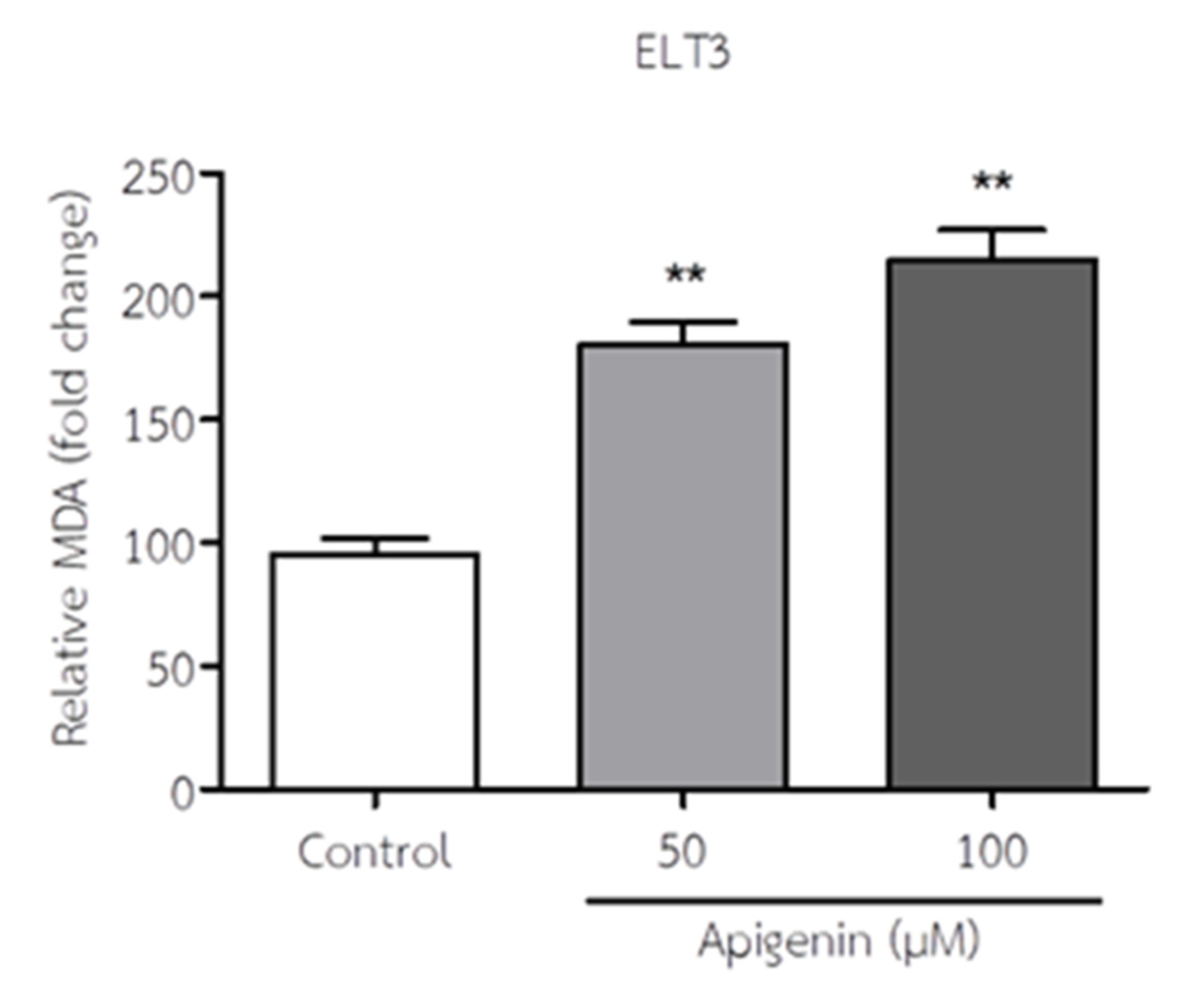
3.4. API Increased MDA Levels of ELT3 Cells
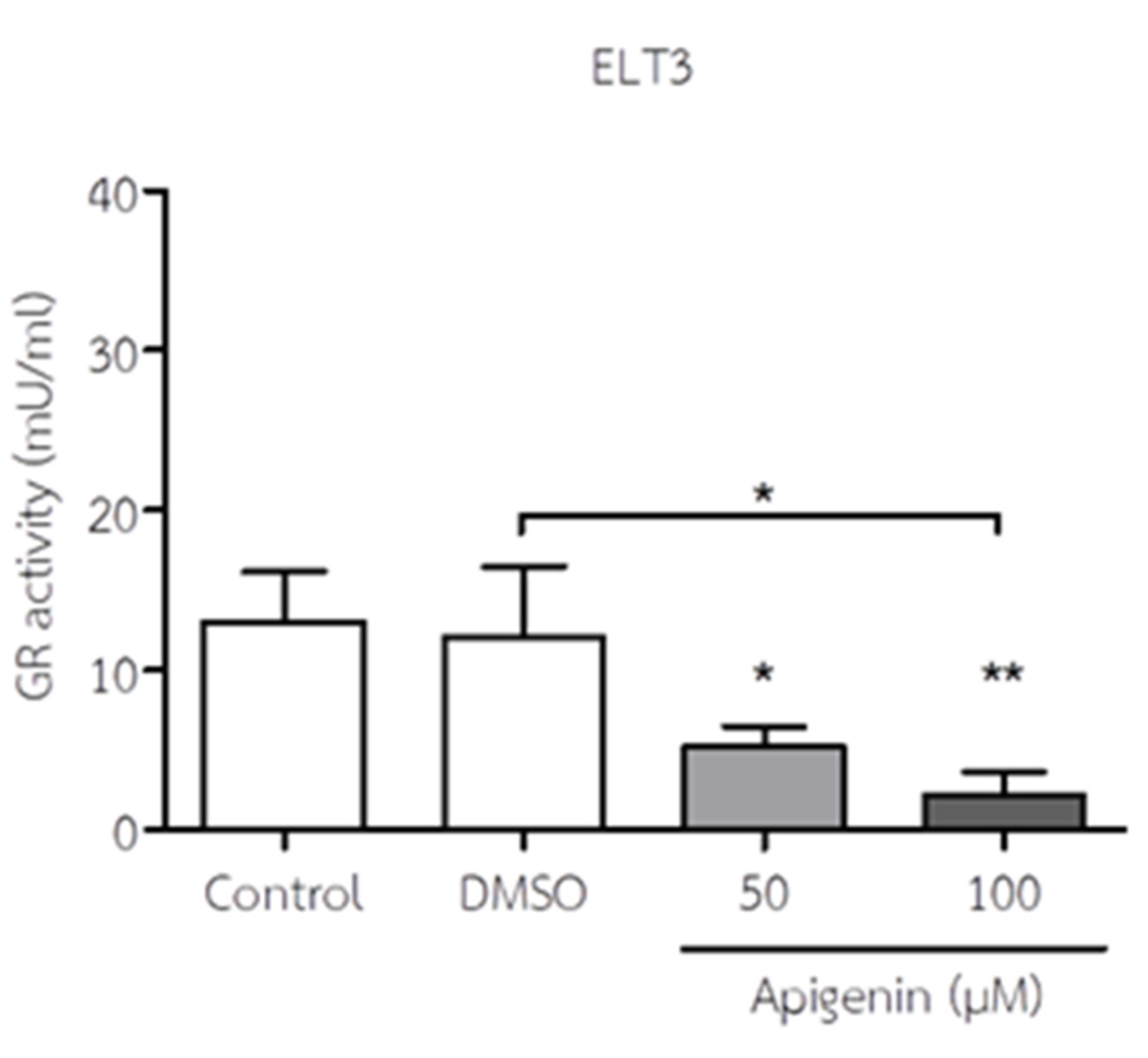
3.5. API Decreased GR Activity of ELT3 Cells
3.6. API Induced Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bak, M.J.; Gupta, S.D.; Wahler, J. Role of dietary bioactive natural products in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol, 2016; 40–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthie, G.; Crozier, A. Plant-derived phenolic antioxidants. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care., 2000, 3, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manach, C.; Scallbert, A.; Morand, C. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavaiability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J. , Dwyer, J. Flavonoids: dietary occurrence and biochemical activity. Nutr. Res., 1998, 18, 1995–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H. , Kanwal, R., Bhaskaran, N. Plant flavone apigenin binds to nucleic acid bases and reduces oxidative DNA damage in prostate epithelial cells. PloS One., 2014, 9, e91588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S. , Gupta, S. Apigenin: a promising molecule for cancer prevention. Pharm. Res., 2010, 27, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsanova-Sanova, S. , Ribarova, F. Flavonoids and flavones in some Bulgarian plant foods. Pol. J. Food Nut. Sci, 2013; 63, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. , Zhou, M.M., Chen, P.L. Optimization of ultrasonic assisted enzymatic hydrolysis for the extraction of luteolin and apigenin from celery. J. Food Sci., 2011, 76, C680–C685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. , Zheng, J., Li, Y. Natural polyphenols for prevention and treatment of cancer. Nutrients., 2016, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y. , Wu, J., Li, S. Apigenin inhibits migration and invasion via modulation of epithelial mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. Mol. Med. Rep., 2015, 11, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, K. , Mandal, M. Oxidative stress triggered by naturally occurring flavone apigenin results in senescence and chemotherapeutic effect in human colirectal cancer cells. Redox Biol., 2015, 5, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Y. , Zhou, S.H., Fan, J. Anticancer mechanism of apigenin and the implications of GULT-1 expression in head and neck cancers. Future Oncol., 2013, 9, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, M. , Zhang, Y., Du, X. Apigenin-7-diglucuronide protects retinas against bright light-induced photoreceptor degeneration through inhibition of retinal oxidative stress and inflammation. Brain Res., 2017, 1663, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birt, D.F. , Walker, B., Tibbles, M.G. Anti-mutagenesis and anti-promotion by apigenin, robinetin and indole-3-carbinol. Carcinogenesis., 1986, 7, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.Y. , Liang, J.Y., Guo, X.J. 5-fluorouracil combined with apigenin enhances anticancer activity through mitochondrial membrane potential (∆Ѱm)-mediated apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., 2014, 42, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, O.H. , Lee, J.H., Kwon, D.Y. Apigenin inhibits release of inflammatory mediators by blocking the NF-kappa B activation pathways in the HMC-1 cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol., 2011, 33, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P. , Shukla, S., Gupta, S. Plant flavonoid apigenin inactivates AKt to trigger apoptosis in human prostate cancer: an in vitro and in vivo study. Carcinogenesis., 2008, 29, 2210–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, M. , Kadioglu, O. , Khalid, H. Activity of dietary flavonoid, apigenin, against multidrug-resistant tumor cell as determined by pharmacogenomics and molecular docking. J. Nutr. Biochem., 2015, 26, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X. , Li, M., Chen, W. Apigenin attenuates oxidative injury in ARPE-19 cells through activation of Nrf2 pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev, 2016, 4378461. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. , Wang, X. Y., Xue, J. Protective effect of apigenin on mouse acute liver injury induced by acetaminophen is associated with increment of hepatic glutathione reductase activity. Food Funct., 2013, 4, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.N. , Chi, C.W., Lin, Y.L. The neuroprotective effects of phytoeatrogen on amyloid beta protein-induced toxicity are mediated by abrogating the activation of caspase cascade in rat cortical neurons. J. Biol. Chem., 2001, 276, 5287–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, R.S. , Grass, L., Jenkins, D.J. Modulation of androgen and progesterone receptors by phytochemicals in breast cancer cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1998, 248, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroheker, T. , Picard, K., Lhuguenot, J.C. Steroid activities comparison of natural and food wrap compounds in human breast cancer cell lines. Food Chem. Toxicol., 2004, 42, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, M.F. , Mendonca, E., Eddie, S.L. Kaempferol exhibits progestogenic effects in ovariectomized rats. J. Steroids Horm. Sci., 2014, 5, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, M. , Murphy, B.T., Burdette, J.E. Phytosteroids beyond estrogens: regulators of reproductive and endocrine function in natural products. Mol. Cell Endocrinol., 2017, 442, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H. , Chan, W.H. Protective effects of liquiritienin against citrinin-triggered, oxidative-stress-mediated apoptosis and disruption of embryonic development in mouse blastocyst. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2017, 18. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. , Du, K.J., Fang, Z. Chemical and biological insights into uranium-induced apoptosis of rat hepatic cell line. Radiat. Environ. Biophys., 2015, 54, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corey, F.S. , Lawrence, J.A. Tumors of the female reproductive system. Withrow and MacEwen’s Small Animal Clinical Oncology 5th Ed, 2013, 532-537.
- Nicole, L.S. , Susan, S.W. Antineoplastic therapy side effects and polypharmacy in older adults with cancer. Top Geriatr. Rehabil, 2019; 35, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jittapalapong, S.; Poompoung, T.; Sutjarit, S. Apigenin induces oxidative stress in mouse Sertoli TM4 cells. Vet World 2021, 14, 3132–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdameri, G., Lima, M.T., Worfel, P.R. Involvement of catalase in the apoptotic mechanism induced by apigenin in HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Chem. Biol. Interact., 2011, 193(2), 180-189. [CrossRef]
- Jayasooriya, R.G.P.T. , Kang, S.H., Kang, C.H. Apigenin decreases cell viability and telomerase activity in human leukemia cell lines. Food Chem. Toxicol., 2012, 50, 2605–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, A.R. , Shawkey, A.E., Rabeh, A.O. Expression of P53, BAX, and BCL-2 in human malignant melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma cells after tea tree oil treatment in vitro. Cytotech., 2019, 71, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.H. , Fang, W.L., Li, A.F.Y., Liang, P.H., Wu, C.W., Shyr, Y.M., Yang, M.H. Caspase-3, a key apoptotic protein, as a prognostic marker in gastric cancer after curative surgery. In. J. Surg., 2018, 52, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.J., Robb, V.A., Morrison, T.A., Ariazi, E.A., Karbowniczek, M., Astrinidis, A., Wang, C., Hernadez-Cuebas, L., Seeholzer, L.F., Nicolas, E., Hensley, H., Jordan, V.C., Walker, C.L., Henske, E.P. Estrogen promotes the survival and pulmonary metastasis of tuberin-null cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2009, 106(8), 2635–2640. [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, I.L. Uterine Leiomyoma in the Eker Rat: A Unique Model for Important Diseases of Women. Genes Chromosomes. Cancer., 2003, 38(4), 349-56. [CrossRef]
- Weyermann, J. , Lochmann, D., Zimmer, A. A practical note on the use of cytotoxicity assays. Int. J. Pharm., 2005, 288, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, K.M.C. , Kenta, M., Maria, J.D.R. Detection of Necrosis by Release of Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Activity. Methods Mol. Biol., 2013, 979, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhasitanont, P. , Chokchaichamnankit, D., Chiablaem, K. Apigenin inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett., 2017, 14, 4361–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, M.E. , Coombs, M.R.P., Delaney, L.M. Exposure of breast cancer cells to a subcytotoxic dose of apigenin causes growth inhibition, oxidative stress, and hypophosphorylation of Akt. Exp. Mol. Pathol., 2014, 97, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaozhen, L. , Shaoping, N., Danfei, H. Mitogen-activated protein kinase and Akt pathways are involved in 4-n-nonyphenol induced apoptosis in mouse Sertoli ELT3 cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2015, 39, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.H. , Molagoda, I.M.N., Choi, Y.H. Apigenin promotes TRAIL-mediated apoptosis regardless of ROS generation. Food Chem. Toxicol., 2018, 11, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garwel, S.; Maria, W.; Elzbieta, N. Malondialdehyde (MDA) as a lipid peroxidation marker. Wiad Lek 2004, 57, 453–455. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasiya, V.S. Anastasiya, V.S., Anna, V.K., Olga, L.K., Maria, V.S., Nataliya, V.M., George, S.K., Alexy, A.D. ROS generation and antioxidant defense systems in normal and malignant cells. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev., 2019, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Susan, E. Apoptosis: A Review of Programmed Cell Death. Toxico.l Pathol., 2007, 35(4), 495–516. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, F.; Yin, H.L.; Huang, Z.J.; Lin, Z.T.; Mao, N.; Sun, B.; Wang, G. Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhuriya, Y.K.; Sharma, D. Necroptosis: a regulated inflammatory mode of cell death. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z. , Klionsly, D.J. Autophagosome formation: core machinery and adaptations. Nat. Cell Biol., 2007, 9, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, B., Chung, H.Y., Kim, N.D. Role of apigenin in cancer prevention via the induction of apoptosis and autophagy. J. Cancer Prev., 2016, 21(4), 216-226. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. , Sung, B., Kang, Y.J., Kim, D.H., Jang, J.Y., Hwang, S.Y., Kim, M., Lim, H.S., Toon, J.H., Chung, H.Y., Kim, N.D. Apigenin-induced apoptosis is enhanced by inhibition of autophagy formation in HCT116 human colon cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol., 2014, 44, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S. , Debatin, K.M. Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene., 2006, 25, 4798–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulda, S. Molecular pathways: targeting death receptors and smacmimetric. Clin. Cancer Res., 2014, 20, 3915–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. , Cong, X., Zheng, L. Dioscin, a natural steroid saponin, shows remarkable protective effect against acetaminophen-induced liver damage in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Lett., 2012, 214, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, S., Pascal, D., Anne, M., Marlene, B., Valerie, D.C., Veronique, B., Evelyne, M. A comprehensive study of p53 transcriptional activity in thymus and spleen of γ irradiated mouse: High sensitivity of genes involved in the two main apoptotic pathways. Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 2006, 82(11), 761-770. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J. , Tait, S.W.G. Mitochondrial apoptosis: killing cancer using the enemy within. Br. J. Canc., 2015, 112, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indo, H.P. , Davidson, M. , Yen, H.C. Evidence of ROS generation by mitochondria in cells with impaired electron transport chain and mitochondrial DNA damage. Mitochondrion., 2007, 7, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, S. Marchi, S., Giorgim, C., Suski, J.M. Mitochondria-ros crosstalk in the control of cell death and aging. J. Signal. Transduct., 2012, 329635. [CrossRef]
- Anuradha, C.D. , Kanno, S., Hirano, S. Oxidative damage to mitochondria is a preliminary step to caspase-3 activation in fluoride-induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 2001, 31, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M. , Guerrero, A.D., Huang, L. Caspase-9-induced mitochondrial disruption through cleavage of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members. J. Biol. Chem., 2007, 282, 33888–33895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.F. , Chie, Y.J., Yang, M.S. Apigenin induces apoptosis in human lung cancer H460 cells through caspase-and mitochondria-dependent pathways. Hum. Exp. Toxicol., 2011, 30, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Shukla, S.; Gupta, S. Apigenin and cancer chemoprevention: progress, potential and promise (review). Int. J. Oncol., 2007, 30, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W. , Qiao, Z., Wang, H. Flavonoids: promising anticancer agents. Med. Res. Rev., 2003, 23, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkin, R. , Lavoie, J.F., Kaplan, D.R. Induction of caspase-dependent, p53-mediated apoptosis by apigenin in human neuroblastoma. Mol. Cancer Ther., 2005, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, G., Furrukh, A., Hasan, M. Selective Growth-Inhibitory, Cell-Cycle Deregulatory and Apoptotic Response of Apigenin in Normal versus Human Prostate Carcinoma Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2001, 287(4), 914-920. [CrossRef]

| Gene name | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| GAPDH | ATGGGAAGCTGGTCATCAAC | GTGGTTCACACCCATCACAA |
| Tp53 | TCTCCCCAGCAAAAGAAAAA | TTTTATGGCGGGACGTAGAC |
| Bax | AAAGACATTGGAGCCACCAC | TATTGCCTGCCACAAACTCA |
| Bcl2 | GGGATGCCTTTGTGGAACTA | CATATTTGTTTGGGGCAGGT |
| Caspase3 | AGGGGCATGTTTCTGTTTTG | CATTGCAGGCAGTGGTATTG |
| Caspase9 | TCATTCTTGCAAAGCAGTGG | TGGGTGTTTCTGGTGTGAGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





