Submitted:
24 July 2024
Posted:
25 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Current Survey Mission
- Development of Resources: We contribute to the development of resources for less-resourced languages such as English, Romanian, and Hungarian.
- Extensive Datasets: We developed extensive datasets for English, Romanian, and Hungarian, containing both human-authored and machine-generated texts, using several large language models (LLMs).
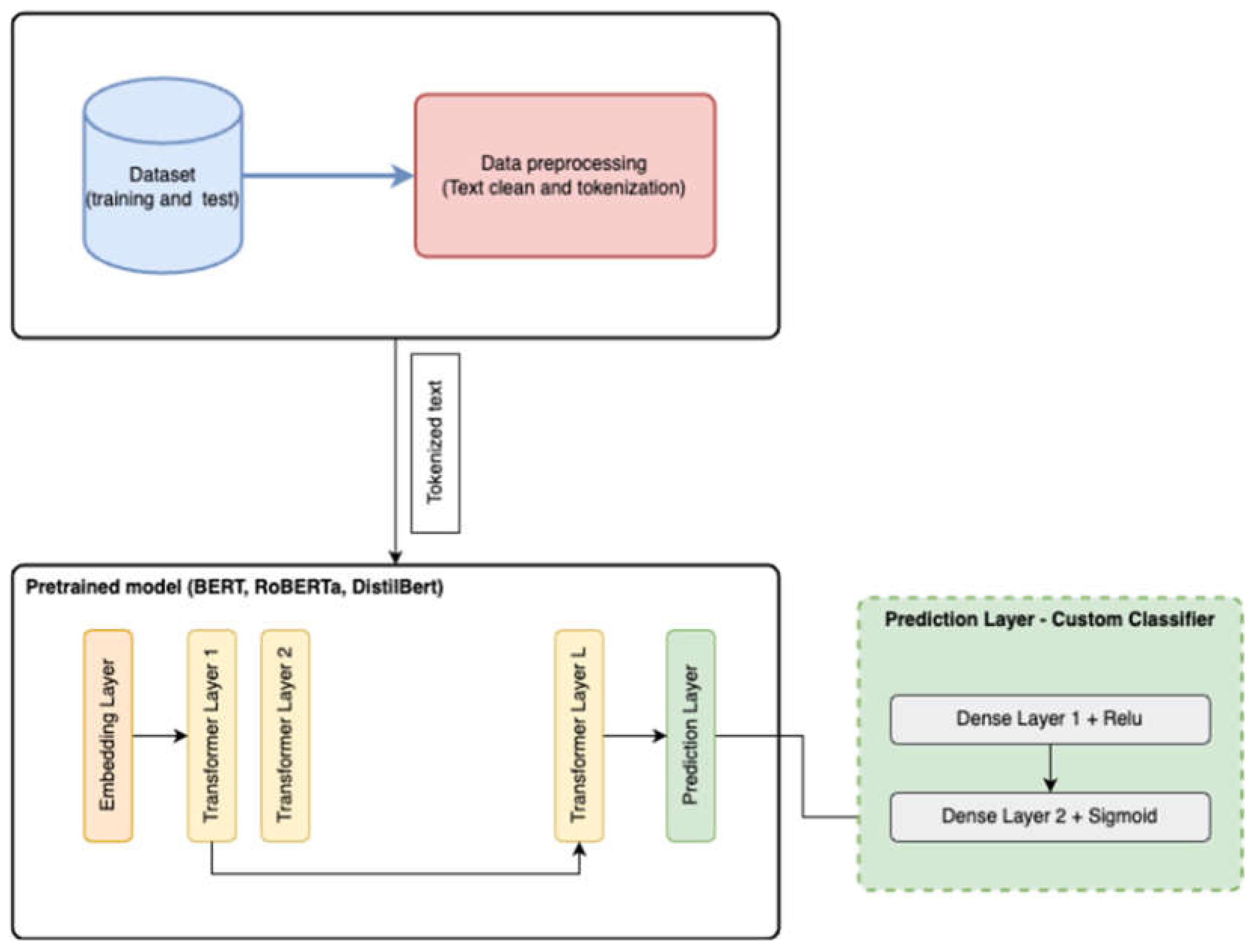
- Implementation of Classification Models: We implemented classification models based on different architectures, including Transformer-based models (such as BERT-base, RoBERTa-base, RoBERTa-large, DistilBERT-base-uncased, XLM-RoBERTa-base, BERT-base-multilingual-cased, and DistilBERT-base-multilingual-cased) and classic machine learning (ML) models, designed to automatically classify texts in several languages.
2. Transformers for Human and Machine-Generated
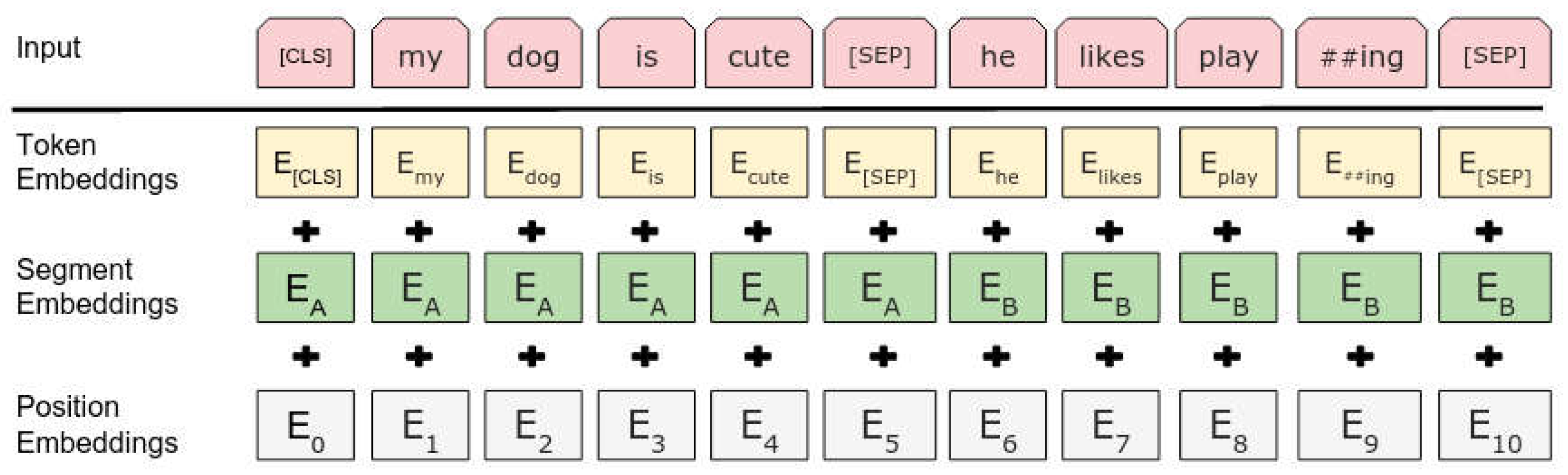
2.1. BERT
2.2. RoBERTa
2.3. DistilBERT
3. Materials and Methods
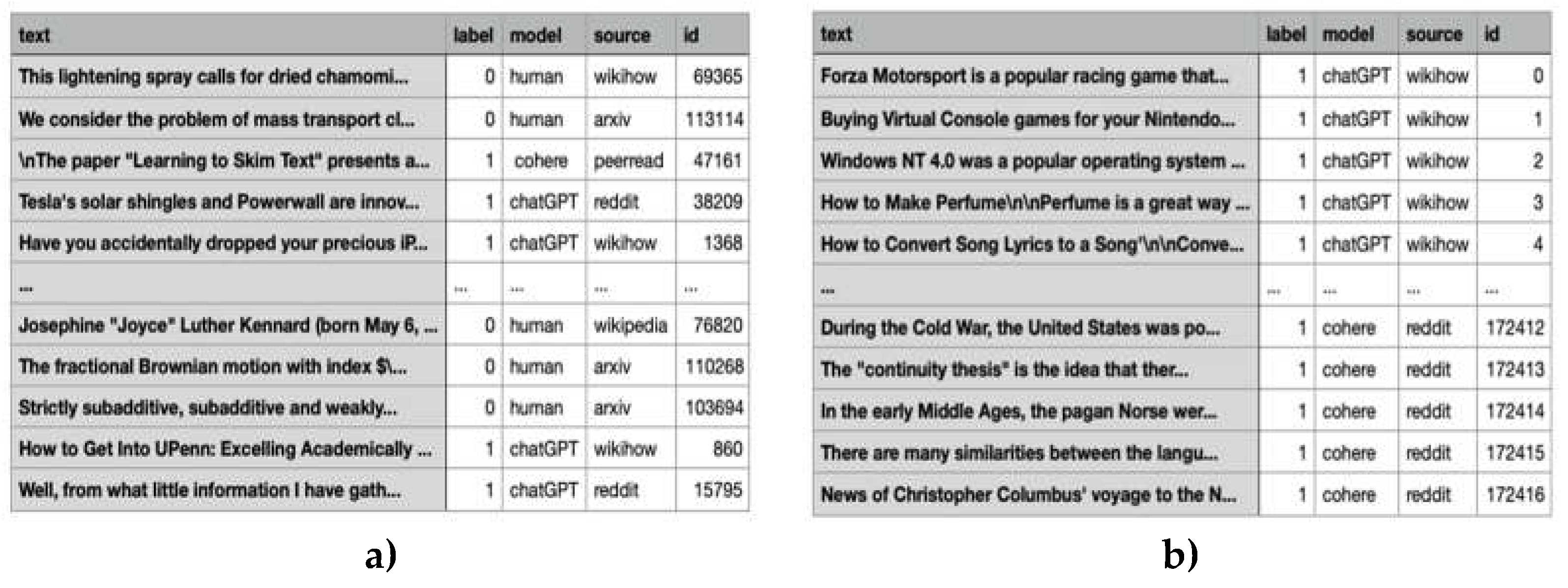
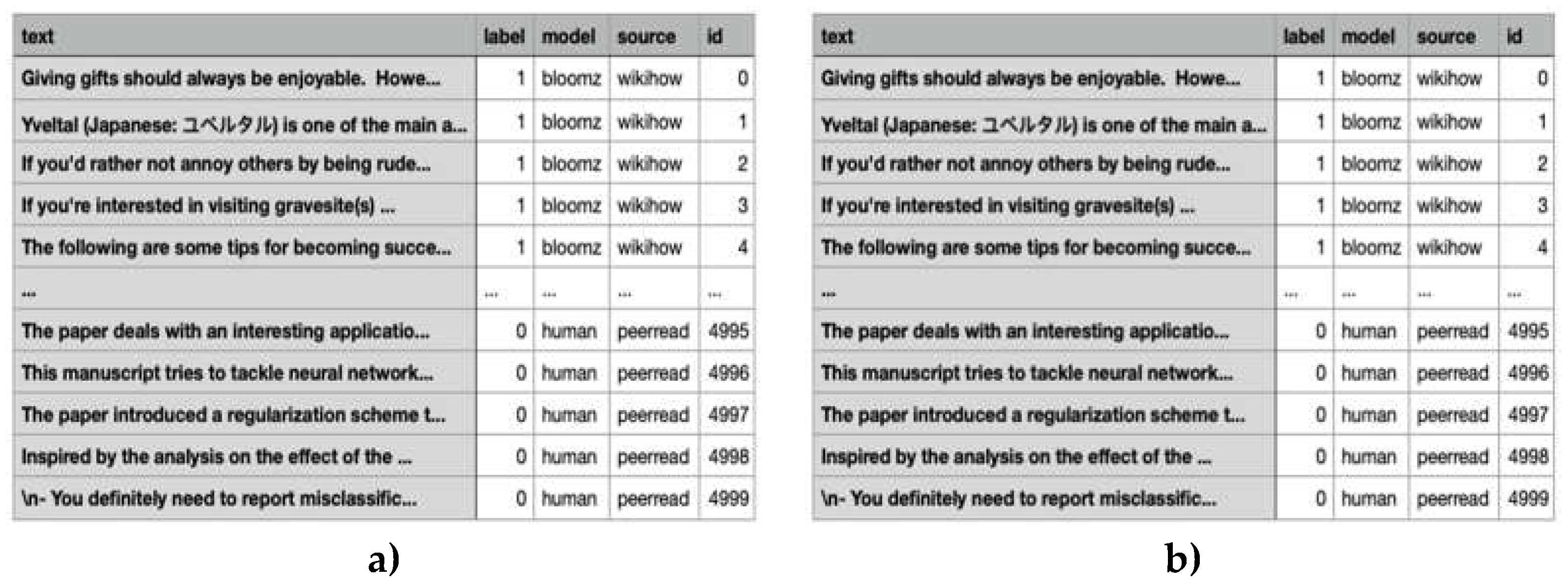
3.1. Dataset
- M4 dataset (https://paperswithcode.com/datasets, accessed on 22 July 2024): Contains human-written text from sources such as Wikipedia, Wiki-How [34], Reddit (ELI5), arXiv, and PeerRead [35] for Chinese, as well as news articles for Urdu, RuATD [36] for Russian, and Indonesian news articles. Machine-generated text is sourced from multilingual LLMs such as ChatGPT, textdavinci-003, LLaMa [37], FlanT5 [38], Cohere, Dolly-v2, and BLOOMz [39];
- AI Crowd FakeNews Dataset (https://www.aicrowd.com/challenges/kiit-ai-mini-blitz/problems/fake-news-detection, accessed on 22 July 2024): Contains texts from various news articles and texts generated by OpenAI’s GPT-2. The dataset was published by AI Crowd as part of the KIIT AI (mini)Blitz Challenge;
- Indonesian Hoax News Detection Dataset (INDONESIAN HOAX NEWS DETECTION DATASET—Mendeley Data, accessed on 22 July) [40]: Contains valid and hoax news articles in Indonesian. It has a simple structure, with CSV files consisting of 2 columns: text and label;
- TURNBACKHOAX Dataset (https://github.com/jibranfawaid/turnbackhoax-dataset/tree/main?tab=readme-ov-file#turnbackhoax-dataset, accessed on 22 July 2024): Contains valid and hoax news articles in Indonesian. It has a simple structure, with a CSV file consisting of 3 columns: label, headline, body.
- The task formulation is different;
- Human text was upsampled to balance the data;
- New and surprising domains, generators, and languages will appear in the test sets. Real test sets will not include information about generators, domains, and languages.
3.2. System Overview
| Hyperparameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Learning rate | 2e-5 |
| Batch Size | 16 |
| Epochs | 3 |
| Weight decay | 0,01 |
| Hyperparameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Learning rate | 1e-5 |
| Batch Size | 8 |
| Epochs | 5 |
3.3. Experiments
- Preprocessing
- Feature Engineering
- Modelling
- Prediction
4. Results
5. Discussion
- For monolingual models, the results revealed notable insights. Specifically, the RoBERTa-large model, in conjunction with a custom classification layer, demonstrated the highest performance levels among all tested models. This performance exceeded baseline results observed in competitions such as SemEval-2024 Task 8. Despite its slightly lower accuracy, DistilBERT showcased efficient resource utilization. Additionally, the RoBERTa-base model exhibited performance closely comparable to that of RoBERTa-large while boasting significantly faster training times. Particularly noteworthy was the performance of a hybrid model combining a pre-trained model with DistilBERT alongside a custom classifier. Despite a marginally lower accuracy of 0.68, this model exhibited com-mendable precision at 0.73, underscoring its resource efficiency and satisfactory performance.
- In the case of multilingual models, the results indicated lower accuracy levels and longer training times due to the larger dataset. Interestingly, the DistilBERT model surpassed its teacher, BERT, in this subtask, achieving an accuracy of 0.70 compared to the baseline accuracy of 0.68. This outcome suggests the necessity for distinct approaches when addressing monolingual and multilingual tasks.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | Accuracy |
| ADAM | Adaptive Moment Estimation |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| BoW | Bag of Words |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| BiLSTM | Bidirectional Long-Short Term Memory |
| BLOOM | Big Science Large Open-science Open-access Multilingual Language Model |
| BPE | Byte Pair Encoding |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| DTs | Decision Trees |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DistilBERT | Distilled BERT |
| GPT | Generative Pre-trained Transformer |
| JSON | JavaScript Object Notation |
| JSONL | JSON Lines |
| LLMs | Large Language Models |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MLM | Masked Language Model |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MT | Machine Translation |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| NSP | Next Sentence Prediction |
| P | Precision |
| QA | Question Answering |
| R | Recall |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| RoBERTa | Robustly Optimized BERT |
| SVMs | Support Vector Machines |
| TC | Text Classification |
| TG | Text Generation |
| TS | Text Summarization |
| word2vec | Word to Vectors |
| 1 | BLOOMZ, a variant of BLOOM model, supports 46 human languages. Hugging Face reports that the 7 billion-parameter BLOOMZ runs three times faster on the Intel Habana Gaudi2 compared to the A100-80G. |
References
- Weidinger, L.; Mellor, J.F.; Rauh, M.; Griffin, C.; Uesato, J.; Huang, P.; Cheng, M.; Glaese, M.; Balle, B.; Kasirzadeh, A.A.; et al. Ethical and social risks of harm from Language Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.04359. [Google Scholar]
- Solaiman, I.; Brundage, M.; Clark, J.; Askell, A.; Herbert-Voss, A.; Wu, J.; Radford, A.; Krueger, G.; Kim, J.W.; Kreps, S.; et al. Release Strategies and the Social Impacts of Language Models. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.09203. [Google Scholar]
- Gîfu, D. An Intelligent System for Detecting Fake News. Procedia Computer Science, open access journal, edited by Yong Shi, ELSEVIER, Vol. 221, 2023, pp. 1058-1065. [CrossRef]
- Ermurachi, V.; Gîfu, D. UAIC1860 at SemEval-2020 Task 11: Detection of Propaganda Techniques in News Articles. Proceedings of the Fourteenth Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, (SemEval-2020), Association for Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain, 2020, pp. 1835-1840.
- Gîfu, D. Utilization of Technologies for Linguistic Processing in an Electoral Context: Method LIWC-2007. Proceedings of the Communication, Context, Interdisciplinarity Congress, 19-20 Nov. 2010, Vol. 1, “Petru Maior” University Publishing House, Târgu-Mureș, 2010, pp. 87-98.
- Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Yi, F.; Cheng, Q.; Huang, Y.; Lu, W.; Liu, X. AI vs. Human-Differentiation Analysis of Scientific Content Generation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10416. [Google Scholar]
- Ouatu, B.; Gîfu, D. Chatbot, the Future of Learning? Ludic, Co-design and Tools Supporting Smart Learning Ecosystems and Smart Education, Springer, 2020, pp. 263-268.
- Wang, Y.; Mansurov, J.; Ivanov, P.; Su, J.; Shelmanov, A.; Tsvigun, A.; Whitehouse, C.; Afzal, O.M.; Mahmoud, T.; Sasaki, T.; Arnold, T.; Aji, A.F.; Habash, N.; Gurevych, I.; Nakov, P. M4: Multi-Generator, Multi-Domain, and Multi-Lingual Black-Box Machine-Generated Text Detection, May 24. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.14902. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. North American Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019.
- Manoleasa, T.; Sandu, I.; Gîfu, D.; Trandabăț, D. FII UAIC at SemEval-2022 Task 6: iSarcasmEval—Intended Sarcasm Detection in English and Arabic. Proceedings of the 16th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, (SemEval-2022), Association for Computational Linguistics, Seattle, Washington, US, 2022, pp. 970-977.
- Alexa, L.; Lorenț, A.; Gîfu, D.; Trandabăț, D. The Dabblers at SemEval-2018 Task 2: Multilingual Emoji Prediction. Proceedings of the 12th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, (SemEval-2018), Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL HLT 2018), New Orleans, Louisiana, United States, 2018, pp. 405-409.
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All You Need. Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Agarwal, S.; Herbert-Voss, A.; Krueger, G.; Henighan, T.; Child, R.; Ramesh, A.; Ziegler, D.; Wu, J.; Winter, C.; Hesse, C.; Chen, M.; Sigler, E.; Litwin, M.; Gray, S.; Chess, B.; Clark, J.; Berner, C.; McCandlish, S.; Radford, A.; Sutskever, I.; Amodei, D. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2020.
- Niu, P.; Zhou, T.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Jin, R. Attention as Robust Representation for Time Series Forecasting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.05370v1. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, E.; August, T.; Serrano, S.; Haduong, N.; Gururangan, S.; Smith, N.A. All That’s ‘Human’ Is Not Gold: Evaluating Human Evaluation of Generated Text. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Bangkok, Thailand, 1–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lapata, M. Text Summarization with Pretrained Encoders. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019, pp. 3730–3740.
- Sanh, V.; Debut, L.; Chaumond, J.; Wolf, T. DistilBERT, a Distilled Version of BERT: Smaller, Faster, Cheaper and Lighter. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1910.01108. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Sennrich, R.; Nivre, J. An Analysis of Attention Mechanisms: The Case of Word Sense Disambiguation in Neural Machine Translation. Proceedings of the Third Conference on Machine Translation: Research Papers, Belgium, Brussels. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2018, pp. 26–35.
- Rajpurkar, P.; Zhang, J.; Lopyrev, K.; Liang, P. SQuAD: 100,000+ Questions for Machine Comprehension of Text, 2016, pp. 2383-2392. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cer, D.; Ahmad, A.; Guo, M.; Law, J.; Constant, N.; Abrego, G.H.; Yuan, S.; Tar, C.; Sung, Y.-H.; et al. Multilingual universal sentence encoder for semantic retrieval. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.04307. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y., Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, and Veselin Stoyanov: RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692.
- Zhang, H.; Cai, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, J. Pretraining-Based Natural Language Generation for Text Summarization. Proceedings of the 23rd Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning (CoNLL), Hong Kong, China. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019, pp. 789–797.
- Sun, C.; Qiu, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, X. How to Fine-Tune BERT for Text Classification? China National Conference on Chinese Computational Linguistics, Springer, Cham, 2019, pp. 194-206.
- Yang, Z.; Yang, D.; Dyer, C.; He, X.; Smola, A.J.; Hovy, E. XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding. Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2020), 2020, pp. 5754-5764. https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08237.
- Awalina, A.; Krisnabayu, R.Y.; Yudistira, N.; Fawaid, J. Indonesia’s Fake News Detection using Transformer Network. 6th International Conference on Sustainable Information Engineering and Technology, Malang Indonesia: ACM, 2021, pp. 247–251. [CrossRef]
- Azizah, A.F.N.; Cahyono, H.D.; Sihwi, S.W.; Widiarto, W. Performance Analysis of Transformer Based Models (BERT, ALBERT and RoBERTa) in Fake News Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.04950. [Google Scholar]
- Zecong, W.; Jiaxi, C.; Chen, C.; Chenhao, Y. Implementing BERT and Fine-Tuned RobertA to Detect AI Generated News by ChatGPT. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.07401. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Shafig, M.O. Survey of Transformers and Towards Ensemble Learning Using Transformers for Natural Language Processing. Journal of Big Data, 2024; 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Luong, M.T.; Le, Q.V.; Tannenbaum, K. ELECTRA: Pre-Training Text Encoders as Discriminators Rather than Generators. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2020), 2020. https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555.
- Sennrich, R.; Haddow, B.; Birch, A. Neural Machine Translation of Rare Words with Subword Units. Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL 2016), 2016, pp. 1715-1725. [CrossRef]
- Gage, P. A New Algorithm for Data Compression. C Users Journal 1994, 12, 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, C.; Shinn, C.; Roberts, A. Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2020, 21, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.; Lee, K.; Kumar, A. Optimizing Transformer Models for Mobile Devices: A Comparative Study. Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP 2021), 2021, pp. 234-245. [CrossRef]
- Koupaee, M.; Wang, W.Y. Wikihow: A Large-Scale Text Summarization Dataset. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Ammar, W.; Dalvi, B.; van Zuylen, M.; Kohlmeier, S.; Hovy, E.; Schwartz, R. A Dataset of Peer Reviews (PeerRead): Collection, Insights and NLP Applications. Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Vol. 1 (Long Papers), New Orleans, Louisiana. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2018, pp. 1647–1661.
- Shamardina, T.; Mikhailov, V.; Cherniavskii, D.; Fenogenova, A.; Saidov, M.; Valeeva, A.; Shavrina, T.; Smurov, I.; Tutubalina, E.; Artemova, E. Findings of the Ruatd Shared Task 2022 on Artificial Text Detection in Russian. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touvron, H.; Lavril, T.; Izacard, G.; Martinet, X.; Lachaux, M.-A.; Lacroix, T.; Rozière, B.; Goyal, N.; Hambro, E.; Azhar, F.; Rodriguez, A.; Joulin, A.; Grave, E.; Lample, G. Llama: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.13971. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.W.; Hou, L.; Longpre, S.; Zoph, B.; Tay, Y.; Fedus, W.; Li, E.; Wang, X.; Dehghani, M.; Brahma, S.; Webson, A.; Gu, S.S.; Dai, Z.; Suzgun, M.; Chen, X.; Chowdhery, A.; Narang, S.; Mishra, G.; Yu, A.; Zhao, V.Y.; Huang, Y.; Dai, A.M.; Yu, H.; Petrov, S.; Chi, E.H.; Dean, J.; Devlin, J.; Roberts, A.; Zhou, D.; Le, Q.V.; Wei, J. Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.11416. [Google Scholar]
- Muennighoff, N.; Wang, T.; Sutawika, L.; Roberts, A.; Biderman, S.; Scao, T.L.; Bari, M.S.; Shen, S.; Yong, Z.X.; Schoelkopf, H.; Tang, X.; Radev, D.; Aji, A.F.; Almubarak, K.; Albanie, S.; Alyafeai, Z.; Webson, A.; Raff, E.; Raffel, C. Crosslingual Generalization Through Multitask Finetuning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.01786. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal, R.; Inggrid, Y.; Rosa, A. Indonesian Hoax News Detection Dataset. Mendeley Data, V1, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.E.; Neumann, M.; Iyyer, M.; Gardner, M.; Clark, C.; Lee, K.; Zettlemoyer, L. Deep Contextualized Word Representations. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, B.; Bradbury, J.; Xiong, C.; Socher, R. Learned in Translation: Contextualized Word Vectors. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30, I. Guyon, U.V. Luxburg, S. Bengio, H. Wallach, R. Fergus, S. Vishwanathan, and R. Garnett (eds.), 2017, pp. 6294–6305. Curran Associates, Inc.
- Howard, J.; Ruder, S. Universal Language Model Fine-Tuning for Text Classification. Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Volume 1: Long Papers, 2018, pp. 328–339, Melbourne, Australia. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Wolf, T.; Debut, L.; Sanh, V.; Chaumond, J.; Delangue, C.; Moi, A.; Cistac, P.; Rault, T.; Louf, R.; Funtowicz, M.; Davison, J.; Shleifer, S.; von Platen, P.; Ma, C.; Jernite, Y.; Plu, J.; Xu, C.; Scao, T.L.; Gugger, S.; Drame, M.; Lhoest, Q.; Rush, A.M. Huggingface’s Transformers: State-of-the-Art Natural Language Processing. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.03771. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z.; Chen, M.; Goodman, S.; Gimpel, K.; Sharma, P.; Soricut, R. ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-Supervised Learning of Language Representations. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1909.11942v6. [Google Scholar]
| Source | Lang. 1 | Only Human |
Source-generated data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | Davinci003 | ChatGPT | Cohere | Dolly-v2 | BLOOM | Total | |||
| Wikipedia | EN | 6.458.670 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 2.995 | 2.336 | 2.702 | 3000 | 17033 |
| Reddit ELIS | EN | 558.669 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 18.000 |
| WikiHow | EN | 31.102 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 18.000 |
| PeerRead | EN | 5.798 | 5.798 | 2.344 | 2.344 | 2.344 | 2.344 | 2.344 | 17.518 |
| arXiv abstract | EN | 2.219.423 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 18.000 |
| Baike/Web OA | ZH | 113.313 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | - | - | - | 9.000 |
| RuATD | RU | 75.291 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | - | - | - | 9.000 |
| Urdu-news | UR | 107.881 | 3.000 | - | 3.000 | - | - | - | 9.000 |
| id_newspapers_2018 | ID | 499.164 | 3.000 | - | 3.000 | - | - | - | 6.000 |
| Arabic-Wikipedia | AR | 1.209.042 | 3.000 | - | 3.000 | - | - | - | 6.000 |
| True & Fake News | BG | 94.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 | - | - | - | 9.000 |
| Total | 35.798 | 23.344 | 32.339 | 13.680 | 14.046 | 14.344 | 133.551 | ||
| Language approach | #Training records | #Testing records |
|---|---|---|
| M4—Monolingual | 119.757 | 5.000 |
| AICrowd—Monolingual | 232.003 | 38.666 |
| M4—Multilingual | 172.417 | 4.000 |
| Indonesian Hoax News Detection—Multilingual | 600 | 250 |
| TURNBACKHOAX Dataset—Multilingual | 800 | 316 |
| Model | Acc (%) | P (%) | R (%) | F-score (%) | Model runtime (min.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 74 | ||||
| RoBERTa-large | 83 | 84 | 83 | 83 | 607 |
| RoBERTa-base | 81 | 83 | 81 | 81 | 166 |
| BERT-base | 71 | 74 | 71 | 70 | 162 |
| DistilBERT-base-uncased | 68 | 73 | 68 | 66 | 77 |
| Model | Acc (%) | P (%) | R (%) | F-score (%) | Model runtime (min.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 69 | ||||
| XML-RoBERTa-base | 68 | 70 | 68 | 68 | 522 |
| BERT-base-cased | 63 | 68 | 64 | 61 | 415 |
| DistilBERT-base-uncased | 70 | 71 | 71 | 70 | 203 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




