Submitted:
22 July 2024
Posted:
24 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Background
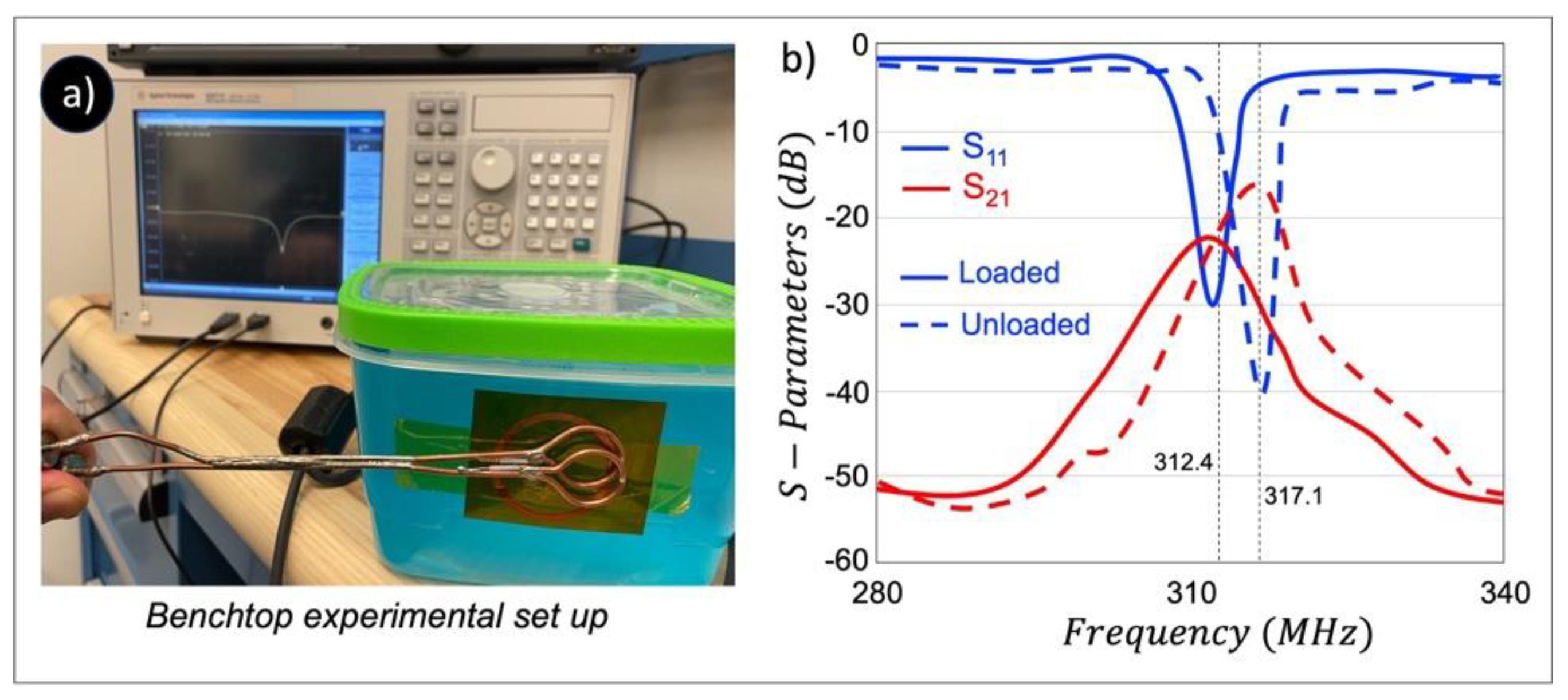
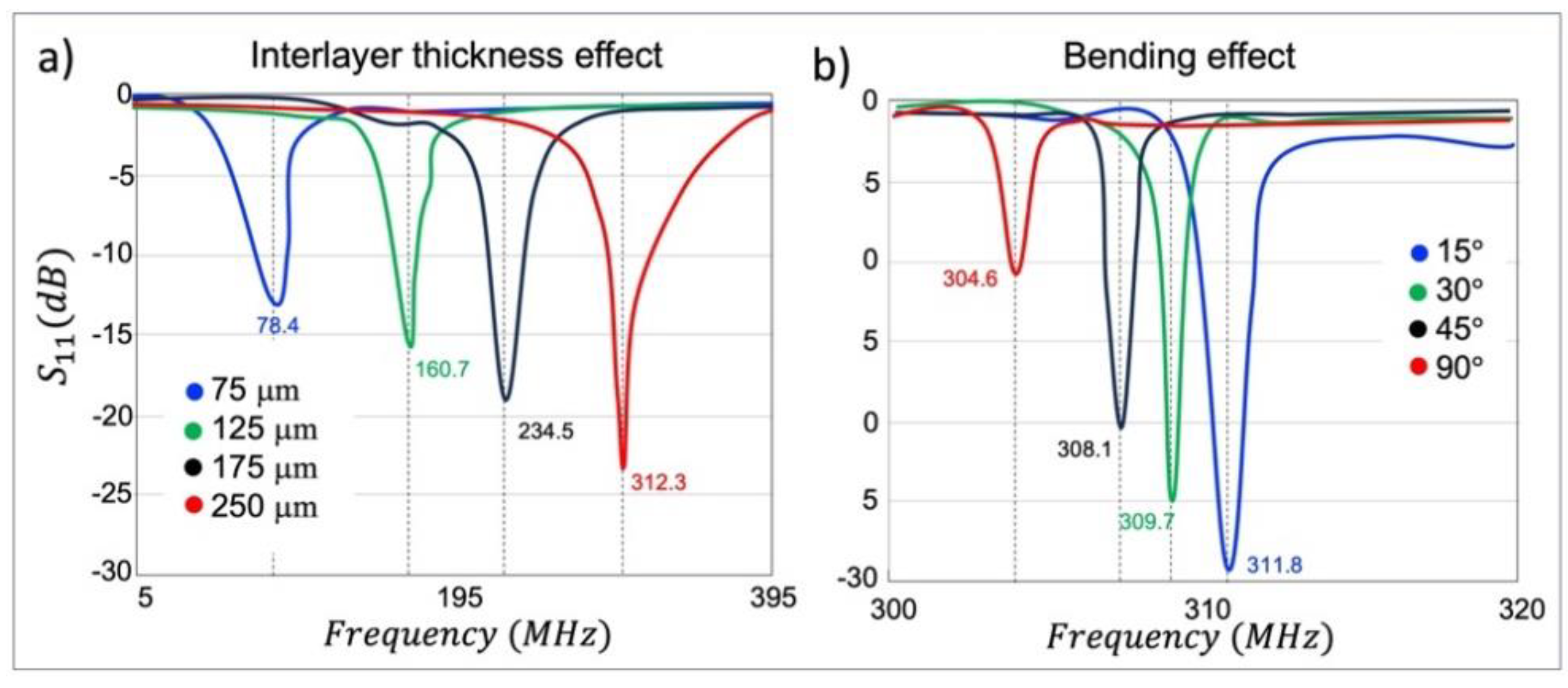
2.2. RF Enhancer
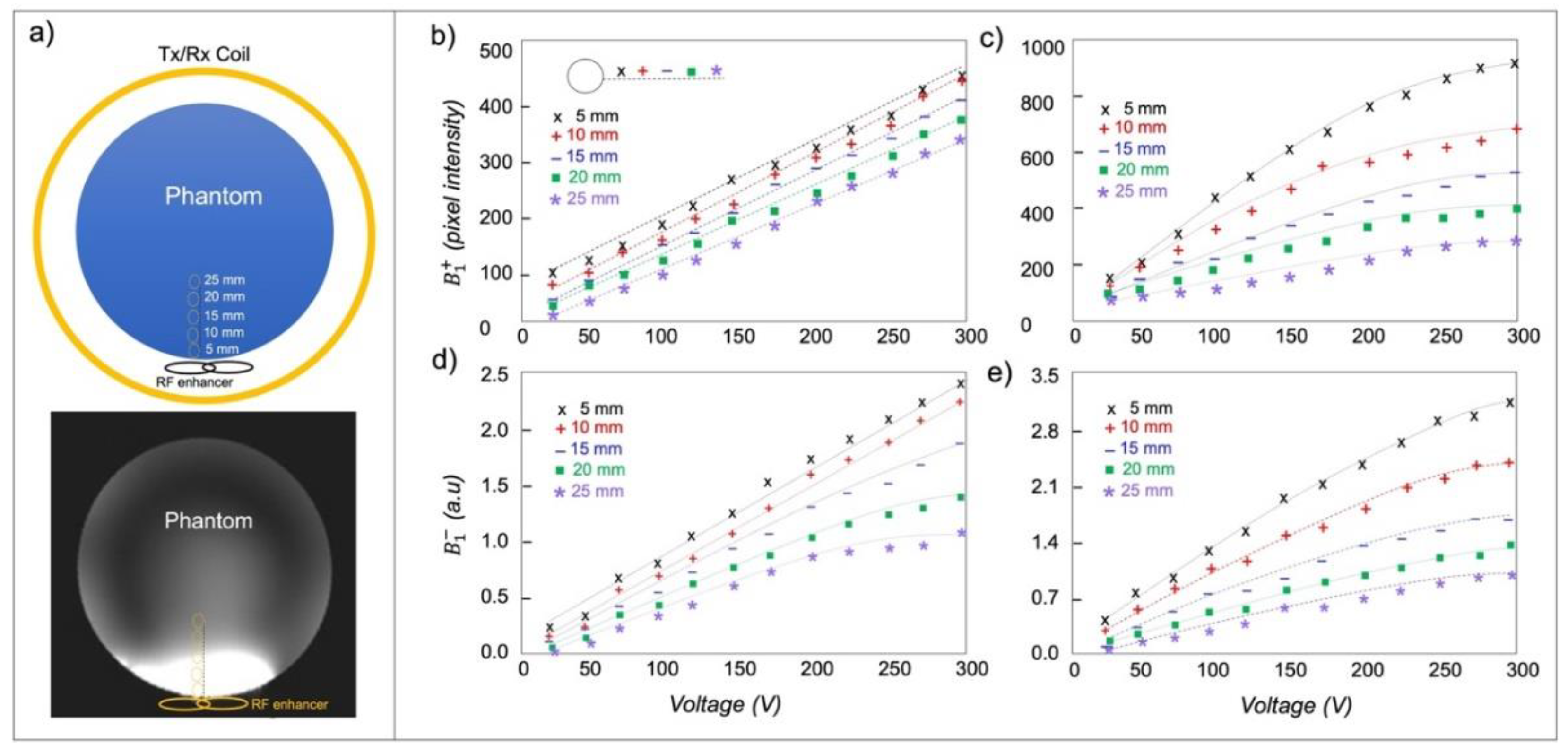
2.3. MRI Experiments
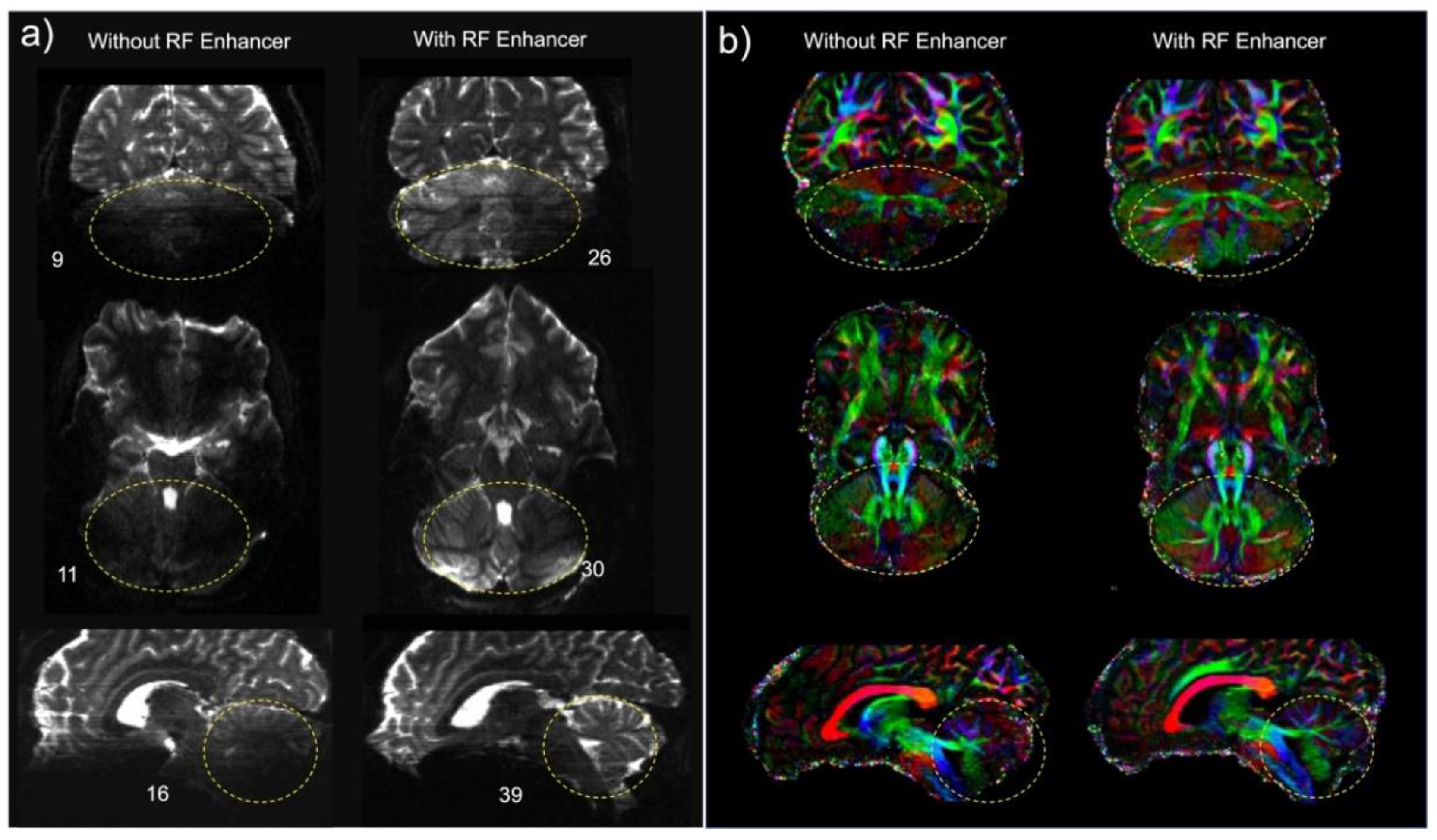
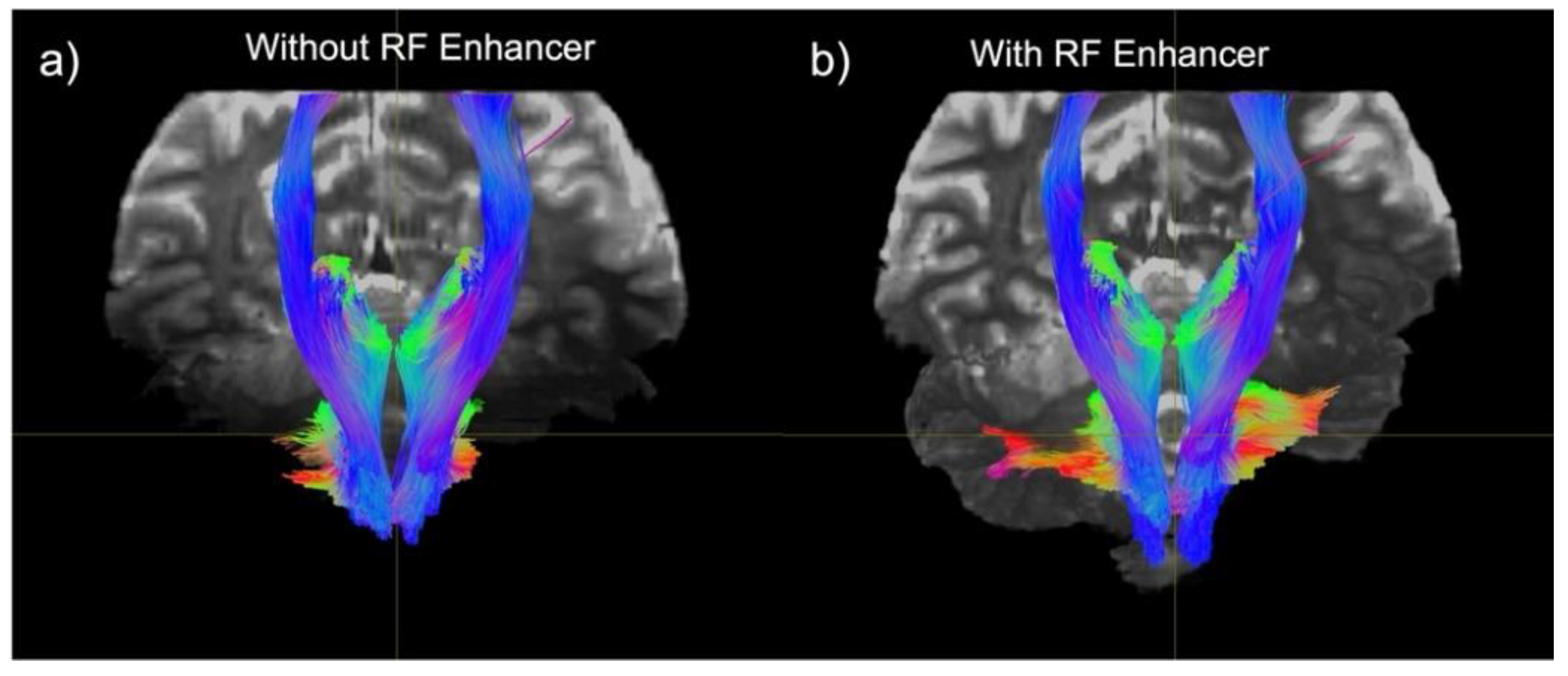
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Callaghan, P.T., 45Physics of Diffusion, in Diffusion MRI: Theory, Methods, and Applications, P.D.K. Jones, Editor. 2010, Oxford University Press. p. 0.
- Mueller, B.A.; Lim, K.O.; Hemmy, L.; Camchong, J. Diffusion MRI and its Role in Neuropsychology. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2015, 25, 250–271. [CrossRef]
- Aboitiz, F.; Scheibel, A.B.; Fisher, R.S.; Zaidel, E. Fiber composition of the human corpus callosum. Brain Res. 1992, 598, 143–153. [CrossRef]
- Coelho, S.; Pozo, J.M.; Jespersen, S.N.; Jones, D.K.; Frangi, A.F. Resolving degeneracy in diffusion MRI biophysical model parameter estimation using double diffusion encoding. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 395–410. [CrossRef]
- Lehéricy, S.; Ducros, M.; Van De Moortele, P.; Francois, C.; Thivard, L.; Poupon, C.; Swindale, N.; Ugurbil, K.; Kim, D. Diffusion tensor fiber tracking shows distinct corticostriatal circuits in humans. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 522–529. [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Ma, S.J.; Casey, M.; D’orazio, L.; Ringman, J.M.; Wang, D.J. Mapping water exchange across the blood–brain barrier using 3D diffusion-prepared arterial spin labeled perfusion MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 3065–3079. [CrossRef]
- Uğurbil, K.; Xu, J.; Auerbach, E.J.; Moeller, S.; Vu, A.T.; Duarte-Carvajalino, J.M.; Lenglet, C.; Wu, X.; Schmitter, S.; Van de Moortele, P.F.; et al. Pushing spatial and temporal resolution for functional and diffusion MRI in the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage 2013, 80, 80–104. [CrossRef]
- Gallichan, D. Diffusion MRI of the human brain at ultra-high field (UHF): A review. NeuroImage 2018, 168, 172–180. [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, S.; Fukunaga, M.; Fautz, H.-P.; Heidemann, R.; Sadato, N. Comparison of 3T and 7T MRI for the visualization of globus pallidus sub-segments. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi-Tarakameh, A.; DelaBarre, L.; Lagore, R.L.; Torrado-Carvajal, A.; Wu, X.; Grant, A.; Adriany, G.; Metzger, G.J.; Van de Moortele, P.; Ugurbil, K.; et al. In vivo human head MRI at 10.5T: A radiofrequency safety study and preliminary imaging results. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 484–496. [CrossRef]
- Verma, G.; Balchandani, P. Ultrahigh field MR Neuroimaging. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 28, 137–144. [CrossRef]
- Vu, A.; Auerbach, E.; Lenglet, C.; Moeller, S.; Sotiropoulos, S.; Jbabdi, S.; Andersson, J.; Yacoub, E.; Ugurbil, K. High resolution whole brain diffusion imaging at 7 T for the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage 2015, 122, 318–331. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Auerbach, E.J.; Vu, A.T.; Moeller, S.; Lenglet, C.; Schmitter, S.; Van de Moortele, P.; Yacoub, E.; Uğurbil, K. High-resolution whole-brain diffusion MRI at 7T using radiofrequency parallel transmission. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 1857–1870. [CrossRef]
- Vaughan JT, G.M., Collins CM, et al, 7T vs. 4T: RF power, homogeneity, and signal-to-noise comparison in head images. Magn Reson Med, 2001. 46(1): p. 24-30.
- Ladd, M.E.; Bachert, P.; Meyerspeer, M.; Moser, E.; Nagel, A.M.; Norris, D.G.; Schmitter, S.; Speck, O.; Straub, S.; Zaiss, M. Pros and cons of ultra-high-field MRI/MRS for human application. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2018, 109, 1–50. [CrossRef]
- Van de Moortele PF, A.C., Adriany G, et al, B1 destructive interferences and spatial phase patterns at 7 T with a head trans- ceiver array coil. Magn Reson Med, 2005. 54: p. 1503-1518.
- Katscher, U.; Börnert, P. Parallel RF transmission in MRI. NMR Biomed. 2006, 19, 393–400. [CrossRef]
- Balchandani, P.; Khalighi, M.M.; Glover, G.; Pauly, J.; Spielman, D. Self-refocused adiabatic pulse for spin echo imaging at 7 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 67, 1077–1085. [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, V.; Shchelokova, A.; Zivkovic, I.; Slobozhanyuk, A.; Baena, J.D.; del Risco, J.P.; Abdeddaim, R.; Webb, A.; Glybovski, S. An artificial dielectric slab for ultra high-field MRI: Proof of concept. J. Magn. Reson. 2020, 320, 106835. [CrossRef]
- Webb, A. Dielectric materials in magnetic resonance. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part A 2011, 38A, 148–184. [CrossRef]
- Yang QX, M.W., Wang J, et al, Manipulation of image intensity distribution at 7.0 T: passive RF shimming and focusing with dielectric materials. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2006. 24(1): p. 197-202.
- Haines, K., N.B. Smith, and A.G. Webb, New high dielectric constant materials for tailoring the B1+ distribution at high magnetic fields. J Magn Reson, 2010. 203(2): p. 323-7.
- Schmidt, R.; Slobozhanyuk, A.; Belov, P.; Webb, A. Flexible and compact hybrid metasurfaces for enhanced ultra high field in vivo magnetic resonance imaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Koloskov, V.; Brink, W.M.; Webb, A.G.; Shchelokova, A. Flexible metasurface for improving brain imaging at 7T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2024, 92, 869–880. [CrossRef]
- Motovilova, E.; Huang, S.Y. Hilbert Curve-Based Metasurface to Enhance Sensitivity of Radio Frequency Coils for 7-T MRI. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 615–625. [CrossRef]
- Gomez, T.S.V.; Dubois, M.; Rustomji, K.; Georget, E.; Antonakakis, T.; Vignaud, A.; Rapacchi, S.; Girard, O.M.; Kober, F.; Enoch, S.; et al. Hilbert fractal inspired dipoles for passive RF shimming in ultra-high field MRI. Photon- Nanostructures - Fundam. Appl. 2022, 48, 100988. [CrossRef]
- Stoja, E.; Konstandin, S.; Philipp, D.; Wilke, R.N.; Betancourt, D.; Bertuch, T.; Jenne, J.; Umathum, R.; Günther, M. Improving magnetic resonance imaging with smart and thin metasurfaces. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Alipour, A.; Seifert, A.C.; Delman, B.N.; Hof, P.R.; Fayad, Z.A.; Balchandani, P. Enhancing the brain MRI at ultra-high field systems using a meta-array structure. Med Phys. 2023, 50, 7606–7618. [CrossRef]
- Alipour, A., et al., Enhanced Ultra-High Field Brain MRI Using a Wireless Radiofrequency Sheet. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2021.
- Alipour, A.; Seifert, A.C.; Delman, B.N.; Robson, P.M.; Shrivastava, R.; Hof, P.R.; Adriany, G.; Fayad, Z.A.; Balchandani, P. Improvement of magnetic resonance imaging using a wireless radiofrequency resonator array. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Alipour, A.; Gokyar, S.; Algin, O.; Atalar, E.; Demir, H.V. An inductively coupled ultra-thin, flexible, and passive RF resonator for MRI marking and guiding purposes: Clinical feasibility. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 361–370. [CrossRef]
- Gokyar, S.; Alipour, A.; Unal, E.; Atalar, E.; Demir, H.V. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Assisted by Wireless Passive Implantable Fiducial e-Markers. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 19693–19702. [CrossRef]
- Syms, R.R.A.; Young, I.R.; Ahmad, M.M.; Rea, M. Magnetic resonance imaging using linear magneto-inductive waveguides. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112. [CrossRef]
- Alipour, A.; Unal, E.; Gokyar, S.; Demir, H.V. Development of a distance-independent wireless passive RF resonator sensor and a new telemetric measurement technique for wireless strain monitoring. Sensors Actuators A: Phys. 2017, 255, 87–93. [CrossRef]
- Gokyar, S.; Alipour, A.; Unal, E.; Atalar, E.; Demir, H.V. Wireless deep-subwavelength metamaterial enabling sub-mm resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Sensors Actuators A: Phys. 2018, 274, 211–219. [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.J.; Lopez, M.A.; Meise, F.; Algarin, J.M.; Jakob, P.M.; Bock, M.; Marques, R. A Broadside-Split-Ring Resonator-Based Coil for MRI at 7 T. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2013, 32, 1081–1084. [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.; Mesa, F.; Martel, J.; Medina, F. Comparative analysis of edge- and broadside-coupled split ring resonators for metamaterial design - Theory and experiments. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2003, 51, 2572–2581. [CrossRef]
- Dia, K.K.H.; Hajiaghajani, A.; Escobar, A.R.; Dautta, M.; Tseng, P. Broadside-Coupled Split Ring Resonators as a Model Construct for Passive Wireless Sensing. Adv. Sens. Res. 2023, 2. [CrossRef]
- Eryaman, Y.; Akin, B.; Atalar, E. Reduction of implant RF heating through modification of transmit coil electric field. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 65, 1305–1313. [CrossRef]
- Celik, H.; Atalar, E. Reverse polarized inductive coupling to transmit and receive radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 67, 446–456. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Murphy-Boesch, J.; Merkle, H.; Koretsky, A.P.; Duyn, J.H. $B_1$ Homogenization in MRI by Multilayer Coupled Coils. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2009, 28, 551–554. [CrossRef]
- Tournier, J.-D.; Smith, R.; Raffelt, D.; Tabbara, R.; Dhollander, T.; Pietsch, M.; Christiaens, D.; Jeurissen, B.; Yeh, C.-H.; Connelly, A. MRtrix3: A fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation. NeuroImage 2019, 202, 116137. [CrossRef]
- Wasserthal, J.; Neher, P.; Maier-Hein, K.H. TractSeg - Fast and accurate white matter tract segmentation. NeuroImage 2018, 183, 239–253. [CrossRef]
- ASTM, Measurement of radio frequency induced heating on or near passive implants during magnetic resonance imaging. F2482-11a, 2011. ASTM F2482-11a.
- FDA, Safety Guidelines for Magnetic Resonance Imaging Equipment in Clinical Use. 2014.
- Moniruzzaman; Islam, M.T.; Islam, R.; Misran, N.; Samsuzzaman Coupled ring split ring resonator (CR-SRR) based epsilon negative metamaterial for multiband wireless communications with high effective medium ratio. Results Phys. 2020, 18, 103248. [CrossRef]
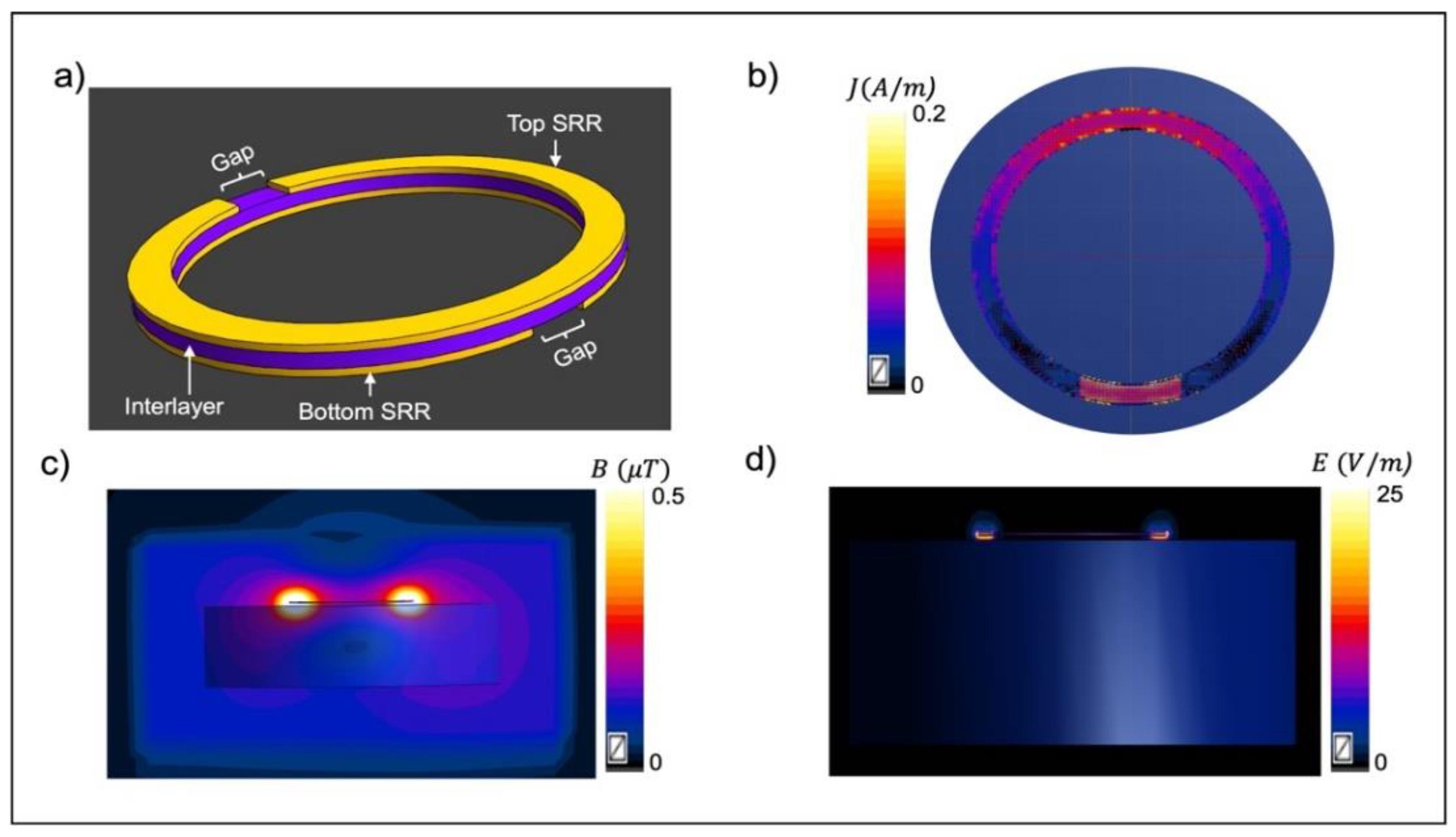
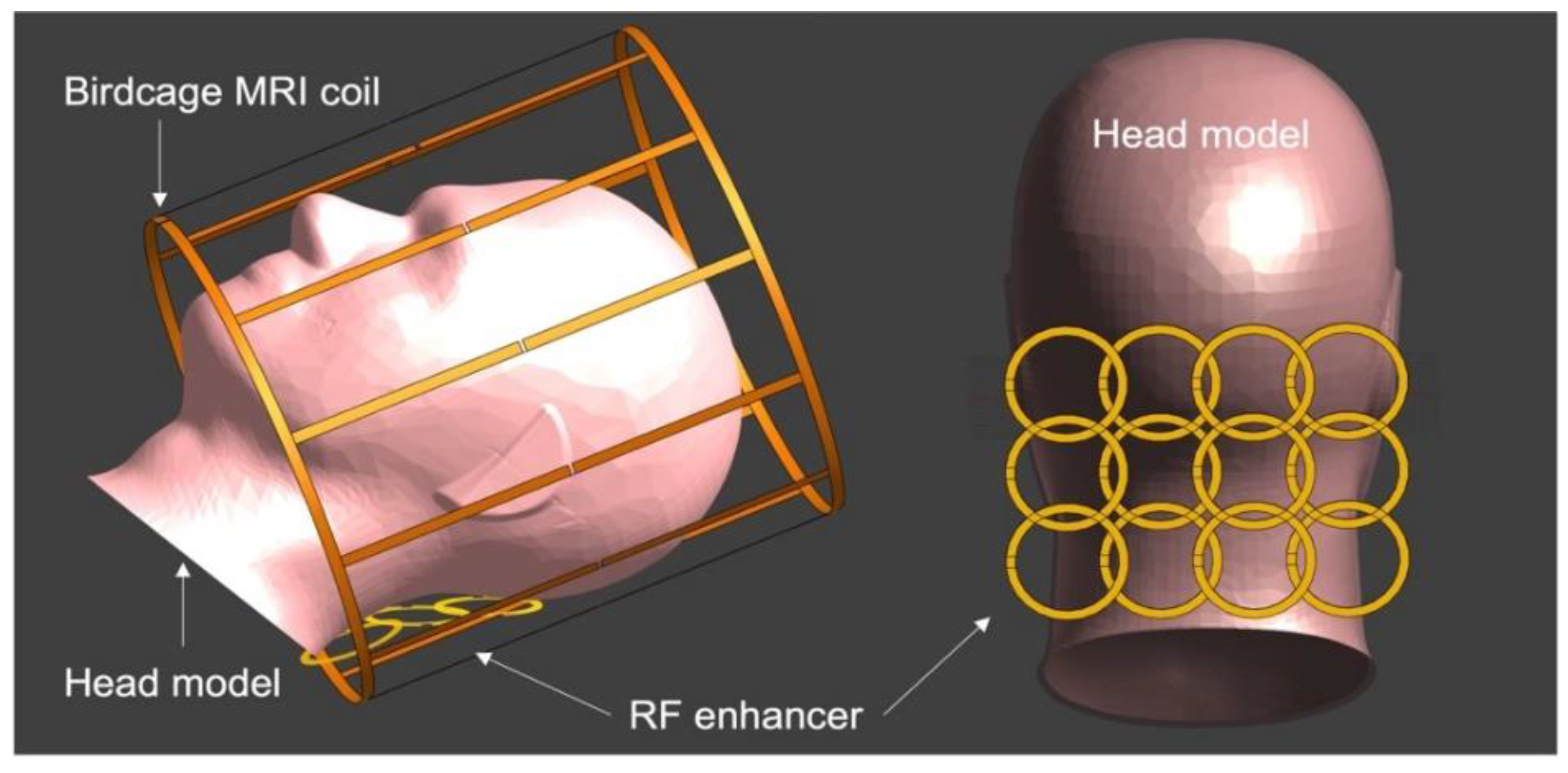
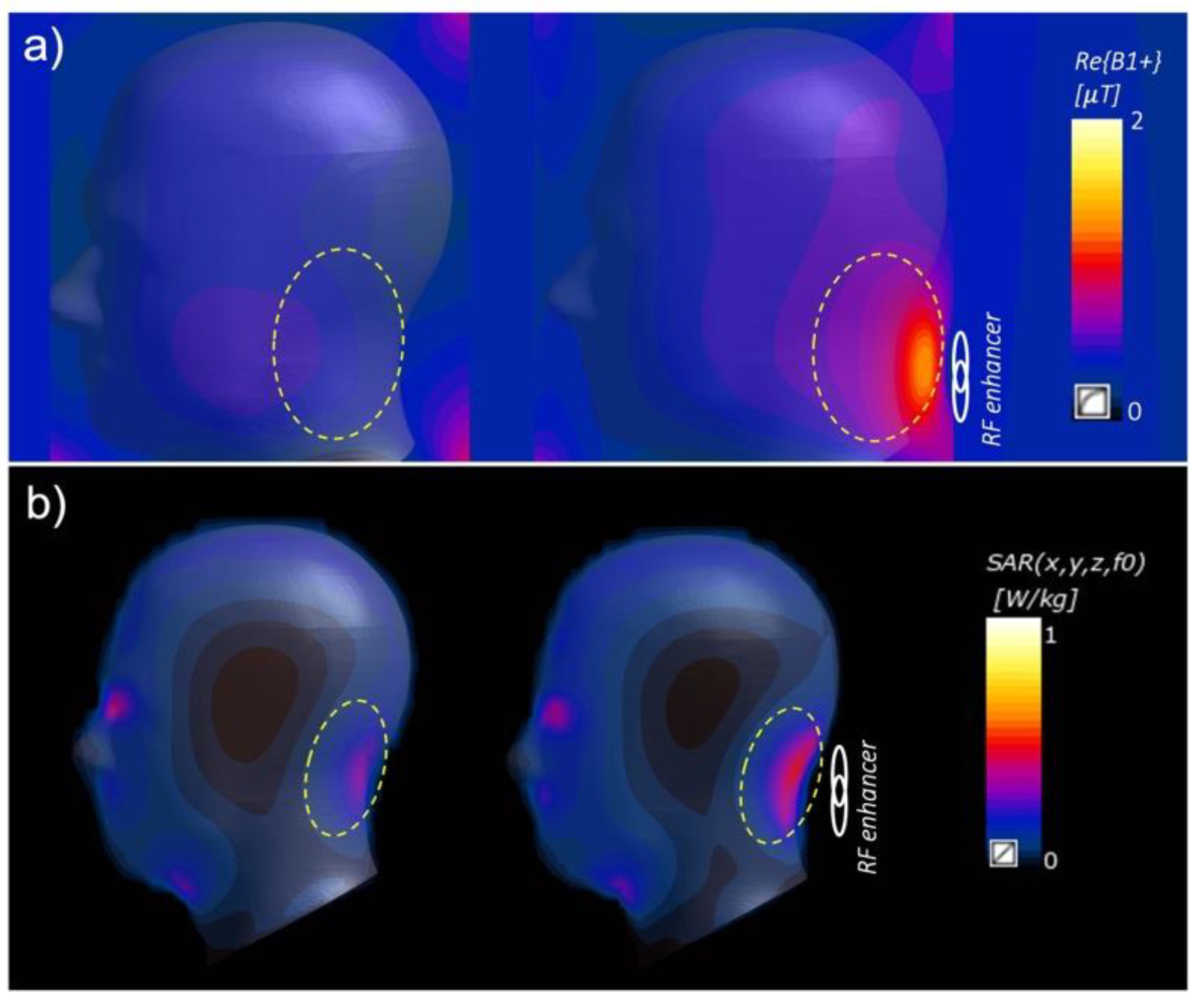
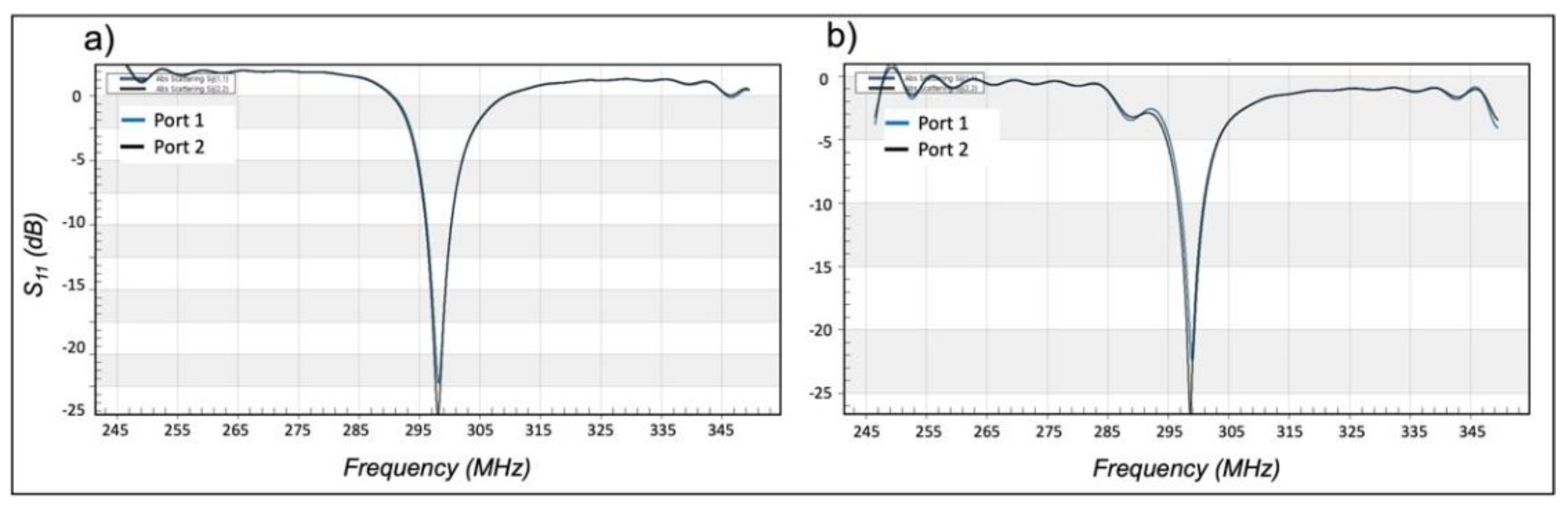
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




