Submitted:
22 July 2024
Posted:
23 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
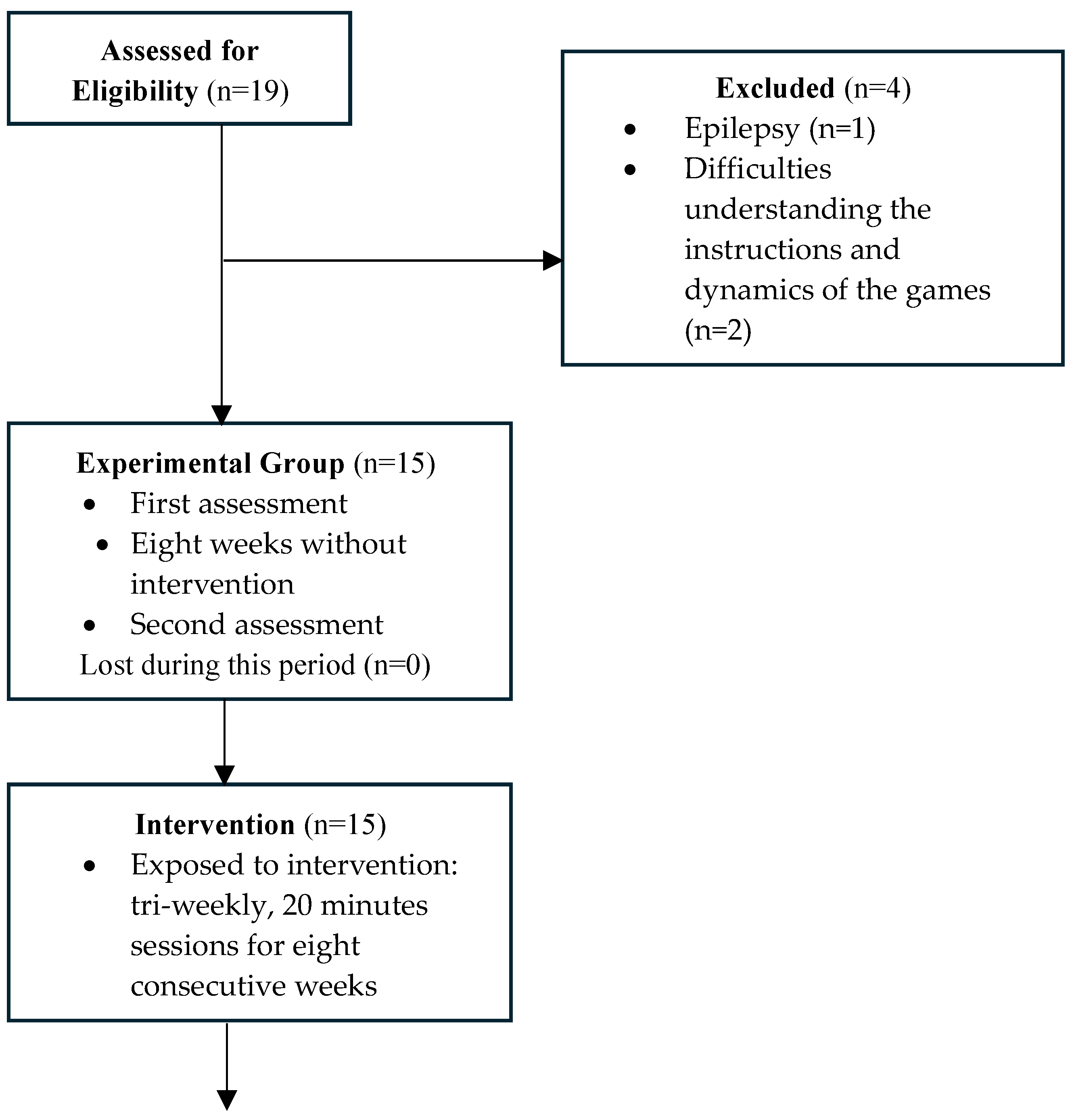
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instruments
2.2.1. Corsi Block-Tapping Task
2.2.2. Simple Reaction Time Task
2.2.3. Stop Signal Task
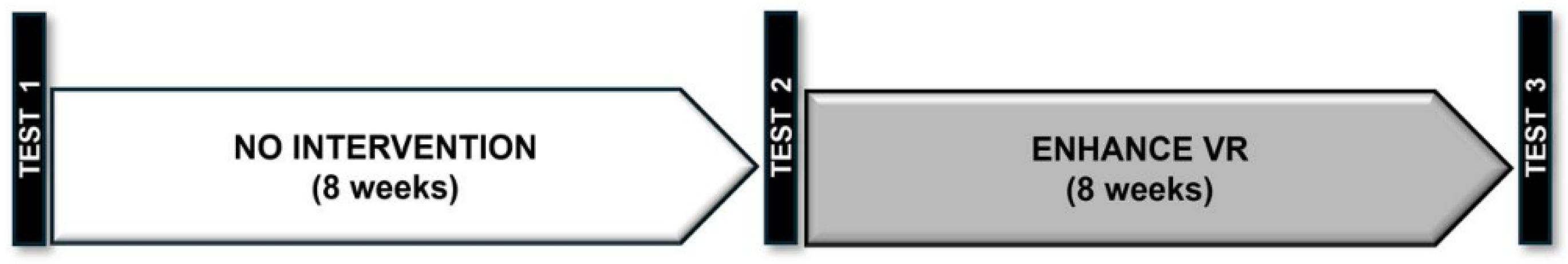
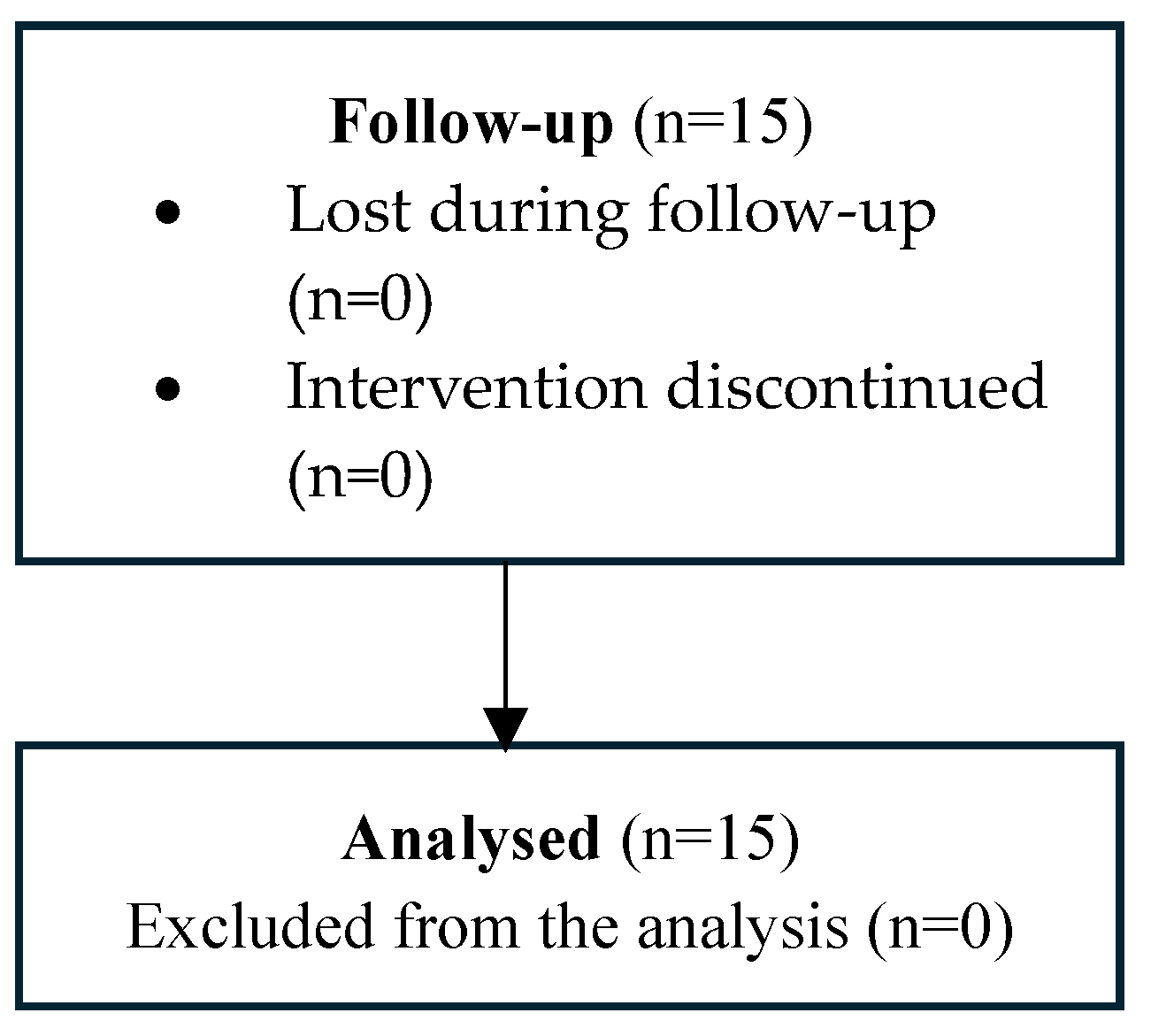
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Intervention Program: Enhance VR — Virtuleap
2.3.2. React
2.3.3. Memory Wall
2.3.4. Whack-A-Mole
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders 5th ed.; 2022.
- Schalock, R.L.; Borthwick-Duffy, S.A.; Bradley, V.J.; Buntinx, W.H.; Coulter, D.L.; Craig, E.M.; Gomez, S.C.; Lachapelle, Y.; Luckasson, R.; Reeve, A. Intellectual disability: Definition, classification, and systems of supports; ERIC: 2010.
- American Association on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities. Definition of Intellectual Disability. Available online: https://www.operationhousecall.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/AAIDD_definition_of_ID-DD_2009.pdf (accessed on 23 de Abril).
- Carulla, L.S.; Reed, G.M.; Vaez-Azizi, L.M.; Cooper, S.-A.; Leal, R.M.; Bertelli, M.; Adnams, C.; Cooray, S.; Deb, S.; Dirani, L.A.; et al. Intellectual developmental disorders: towards a new name, definition and framework for “mental retardation/intellectual disability” in ICD-11. World Psychiatry 2011, 10, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, D.J.; Lanfranchi, S. Executive function and intellectual disability: innovations, methods and treatment. J Intellect Disabil Res 2022, 66, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shree, A.; Shukla, P. Intellectual Disability: Definition, classification, causes and characteristics. Learning Community-An International Journal of Educational and Social Development 2016, 7, 9. [CrossRef]
- Srour, M.; Shevell, M. Genetics and the investigation of developmental delay/intellectual disability. Arch Dis Child 2014, 99, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, K.; Cole, V.; Longhi, E.; Karmiloff-Smith, A.; Scerif, G. Mapping developmental trajectories of attention and working memory in fragile X syndrome: developmental freeze or developmental change? Dev Psychopathol 2013, 25, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, R.; Hatton, D.; Sideris, J.; Sullivan, K.; Ornstein, A.; Bailey, J. Developmental trajectories of executive functions in young males with fragile X syndrome. Res Dev Disabil 2018, 81, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertelli, M.O.; Cooper, S.A.; Salvador-Carulla, L. Intelligence and specific cognitive functions in intellectual disability: implications for assessment and classification. Curr Opin Psychiatry 2018, 31, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsson, H.; Henry, L.; Rönnberg, J.; Nilsson, L.-G. Executive functions in individuals with intellectual disability. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2010, 31, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagaria, T.; Antonucci, G.; Buono, S.; Recupero, M.; Zoccolotti, P. Executive Functions and Attention Processes in Adolescents and Young Adults with Intellectual Disability. Brain Sci 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, A. Executive functions. Annu Rev Psychol 2013, 64, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacs, Z.K.; Kassai, R. The efficacy of different interventions to foster children’s executive function skills: A series of meta-analyses. Psychol Bull 2019, 145, 653–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.A.; Parikh, S.; Patel, D.R. Understanding basic concepts of developmental diagnosis in children. Transl Pediatr 2020, 9, S9–s22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, J. The prefrontal cortex, 5 ed.; ELSEVIER, Ed.; Academic press: 2015.
- Lalonde, G.; Henry, M.; Drouin-Germain, A.; Nolin, P.; Beauchamp, M.H. Assessment of executive function in adolescence: A comparison of traditional and virtual reality tools. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 2013, 219, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menghini, D.; Addona, F.; Costanzo, F.; Vicari, S. Executive functions in individuals with Williams syndrome. J Intellect Disabil Res 2010, 54, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanfranchi, S.; Jerman, O.; Dal Pont, E.; Alberti, A.; Vianello, R. Executive function in adolescents with Down Syndrome. J Intellect Disabil Res 2010, 54, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés Pascual, A.; Moyano Muñoz, N.; Quílez Robres, A. The Relationship Between Executive Functions and Academic Performance in Primary Education: Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Psychol 2019, 10, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela-Aldás, J.; Palacios-Navarro, G.; Amariglio, R.; García-Magariño, I. Head-Mounted Display-Based Application for Cognitive Training. Sensors (Basel) 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Aguirre, E.; Carter, J.; Hoare, S.; Brackley, K.; Goulden, N.; Hoare, Z.; Clarke, C.S.; Charlesworth, G.; Acton, D.; et al. Group cognitive stimulation therapy versus usual care for people with intellectual disabilities and dementia (CST-IDD) in the UK: protocol for a mixed-methods feasibility randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e072391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, G.; Mancuso, V.; Cavedoni, S.; Stramba-Badiale, C. Virtual reality in neurorehabilitation: a review of its effects on multiple cognitive domains. Expert Rev Med Devices 2020, 17, 1035–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Brown, E.; Tsang, W.; Spector, A.; Aguirre, E.; Hoare, S.; Hassiotis, A. Individual cognitive stimulation therapy (iCST) for people with intellectual disability and dementia: a feasibility randomised controlled trial. Aging Ment Health 2022, 26, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, M.; Bauer, A.; Wittenberg, R.; Comas-Herrera, A.; Cyhlarova, E.; Hu, B.; Jagger, C.; Kingston, A.; Patel, A.; Spector, A.; et al. What are the current and projected future cost and health-related quality of life implications of scaling up cognitive stimulation therapy? Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2022, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugada-Ramentol, V.; Bozorgzadeh, A.; Jalali, H. Enhance VR: A Multisensory Approach to Cognitive Training and Monitoring. Frontiers in Digital Health 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, N. Combined Effects of Virtual Reality and Computer Game-Based Cognitive Therapy on the Development of Visual-Motor Integration in Children with Intellectual Disabilities: A Pilot Study. Occup Ther Int 2021, 2021, 6696779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio, M.G.; Maresca, G.; De Luca, R.; Stagnitti, M.C.; Porcari, B.; Ferrera, M.C.; Galletti, F.; Casella, C.; Manuli, A.; Calabrò, R.S. The Growing Use of Virtual Reality in Cognitive Rehabilitation: Fact, Fake or Vision? A Scoping Review. J Natl Med Assoc 2019, 111, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standen, P.J.; Brown, D.J. Virtual reality in the rehabilitation of people with intellectual disabilities: review. Cyberpsychol Behav 2005, 8, 272-282; discussion 283-278. [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.; Brivio, E.; Riva, G.; Baños, R.M. Immersive Versus Non-immersive Experience: Exploring the Feasibility of Memory Assessment Through 360° Technology. Front Psychol 2019, 10, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, A.; Browning, M.; Jiang, S. Using Immersive Virtual Environments (IVEs) to Conduct Environmental Design Research: A Primer and Decision Framework. Herd 2020, 13, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panerai, S.; Catania, V.; Rundo, F.; Ferri, R. Remote Home-Based Virtual Training of Functional Living Skills for Adolescents and Young Adults With Intellectual Disability: Feasibility and Preliminary Results. Frontiers in Psychology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Hwang, E.; Shin, H.; Gil, Y.H.; Lee, J. Top-down, bottom-up, and history-driven processing of multisensory attentional cues in intellectual disability: An experimental study in virtual reality. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0261298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieri, G.; Morone, G.; Paolucci, S.; Iosa, M. Virtual reality in cognitive and motor rehabilitation: facts, fiction and fallacies. Expert Rev Med Devices 2018, 15, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachero, A.; Quadrini, A.; Pisano, F.; Calati, M.; Rugiero, C.; Ferrero, L.; Pia, L.; Marangolo, P. Procedural Learning through Action Observation: Preliminary Evidence from Virtual Gardening Activity in Intellectual Disability. Brain Sci 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabors, L.; Monnin, J.; Jimenez, S. A Scoping Review of Studies on Virtual Reality for Individuals with Intellectual Disabilities. Advances in Neurodevelopmental Disorders 2020, 4, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohil, C.J.; Alicea, B.; Biocca, F.A. Virtual reality in neuroscience research and therapy. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011, 12, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Garrett, B.; Taverner, T.; Cordingley, E.; Sun, C. Immersive virtual reality health games: a narrative review of game design. J Neuroeng Rehabil 2021, 18, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, R.A.; Augello, A.; Gallo, L.; Caggianese, G.; Malizia, V.; La Grutta, S.; Murero, M.; Valenti, D.; Tullo, A.; Balech, B.; et al. Serious Games in the new era of digital-health interventions: A narrative review of their therapeutic applications to manage neurobehavior in neurodevelopmental disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2023, 149, 105156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boato, E.; Melo, G.; Filho, M.; Moresi, E.; Lourenço, C.; Tristão, R. The Use of Virtual and Computational Technologies in the Psychomotor and Cognitive Development of Children with Down Syndrome: A Systematic Literature Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.Y.; Chen, I.H.; Lin, Y.J.; Chen, Y.; Hsu, W.C. Effects of Virtual Reality-Based Physical and Cognitive Training on Executive Function and Dual-Task Gait Performance in Older Adults With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Control Trial. Front Aging Neurosci 2019, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Iglesias, D.; Martínez-de-Quel, Ó.; Marín Moldes, J.R.; Ayán Pérez, C. Effects of Videogaming on the Physical, Mental Health, and Cognitive Function of People with Intellectual Disability: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Games Health J 2021, 10, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des Jarlais, D.C.; Lyles, C.; Crepaz, N.; Group, T. Improving the reporting quality of nonrandomized evaluations of behavioral and public health interventions: the TREND statement. American journal of public health 2004, 94, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; McGregor, J.; Perencevich, E.; Furuno, J.; Zhu, J.; Peterson, D.; Finkelstein, J. The use and interpretation of quasi-experimental studies in medical informatics. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2006, 13, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyer, B. Quasi-experimental research designs; Oxford University Press: 2012.
- Kim, H.S.; Yeon, H.W.; Choi, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, J.S.; Park, J.Y.; Jun, J.H.; Yi, J.H.; Tack, G.R.; Chung, S.C. Development of a tactile stimulator with simultaneous visual and auditory stimulation using E-Prime software. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2013, 16, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Gabriel, U.; Gygax, P. Testing the effectiveness of the Internet-based instrument PsyToolkit: A comparison between web-based (PsyToolkit) and lab-based (E-Prime 3.0) measurements of response choice and response time in a complex psycholinguistic task. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0221802. [CrossRef]
- Spapé, M.; Verdonschot, R.; Van Dantzig, S.; Steenbergen, H. The E-Primer: An Introduction to Creating Psychological Experiments in E-Prime; 2014.
- Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D. CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Journal of Pharmacology and pharmacotherapeutics 2010, 1, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, T.; McMullen, K. The Corsi Block-Tapping Test: Evaluating methodological practices with an eye towards modern digital frameworks. Computers in Human Behavior Reports 2021, 4, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessen, M.H.; van der Ham, I.J.; van Zandvoort, M.J. Computerization of the standard corsi block-tapping task affects its underlying cognitive concepts: a pilot study. Appl Neuropsychol Adult 2015, 22, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissberg, R.; Ruff, H.A.; Lawson, K.R. The usefulness of reaction time tasks in studying attention and organization of behavior in young children. J Dev Behav Pediatr 1990, 11, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajdel, R.; Nowak, D. Simple and complex reaction time measurement A preliminary evaluation of new approach and diagnostic tool. Comput Biol Med 2007, 37, 1724–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caglayan, A.; Stumpenhorst, K.; Winter, Y. The Stop Signal Task for Measuring Behavioral Inhibition in Mice With Increased Sensitivity and High-Throughput Operation. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friehs, M.A.; Dechant, M.; Vedress, S.; Frings, C.; Mandryk, R.L. Effective Gamification of the Stop-Signal Task: Two Controlled Laboratory Experiments. JMIR Serious Games 2020, 8, e17810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. Jama 2013, 310, 2191-2194.
- Smith, G.; Morrow, H.; Ross, A. Field Trials of Health Interventions: A Toolbox; OUP Oxford © London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine 2015.: Oxford (UK), 2015.
- Zweben, A.; Fucito, L.M.; O’Malley, S.S. Effective strategies for maintaining research participation in clinical trials. Drug Information Journal: DIJ/Drug Information Association 2009, 43, 459-467.
- Grant, D.A.; Berg, E.A. A behavioral analysis of degree of reinforcement and ease of shifting to new responses in a Weigl-type card-sorting problem. J Exp Psychol 1948, 38, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroop, J.R. Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. Journal of experimental psychology 1935, 18, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Sala, S.; Gray, C.; Baddeley, A.; Wilson, L. Visual Patterns Test: A test of short-term visual recall. 1997.
- Dinges, D.F.; Powell, J.W. Microcomputer analyses of performance on a portable, simple visual RT task during sustained operations. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers 1985, 17, 652-655,. [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows Armonk; IBM Corp.: NY, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Marôco, J. Análise Estatística com o SPSS Statistics.: 7ª edição; ReportNumber, Lda: 2018.
- Gignac, G.E. How2statsbook (Online Edition 1); Author: Perth, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Molen, M.J.; Van Luit, J.E.; Van der Molen, M.W.; Klugkist, I.; Jongmans, M.J. Effectiveness of a computerised working memory training in adolescents with mild to borderline intellectual disabilities. J Intellect Disabil Res 2010, 54, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roording-Ragetlie, S.; Spaltman, M.; de Groot, E.; Klip, H.; Buitelaar, J.; Slaats-Willemse, D. Working memory training in children with borderline intellectual functioning and neuropsychiatric disorders: a triple-blind randomised controlled trial. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 2022, 66, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-C.; Lee, H.-s. Effect of game-based cognitive training programs on cognitive learning of children with intellectual disabilities. Applied sciences 2021, 11, 8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlinchey, E.; McCarron, M.; Holland, A.; McCallion, P. Examining the effects of computerised cognitive training on levels of executive function in adults with Down syndrome. J Intellect Disabil Res 2019, 63, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bexkens, A.; Ruzzano, L.; Collot d’ Escury-Koenigs, A.M.L.; Van der Molen, M.W.; Huizenga, H.M. Inhibition deficits in individuals with intellectual disability: a meta-regression analysis. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 2014, 58, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigg, J.T. On inhibition/disinhibition in developmental psychopathology: views from cognitive and personality psychology and a working inhibition taxonomy. Psychological bulletin 2000, 126, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsson, H.; Henry, L.; Messer, D.; Rönnberg, J. Strengths and weaknesses in executive functioning in children with intellectual disability. Research in developmental disabilities 2012, 33, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorell, L.B.; Lindqvist, S.; Bergman Nutley, S.; Bohlin, G.; Klingberg, T. Training and transfer effects of executive functions in preschool children. Dev Sci 2009, 12, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, H.E.; Gray, K.M.; Ellis, K.; Taffe, J.; Cornish, K.M. Computerised attention training for children with intellectual and developmental disabilities: a randomised controlled trial. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 2016, 57, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affes, S.; Borji, R.; Zarrouk, N.; Sahli, S.; Rebai, H. Effects of running exercises on reaction time and working memory in individuals with intellectual disability. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 2021, 65, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, F.; Varuzza, C.; Menghini, D.; Addona, F.; Gianesini, T.; Vicari, S. Executive functions in intellectual disabilities: a comparison between Williams syndrome and Down syndrome. Research in developmental disabilities 2013, 34, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melam, G.; Buragadda, S.; Alhusaini, A.; Dhamija, P. Reaction and movement time in Down syndrome children under different visual feedback conditions. J Nov Physiother 2014, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, K.; Scerif, G.; Karmiloff-Smith, A. Tracing syndrome-specific trajectories of attention across the lifespan. Cortex 2007, 43, 672–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, F.; Cornish, K.M.; Wilding, J. A neuropsychological profile of attention deficits in young males with fragile X syndrome. Neuropsychologia 2000, 38, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafeiridis, A.; Giagazoglou, P.; Dipla, K.; Salonikidis, K.; Karra, C.; Kellis, E. Muscle fatigue during intermittent exercise in individuals with mental retardation. Research in developmental disabilities 2010, 31, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, T.; Schneider, S.; Abeln, V.; Anneken, V.; Strüder, H.K. Exercise, mood and cognitive performance in intellectual disability—A neurophysiological approach. Behavioural brain research 2012, 226, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringenbach, S.D.; Albert, A.R.; Chen, C.-C.; Alberts, J.L. Acute bouts of assisted cycling improves cognitive and upper extremity movement functions in adolescents with Down syndrome. Mental Retardation 2014, 52, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Ringenbach, s. Dose–response relationship between intensity of exercise and cognitive performance in individuals with Down syndrome: a preliminary study. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 2016, 60, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erostarbe-Pérez, M.; Reparaz-Abaitua, C.; Martínez-Pérez, L.; Magallón-Recalde, S. Executive functions and their relationship with intellectual capacity and age in schoolchildren with intellectual disability. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 2022, 66, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memisevic, H.; Sinanovic, O. Executive function in children with intellectual disability–the effects of sex, level and aetiology of intellectual disability. Journal of intellectual disability research 2014, 58, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchardt, K.; Gebhardt, M.; Mäehler, C. Working memory functions in children with different degrees of intellectual disability. Journal of intellectual disability research 2010, 54, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, M.G.; Maresca, G.; De Luca, R.; Stagnitti, M.C.; Porcari, B.; Ferrera, M.C.; Galletti, F.; Casella, C.; Manuli, A.; Calabrò, R.S. The growing use of virtual reality in cognitive rehabilitation: fact, fake or vision? A scoping review. Journal of the National Medical Association 2019, 111, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, R.; Lo Buono, V.; Leo, A.; Russo, M.; Aragona, B.; Leonardi, S.; Buda, A.; Naro, A.; Calabrò, R.S. Use of virtual reality in improving poststroke neglect: Promising neuropsychological and neurophysiological findings from a case study. Applied Neuropsychology: Adult 2019, 26, 96-100.
- Knobel, S.E.; Kaufmann, B.C.; Gerber, S.M.; Cazzoli, D.; Müri, R.M.; Nyffeler, T.; Nef, T. Immersive 3D virtual reality cancellation task for visual neglect assessment: a pilot study. Frontiers in human neuroscience 2020, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldana, D.; Neureither, M.; Schmiesing, A.; Jahng, E.; Kysh, L.; Roll, S.C.; Liew, S.-L. Applications of head-mounted displays for virtual reality in adult physical rehabilitation: a scoping review. The American Journal of Occupational Therapy 2020, 74, 7405205060p7405205061–7405205060p7405205015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalon-Chamovitz, S.; Weiss, P.L. Virtual reality as a leisure activity for young adults with physical and intellectual disabilities. Res Dev Disabil 2008, 29, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadwick, O.; Cuddy, M.; Kusel, Y.; Taylor, E. Handicaps and the development of skills between childhood and early adolescence in young people with severe intellectual disabilities. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 2005, 49, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.; Shields, N.; Imms, C.; Black, M.; Ardern, C. Participation of children with intellectual disability compared with typically developing children. Research in developmental disabilities 2013, 34, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derks, S.; Willemen, A.M.; Sterkenburg, P.S. Improving adaptive and cognitive skills of children with an intellectual disability and/or autism spectrum disorder: Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials on the effects of serious games. International Journal of Child-Computer Interaction 2022, 33, 100488.
| x ± SD | N (%) | ||
| Age (years) | 28.07 ± 3.97 | ||
| Gender | Male | 10 (66.70) | |
| Female | 5 (33.30) | ||
| Levels of IDD | Mild | 8 (53.30) | |
| Moderate | 7 (46.70) | ||
| Literacy | Yes | 7 (46.70) | |
| No | 8 (53.30) | ||
| Previous experience with VR | Yes | 0 (.00) | |
| No | 15 (100.00) |
| test1 x ± SD | test2 x ± SD | test3 x ± SD | p-value | Power | |
| CBTT | 11.53 ± 2.03 | 11.07 ± 2.54 | 13.93 ± 1.91 | .001* | .960 |
| SRT | 55.86 ± 5.41 | 53.47 ± 11.21 | 57.73 ± 3.57 | .101 | .373 |
| SST | 90.40 ± 22.76 | 90.87 ± 23.89 | 99.53 ± 27.58 | .043* | .545 |
| CBTT | SST | |||
| Mean difference | p-valuea | Mean difference | p-valuea | |
| Test1 vs. Test2 | .467 | 1.000 | -.467 | 1.000 |
| Test1 vs. Test3 | -2.400 | .004* | -9.133 | .010* |
| Test2 vs. Test3 | -2.867 | .002* | -8.667 | .039* |
| IDD levels | test1 | test2 | test3 | p-valuea | p-valueb | powera | powerb | |
| CBTT | Mild | 11.63±2.26 | 11.25±3.28 | 14.50±2.33 | .002* | .418 | .949 | .121 |
| Moderate | 11.43±1.90 | 10.86±1.57 | 13.29±1.11 | |||||
| SRT | Mild | 55.25±5.44 | 56.88±4.58 | 56.88±4.58 | .112 | .818 | .352 | .055 |
| Moderate | 56.57±5.71 | 57.00±3.32 | 58.71±1.80 | |||||
| SST | Mild | 99.63± 7.46 | 98.75± 8.16 | 103.38± 10.00 | .032* | .168 | .605 | .272 |
| Moderate | 79.86± 7.98 | 81.86± 8.72 | 95.14±10.69 |
| Level of IDD | ||||
| CBTT | SST | |||
| Mean difference ±sd | p-valuea | Mean difference ±sd | p-valuea | |
| Test1 vs. Test2 | .47 ± .61 | .450 | .56 ± 2.03 | .786 |
| Test1 vs. Test3 | -2.37 ± .61 | .002* | 9.52 ± 3.95 | .032* |
| Test2 vs. Test3 | -2.84 ± .69 | .001* | 8.96 ± 2.93 | .009* |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





