Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
17 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Expression and Purification of CVB3 3CPro
2.2. Analytical Gel Filtration
2.3. Crystallization, Data Collection and Structure Solution
2.4. NMR Spectroscopy
2.5. Enzyme Inhibition Kinetics Assay
3. Results
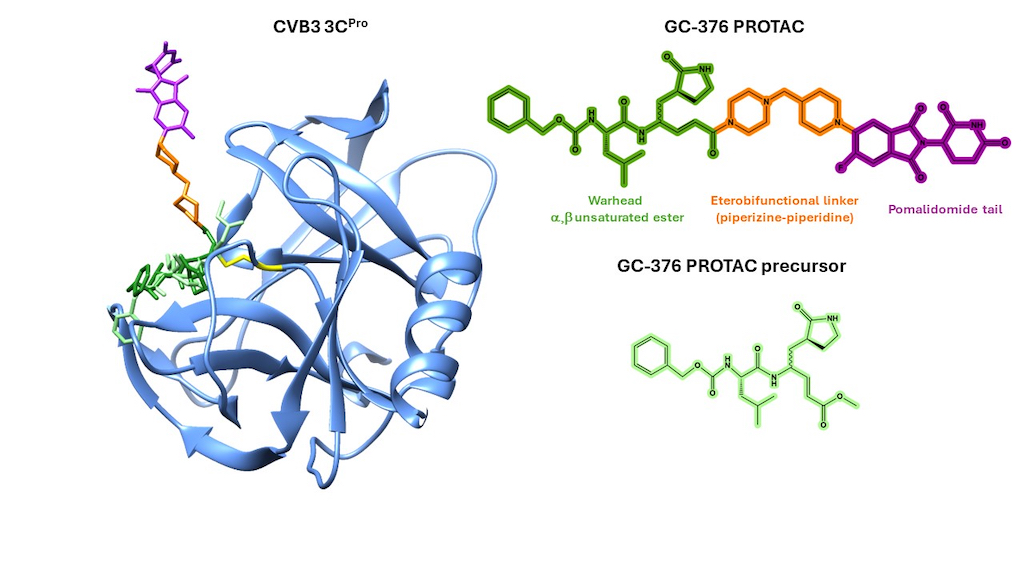
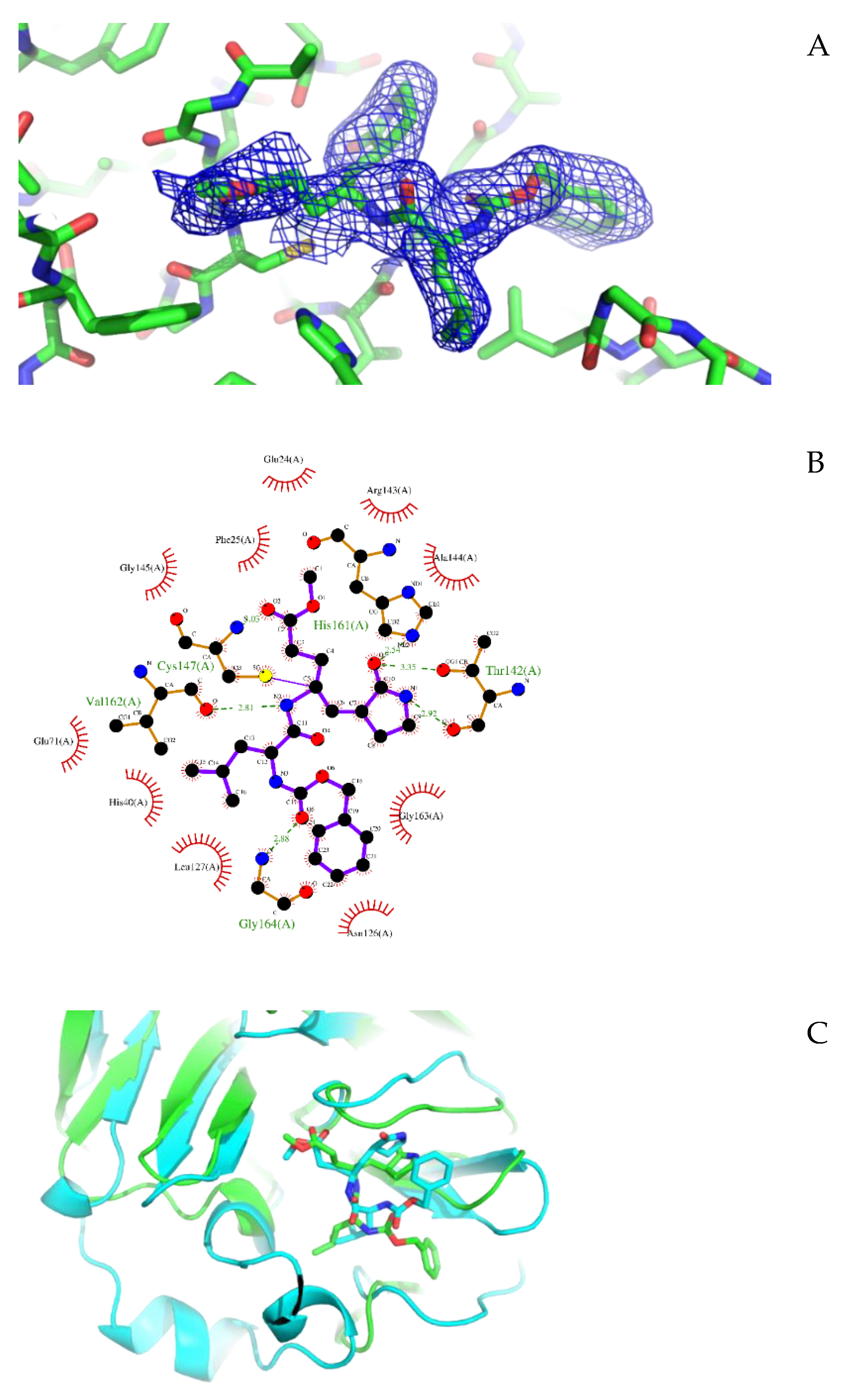
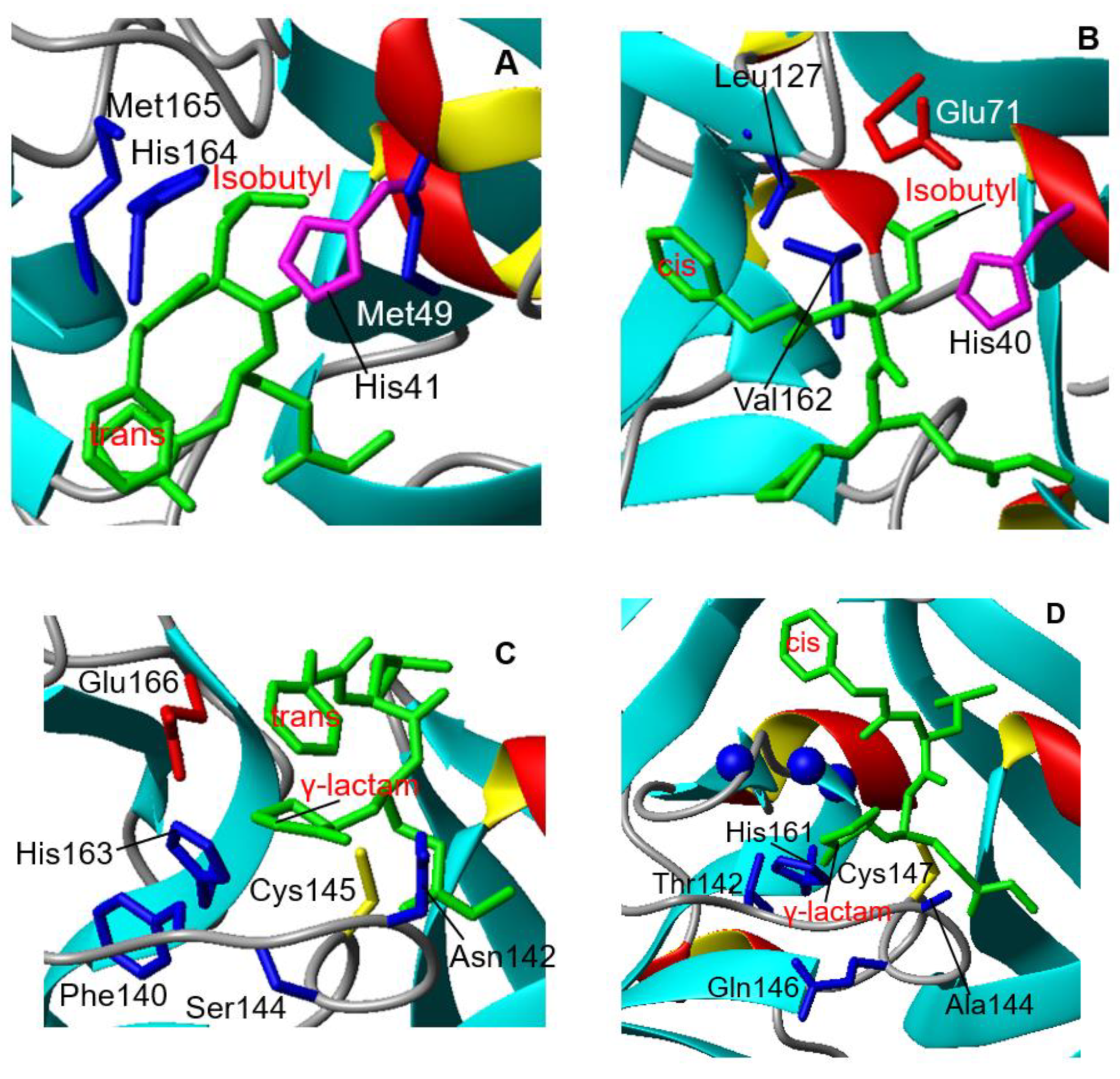
3.1. Crystal Structure of CVB3 3CPro in Complex with GC-376 PROTAC Precursor
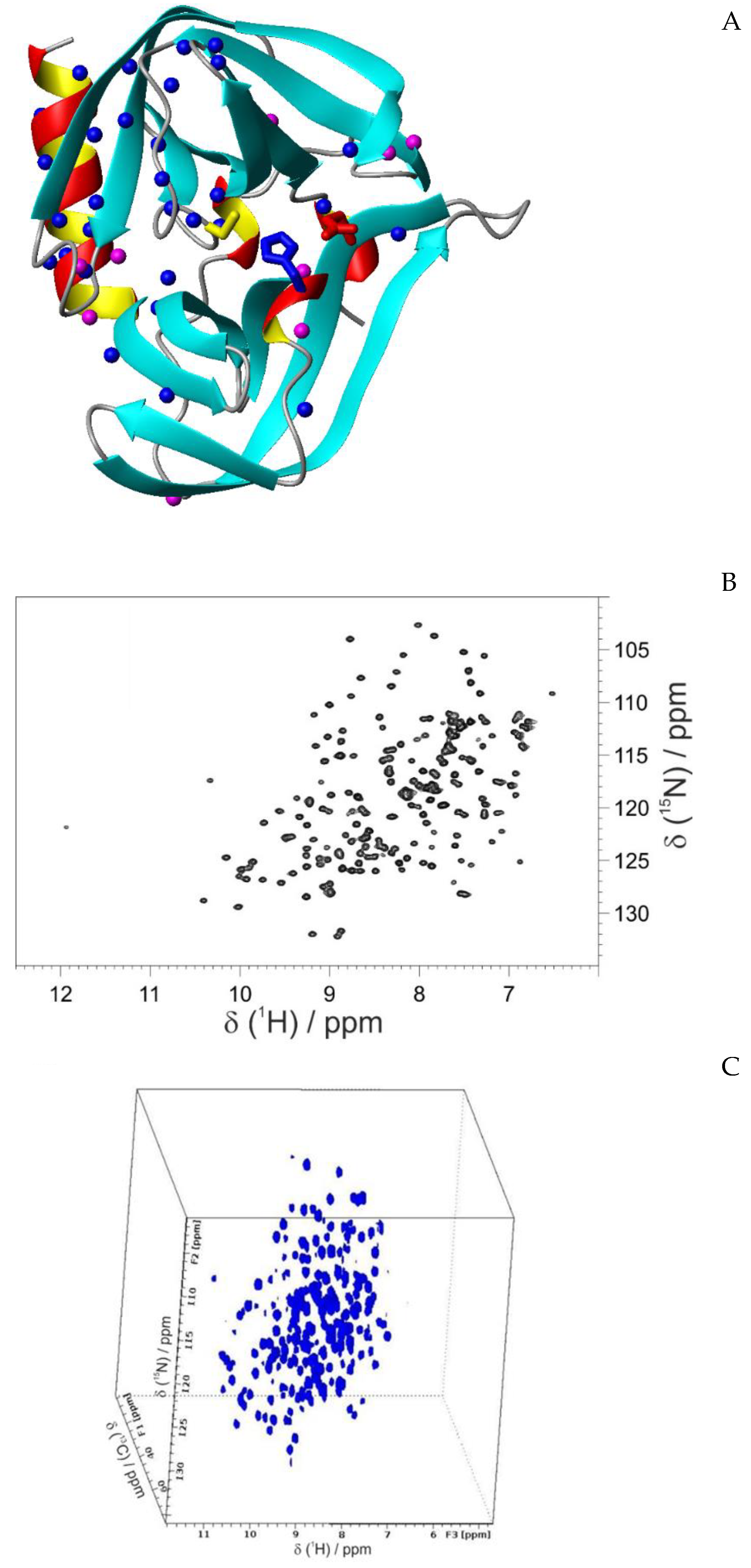
3.2. Structural characterization of CVB3 3CPro by solution NMR
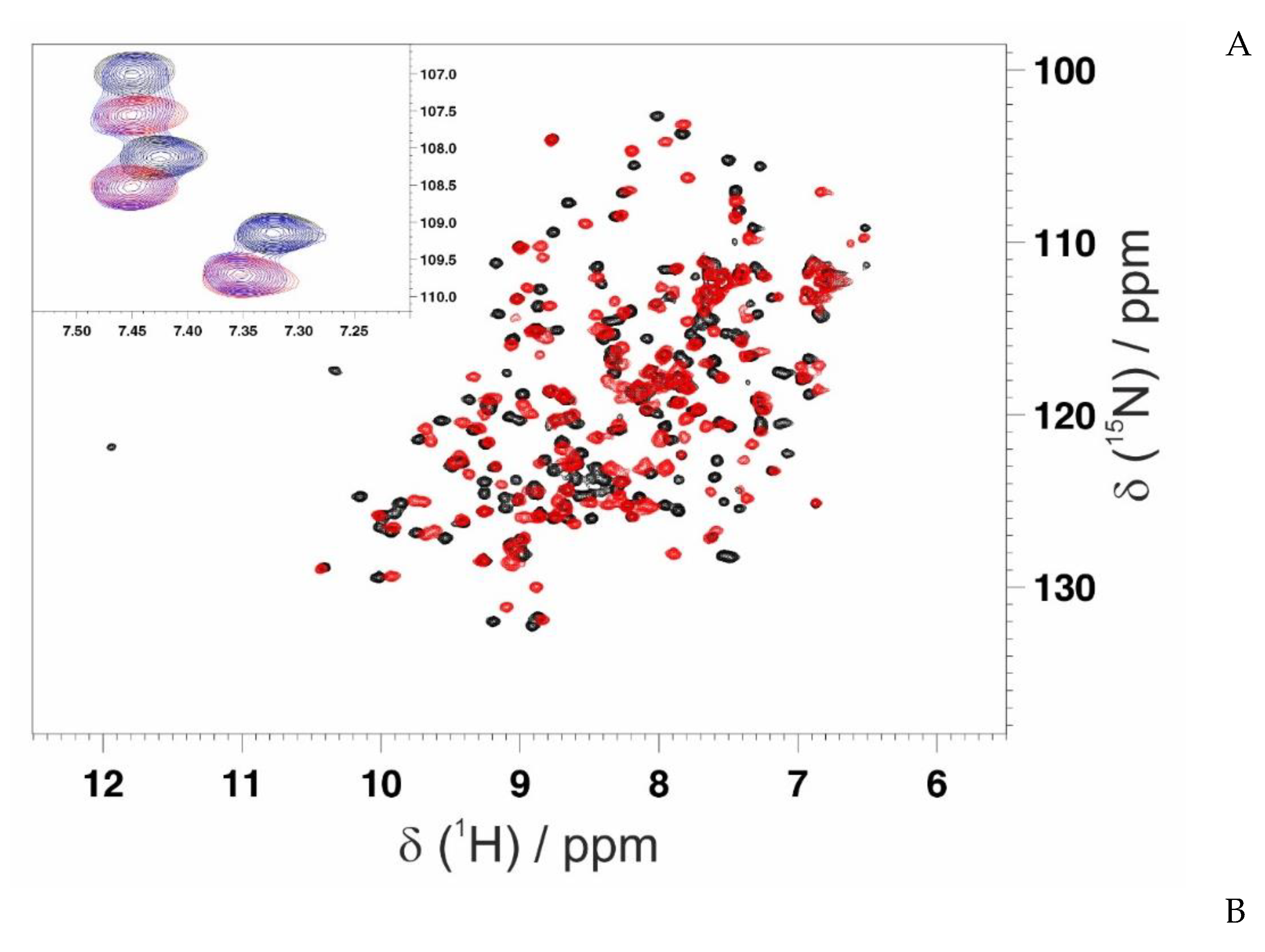
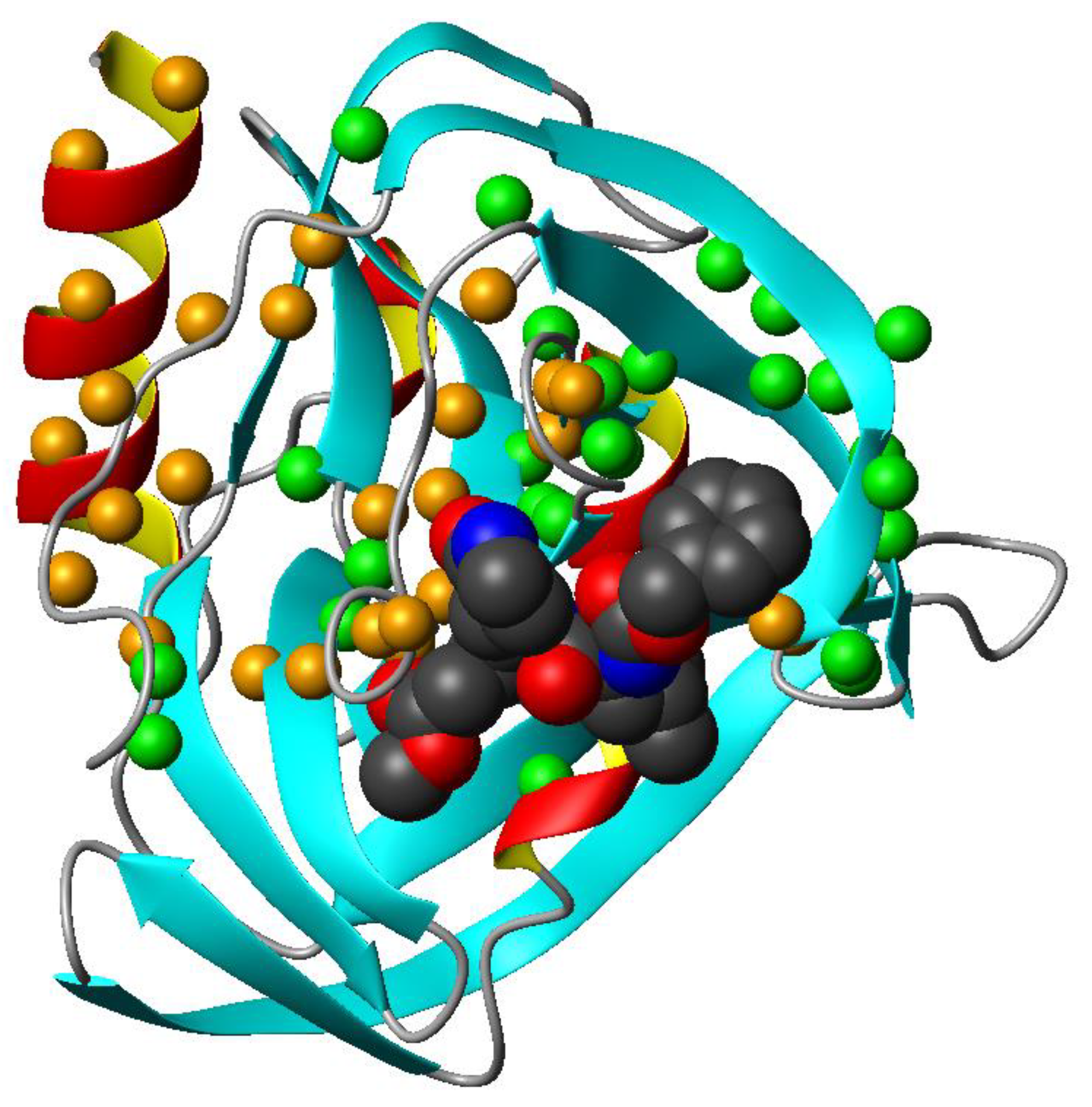
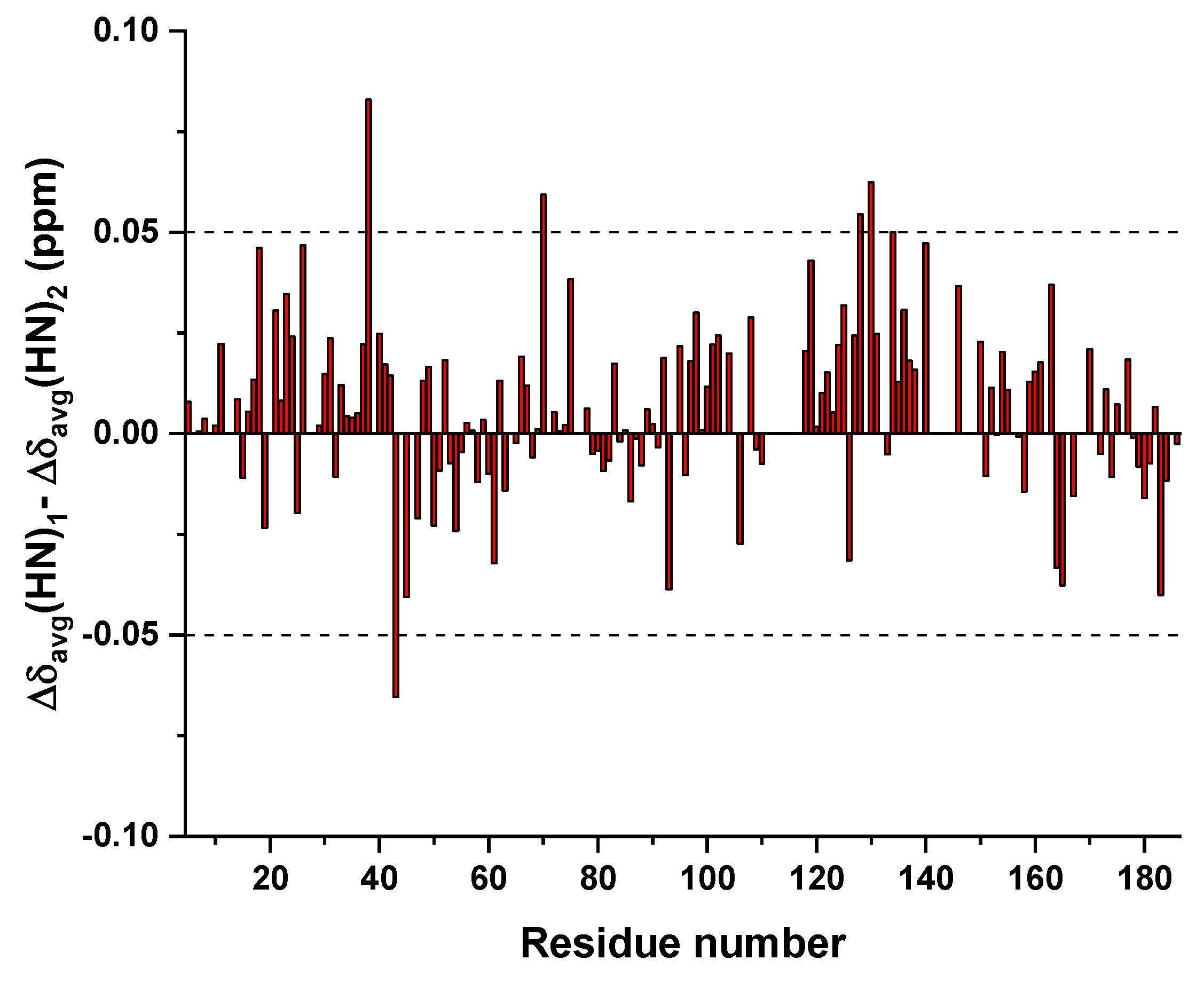
3.3. Mapping the Interaction of GC-376 PROTAC and Its Precursor with CVB3 3CPro by Solution NMR
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komander, D.; Rape, M. The ubiquitin code. Annu Rev Biochem 2012, 81, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Shabek, N. Ubiquitin Ligases: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Annu Rev Biochem 2017, 86, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morreale, F.E.; Walden, H. Types of Ubiquitin Ligases. Cell 2016, 165, 248–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshaies, R.J.; Joazeiro, C.A. RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu Rev Biochem 2009, 78, 399–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, B.A.; Harper, J.W. Ubiquitin-like protein activation by E1 enzymes: the apex for downstream signalling pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009, 10, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Rape, M. Building ubiquitin chains: E2 enzymes at work. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009, 10, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finley, D. Recognition and processing of ubiquitin-protein conjugates by the proteasome. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2009, 78, 477–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Crews, C.M. PROTACs: past, present and future. Chem Soc Rev 2022, 51, 5214–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciulli, A.H., O. PROTAC Degraders Mechanism, Recent Advances, and Future Challenges. In Protein Homeostasis in Drug Discovery: A Chemical Biology Perspective, Jones, M.K.L.H., Ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: 2022; pp. 317-356.
- Toure, M.; Crews, C.M. Small-Molecule PROTACS: New Approaches to Protein Degradation. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2016, 55, 1966–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alugubelli, Y.R.; Xiao, J.; Khatua, K.; Kumar, S.; Sun, L.; Ma, Y.; Ma, X.R.; Vulupala, V.R.; Atla, S.; Blankenship, L.R. , et al. Discovery of First-in-Class PROTAC Degraders of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. J Med Chem 2024, 67, 6495–6507. [Google Scholar]
- Grifagni, D.; Lenci, E.; De Santis, A.; Orsetti, A.; Barracchia, C.G.; Tedesco, F.; Bellini Puglielli, R.; Lucarelli, F.; Lauriola, A.; Assfalg, M. , et al. Development of a GC-376 Based Peptidomimetic PROTAC as a Degrader of 3-Chymotrypsin-like Protease of SARS-CoV-2. ACS Med Chem Lett 2024, 15, 250–257. [Google Scholar]
- Desantis, J.; Bazzacco, A.; Eleuteri, M.; Tuci, S.; Bianconi, E.; Macchiarulo, A.; Mercorelli, B.; Loregian, A.; Goracci, L. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of first-in-class indomethacin-based PROTACs degrading SARS-CoV-2 main protease and with broad-spectrum antiviral activity. European journal of medicinal chemistry 2024, 268, 116202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; An, J.; Warshel, A.; Huang, Z. A Chemical Strategy for the Degradation of the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2 in Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 27248–27253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anand, K.; Ziebuhr, J.; Wadhwani, P.; Mesters, J.R.; Hilgenfeld, R. Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science 2003, 300, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marjomäki, V.; Kalander, K.; Hellman, M.; Permi, P. Enteroviruses and coronaviruses: similarities and therapeutic targets. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets 2021, 25, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, W.; Qi, Z.; Wang, J. The Function and Mechanism of Enterovirus 71 (EV71) 3C Protease. Current microbiology 2020, 77, 1968–1975. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, O.H.; Svedin, E.; Kapell, S.; Nurminen, A.; Hytönen, V.P.; Flodström-Tullberg, M. Enteroviral proteases: structure, host interactions and pathogenicity. Reviews in medical virology 2016, 26, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; George, S.; Kusov, Y.; Perbandt, M.; Anemüller, S.; Mesters, J.R.; Norder, H.; Coutard, B.; Lacroix, C.; Leyssen, P. , et al. 3C protease of enterovirus 68: structure-based design of Michael acceptor inhibitors and their broad-spectrum antiviral effects against picornaviruses. J Virol 2013, 87, 4339–4351. [Google Scholar]
- Nikonov, O.S.; Chernykh, E.S.; Garber, M.B.; Nikonova, E.Y. Enteroviruses: Classification, Diseases They Cause, and Approaches to Development of Antiviral Drugs. Biochemistry. Biokhimiia 2017, 82, 1615–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, R.; Krebs, P.; Ludewig, B. Immunopathological basis of virus-induced myocarditis. Clinical & developmental immunology 2004, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gauntt, C.; Huber, S. Coxsackievirus experimental heart diseases. Front Biosci 2003, 8, e23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugo, D.; Krogstad, P. Enteroviruses in the early 21st century: new manifestations and challenges. Current opinion in pediatrics 2016, 28, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; McDougal, M.B.; Schoggins, J.W. Enterovirus 3C Protease Cleaves TRIM7 To Dampen Its Antiviral Activity. J Virol 2022, 96, e0133222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Donchenko, A.P.; Blinov, V.M.; Koonin, E.V. Cysteine proteases of positive strand RNA viruses and chymotrypsin-like serine proteases. A distinct protein superfamily with a common structural fold. FEBS Lett 1989, 243, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.; Wei, P.; Feng, Q.; Chen, S.; Huang, C.; Ma, L.; Lai, B.; Pei, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. , et al. Biosynthesis, purification, and substrate specificity of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3C-like proteinase. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, D.; Kusov, Y.; Nian, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wang, J.; von Brunn, A.; Leyssen, P.; Lanko, K.; Neyts, J. , et al. α-Ketoamides as Broad-Spectrum Inhibitors of Coronavirus and Enterovirus Replication: Structure-Based Design, Synthesis, and Activity Assessment. J Med Chem 2020, 63, 4562–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, K.; Palm, G.J.; Mesters, J.R.; Siddell, S.G.; Ziebuhr, J.; Hilgenfeld, R. Structure of coronavirus main proteinase reveals combination of a chymotrypsin fold with an extra alpha-helical domain. Embo j 2002, 21, 3213–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fàbrega-Ferrer, M.; Herrera-Morandé, A.; Muriel-Goñi, S.; Pérez-Saavedra, J.; Bueno, P.; Castro, V.; Garaigorta, U.; Gastaminza, P.; Coll, M. Structure and inhibition of SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 main proteases by oral antiviral compound AG7404. Antiviral research 2022, 208, 105458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göhl, M.; Zhang, L.; El Kilani, H.; Sun, X.; Zhang, K.; Brönstrup, M.; Hilgenfeld, R. From Repurposing to Redesign: Optimization of Boceprevir to Highly Potent Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockbaum, G.J.; Henes, M.; Lee, J.M.; Timm, J.; Nalivaika, E.A.; Thompson, P.R.; Kurt Yilmaz, N.; Schiffer, C.A. Pan-3C Protease Inhibitor Rupintrivir Binds SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease in a Unique Binding Mode. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 2925–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Jochmans, D.; Xie, H.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Su, H.; Chang, D.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Zhu, L. , et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Peptidomimetic Aldehydes as Broad-Spectrum Inhibitors against Enterovirus and SARS-CoV-2. J Med Chem 2022, 65, 2794–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramajayam, R.; Tan, K.P.; Liu, H.G.; Liang, P.H. Synthesis and evaluation of pyrazolone compounds as SARS-coronavirus 3C-like protease inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 2010, 18, 7849–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramajayam, R.; Tan, K.P.; Liang, P.H. Recent development of 3C and 3CL protease inhibitors for anti-coronavirus and anti-picornavirus drug discovery. Biochem Soc Trans 2011, 39, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandadapu, S.R.; Weerawarna, P.M.; Prior, A.M.; Uy, R.A.; Aravapalli, S.; Alliston, K.R.; Lushington, G.H.; Kim, Y.; Hua, D.H.; Chang, K.O. , et al. Macrocyclic inhibitors of 3C and 3C-like proteases of picornavirus, norovirus, and coronavirus. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2013, 23, 3709–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Shin, J.S.; Shie, J.J.; Ku, K.B.; Kim, C.; Go, Y.Y.; Huang, K.F.; Kim, M.; Liang, P.H. Identification and evaluation of potent Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) 3CL(Pro) inhibitors. Antiviral research 2017, 141, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Kuo, C.J.; Ko, T.P.; Hsu, M.F.; Tsui, Y.C.; Chang, S.C.; Yang, S.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, H.C.; Hsu, M.C. , et al. Structural basis of inhibition specificities of 3C and 3C-like proteases by zinc-coordinating and peptidomimetic compounds. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 7646–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.J.; Liu, H.G.; Lo, Y.K.; Seong, C.M.; Lee, K.I.; Jung, Y.S.; Liang, P.H. Individual and common inhibitors of coronavirus and picornavirus main proteases. FEBS Lett 2009, 583, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fili, S.; Valmas, A.; Christopoulou, M.; Spiliopoulou, M.; Nikolopoulos, N.; Lichière, J.; Logotheti, S.; Karavassili, F.; Rosmaraki, E.; Fitch, A. , et al. Coxsackievirus B3 protease 3C: expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary structural insights. Acta crystallographica. Section F, Structural biology communications 2016, 72, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabsch, W. XDS. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr 2010, 66, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagin, A.A.; Teplyakov, A. An approach to multi-copy search in molecular replacement. Acta Cryst. D 2000, 56, 1622–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkoczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W. , et al. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr 2010, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Cryst. D 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B., III.; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Cryst. D 2010, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzesiek, S.; Bax, A. Amino acid type determination in the sequential assignment procedure of uniformly 13C/15N-enriched proteins. J. Biomol. NMR 1993, 3, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, M.P. Using chemical shift perturbation to characterise ligand binding. Prog. Nucl. Magn Reson. Spectrosc 2013, 73, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrow, N.A.; Muhandiram, R.; Singer, A.U.; Pascal, S.M.; Kay, C.M.; Gish, G.; Shoelson, S.E.; Pawson, T.; Forman-Kay, J.D.; Kay, L.E. Backbone dynamics of a free and phosphopeptide-complexed Src homology 2 domain studied by 15N NMR relaxation. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 5984–6003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grzesiek, S.; Bax, A. The Importance of Not Saturating H2o in Protein Nmr - Application to Sensitivity Enhancement and Noe Measurements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 12593–12594. [Google Scholar]
- Mandel, M.A.; Akke, M.; Palmer, A.G., III. Backbone dynamics of Escherichia coli ribonuclease HI: correlations with structure and function in an active enzyme. J. Mol. Biol 1995, 246, 144–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia de la Torre, J.; Huertas, M.L.; Carrasco, B. HYDRONMR: prediction of NMR relaxation of globular proteins from atomic-level structures and hydrodynamic calculations. J Magn Reson 2000, 147, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.A.; Dragovich, P.S.; Webber, S.E.; Fuhrman, S.A.; Patick, A.K.; Zalman, L.S.; Hendrickson, T.F.; Love, R.A.; Prins, T.J.; Marakovits, J.T. , et al. Structure-assisted design of mechanism-based irreversible inhibitors of human rhinovirus 3C protease with potent antiviral activity against multiple rhinovirus serotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999, 96, 11000–11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.O.; Hua, Y.; Luu, H.T.; Brown, E.L.; Chan, F.; Chu, S.S.; Dragovich, P.S.; Eastman, B.W.; Ferre, R.A.; Fuhrman, S.A. , et al. Structure-based design of a parallel synthetic array directed toward the discovery of irreversible inhibitors of human rhinovirus 3C protease. J Med Chem 2002, 45, 2016–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golovanov, A.P.; Hautbergue, G.M.; Wilson, S.A.; Lian, L.Y. A simple method for improving protein solubility and long-term stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2004, 126, 8933–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Ye, F.; Feng, Y.; Yu, F.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Sun, H.; Huang, B.; Niu, P. , et al. Both Boceprevir and GC376 efficaciously inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by targeting its main protease. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zou, X.; Zeng, X.; Wang, J.; Zeng, P.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J. , et al. Structural Basis for Coronaviral Main Proteases Inhibition by the 3CLpro Inhibitor GC376. J Mol Biol 2024, 436, 168474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Feng, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, T.; Lv, X.; Tong, X.; Xi, G.; Ye, X.; Li, X. Development of novel antivrial agents that induce the degradation of the main protease of human-infecting coronaviruses. European journal of medicinal chemistry 2024, 275, 116629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




