Submitted:
15 July 2024
Posted:
16 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
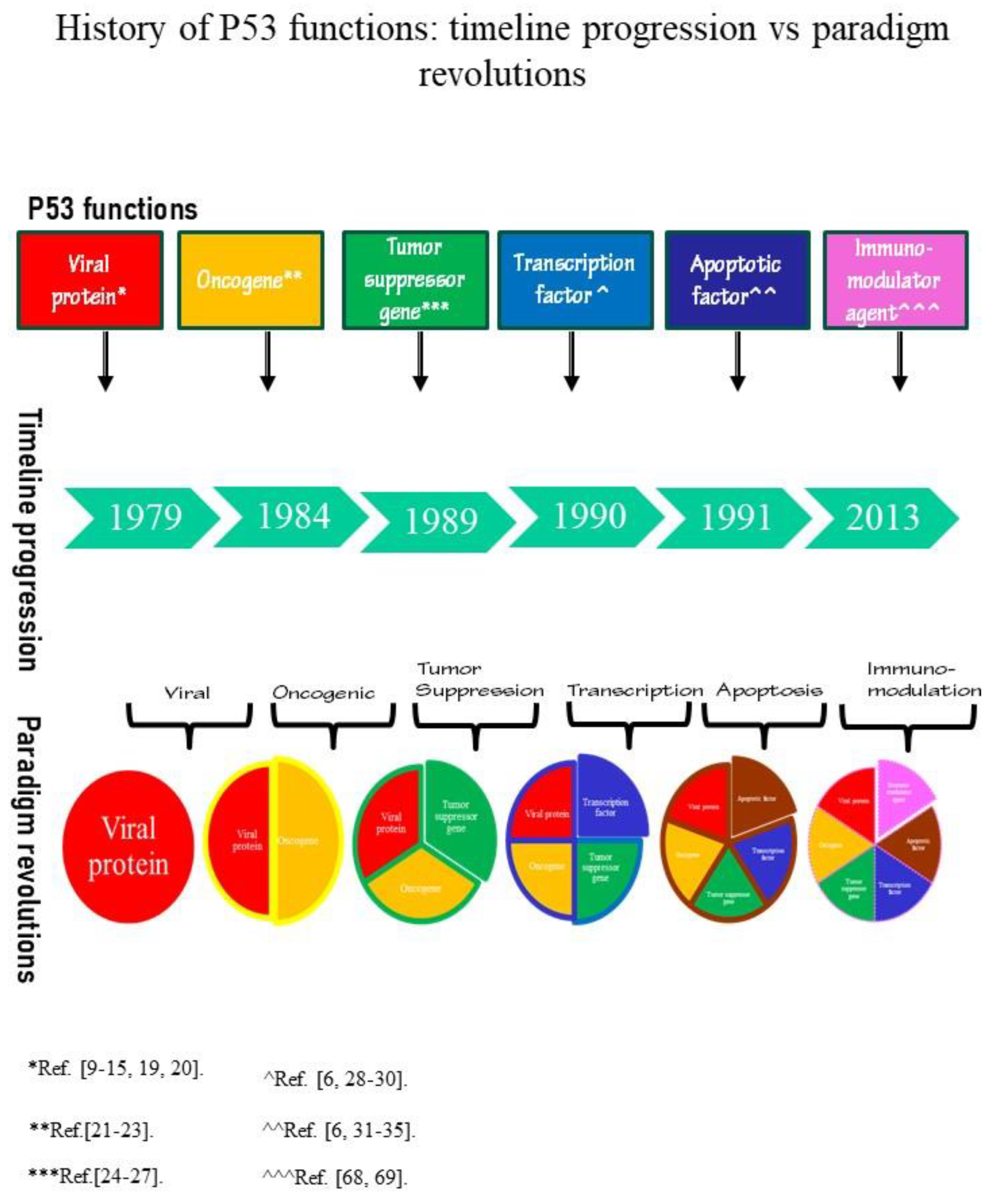
2. P53 History: Timeline Progression Vs Paradigm Revolutions
P53 Timeline
P53 Paradigms
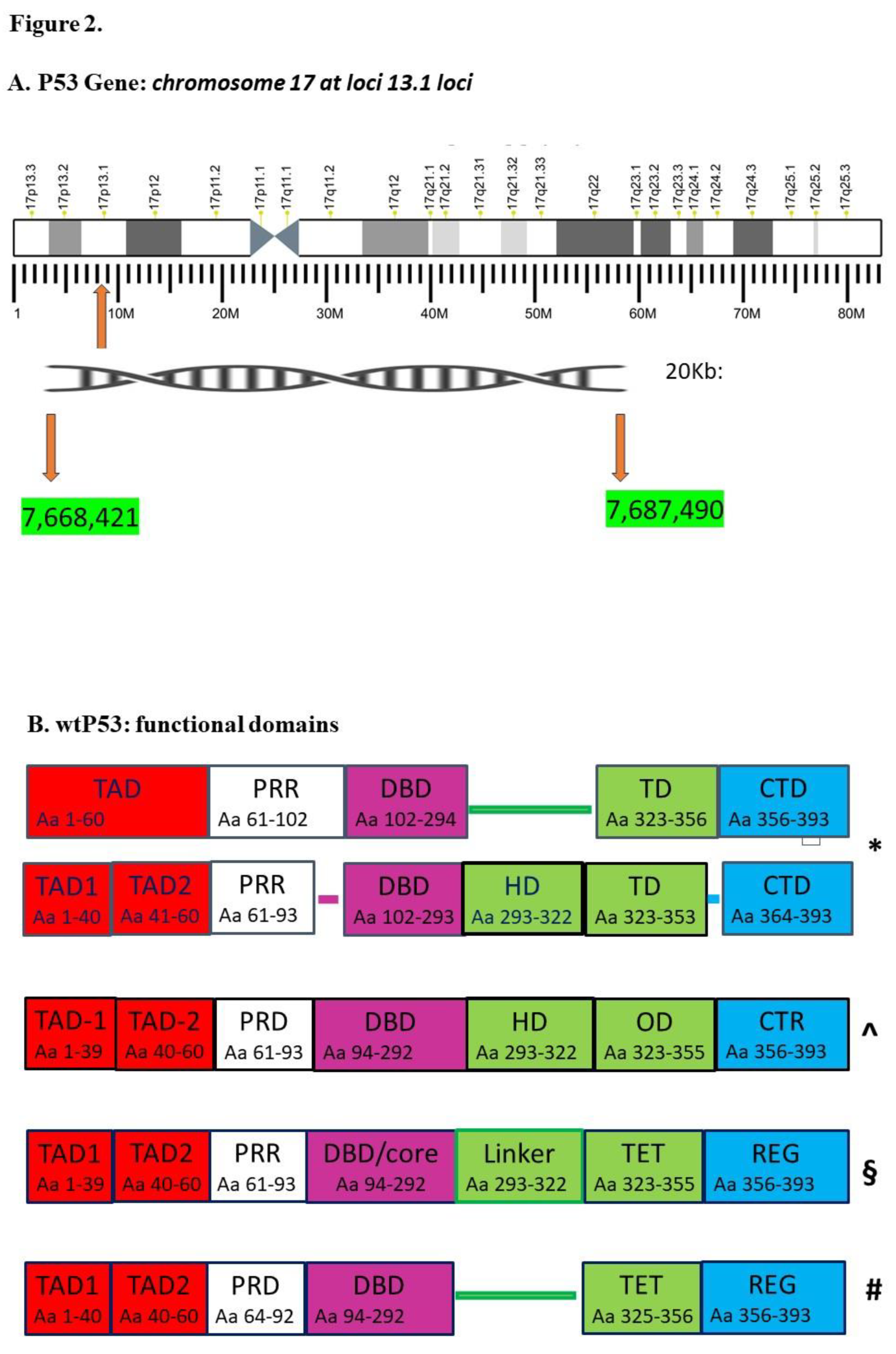
3. What Remains of the Five P53 Disassembled Paradigms: Evidences, Functions and Hypotheses
4. The Last P53 Paradigm
5. Time Viral Np: Tumor Promoting And Non-Oncogenic Viruses
6. Conclusion And PerspectiveS
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Levine, A.J.; Oren, M. The First 30 Years of P53: Growing Ever More Complex. Nat Rev Cancer 2009, 9, 749–758. [CrossRef]
- Soussi, T. The History of P53: A Perfect Example of the Drawbacks of Scientific Paradigms. EMBO Reports 2010, 11, 822–826. [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, T.S.; Hacking, I. The Structure of Scientific Revolutions; Fourth edition.; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago ; London, 2012; ISBN 9780226458113.
- Trovato, M. Update on International Medical Taxonomies of Biomarkers and Their Applications in Management of Thyroid Cancers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 662. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Xu, D.; Zhang, T.; Hu, W.; Feng, Z. Gain-of-Function Mutant P53 in Cancer Progression and Therapy. Journal of Molecular Cell Biology 2020, 12, 674–687. [CrossRef]
- Hassin, O.; Oren, M. Drugging P53 in Cancer: One Protein, Many Targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2023, 22, 127–144. [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, S.; Iwakuma, T. Drugs Targeting P53 Mutations with FDA Approval and in Clinical Trials. Cancers 2023, 15, 429. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Targeting P53 Pathways: Mechanisms, Structures, and Advances in Therapy. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8, 92. [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.P.; Crawford, L.V. T Antigen Is Bound to a Host Protein in SY40-Transformed Cells. Nature 1979, 278, 261–263. [CrossRef]
- Melero, JoséA.; Stitt, D.T.; Mangel, W.F.; Carroll, R.B. Identification of New Polypeptide Species (48–55K) Immunoprecipitable by Antiserum to Purified Large T Antigen and Present in SV40-Infected and -Transformed Cells. Virology 1979, 93, 466–480. [CrossRef]
- Linzer, D.I.H.; Levine, A.J. Characterization of a 54K Dalton Cellular SV40 Tumor Antigen Present in SV40-Transformed Cells and Uninfected Embryonal Carcinoma Cells. Cell 1979, 17, 43–52. [CrossRef]
- DeLeo, A.B.; Jay, G.; Appella, E.; Dubois, G.C.; Law, L.W.; Old, L.J. Detection of a Transformation-Related Antigen in Chemically Induced Sarcomas and Other Transformed Cells of the Mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1979, 76, 2420–2424. [CrossRef]
- Kress, M.; May, E.; Cassingena, R.; May, P. Simian Virus 40-Transformed Cells Express New Species of Proteins Precipitable by Anti-Simian Virus 40 Tumor Serum. J Virol 1979, 31, 472–483. [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.E.; Smith, R.; Paucha, E. Characterization of Different Tumor Antigens Present in Cells Transformed by Simian Virus 40. Cell 1979, 18, 335–346. [CrossRef]
- Linzer, D.I.H.; Maltzman, W.; Levine, A.J. The SV40 a Gene Product Is Required for the Production of a 54,000 MW Cellular Tumor Antigen. Virology 1979, 98, 308–318. [CrossRef]
- Buck, C.B.; Van Doorslaer, K.; Peretti, A.; Geoghegan, E.M.; Tisza, M.J.; An, P.; Katz, J.P.; Pipas, J.M.; McBride, A.A.; Camus, A.C.; et al. The Ancient Evolutionary History of Polyomaviruses. PLoS Pathog 2016, 12, e1005574. [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, B.; Anoh, A.E.; Ben Salem, N.; Broll, S.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Fischer, D.; Gedvilaite, A.; Ingenhütt, N.; Liebmann, S.; Martin, M.; et al. Novel Polyomaviruses in Mammals from Multiple Orders and Reassessment of Polyomavirus Evolution and Taxonomy. Viruses 2019, 11, 930. [CrossRef]
- Crawford, L. The 53,000-Dalton Cellular Protein and Its Role in Transformation. Int Rev Exp Pathol 1983, 25, 1–50.
- Wolf, D.; Rotter, V. Inactivation of P53 Gene Expression by an Insertion of Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus-Like DNA Sequences. Molecular and Cellular Biology 1984, 4, 1402–1410. [CrossRef]
- Mietz, J.A.; Unger, T.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Howley, P.M. The Transcriptional Transactivation Function of Wild-Type P53 Is Inhibited by SV40 Large T-Antigen and by HPV-16 E6 Oncoprotein. The EMBO Journal 1992, 11, 5013–5020. [CrossRef]
- Eliyahu, D.; Raz, A.; Gruss, P.; Givol, D.; Oren, M. Participation of P53 Cellular Tumour Antigen in Transformation of Normal Embryonic Cells. Nature 1984, 312, 646–649. [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.R.; Rudge, K.; Currie, G.A. Cellular Immortalization by a cDNA Clone Encoding the Transformation-Associated Phosphoprotein P53. Nature 1984, 312, 651–654. [CrossRef]
- Parada, L.F.; Land, H.; Weinberg, R.A.; Wolf, D.; Rotter, V. Cooperation between Gene Encoding P53 Tumour Antigen and Ras in Cellular Transformation. Nature 1984, 312, 649–651. [CrossRef]
- Wolf, D.; Rotter, V. Major Deletions in the Gene Encoding the P53 Tumor Antigen Cause Lack of P53 Expression in HL-60 Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1985, 82, 790–794. [CrossRef]
- Eliyahu, D.; Goldfinger, N.; Pinhasi-Kimhi, O.; Shaulsky, G.; Skurnik, Y.; Arai, N.; Rotter, V.; Oren, M. Meth A Fibrosarcoma Cells Express Two Transforming Mutant P53 Species. Oncogene 1988, 3, 313–321.
- Baker, S.J.; Fearon, E.R.; Nigro, J.M.; Hamilton, S.R.; Preisinger, A.C.; Jessup, J.M.; vanTuinen, P.; Ledbetter, D.H.; Barker, D.F.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Chromosome 17 Deletions and P53 Gene Mutations in Colorectal Carcinomas. Science 1989, 244, 217–221. [CrossRef]
- Finlay, C.A.; Hinds, P.W.; Levine, A.J. The P53 Proto-Oncogene Can Act as a Suppressor of Transformation. Cell 1989, 57, 1083–1093. [CrossRef]
- Kastan, M.B.; Canman, C.E.; Leonard, C.J. P53, Cell Cycle Control and Apoptosis: Implications for Cancer. Cancer Metast Rev 1995, 14, 3–15. [CrossRef]
- Fridman, J.S.; Lowe, S.W. Control of Apoptosis by P53. Oncogene 2003, 22, 9030–9040. [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.B.; Schumacher, B. P53 in the DNA-Damage-Repair Process. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016, 6, a026070. [CrossRef]
- Speidel, D. Transcription-Independent P53 Apoptosis: An Alternative Route to Death. Trends in Cell Biology 2010, 20, 14–24. [CrossRef]
- Kastenhuber, E.R.; Lowe, S.W. Putting P53 in Context. Cell 2017, 170, 1062–1078. [CrossRef]
- Moll, U.M.; Marchenko, N.; Zhang, X. P53 and Nur77/TR3 – Transcription Factors That Directly Target Mitochondria for Cell Death Induction. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4725–4743. [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.; Tan, B.X.; Lane, D. How the Other Half Lives: What P53 Does When It Is Not Being a Transcription Factor. IJMS 2019, 21, 13. [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, Q.; Mao, Y.; Gao, W.; Duan, S. Targeting the P53 Signaling Pathway in Cancers: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Studies. MedComm 2023, 4, e288. [CrossRef]
- Raver-Shapira, N.; Marciano, E.; Meiri, E.; Spector, Y.; Rosenfeld, N.; Moskovits, N.; Bentwich, Z.; Oren, M. Transcriptional Activation of miR-34a Contributes to P53-Mediated Apoptosis. Molecular Cell 2007, 26, 731–743. [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-C.; Wentzel, E.A.; Kent, O.A.; Ramachandran, K.; Mullendore, M.; Lee, K.H.; Feldmann, G.; Yamakuchi, M.; Ferlito, M.; Lowenstein, C.J.; et al. Transactivation of miR-34a by P53 Broadly Influences Gene Expression and Promotes Apoptosis. Mol Cell 2007, 26, 745–752. [CrossRef]
- Tuval, A.; Strandgren, C.; Heldin, A.; Palomar-Siles, M.; Wiman, K.G. Pharmacological Reactivation of P53 in the Era of Precision Anticancer Medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2024, 21, 106–120. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; Tavana, O.; Gu, W. Understanding the Complexity of P53 in a New Era of Tumor Suppression. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 946–967. [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J. P53 and The Immune Response: 40 Years of Exploration—A Plan for the Future. IJMS 2020, 21, 541. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.E.; Stryhn, A.; Justesen, S.; Harndahl, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Donskov, F.; Claesson, M.H.; Pedersen, J.W.; Wandall, H.H.; Svane, I.M.; et al. Wildtype P53-Specific Antibody and T-Cell Responses in Cancer Patients. Journal of Immunotherapy 2011, 34, 629–640. [CrossRef]
- The TP53 database. Available online: https://tp53.isb-cgc.org/ (accessed on 01 July 2024).
- Nishimura, M.; Takizawa, Y.; Nozawa, K.; Kurumizaka, H. Structural Basis for P53 Binding to Its Nucleosomal Target DNA Sequence. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1, pgac177. [CrossRef]
- Gregory, E.; Daughdrill, G.W. Sequence Properties of an Intramolecular Interaction That Inhibits P53 DNA Binding. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1558. [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.J.; Sørensen, H.V.; Skepö, M. Exploring the Role of Globular Domain Locations on an Intrinsically Disordered Region of P53: A Molecular Dynamics Investigation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2024, 20, 1423–1433. [CrossRef]
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NC_000017.11?report=fasta&from=7668421&to=7687490&strand=true (accessed on 01 July 2024).
- Belyi, V.A.; Ak, P.; Markert, E.; Wang, H.; Hu, W.; Puzio-Kuter, A.; Levine, A.J. The Origins and Evolution of the P53 Family of Genes. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 2010, 2, a001198–a001198. [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, R.M.; Vicchio, T.M.; Giovinazzo, S.; Certo, R.; Alibrandi, A.; Trimarchi, F.; Benvenga, S.; Trovato, M. TP53 Polymorphism May Contribute to Genetic Susceptibility to Develop Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. J Endocrinol Invest 2015, 38, 1175–1182. [CrossRef]
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/7157/ (accessed on 01 July 2024).
- Solares, M.J.; Jonaid, G.M.; Luqiu, W.Y.; Berry, S.; Khadela, J.; Liang, Y.; Evans, M.C.; Pridham, K.J.; Dearnaley, W.J.; Sheng, Z.; et al. High-Resolution Imaging of Human Cancer Proteins Using Microprocessor Materials. ChemBioChem 2022, 23, e202200310. [CrossRef]
- Gencel-Augusto, J.; Lozano, G. P53 Tetramerization: At the Center of the Dominant-Negative Effect of Mutant P53. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1128–1146. [CrossRef]
- Vaseva, A.V.; Moll, U.M. The Mitochondrial P53 Pathway. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 2009, 1787, 414–420. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.-M.; Li, W.; Dalen, H.; Lotem, J.; Kama, R.; Sachs, L.; Brunk, U.T. Lysosomal Destabilization in P53-Induced Apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2002, 99, 6286–6291. [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, G.; Takano, N.; Kazama, H.; Tsukahara, K.; Miyazawa, K. P53 Regulates Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization as Well as Cytoprotective Autophagy in Response to DNA-Damaging Drugs. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, C.; Bonora, M.; Sorrentino, G.; Missiroli, S.; Poletti, F.; Suski, J.M.; Galindo Ramirez, F.; Rizzuto, R.; Di Virgilio, F.; Zito, E.; et al. P53 at the Endoplasmic Reticulum Regulates Apoptosis in a Ca 2+ -Dependent Manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2015, 112, 1779–1784. [CrossRef]
- Gila, L.; Elena, N.; Yechezkel, S.; Mary, B. P53-Associated 3′→5′ Exonuclease Activity in Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Compartments of Cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 233–245. [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Kaghad, M.; Wang, Y.; Gillett, E.; Fleming, M.D.; Dötsch, V.; Andrews, N.C.; Caput, D.; McKeon, F. P63, a P53 Homolog at 3q27–29, Encodes Multiple Products with Transactivating, Death-Inducing, and Dominant-Negative Activities. Molecular Cell 1998, 2, 305–316. [CrossRef]
- Kaghad, M.; Bonnet, H.; Yang, A.; Creancier, L.; Biscan, J.-C.; Valent, A.; Minty, A.; Chalon, P.; Lelias, J.-M.; Dumont, X.; et al. Monoallelically Expressed Gene Related to P53 at 1p36, a Region Frequently Deleted in Neuroblastoma and Other Human Cancers. Cell 1997, 90, 809–819. [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, J.-C. P53 and Its Isoforms in Cancer. Br J Cancer 2007, 97, 277–282. [CrossRef]
- Khoury, M.P.; Bourdon, J.-C. The Isoforms of the P53 Protein. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 2010, 2, a000927–a000927. [CrossRef]
- Trovato, M.C.; Ruggeri, R.M.; Scardigno, M.; Sturniolo, G.; Vita, R.; Vitarelli, E.; Arena, G.; Gambadoro, O.; Sturniolo, G.; Trimarchi, F.; et al. Immunoreactions for P53 Isoforms Are Associated with Ultrastructural Proliferative Profiles in Benign Thyroid Nodules. Histology and Histopathology 2016, 1079–1087. [CrossRef]
- Trovato, M.; Ruggeri, R.; Guzzo, E.; Certo, R.; Alibrandi, A.; Scifo, S.; Scardigno, M.; Vitarelli, E.; Arena, G.; Gambadoro, O.; et al. Expression of P53 and Isoforms in Beningn and Malignant Lesions of the Head and Neck. Histology and Histopathology 2017, 371–377. [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, J.-C.; Surget, S.; Khoury, M.P. Uncovering the Role of P53 Splice Variants in Human Malignancy: A Clinical Perspective. OTT 2013, 57. [CrossRef]
- Vieler, M.; Sanyal, S. P53 Isoforms and Their Implications in Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 288. [CrossRef]
- Stiewe, T.; Haran, T.E. How Mutations Shape P53 Interactions with the Genome to Promote Tumorigenesis and Drug Resistance. Drug Resistance Updates 2018, 38, 27–43. [CrossRef]
- Kotler, E.; Segal, E.; Oren, M. Functional Characterization of the P53 “Mutome.” Molecular & Cellular Oncology 2018, 5, e1511207. [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.R.; Krämer, A.; Settanni, G.; Jones, R.N.; Ni, X.; Khan Tareque, R.; Fersht, A.R.; Spencer, J.; Joerger, A.C. Targeting Cavity-Creating P53 Cancer Mutations with Small-Molecule Stabilizers: The Y220X Paradigm. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 657–668. [CrossRef]
- Blagih, J.; Buck, M.D.; Vousden, K.H. P53, Cancer and the Immune Response. Journal of Cell Science 2020, 133, jcs237453. [CrossRef]
- Truffi, M.; Sorrentino, L.; Corsi, F. Fibroblasts in the Tumor Microenvironment. In Tumor Microenvironment; Birbrair, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; Vol. 1234, pp. 15–29 ISBN 9783030371838.
- Boesch, M.; Baty, F.; Rumpold, H.; Sopper, S.; Wolf, D.; Brutsche, M.H. Fibroblasts in Cancer: Defining Target Structures for Therapeutic Intervention. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer 2019, 1872, 111–121. [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Dai, L.-J.; Wu, S.-Y.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, D.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Shao, Z.-M. Spatial Architecture of the Immune Microenvironment Orchestrates Tumor Immunity and Therapeutic Response. J Hematol Oncol 2021, 14, 98. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Sharma, S.; Advani, D.; Khosla, A.; Kumar, P.; Ambasta, R.K. Unboxing the Molecular Modalities of Mutagens in Cancer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2022, 29, 62111–62159. [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, L.; Jenkins, J.; Purvis, G.; Lee, J.; Franco, A.T. The Thyroid Tumor Microenvironment: Potential Targets for Therapeutic Intervention and Prognostication. HORM CANC 2020, 11, 205–217. [CrossRef]
- Fozzatti, L.; Cheng, S. Tumor Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: A Synergistic Crosstalk to Promote Thyroid Cancer. Endocrinol Metab 2020, 35, 673–680. [CrossRef]
- Trovato, M.; Sciacchitano, S.; Facciolà, A.; Valenti, A.; Visalli, G.; Di Pietro, A. Interleukin 6 Signalling as a Valuable Cornerstone for Molecular Medicine (Review). Int J Mol Med 2021, 47, 107. [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, R.M.; Villari, D.; Simone, A.; Scarfì, R.; Attard, M.; Orlandi, F.; Barresi, G.; Trimarchi, F.; Trovato, M.; Benvenga, S. Co-Expression of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Interleukin-6 Receptor (IL-6R) in Thyroid Nodules Is Associated with Co-Expression of CD30 Ligand/CD30 Receptor. J Endocrinol Invest 2002, 25, 959–966. [CrossRef]
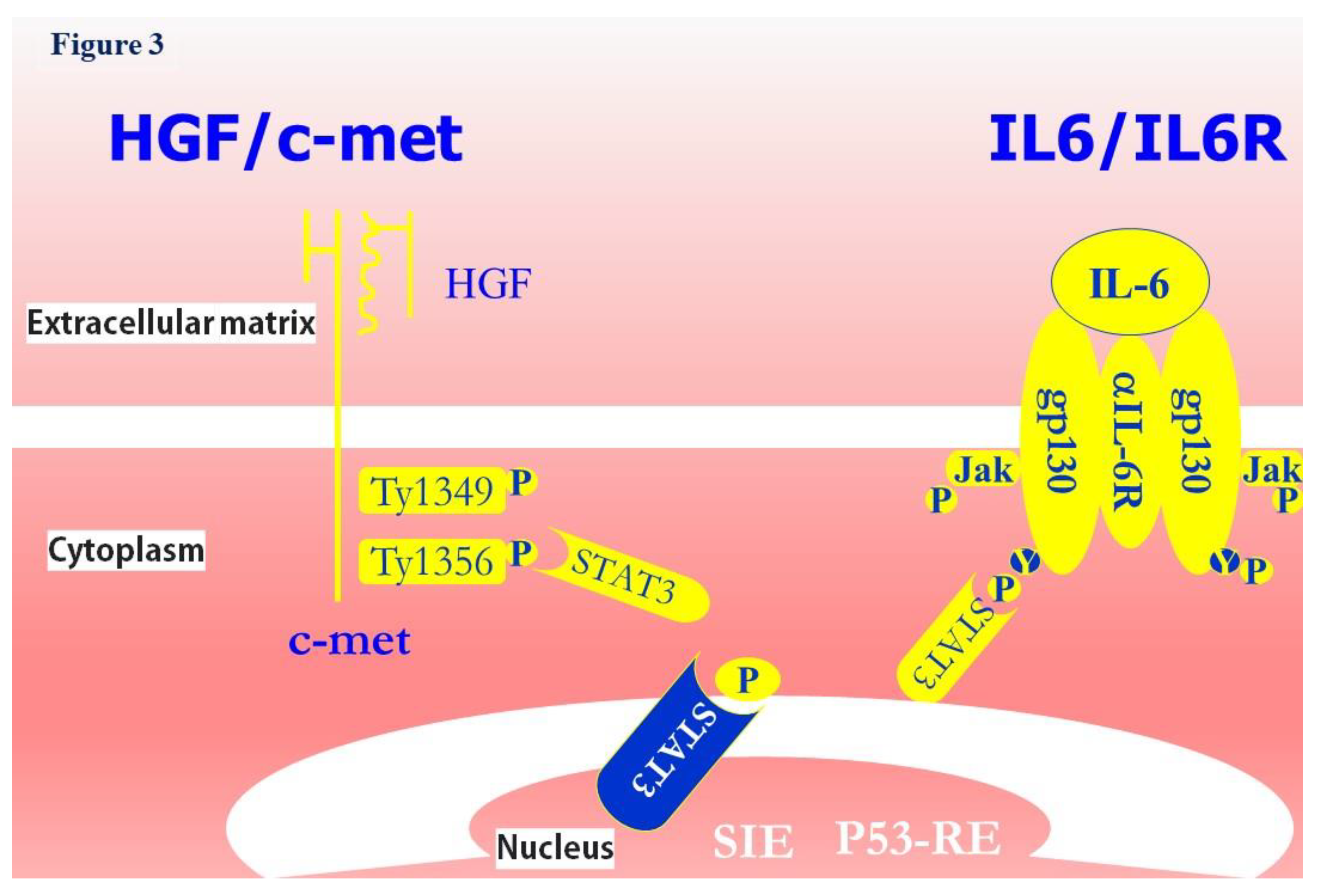
- Trovato, M.; Campennì, A.; Giovinazzo, S.; Siracusa, M.; Ruggeri, R.M. Hepatocyte Growth Factor/C-Met Axis in Thyroid Cancer: From Diagnostic Biomarker to Therapeutic Target. Biomark�Insights 2017, 12, 117727191770112. [CrossRef]
- Trovato, M.; Villari, D.; Bartolone, L.; Spinella, S.; Simone, A.; Violi, M.A.; Trimarchi, F.; Batolo, D.; Benvenga, S. Expression of the Hepatocyte Growth Factor and c-Met in Normal Thyroid, Non-Neoplastic, and Neoplastic Nodules. Thyroid 1998, 8, 125–131. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.-I.; Matoso, A.; Corney, D.C.; Flesken-Nikitin, A.; Körner, S.; Wang, W.; Boccaccio, C.; Thorgeirsson, S.S.; Comoglio, P.M.; Hermeking, H.; et al. Wild-Type P53 Controls Cell Motility and Invasion by Dual Regulation of MET Expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2011, 108, 14240–14245. [CrossRef]
- Rassidakis, G.Z. The Emerging Role of CD30 and P53 as Novel Targets for Therapy in Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Front Biosci 2016, 8, 61–71. [CrossRef]
- Sistigu, A.; Di Modugno, F.; Manic, G.; Nisticò, P. Deciphering the Loop of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Inflammatory Cytokines and Cancer Immunoediting. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews 2017, 36, 67–77. [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.T.; Truong, N.V.; Wu, W.-G.; Su, Y.-C.; Hsu, T.-S.; Lin, L.-Y. Tumor Suppressor P53 Mediates Interleukin-6 Expression to Enable Cancer Cell Evasion of Genotoxic Stress. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 340. [CrossRef]
- Boccaccio, C.; Andò, M.; Tamagnone, L.; Bardelli, A.; Michieli, P.; Battistini, C.; Comoglio, P.M. Induction of Epithelial Tubules by Growth Factor HGF Depends on the STAT Pathway. Nature 1998, 391, 285–288. [CrossRef]
- Maffè, A.; Comoglio, P.M. HGF Controls Branched Morphogenesis in Tubular Glands. Eur J Morphol 1998, 36 Suppl, 74–81.
- Hirano, T. Interleukin 6 and Its Receptor: Ten Years Later. International Reviews of Immunology 1998, 16, 249–284. [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Wright, K.L.; Ma, Y.; Wright, G.M.; Huang, M.; Irby, R.; Briggs, J.; Karras, J.; Cress, W.D.; Pardoll, D.; et al. Role of Stat3 in Regulating P53 Expression and Function. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2005, 25, 7432–7440. [CrossRef]
- Trovato, M.; Grosso, M.; Vitarelli, E.; Ruggeri, R.; Alesci, S.; Trimarchi, F.; Barresi, G.; Benvenga, S. Distinctive Expression of STAT3 in Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas and a Subset of Follicular Adenomas. Histology and Histopathology 2003, 393–399. [CrossRef]
- Trovato, M.; Torre, M.L.; Ragonese, M.; Simone, A.; Scarfì, R.; Barresi, V.; Giuffrè, G.; Benvenga, S.; Angileri, F.F.; Tuccari, G.; et al. HGF/c-Met System Targeting PI3K/AKT and STAT3/Phosphorylated-STAT3 Pathways in Pituitary Adenomas: An Immunohistochemical Characterization in View of Targeted Therapies. Endocrine 2013, 44, 735–743. [CrossRef]
- Trovato, M.; Vitarelli, E.; Grosso, M.; Alesci, S.; Benvenga, S.; Trimarchi, F.; Barresi, G. Immunohistochemical Expression of HGF, c-MET and Transcription Factor STAT3 in Colorectal Tumors. Eur J Histochem 2004, 48, 291–297.
- Li, S.; Kong, L.; Yu, X.; Zheng, Y. Host–Virus Interactions: From the Perspectives of Epigenetics. Reviews in Medical Virology 2014, 24, 223–241. [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, L.; Milavetz, B. Epigenetic Regulation of Viral Biological Processes. Viruses 2017, 9, 346. [CrossRef]
- Łasut-Szyszka, B.; Rusin, M. The Wheel of P53 Helps to Drive the Immune System. IJMS 2023, 24, 7645. [CrossRef]
- Lazo, P.A.; Santos, C.R. Interference with P53 Functions in Human Viral Infections, a Target for Novel Antiviral Strategies? Reviews in Medical Virology 2011, 21, 285–300. [CrossRef]
- Aloni-Grinstein, R.; Charni-Natan, M.; Solomon, H.; Rotter, V. P53 and the Viral Connection: Back into the Future ‡. Cancers 2018, 10, 178. [CrossRef]
- Harford, J.B. A Second Career for P53 as A Broad-Spectrum Antiviral? Viruses 2023, 15, 2377. [CrossRef]
- Durzynska, J.; Lesniewicz, K.; Poreba, E. Human Papillomaviruses in Epigenetic Regulations. Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research 2017, 772, 36–50. [CrossRef]
- Maruzuru, Y.; Fujii, H.; Oyama, M.; Kozuka-Hata, H.; Kato, A.; Kawaguchi, Y. Roles of P53 in Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Replication. J Virol 2013, 87, 9323–9332. [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.; Fricke, I.; Imarogbe, C.; Padrón González, A.A.; Batista, O.A.; Mensah, P.; Chacon-Cruz, E. Immunopathogenesis of Orthopoxviridae: Insights into Immunology from Smallpox to Monkeypox (Mpox). Explor Immunol 2023, 525–553. [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.K.; Samolej, J.; Olson, A.T.; Bertoli, C.; Wiebe, M.S.; De Bruin, R.A.M.; Mercer, J. Vaccinia Virus Arrests and Shifts the Cell Cycle. Viruses 2022, 14, 431. [CrossRef]
- Turpin, E.; Luke, K.; Jones, J.; Tumpey, T.; Konan, K.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Influenza Virus Infection Increases P53 Activity: Role of P53 in Cell Death and Viral Replication. J Virol 2005, 79, 8802–8811. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jiang, H.; Peng, H.; Zeng, W.; Zhong, Y.; He, M.; Xie, L.; Chen, J.; Guo, D.; Wu, J.; et al. Non-Structural Protein 5 of Zika Virus Interacts with P53 in Human Neural Progenitor Cells and Induces P53-Mediated Apoptosis. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 1411–1420. [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-R.; Lee, S.R.; Oh, W.; Lee, E.-W.; Yeh, J.-Y.; Nah, J.-J.; Joo, Y.-S.; Shin, J.; Lee, H.-W.; Pyo, S.; et al. West Nile Virus Capsid Protein Induces P53-Mediated Apoptosis via the Sequestration of HDM2 to the Nucleolus. Cell Microbiol 2007, 0, 070816152918002-???. [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, M.M.; Abuharfeil, N.M.; Darmani, H. The Role of P53 in HIV Infection. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 2023, 20, 419–427. [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J. The Common Mechanisms of Transformation by the Small DNA Tumor Viruses: The Inactivation of Tumor Suppressor Gene Products: P53. Virology 2009, 384, 285–293. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Marmorstein, R. When Viral Oncoprotein Meets Tumor Suppressor: A Structural View. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2332–2337. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Abate, M.; Rice, P.W.; Cole, C.N. The Ability of Simian Virus 40 Large T Antigen to Immortalize Primary Mouse Embryo Fibroblasts Cosegregates with Its Ability to Bind to P53. J Virol 1991, 65, 6872–6880. [CrossRef]
- Hermannstädter, A.; Ziegler, C.; Kühl, M.; Deppert, W.; Tolstonog, G.V. Wild-Type P53 Enhances Efficiency of Simian Virus 40 Large-T-Antigen-Induced Cellular Transformation. J Virol 2009, 83, 10106–10118. [CrossRef]
- Trovato, M.; D’Armiento, M.; Lavra, L.; Ulivieri, A.; Dominici, R.; Vitarelli, E.; Grosso, M.; Vecchione, R.; Barresi, G.; Sciacchitano, S. Expression of P53/Hgf/c-Met/STAT3 Signal in Fetuses with Neural Tube Defects. Virchows Arch 2007, 450, 203–210. [CrossRef]
- Danilova, N.; Sakamoto, K.M.; Lin, S. P53 Family in Development. Mechanisms of Development 2008, 125, 919–931. [CrossRef]
- Izumi, T.; Io, K.; Matsui, M.; Shirakawa, K.; Shinohara, M.; Nagai, Y.; Kawahara, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Kondoh, H.; Misawa, N.; et al. HIV-1 Viral Infectivity Factor Interacts with TP53 to Induce G2 Cell Cycle Arrest and Positively Regulate Viral Replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2010, 107, 20798–20803. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




