Submitted:
12 July 2024
Posted:
15 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background of the Study
1.2. Problem Statement
1.3. Research Rationale
1.4. Research Aims and Objectives
- Primary aim: The primary aim of the study is to identify the key factors contributing to the traffic collisions in Chicago by comprehensively analysing the crash dataset.
- Secondary aim: The secondary aim of the study is to develop predictive models that can be able to forecast the possibilities of different collisions depending on factors like weather, road condition, time, and driver behaviour.
- To extensively analyse the crash dataset for gaining an in-depth understanding of the factors such as weather, road conditions and driving behaviours contributing to the collisions in Chicago.
- To generate predictive models for forecasting the likelihood of the different types of collisions based on a range of factors including weather, time of the day, road conditions.
- To perform analysis of the dataset, identifying collision hotspots and patterns related to specific locations, roads, and intersections.
1.5. Research Questions
- What are the key primary factors contributing to the traffic collisions in Chicago?
- How well can machine learning models forecast the possibility of various collision types depending on changing conditions like the weather, state of the road, and the time of the day?
- What are the locations, roads and intersections that are related to certain collision hotspots in Chicago?
1.6. Research Hypothesis
- The machine learning models developed in this research project and the results obtained from this analysis will be extendable on other similar datasets from other parts of the world.
- Specific machine learning algorithms developed as part of this research might perform better or worse based on the nature of the data, its complexity, and the relationship between features and outcomes.
- Machine learning algorithms can uncover hidden patterns, relationships, or associations within the data that might not be immediately apparent through traditional analysis.
- Machine learning models will identify and utilise the most relevant features, thereby improving prediction accuracy and reducing overfitting.
1.7. Novelty of the Research
1.8. Organisation of the Study
- The introduction explains the foundation for research while outlining the objective and reason for the study.
- The literature review reviews past publications on this issue and highlights shortcomings to be addressed.
- Research Methodology explains the models, and data collection approach, along with the method and philosophy undertaken to ethically establish the research.
- Data Analytics applies the ML models to the collected data for predictive analytics.
- The discussion summarises the findings from the models and aligns with prior research.
- The conclusion addresses the research problem concerning the findings and also provides suggestions for future study.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Trends in Traffic Accidents and Fatalities Across the World
2.2. Factors Included in Major Traffic Accidents
2.3. Role of Technology in Road Safety
2.4. Predictive Modelling for Enhancing Road Safety
2.5. Literature Gap
3. Methodology
3.1. Proposed Methodological Architecture
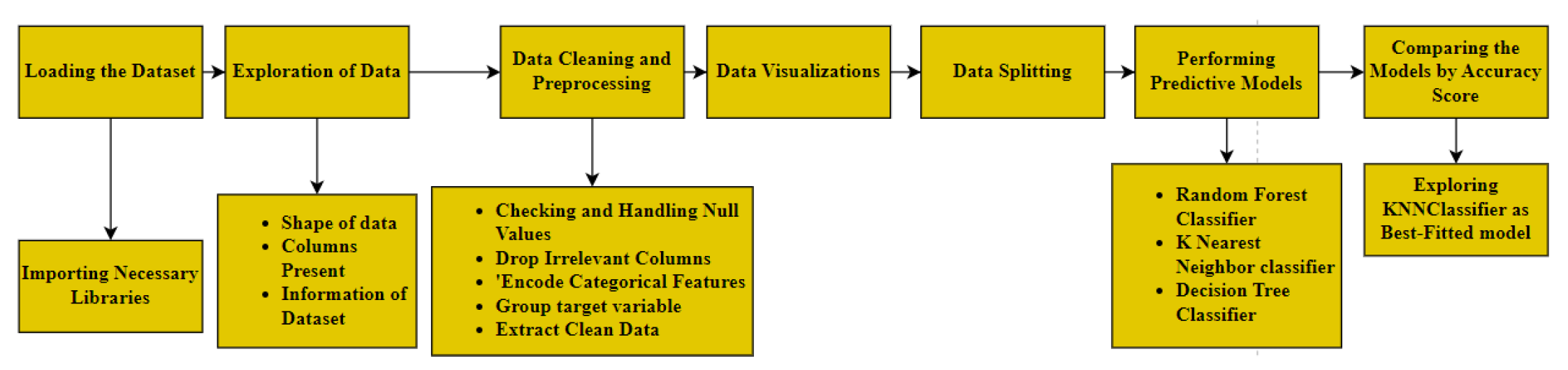
3.2. Data Collection
3.3. Machine Learning Models
3.4. Chapter Summary
4. Data Analysis and Findings
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Dataset Exploration
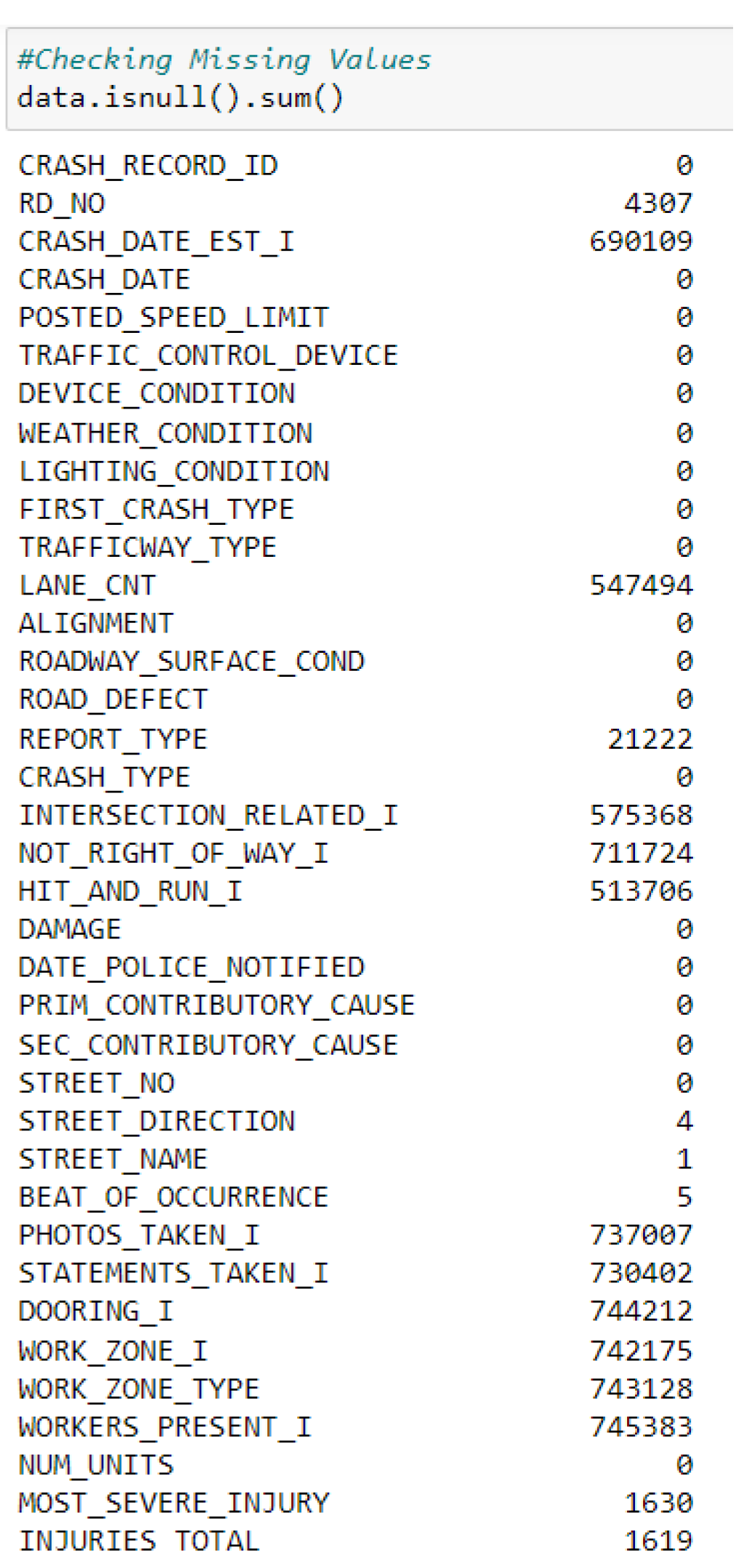
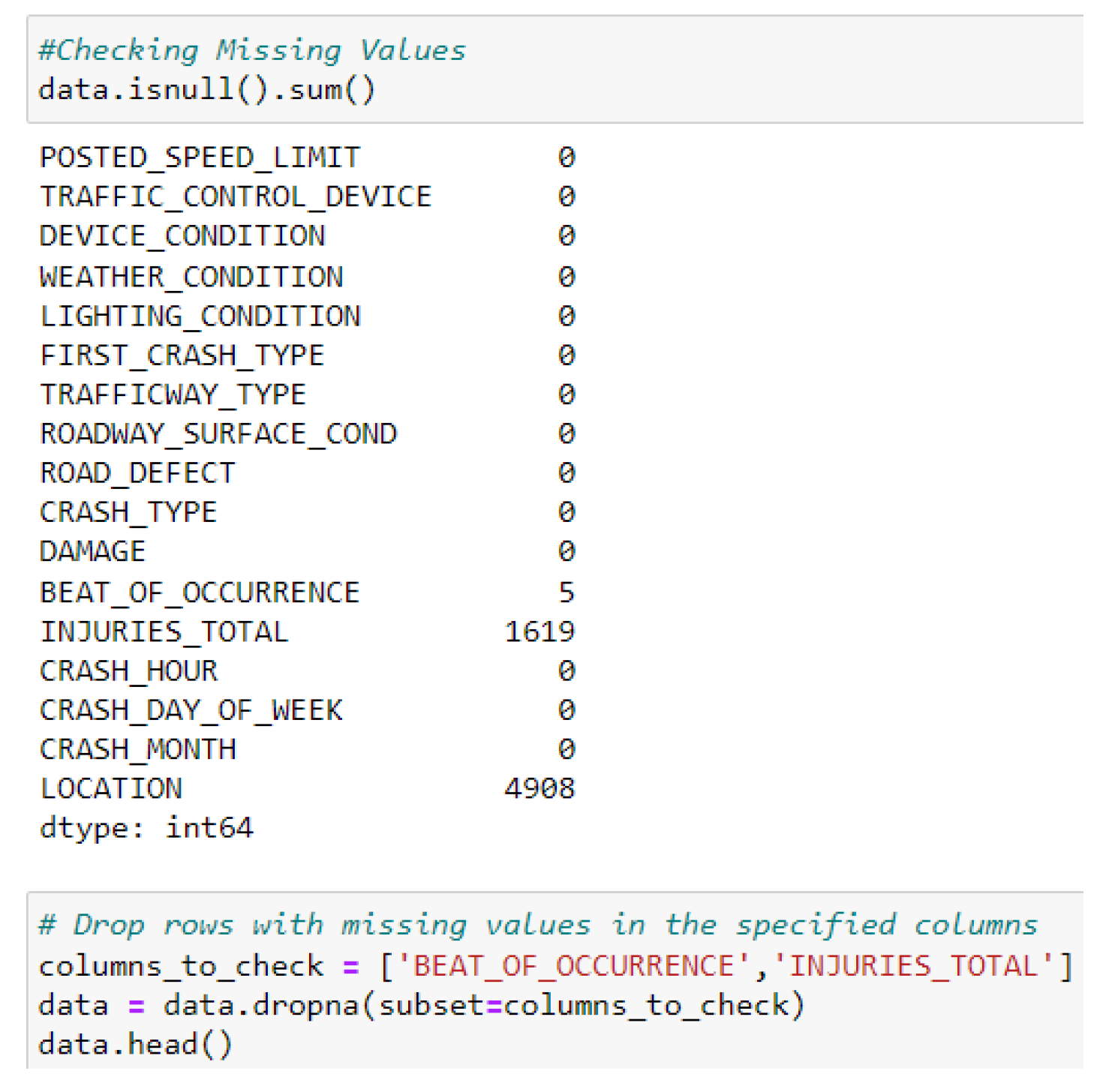
4.3. Data Preprocessing
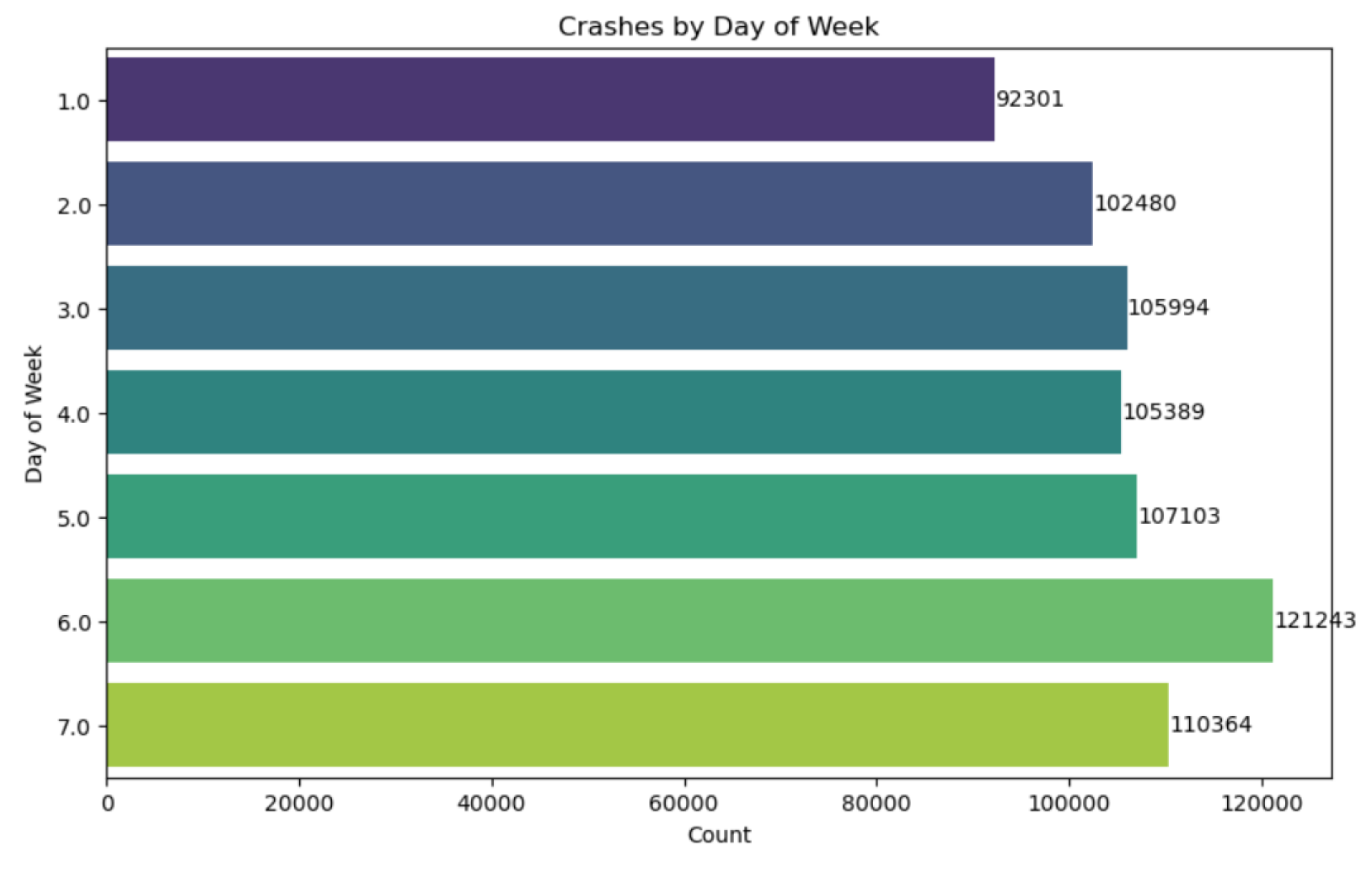
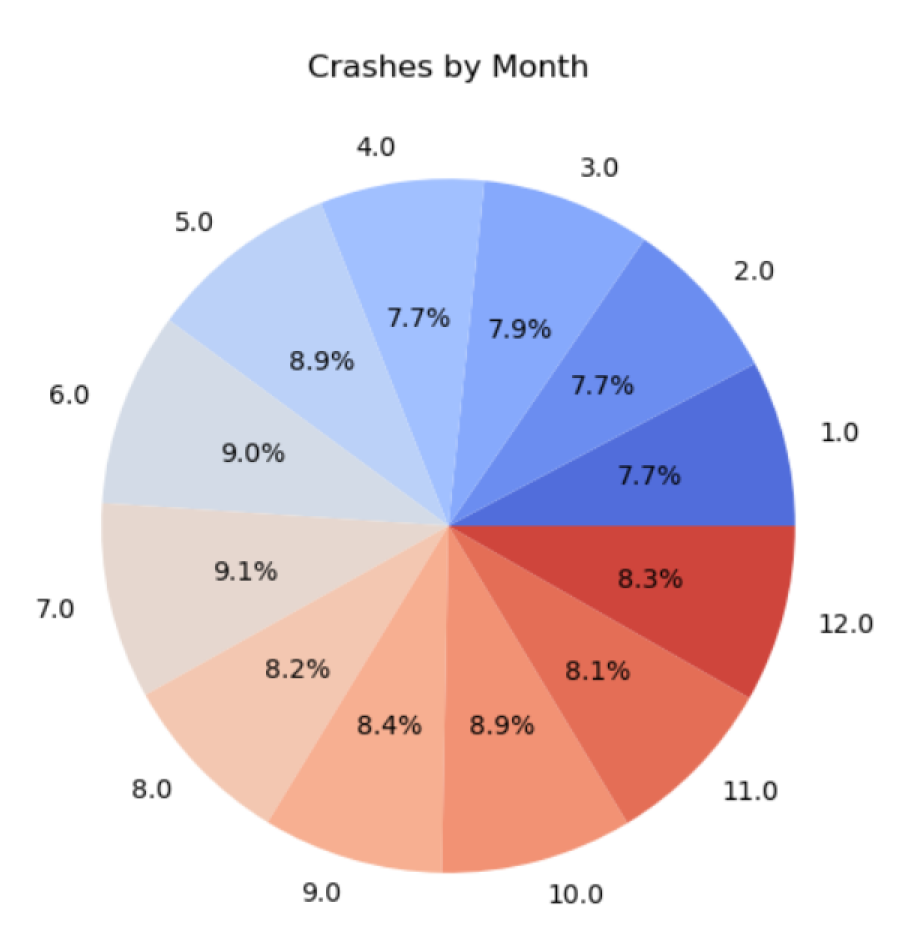
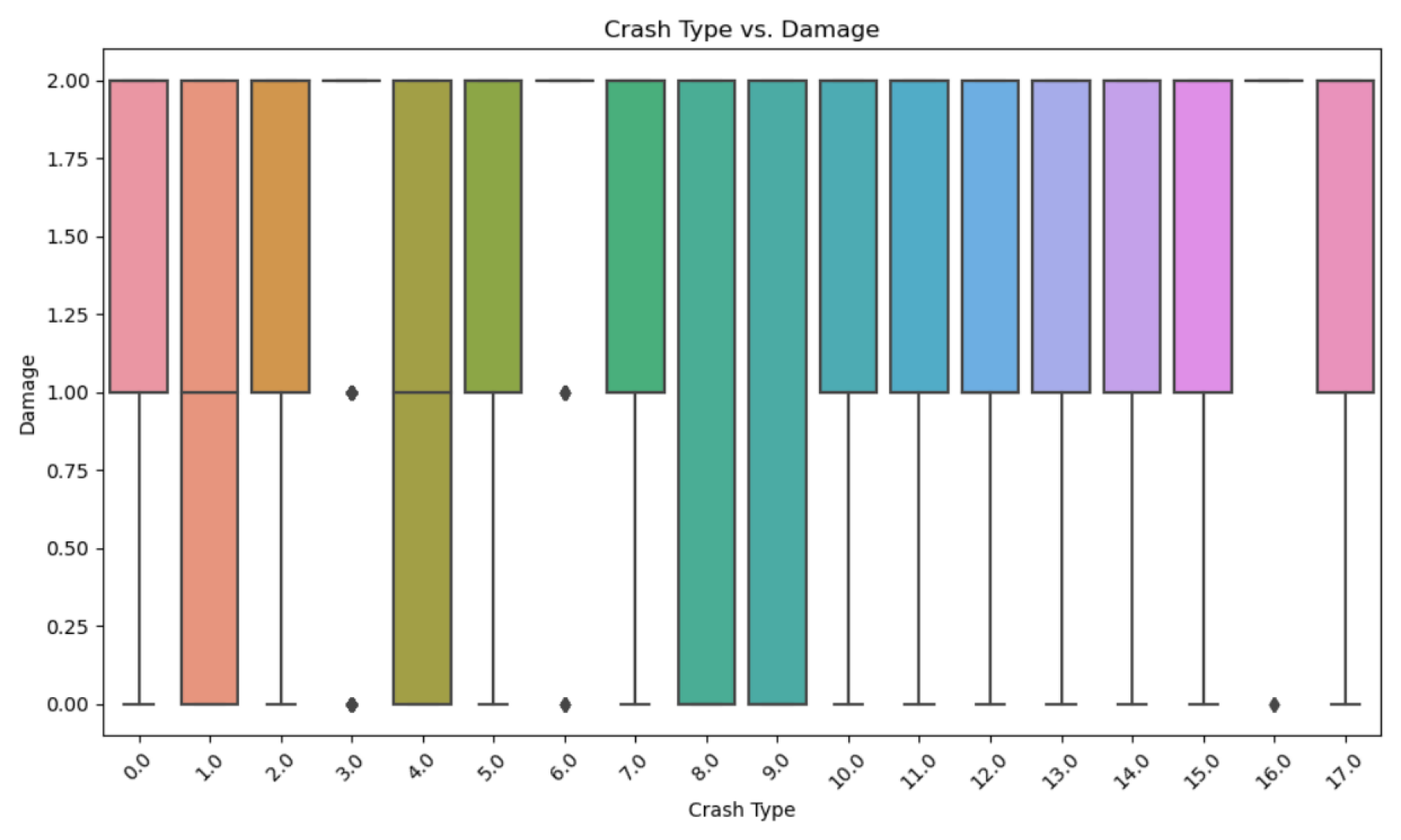
4.4. Exploratory Data Analysis and Data Visualisations
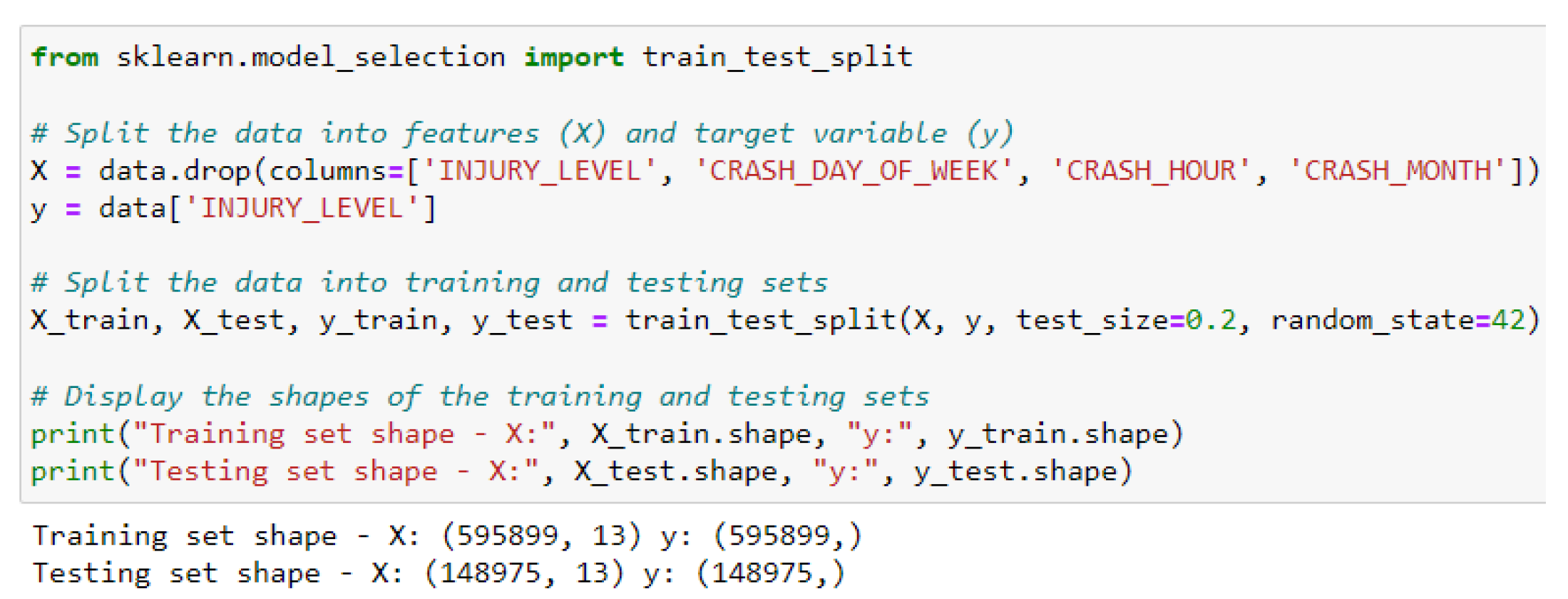
4.5. Predictive Models
4.5.1. Random Forest Classifier
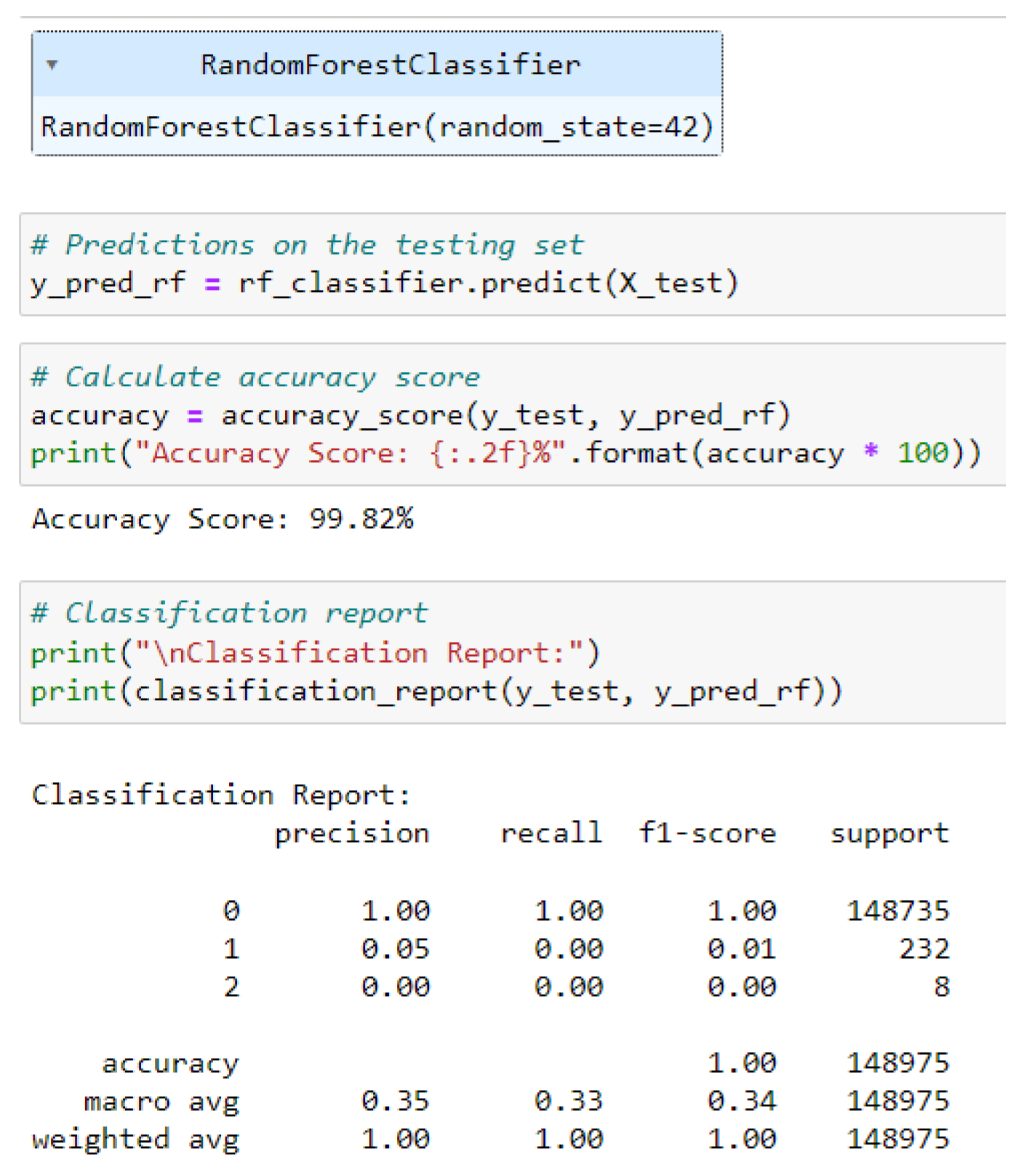
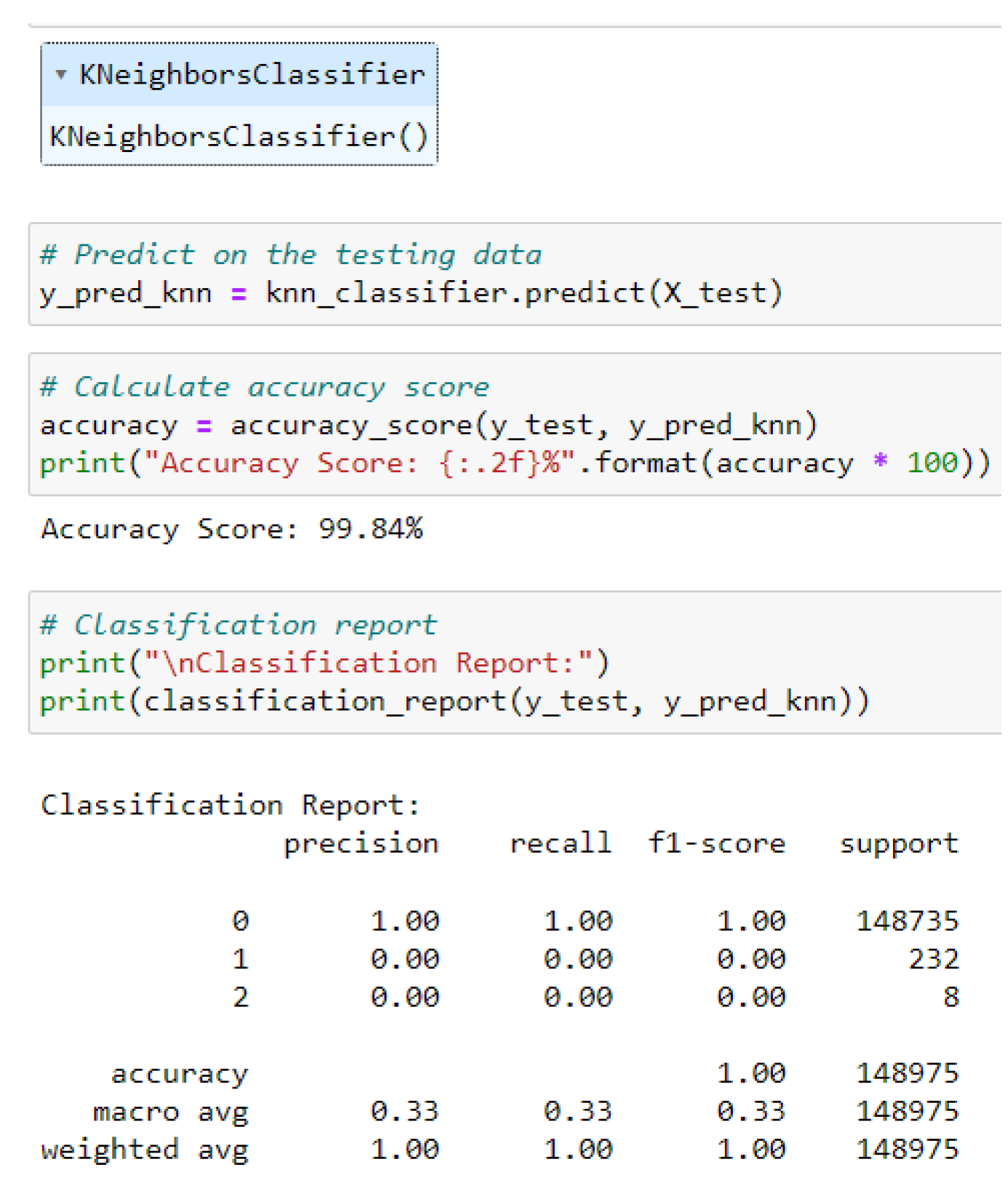
4.5.2. KNN Classifier
4.5.3. Decision Tree Classifier
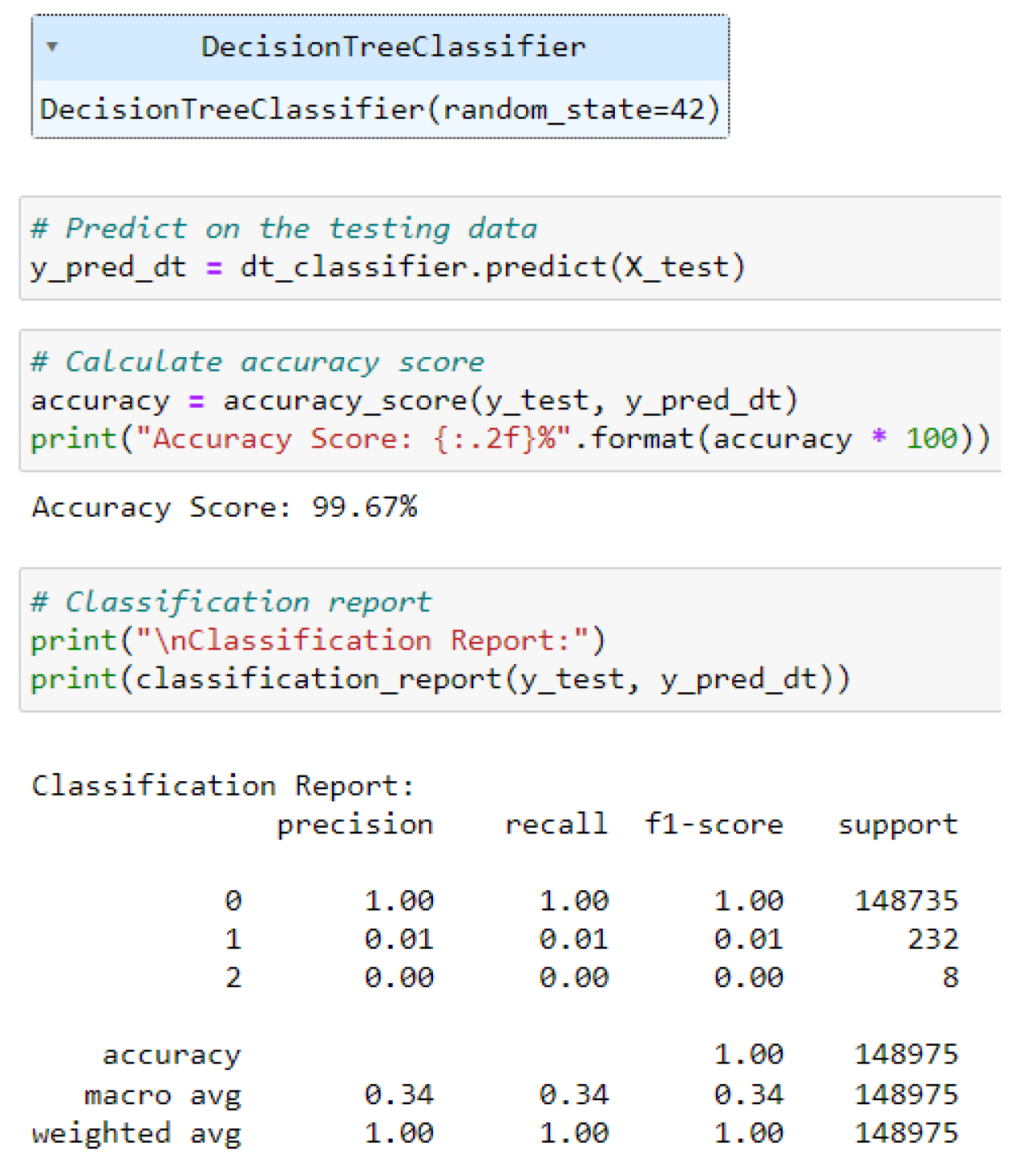
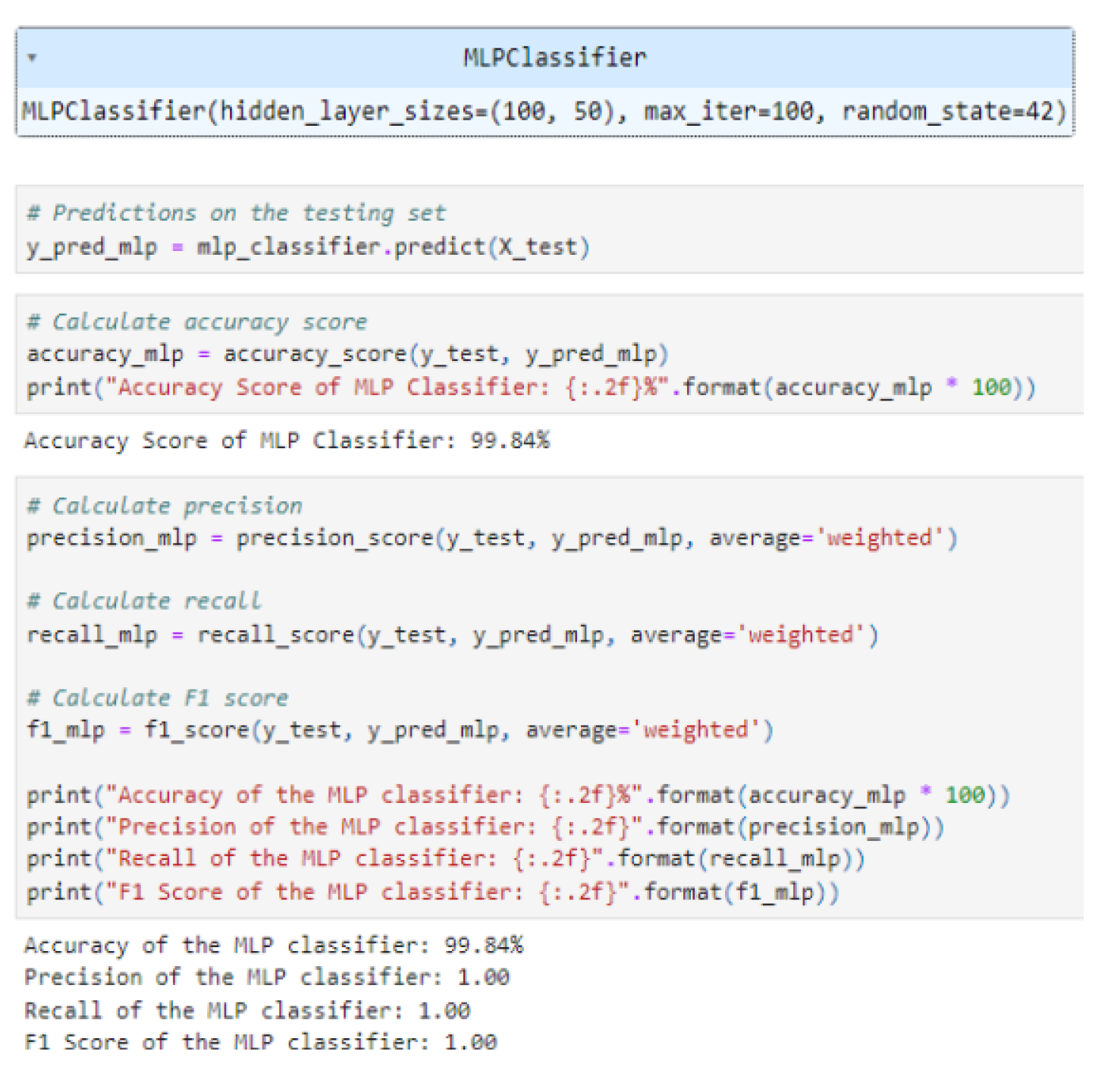
4.5.4. MLP Classifier
4.6. Comparison Between the Model Accuracy
5. Discussion
5.1. Summary of Findings
5.2. Discussion of the Findings with Respect to Prior Research
6. Conclusions and Future Work
6.1. Linking with Objectives and Hypotheses
6.2. Implications of the Results and Applications of the Research
6.3. Recommendations for Future Work
References
- Kumar, T., Mileo, A. & Bendechache, M. KeepOriginalAugment: Single Image-based Better Information-Preserving Data Augmentation Approach. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2405.06354. (2024).
- Roy, A., Bhaduri, J., Kumar, T. & Raj, K. A computer vision-based object localization model for endangered wildlife detection. Ecological Economics, Forthcoming. (2022).
- Kumar, T., Mileo, A., Brennan, R. & Bendechache, M. Image data augmentation approaches: A comprehensive survey and future directions. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2301.02830. (2023).
- Kumar, T., Mileo, A., Brennan, R. & Bendechache, M. RSMDA: Random Slices Mixing Data Augmentation. Applied Sciences. 13, 1711 (2023).
- Chandio, A., Gui, G., Kumar, T., Ullah, I., Ranjbarzadeh, R., Roy, A., Hussain, A. & Shen, Y. Precise single-stage detector. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2210.04252. (2022).
- Kumar, T., Turab, M., Raj, K., Mileo, A., Brennan, R. & Bendechache, M. Advanced Data Augmentation Approaches: A Comprehensive Survey and Future directions. arXiv 2023. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2301.02830.
- Kumar, T., Park, J., Ali, M., Uddin, A. & Bae, S. Class specific autoencoders enhance sample diversity. Journal Of Broadcast Engineering. 26, 844-854 (2021).
- Aleem, S., Kumar, T., Little, S., Bendechache, M., Brennan, R. & McGuinness, K. Random data augmentation based enhancement: A generalized enhancement approach for medical datasets. arXiv 2022. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2210.00824.
- Kumar, T., Park, J., Ali, M., Uddin, A., Ko, J. & Bae, S. Binary-classifiers-enabled filters for semi-supervised learning. IEEE Access. 9 pp. 167663-167673 (2021).
- Chandio, A., Gui, G., Kumar, T., Ullah, I., Ranjbarzadeh, R., Roy, A., Hussain, A. & Shen, Y. Precise single-stage detector. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2210.04252. (2022).
- Chandio, A., Shen, Y., Bendechache, M., Inayat, I. & Kumar, T. AUDD: audio Urdu digits dataset for automatic audio Urdu digit recognition. Applied Sciences. 11, 8842 (2021).
- Turab, M., Kumar, T., Bendechache, M. & Saber, T. Investigating multi-feature selection and ensembling for audio classification. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2206.07511. (2022).
- Raj, K., Singh, A., Mandal, A., Kumar, T. & Roy, A. Understanding EEG signals for subject-wise definition of armoni activities. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2301.00948. (2023).
- Kumar, T., Park, J. & Bae, S. Intra-Class Random Erasing (ICRE) augmentation for audio classification. Proceedings Of The Korean Society Of Broadcast Engineers Conference. pp. 244-247 (2020).
- Park, J., Kumar, T. & Bae, S. Search for optimal data augmentation policy for environmental sound classification with deep neural networks. Journal Of Broadcast Engineering. 25, 854-860 (2020).
- Park, J., Kumar, T. & Bae, S. Search of an optimal sound augmentation policy for environmental sound classification with deep neural networks. Proceedings Of The Korean Society Of Broadcast Engineers Conference. pp. 18-21 (2020).
- Kumar, T., Turab, M., Mileo, A., Bendechache, M. & Saber, T. AudRandAug: Random Image Augmentations for Audio Classification. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2309.04762. (2023).
- Singh, A., Raj, K., Meghwar, T. & Roy, A. Efficient Paddy Grain Quality Assessment Approach Utilizing Affordable Sensors. AI. 5, 686-703 (2024).
- Khan, W., Kumar, T., Cheng, Z., Raj, K., Roy, A. & Luo, B. SQL and NoSQL Databases Software architectures performance analysis and assessments—A Systematic Literature review. arXiv 2022. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2209.06977.
- Silva, P. B., Andrade, M. and Ferreira, S. (2020) ‘Machine learning applied to road safety modelling: A systematic literature review’, Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), 7(6), pp. 775–790. [CrossRef]
- Gebresenbet, R. F. and Aliyu, A. D. (2019) ‘Injury severity level and associated factors among road traffic accident victims attending emergency department of Tirunesh Beijing Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: A cross sectional hospital-based study’, PLOS ONE. Edited by Y. Guo, 14(9), p. e0222793. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S. K. et al. (2023) ‘Road traffic accidental injuries and deaths: A neglected global health issue’, Health Science Reports, 6(5). [CrossRef]
- Goodari, M. B. et al. (2023) ‘Factors affecting the number of road traffic accidents in Kerman province, southeastern Iran (2015–2021)’, Scientific Reports, 13(1). [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.-J. et al. (2022) ‘Analysis of Environmental Factors on Intersection Accidents’, Sustainability, 14(3), p. 1764. [CrossRef]
- Nizetic, S. et al. (2020) ‘Internet of Things (IoT): Opportunities, issues and challenges towards a smart and sustainable future’, Journal of Cleaner Production, 274(1), p. 122877. [CrossRef]
- Satla, S. P., Manchala, S. and Buradagunta, S. (2020) ‘Dangerous Prediction in Roads by Using Machine Learning Models’, Ingénierie des systèmes d’information/Ingénierie des systèmes d’Information, 25(5), pp. 637–644. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A., Awasthi, Y. and Kumar, S. (2020) The Role of Blockchain, AI and IoT for Smart Road Traffic Management System, IEEE Xplore. [CrossRef]
- Tonhauser, M. and Ristvej, J. (2021) ‘Implementation of New Technologies to Improve Safety of Road Transport’, Transportation Research Procedia, 55, pp. 1599–1604. [CrossRef]

| Classifier | Accuracy Score (%) |
|---|---|
| Random Forest | 99.82 |
| KNN | 99.84 |
| Decision Tree | 99.67 |
| MLP Classifier | 99.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




