Submitted:
13 July 2024
Posted:
15 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
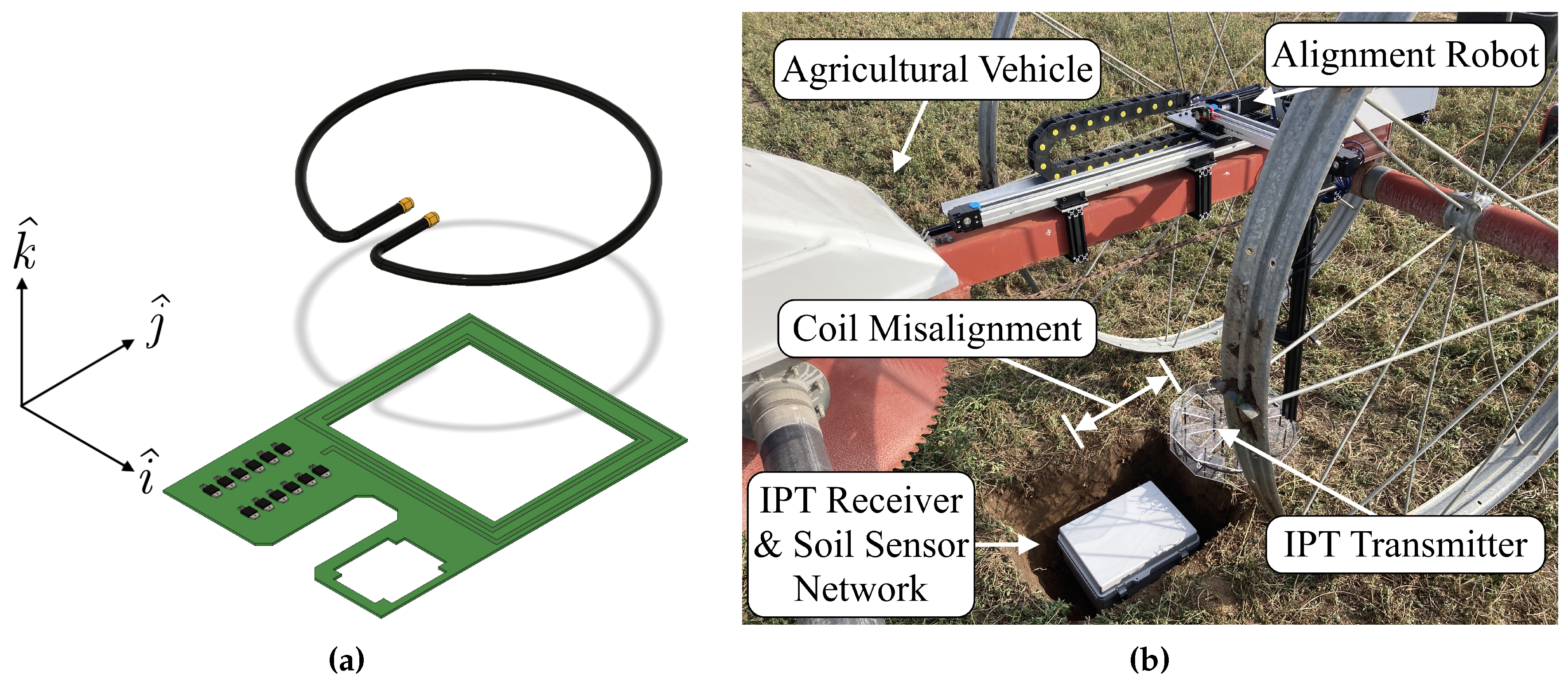
2.1. Inductive Power Transmission Hardware and Perception of Coil Misalignment
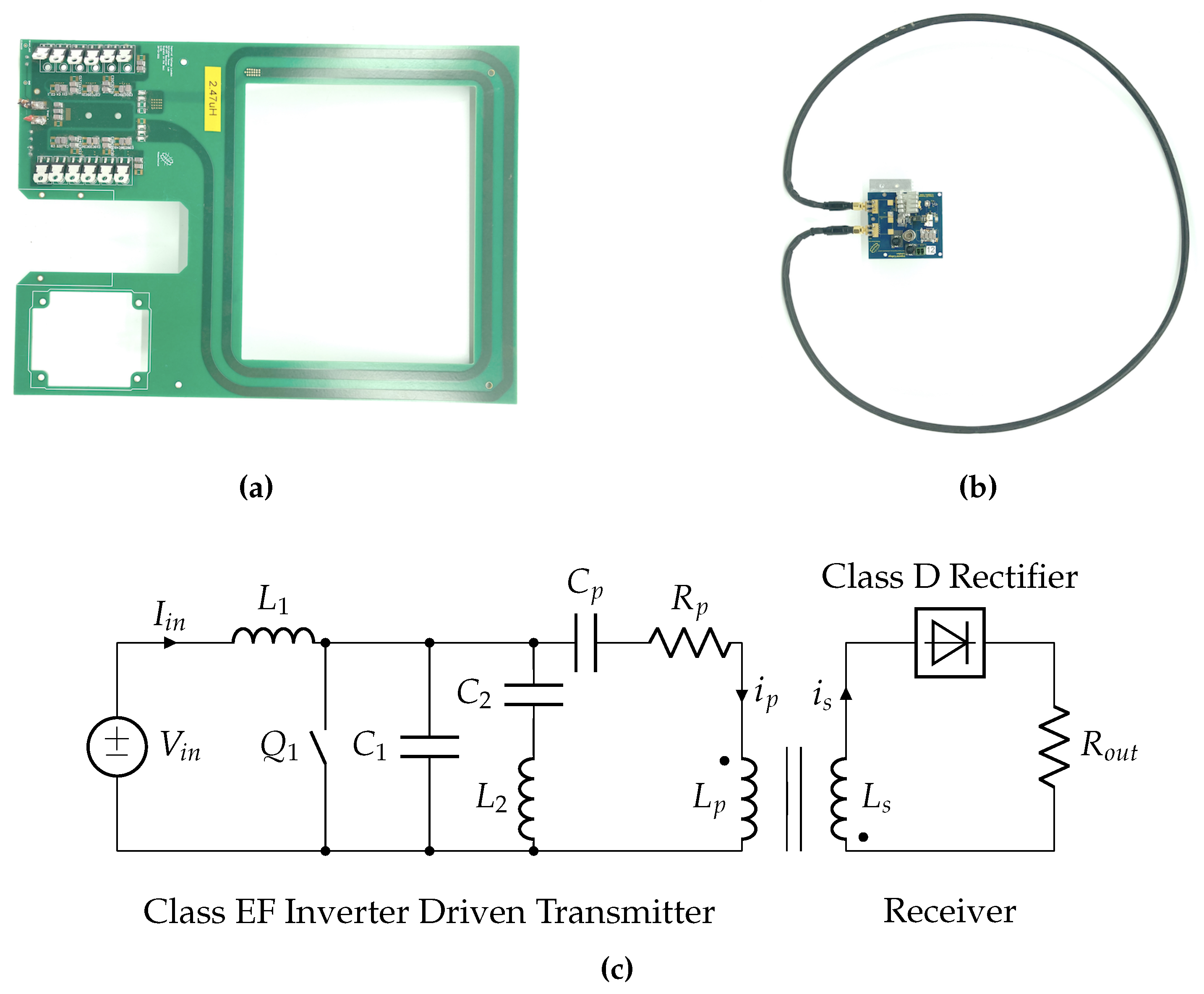
2.1.1. Misalignment Estimation with a Class EF Inverter
2.1.2. Numerically Modeling Misalignment with a Class EF Inverter
2.2. Automated Alignment Approach
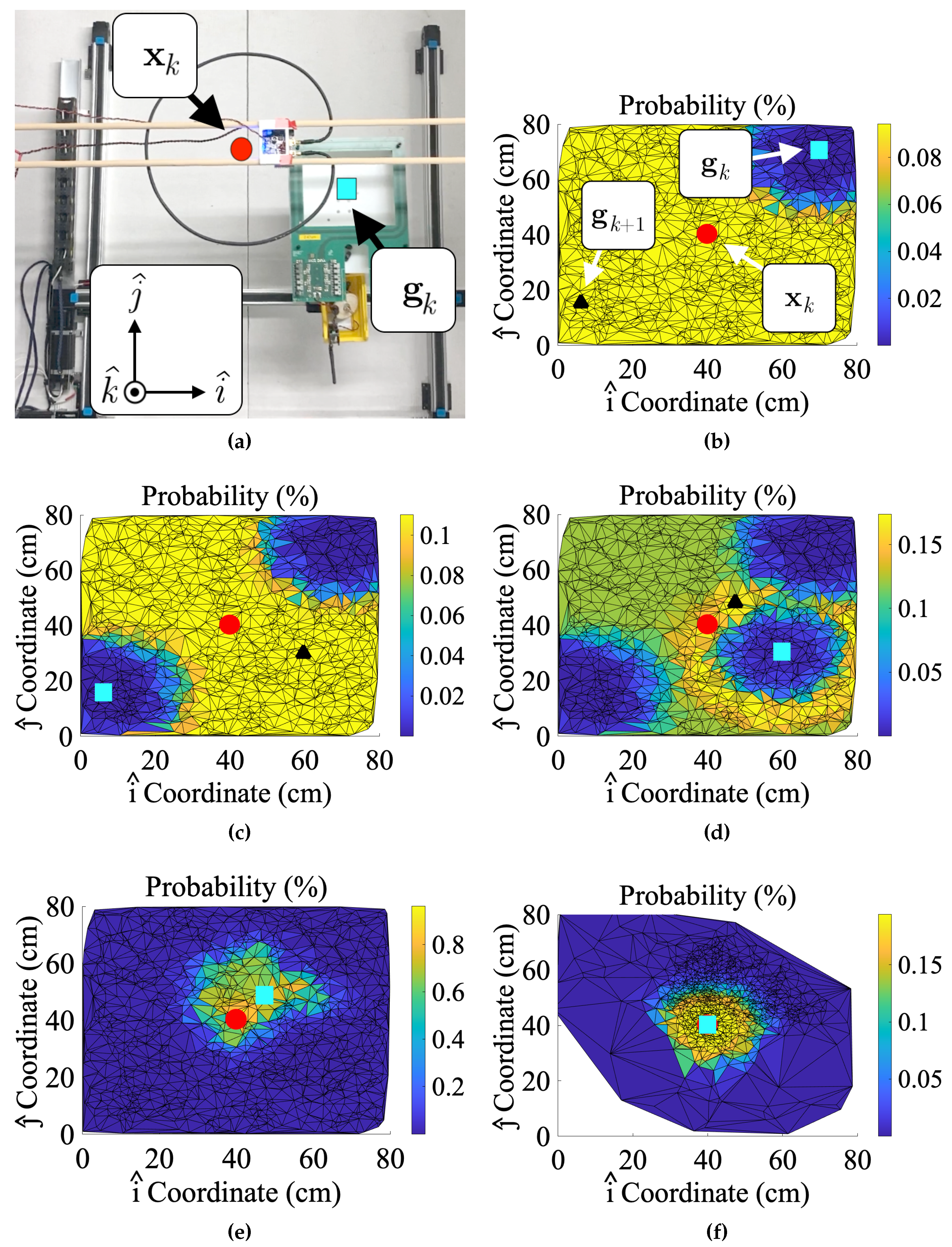
2.2.1. Coil Alignment Particle Filter Formulation
2.2.2. Particle Resampling
2.2.3. 3D Particle Filter Extension
3. Results
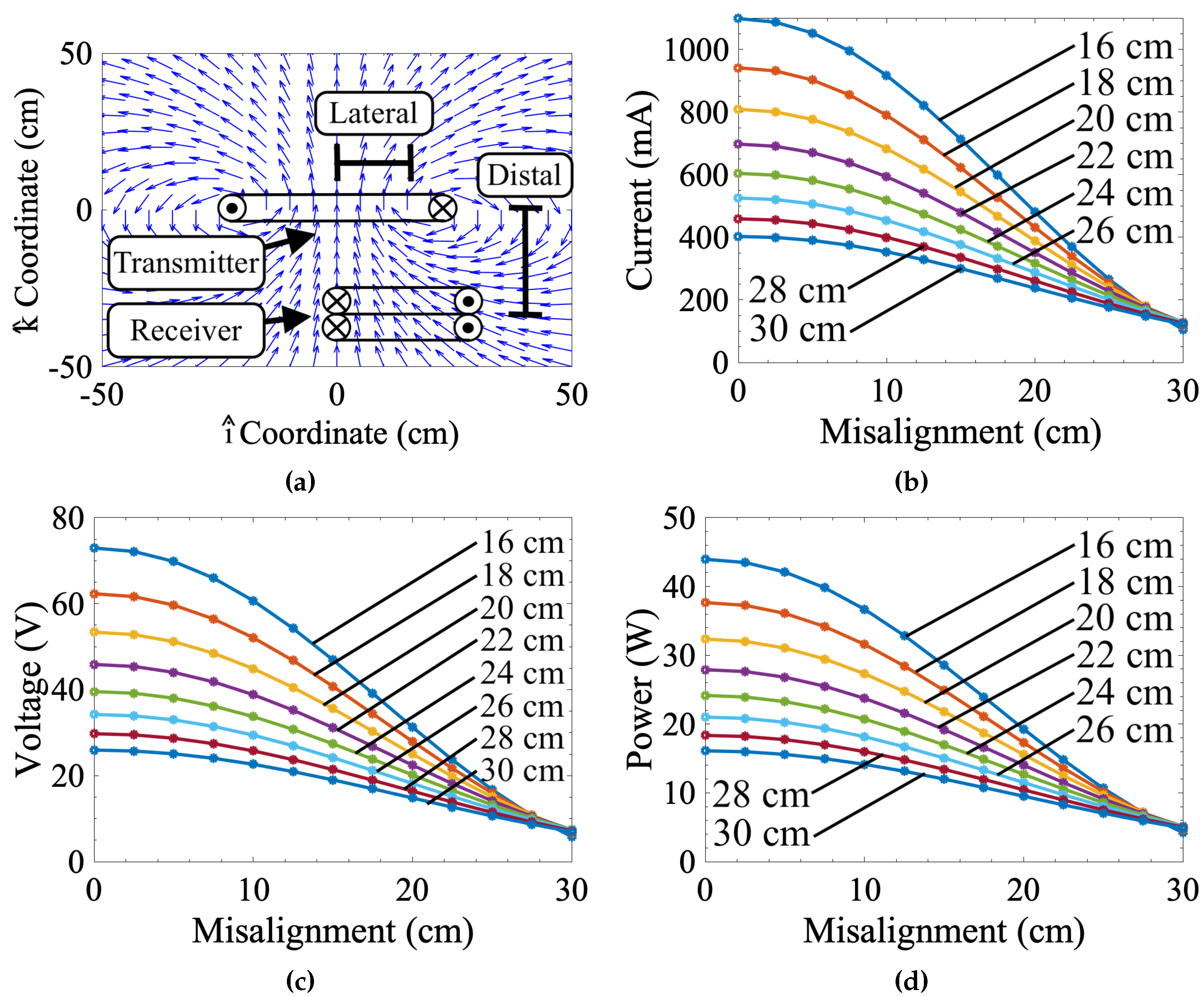
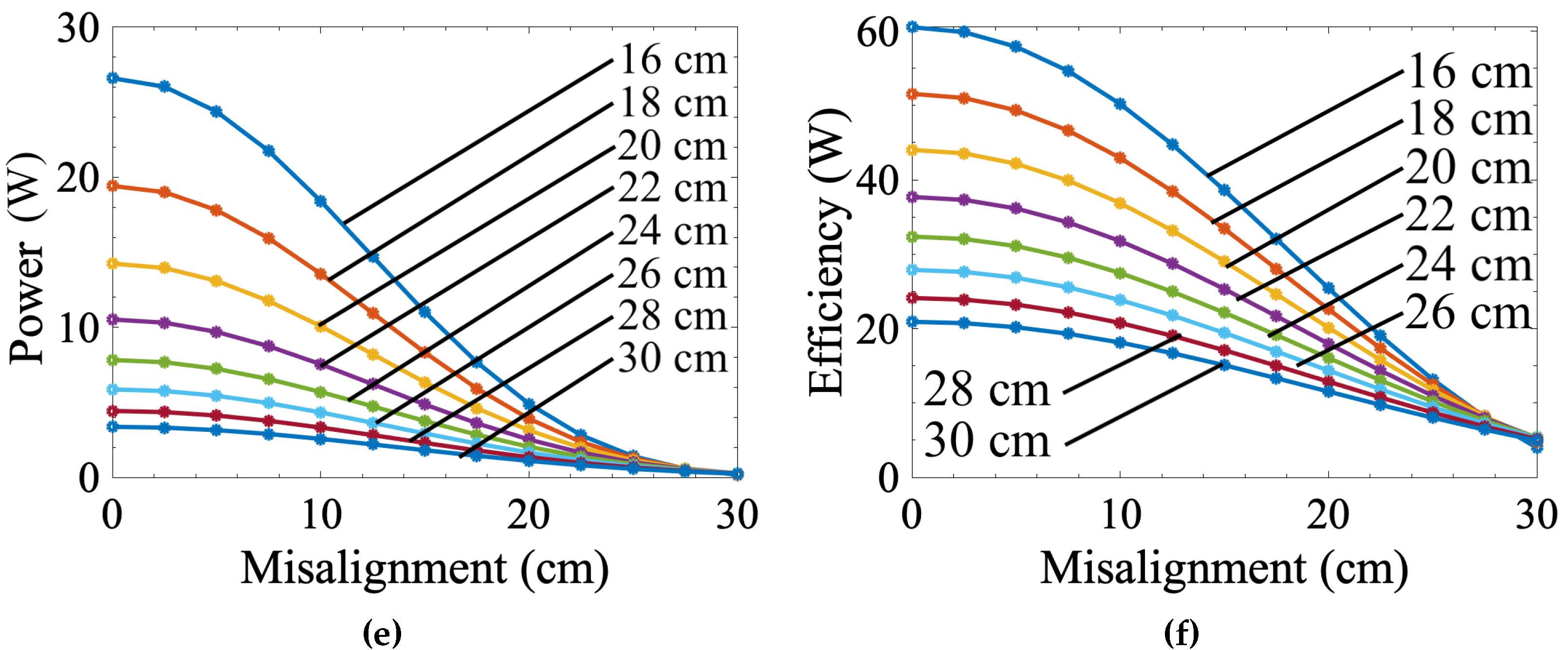
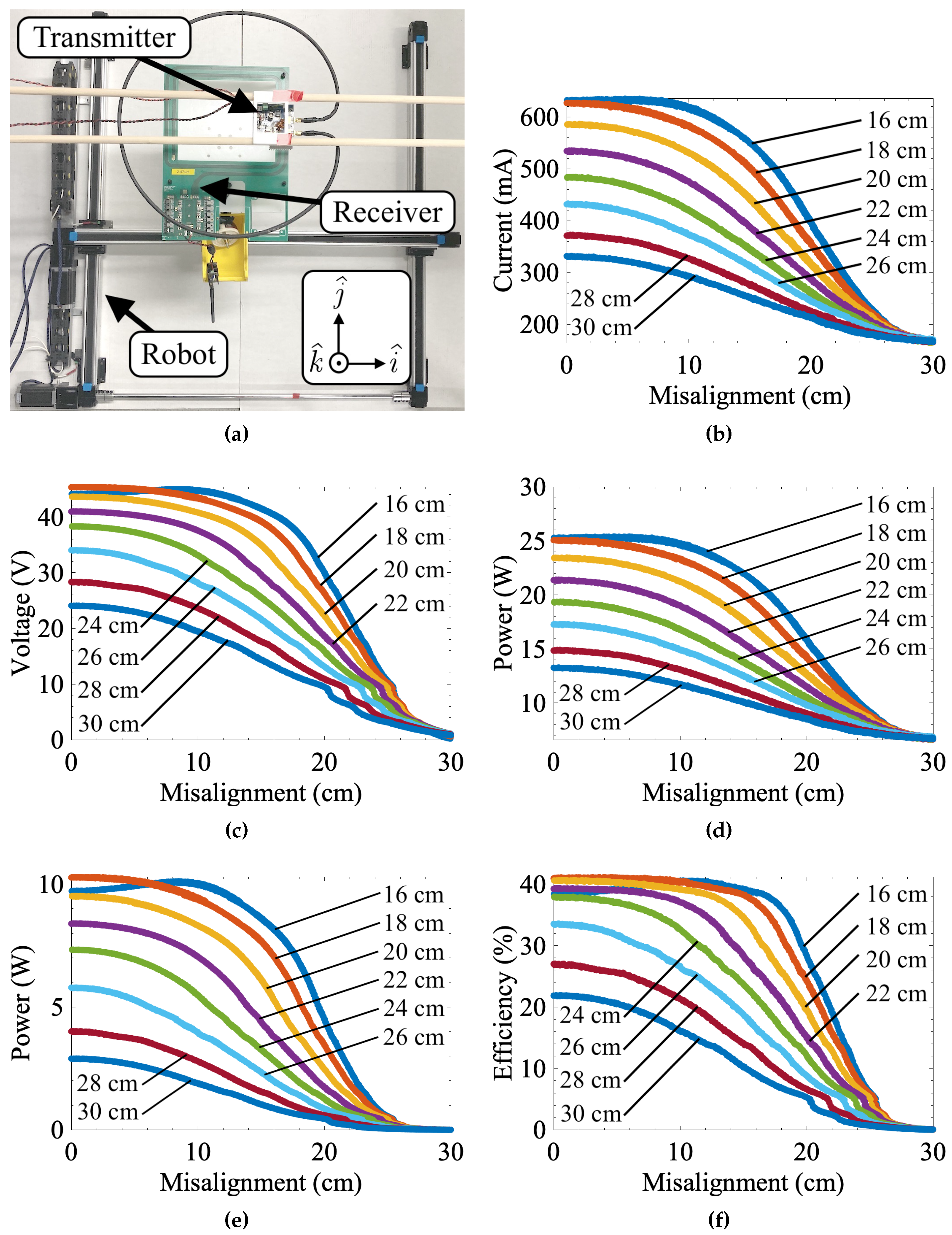
3.1. Measured Misalignment Response
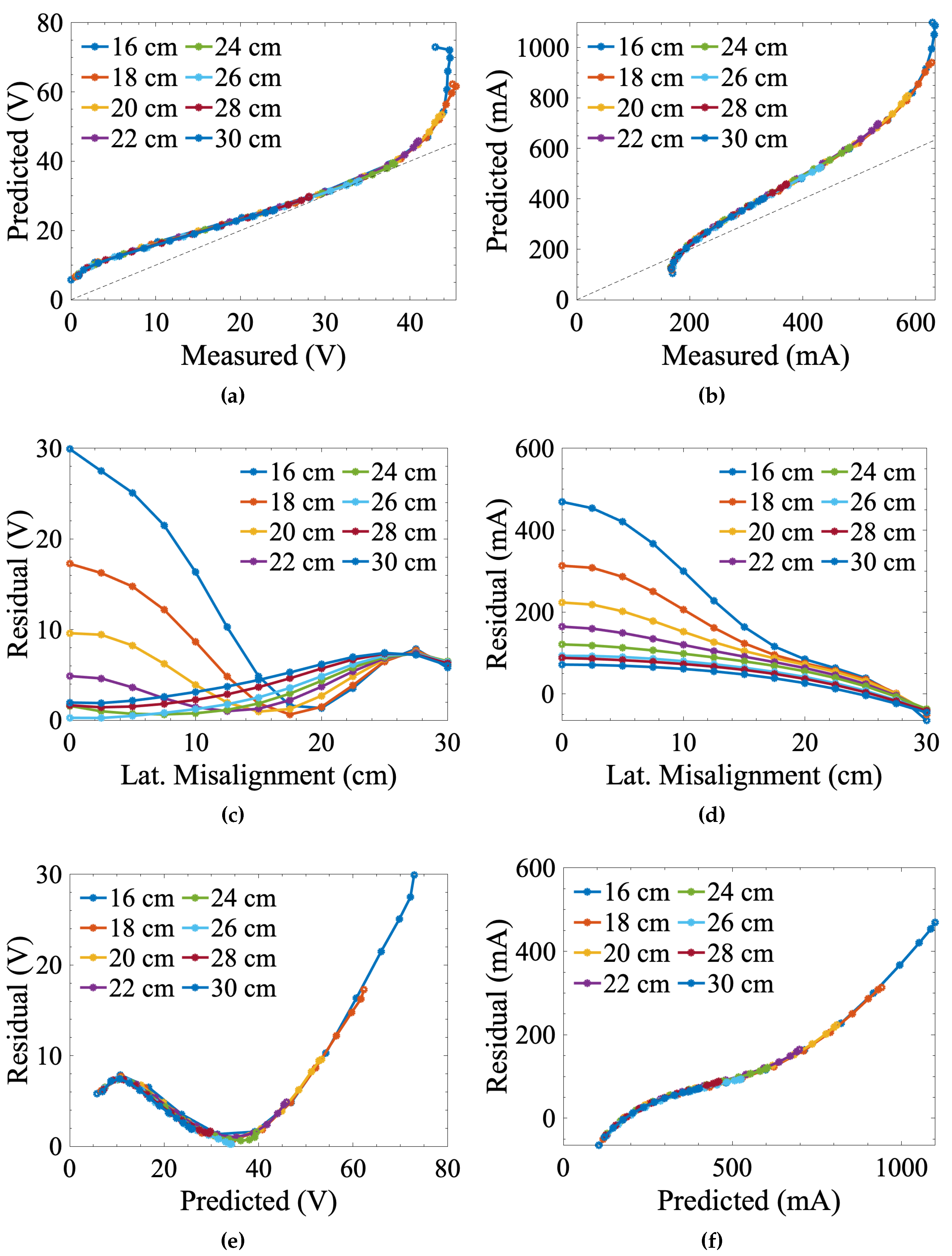
3.2. Numerically Modeled vs. Measured Data
3.3. Emperical Modeling
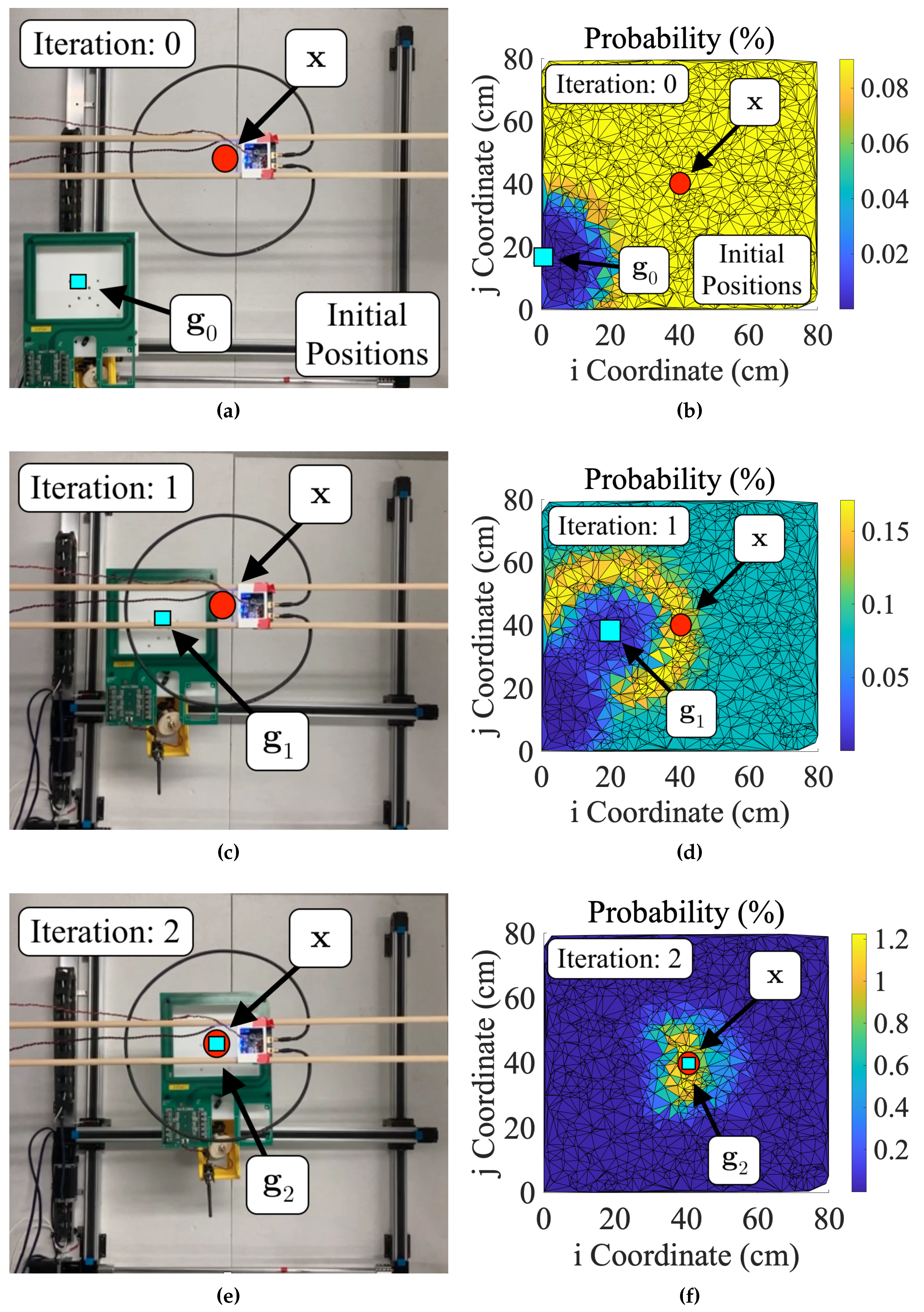
3.4. Benchmarking Alignment Algorithm Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. Mobile Transmitter vs. Mobile Receiver Localization Capabilities
4.2. Performance Metrics: Accuracy and Speed
4.3. Field Testing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IPT | Inductive power transfer |
| SIS | Sequential importance sampling |
| SIR | Sequential Importance resampling |
| WPT | Wireless power transfer |
| SLAM | Simultaneous localization and mapping |
References
- Zhang, Z.; Pang, H.; Georgiadis, A.; Cecati, C. Wireless Power Transfer—An Overview. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2019, 66, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Castellanos, S.; Xu, S.; Wood, B.; Tse, Z. Applications of Wireless Power Transfer in Medicine: State-of-the-Art Reviews. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 2018, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, J.; Mitcheson, P.; Yeatman, E. Development of a Fast-Charging Platform for Buried Sensors Using High Frequency IPT for Agricultural Applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC). IEEE, 2022.
- Vi, V.; Ramezani, A.; Triviño, A.; González, J.; Kadandani, N.; Dahidah, M.; Pickert, V.; Narimani, M.; Aguado, J. Operation of Inductive Charging Systems Under Misalignment Conditions: A Review for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. on Power Electron. 2023, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Sample, A.P.; Meyer, D.T.; Smith, J.R. Analysis, Experimental Results, and Range Adaptation of Magnetically Coupled Resonators for Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2011, 58, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, R.; Badstübner, U.; Kolar, J.W.; Stevanović, I. Comparative evaluation of control methods for Inductive Power Transfer. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA); 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Cai, T.; Duan, S.; Zhang, X.; Niu, J.; Feng, H. An Optimal Variable Frequency Phase Shift Control Strategy for ZVS Operation Within Wide Power Range in IPT Systems. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2020, 35, 5517–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Duan, C.; Oliveira, A.A.; Ginart, A.; Farley, K.B.; Tse, Z.T.H. 3-D Coil Positioning Based on Magnetic Sensing for Wireless EV Charging. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 2017, 3, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Q.; Ke, G.; Xu, L.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Z. Coil Positioning Based on DC Pre-excitation and Magnetic Sensing for Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2021, 68, 3820–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittleider, A.; Griffin, B.; Detweiler, C. Experimental Analysis of a UAV-Based Wireless Power Transfer Localization System. In Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics; Springer, 2016; Vol. 109, pp. 357–371. [Google Scholar]
- Aldhaher, S.; Yates, D.C.; Mitcheson, P.D. Load-Independent Class E/EF Inverters and Rectifiers for MHz-Switching Applications. IEEE Trans. on Power Electron. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.; M. Arteaga, J.; Pucci, N.; Mitcheson, P.; Yeatman, E.; Young, D.; Roundy, S. Misalignment parameterization of a 13.56 mhz inductive power transfer system for in-situ soil sensing. In Proceedings of the PowerMEMS Conference Proceedings, 2022.
- Lan, L.; Polonelli, T.; Qin, Y.; Pucci, N.; Kwan, C.H.; Arteaga, J.M.; Boyle, D.; Yates, D.C.; Yeatman, E.M.; Mitcheson, P.D. An Induction-Based Localisation Technique for Wirelessly Charged Drones. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE PELS Workshop on Emerging Technologies: Wireless Power Transfer (WoW); 2020; pp. 275–277. [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga, J.; Pucci, N.; Lan, L.; Mitcheson, P. Load Characterization in High-Frequency IPT Systems Using Class EF Switching Waveforms. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2021, 36, 11036–11044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinuela, M.; Yates, D.C.; Lucyszyn, S.; Mitcheson, P.D. Maximizing DC-to-Load Efficiency for Inductive Power Transfer. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2013, 28, 2437–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svečko, J.; Malajner, M.; Gleich, D. Distance estimation using RSSI and particle filter. ISA Transactions 2015, 55, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Xu, W.; Guo, N.; Wei, Z. Joint Sensor Localization and Data Collection in UAV-Assisted Wireless Sensor Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 14th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP); 2022; pp. 894–899. [Google Scholar]
- Arulampalam, M.; Maskell, S.; Gordon, N.; Clapp, T. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 2002, 50, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Bolic, M.; Djuric, P.M. Resampling methods for particle filtering: classification, implementation, and strategies. IEEE Signal processing magazine 2015, 32, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemerlo, M.; Thrun, S.; Koller, D.; Wegbreit, B.; et al. FastSLAM: A factored solution to the simultaneous localization and mapping problem. Aaai/iaai 2002, 593598. [Google Scholar]
- Montemerlo, M.; Thrun, S.; Koller, D.; Wegbreit, B.; et al. FastSLAM 2.0: An improved particle filtering algorithm for simultaneous localization and mapping that provably converges. In Proceedings of the IJCAI; 2003; Vol. 3, pp. 1151–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, J.; Arteaga, J.; Zesiger, C.; Young, D.; Goel, R.; Mitcheson, P.; Yeatman, E.; Roundy, S. Integration of a high frequency inductive power transfer system to energize agricultural sensors through soil. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Power Week (WPW) Proceedings; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Acclima. Acclima TDR Sensor User Manual For Sensor Models: TDR305H TDR310H TDR315H. Acclima, 2022. Available at https://acclima.com/digital-true-tdr-310h-sensor-sdi-12-data-sheet.

| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Turns in Receiver Coil | N | 2 |
| Transmission Frequency | , f | 85.2 Mrad/s, 13.56 MHz |
| Current in Primary Coil | 6.25 A | |
| Primary Coil Self-Inductance | 1181 nF | |
| Secondary Coil Self-Inductance | 2470 nF | |
| DC Input Voltage | 40 V | |
| Output Load | 200 | |
| Quality Factor | , | 767 |
| Distal Separation (cm) | RMSE Voltage Signal (V) | RMSE Current Signal (mA) |
|---|---|---|
| 16 | 15.9 | 268 |
| 18 | 9.55 | 185 |
| 20 | 6.09 | 135 |
| 22 | 4.48 | 104 |
| 24 | 4.08 | 82.2 |
| 26 | 4.22 | 65.6 |
| 28 | 4.66 | 60.5 |
| 30 | 4.96 | 50.6 |
| Distal Separation (cm) | RMSE Voltage Signal (V) | RMSE Current Signal (mA) |
|---|---|---|
| 16 | 0.397 | 3.19 |
| 18 | 0.256 | 2.64 |
| 20 | 0.245 | 2.25 |
| 22 | 0.224 | 1.35 |
| 24 | 0.224 | 1.63 |
| 26 | 0.216 | 0.938 |
| 28 | 0.235 | 1.17 |
| 30 | 0.240 | 0.986 |
| Filter | IU, IC | Avg. Error | Avg. | Std. | Avg. Speed | Std. Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D SIS, I | 59, 41 | 3.8 cm | 40.3% | 0.974% | 3.10 | 1.05 |
| 2D SIS, V | 56, 44 | 2.4 cm | 40.5% | 0.819% | 2.86 | 1.10 |
| 2D SIS, C | 57, 43 | 8.3 cm | 39.9% | 0.952% | 2.79 | 1.67 |
| 2D SIR, I | 26, 24 | 3.1 cm | 40.4% | 1.04% | 4.00 | 1.47 |
| *2D SIR, V | 34, 16 | 0.0 cm | 41.2% | 0.966% | 3.13 | 1.15 |
| *3D SIS, I | 20, 30 | 0.0 cm | 41.0% | 1.16% | 3.80 | 1.65 |
| *3D SIS, V | 35, 15 | 0.0 cm | 41.0% | 1.06% | 3.80 | 2.48 |
| Compare | Filter | Metric | Difference | df | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I vs. V | 2D SIS | -0.186% | 192 | .146 | |
| Speed | 0.234 | 60 | .500 | ||
| 2D SIR | -0.846% | 98 | <.001 | ||
| Speed | 0.875 | 37 | .0422 | ||
| 3D SIS | 0.0651% | 97 | .771 | ||
| Speed | 0.00 | 20 | 1.00 | ||
| I vs. C | 2D SIS | 0.443% | 198 | .00132 | |
| Speed | 0.307 | 79 | .443 | ||
| V vs. C | 2D SIS | 0.629% | 194 | <.001 | |
| Speed | 0.0729 | 70 | .808 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




