Submitted:
11 July 2024
Posted:
15 July 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
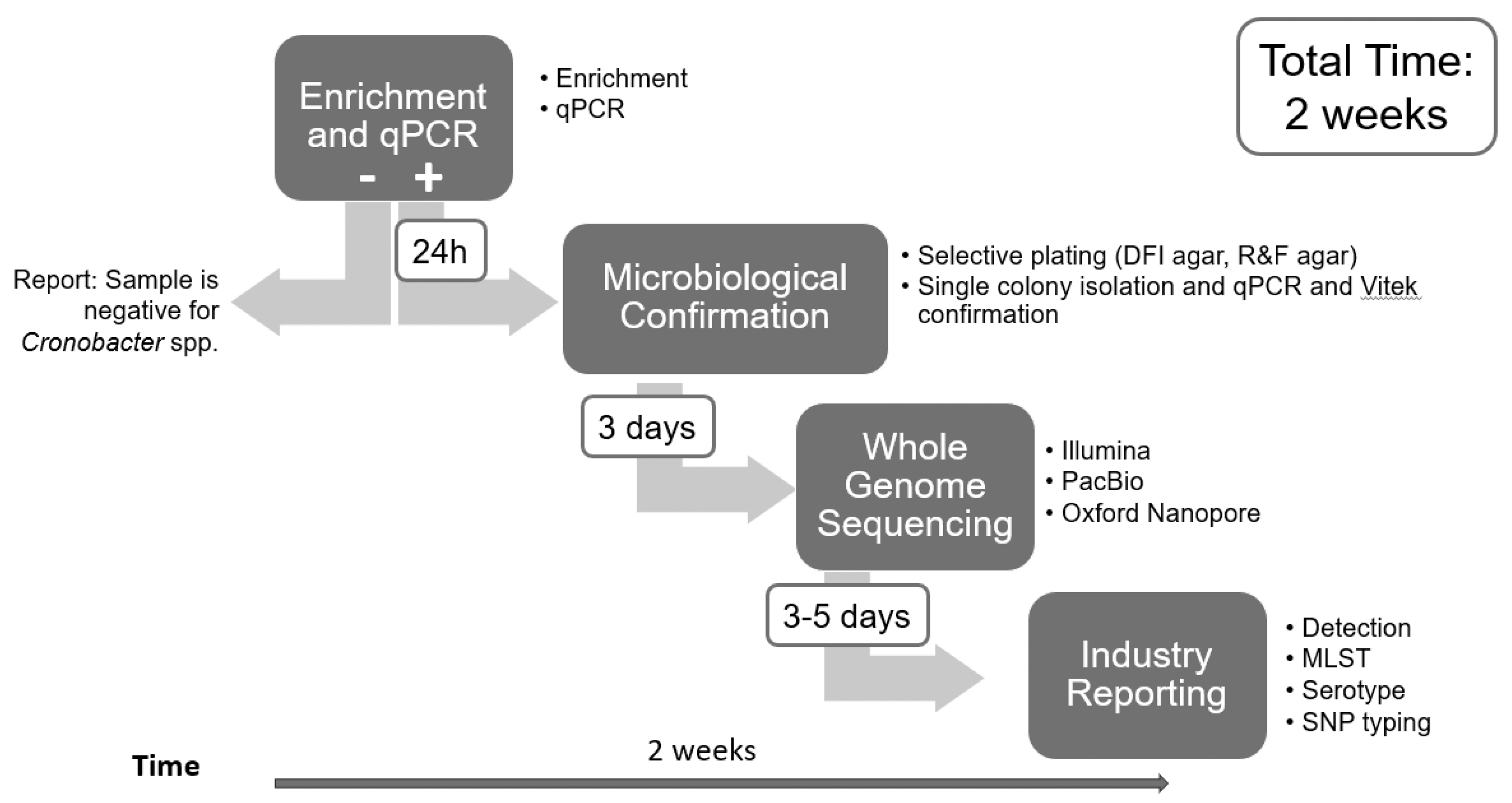
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
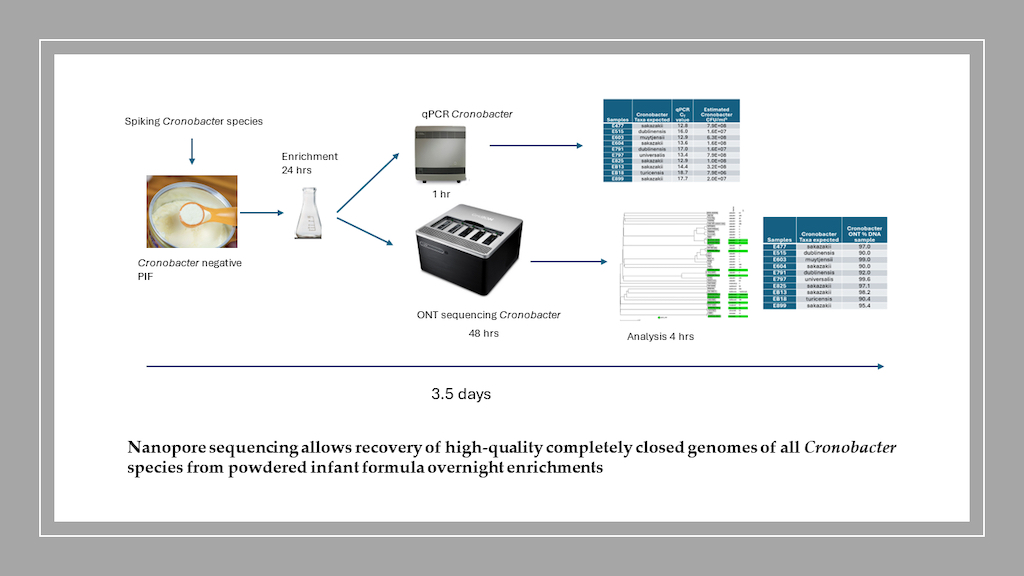
- 3.1.1. Cronobacter-Spiked Sample Enrichment Preparation for Nanopore Sequencing
- 3.1.2. Nanopore Long-Read Sequencing Results
- 3.1.3. Nanopore Long-Read GENOME assembly of Cronobacter PIF Enriched Samples
- 3.1.4. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) and Serotyping Analysis
- 3.1.5. wgMLST Analysis of Cronobacter PIF Overnight Enriched samples And Taxa Classification Using a Phylogenetic Tree
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, E.U. Dessai, S. McGarry and P. Gerner-Smidt. "Use of whole-genome sequencing for food safety and public health in the United States." Foodborne Pathog Dis 16 (2019): 441-50. 10.1089/fpd.2019.2662. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31194586.
- Huang, A. D., C. Luo, A. Pena-Gonzalez, M. R. Weigand, C. L. Tarr and K. T. Konstantinidis. "Metagenomics of two severe foodborne outbreaks provides diagnostic signatures and signs of coinfection not attainable by traditional methods." Appl Environ Microbiol 83 (2017): 10.1128/AEM.02577-16. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27881416.
- Loman, N. J., C. Constantinidou, M. Christner, H. Rohde, J. Z. Chan, J. Quick, J. C. Weir, C. Quince, G. P. Smith, J. R. Betley, et al. "A culture-independent sequence-based metagenomics approach to the investigation of an outbreak of shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli O104:H4." JAMA 309 (2013): 1502-10. 10.1001/jama.2013.3231. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23571589.
- Maguire, M., P. Ramachandran, S. Tallent, M. K. Mammel, E. W. Brown, M. W. Allard, S. M. Musser and N. Gonzalez-Escalona. "Precision metagenomics sequencing for food safety: Hybrid assembly of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in enriched agricultural water." Front Microbiol 14 (2023): 1221668. 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1221668. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37720160.
- Cechin, C. D. F., G. G. Carvalho, C. P. Bastos and D. Y. Kabuki. "Cronobacter spp. In foods of plant origin: Occurrence, contamination routes, and pathogenic potential." Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 63 (2023): 12398-412. 10.1080/10408398.2022.2101426. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35866516.
- Haston, J. C., S. Miko, J. R. Cope, H. McKeel, C. Walters, L. A. Joseph, T. Griswold, L. S. Katz, A. A. Andujar, L. Tourdot, et al. "Cronobacter sakazakii infections in two infants linked to powdered infant formula and breast pump equipment - United States, 2021 and 2022." MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 72 (2023): 223-26. 10.15585/mmwr.mm7209a2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36862586.
- Archer, D. L. "The evolution of fda's policy on Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat foods in the United States." Current Opinion in Food Science 20 (2018): 64-68. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214799317301728. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., G. Lin, L. Zhang, Y. Hu, C. Hong, A. Xie and L. Fang. "Genomic insights into Cronobacter spp. recovered from food and human clinical cases in zhejiang province, china (2008-2021)." J Appl Microbiol 134 (2023): 10.1093/jambio/lxad033. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36807689.
- Drudy, D., N. R. Mullane, T. Quinn, P. G. Wall and S. Fanning. "Enterobacter sakazakii: An emerging pathogen in powdered infant formula." Clin Infect Dis 42 (2006): 996-1002. 10.1086/501019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16511766.
- Strysko, J., J. R. Cope, H. Martin, C. Tarr, K. Hise, S. Collier and A. Bowen. "Food safety and invasive Cronobacter infections during early infancy, 1961-2018." Emerg Infect Dis 26 (2020): 857-65. 10.3201/eid2605.190858. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32310746.
- Joseph, S.H. Sonbol, S. Hariri, P. Desai, M. McClelland and S. J. Forsythe. "Diversity of the Cronobacter genus as revealed by multilocus sequence typing." Journal of clinical microbiology 50 (2012): 3031-39. 10.1128/Jcm.00905-12. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22785185/. [CrossRef]
- Iversen, C., N. Mullane, B. McCardell, B. D. Tall, A. Lehner, S. Fanning, R. Stephan and H. Joosten. "Cronobacter gen. Nov., a new genus to accommodate the biogroups of Enterobacter sakazakii, and proposal of Cronobacter sakazakii gen. nov., comb. nov., Cronobacter malonaticus sp. nov., Cronobacter turicensis sp. nov., Cronobacter muytjensii sp. nov., Cronobacter dublinensis sp. nov., Cronobacter genomospecies 1, and of three subspecies, Cronobacter dublinensis subsp. dublinensis subsp. nov., Cronobacter dublinensis subsp. :Lausannensis subsp. nov. and Cronobacter dublinensis subsp. Lactaridi subsp. nov." Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58 (2008): 1442-7. 10.1099/ijs.0.65577-0. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18523192.
- Hariri, S., S. Joseph and S. J. Forsythe. "Cronobacter sakazakii st4 strains and neonatal meningitis, United States." Emerg Infect Dis 19 (2013): 175-7. 10.3201/eid1901.120649. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23260316.
- Ling, N., X. T. Jiang, S. Forsythe, D. F. Zhang, Y. Z. Shen, Y. Ding, J. Wang, J. M. Zhang, Q. P. Wu and Y. W. Ye. "Food safety risks and contributing factors of Cronobacter spp." Engineering 12 (2022): 128-38. 10.1016/j.eng.2021.03.021. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S209580992100254X.
- Chen, Y. M., N. E.; Liu, K. C.; Mullins, J. S.; Lampel, K.; Hammack, T. "BAM chapter 29: Cronobacter." 2023. https://www.fda.gov/food/laboratory-methods-food/bam-chapter-29-Cronobacter.
- Bertrand, D., J. Shaw, M. Kalathiyappan, A. H. Q. Ng, M. S. Kumar, C. Li, M. Dvornicic, J. P. Soldo, J. Y. Koh, C. Tong, et al. "Hybrid metagenomic assembly enables high-resolution analysis of resistance determinants and mobile elements in human microbiomes." Nat Biotechnol 37 (2019): 937-44. 10.1038/s41587-019-0191-2. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31359005/.
- Maguire, M., A. S. Khan, A. A. Adesiyun, K. Georges and N. Gonzalez-Escalona. "Closed genome sequence of a Salmonella enterica serotype senftenberg strain carrying the mcr-9 gene isolated from broken chicken eggshells in trinidad and tobago." Microbiol Resour Announc 10 (2021): e0146520. 10.1128/MRA.01465-20. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34042489.
- Maguire, M., J. A. Kase, D. Roberson, T. Muruvanda, E. W. Brown, M. Allard, S. M. Musser and N. Gonzalez-Escalona. "Precision long-read metagenomics sequencing for food safety by detection and assembly of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in irrigation water." PLoS One 16 (2021): e0245172. 10.1371/journal.pone.0245172. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33444384.
- Sanderson, N. D.K. M. V. Hopkins, M. Colpus, M. Parker, S. Lipworth, D. Crook and N. Stoesser. "Evaluation of the accuracy of bacterial genome reconstruction with oxford nanopore R10.4.1 long-read-only sequencing." Microb Genom 10 (2024): 10.1099/mgen.0.001246. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38713194. [CrossRef]
- Lerminiaux, N., K. Fakharuddin, M. R. Mulvey and L. Mataseje. "Do we still need illumina sequencing data? Evaluating oxford nanopore technologies R10.4.1 flow cells and the rapid v14 library prep kit for gram negative bacteria whole genome assemblies." Canadian Journal of Microbiology (2024): 10.1139/cjm-2023-0175. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38354391/.
- Bogaerts, B., A. Van den Bossche, B. Verhaegen, L. Delbrassinne, W. Mattheus, S. Nouws, M. Godfroid, S. Hoffman, N. H. C. Roosens, S. C. J. De Keersmaecker, et al. "Closing the gap: Oxford nanopore technologies R10 sequencing allows comparable results to illumina sequencing for snp-based outbreak investigation of bacterial pathogens." J Clin Microbiol (2024): e0157623. 10.1128/jcm.01576-23. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38441926.
- Buytaers, F. E., B. Verhaegen, T. Van Nieuwenhuysen, N. H. C. Roosens, K. Vanneste, K. Marchal and S. C. J. De Keersmaecker. "Strain-level characterization of foodborne pathogens without culture enrichment for outbreak investigation using shotgun metagenomics facilitated with nanopore adaptive sampling." Front Microbiol 15 (2024): 1330814. 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1330814. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38495515.
- Seo, K. H. and R. E. Brackett. "Rapid, specific detection of enterobacter sakazakii in infant formula using a real-time pcr assay." J Food Prot 68 (2005): 59-63. 10.4315/0362-028x-68.1.59. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15690804.
- Kolmogorov, M., J. Yuan, Y. Lin and P. A. Pevzner. "Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs." Nat Biotechnol 37 (2019): 540-46. 10.1038/s41587-019-0072-8.
- Wood, D. E., J. Lu and B. Langmead. "Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2." Genome Biology 20 (2019): 257. 10.1186/s13059-019-1891-0. [CrossRef]
- Gangiredla, J., H. Rand, D. Benisatto, J. Payne, C. Strittmatter, J. Sanders, W. J. Wolfgang, K. Libuit, J. B. Herrick, M. Prarat, et al. "Galaxytrakr: A distributed analysis tool for public health whole genome sequence data accessible to non-bioinformaticians." BMC Genomics 22 (2021): https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33568057/.
- Wang, L., W. Zhu, G. Lu, P. Wu, Y. Wei, Y. Su, T. Jia, L. Li, X. Guo, M. Huang, et al. "In silico species identification and serotyping for Cronobacter isolates by use of whole-genome sequencing data." Int J Food Microbiol 358 (2021): 109405. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109405. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34563883.
- Maguire, M., A. S. Khan, A. A. Adesiyun, K. Georges and N. Gonzalez-Escalona. "Genomic comparison of eight closed genomes of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica strains isolated from broiler farms and processing plants in trinidad and tobago." Front Microbiol 13 (2022): 863104. 10.3389/fmicb.2022.863104. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35620095.
- Duarte, F., E. Cordero, M. Calderon, A. Godinez, B. Ross, M. Allard and N. Gonzalez-Escalona. "Closed genomes of four multidrug resistance Salmonella enterica serotype infantis isolated in Costa Rrica." Microbiol Resour Announc 13 (2024): e0025723. 10.1128/MRA.00257-23. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38019019.
- Chen, Z., D. Kuang, X. Xu, N. Gonzalez-Escalona, D. L. Erickson, E. Brown and J. Meng. "Genomic analyses of multidrug-resistant Salmonella Indiana, Typhimurium, and Enteritidis isolates using minion and miseq sequencing technologies." PLoS One 15 (2020): e0235641. 10.1371/journal.pone.0235641. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32614888.
- Hoffmann, M.Y. Luo, S. R. Monday, N. Gonzalez-Escalona, A. R. Ottesen, T. Muruvanda, C. Wang, G. Kastanis, C. Keys, D. Janies, et al. "Tracing origins of the Salmonella Bareilly strain causing a food-borne outbreak in the United States." J. Infect Dis 213 (2016): 502-08. jiv297 [pii];10.1093/infdis/jiv297 [doi]. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25995194. Not in File. [CrossRef]
- Bottichio, L., A. Keaton, D. Thomas, T. Fulton, A. Tiffany, A. Frick, M. Mattioli, A. Kahler, J. Murphy, M. Otto, et al. "Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections associated with romaine lettuce-United States, 2018." Clin Infect Dis 71 (2020): e323-e30. 10.1093/cid/ciz1182. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31814028.
- Gobin, M., J. Hawker, P. Cleary, T. Inns, D. Gardiner, A. Mikhail, J. McCormick, R. Elson, D. Ready, T. Dallman, et al. "National outbreak of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 linked to mixed salad leaves, United Kingdom, 2016." Euro Surveill 23 (2018): 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2018.23.18.17-00197. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29741151.
- Carleton, H. A., J. Besser, A. J. Williams-Newkirk, A. Huang, E. Trees and P. Gerner-Smidt. "Metagenomic approaches for public health surveillance of foodborne infections: Opportunities and challenges." Foodborne Pathogens and Disease 16 (2019): 474-79. 10.1089/fpd.2019.2636. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31170005/.
- Pena-Gonzalez, A., M. J. Soto-Giron, S. Smith, J. Sistrunk, L. Montero, M. Paez, E. Ortega, J. K. Hatt, W. Cevallos, G. Trueba, et al. "Metagenomic signatures of gut infections caused by different Escherichia coli pathotypes." Appl Environ Microbiol 85 (2019): 10.1128/AEM.01820-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31585992.

| Samples | Cronobacter species | Source | Country of Origin | Available at NCBI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E477 | sakazakii | Human (throat) | Unknown | ATCC 29544 |
| E515 | dublinensis | Water | Switzerland | NA |
| E603 | muytjensii | Unknown | unknown | ATCC 51329 |
| E604 | sakazakii | Clinical | Canada | SK90 |
| E791 | dublinensis | Human (blood) | USA | CDC 5960-70 |
| E797 | universalis | Water | UK | NCTC 9529 |
| E825 | sakazakii | Human (breast abscess) | USA | NA |
| EB13 | sakazakii | Neonate (meningitis) | Switzerland | NA |
| EB18 | turicensis | Neonate (meningitis) | Switzerland | NA |
| E899 | sakazakii | Clinical | USA | NA |
| Samples | Cronobacter Taxa expected | Cronobacter Taxa observed WIMPa | Cronobacter Taxa observed by phylogenetic tree | qPCR CT value | Estimated Cronobacter CFU/mlb | Cronobacter ONT % DNA sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E477 | sakazakii | sakazakii | sakazakii | 12.8 | 7.9E+08 | 97.0 |
| E515 | dublinensis | dublinensis | dublinensis | 16.0 | 1.6E+07 | 90.0 |
| E603 | muytjensii | muytjensii | muytjensii | 12.9 | 6.3E+08 | 99.0 |
| E604 | sakazakii | sakazakii | sakazakii | 13.6 | 1.6E+08 | 90.0 |
| E791 | dublinensis | dublinensis | dublinensis | 17.0 | 1.6E+07 | 92.0 |
| E797 | universalis | universalis | universalis | 13.4 | 7.9E+08 | 99.6 |
| E825 | sakazakii | sakazakii | sakazakii | 12.9 | 1.0E+08 | 97.1 |
| EB13 | sakazakii | sakazakii | sakazakii | 14.4 | 3.2E+08 | 98.2 |
| EB18 | turicensis | universalis | turicensis | 18.7 | 7.9E+06 | 90.4 |
| E899 | sakazakii | sakazakii | sakazakii | 17.7 | 2.0E+07 | 95.4 |
| Samples | Total reads | Total Mb | Estimated coverage Cronobacter genome all reads (X) | Reads above 4000 bp | Total Mb above 4000 bp | Estimated coverage Cronobacter genome > 4kb reads (X) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E477 | 228,000 | 1,069 | 238 | 82,998 | 732 | 163 |
| E515 | 70,096 | 354 | 79 | 26,066 | 248 | 55 |
| E603 | 523,730 | 2,665 | 592 | 203,038 | 1,889 | 420 |
| E604 | 127,684 | 643 | 143 | 47,322 | 455 | 101 |
| E791 | 257,927 | 1,148 | 255 | 85,301 | 752 | 167 |
| E797 | 278,012 | 1,382 | 307 | 105,162 | 969 | 215 |
| E825 | 210,799 | 1,010 | 224 | 77,642 | 697 | 155 |
| EB13 | 239,315 | 1,228 | 273 | 91,575 | 870 | 193 |
| EB18 | 319,323 | 1,648 | 366 | 125,660 | 1,168 | 260 |
| E899 | 191,946 | 941 | 209 | 70,517 | 647 | 144 |
| Samples | Contig No. | %GC content | Genome size (bp) | Genome coverage (X) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E477 | 3 | 56.6 | 4507829; 93905; 53449 | 136; 156; 287 |
| E515 | 1 | 57.9 | 4487108 | 65 |
| E603 | 1 | 57.7 | 4305928 | 516 |
| E604 | 3 | 56.6 | 4412859; 117865; 52143 | 115; 123;179 |
| E791 | 2 | 58.1 | 4349860; 166041 | 208; 239 |
| E797 | 2 | 57.9 | 4075540; 129777 | 273; 306 |
| E825 | 3 | 56.8 | 4257543; 97419; 53456 | 185; 163; 260 |
| EB13 | 3 | 56.7 | 4347023; 131190; 31203 | 214; 265; 1269 |
| EB18 | 4 | 57.2 | 4384296; 144804; 53716; 44722 | 283; 357; 552; 375 |
| E899 | 2 | 56.7 | 4340415; 53472 | 176; 284 |
| Samples | STa | Cronobacter Taxa by ST | Serotypeb |
|---|---|---|---|
| E477 | 8 | sakazakii | SO1 |
| E515 | 80 | dublinensis | DO2 |
| E603 | 81 | muytjensii | MuO2 |
| E604 | 15 | sakazakii | SO2 |
| E791 | novel | dublinensis | DO1a |
| E797 | 54 | universalis | UO1 |
| E825 | 8 | sakazakii | SO1 |
| EB13 | 1 | sakazakii | SO1 |
| EB18 | 19 | turicensis | TO1 |
| E899 | 4 | sakazakii | SO2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





