Submitted:
09 July 2024
Posted:
11 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Vector Fields That Augment the Image Features
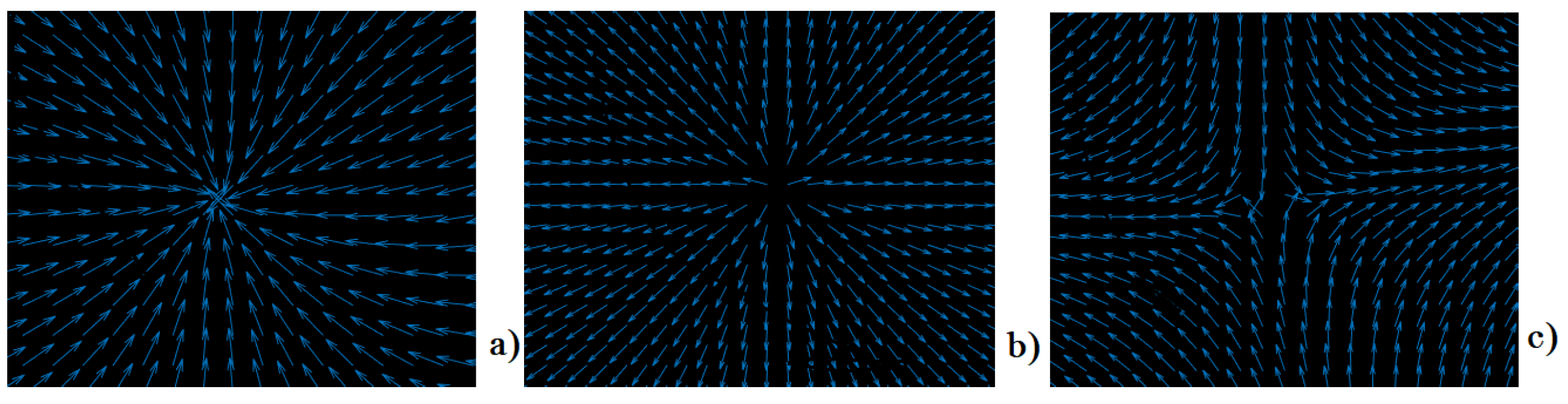
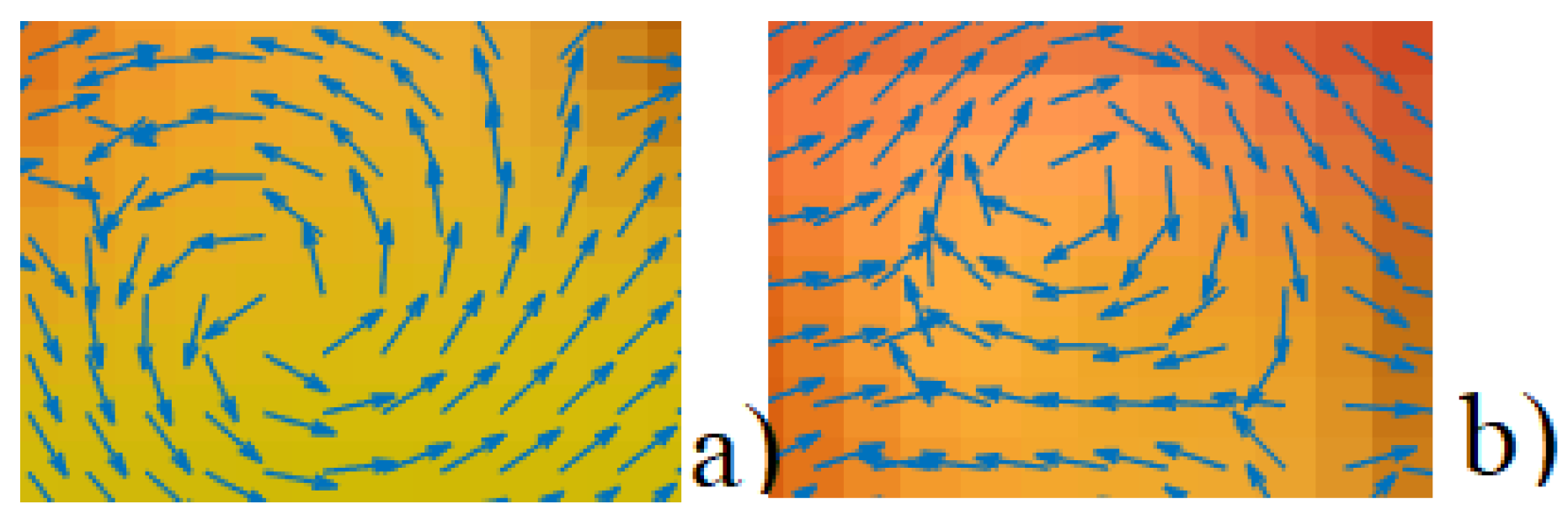
2.1. Definition of Vector Fields
2.2. Vector Fields SPs for Image Features Augmentation
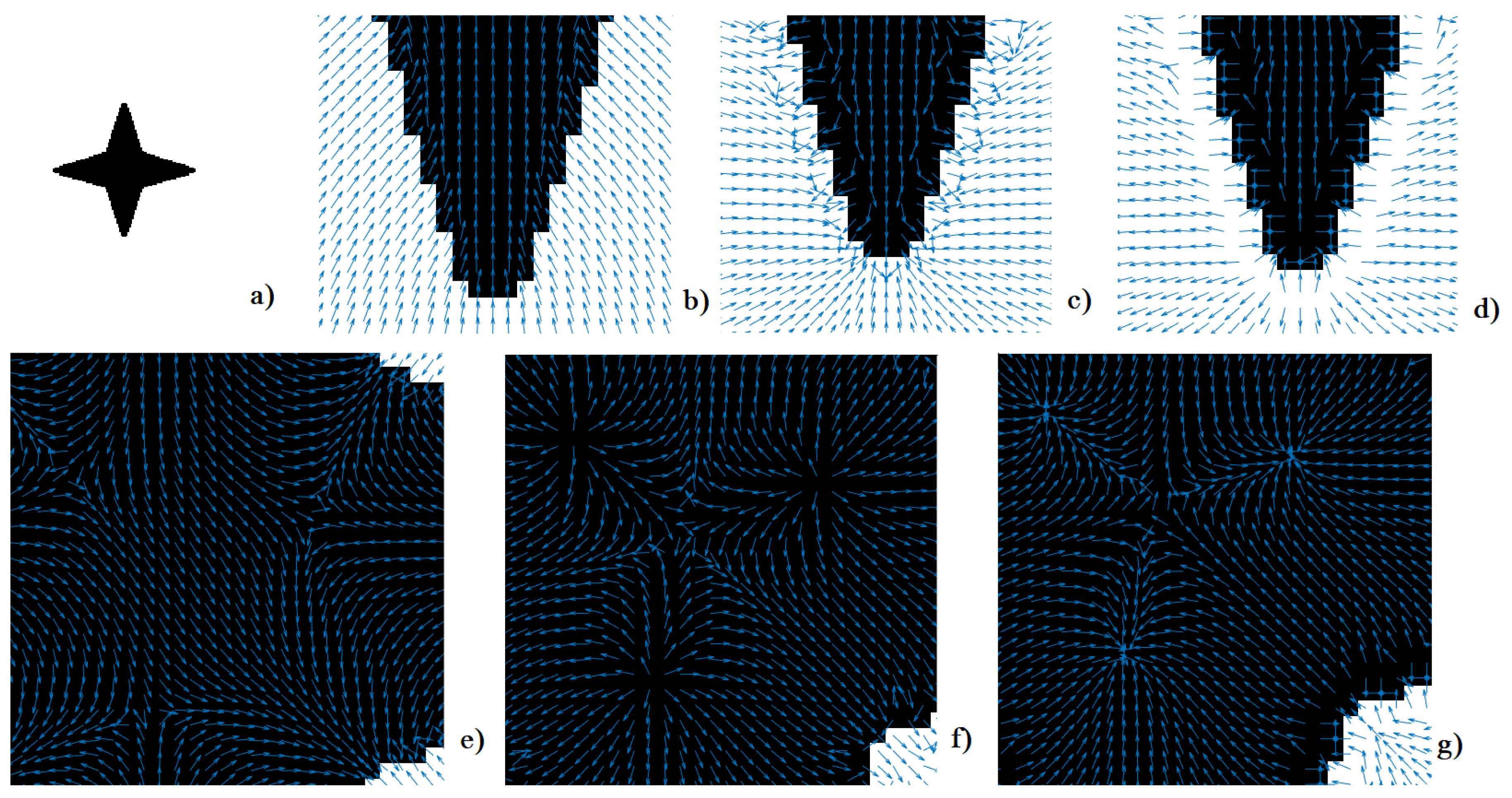
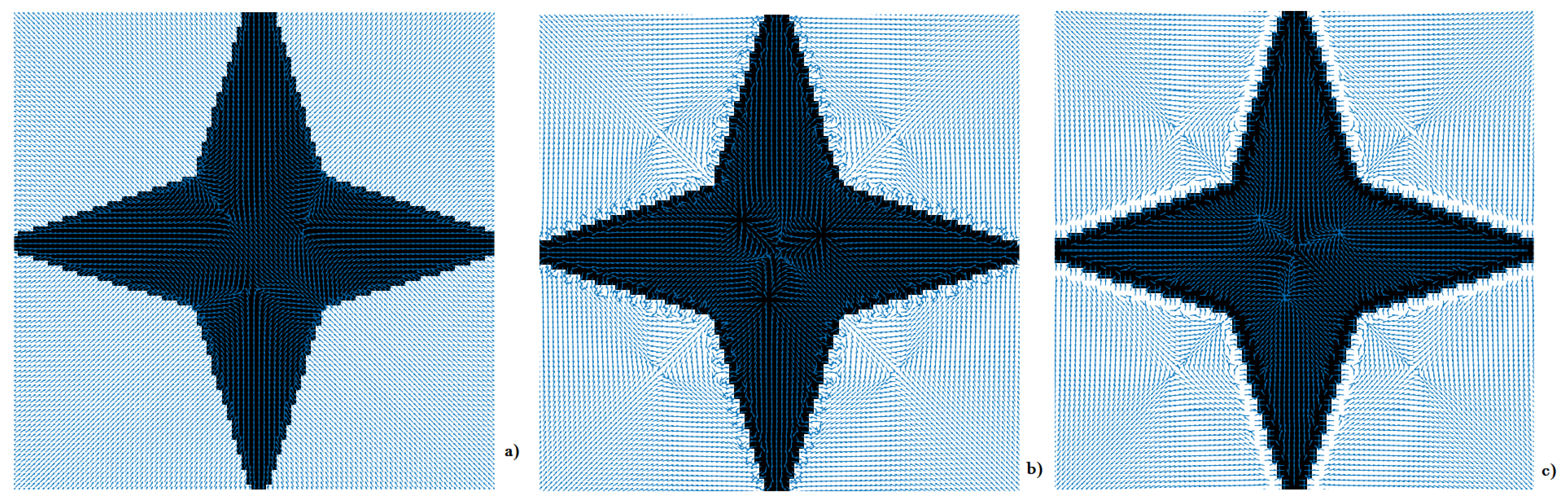
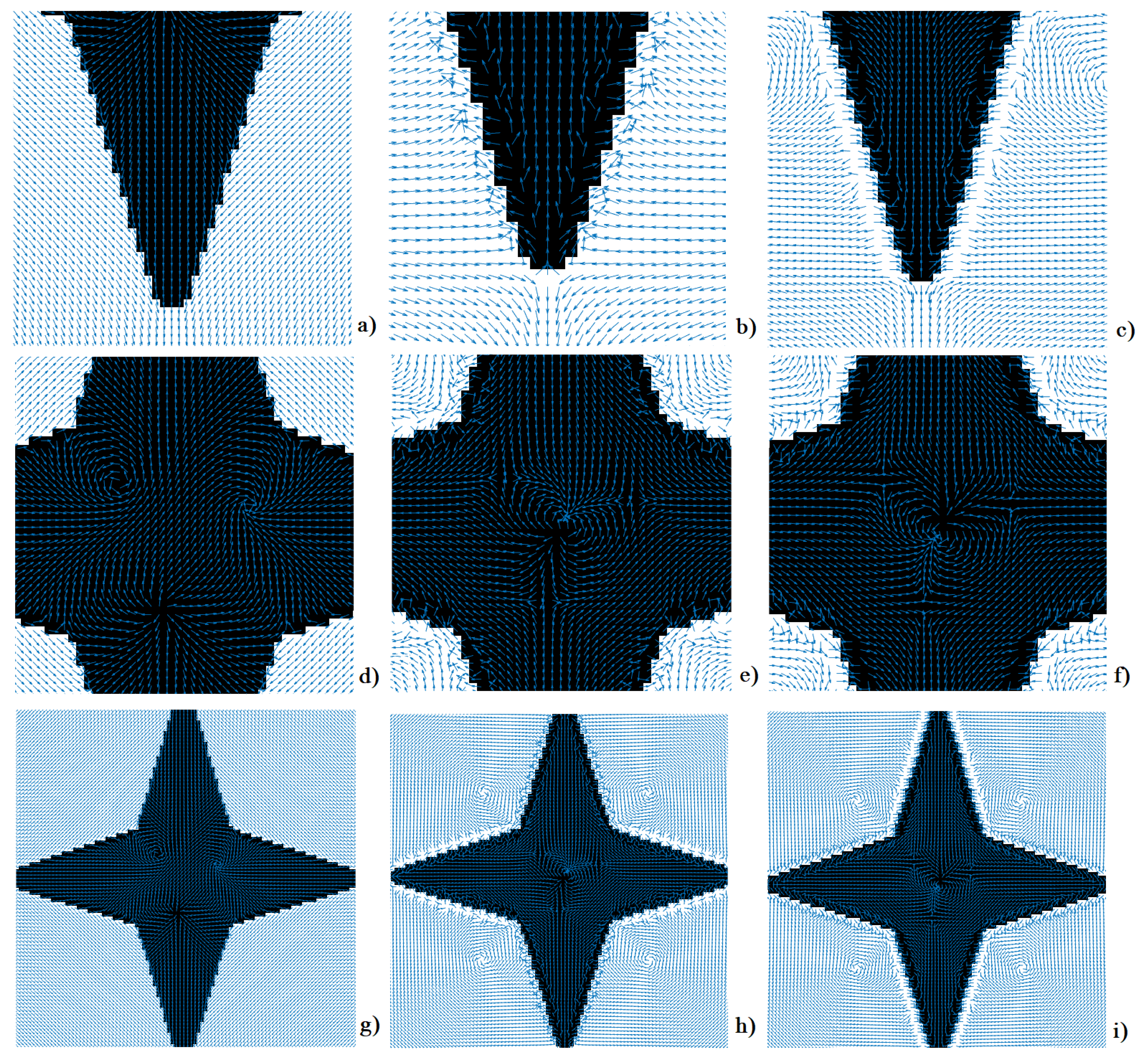
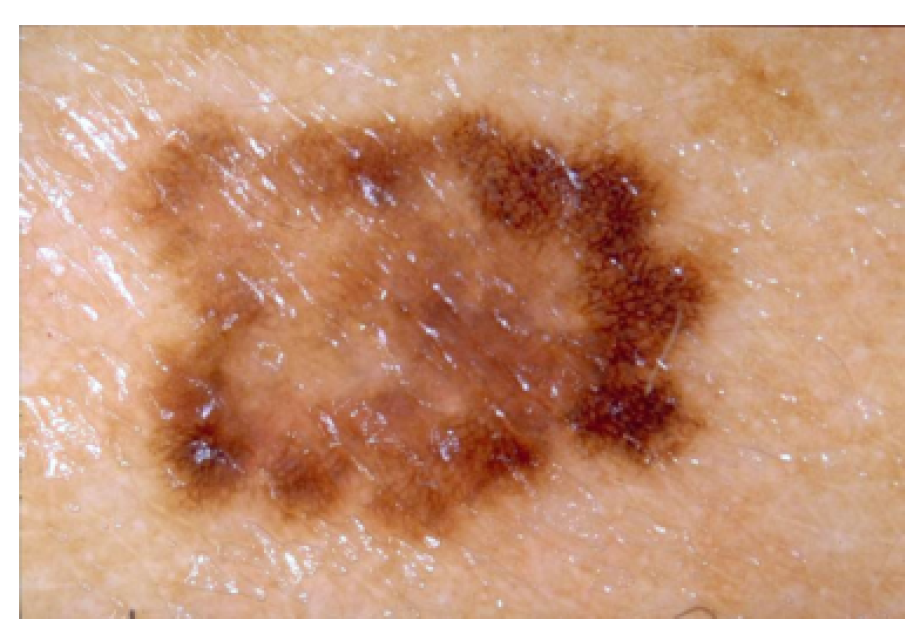
3. Repository of Image Databases with Embedded VFs
3.1. Original Datasets
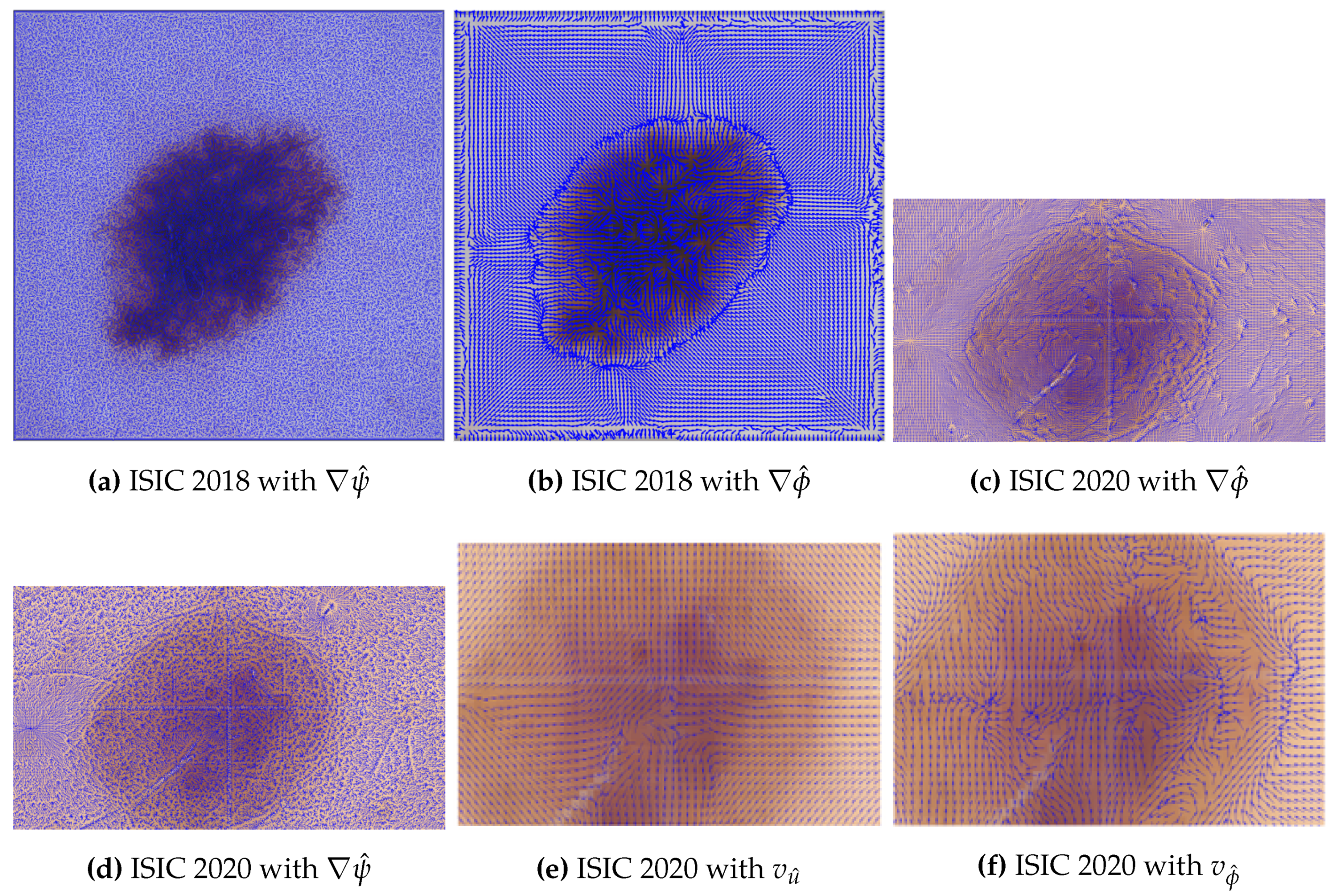
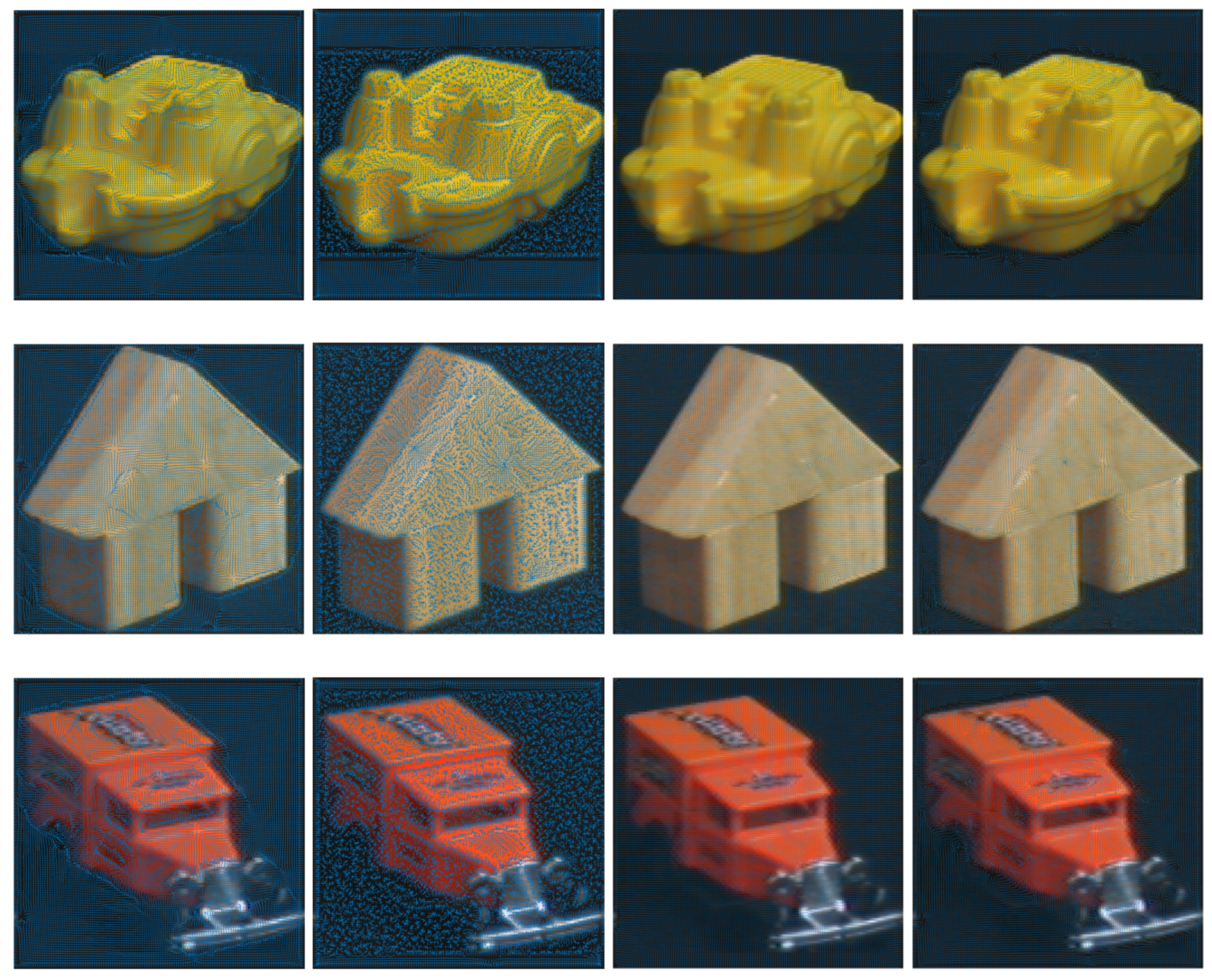
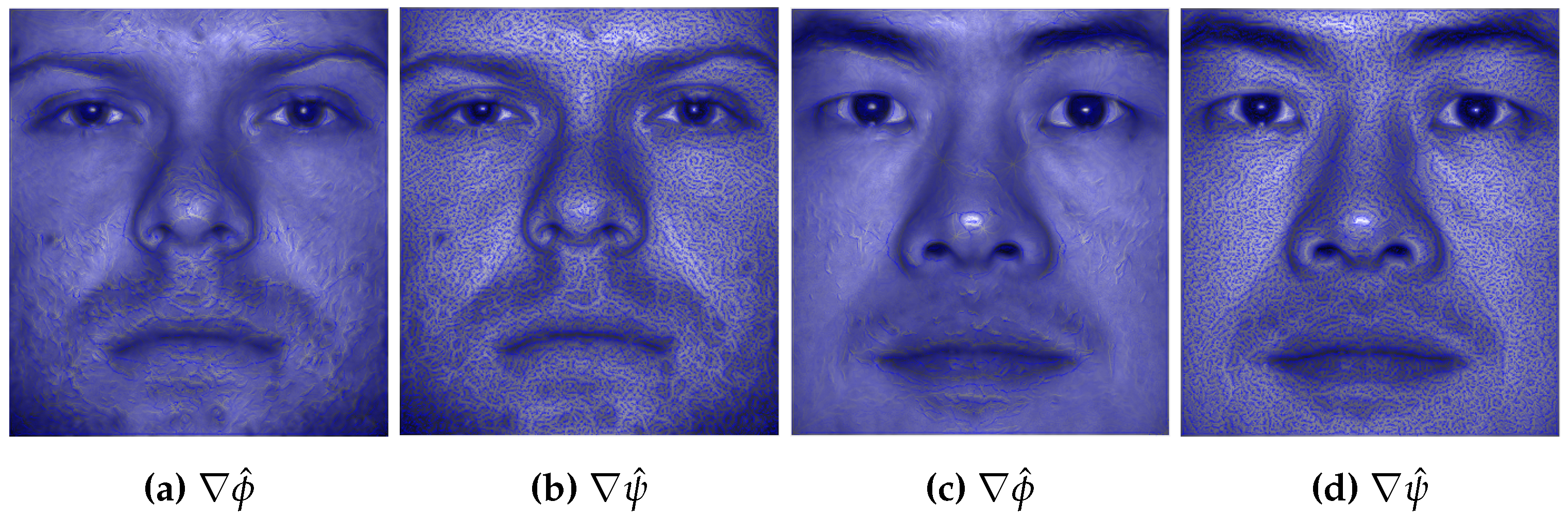
3.2. Image Datasets with Augmented Image Features
- ISIC2018 and ISIC2018
- ISIC2018 and ISIC2018
- ISIC2020 and ISIC2020
- ISIC2020 and ISIC2020 .
- ISIC2020 and ISIC2020
- ISIC2020 and ISIC2020
- COIL100 and COIL100
- ISIC2020 and ISIC2020
- ISIC2020 and ISIC2020.
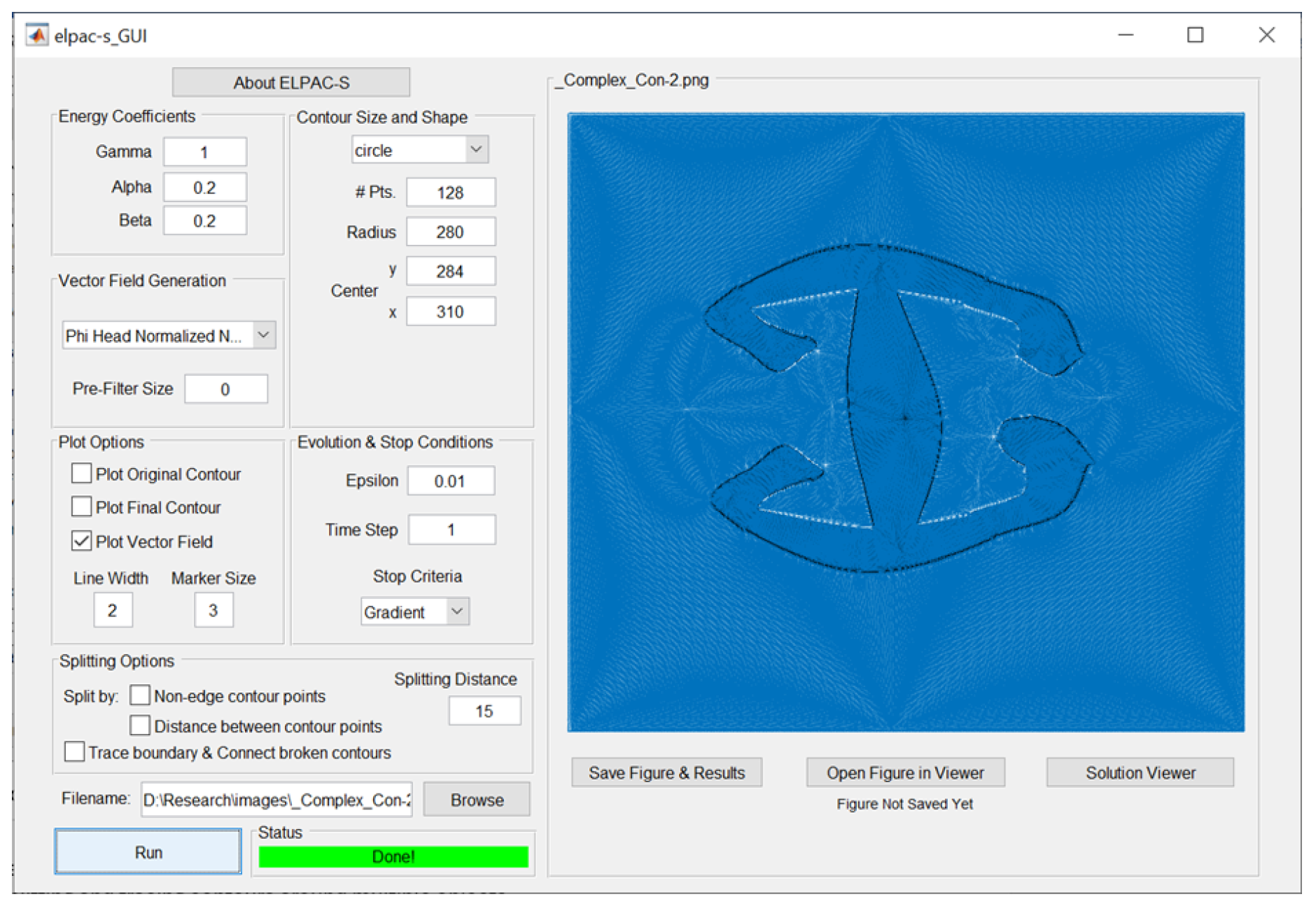
3.3. Software
- Segmentation via an evolving contour directed by VF flow. To guide the active contour, with parameters customizeable under "Contour Size and Shape", a VF should be selected from the drop-down menu under "Vector Field Generation". The recommended choice is "Norm of Grad in Poisson Eq" ;
- Splitting and tracing contours around multiple objects for full image segmentation. Such options are available under "Splitting Options";
- Selecting any of the VFs from the "Vector Field Generation" drop-down menu. The six VFs described in section 2 are at the top of the list. The first 3 of them have real shaped SPs [1], while the next 3 have real and complex shaped SPs [3]. The selected VF will be embedded into the image file chosen using the Browse option.
4. Conclusions
- Definition of the SPs locations according to the image objects, shown in Table 1
- Generalization of the mappings between the SPs shapes, as shown in Figure 8, if the six VFs are separately embedded into the same image
- Definition of the new type of image and image database named "imprint of an image and imprint of an image database in a VF".
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ML | machine learning |
| VF | vector field |
| GVF | gradient vector field |
| SP | singular points |
| CP | critical points |
| NN | neural network |
| SRWC | sparce representation wevelets classification |
| SRCQW | sparce representation classification quaternions wevelets |
| CNN | convolutional NN |
| SL | skin lesion |
References
- Sirakov, N.M., Bowden, A., Chen, M., Ngo, L.H., Luong, M. Embedding vector field into image features to enhance classification, J of Computational and Applied Mathematics 2024, V 441, 115685, ISSN 0377-0427. [CrossRef]
- Igbasanmi, O., Sirakov, N.M., Bowden, A. CNN for Efficient Objects Classification with Embedded Vector Fields, In: García Márquez, F.P., Jamil, A., Ramirez, I.S., Eken, S., Hameed, A.A. (eds), Computing, Internet of Things and Data Analytics, pp. 297-309. ICCIDA 2023. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 1145. Springer, Cham. (2024). [CrossRef]
- Igbasanmy, O. D., Sirakov, N. M. On the Usefulness of the Vector Field Singular Points Shapes for Classification, International Journal of Applied and Computational Mathematics, Springer, 10, 52. March (2024). [CrossRef]
- Tari, S., Genctav, M., From a non-local Ambrosio-Tortorelli phase field to a randomized part hierarchy tree, J. of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 49(1), 69–86, (2014). [CrossRef]
- Li, B., Acton, S.: Automatic active model initialization via Poisson inverse gradient. In: IEEE Trans. On Image Processing, vol. 17, 1406–1420, (2008). [CrossRef]
- Ma, J., Ma, Y., Zhao, J., Tian, J. Image Feature Matching via Progressive Vector Field Consensus, IEEE Signal Processing Letters, Vol. 22, No. 6, June (2015). [CrossRef]
- Legaz-Aparicio, A.G., Verdu-Monedero, R., Angulo, J. Adaptive morphological filters based on a multiple orientation vector field dependent on image local features. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 330, pp.965 - 981. (2018). [CrossRef]
- Leevy, Joffrey L and Khoshgoftaar, Taghi M and Bauder, Richard A and Seliya, Naeem. A survey on addressing high-class imbalance in big data, Journal of Big Data 2018, 5, 1, 1–30. 10.1186/s40537-018-0151-6.
- Connor Shorten and Taghi M. Khoshgoftaar. A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning, J of Big Data-Springer 2019, 6, 60. [CrossRef]
- Zhun Zhong, Liang Zheng, Guoliang Kang, Shaozi Li, and Yi Yang. Random erasing data augmentation. In Proc. of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), (2020).
- Chen, M and Sirakov, N. M. Poisson Equation Solution and its Gradient Vector Field to Geometric Features Detection, In Lecture Notes in Computer Science 11324 D. Fagan et al. Eds.; Springer Nature, 2018, pp. 36-48.
- Bowden, A., Sirakov, M. N, Active Contour Directed by the Poisson Gradient Vector Field and Edge Tracking, Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision – Springer, 63:665–680, 2021 https://rdcu.be/cflaI, (2021).
- Wei L., Eraldo R. Detecting Singular Patterns in 2-D Vector Fields Using Weighted Laurent Polynomial, Pattern Recognition, 45(11), 3912-3925, (2012).
- Zhang, E., Mischaikow, K., Turk, G. Vector field design on surfaces, ACM Trans. on Graphic, 25(4), 1294-1326, (2006). [CrossRef]
- Sosinsky, A., Vector fields on the plane, Retrieved from: http://ium.mccme.ru/postscript/s16/topology1-Lec7.pdf, (2015).
- Nene, S. A., Nayar, S. K., Murase, H., et al. Columbia object image library(coil-100), Technical Report, CUCS-006-96, (1996).
- Argenziano, G., Soyer, H., De Giorgi, V.: Dermoscopy: A Tutorial. Edra Medical Pub., New Media, Milan (2000).
- Georghiades, A. S., Belhumeur, P. N., D. J. Kriegman, P. N. From few to many: Illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose, IEEE Trans. on PAMI, 23 (6) 643-515 660. (2001). [CrossRef]
- Codella, N., Rotemberg, V., Tschandl, P., Celebi, E., Dusza, S., Gutman, D., Helba, B., Kalloo, A., Liopyris, K., Marchetti, M., Kittler, H., Halpern, A. Skin Lesion Analysis Toward Melanoma Detection 2018: A Challenge Hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC) 2018; https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.03368, (2018).
- International Skin Imaging Collaboration. SIIM-ISIC 2020 Challenge Dataset. Internat. Skin Imaging Collaboration.(accessed May, 2023). [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, K., Bouix, S., Tannenbaum, S. W. Hamilton–Jacobi skeletons, Int. J. Comput. Vis. 48 (2002) 215, em, (2002). [CrossRef]
- Bina, T., Yib, L. CNN-based flow field feature visualization method. Int. J. Performability Eng. 14(3), 434–444, (2018). [CrossRef]
- digits-MNIST image database, http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/, last visited July (2024).

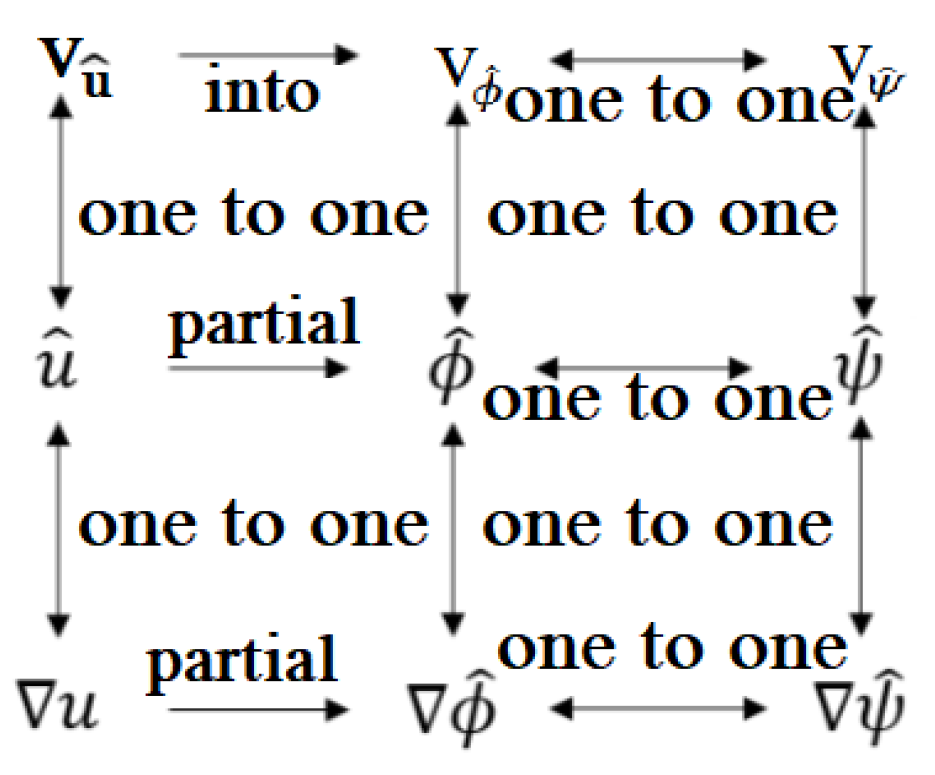
| VF | SP/Location | SP/Location | SP/Location |
| saddle / core | sinking/concavity corners | ||
| , | saddle/core, branches, concavities | sink/convex vertices, edges | spring/core |
| saddle/core, branches, concavities | sink/core | spring/edges, convex vertices | |
| saddle/core | sink/ core | spring/core; | |
| spiral (in and out)/core | orbits/homogenous regions | ||
| , | saddle/core, convex vertices | sink/core, edges, branches | spring/core, edges, branches |
| , | spiral (in and out)/core, concavities, branches | orbits/homogenous regions |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





