Submitted:
05 July 2024
Posted:
10 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
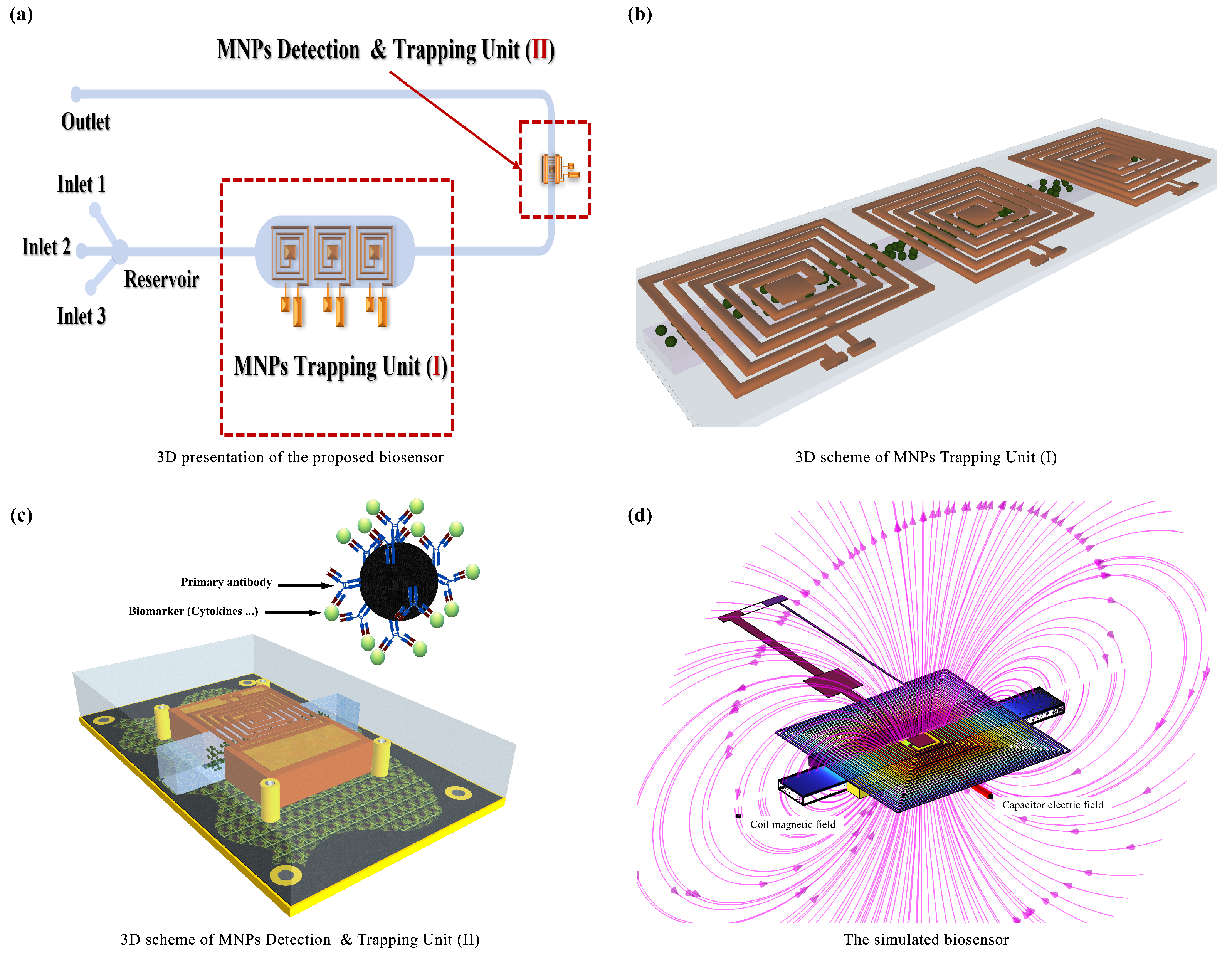
2. Overview
2.1. Problem Formulation
- Magnetic Field Domain: This domain focuses on calculating the magnetic field distribution generated by the coils. Accurate prediction of the magnetic field is crucial for understanding how MNPs are manipulated and trapped within the microfluidic channels.
- Fluid Dynamics Domain: This domain simulates the behavior of the biofluid (sweat) within the microfluidic channels, considering the complex interactions between the fluid, MNPs, and channel walls. This simulation helps optimize channel geometry and flow conditions for efficient biomarker capture.
- Electrical Domain: This domain analyzes the electrical behavior of the system, particularly the capacitive response resulting from the presence of MNPs within the dielectric domain. Precise modeling of the electrical properties ensures accurate biomarker quantification.
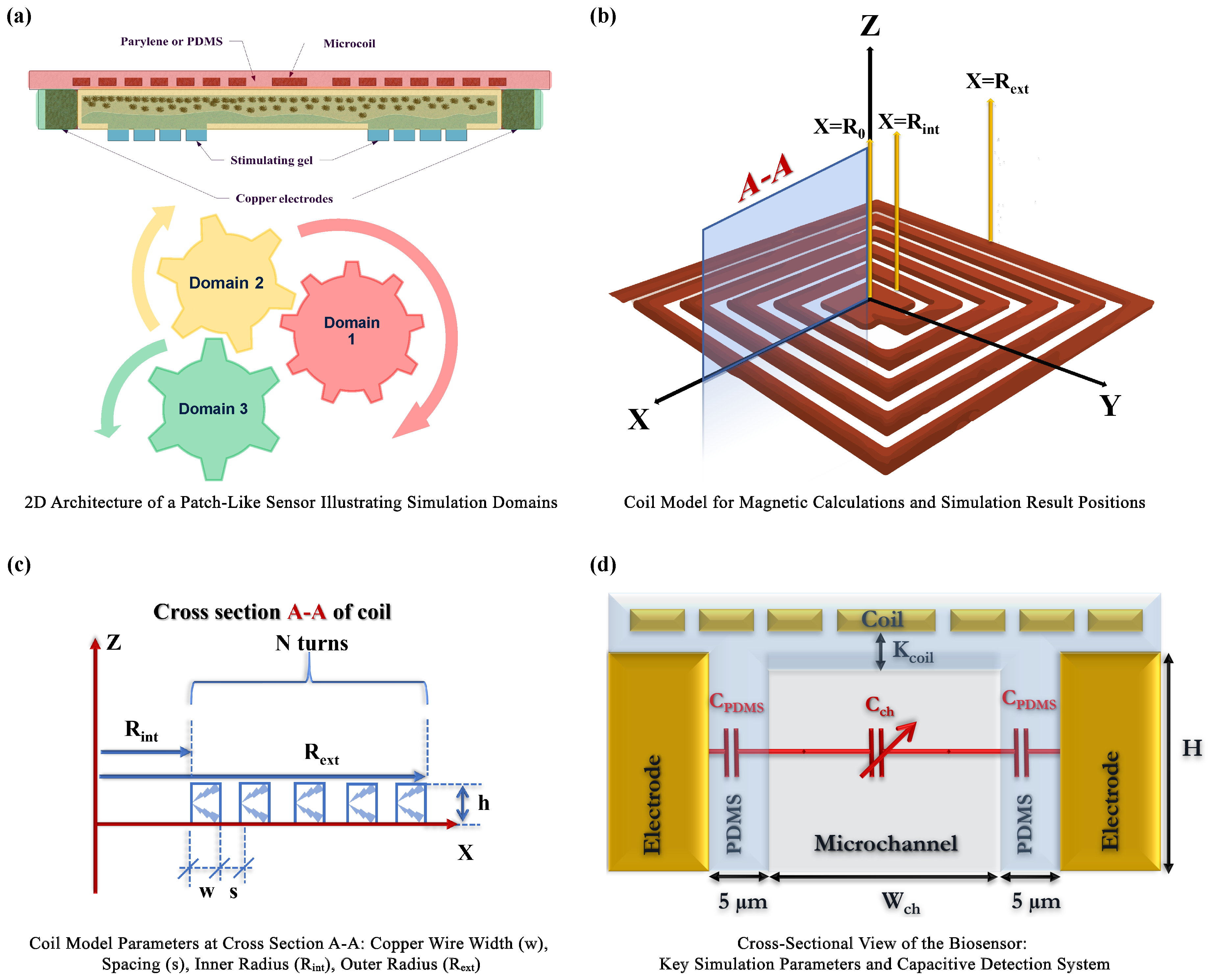
2.2. Physics and Mathematical Framework of the Biosensor
2.3. Implementation Details
- AC/DC Module for Electromagnetic Field Simulation: This module was employed to rigorously simulate the electromagnetic landscape within the biosensor. By applying Maxwell’s equations, we accurately characterized both the magnetic fields generated by the coils and the electric fields across the electrodes. This precise simulation of electromagnetic fields is fundamental to understanding their interplay with biological media, ultimately determining the efficacy of MNP detection.
- CFD Module for Fluid Dynamics Analysis: To model the intricate flow of biofluids, particularly sweat, through the microchannels, we harnessed the Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Module. By solving the Navier-Stokes equations, we captured the nuances of fluid behavior, including velocity profiles, and pressure gradients. This comprehensive understanding of fluid dynamics proved essential for optimizing microchannel design and ensuring efficient biomarker and MNP transport.
- Particle Tracing Module for Nanoparticle Dynamics Investigation: The Particle Tracing Module enabled us to simulate the dynamic behavior of magnetic nanoparticles within the microfluidic environment. By considering the forces acting upon the MNPs, including magnetic forces and viscous drag, we predicted their trajectories and interactions with the surrounding fluid and channel walls. This analysis was pivotal for understanding the mechanisms underlying MNP capture, concentration, and ultimately, biomarker detection.
3. Results and Discussion
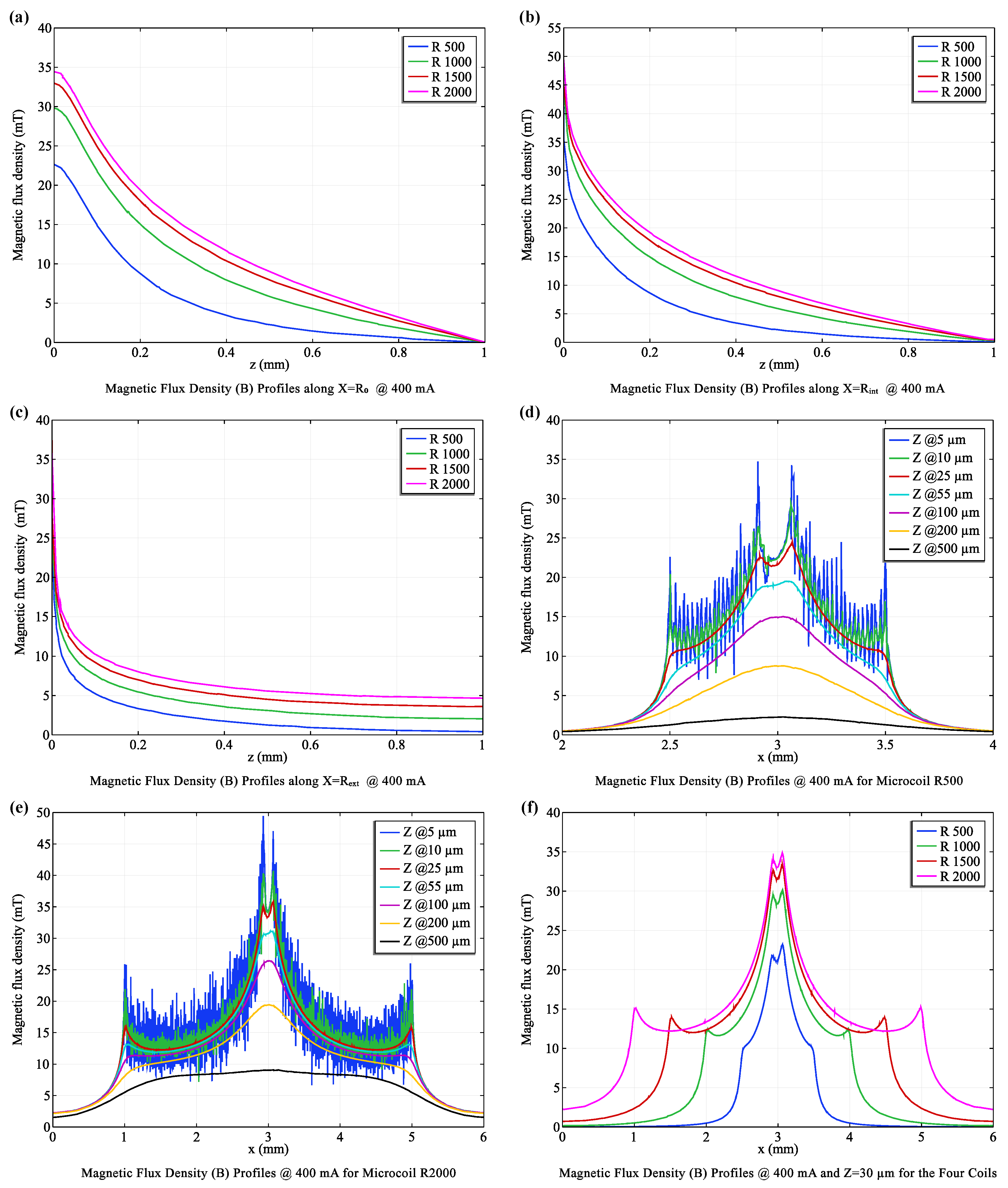
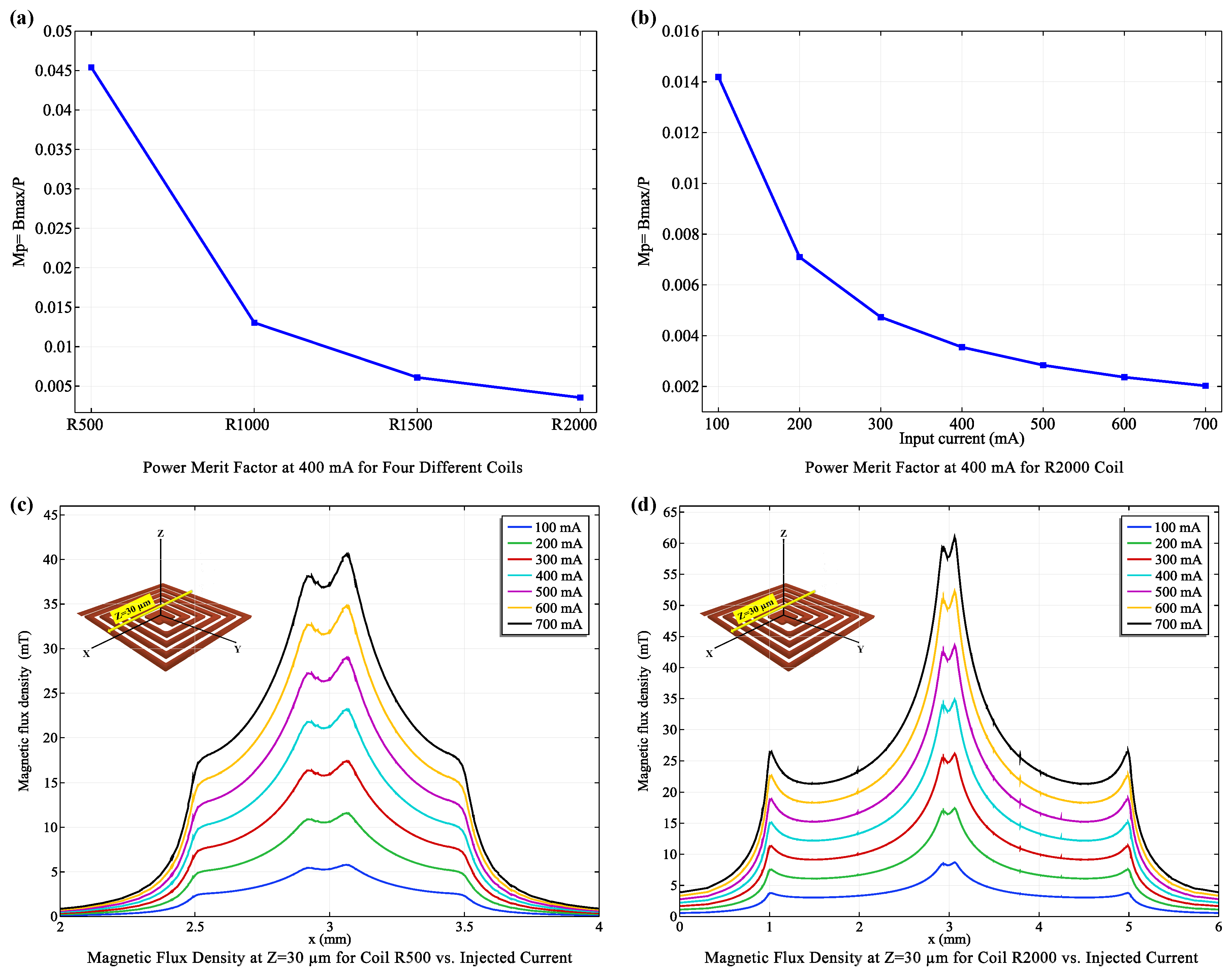
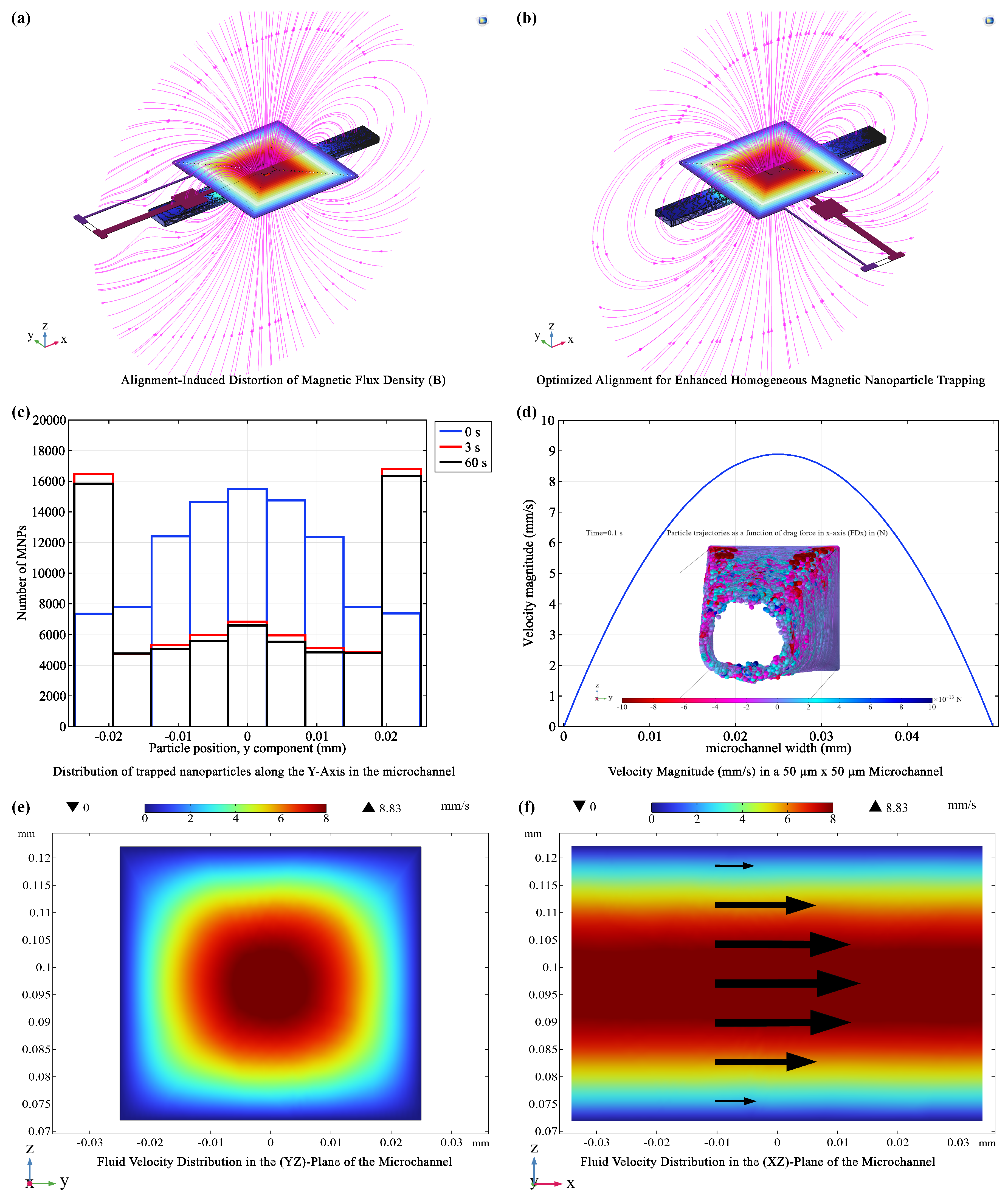
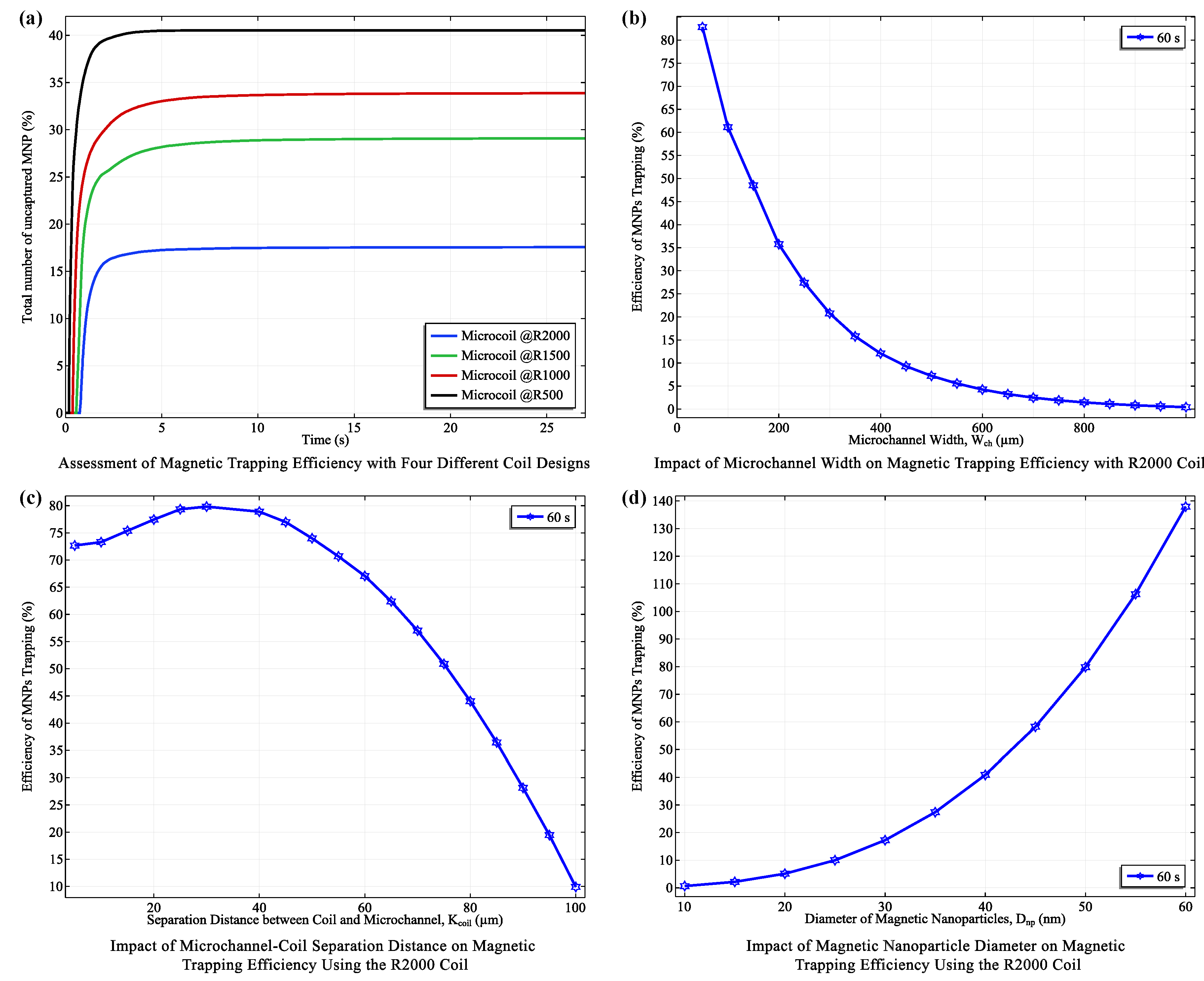
3.1. Optimizing coil Configurations: Balancing Efficiency and Functionality
- X = : Directly above the coil center, the R2000 coil (with more turns) generated a significantly stronger (20.58 mT) compared to the R500 coil (10.05 mT), demonstrating the influence of coil turns on field strength.
- X = : At an intermediate distance, this trend persisted, with the R2000 coil maintaining a higher (21.92 mT) than the R500 coil (11.58 mT).
- X = : Even at the furthest distance, the R2000 coil produced a stronger (9.42 mT) compared to the R500 coil (5.19 mT).
3.2. Fluid Dynamics and Magnetic Trapping Performance in Microfluidic Platform
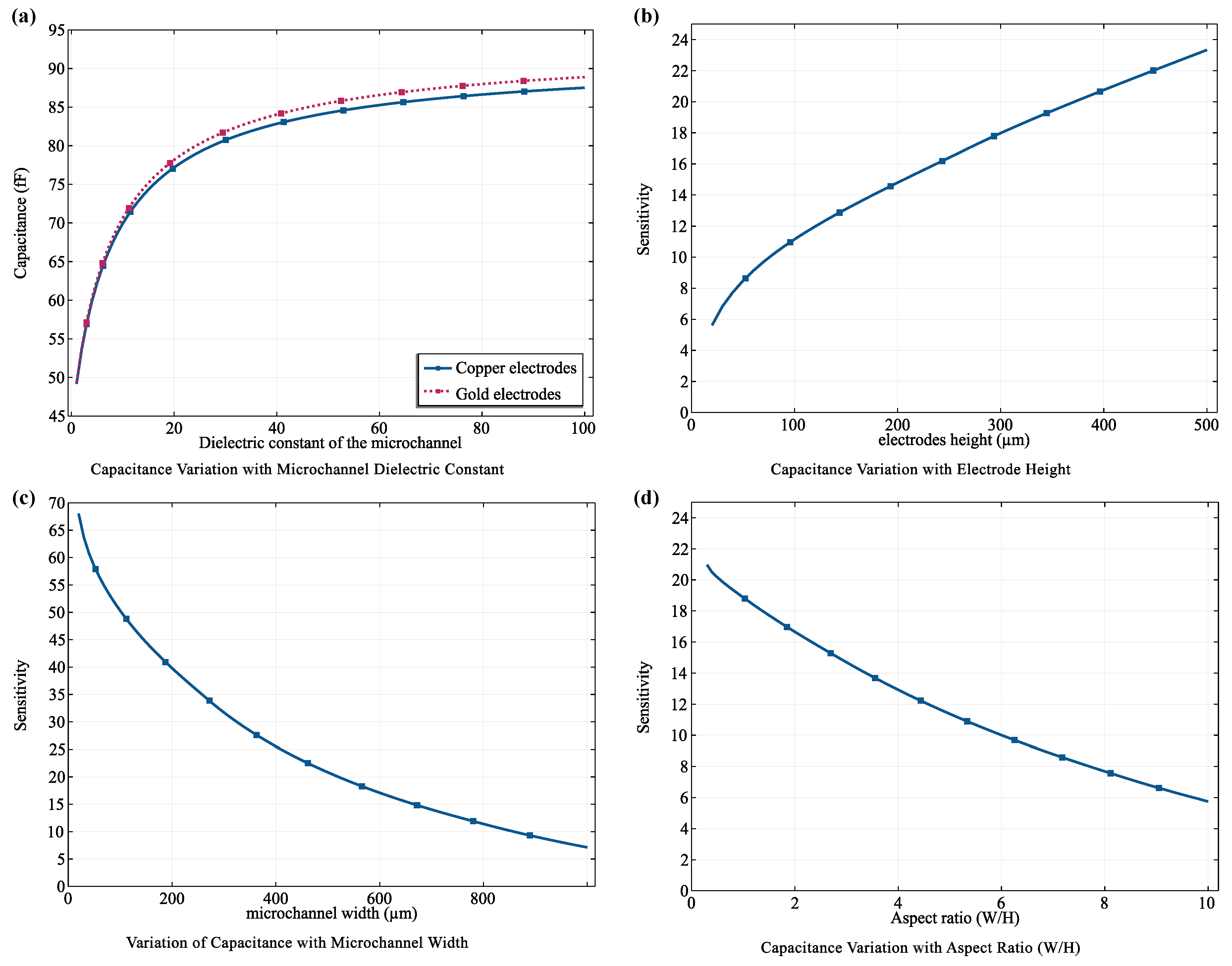
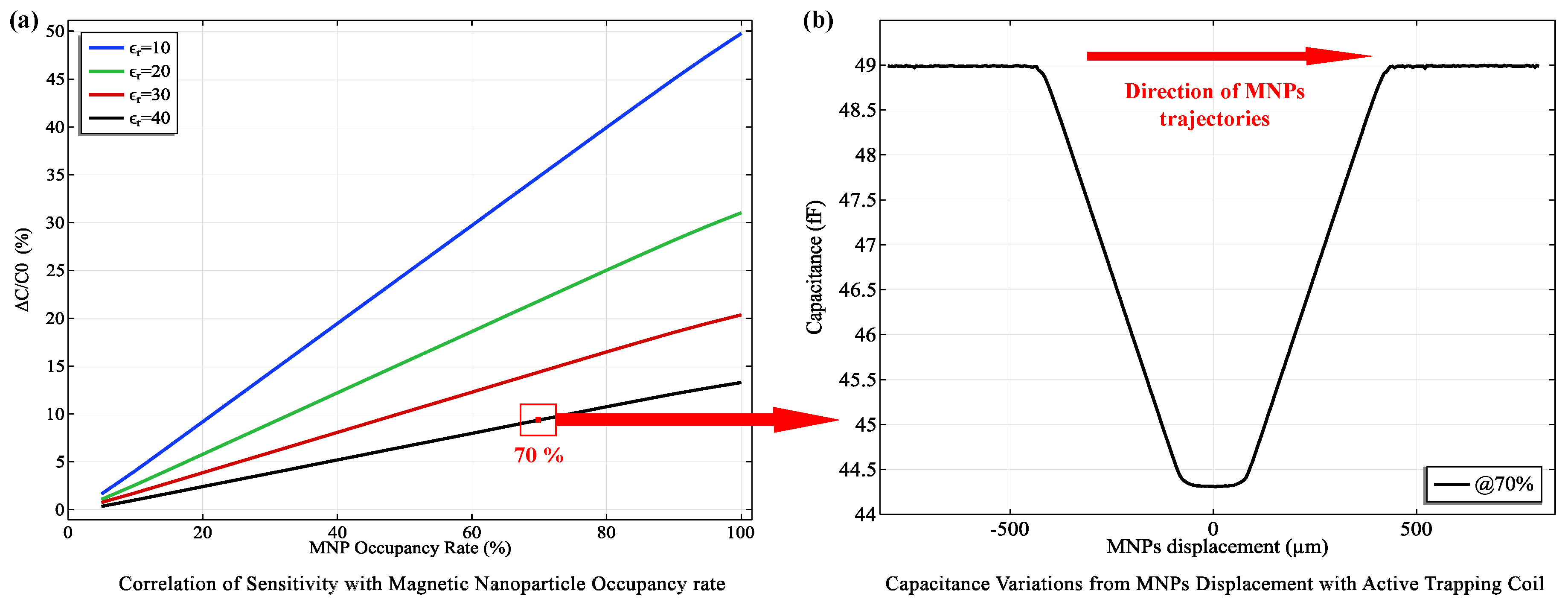
3.3. Capacitive Sensing Performance and Implications
4. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Organization, W.H. WHO announces COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic, 2020.
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. COVID-19 Map. Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center, 2024. Accessed: 2024-20-04.
- Cho, B.; Lee, S.H.; Song, J.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Feng, J.; Hong, S.; Song, M.; Kim, W.; Lee, J.; Bang, D. Nanophotonic cell lysis and polymerase chain reaction with gravity-driven cell enrichment for rapid detection of pathogens. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13866–13874.
- Tombuloglu, H.; Sabit, H.; Al-Khallaf, H.; Kabanja, J.H.; Alsaeed, M.; Al-Saleh, N.; Al-Suhaimi, E. Multiplex real-time RT-PCR method for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 by targeting viral N, RdRP and human RP genes. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 1–10.
- Prabowo, B.A.; Cabral, P.D.; Freitas, P.; Fernandes, E. The challenges of developing biosensors for clinical assessment: a review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 299.
- Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, J. Biochips under COVID-19: a new stage of well-grounded development and accelerated translation. Science Bulletin 2022.
- Bontekoe, E.; Brailovsky, Y.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Bontekoe, J.; Siddiqui, F.; Newman, J.; Iqbal, O.; Reed, T.; Fareed, J.; Darki, A. Upregulation of inflammatory cytokines in pulmonary embolism using biochip-array profiling. Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis 2021, 27, 10760296211013107.
- Noushin, T.; Tabassum, S. WRRIST: a wearable, rapid, and real-time infection screening tool for dual-mode detection of inflammatory biomarkers in sweat. In Proceedings of the Microfluidics, BioMEMS, and Medical Microsystems XX. SPIE, 2022, Vol. 11955, p. 1195502.
- Chen, W.L.; Jayan, M.; Kwon, J.S.; Chuang, H.S. Facile open-well immunofluorescence enhancement with coplanar-electrodes-enabled optoelectrokinetics and magnetic particles. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2021, 193, 113527.
- Mohammadi, M.H.; Mulder, S.; Khashayar, P.; Kalbasi, A.; Azimzadeh, M.; Aref, A.R. Saliva Lab-on-a-chip biosensors: Recent novel ideas and applications in disease detection. Microchemical Journal 2021, 168, 106506.
- Chen, M.; Liao, T.; Zeng, L.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, G. Plasmonic Gold Chip for Multiplexed Detection of Ovarian Cancer Biomarker in Urine. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities 2022, 38, 935–940.
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Qiu, J.; Gao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, L. Ultrasensitive, high-throughput, and rapid simultaneous detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigens and IgG/IgM antibodies within 10 min through an immunoassay biochip. Microchimica Acta 2021, 188, 1–15.
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Dou, Y.; Su, J.; Shi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Fan, C. A nano-integrated microfluidic biochip for enzyme-based point-of-care detection of creatinine. Chemical Communications 2021, 57, 4726–4729.
- Burdó-Masferrer, M.; Díaz-González, M.; Sanchis, A.; Calleja, Á.; Marco, M.P.; Fernández-Sánchez, C.; Baldi, A. Compact Microfluidic Platform with LED Light-Actuated Valves for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Automation. Biosensors 2022, 12, 280.
- Xie, X.; Gong, M.; Zhang, Z.; Dou, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Du, Y.; Xu, X. Optimization of an electrical impedance flow cytometry system and analysis of submicron particles and bacteria. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2022, 360, 131432.
- Haghayegh, F.; Salahandish, R.; Zare, A.; Khalghollah, M.; Sanati-Nezhad, A. Immuno-biosensor on a chip: a self-powered microfluidic-based electrochemical biosensing platform for point-of-care quantification of proteins. Lab on a Chip 2022, 22, 108–120.
- Chiu, W.H.; Kong, W.Y.; Chueh, Y.H.; Wen, J.W.; Tsai, C.M.; Hong, C.; Chen, P.Y.; Ko, C.H. Using an ultra-compact optical system to improve lateral flow immunoassay results quantitatively. Heliyon 2022, p. e12116.
- Narita, F.; Wang, Z.; Kurita, H.; Li, Z.; Shi, Y.; Jia, Y.; Soutis, C. A review of piezoelectric and magnetostrictive biosensor materials for detection of COVID-19 and other viruses. Advanced Materials 2021, 33, 2005448.
- Cunha, A.P.; Henriques, R.; Cardoso, S.; Freitas, P.P.; Carvalho, C.M. Rapid and multiplex detection of nosocomial pathogens on a phage-based magnetoresistive lab-on-chip platform. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 2021, 118, 3164–3174.
- Giouroudi, I.; Kokkinis, G. Recent advances in magnetic microfluidic biosensors. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 171.
- Uddin, S.M.; Sayad, A.; Chan, J.; Skafidas, E.; Kwan, P. Design and Optimisation of Elliptical-Shaped Planar Hall Sensor for Biomedical Applications. Biosensors 2022, 12, 108.
- Salvador, M.; Marqués-Fernández, J.L.; Bunge, A.; Martínez-García, J.C.; Turcu, R.; Peddis, D.; García-Suárez, M.d.M.; Cima-Cabal, M.D.; Rivas, M. Magnetic Nanoclusters Increase the Sensitivity of Lateral Flow Immunoassays for Protein Detection: Application to Pneumolysin as a Biomarker for Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2044.
- Sun, X.c.; Lei, C.; Guo, L.; Zhou, Y. Sandwich immunoassay for the prostate specific antigen using a micro-fluxgate and magnetic bead labels. Microchimica Acta 2016, 183, 2385–2393.
- Chugh, V.K.; Wu, K.; Nair, A.; di Girolamo, A.; Schealler, J.; Vuong, H.; Davies, W.; Wall, A.; Whitely, E.; Saha, R.; et al. Magnetic Particle Spectroscopy-Based Handheld Device for Wash-Free, Easy-to-Use, and Solution-Phase Immunoassay Applications. In Proceedings of the Frontiers in Biomedical Devices. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2020, Vol. 83549, p. V001T10A011.
- Gao, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhang, L.; Lian, J.; Tao, W.; Song, C.; Tang, J.; Shi, S.; Gao, Y. Multiplex measurement of twelve tumor markers using a GMR multi-biomarker immunoassay biosensor. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2019, 123, 204–210.
- Couniot, N.; Afzalian, A.; Van Overstraeten-Schlögel, N.; Francis, L.; Flandre, D. Capacitive biosensing of bacterial cells: Analytical model and numerical simulations. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2015, 211, 428–438.
- Wang, L.; Veselinovic, M.; Yang, L.; Geiss, B.J.; Dandy, D.S.; Chen, T. A sensitive DNA capacitive biosensor using interdigitated electrodes. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2017, 87, 646–653.
- Weaver, S.; Mohammadi, M.H.; Nakatsuka, N. Aptamer-functionalized capacitive biosensors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2023, 224, 115014.
- Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Ye, R.; Yan, B.; Zhou, X.; Xu, W.; Guo, J. Capacitive biosensors for label-free and ultrasensitive detection of biomarkers. Talanta 2023, p. 124951.
- Liu, D.; Zhou, L.; Huang, L.; Zuo, Z.; Ho, V.; Jin, L.; Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Qian, D.; et al. Microfluidic integrated capacitive biosensor for C-reactive protein label-free and real-time detection. Analyst 2021, 146, 5380–5388.
- Subramani, I.G.; Ayub, R.; Gopinath, S.C.; Perumal, V.; Fathil, M.; Arshad, M.M. Lectin bioreceptor approach in capacitive biosensor for prostate-specific membrane antigen detection in diagnosing prostate cancer. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers 2021, 120, 9–16.
- Furlani, E.P. Permanent magnet and electromechanical devices: materials, analysis, and applications; Academic Press: New York, 2001.
- Bird, R.B.; Curtiss, C.F.; Armstrong, R.C.; Hassager, O. Dynamics of polymeric liquids, volume 2: Kinetic theory; Wiley: New York, 1987.
- Jones, T.B. Dielectrophoresis and magnetophoresis. Electromechanics of particles 1995, pp. 34–82.
- Kirby, B.J. Micro-and nanoscale fluid mechanics: transport in microfluidic devices; Cambridge University Press: New York, 2010.
- Mark, J.E. Polymer data handbook; Oxford University Press, 2009.
- Ammar, M.; Smadja, C.; Phuong Ly, G.T.; Tandjigora, D.; Vigneron, J.; Etcheberry, A.; Taverna, M.; Dufour-Gergam, E. Chemical engineering of self-assembled Alzheimer’s peptide on a silanized silicon surface. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5863–5872.
- Lefebvre, O.; Cao, H.H.; Cortés Francisco, M.; Woytasik, M.; Dufour-Gergam, E.; Ammar, M.; Martincic, E. Reusable embedded microcoils for magnetic nano-beads trapping in microfluidics: magnetic simulation and experiments. Micromachines 2020, 11, 257.
- Lefebvre, O.; Smadja, C.; Martincic, E.; Woytasik, M.; Ammar, M. Integration of microcoils for on-chip immunosensors based on magnetic nanoparticles capture. Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research 2017, 13, 115–121.
- Cao, H.H. The fabrication process of microfluidic devices integrating microcoils for trapping magnetic nano particles for biological applications. Theses, Université Paris Sud - Paris XI, 2015.

| Parameter Description | Symbol | Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| Current in the coil | 100 mA – 700 mA | |
| Electrode height | H | 20 m – 500 m |
| Nanoparticle diameter | 10 nm – 60 nm | |
| Coil-to-channel separation | 5 m – 100 m | |
| Microchannel width | 50 m – 1000 m | |
| Microchannel height | 50 m | |
| Electrodes Voltage | U | 5V |
| coil wire height | 10 m | |
| coil wire width | 10 m | |
| Fluid flow rate | Q | 1 l/min |
| Material Property | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Copper Electrical conductivity | 59.6 MS/m (1) | |
| Gold Electrical conductivity | 41 MS/m (1) | |
| Density of sweat | 1000 kg/m3 (2) | |
| Dynamic viscosity of sweat | (3) | |
| PDMS Electrical conductivity | (4) | |
| PDMS Relative permittivity | 2.7 (4) | |
| Permeability of magnetite nanoparticles | 5000 (5) | |
| Dielectric constant of MNPs | 10 - 40 (6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





