Submitted:
05 July 2024
Posted:
09 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Treatments
2.3. In Vitro Dynamic Gastric Digestion
2.4. Microstructure Characterization
2.5. Determination of Gastric Emptying Rate
2.6. Determination of Protein Hydrolysis Degree
2.7. SDS-PAGE Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
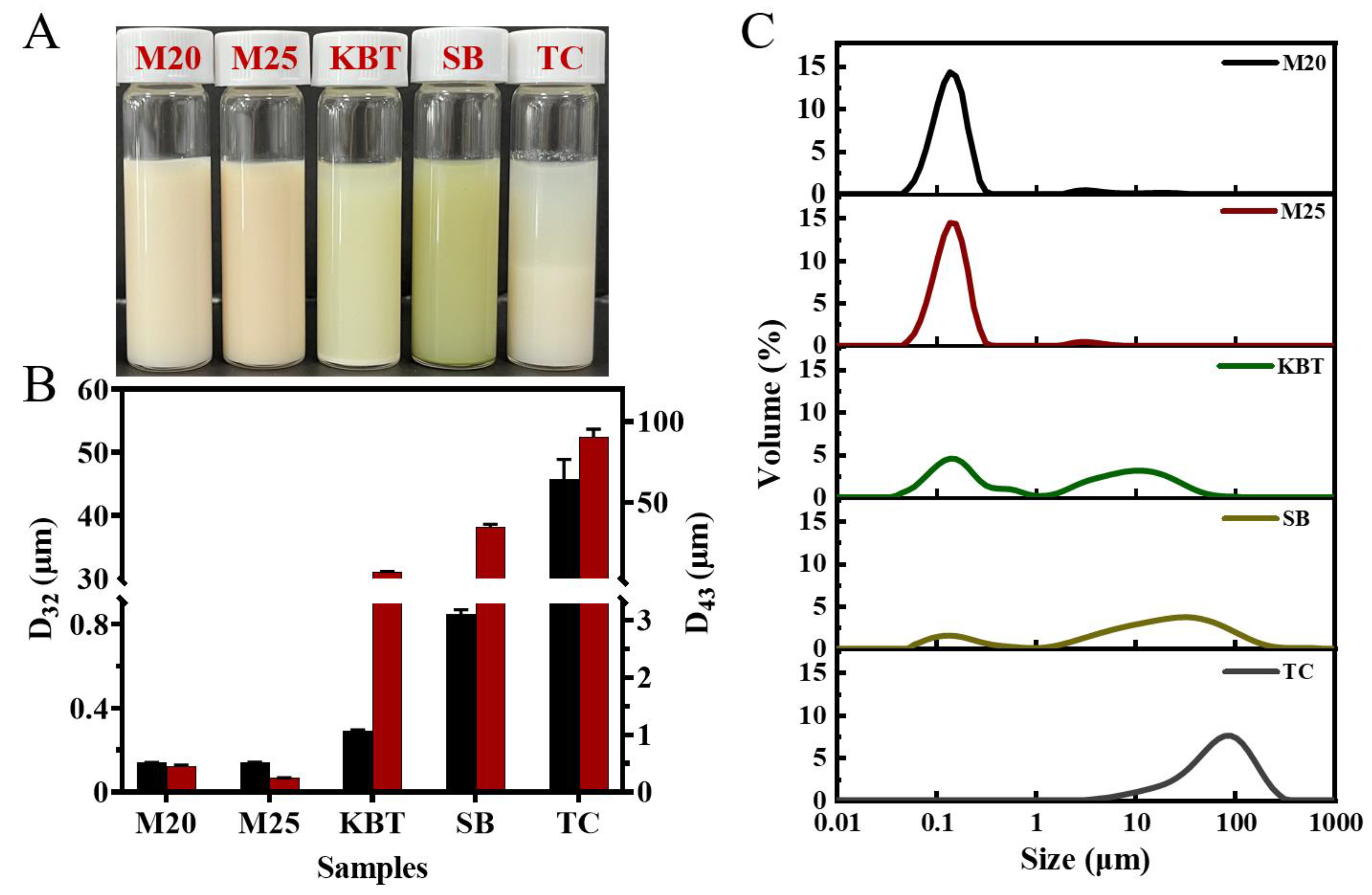
3.1. Physical Statement and Particle Size of Commercial Protein Sports Supplements
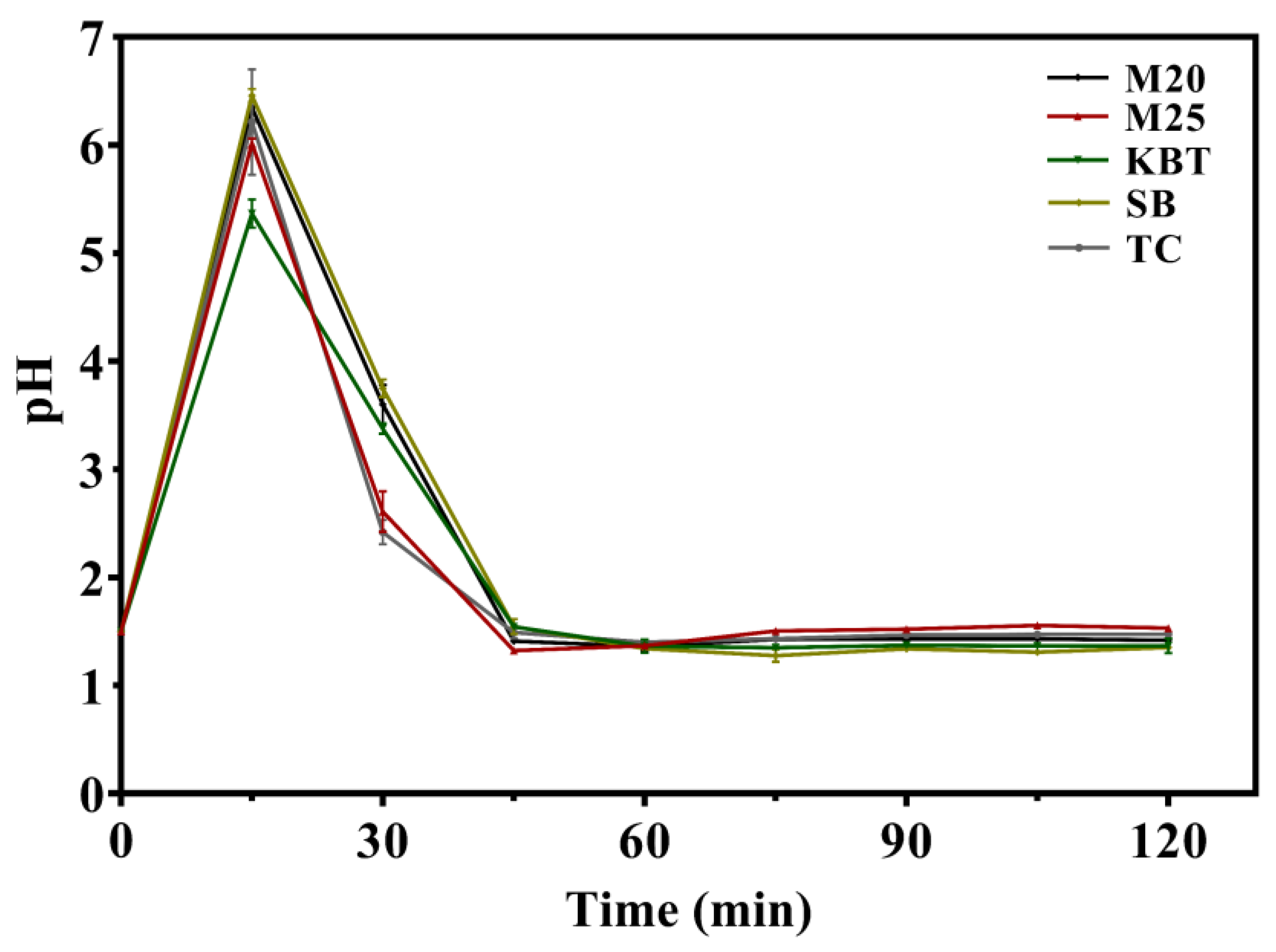
3.2. Variation of pH Values during Gastric Digestion
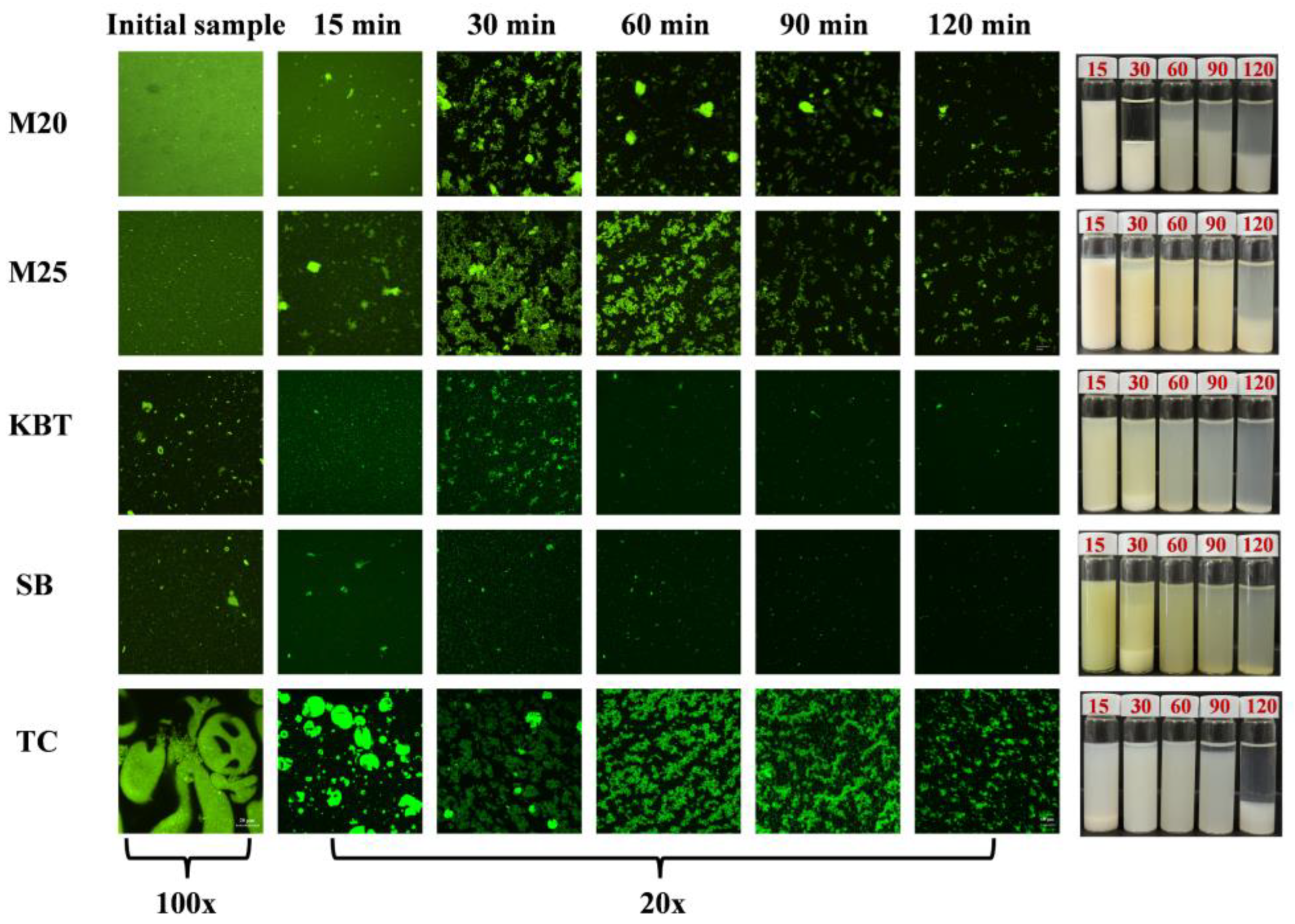
3.3. Microstructure Change of Protein Digesta during Gastric Digestion
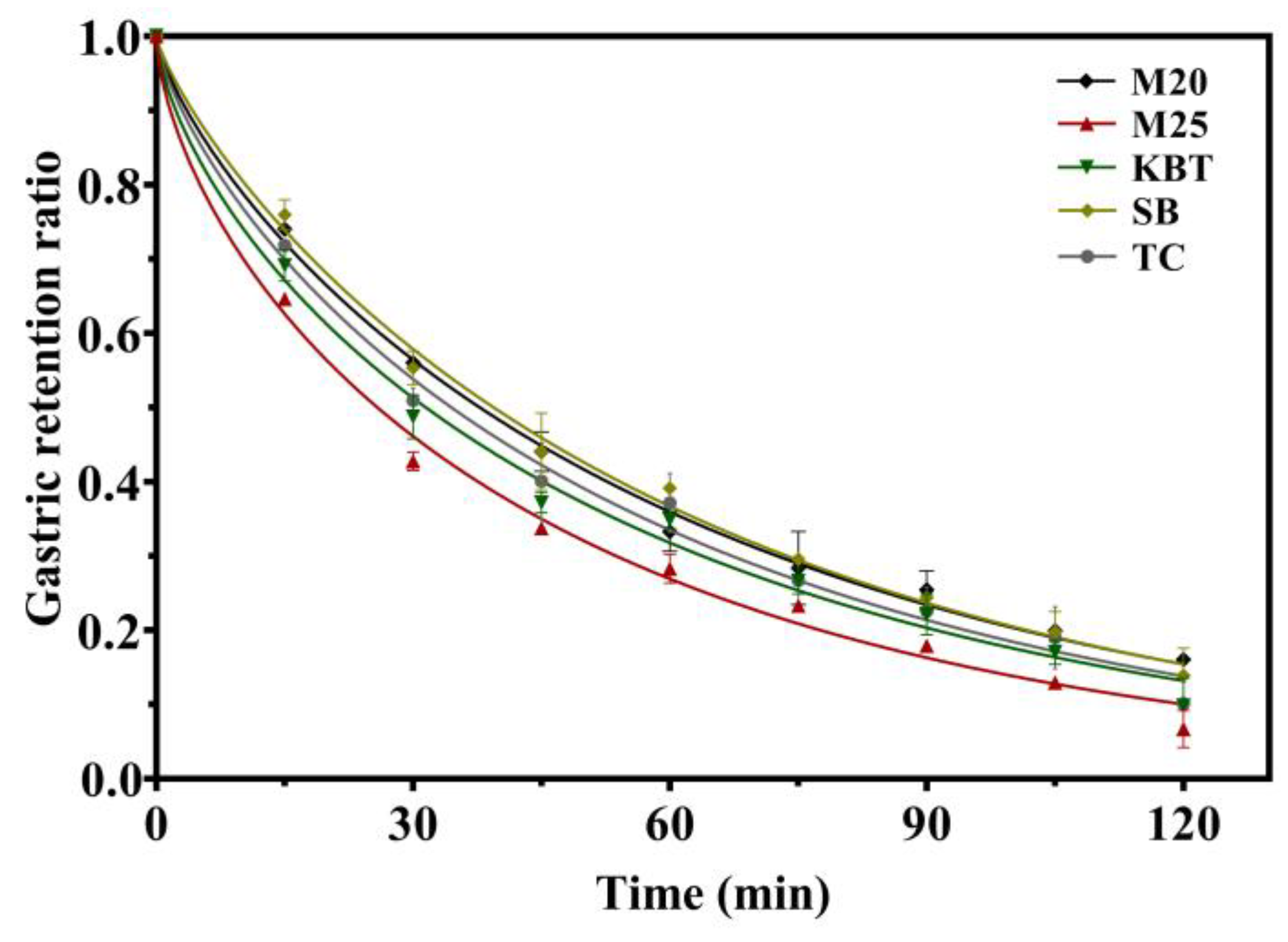
3.4. Gastric Emptying Curves
| Sample | k × 10-2 (1/min) | β | t1/2 (min) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M20 | 1.35 ± 0.07b | 0.754 ± 0.014b | 37.82 ± 1.21a | 0.9963 |
| M25 | 1.55 ± 0.02ab | 0.626 ± 0.009c | 25.83 ± 0.12d | 0.9938 |
| KBT | 1.38 ± 0.06b | 0.663 ± 0.002c | 31.52 ± 1.50c | 0.9927 |
| SB | 1.40 ± 0.09b | 0.806 ± 0.026a | 39.43± 0.98a | 0.9948 |
| TC | 1.41 ± 0.15b | 0.726 ± 0.028b | 34.58 ± 1.97b | 0.9923 |
3.5. Protein Hydrolysis Degree of Commercial Protein Supplements
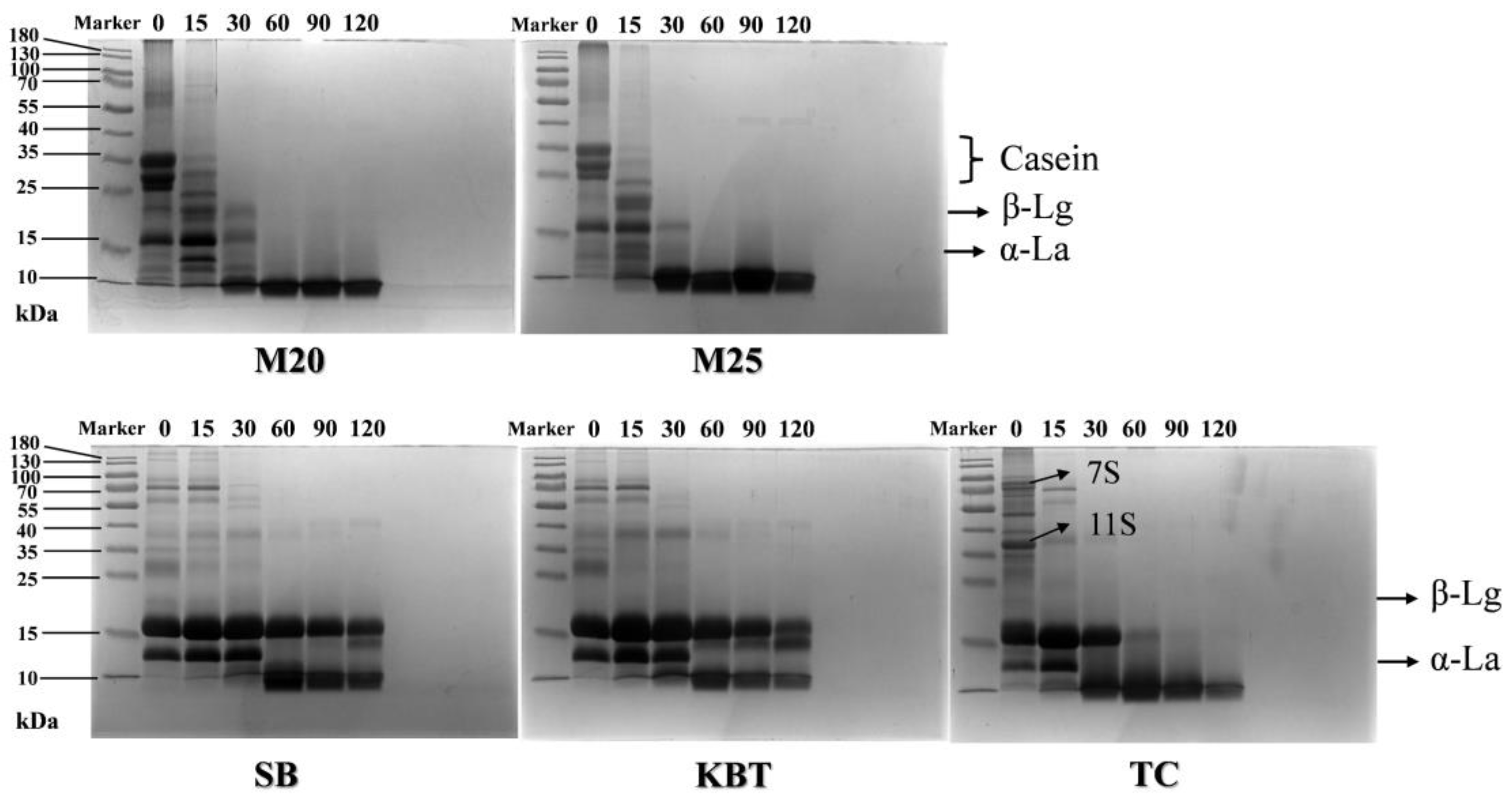
3.6. Protein Composition after Gastric Digestion by SDS-PAGE Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, P.; Li, M.; Yu, M.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. Advances in sports food: Sports nutrition, food manufacture, opportunities and challenges. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111258. [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.R.; Fernández-García, B. Evolution of the use of sports supplements. PharmaNutrition 2020, 14, 100239. [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, M.I.; Miguel, M.; Garcés-Rimón, M. Protein and Sport: Alternative Sources and Strategies for Bioactive and Sustainable Sports Nutrition. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 926043. [CrossRef]
- Maeda, N.; Dulko, D.; Macierzanka, A.; Jungnickel, C. Analysis of the Factors Affecting Static In Vitro Pepsinolysis of Food Proteins. Molecules 2022, 27, 1260. [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, S.K.; Khatkar, A.B.; Mehta, N.; Kaur, G.; Dhull, S.B.; Prakash, S. Effective strategies for elevating the techno-functional properties of milk protein concentrate. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 140. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, D.; Tao, X.; Zhang, J.; Huppertz, T.; Regenstein, J.M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, P. Decalcification strongly affects in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of bovine casein micelles under infant, adult and elderly conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, C.; Hou, Y.; Wu, T.; Deng, Z.; Zheng, L. Comparative Analysis of Protein Digestion Characteristics in Human, Cow, Goat, Sheep, Mare, and Camel Milk under Simulated Infant Condition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 15035–15047. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Keijzer, P.; Wichers, H.J.; Hettinga, K.A. Glycation of goat milk with different casein-to-whey protein ratios and its effects on simulated infant digestion. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139346. [CrossRef]
- Lavoisier, A.; Morzel, M.; Chevalier, S.; Henry, G.; Jardin, J.; Harel-Oger, M.; Garric, G.; Dupont, D. In vitro digestion of two protein-rich dairy products in the ageing gastrointestinal tract. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 9377–9390. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Afsar, S.; Day, L. Differences in the microstructure and rheological properties of low-fat yoghurts from goat, sheep and cow milk. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 423–429. [CrossRef]
- Miralles, B.; Sanchón, J.; Sánchez-Rivera, L.; Martínez-Maqueda, D.; Le Gouar, Y.; Dupont, D.; Amigo, L.; Recio, I. Digestion of micellar casein in duodenum cannulated pigs. Correlation between in vitro simulated gastric digestion and in vivo data. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128424. [CrossRef]
- Ashkar, F.; Wu, J. Effects of Food Factors and Processing on Protein Digestibility and Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8685–8698. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Mao, B.; Beniwal, A.S.; Abhilasha; Kaur, R.; Chian, F.M.; Singh, J. Alternative proteins vs animal proteins: The influence of structure and processing on their gastro-small intestinal digestion. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 122, 275–286. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Suolang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Luo, Z.; Shang, P.; Chen, X.D.; Wu, P. Formation of structured clots, gastric emptying and hydrolysis kinetics of yak milk during in vitro dynamic gastrointestinal digestion: Impact of different heat treatments. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111958. [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food–an international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113-1124.
- Elashoff, J.D.; Reedy, T.J.; Meyer, J.H. Analysis of Gastric Emptying Data. Gastroenterology 1982, 83, 1306–1312. [CrossRef]
- Urbain, J.-L.C.; Siegel, J.A.; Charkes, N.D.; Maurer, A.H.; Malmud, L.S.; Fisher, R.S. The two-component stomach: effects of meal particle size on fundal and antral emptying. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1989, 15, 254–259. [CrossRef]
- Barbano, D.M.; Lynch, J.M.; Fleming, J.R. Direct and Indirect Determination of True Protein Content of Milk by Kjeldahl Analysis: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 1991, 74, 281–288. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wen, X.; Tao, H.; Wang, K.; Fu, R.; Tao, H.; Wang, F.; Chen, N.; Ni, Y. Conformational changes and the formation of new bonds achieving robust nanoemulsions by electrostatic interactions between whey protein isolate and chondroitin sulfate. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136. [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zheng, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, M. Desirable characteristics of casein peptides with simultaneously enhanced emulsion forming ability and antioxidative capacity in O/W emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Fan, T.; Liao, Z.; Wu, P.; Wu, X.; Chen, X.D. Gastric emptying and morphology of a ‘near real’in vitro human stomach model (RD-IV-HSM). J. Food Eng. 2016, 183, 1-8.
- Ye, Q.; Ge, F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, P.; Chen, X.D.; Selomulya, C. Digestion of curcumin-fortified yogurt in short/long gastric residence times using a near-real dynamic in vitro human stomach. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131327. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Ouyang, C.; Luo, N.; Ye, A. Coagulation of model infant formulae: Impact on their in vitro dynamic gastric digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141. [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Duley, J.A.; Cowley, D.M.; Reed, S.; Arachchige, B.J.; Koorts, P.; Shaw, P.N.; Bansal, N. Digestibility of proteins in camel milk in comparison to bovine and human milk using an in vitro infant gastrointestinal digestion system. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131704. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ye, A.; Pan, Z.; Cui, J.; Dave, A.; Singh, H. Dynamic in vitro gastric digestion behavior of goat milk: Effects of homogenization and heat treatments. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 965–980. [CrossRef]
- Ahlborn, N.G.; Montoya, C.A.; Hodgkinson, S.M.; Dave, A.; Ye, A.; Samuelsson, L.M.; Roy, N.C.; McNabb, W.C. Heat treatment and homogenization of bovine milk loosened gastric curd structure and increased gastric emptying in growing pigs. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137. [CrossRef]
- Mayar, M.; de Vries, M.; Smeets, P.; van Duynhoven, J.; Terenzi, C. MRI assessment of pH and coagulation during semi-dynamic in vitro gastric digestion of milk proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 152, 109866.
- Wu, X.; Gao, T.; Xu, Z.; Liu, C.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Effect of combined enzyme and ultrasound treatment on the structure and gel properties of soy protein isolate: A comparative study of alkaline protease and pepsin. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 687. [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T.; Chia, L.W. Milk protein coagulation under gastric conditions: A review. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 113, 104882. [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Qi, C.; Wang, X.; Jin, Q.; McClements, D.J. Influence of Homogenization and Thermal Processing on the Gastrointestinal Fate of Bovine Milk Fat: In Vitro Digestion Study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 11109–11117. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ye, A.; Lin, Q.; Han, J.; Singh, H. Gastric digestion of milk protein ingredients: Study using an in vitro dynamic model. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6842–6852. [CrossRef]
- Mulet-Cabero, A.-I.; Torcello-Gómez, A.; Saha, S.; Mackie, A.R.; Wilde, P.J.; Brodkorb, A. Impact of caseins and whey proteins ratio and lipid content on in vitro digestion and ex vivo absorption. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126514. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Boiani, M.; He, T.; Wichers, H.J.; Hettinga, K.A. Heating affects protein digestion of skimmed goat milk proteins with different casein:whey ratios under simulated infant conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 148. [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.K.; Guo, Y.; Mashimo, H. Advances in the physiology of gastric emptying. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13546. [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hu, Z.; Wu, P.; Kirk, T.; Chen, X.D. In vitro release and bioaccessibility of oral solid preparations in a dynamic gastrointestinal system simulating fasted and fed states: A case study of metformin hydrochloride tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 652, 123869. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Zhang, P.; Wu, P.; Yin, Q.; Hidayat, K.; Chen, X.D. Modulation of viscosity, microstructure and lipolysis of W/O emulsions by cellulose ethers during in vitro digestion in the dynamic and semi-dynamic gastrointestinal models. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107584. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wu, P.; Wang, J.; Dupont, D.; Menard, O.; Jeantet, R.; Chen, X.D. Achieving realistic gastric emptying curve in an advanced dynamic in vitro human digestion system: experiences with cheese—a difficult to empty material. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3965–3977. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Gu, B.; Ge, F.; Chen, X.D. In vitro gastric digestion and emptying of cooked white and brown rice using a dynamic human stomach system. Food Struct. 2022, 31, 100245.
- Zhang, P.; Iqbal, S.; Deng, R.; Duan, X.; Han, H.; Chen, X.D.; Wu, P. Impact of elderly gastrointestinal alterations on gastric emptying and enzymatic hydrolysis of skim milk: An in vitro study using a dynamic stomach system. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134365. [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Cui, J.; Carpenter, E.; Prosser, C.; Singh, H. Dynamic in vitro gastric digestion of infant formulae made with goat milk and cow milk: Influence of protein composition. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 97, 76–85. [CrossRef]
- Mulet-Cabero, A.-I.; Mackie, A.R.; Wilde, P.J.; Fenelon, M.A.; Brodkorb, A. Structural mechanism and kinetics of in vitro gastric digestion are affected by process-induced changes in bovine milk. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 86, 172–183. [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, A.J.; Wallace, O.A.; Boggs, I.; Broadhurst, M.; Prosser, C.G. Gastric digestion of cow and goat milk: Impact of infant and young child in vitro digestion conditions. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 275–281. [CrossRef]
- Loveday, S.M. Protein digestion and absorption: the influence of food processing. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2023, 36, 544–559. [CrossRef]
- Halabi, A.; Croguennec, T.; Ménard, O.; Briard-Bion, V.; Jardin, J.; Le Gouar, Y.; Hennetier, M.; Bouhallab, S.; Dupont, D.; Deglaire, A. Protein structure in model infant milk formulas impacts their kinetics of hydrolysis under in vitro dynamic digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126. [CrossRef]
- Nasrabadi, M.N.; Doost, A.S.; Mezzenga, R. Modification approaches of plant-based proteins to improve their techno-functionality and use in food products. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106789.
- Han, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Tang, L. Effects of high-pressure homogenization and ultrasonic treatment on the structure and characteristics of casein. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 130, 109560. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hartinger, C.; Zhu, F. Physicochemical properties of infant formula model emulsions stabilised by different whey protein hydrolysates and characteristics of interfacial peptides. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145. [CrossRef]
- Tunick, M.H.; Ren, D.X.; Van Hekken, D.L.; Bonnaillie, L.; Paul, M.; Kwoczak, R.; Tomasula, P.M. Effect of heat and homogenization on in vitro digestion of milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4124–4139. [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Ye, A.; Li, S.; Dave, A.; Fraser, K.; Singh, H. Dynamic In Vitro Gastric Digestion of Sheep Milk: Influence of Homogenization and Heat Treatment. Foods 2021, 10, 1938. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wu, P.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Chen, X.D. Exploring in vitro release and digestion of commercial DHA microcapsules from algae oil and tuna oil with whey protein and casein as wall materials. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 978-989.
- Zhao, P.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Wei, W.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X. Development of in vitro digestion simulation of gastrointestinal tract to evaluate lipolysis and proteolysis: Comparison of infant model digestion of breast milk and adult model digestion of cow milk. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 142. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Fang, L.; Qi, B.; Xie, F.; Li, Y. Dynamic gastric stability and in vitro lipid digestion of soybean protein isolate and three storage protein-stabilized emulsions: Effects of ultrasonic treatment. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110666. [CrossRef]
| Key parameters | Settings |
|---|---|
| Sample volume | 230 mL |
| pH value of SGF | 1.6 ± 0.1 |
| Pre-volume of SGF | 30 mL |
| Pepsin activity | 4000 U/ mL |
| Secretion rate of SGF | 0-10 min, 1.2mL/min; 10-20 min, 1.6mL/min; 20-30 min, 2.0mL/min; 30-40 min, 2.5mL/min; 40-50 min, 2.1mL/min; 50-60 min, 1.6 mL/min; 60-120 min, 1.2 mL/min; |
| Secretion rate of HCl | 0-30 min, 1.0 mL/min; |
| Tilt angle of stomach vessel | 0-5min, 2°/min; 5-30min, -0.6°/min; 30-120min, -0.4°/min; |
| Time Sample |
15 min | 30 min | 60 min | 90 min | 120 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M20 | 8.12 ± 0.29Ea | 16.95 ± 0.20Da | 27.84 ± 1.16Ca | 31.86 ± 0.41Ba | 35.74 ± 0.33Aa |
| M25 | 8.67 ± 0.54Da | 18.61 ± 1.45Ca | 22.03 ± 1.61BCb | 25.68 ± 2.27Bb | 30.44 ± 3.45Ab |
| KBT | 4.02 ± 0.81Db | 8.38 ± 1.55Cb | 10.24 ± 1.44Cc | 13.25 ± 1.36Bc | 16.16 ± 1.54Ac |
| SB | 3.12 ± 0.60Ebc | 7.89 ± 1.62Db | 10.84 ± 0.40Cc | 13.82 ± 0.10Bc | 16.66 ± 0.08Ac |
| TC | 2.34 ± 0.50Ec | 7.23 ± 1.10Db | 9.99 ± 1.18Cc | 13.07 ± 1.55Bc | 17.90 ± 0.58Ac |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





