Submitted:
27 June 2024
Posted:
02 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
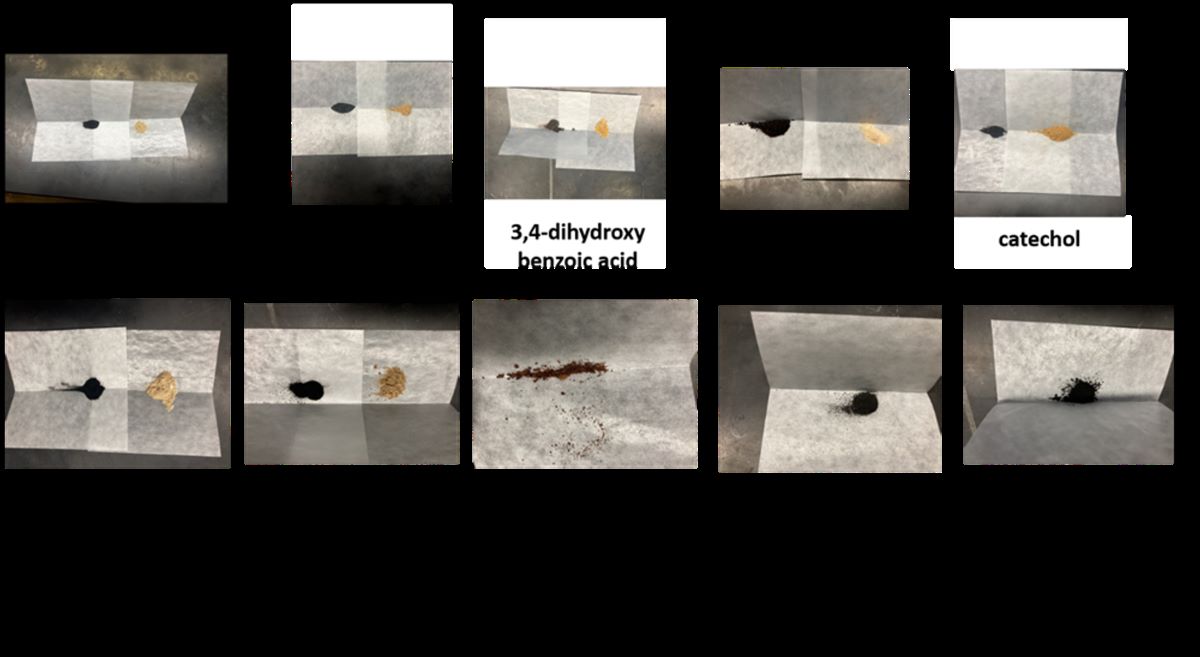
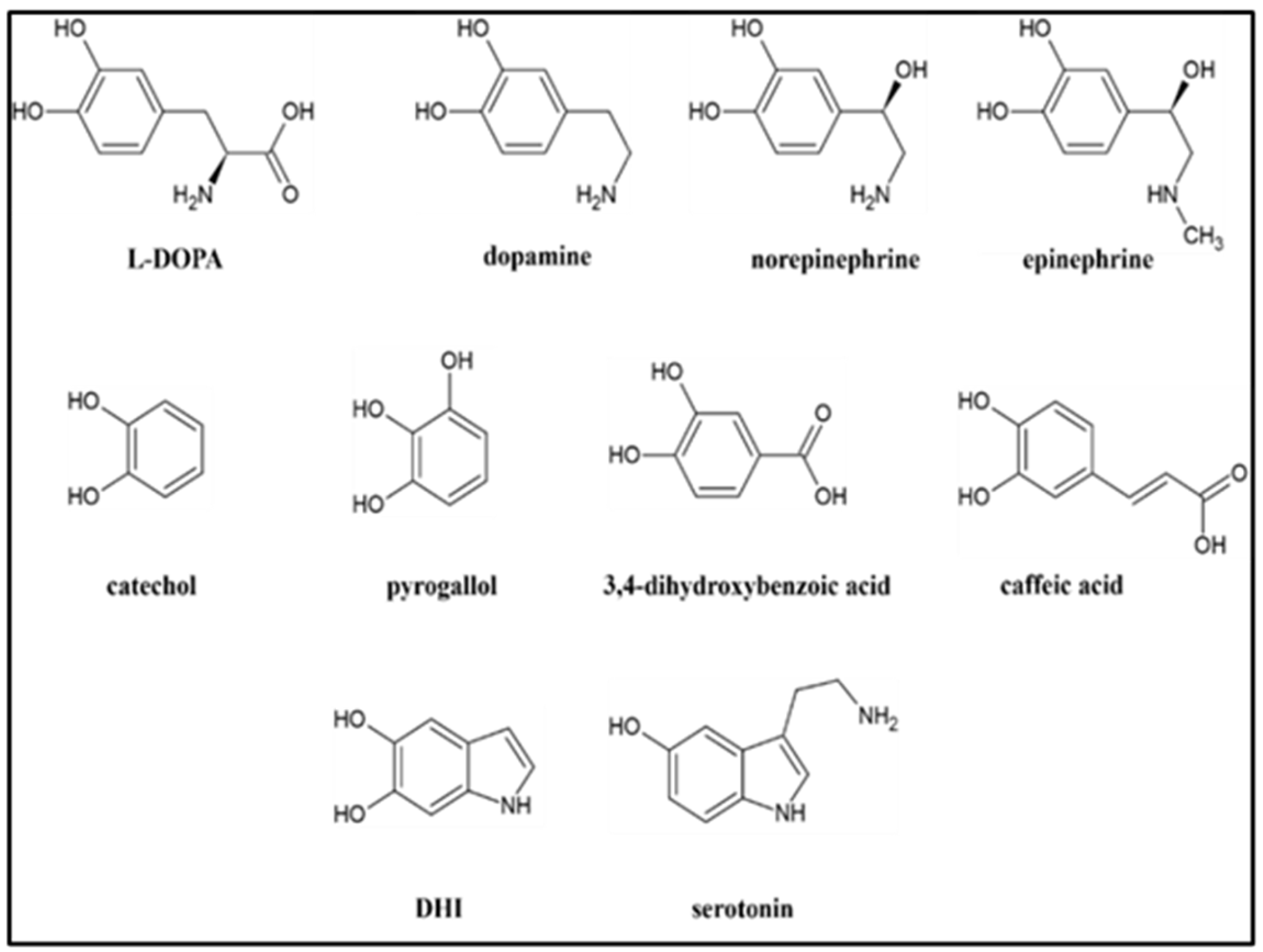
2.1. Observations during synthesis of materials.
2.1.1. DHI
2.1.2. Serotonin
2.1.3. Other precursors
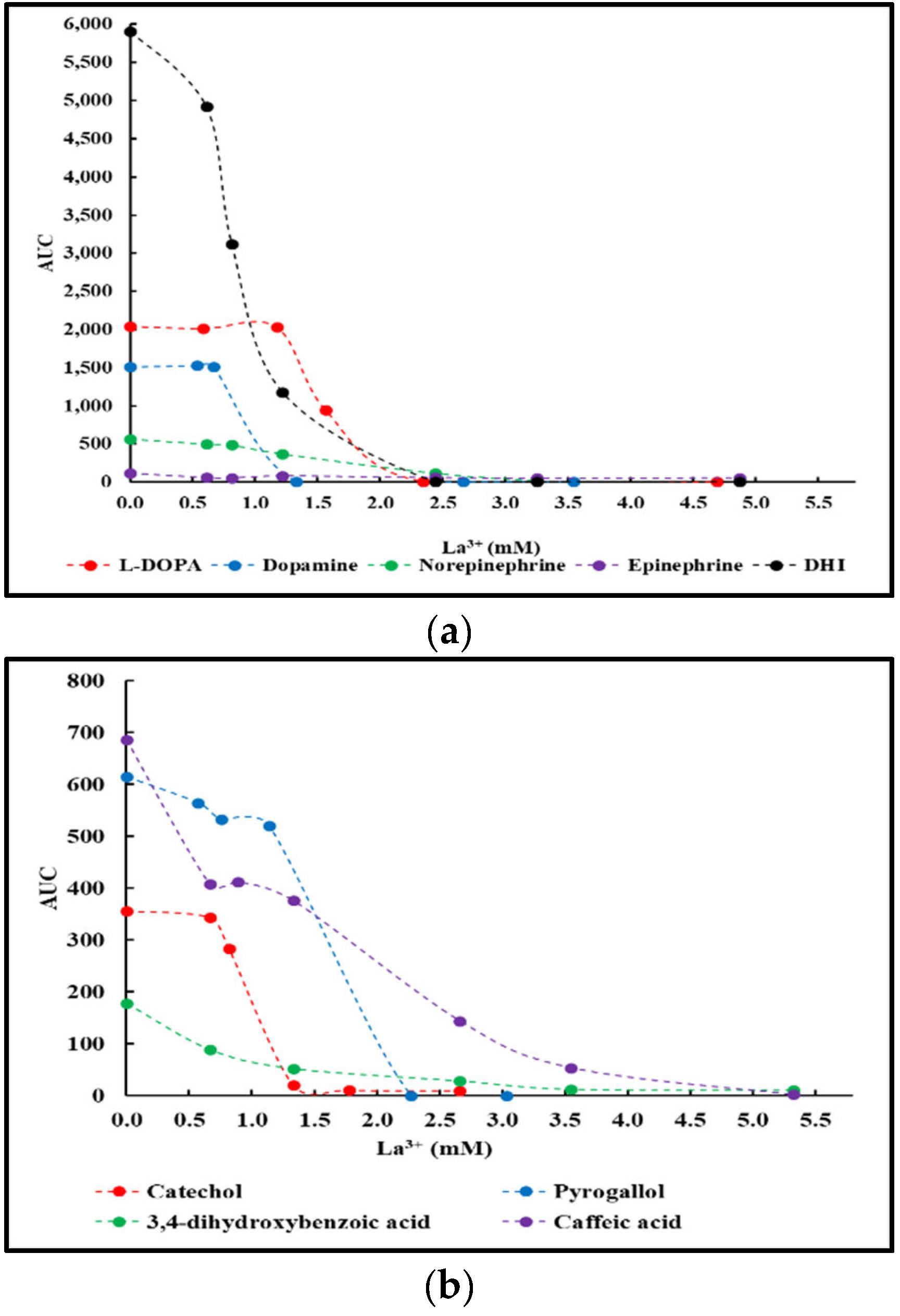
2.2. La3+ precipitation tests of crude reaction mixtures
2.3. Fractionation of MN materials
2.4. Characterization of fractions
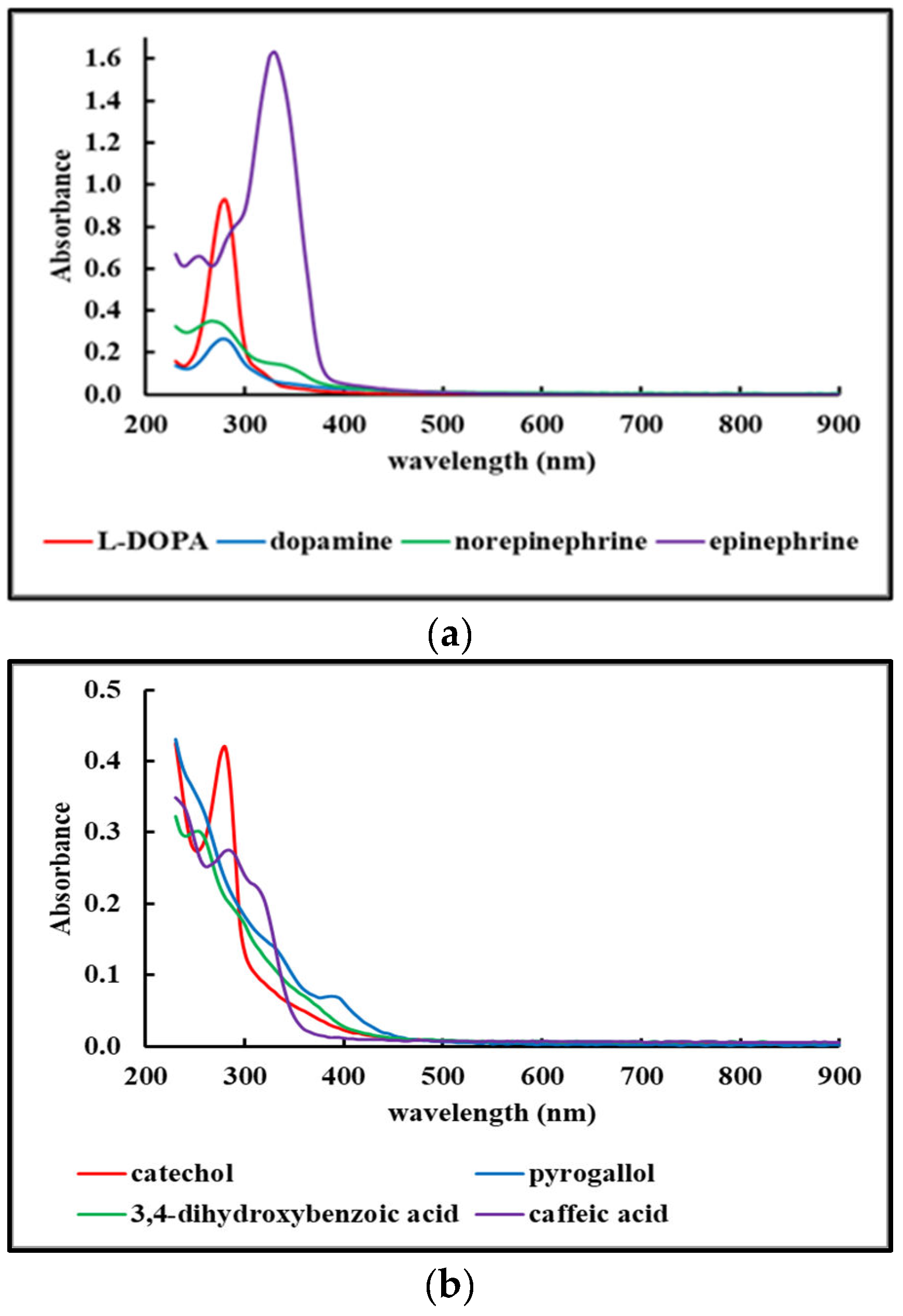
2.4.1. UV-Vis spectra of Fdisp fractions.
2.4.2. Concentration-dependent fluorescence of Fdisp fractions.
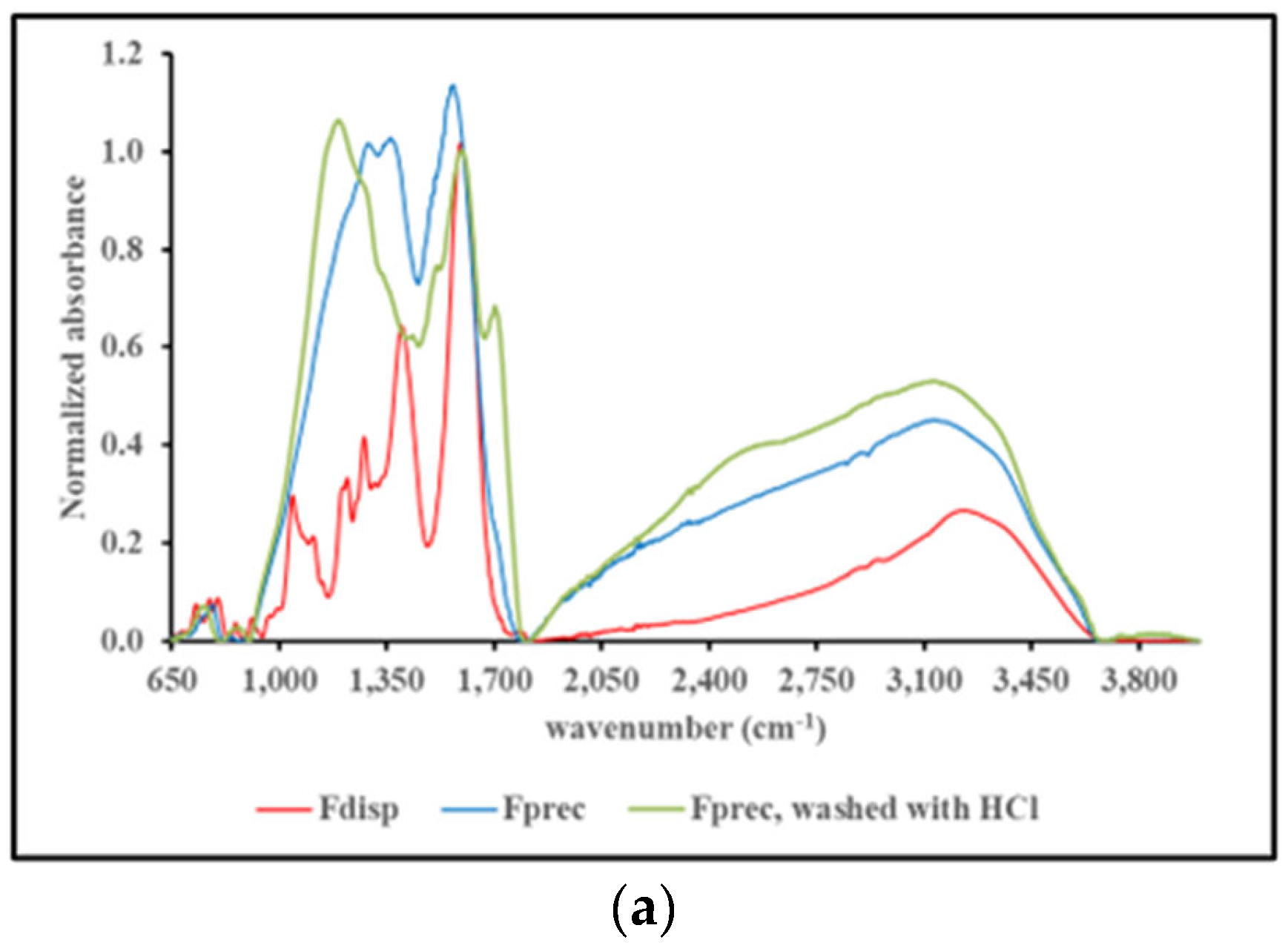
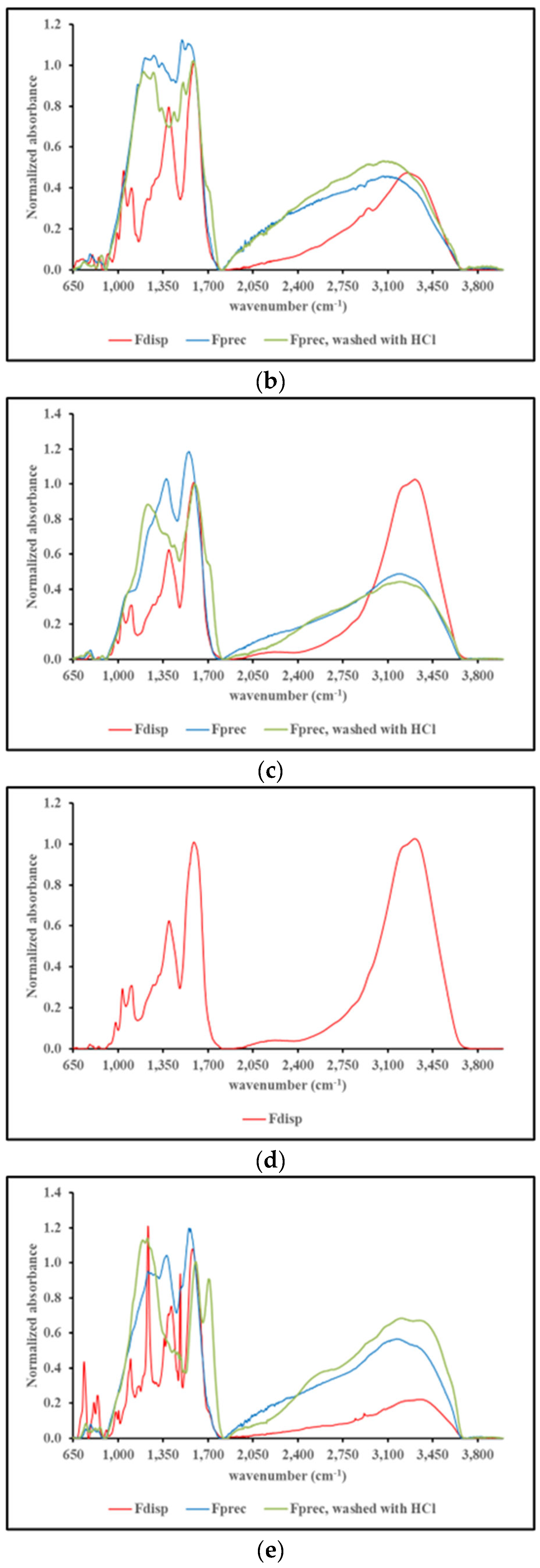
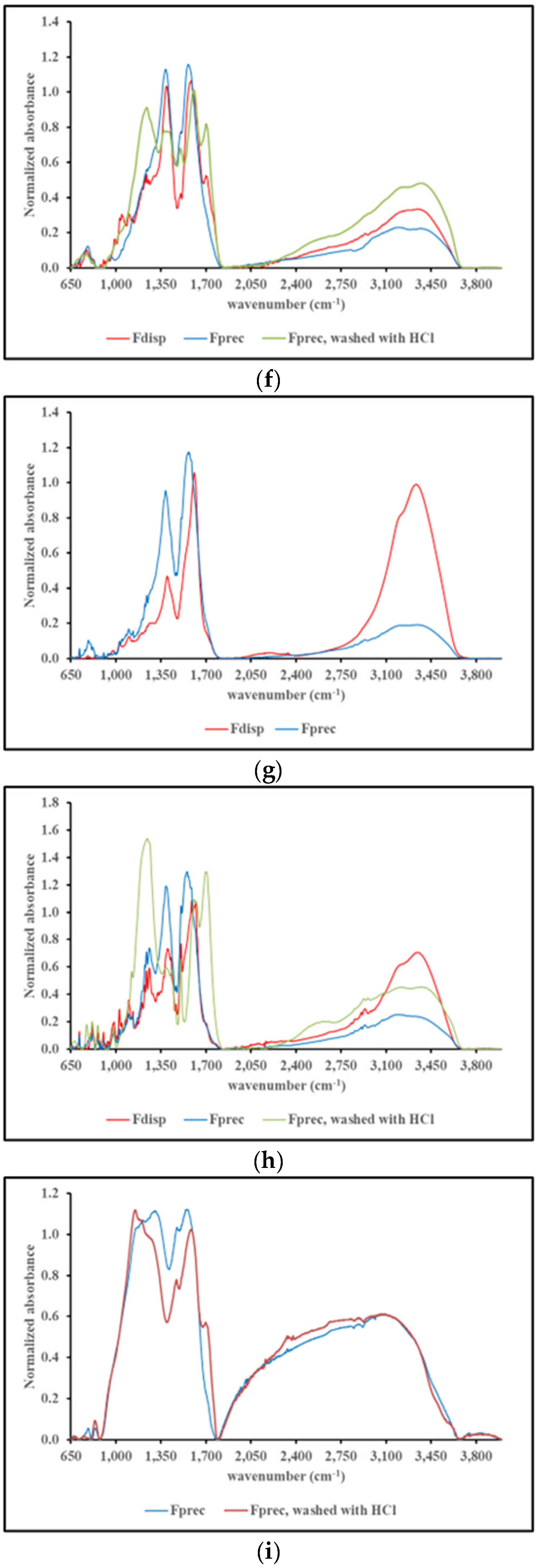
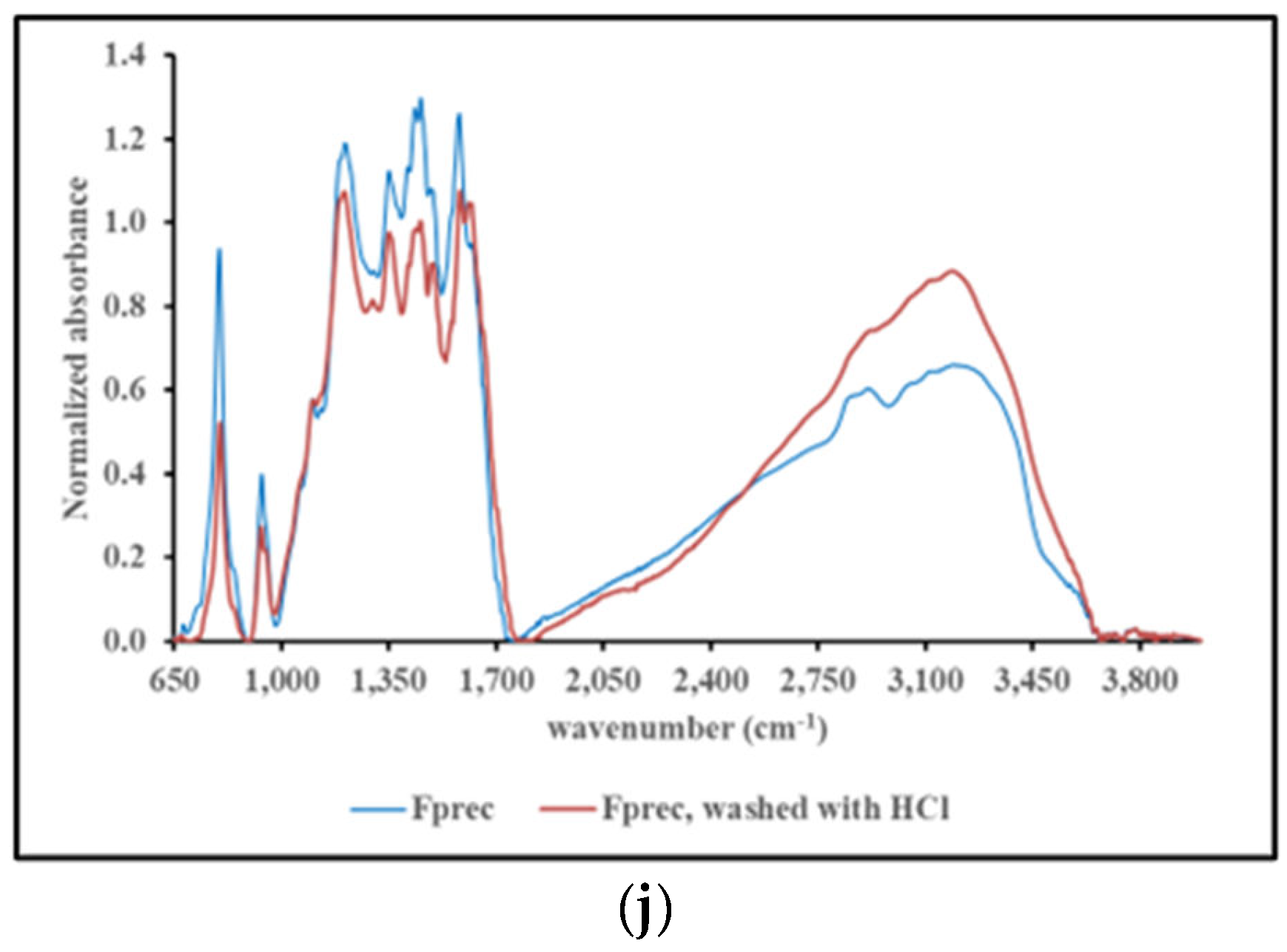
2.4.3. FT-IR spectroscopy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and methods
4.1. Materials and solutions
4.2. Synthesis of MN materials
4.3. Fractionation of dialyzed MN reaction mixtures
4.4. Washing of materials with HCl
4.5. UV-Vis spectroscopy
4.6. Fluorescence spectroscopy
4.7. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
4.8. FT-IR spectroscopy
4.9. Dialysis and freeze drying
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
References
- Cao, D.; Gong, S.; Yang, J.; Li, W.; Ge, Y.; Wei, Y. Melanin deposition ruled out as cause of color changes in the red-eared sliders (Trachemys scripta elegans). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 2018, 217, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranduca, M.A.; Branisteanu, D.; Serban, D.N.; Branisteanu, D.C.; Stoleriu, G.; Manolache, N.; Serban, I.L. Synthesis and physiological implications of melanic pigments. Oncol Lett 2019, 17, 4183–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.D.; Peles, D.N. The red and the black. Acc Chem Res 2010, 43, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, F. Melanins: Skin Pigments and Much More—Types, Structural Models, Biological Functions, and Formation Routes. New Journal of Science 2014, 2014, 498276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamatsu, K.; Ito, S. Recent Advances in Characterization of Melanin Pigments in Biological Samples. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostert, A.B. Melanin, the What, the Why and the How: An Introductory Review for Materials Scientists Interested in Flexible and Versatile Polymers. Polymers 2021, 13, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pralea, I.E.; Moldovan, R.C.; Petrache, A.M.; Ilies, M.; Heghes, S.C.; Ielciu, I.; Nicoara, R.; Moldovan, M.; Ene, M.; Radu, M.; et al. From Extraction to Advanced Analytical Methods: The Challenges of Melanin Analysis. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Li, D.; Li, P.; Xing, R. Melanin: insights into structure, analysis, and biological activities for future development. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2023, 11, 7528–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. Quantitative analysis of eumelanin and pheomelanin in humans, mice, and other animals: a comparative review. Pigment Cell Res 2003, 16, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. Chemistry of Mixed Melanogenesis—Pivotal Roles of Dopaquinone†. Photochemistry and Photobiology 2008, 84, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Miyake, S.; Maruyama, S.; Suzuki, I.; Commo, S.; Nakanishi, Y.; Wakamatsu, K. Acid hydrolysis reveals a low but constant level of pheomelanin in human black to brown hair. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 2018, 31, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Sarna, T. Photodegradation of Eumelanin and Pheomelanin and Its Pathophysiological Implications. Photochem Photobiol 2018, 94, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Q.Z.; Sierra, B.N.; La Clair, J.J.; Burkart, M.D. Chemoenzymatic elaboration of the Raper–Mason pathway unravels the structural diversity within eumelanin pigments. Chemical Science 2020, 11, 7836–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasti, T.H.; Timares, L. MC1R, eumelanin and pheomelanin: their role in determining the susceptibility to skin cancer. Photochem Photobiol 2015, 91, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K. Redhead pigment boosts skin-cancer risk. Nature 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaco, L.C.; Tomas, A.; Pojo, M.; Barral, D.C. The Dark Side of Melanin Secretion in Cutaneous Melanoma Aggressiveness. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 887366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saud, A.; Sagineedu, S.R.; Ng, H.S.; Stanslas, J.; Lim, J.C.W. Melanoma metastasis: What role does melanin play? (Review). Oncol Rep 2022, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, R.M.; Sarna, T.; Plonka, P.M.; Raman, C.; Brozyna, A.A.; Slominski, A.T. Melanoma, Melanin, and Melanogenesis: The Yin and Yang Relationship. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 842496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, K.-Y.; Fischer, M.C.; Warren, W.S. Understanding the Role of Aggregation in the Broad Absorption Bands of Eumelanin. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 12050–12061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraglia, R.; Traldi, P.; Elli, G.; Bertazzo, A.; Costa, C.; Allegri, G. Laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry in the study of natural and synthetic melanins. I—Tyrosine melanins. Biological Mass Spectrometry 1993, 22, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertazzo, A.; Costa, C.; Allegri, G.; Seraglia, R.; Traldi, P. Biosynthesis of melanin from dopamine. An investigation of early oligomerization products. Rapid communications in mass spectrometry : RCM 1995, 9, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroesche, C.; Peter, M.G. Detection of melanochromes by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 3947–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, A.; Pezzella, A.; Prota, G.; Seraglia, R.; Traldi, P. A Reassessment of the Structure of 5,6-Dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic Acid Melanins by Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 1996, 10, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, S.; Crucianelli, M.; Pezzella, A.; d'Ischia, M.; De Angelis, F. Exploring the frontiers of synthetic eumelanin polymers by high-resolution matrix-assisted laser/desorption ionization mass spectrometry. Journal of mass spectrometry : JMS 2012, 47, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, A.; Pezzella, A.; Prota, G.; Seraglia, R.; Traldi, P. Structural Analysis of Synthetic Melanins from 5,6-Dihydroxyindole by Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 1996, 10, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertazzo, A.; Costa, C.V.; Allegri, G.; Favretto, D.; Traldi, P. Application of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry to the detection of melanins formed from Dopa and dopamine. Journal of mass spectrometry : JMS 1999, 34, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chan, H.W.; Wang, L.; Chan, W. Mass Spectrometric and Spectrophotometric Analyses Reveal an Alternative Structure and a New Formation Mechanism for Melanin. Analytical Chemistry 2015, 87, 7958–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfieri, M.L.; Micillo, R.; Panzella, L.; Crescenzi, O.; Oscurato, S.L.; Maddalena, P.; Napolitano, A.; Ball, V.; d’Ischia, M. Structural Basis of Polydopamine Film Formation: Probing 5,6-Dihydroxyindole-Based Eumelanin Type Units and the Porphyrin Issue. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2018, 10, 7670–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Hsueh, N.; Chai, C.L.L. Direct Evidence for the Critical Role of 5,6-Dihydroxyindole in Polydopamine Deposition and Aggregation. Langmuir 2019, 35, 5191–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Hsueh, N.; Chai, C.L.L. Unravelling the polydopamine mystery: is the end in sight? Polymer Chemistry 2019, 10, 5771–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Miller, D.J.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W. Elucidating the structure of poly(dopamine). Langmuir 2012, 28, 6428–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Na, Y.S.; Choi, S.; Song, I.T.; Kim, W.Y.; Lee, H. Non-Covalent Self-Assembly and Covalent Polymerization Co-Contribute to Polydopamine Formation. Advanced Functional Materials 2012, 22, 4711–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeb, H.A.; Eichhorn, J.; Harley, S.; Robson, A.J.; Martocq, L.; Nicholson, S.J.; Ashton, M.D.; Abdelmohsen, H.A.M.; Pelit, E.; Baldock, S.J.; et al. Phenolic Polymers as Model Melanins. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics 2023, 224, 2300025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, K.P.; Govan, V.; Winford, J. "Invisible" ligands stabilize colloidal melanin-particles = the case of L-DOPA. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Mavridi-Printezi, A.; Giordani, S.; Menichetti, A.; Mordini, D.; Zattoni, A.; Roda, B.; Ferrazzano, L.; Reschiglian, P.; Marassi, V.; Montalti, M. The dual nature of biomimetic melanin. Nanoscale 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercruysse, K.P. Evaluating the “Darkness” of Melanin Materials. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Ozeki, H.; Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Thody, A.J. Spectrophotometric characterization of eumelanin and pheomelanin in hair. Pigment Cell Res 1996, 9, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakamatsu, K.; Nagao, A.; Watanabe, M.; Nakao, K.; Ito, S. Pheomelanogenesis is promoted at a weakly acidic pH. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 2017, 30, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercruysse, K.P. The “Unconventional” Effect of Cysteine on the In Vitro Synthesis of Melanin. ACS Omega 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishino, K.; Nishitani, S.; Man, Y.; Saito, A.; Sakata, T. Surface Characteristics and Formation of Polyserotonin Thin Films for Bioelectrical and Biocompatible Interfaces. Langmuir 2022, 38, 8633–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercruysse, K.P.; Govan, V. Melanogenesis: A Search for Pheomelanin and Also, What Is Lurking Behind Those Dark Colors? . 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, K.P.; Govan, V. The yellow and the black of synthetic melanins. . 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.C. The C=O bond, Part III: Carboxylic Acids. Spectroscopy 2018, 33, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.C. The Carbonyl Group, Part V: Carboxylates - Coming Clean. Spectroscopy 2018, 33, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.C. Organic Nitrogen Compounds V: Amine Salts. Spectroscopy 2019, 34, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- d'Ischia, M.; Wakamatsu, K.; Napolitano, A.; Briganti, S.; Garcia-Borron, J.C.; Kovacs, D.; Meredith, P.; Pezzella, A.; Picardo, M.; Sarna, T.; et al. Melanins and melanogenesis: methods, standards, protocols. Pigm Cell Melanoma Res 2013, 26, 616–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.T.; Kim, T.K.; Kleszczyński, K.; Semak, I.; Janjetovic, Z.; Sweatman, T.; Skobowiat, C.; Steketee, J.D.; Lin, Z.; Postlethwaite, A.; et al. Characterization of serotonin and N-acetylserotonin systems in the human epidermis and skin cells. Journal of pineal research 2020, 68, e12626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derizhanova, I.S. [Melanosis of the large intestine]. Arkhiv patologii 1975, 37, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem Rev 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavridi-Printezi, A.; Menichetti, A.; Guernelli, M.; Montalti, M. The Photophysics and Photochemistry of Melanin- Like Nanomaterials Depend on Morphology and Structure. Chemistry 2021, 27, 16309–16319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, M.; Vanna, R.; Bellei, C.; Zucca, F.A.; Wakamatsu, K.; Monzani, E.; Ito, S.; Casella, L.; Zecca, L. Neuromelanins of human brain have soluble and insoluble components with dolichols attached to the melanic structure. PLoS One 2012, 7, e48490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leupold, D.; Szyc, L.; Stankovic, G.; Strobel, S.; Volker, H.U.; Fleck, U.; Muller, T.; Scholz, M.; Riederer, P.; Monoranu, C.M. Melanin and Neuromelanin Fluorescence Studies Focusing on Parkinson's Disease and Its Inherent Risk for Melanoma. Cells 2019, 8, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasowska, D.; Malek, A.; Kurzepa, J.; Kapka-Skrzypczak, L.; Krasowska, D.; Kurzepa, J. Melanin-The Eminence Grise of Melanoma and Parkinson's Disease Development. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




