Submitted:
26 June 2024
Posted:
28 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Long COVID-19 and (MIS-C) are Different
3. The GM Supports Barrier Protection Functionality
4. The Link between Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis and MIS-C
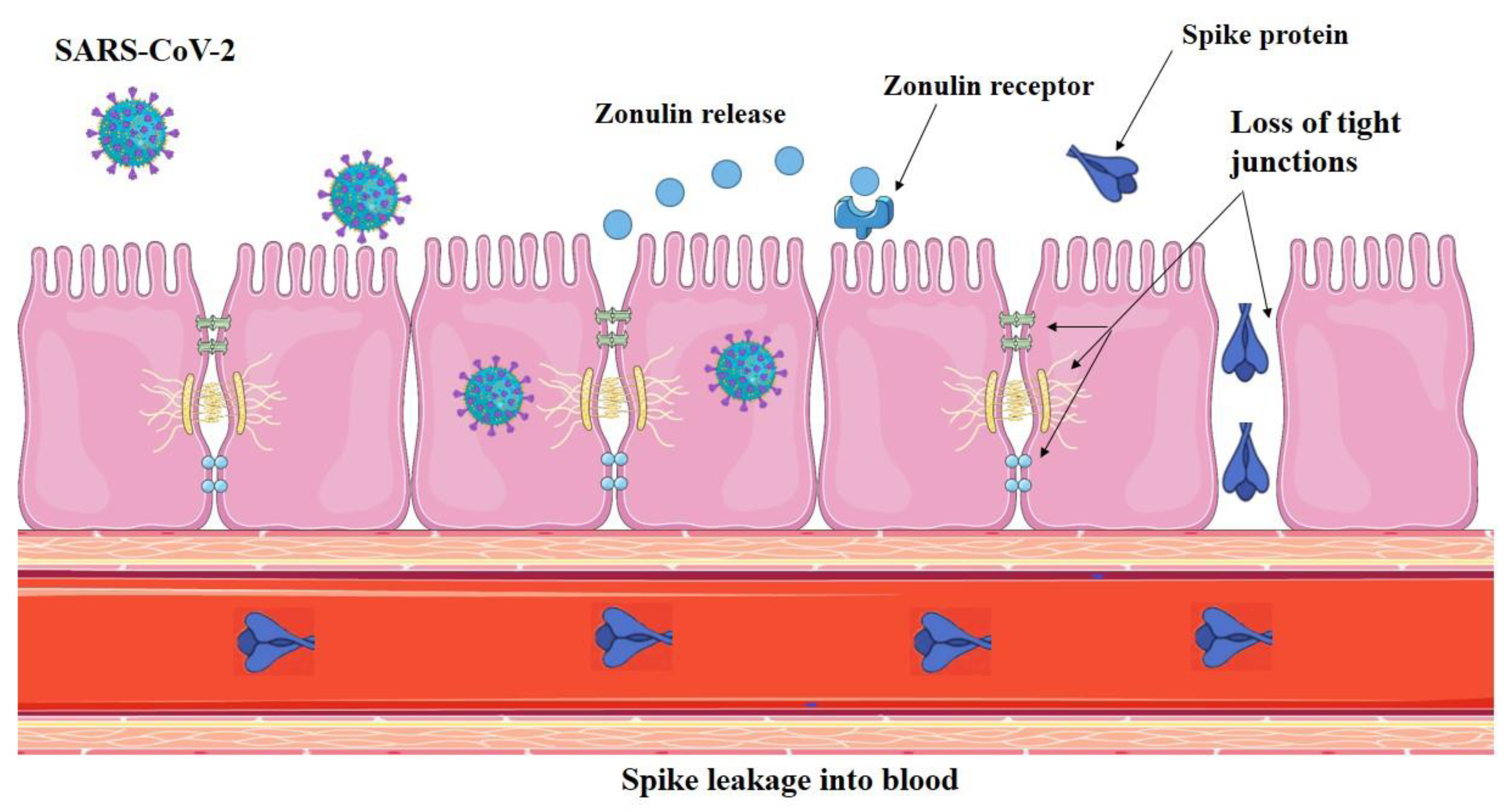
4.1. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Impairs Gut Barrier Integrity by Inducing Zonulin Release
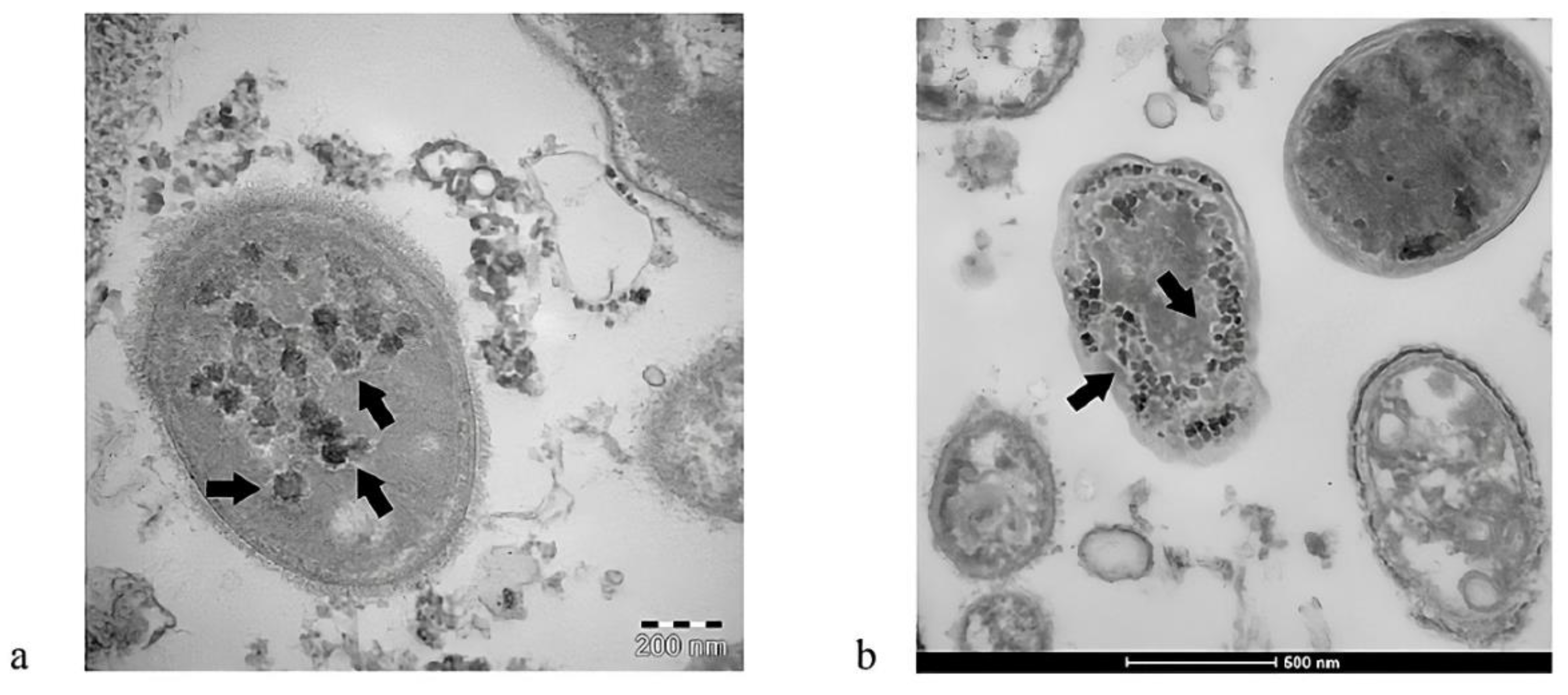
4.2. Bacteriophage-Like Behavior of SARS-CoV-2 and MISC
5. The Link between IL-6 Levels, Gut Barrier Integrity, and MIS-C
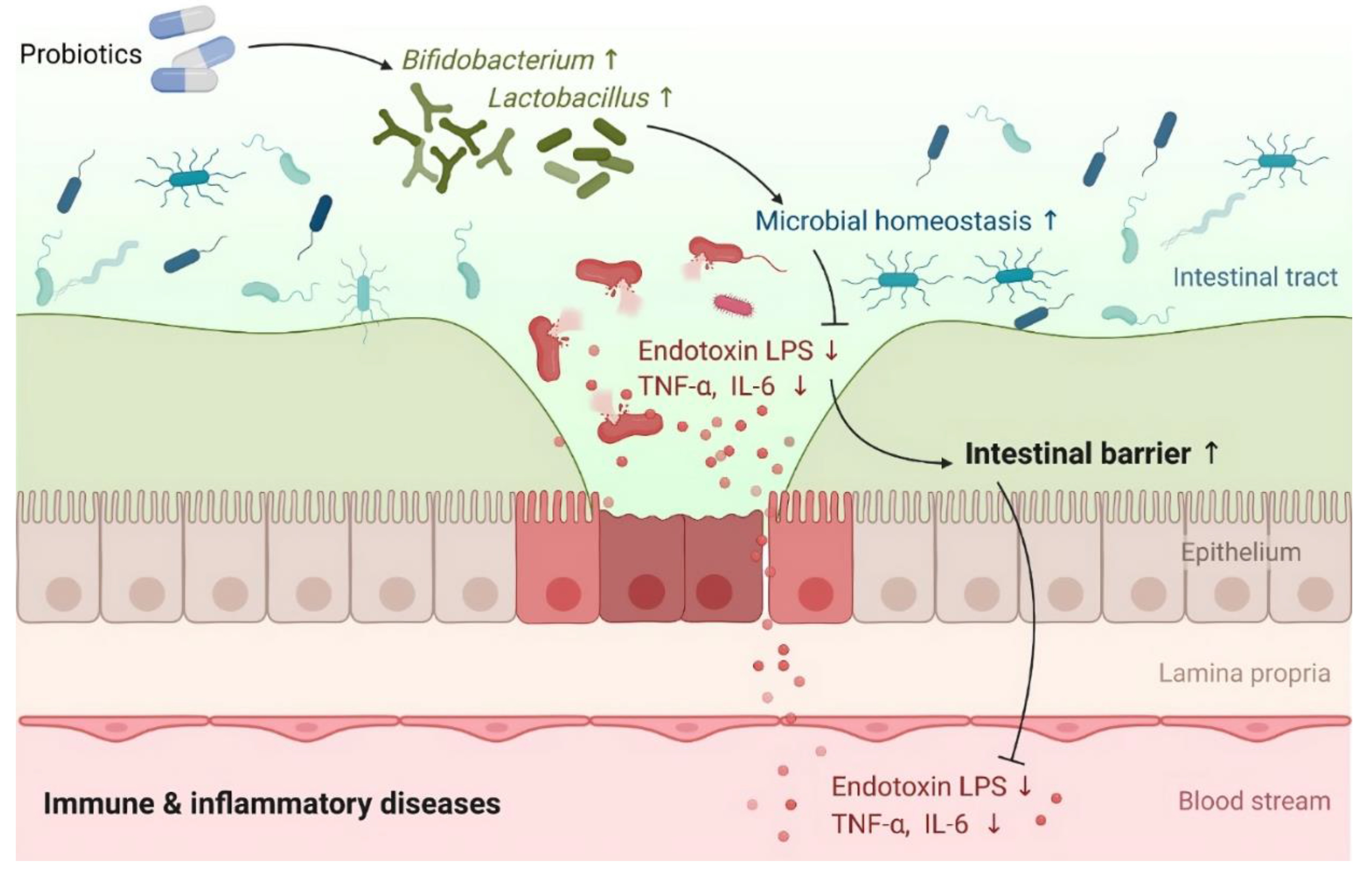
6. Preventive and Therapeutic Strategies for MIS-C
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forrest, C.B.; Burrows, E.K.; Mejias, A.; Razzaghi, H.; Christakis, D.; Jhaveri, R.; Lee, G.M.; Pajor, N.M.; Rao, S.; Thacker, D. Severity of acute COVID-19 in children< 18 years old March 2020 to December 2021. Pediatrics 2022, 149, e2021055765. [Google Scholar]
- Bhopal, S.S.; Bagaria, J.; Olabi, B.; Bhopal, R. Children and young people remain at low risk of COVID-19 mortality. The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health 2021, 5, e12–e13. [Google Scholar]
- Brodin, P. SARS-CoV-2 infections in children: Understanding diverse outcomes. Immunity 2022, 55, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Why does the severity of COVID-19 differ with age?: understanding the mechanisms underlying the age gradient in outcome following SARS-CoV-2 infection. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2022, 41, e36–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Why is COVID-19 less severe in children? A review of the proposed mechanisms underlying the age-related difference in severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections. Archives of disease in childhood 2021, 106, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundle, N.; Dave, N.; Pharris, A.; Spiteri, G.; Deogan, C.; Suk, J.E. COVID-19 trends and severity among symptomatic children aged 0–17 years in 10 European Union countries, 3 August 2020 to 3 October 2021. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2101098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thors, V.; Bjornsdottir, K.L.; Love, T.; Haraldsson, A. SARS-CoV-2 infections in icelandic children: close follow-up of all confirmed cases in a nationwide study. The Pediatric infectious disease journal 2022, 41, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Gu, J.; Chen, Q.; Deng, N.; Li, J.; Huang, L.; Zhou, X. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infections in China: A multicenter case series. PLoS medicine 2020, 17, e1003130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Say, D.; Crawford, N.; McNab, S.; Wurzel, D.; Steer, A.; Tosif, S. Post-acute COVID-19 outcomes in children with mild and asymptomatic disease. The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health 2021, 5, e22–e23. [Google Scholar]
- Cloete, J.; Kruger, A.; Masha, M.; du Plessis, N.M.; Mawela, D.; Tshukudu, M.; Manyane, T.; Komane, L.; Venter, M.; Jassat, W. Paediatric hospitalisations due to COVID-19 during the first SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B. 1.1. 529) variant wave in South Africa: a multicentre observational study. The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health 2022, 6, 294–302. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Berger, N.A.; Kaelber, D.C.; Davis, P.B.; Volkow, N.D.; Xu, R. Incidence rates and clinical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection with the omicron and delta variants in children younger than 5 years in the US. JAMA pediatrics 2022, 176, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.L.; Harwood, R.; Kenny, S.; Cruz, J.; Clark, M.; Davis, P.J.; Draper, E.S.; Hargreaves, D.; Ladhani, S.N.; Gent, N. Pediatric hospitalizations and ICU admissions due to COVID-19 and pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2 in England. JAMA pediatrics 2023, 177, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungar, S.P.; Solomon, S.; Stachel, A.; Shust, G.F.; Clouser, K.N.; Bhavsar, S.M.; Lighter, J. Hospital and ICU admission risk associated with comorbidities among children with COVID-19 ancestral strains. Clinical Pediatrics 2023, 62, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.; Cunniffe, N.; Donnelly, R. COVID-19 hospitalization rates rise exponentially with age, inversely proportional to thymic T-cell production. Journal of the Royal Society Interface 2021, 18, 20200982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.M.D.; Du-Fay-de-Lavallaz, J.M.; Fugar, S.; Sarau, A.; Simmons, J.A.; Clark, B.; Sanghani, R.M.; Aggarwal, N.T.; Williams, K.A.; Doukky, R. Sex differences in COVID-19 hospitalization and mortality. Journal of Women's health 2021, 30, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biolè, C.; Bianco, M.; Núñez-Gil, I.J.; Cerrato, E.; Spirito, A.; Roubin, S.R.; Viana-Llamas, M.C.; Gonzalez, A.; Castro-Mejía, A.F.; Eid, C.M. Gender Differences in the Presentation and Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19. Journal of Hospital Medicine 2021, 16, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Chinn, J.; De Ferrante, M.; Kirby, K.A.; Hohmann, S.F.; Amin, A. Male gender is a predictor of higher mortality in hospitalized adults with COVID-19. PloS one 2021, 16, e0254066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banoun, H. Why are children and many adults not affected by COVID-19? Role of the host immune response. Infectious Diseases Research 2022, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukinoki, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Saito, J.; Sakaguchi, W.; Iguchi, K.; Inoue, Y.; Ishii, S.; Sato, C.; Yokoyama, M.; Shiraishi, Y. Prevalence of saliva immunoglobulin A antibodies reactive with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 among Japanese people unexposed to the virus. Microbiology and Immunology 2022, 66, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Worlock, K.B.; Huang, N.; Lindeboom, R.G.; Butler, C.R.; Kumasaka, N.; Dominguez Conde, C.; Mamanova, L.; Bolt, L.; Richardson, L. Local and systemic responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children and adults. Nature 2022, 602, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vono, M.; Huttner, A.; Lemeille, S.; Martinez-Murillo, P.; Meyer, B.; Baggio, S.; Sharma, S.; Thiriard, A.; Marchant, A.; Godeke, G.-J. Robust innate responses to SARS-CoV-2 in children resolve faster than in adults without compromising adaptive immunity. Cell reports 2021, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traxinger, B.R.; Richert-Spuhler, L.E.; Lund, J.M. Mucosal tissue regulatory T cells are integral in balancing immunity and tolerance at portals of antigen entry. Mucosal Immunology 2022, 15, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, E.; Wubben, R.; Isaza-Correa, J.M.; Melo, A.M.; Mhaonaigh, A.U.; Conlon, N.; O’Donnell, J.S.; Ní Cheallaigh, C.; Hurley, T.; Stevenson, N.J. Neutrophils in COVID-19: not innocent bystanders. Frontiers in Immunology 2022, 13, 864387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chunxi, L.; Haiyue, L.; Yanxia, L.; Jianbing, P.; Jin, S. The gut microbiota and respiratory diseases: new evidence. Journal of immunology research 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, R.; Orta-Resendiz, A.; Dockrell, D.; Müller-Trutwin, M.; Mazein, A. Severe COVID-19 versus multisystem inflammatory syndrome: comparing two critical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection. European Respiratory Review 2023, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.; Siles, N.; Kelley, M.; Wylie, D.; Melamed, E.; Brode, W.M. Clinical characteristics of Long COVID patients presenting to a dedicated academic post-COVID-19 clinic in Central Texas. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 21971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantin, T.; Pék, T.; Horváth, Z.; Garan, D.; Szabó, A.J. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C): Implications for long COVID. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley, A.H. Understanding SARS-CoV-2-related multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. Nature Reviews Immunology 2020, 20, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.M.; Brummer, R.J.; Derrien, M.; MacDonald, T.T.; Troost, F.; Cani, P.D.; Theodorou, V.; Dekker, J.; Méheust, A.; De Vos, W.M. Homeostasis of the gut barrier and potential biomarkers. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 2017, 312, G171–G193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M. Leaky gut: mechanisms, measurement and clinical implications in humans. Gut 2019, 68, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binienda, A.; Twardowska, A.; Makaro, A.; Salaga, M. Dietary carbohydrates and lipids in the pathogenesis of leaky gut syndrome: An overview. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21, 8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiippala, K.; Jouhten, H.; Ronkainen, A.; Hartikainen, A.; Kainulainen, V.; Jalanka, J.; Satokari, R. The potential of gut commensals in reinforcing intestinal barrier function and alleviating inflammation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenwald, M.A.; Turner, J.R. The intestinal epithelial barrier: a therapeutic target? Nature reviews Gastroenterology & hepatology 2017, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.-Y.; He, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N.-H. Role of gut microbiota on intestinal barrier function in acute pancreatitis. World journal of gastroenterology 2020, 26, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Kirby, J.; Reilly, C.M.; Luo, X.M. Leaky gut as a danger signal for autoimmune diseases. Frontiers in immunology 2017, 8, 269575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Régnier, M.; Van Hul, M.; Knauf, C.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome, endocrine control of gut barrier function and metabolic diseases. Journal of Endocrinology 2021, 248, R67–R82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Whitley, C.S.; Haribabu, B.; Jala, V.R. Regulation of intestinal barrier function by microbial metabolites. Cellular and molecular gastroenterology and hepatology 2021, 11, 1463–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and systemic inflammation: A narrative review. Internal and emergency medicine 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacorn, M.; Romero-Soto, H.N.; Levy, S.; Chen, Q.; Hourigan, S.K. The Gut Microbiome of Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonker, L.M.; Gilboa, T.; Ogata, A.F.; Senussi, Y.; Lazarovits, R.; Boribong, B.P.; Bartsch, Y.C.; Loiselle, M.; Rivas, M.N.; Porritt, R.A. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children is driven by zonulin-dependent loss of gut mucosal barrier. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2022, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochemical journal 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, M.; D'Amico, F.; Brigidi, P.; Turroni, S. Gut microbiome–micronutrient interaction: The key to controlling the bioavailability of minerals and vitamins? Biofactors 2022, 48, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, K.D.; Carnero, E.A.; Dirks, B.; Igudesman, D.; Yi, F.; Marcus, A.; Davis, T.L.; Pratley, R.E.; Rittmann, B.E.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Host-diet-gut microbiome interactions influence human energy balance: A randomized clinical trial. Nature communications 2023, 14, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Alden, N.; Lee, K. Pathways and functions of gut microbiota metabolism impacting host physiology. Current opinion in biotechnology 2015, 36, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, C.; Kandalgaonkar, M.R.; Golonka, R.M.; Yeoh, B.S.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Saha, P. Crosstalk between gut microbiota and host immunity: impact on inflammation and immunotherapy. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascher, S.; Reinhardt, C. The gut microbiota: an emerging risk factor for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease. European Journal of Immunology 2018, 48, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Clément, K. The gut microbiome, diet, and links to cardiometabolic and chronic disorders. Nature Reviews Nephrology 2016, 12, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.W.; Kitai, T.; Hazen, S.L. Gut microbiota in cardiovascular health and disease. Circulation research 2017, 120, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Oliveira, T.Y. Evolution of antibody immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giron, L.B.; Dweep, H.; Yin, X.; Wang, H.; Damra, M.; Goldman, A.R.; Gorman, N.; Palmer, C.S.; Tang, H.-Y.; Shaikh, M.W. Plasma markers of disrupted gut permeability in severe COVID-19 patients. Frontiers in immunology 2021, 12, 686240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottein, F.; Sokol, H. Potential causes and consequences of gastrointestinal disorders during a SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell reports 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoh, Y.K.; Zuo, T.; Lui, G.C.-Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; Li, A.Y.; Chung, A.C.; Cheung, C.P.; Tso, E.Y.; Fung, K.S. Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19. Gut 2021, 70, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, S.M.; Singer, D.; Makrides, V.; Huggel, K.; Pos, K.M.; Wagner, C.A.; Kuba, K.; Danilczyk, U.; Skovby, F.; Kleta, R. Tissue-specific amino acid transporter partners ACE2 and collectrin differentially interact with hartnup mutations. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Perlot, T.; Rehman, A.; Trichereau, J.; Ishiguro, H.; Paolino, M.; Sigl, V.; Hanada, T.; Hanada, R.; Lipinski, S. ACE2 links amino acid malnutrition to microbial ecology and intestinal inflammation. Nature 2012, 487, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlot, T.; Penninger, J.M. ACE2–From the renin–angiotensin system to gut microbiota and malnutrition. Microbes and infection 2013, 15, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, S.D.; Nunes, S.; Reis, F. ACE2 imbalance as a key player for the poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients with age-related comorbidities–role of gut microbiota dysbiosis. Ageing research reviews 2020, 62, 101123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Mak, J.W.Y.; Su, Q.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Lui, G.C.-Y.; Ng, S.S.S.; Zhang, F.; Li, A.Y.; Lu, W.; Hui, D.S.-C. Gut microbiota dynamics in a prospective cohort of patients with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Gut 2022, 71, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, P.; Tang, J.; Yang, B.; Li, H.; Liang, M.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Y. Gut microbiota dysbiosis correlates with long COVID-19 at one-year after discharge. Journal of Korean Medical Science 2023, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suskun, C.; Kilic, O.; Yilmaz Ciftdogan, D.; Guven, S.; Karbuz, A.; Ozkaya Parlakay, A.; Kara, Y.; Kacmaz, E.; Sahin, A.; Boga, A. Intestinal microbiota composition of children with infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C). European journal of pediatrics 2022, 181, 3175–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, L.; Del Chierico, F.; Macari, G.; Pane, S.; Ristori, M.V.; Guarrasi, V.; Gardini, S.; Pascucci, G.R.; Cotugno, N.; Perno, C.F. The relationship between pediatric gut microbiota and SARS-CoV-2 infection. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2022, 12, 908492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Dorfman, R.G.; Liu, H.; Yu, T.; Chen, X.; Tang, D.; Xu, L.; Yin, Y. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii produces butyrate to maintain Th17/Treg balance and to ameliorate colorectal colitis by inhibiting histone deacetylase 1. Inflammatory bowel diseases 2018, 24, 1926–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Luckey, D.; Taneja, V. Autoimmunity-associated gut commensals modulate gut permeability and immunity in humanized mice. Military medicine 2019, 184, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konig, J.; Wells, J.; Cani, P.; Garcia-Rodenas, C.; MacDonald, T.; Mercenier, A.; Whyte, J.; Troost, F.; Brummer, R. Human intestinal barrier function in health and disease. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2016; 7 (10): e196.
- Takiishi, T.; Fenero, C.I.M.; Câmara, N.O.S. Intestinal barrier and gut microbiota: Shaping our immune responses throughout life. Tissue barriers 2017, 5, e1373208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaolalla, R.; Abreu, M.T. Innate immunity in the small intestine. Current opinion in gastroenterology 2012, 28, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, M.; Trinchieri, G. Innate immune mechanisms of colitis and colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Nature Reviews Immunology 2011, 11, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiando, A.M.; Graham, W.V.; Turner, J.R. Epithelial barriers in homeostasis and disease. Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease 2010, 5, 119–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukoetter, M.G.; Bruewer, M.; Nusrat, A. Regulation of the intestinal epithelial barrier by the apical junctional complex. Current opinion in gastroenterology 2006, 22, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonker, L.; Neilan, A.; Bartsch, Y. Pediatric SARS-CoV-2: clinical presentation, infectivity, and immune responses [manuscript published online ahead of print 20 August 2020]. J Pediatr 2020, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sang, L.; Ye, F.; Ruan, S.; Zhong, B.; Song, T.; Alshukairi, A.N.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z. Kinetics of viral load and antibody response in relation to COVID-19 severity. The Journal of clinical investigation 2020, 130, 5235–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajnzylber, J.; Regan, J.; Coxen, K.; Corry, H.; Wong, C.; Rosenthal, A.; Worrall, D.; Giguel, F.; Piechocka-Trocha, A.; Atyeo, C. SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality. Nature communications 2020, 11, 5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Omori, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Tamiya, S.; Nouda, R.; Nurdin, J.A.; Yamasaki, M.; Kotaki, T.; Kanai, Y. Effective SARS-CoV-2 replication of monolayers of intestinal epithelial cells differentiated from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 11610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, R.; Castro, M.F.G.; McCune, B.T.; Zeng, Q.; Rothlauf, P.W.; Sonnek, N.M.; Liu, Z.; Brulois, K.F.; Wang, X.; Greenberg, H.B. TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human small intestinal enterocytes. Science immunology 2020, 5, eabc3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanifer, M.L.; Kee, C.; Cortese, M.; Zumaran, C.M.; Triana, S.; Mukenhirn, M.; Kraeusslich, H.-G.; Alexandrov, T.; Bartenschlager, R.; Boulant, S. Critical role of type III interferon in controlling SARS-CoV-2 infection in human intestinal epithelial cells. Cell reports 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, A.O.; Akın, F.; Yazar, A.; Metin Akcan, Ö.; Topcu, C.; Aydın, O. Zonulin and claudin-5 levels in multisystem inflammatory syndrome and SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2022, 58, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyucu, M.; Kehribar, D.Y.; Çapraz, M.; Çapraz, A.; Arslan, M.; Çelik, Z.B.; Usta, B.; Birinci, A.; Ozgen, M.; Özgen, M. The relationship between COVID-19 disease severity and zonulin levels. Cureus 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley-McBain, T.; Manuzak, J.A. Zonulin as a biomarker and potential therapeutic target in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. The Journal of clinical investigation 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino-Kobayashi, L.A.; Ymaña, B.; Ruiz, J.; Mayanga-Herrera, A.; Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Pons, M.J. Zonulin, a marker of gut permeability, is associated with mortality in a cohort of hospitalised peruvian COVID-19 patients. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2022, 12, 1000291. [Google Scholar]
- Llorens, S.; Nava, E.; Muñoz-López, M.; Sánchez-Larsen, Á.; Segura, T. Neurological symptoms of COVID-19: the zonulin hypothesis. Frontiers in Immunology 2021, 12, 665300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, S.; El Asmar, R.; Di Pierro, M.; Grazia Clemente, M.; Sapone, A.T.A.; Thakar, M.; Iacono, G.; Carroccio, A.; D'Agate, C.; Not, T. Gliadin, zonulin and gut permeability: Effects on celiac and non-celiac intestinal mucosa and intestinal cell lines. Scandinavian journal of gastroenterology 2006, 41, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, J.; Vogelsang, H.; Hübl, W.; Waldhoer, T.; Lochs, H. Intestinal permeability and the prediction of relapse in Crohn's disease. The Lancet 1993, 341, 1437–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, M.N.; Wakita, D.; Franklin, M.K.; Carvalho, T.T.; Abolhesn, A.; Gomez, A.C.; Fishbein, M.C.; Chen, S.; Lehman, T.J.; Sato, K. Intestinal permeability and IgA provoke immune vasculitis linked to cardiovascular inflammation. Immunity 2019, 51, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases. F1000Research 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Not, T.; Wang, W.; Uzzau, S.; Berti, I.; Tommasini, A.; Goldblum, S.E. Zonulin, a newly discovered modulator of intestinal permeability, and its expression in coeliac disease. The Lancet 2000, 355, 1518–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Regulation of intercellular tight junctions by zonula occludens toxin and its eukaryotic analogue zonulin. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2000, 915, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Uzzau, S.; Goldblum, S.E.; Fasano, A. Human zonulin, a potential modulator of intestinal tight junctions. Journal of cell science 2000, 113, 4435–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Asmar, R.; Panigrahi, P.; Bamford, P.; Berti, I.; Not, T.; Coppa, G.V.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. Host-dependent zonulin secretion causes the impairment of the small intestine barrier function after bacterial exposure. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, K.E.; Sapone, A.; Fasano, A.; Vogel, S.N. Gliadin stimulation of murine macrophage inflammatory gene expression and intestinal permeability are MyD88-dependent: role of the innate immune response in Celiac disease. The Journal of Immunology 2006, 176, 2512–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Intestinal permeability and its regulation by zonulin: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2012, 10, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, A.F.; Maley, A.M.; Wu, C.; Gilboa, T.; Norman, M.; Lazarovits, R.; Mao, C.-P.; Newton, G.; Chang, M.; Nguyen, K. Ultra-sensitive serial profiling of SARS-CoV-2 antigens and antibodies in plasma to understand disease progression in COVID-19 patients with severe disease. Clinical chemistry 2020, 66, 1562–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogna, C.; Brogna, B.; Bisaccia, D.R.; Lauritano, F.; Marino, G.; Montano, L.; Cristoni, S.; Prisco, M.; Piscopo, M. Could SARS-CoV-2 have bacteriophage behavior or induce the activity of other bacteriophages? Vaccines 2022, 10, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogna, C.; Viduto, V.; Fabrowski, M.; Cristoni, S.; Marino, G.; Montano, L.; Piscopo, M. The importance of the gut microbiome in the pathogenesis and transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Someone on Earth:“.. we moved at the speed of Science!”-Science from the center of the Universe:“Hey man, I’m still waiting for you in the 50s!”. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2244718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrillo, M.; Querci, M.; Brogna, C.; Ponti, J.; Cristoni, S.; Markov, P.V.; Valsesia, A.; Leoni, G.; Benedetti, A.; Wiss, T. Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 bacteriophage potential in human gut microbiota. F1000Research 2022, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogna, C.; Costanzo, V.; Brogna, B.; Bisaccia, D.R.; Brogna, G.; Giuliano, M.; Montano, L.; Viduto, V.; Cristoni, S.; Fabrowski, M. Analysis of bacteriophage behavior of a human RNA virus, SARS-CoV-2, through the integrated approach of immunofluorescence microscopy, proteomics and D-amino acid quantification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogna, C.; Cristoni, S.; Petrillo, M.; Bisaccia, D.R.; Lauritano, F.; Montano, L.; Prisco, M.; Piscopo, M. The first report on detecting SARS-CoV-2 inside bacteria of the human gut microbiome: A case series on asymptomatic family members and a child with COVID-19. F1000Research 2022, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogna, C.; Cristoni, S.; Petrillo, M.; Querci, M.; Piazza, O.; Van den Eede, G. Toxin-like peptides in plasma, urine and faecal samples from COVID-19 patients. F1000Research 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, M.; Brogna, C.; Cristoni, S.; Querci, M.; Piazza, O.; Van den Eede, G. Increase of SARS-CoV-2 RNA load in faecal samples prompts for rethinking of SARS-CoV-2 biology and COVID-19 epidemiology. F1000Research 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Zhang, F.; Lui, G.C.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Li, A.Y.; Zhan, H.; Wan, Y.; Chung, A.C.; Cheung, C.P.; Chen, N. Alterations in gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coomes, E.A.; Haghbayan, H. Interleukin-6 in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Reviews in medical virology 2020, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, Z. The role of interleukin-6 in monitoring severe case of coronavirus disease 2019. EMBO molecular medicine 2020, 12, e12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Pang, J.; Ji, P.; Zhong, Z.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, J. Elevated interleukin-6 is associated with severity of COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Journal of medical virology 2021, 93, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.-X.; Agbana, Y.L.; Sun, Z.-S.; Fei, S.-W.; Zhao, H.-Q.; Zhou, X.-N.; Chen, J.-H.; Kassegne, K. Increased interleukin-6 is associated with long COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infectious Diseases of Poverty 2023, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, M.; Fatima, R.; Assaly, R. Elevated interleukin-6 and severe COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Journal of medical virology 2020, 92, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, M.; Zohora, F.T.; Anka, A.U.; Ali, K.; Maleknia, S.; Saffarioun, M.; Azizi, G. Interleukin-6 cytokine: An overview of the immune regulation, immune dysregulation, and therapeutic approach. International Immunopharmacology 2022, 111, 109130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood 1989, 74, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomarat, P.; Banchereau, J.; Davoust, J.; Karolina Palucka, A. IL-6 switches the differentiation of monocytes from dendritic cells to macrophages. Nature immunology 2000, 1, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narimatsu, M.; Maeda, H.; Itoh, S.; Atsumi, T.; Ohtani, T.; Nishida, K.; Itoh, M.; Kamimura, D.; Park, S.-J.; Mizuno, K. Tissue-specific autoregulation of the stat3 gene and its role in interleukin-6-induced survival signals in T cells. Molecular and cellular biology 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teague, T.K.; Schaefer, B.C.; Hildeman, D.; Bender, J.; Mitchell, T.; Kappler, J.W.; Marrack, P. Activation-induced inhibition of interleukin 6–mediated T cell survival and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 signaling. The Journal of experimental medicine 2000, 191, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curnow, S.J.; Scheel-Toellner, D.; Jenkinson, W.; Raza, K.; Durrani, O.M.; Faint, J.M.; Rauz, S.; Wloka, K.; Pilling, D.; Rose-John, S. Inhibition of T cell apoptosis in the aqueous humor of patients with uveitis by IL-6/soluble IL-6 receptor trans-signaling. The Journal of Immunology 2004, 173, 5290–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6: regulator of Treg/Th17 balance. European journal of immunology 2010, 40, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Therapeutic targeting of the interleukin-6 receptor. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology 2012, 52, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F.; Finotto, S. IL-6 signaling in autoimmunity, chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated cancer. Cytokine & growth factor reviews 2011, 22, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Aricha, R.; Mizrachi, K.; Fuchs, S.; Souroujon, M.C. Blocking of IL-6 suppresses experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. Journal of autoimmunity 2011, 36, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T. IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer. International immunology 2021, 33, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.E.; Maerz, M.D.; Buckner, J.H. IL-6: a cytokine at the crossroads of autoimmunity. Current opinion in immunology 2018, 55, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Iwakura, T.; Matsui, K.; Kawaguchi, H.; Obana, M.; Hayama, A.; Maeda, M.; Izumi, Y.; Komuro, I.; Ohsugi, Y. IL-6-mediated Th17 differentiation through RORγt is essential for the initiation of experimental autoimmune myocarditis. Cardiovascular research 2011, 91, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narazaki, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kishimoto, T. The role and therapeutic targeting of IL-6 in rheumatoid arthritis. Expert review of clinical immunology 2017, 13, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, K.A.; Manieri, N.A.; Liu, T.-C.; Stappenbeck, T.S. IL-6 stimulates intestinal epithelial proliferation and repair after injury. PloS one 2014, 9, e114195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, T.; Ikari, N.; Kouchi, T.; Kowatari, Y.; Kubota, Y.; Shimojo, N.; Tsuji, N.M. The molecular mechanism for activating IgA production by Pediococcus acidilactici K15 and the clinical impact in a randomized trial. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Yang, Z.-j.; Wang, F.-f.; Shang, H.-w.; Hua, R.; Xu, J.-d. Biological characteristics of IL-6 and related intestinal diseases. International journal of biological sciences 2021, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, Y.; Cui, T.; Zhang, J. IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway regulates the proliferation and damage of intestinal epithelial cells in patients with ulcerative colitis via H3K27ac. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 2021, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaza-Correa, J.; Ryan, L.; Kelly, L.; Allen, J.; Melo, A.; Jones, J.; Huggard, D.; Ryan, E.; Ó Maoldomhnaigh, C.; Geoghehan, S. Innate immune dysregulation in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 16463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazizadeh Esslami, G.; Mamishi, S.; Pourakbari, B.; Mahmoudi, S. Systematic review and meta-analysis on the serological, immunological, and cardiac parameters of the multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Journal of Medical Virology 2023, 95, e28927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybkina, K.; Bell, J.N.; Bradley, M.C.; Wohlbold, T.; Scafuro, M.; Meng, W.; Korenberg, R.C.; Davis-Porada, J.; Anderson, B.R.; Weller, R.J. SARS-CoV-2 infection and recovery in children: distinct T cell responses in MIS-C compared to COVID-19. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2023, 220, e20221518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, C.N.; Patel, R.S.; Trachtman, R.; Lepow, L.; Amanat, F.; Krammer, F.; Wilson, K.M.; Onel, K.; Geanon, D.; Tuballes, K. Mapping Systemic Inflammation and Antibody Responses in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). Cell 2023, 186, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerra, P.E.; Stowell, J.; Verkerke, H.; McCoy, J.; Jones, J.; Graciaa, S.; Lu, A.; Hussaini, L.; Anderson, E.J.; Rostad, C.A. Factor H autoantibodies contribute to complement dysregulation in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). American journal of hematology 2023, 98, E98–E101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Leong, M.W.; Rustagi, A.; Beck, A.; Zeng, L.; Holmes, S.; Qi, L.S.; Blish, C.A. SARS-CoV-2 escapes direct NK cell killing through Nsp1-mediated downregulation of ligands for NKG2D. Cell reports 2022, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogna, C.; Montano, L.; Zanolin, M.E.; Bisaccia, D.R.; Ciammetti, G.; Viduto, V.; Fabrowski, M.; Baig, A.M.; Gerlach, J.; Gennaro, I. A retrospective cohort study on early antibiotic use in vaccinated and unvaccinated COVID-19 patients. Journal of Medical Virology 2024, 96, e29507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Torre, E.; Criscuolo, E.; Lanzillotta, M.; Locatelli, M.; Clementi, N.; Mancini, N.; Dagna, L.; Group, C.-B.S. IL-1 and IL-6 inhibition affects the neutralising activity of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in patients with COVID-19. The Lancet. Rheumatology 2021, 3, e829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nature medicine 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres-Székely, A.; Szász, C.; Pap, D.; Szebeni, B.; Bokrossy, P.; Vannay, Á. Zonulin as a potential therapeutic target in microbiota-gut-brain axis disorders: encouraging results and emerging questions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nature reviews Gastroenterology & hepatology.
- Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Surface components and metabolites of probiotics for regulation of intestinal epithelial barrier. Microbial Cell Factories 2020, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Andrew, H.; Kirschner, B.S.; Guandalini, S. Is Lactobacillus GG helpful in children with Crohn’s disease? Results of a preliminary, open-label study. Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition 2000, 31, 453–457. [Google Scholar]
- Ewaschuk, J.B.; Diaz, H.; Meddings, L.; Diederichs, B.; Dmytrash, A.; Backer, J.; Looijer-van Langen, M.; Madsen, K.L. Secreted bioactive factors from Bifidobacterium infantis enhance epithelial cell barrier function. American journal of physiology-gastrointestinal and liver physiology 2008, 295, G1025–G1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Li, D.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wan, J.-Y.; Yao, H.; Yuan, C.-S. Probiotics fortify intestinal barrier function: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Frontiers in Immunology 2023, 14, 1143548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Guo, T.; Cao, Y.; Teng, J.; Hao, X.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Z. Antioxidant status and gut microbiota change in an aging mouse model as influenced by exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum YW11 isolated from Tibetan kefir. Journal of dairy science 2017, 100, 6025–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrof, E.O.; Kojima, K.; Ropeleski, M.J.; Musch, M.W.; Tao, Y.; De Simone, C.; Chang, E.B. Probiotics inhibit nuclear factor-κB and induce heat shock proteins in colonic epithelial cells through proteasome inhibition. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1474–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martorell, P.; Alvarez, B.; Llopis, S.; Navarro, V.; Ortiz, P.; Gonzalez, N.; Balaguer, F.; Rojas, A.; Chenoll, E.; Ramon, D. Heat-treated Bifidobacterium longum CECT-7347: a whole-cell postbiotic with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and gut-barrier protection properties. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, D.; Benzon, B.; Srsen, S.; Polic, B.; Vukovic Novogradec, A.; Milic, P.; Markic, J. The Impact of Vitamin D Levels on Clinical Manifestations of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Cross-Sectional Study. Life 2023, 13, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D. Nonclassic actions of vitamin D. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2009, 94, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, M.; Vidal, M.; Arcidiacono, M.V.; Tebas, P.; Yarasheski, K.E.; Dusso, A.S. HIV-protease inhibitors impair vitamin D bioactivation to 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Aids 2003, 17, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantorna, M.T.; Zhu, Y.; Froicu, M.; Wittke, A. Vitamin D status, 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, and the immune system. The American journal of clinical nutrition 2004, 80, 1717S–1720S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cippitelli, M.; Santoni, A. Vitamin D3: a transcriptional modulator of the interferon-γ gene. European journal of immunology 1998, 28, 3017–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sims, G.P.; Chen, X.X.; Gu, Y.Y.; Chen, S.; Lipsky, P.E. Modulatory effects of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on human B cell differentiation. The Journal of Immunology 2007, 179, 1634–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenngam, N.; Holick, M.F. Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, J.; van den Ouweland, J.; Geven, C.; Pickkers, P.; Kox, M. Vitamin D deficiency in COVID-19: Mixing up cause and consequence. Metabolism-Clinical and Experimental 2021, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Rawat, A.; Alwakeel, M.; Sharif, E.; Al Khodor, S. The potential role of vitamin D supplementation as a gut microbiota modifier in healthy individuals. Scientific reports 2020, 10, 21641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellerba, F.; Muzio, V.; Gnagnarella, P.; Facciotti, F.; Chiocca, S.; Bossi, P.; Cortinovis, D.; Chiaradonna, F.; Serrano, D.; Raimondi, S. The association between vitamin D and gut microbiota: a systematic review of human studies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, K.Y.; Stuhldreher, W.L. Prevalence and correlates of vitamin D deficiency in US adults. Nutrition research 2011, 31, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, K.D.; Dowling, K.G.; Škrabáková, Z.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Valtueña, J.; De Henauw, S.; Moreno, L.; Damsgaard, C.T.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Mølgaard, C. Vitamin D deficiency in Europe: pandemic? The American journal of clinical nutrition 2016, 103, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, E.A.; Rizk, N. The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among female college students at Qatar University. 2011.
- Mullish, B.H.; Marchesi, J.R.; McDonald, J.A.; Pass, D.A.; Masetti, G.; Michael, D.R.; Plummer, S.; Jack, A.A.; Davies, T.S.; Hughes, T.R. Probiotics reduce self-reported symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection in overweight and obese adults: should we be considering probiotics during viral pandemics? Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1900997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, G.; Borrazzo, C.; Pinacchio, C.; Santinelli, L.; Innocenti, G.P.; Cavallari, E.N.; Celani, L.; Marazzato, M.; Alessandri, F.; Ruberto, F. Oral bacteriotherapy in patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study. Frontiers in Nutrition 2021, 7, 613928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, D.; Davies, T.; Jack, A.; Masetti, G.; Marchesi, J.; Wang, D.; Mullish, B.; Plummer, S. Daily supplementation with the Lab4P probiotic consortium induces significant weight loss in overweight adults. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mena, J.; Corona-Cervantes, K.; Cuervo-Zanatta, D.; Benitez-Guerrero, T.; Vélez-Ixta, J.M.; Zavala-Torres, N.G.; Villalobos-Flores, L.E.; Hernández-Quiroz, F.; Perez-Cruz, C.; Murugesan, S. Gut microbiota in a population highly affected by obesity and type 2 diabetes and susceptibility to COVID-19. World Journal of Gastroenterology 2021, 27, 7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkin, V.; Fomin, V.; Moiseev, S.; Brovko, M.; Maslennikov, R.; Ulyanin, A.; Sholomova, V.; Vasilyeva, M.; Trush, E.; Shifrin, O. Efficacy of a Probiotic Consisting of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus PDV 1705, Bifidobacterium bifidum PDV 0903, Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis PDV 1911, and Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum PDV 2301 in the Treatment of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: a Randomized Controlled Trial. Probiotics and antimicrobial proteins 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kurian, S.J.; Unnikrishnan, M.K.; Miraj, S.S.; Bagchi, D.; Banerjee, M.; Reddy, B.S.; Rodrigues, G.S.; Manu, M.K.; Saravu, K.; Mukhopadhyay, C. Probiotics in prevention and treatment of COVID-19: current perspective and future prospects. Archives of medical research 2021, 52, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, H.S.; Bilen, Ö. Oral booster probiotic bifidobacteria in SARS-COV-2 patients. International journal of immunopathology and pharmacology 2021, 35, 20587384211059677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Castrellón, P.; Gandara-Martí, T.; Abreu Y Abreu, A.T.; Nieto-Rufino, C.D.; López-Orduña, E.; Jiménez-Escobar, I.; Jiménez-Gutiérrez, C.; López-Velazquez, G.; Espadaler-Mazo, J. Probiotic improves symptomatic and viral clearance in Covid19 outpatients: a randomized, quadruple-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2018899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; Mak, J.W.; Chow, K.M.; Lui, G.; Li, T.C.; Wong, C.K.; Chan, P.K.; Ching, J.Y.; Fujiwara, Y. Gut microbiota-derived synbiotic formula (SIM01) as a novel adjuvant therapy for COVID-19: An open-label pilot study. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2022, 37, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviano, A.; Potenza, A.; Siciliano, V.; Petruzziello, C.; Tarli, C.; Migneco, A.; Nasella, F.; Franceschi, F.; Ojetti, V. COVID-19 pneumonia and gut inflammation: the role of a mix of three probiotic strains in reducing inflammatory markers and need for oxygen support. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, B.R.; Hao, Q. Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections. Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Arena, M.P.; Capozzi, V.; Russo, P.; Drider, D.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Immunobiosis and probiosis: antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria with a focus on their antiviral and antifungal properties. Applied microbiology and biotechnology 2018, 102, 9949–9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.Y.; Lee, D.K.; Ha, N.J.; Shin, H.S. Antiviral effects of Lactobacillus ruminis SPM0211 and Bifidobacterium longum SPM1205 and SPM1206 on rotavirus-infected Caco-2 cells and a neonatal mouse model. Journal of Microbiology 2015, 53, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanada, S.; Pirzadeh, M.; Carver, K.Y.; Deng, J.C. Respiratory viral infection-induced microbiome alterations and secondary bacterial pneumonia. Frontiers in immunology 2018, 9, 418009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.N.; Siefker, D.; Vu, L.; You, D.; DeVincenzo, J.; Pierre, J.; Cormier, S.A. Altered gut microbiota in infants is associated with respiratory syncytial virus disease severity. BMC microbiology 2020, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, A.; Vijayakumar, V.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Ter Haar, J.; Obis, D.; Espadaler, J.; Binda, S.; Desiraju, S.; Day, R. Viral infections, the microbiome, and probiotics. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2021, 10, 596166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira-Rosário, A.; Marques, C.; Pinheiro, H.; Araújo, J.R.; Ribeiro, P.; Rocha, R.; Mota, I.; Pestana, D.; Ribeiro, R.; Pereira, A. Gut microbiota diversity and C-reactive protein are predictors of disease severity in COVID-19 patients. Frontiers in Microbiology 2021, 12, 705020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, W.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Guo, M.; Zeng, W.; Xu, Z.; Cao, D.; Pan, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K. Analysis of the intestinal microbiota in COVID-19 patients and its correlation with the inflammatory factor IL-18. Medicine in Microecology 2020, 5, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Cai, H.; Shen, Y. Management of corona virus disease-19 (COVID-19): the Zhejiang experience. J Zhejiang Univ (Med Sci) 49 (1): 0. 2020.
- Reinold, J.; Farahpour, F.; Fehring, C.; Dolff, S.; Konik, M.; Korth, J.; van Baal, L.; Hoffmann, D.; Buer, J.; Witzke, O. A pro-inflammatory gut microbiome characterizes SARS-CoV-2 infected patients and a reduction in the connectivity of an anti-inflammatory bacterial network associates with severe COVID-19. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2021, 11, 747816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Wu, X.; Wen, W.; Lan, P. Gut microbiome alterations in COVID-19. Genomics, Proteomics and Bioinformatics 2021, 19, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazan, S.; Stollman, N.; Bozkurt, H.S.; Dave, S.; Papoutsis, A.J.; Daniels, J.; Barrows, B.D.; Quigley, E.M.; Borody, T.J. Lost microbes of COVID-19: Bifidobacterium, Faecalibacterium depletion and decreased microbiome diversity associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection severity. BMJ open Gastroenterology 2022, 9, e000871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on human health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, H.S.; Quigley, E.M. The probiotic Bifidobacterium in the management of Coronavirus: A theoretical basis. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology 2020, 34, 2058738420961304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, J.M. Probiotics, prebiotics, and COVID-19 infection: A review article. Saudi journal of biological sciences 2021, 28, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodavirdipour, A.; Asadimanesh, M.; Masoumi, S.A. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 genetic blueprints on the oral manifestation of COVID-19: a case report. Global Medical Genetics 2021, 8, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vuyst, L.; Moens, F.; Selak, M.; Rivière, A.; Leroy, F. Summer Meeting 2013: growth and physiology of bifidobacteria. Journal of applied microbiology 2014, 116, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.J.; Shin, H.S. Antimicrobial and immunomodulatory effects of bifidobacterium strains: A review. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2020, 30, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.R.; Harnisch, L.C.; Alcon-Giner, C.; Mitra, S.; Wright, C.J.; Ketskemety, J.; van Sinderen, D.; Watson, A.J.; Hall, L.J. Bifidobacterium breve reduces apoptotic epithelial cell shedding in an exopolysaccharide and MyD88-dependent manner. Open biology 2017, 7, 160155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyakov, I.N.; Mavletova, D.A.; Chernyshova, I.N.; Snegireva, N.A.; Gavrilova, M.V.; Bushkova, K.K.; Dyachkova, M.S.; Alekseeva, M.G.; Danilenko, V.N. FN3 protein fragment containing two type III fibronectin domains from B. longum GT15 binds to human tumor necrosis factor alpha in vitro. Anaerobe 2020, 65, 102247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, J.; Hong, B.-y. The gut–lung axis in tuberculosis. Pathogens and Disease 2017, 75, ftx097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L.; Delgado, S.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Sánchez, B.; Margolles, A. Bifidobacteria and their molecular communication with the immune system. Frontiers in microbiology 2017, 8, 302400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenoir, M.; Martín, R.; Torres-Maravilla, E.; Chadi, S.; González-Dávila, P.; Sokol, H.; Langella, P.; Chain, F.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. Butyrate mediates anti-inflammatory effects of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in intestinal epithelial cells through Dact3. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1826748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The controversial role of human gut lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Ma, W.-L.; Wang, X. Linking the gut microbiota to persistent symptoms in survivors of COVID-19 after discharge. Journal of Microbiology 2021, 59, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes de Almeida, V.; Engel, D.F.; Ricci, M.F.; Cruz, C.S.; Lopes, Í.S.; Alves, D.A.; d’Auriol, M.; Magalhães, J.; Machado, E.C.; Rocha, V.M. Gut microbiota from patients with COVID-19 cause alterations in mice that resemble post-COVID symptoms. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2249146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




