Submitted:
12 June 2024
Posted:
13 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Density-Based Topology Optimization
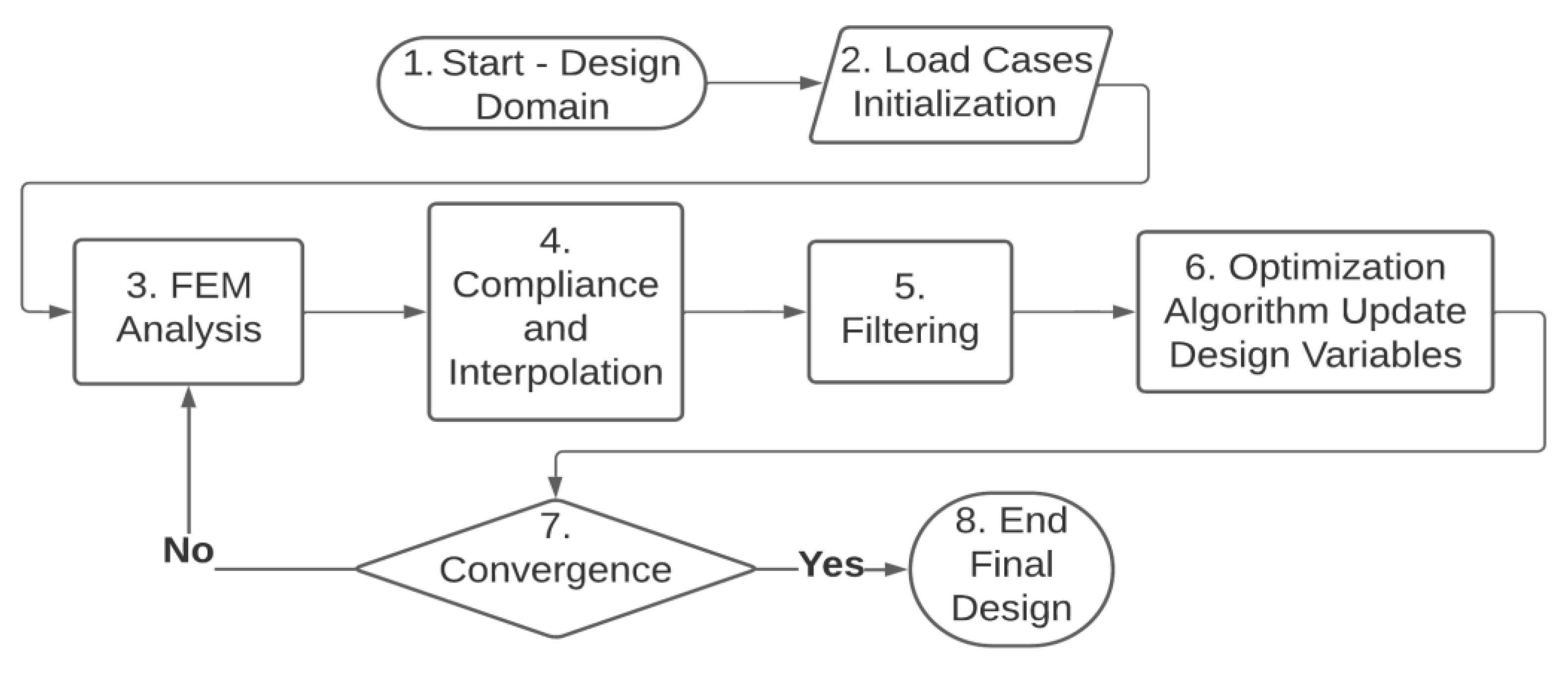
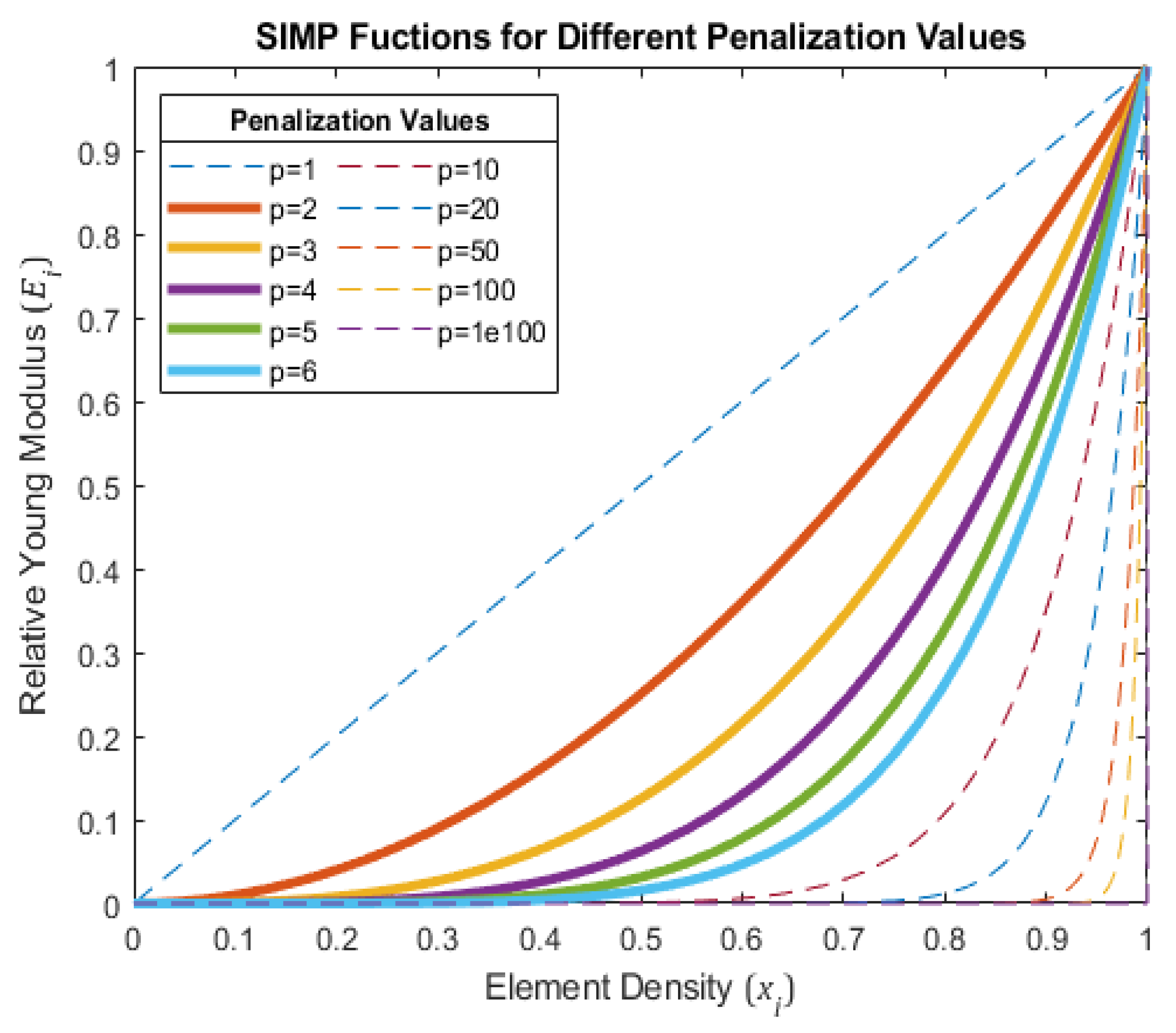
1.2. Interpolation Scheme, the SIMP
1.3. Filtering, the Density Filter
1.4. Study Description and Novelty
- The initial section discusses the chosen parameters values criterion is, along with the load case and material parameters of the main study case for the sensitivity analysis.
- Following that, the parameters used for analyzing the results are exposed and explained, with particular emphasis in the measure of the discreteness and the evaluation of the machinability,
- Subsequently, results of the 92 simulations are exposed and analyzed, being able to obtain the conclusions related to the aim of the study.
- The machining filter is presented and verified through different verification tests.
- Finally, the conclusions drawn from the study and potential avenues for future research are presented.
2. The Case Study
2.1. Parameters’ Values Selection Criterion
- Values used in other mentioned studies (OS).
- Values derived from the Euclidean distance between the element under analysis and the neighboring layer of elements (ED).
- Large estimated values intended to observe the behavior of the method with extreme values (LV).
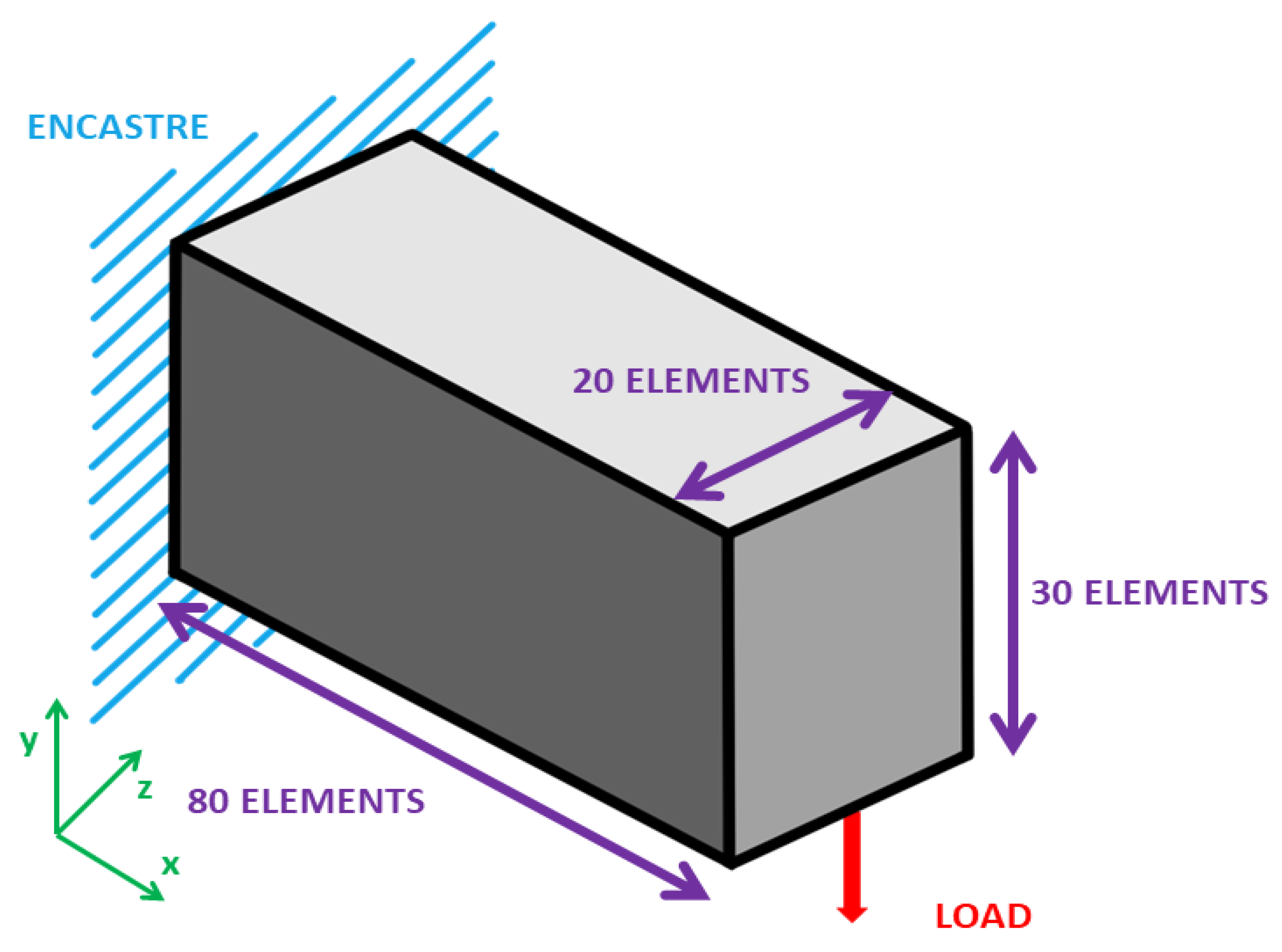
2.2. Case Study Description and Material
2.3. Parameters for the Results Analysis
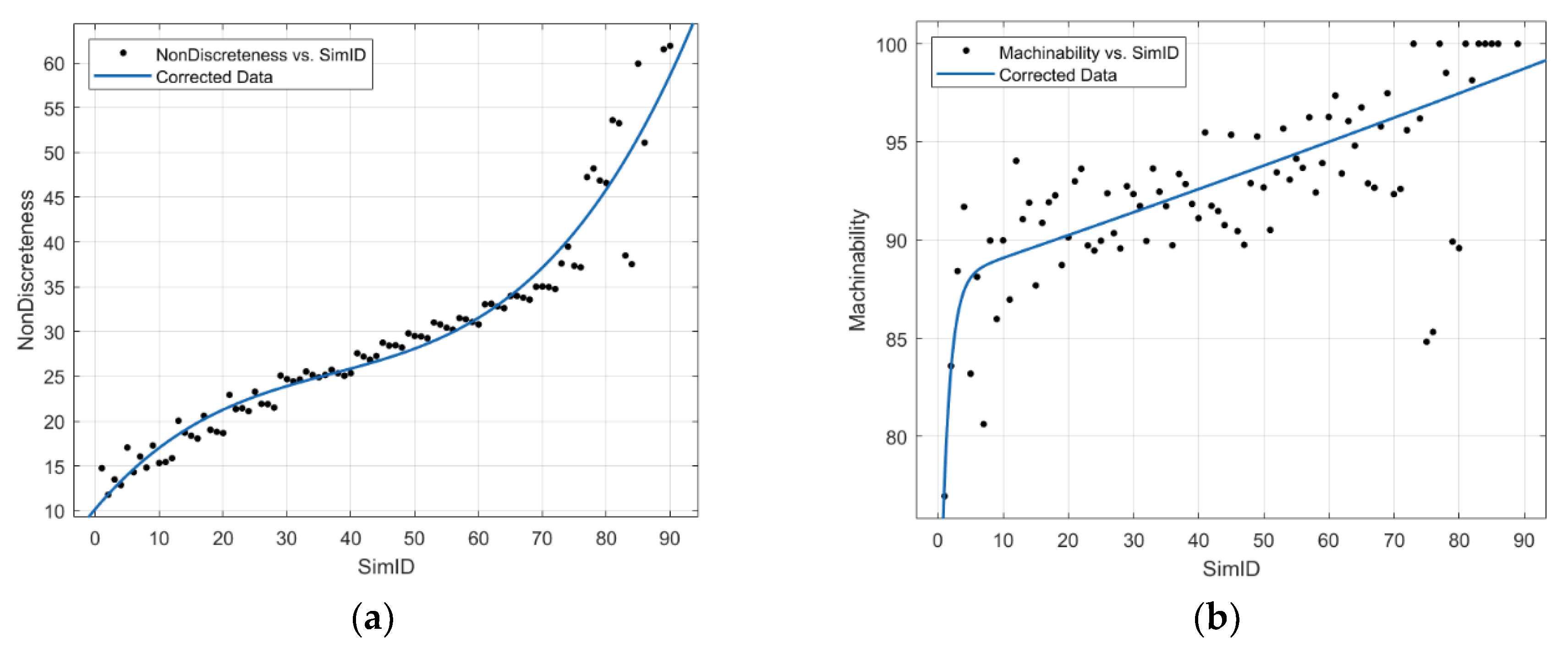
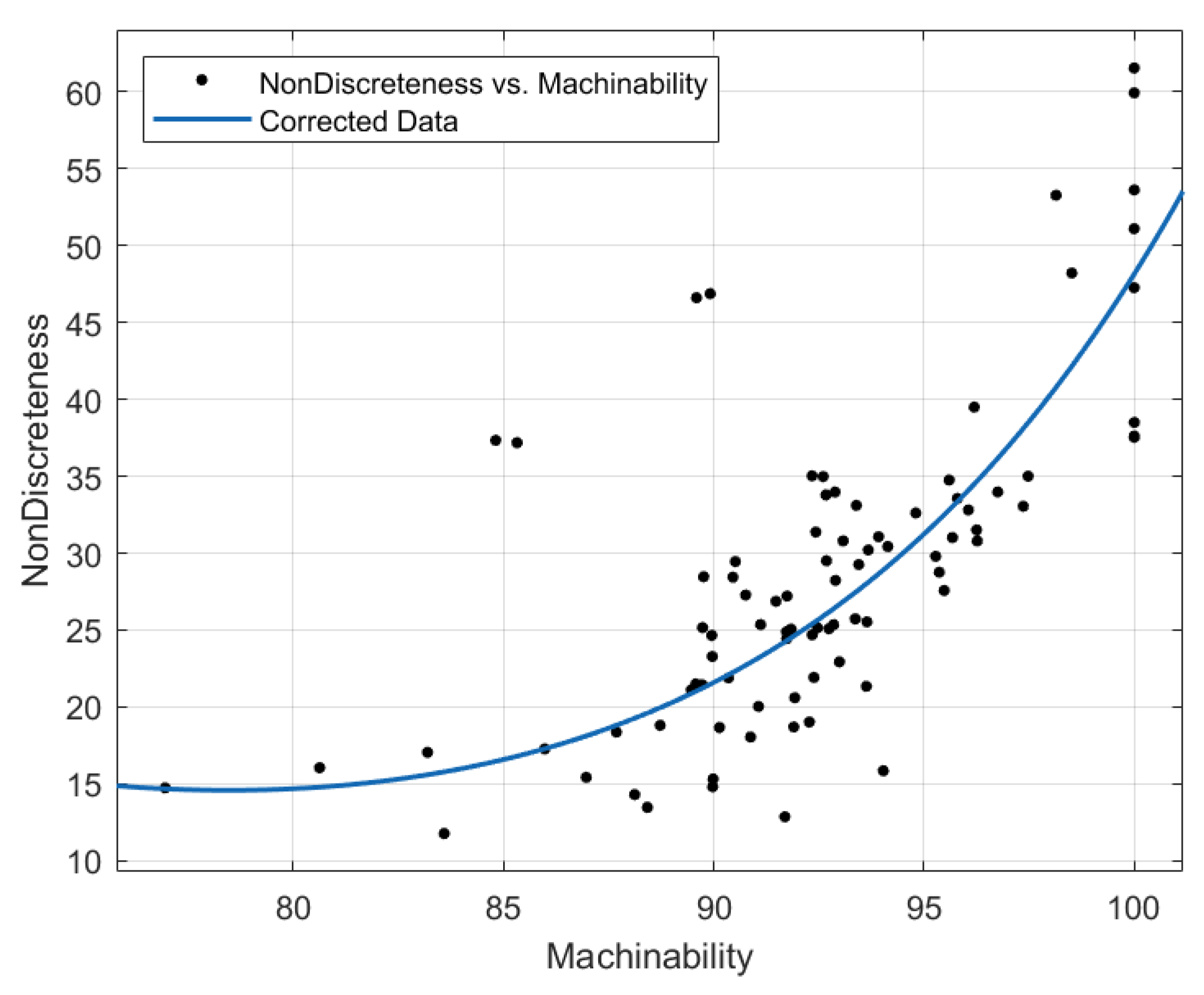
2.3.1. Measure of Non-Discreteness
2.3.2. Machinability
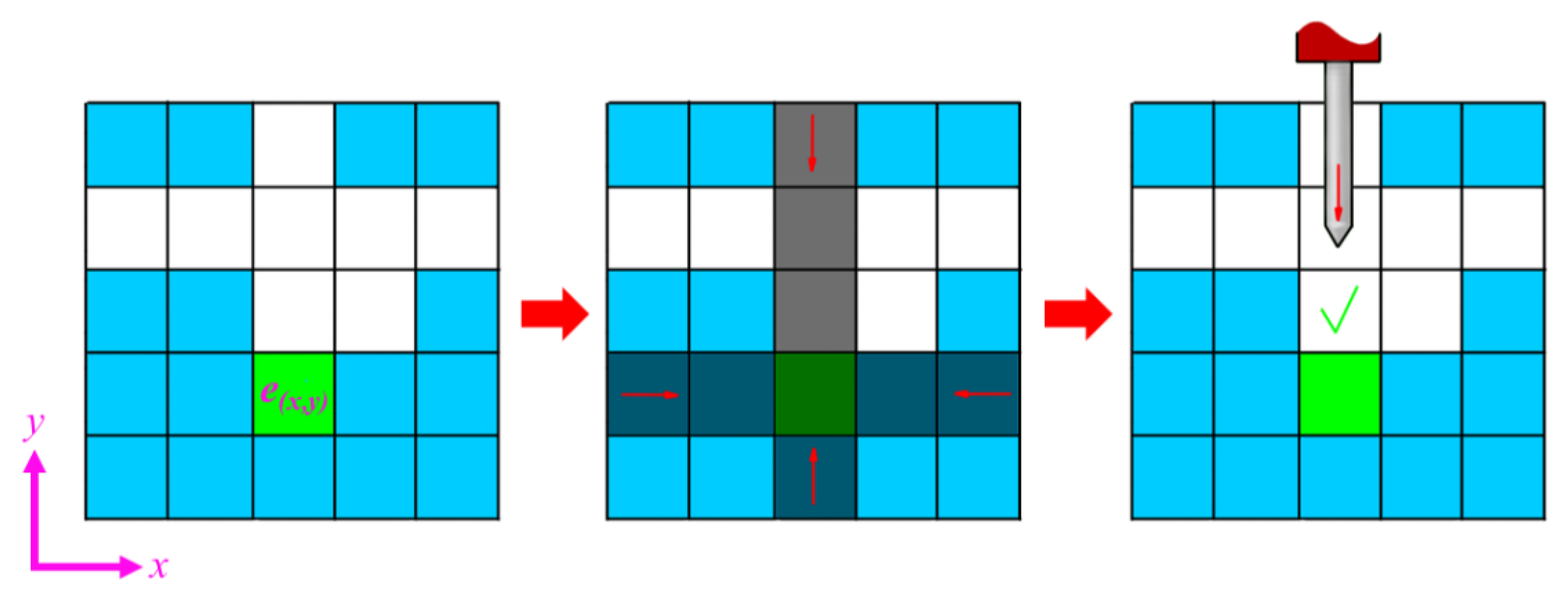
- The external layer (EL): Comprising all the elements located on the boundaries of the design domain. These elements are always accessible because they do not have any solid interface with the exterior.
- The core layers (CL): Representing the internal solid region, consisting of all the elements forming the shape of the part excluding the frontier elements.
- The frontier layer (FL): Consisting of the elements above the density threshold and located between the solid and void phases.
- Elements directly accessible for a tool: These are the elements within the FL that can be readily machined using a tool.
- Elements not directly accessible but machinable by machining a neighboring element: These elements are not directly accessible to a tool but can still be manufactured through the machining of a neighboring element.
- Non-machinable elements: This group consists of elements within the FL that are not machinable.
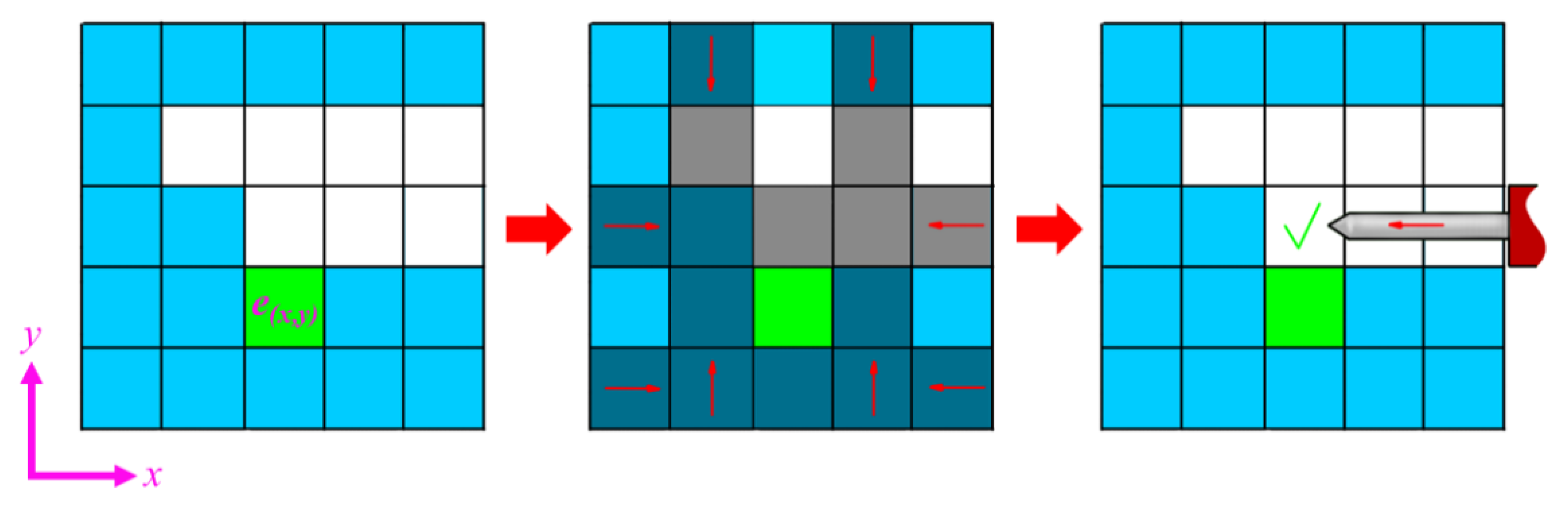
- 1.
- Sensitivity Analysis
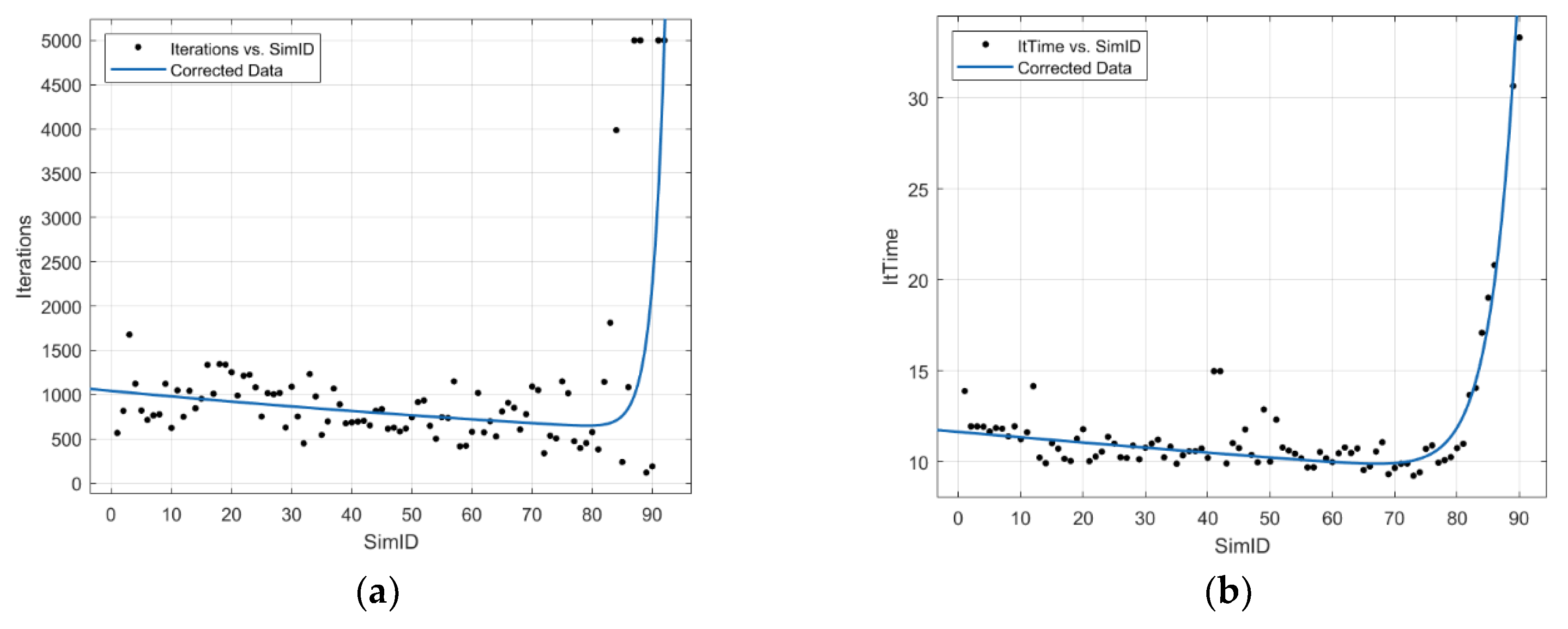
- Numerical results for the analysis are shown in Table 1, being:
- Sim. ID, the identifier of the specific TO case.
- Penalization, p; and Filter Radius R.
- Iterations, the number of iterations required to achieve the convergence condition. Note that a maximum of 5000 iterations was set, so if the TO reaches to this value, convergence is not reached.
- It. Time, the average time the TO took in every iteration.
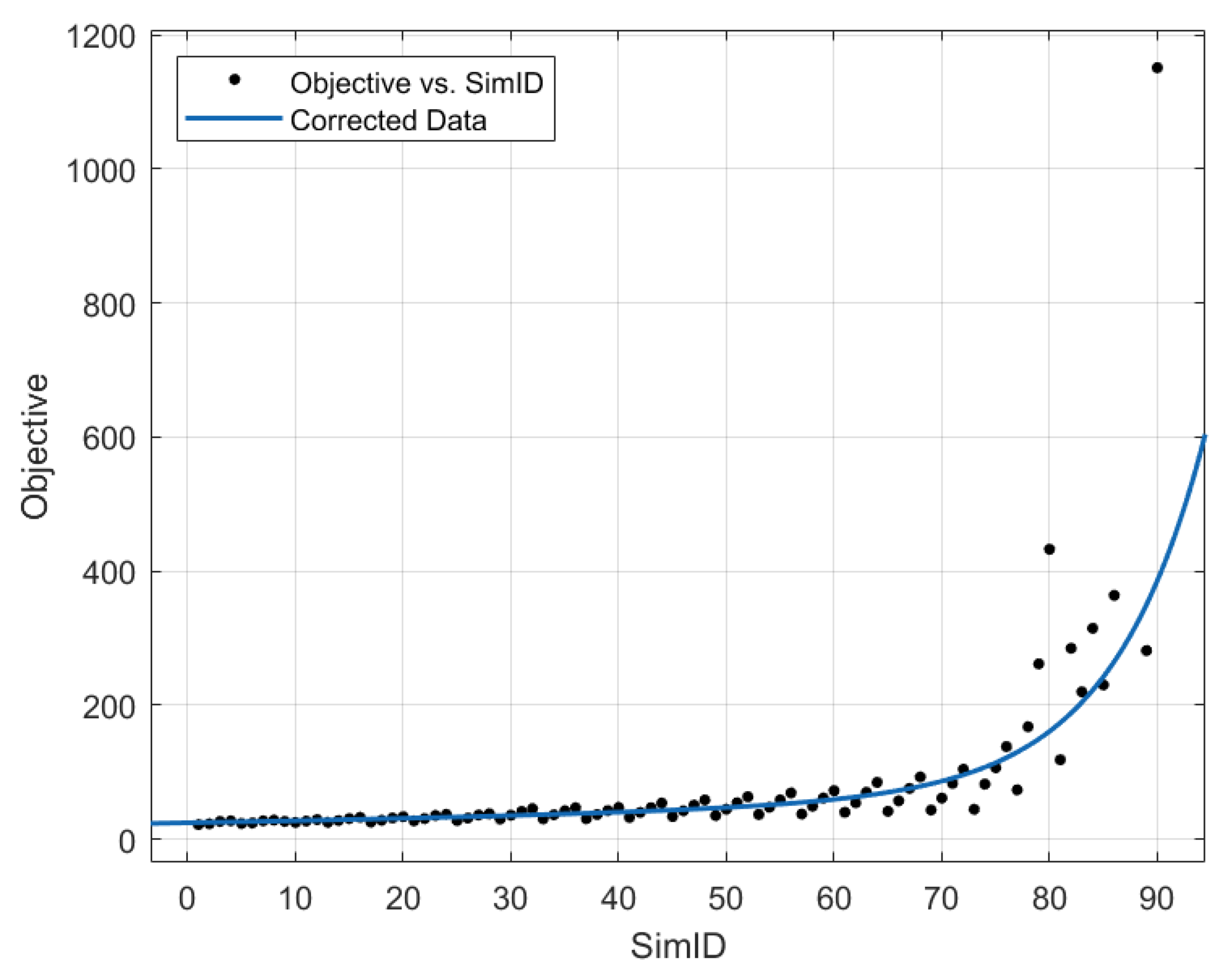
- Objective, the compliance of the structure, calculated as in Equation (8):
- Non-Discreteness, the described parameter in Section 2.3.1.
- Machinability, the described parameter in Section 2.3.2.
- 2.
- Additions to Filtering
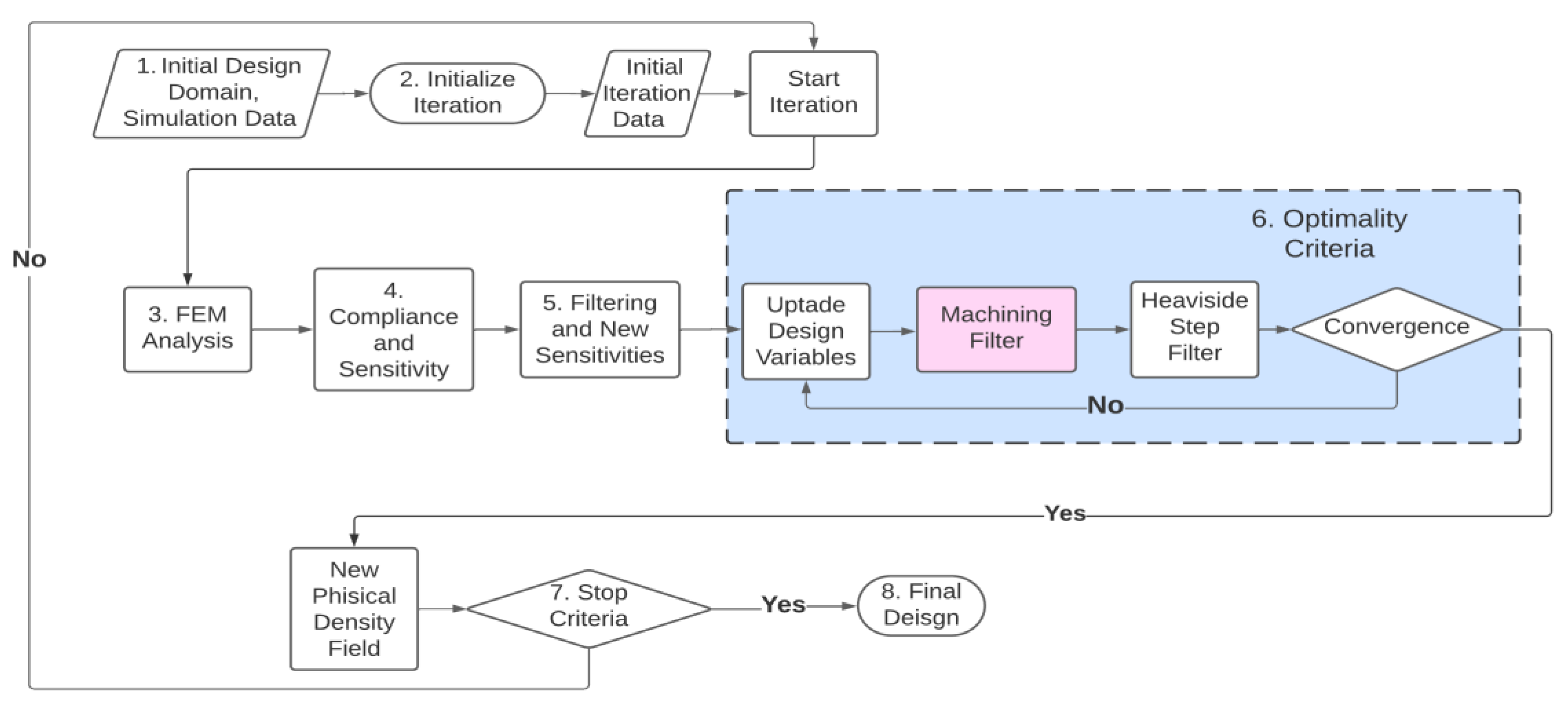
2.4. Machining Filter
2.5. Heaviside Step Filter
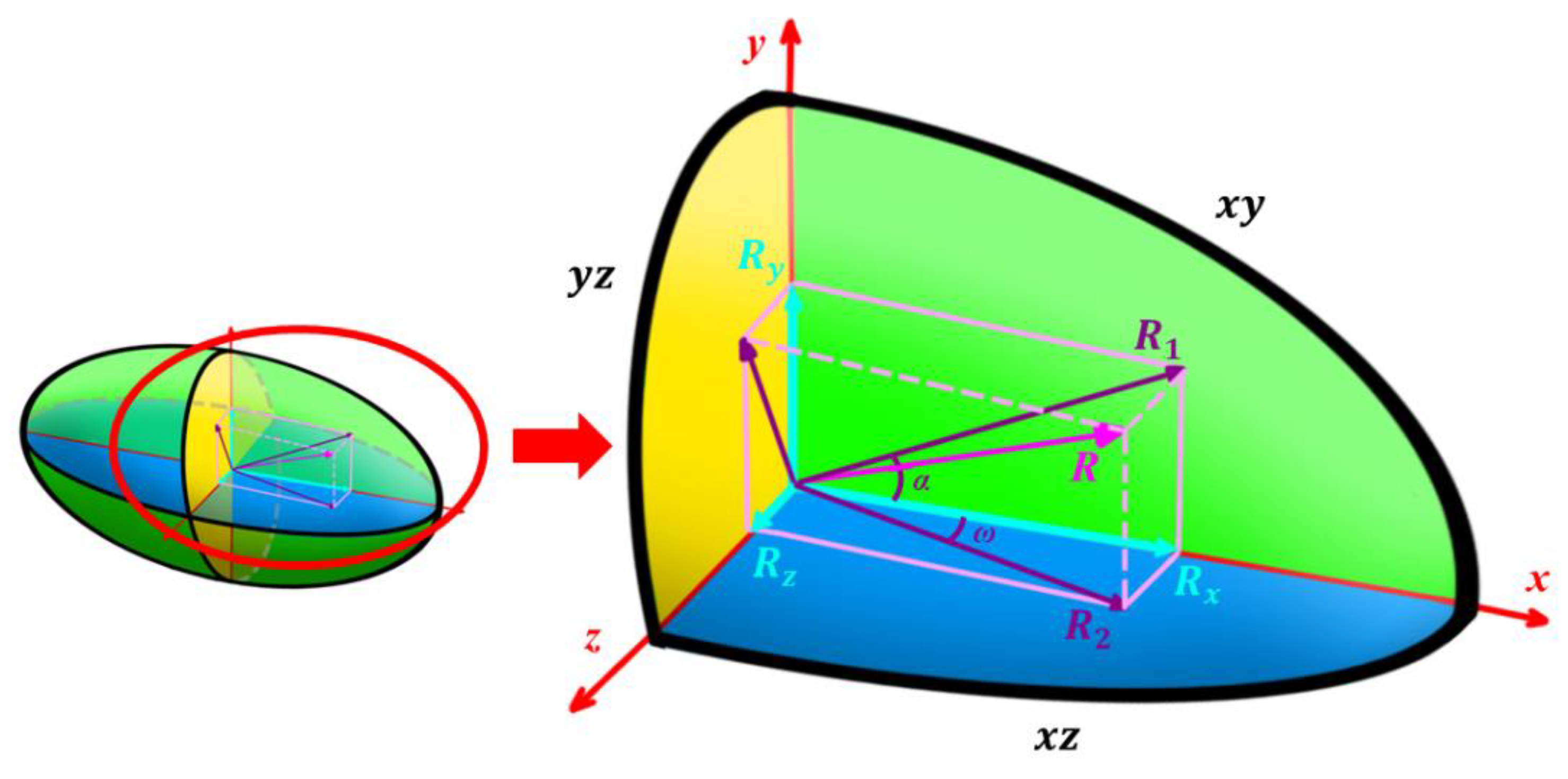
2.6. Ellipsoid-Shaped Density Filter
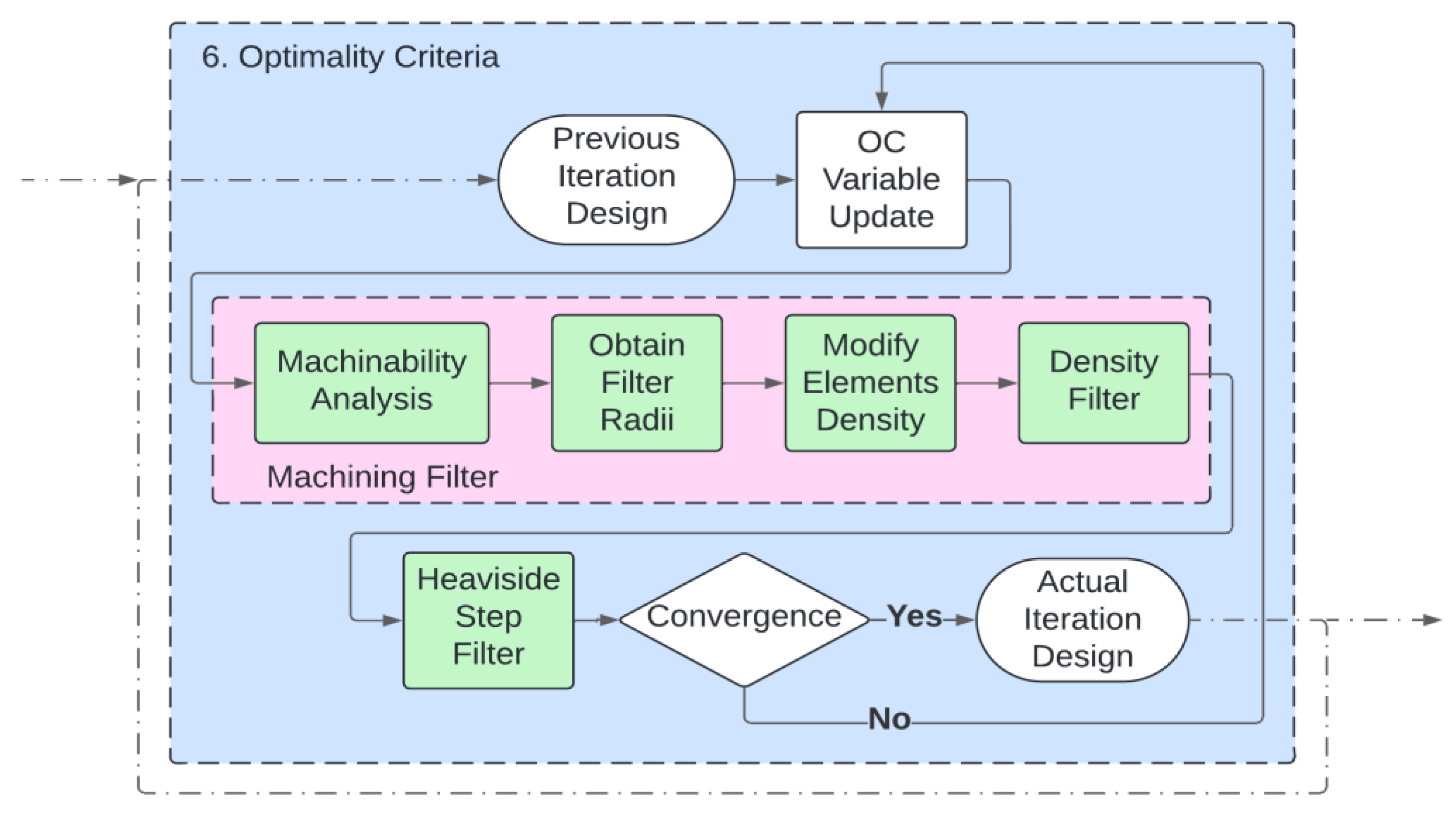
3. Results
3.1. Validation
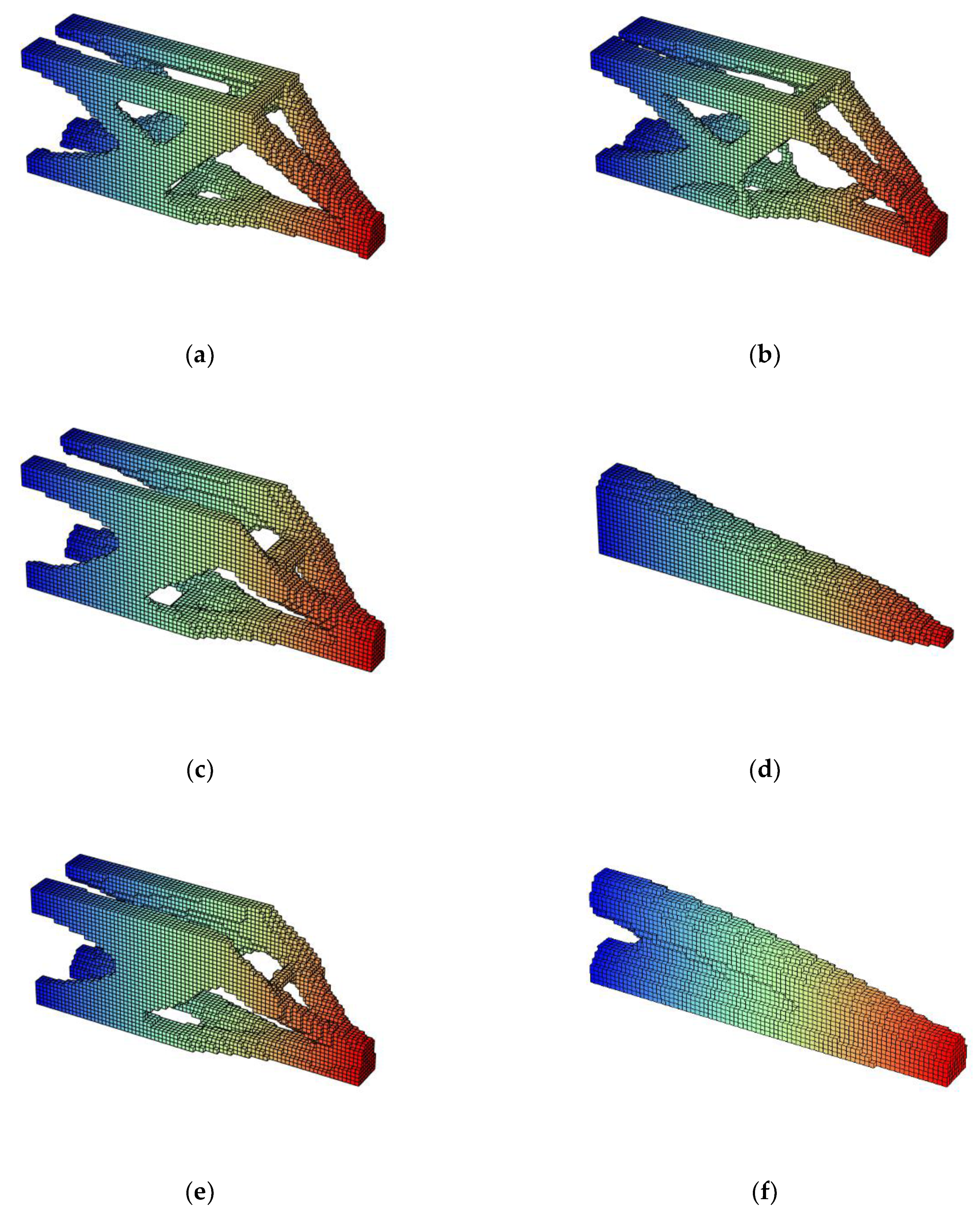
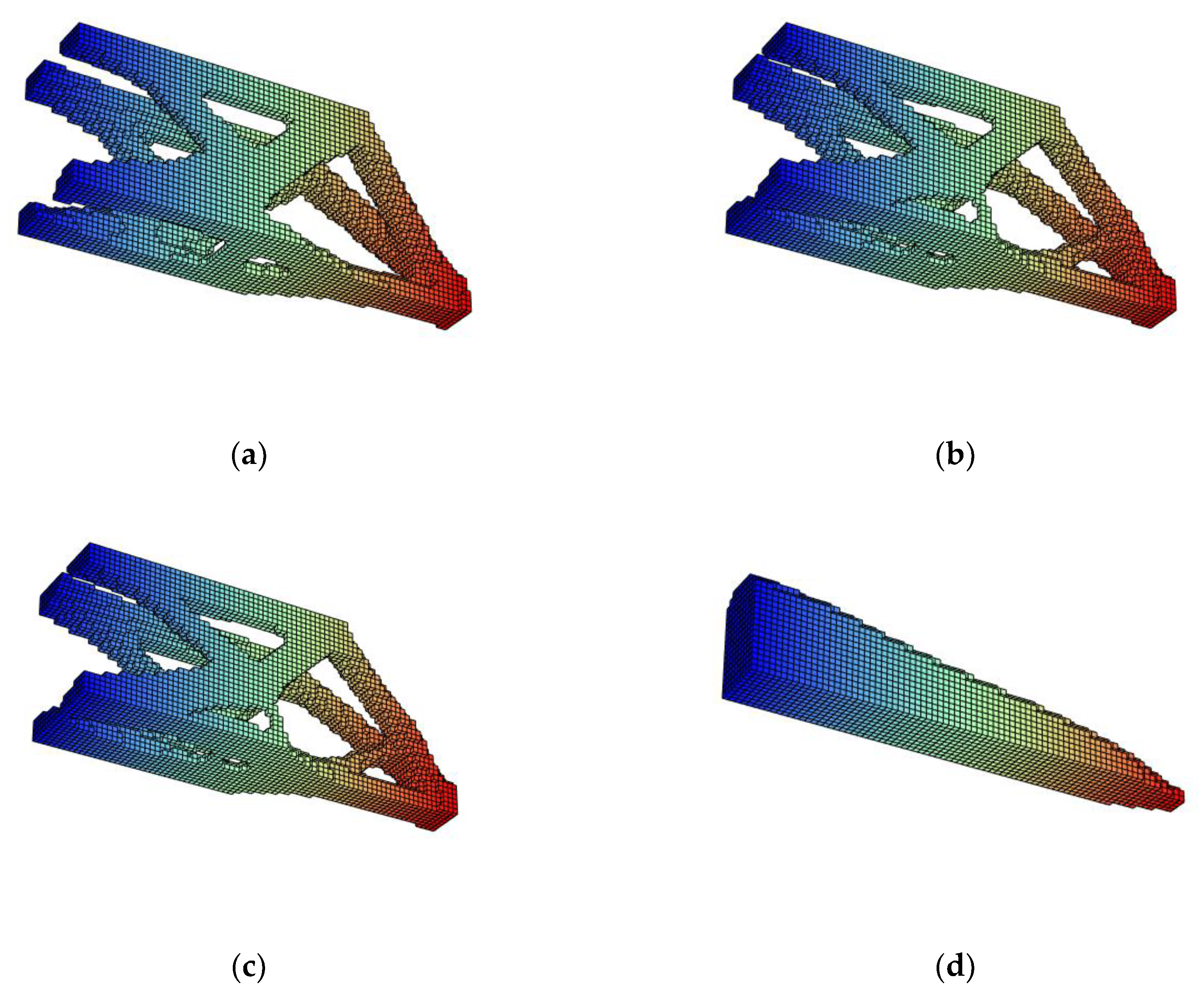
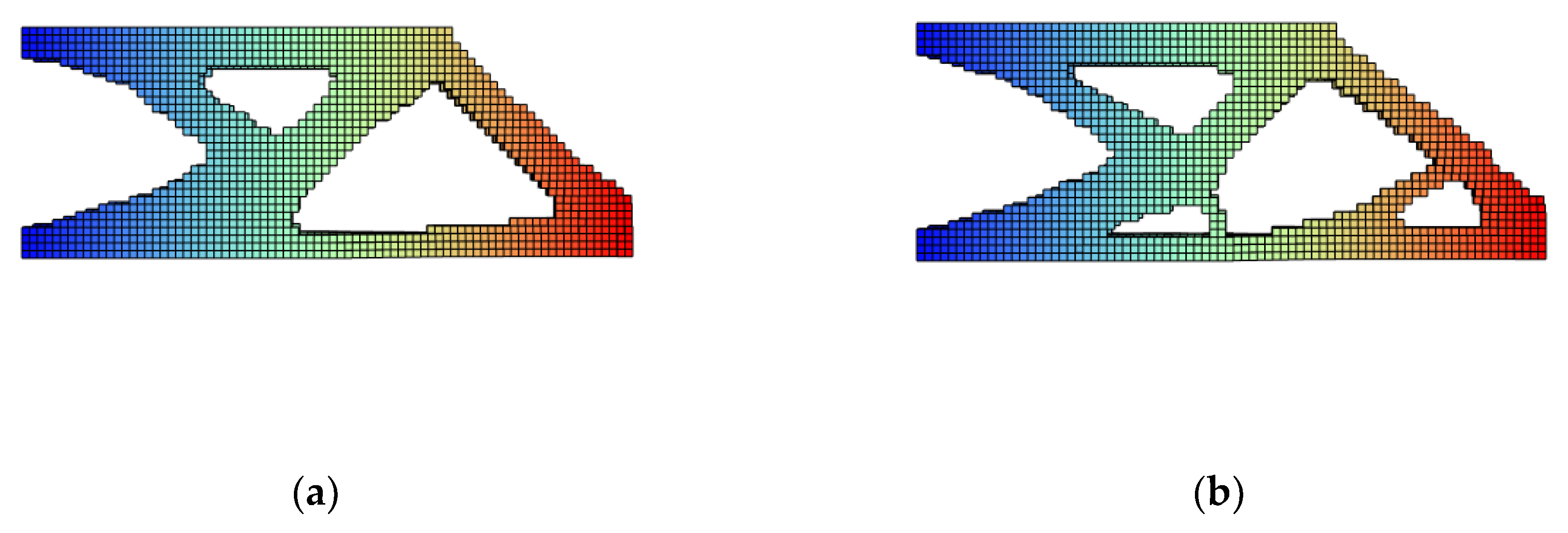
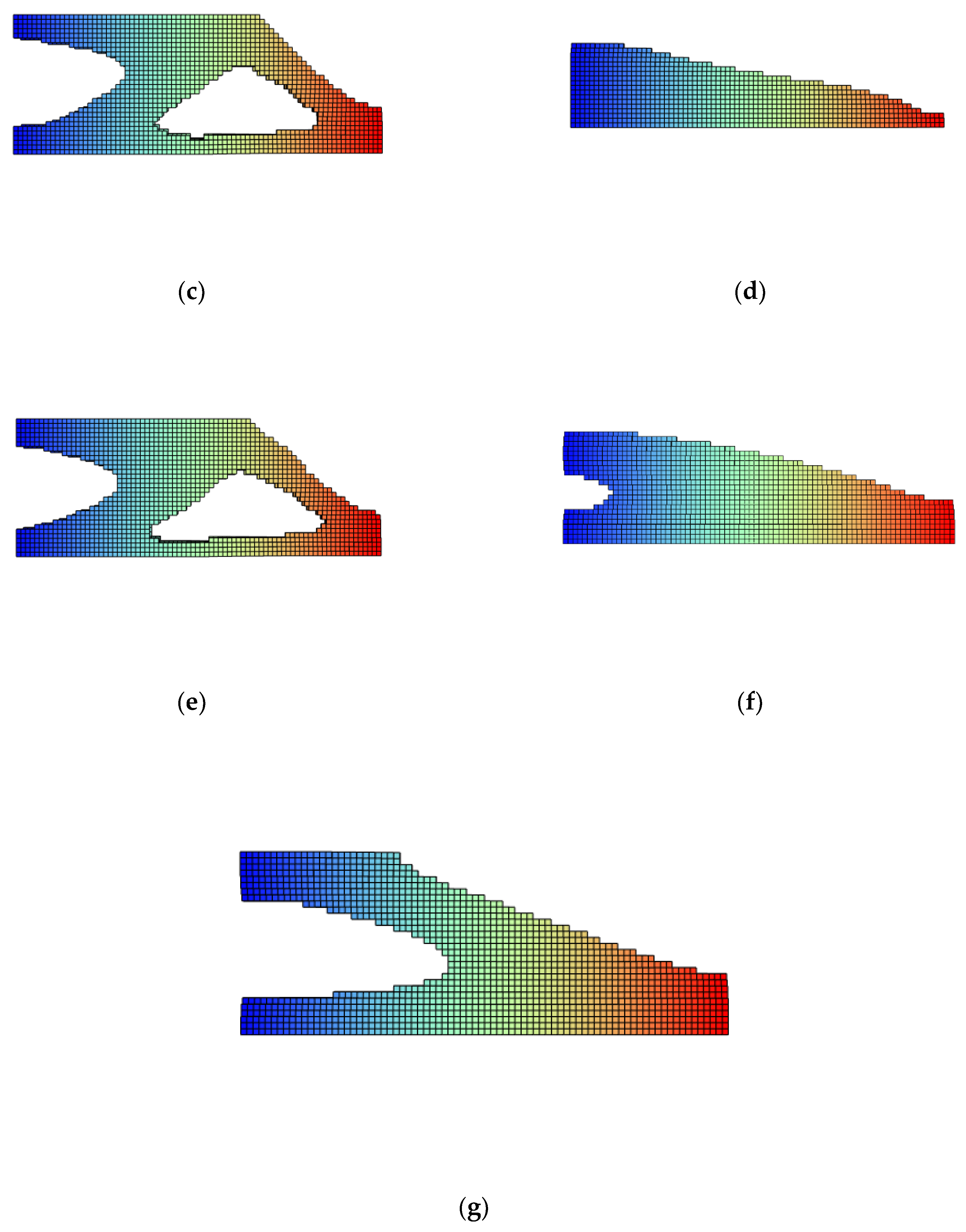
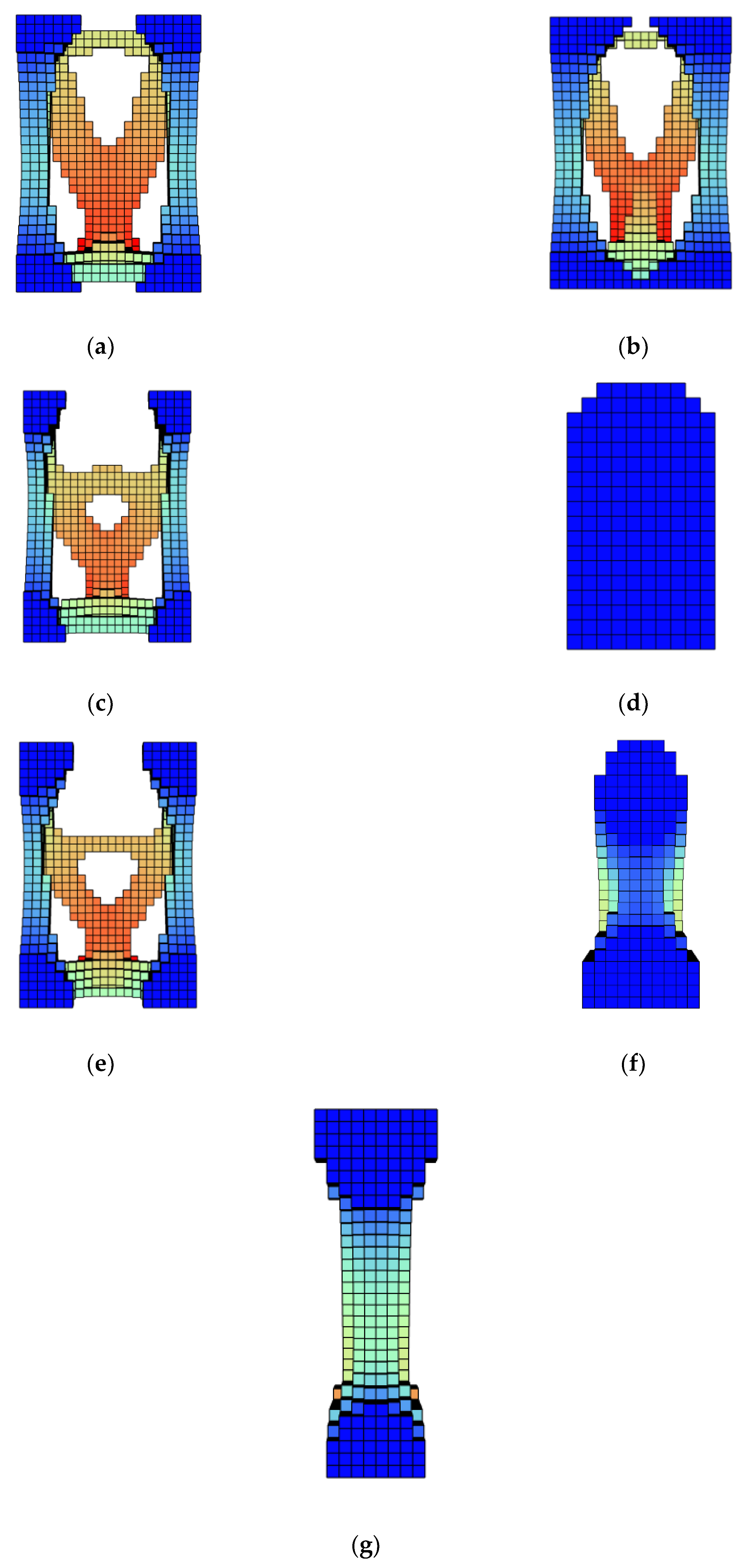
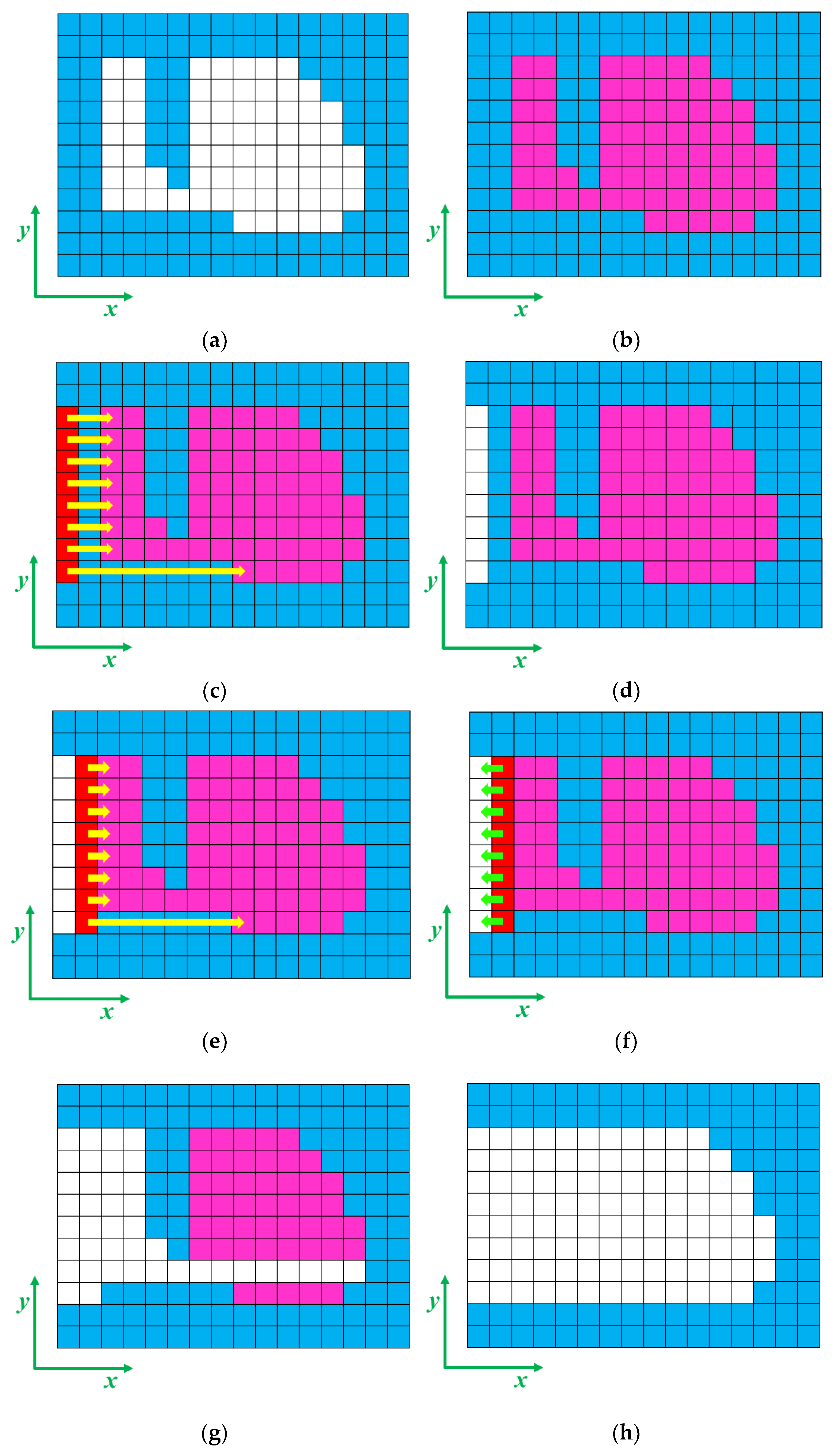
- The case (a) of Figure A1, Figure A2, Figure A3 and Figure A4 of Appendix C.1, Appendix C.2, Appendix C.3 and Appendix C.4 represents the standard case without any additional filter added.
- The case (b) of Figure A1, Figure A2, Figure A3 and Figure A4 of Appendix C.1, Appendix C.2, Appendix C.3 and Appendix C.4 is the resultant shape of the standard case in combination with the Heaviside step filter with η = 0.5. .
- In Figure A1, Figure A2, Figure A3 and Figure A4 (c) of Appendix C.1, Appendix C.2, Appendix C.3 and Appendix C.4, the ellipsoid-shaped density filter is applied to the standard case. Fixing the column of in Appendix B.2, Appendix B.3 and Appendix B.4, the radius of each cartesian direction is chosen in order to obtain the features in that axis of the case in the sensitivity analysis. In this case and are used as filter radii for obtaining a more manufacturable result with the features of R = 6 and p = 6 (Appendix B.4) in x direction, R = 5 and p = 6 (Appendix B.4) in y direction and R = 3.5 and p = 6 (Appendix B.3) in z direction.
- In (d) case, the machining filter is applied to the standard case.
- The case (e) showcases the combination of case (b) and case (c), this is the standard case with Heaviside step filter and ellipsoid-shaped density filter combined.
- Finally, the case (f) evidences the resultant shape of the combination of case (e) with the machining filter. In this case the three additions described in section 4 are applied.
3.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Machinability MATLAB ® Code



Appendix A.2. Filter Radii MATLAB ® Code




Appendix A.3. Machining Filter MATLAB ® Code


Appendix B
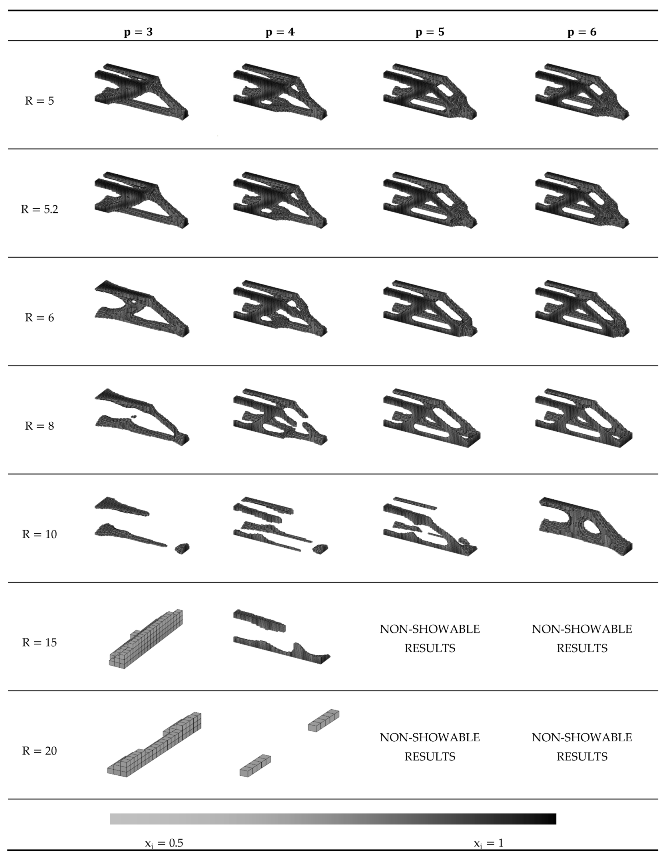
Appendix B.1. Numerical Results of the Sentitivity Analysis
| Sim. ID | Penalization | Filter Radius | Iterations |
It. Time [s] |
Objective | Non-Discreteness | Machinability |
| 1 | 3 | 1,5 | 567 | 13,884 | 21,943 | 14,744 | 76,959 |
| 2 | 4 | 1,5 | 816 | 11,939 | 23,102 | 11,78 | 83,592 |
| 3 | 5 | 1,5 | 1677 | 11,938 | 26,6456 | 13,481 | 88,424 |
| 4 | 6 | 1,5 | 1122 | 11,919 | 27,5479 | 12,866 | 91,694 |
| 5 | 3 | 1,8 | 820 | 11,656 | 23,545 | 17,052 | 83,195 |
| 6 | 4 | 1,8 | 714 | 11,851 | 24,3423 | 14,309 | 88,123 |
| 7 | 5 | 1,8 | 765 | 11,813 | 27,4922 | 16,05 | 80,631 |
| 8 | 6 | 1,8 | 777 | 11,387 | 28,5529 | 14,818 | 89,976 |
| 9 | 3 | 2 | 1122 | 11,944 | 26,6273 | 17,28 | 85,983 |
| 10 | 4 | 2 | 624 | 11,229 | 25,0757 | 15,325 | 89,987 |
| 11 | 5 | 2 | 1048 | 11,618 | 27,2029 | 15,431 | 86,971 |
| 12 | 6 | 2 | 750 | 14,152 | 29,3505 | 15,861 | 94,034 |
| 13 | 3 | 2,45 | 1043 | 10,221 | 25,2856 | 20,039 | 91,066 |
| 14 | 4 | 2,45 | 845 | 9,914 | 27,9992 | 18,703 | 91,904 |
| 15 | 5 | 2,45 | 953 | 11,012 | 30,9835 | 18,375 | 87,688 |
| 16 | 6 | 2,45 | 1336 | 10,713 | 32,7265 | 18,054 | 90,878 |
| 17 | 3 | 2,5 | 1009 | 10,158 | 25,6883 | 20,603 | 91,927 |
| 18 | 4 | 2,5 | 1345 | 10,036 | 28,412 | 19,025 | 92,277 |
| 19 | 5 | 2,5 | 1338 | 11,255 | 31,8068 | 18,811 | 88,728 |
| 20 | 6 | 2,5 | 1253 | 11,784 | 33,5945 | 18,666 | 90,139 |
| Sim. ID | Penalization | Filter Radius | Iterations |
It. Time [s] |
Objective | Non-Discreteness | Machinability |
| 21 | 3 | 2,9 | 989 | 10,025 | 27,5435 | 22,934 | 92,992 |
| 22 | 4 | 2,9 | 1212 | 10,278 | 30,833 | 21,347 | 93,632 |
| 23 | 5 | 2,9 | 1224 | 10,549 | 35,4921 | 21,445 | 89,727 |
| 24 | 6 | 2,9 | 1082 | 11,362 | 37,2027 | 21,114 | 89,466 |
| 25 | 3 | 3 | 752 | 10,991 | 27,9193 | 23,285 | 89,966 |
| 26 | 4 | 3 | 1017 | 10,241 | 31,6539 | 21,926 | 92,385 |
| 27 | 5 | 3 | 1003 | 10,203 | 36,2139 | 21,896 | 90,352 |
| 28 | 6 | 3 | 1018 | 10,88 | 38,0111 | 21,506 | 89,577 |
| 29 | 3 | 3,4 | 628 | 10,129 | 30,2176 | 25,09 | 92,742 |
| 30 | 4 | 3,4 | 1089 | 10,766 | 35,8477 | 24,691 | 92,343 |
| 31 | 5 | 3,4 | 752 | 10,997 | 41,52 | 24,442 | 91,737 |
| 32 | 6 | 3,4 | 449 | 11,209 | 45,7168 | 24,655 | 89,955 |
| 33 | 3 | 3,47 | 1232 | 10,237 | 30,586 | 25,537 | 93,644 |
| 34 | 4 | 3,47 | 979 | 10,822 | 36,5405 | 25,151 | 92,466 |
| 35 | 5 | 3,47 | 545 | 9,888 | 42,4405 | 24,893 | 91,731 |
| 36 | 6 | 3,47 | 697 | 10,344 | 46,9585 | 25,162 | 89,736 |
| 37 | 3 | 3,5 | 1068 | 10,577 | 30,7718 | 25,73 | 93,368 |
| 38 | 4 | 3,5 | 890 | 10,576 | 36,8576 | 25,353 | 92,852 |
| 39 | 5 | 3,5 | 675 | 10,72 | 42,7654 | 25,069 | 91,84 |
| 40 | 6 | 3,5 | 686 | 10,207 | 47,569 | 25,362 | 91,116 |
| Sim. ID | Penalization | Filter Radius | Iterations |
It. Time [s] |
Objective | Non-Discreteness | Machinability |
| 41 | 3 | 3,8 | 695 | 14,976 | 32,6765 | 27,575 | 95,482 |
| 42 | 4 | 3,8 | 704 | 14,976 | 40,071 | 27,215 | 91,743 |
| 43 | 5 | 3,8 | 652 | 9,903 | 47,0157 | 26,87 | 91,478 |
| 44 | 6 | 3,8 | 817 | 11,018 | 54,1068 | 27,279 | 90,762 |
| 45 | 3 | 4 | 836 | 10,748 | 34,034 | 28,765 | 95,363 |
| 46 | 4 | 4 | 614 | 11,769 | 42,5076 | 28,438 | 90,458 |
| 47 | 5 | 4 | 626 | 10,367 | 50,9945 | 28,469 | 89,762 |
| 48 | 6 | 4 | 584 | 9,966 | 58,6735 | 28,232 | 92,896 |
| 49 | 3 | 4,2 | 617 | 12,87 | 35,3255 | 29,798 | 95,279 |
| 50 | 4 | 4,2 | 743 | 10 | 44,8544 | 29,507 | 92,683 |
| 51 | 5 | 4,2 | 915 | 12,313 | 54,5237 | 29,452 | 90,514 |
| 52 | 6 | 4,2 | 934 | 10,778 | 63,434 | 29,257 | 93,449 |
| 53 | 3 | 4,4 | 647 | 10,607 | 36,9453 | 31,019 | 95,679 |
| 54 | 4 | 4,4 | 501 | 10,435 | 47,8507 | 30,796 | 93,079 |
| 55 | 5 | 4,4 | 744 | 10,185 | 58,8192 | 30,438 | 94,141 |
| 56 | 6 | 4,4 | 736 | 9,681 | 69,2076 | 30,209 | 93,676 |
| 57 | 3 | 4,5 | 1149 | 9,686 | 37,6527 | 31,513 | 96,252 |
| 58 | 4 | 4,5 | 415 | 10,5277 | 49,3779 | 31,372 | 92,43 |
| 59 | 5 | 4,5 | 422 | 10,185 | 61,3949 | 31,067 | 93,922 |
| 60 | 6 | 4,5 | 580 | 9,973 | 72,4609 | 30,8 | 96,268 |
| Sim. ID | Penalization | Filter Radius | Iterations |
It. Time [s] |
Objective | Non-Discreteness | Machinability |
| 61 | 3 | 4,8 | 1019 | 10,463 | 40,1734 | 33,049 | 97,36 |
| 62 | 4 | 4,8 | 573 | 10,778 | 54,4644 | 33,106 | 93,393 |
| 63 | 5 | 4,8 | 699 | 10,476 | 70,182 | 32,808 | 96,059 |
| 64 | 6 | 4,8 | 528 | 10,727 | 84,8949 | 32,616 | 94,806 |
| 65 | 3 | 5 | 810 | 9,537 | 41,7655 | 33,98 | 96,755 |
| 66 | 4 | 5 | 907 | 9,736 | 57,4949 | 33,979 | 92,887 |
| 67 | 5 | 5 | 851 | 10,553 | 75,8592 | 33,789 | 92,671 |
| 68 | 6 | 5 | 606 | 11,068 | 93,0405 | 33,562 | 95,795 |
| 69 | 3 | 5,2 | 779 | 9,313 | 43,6644 | 35,008 | 97,477 |
| 70 | 4 | 5,2 | 1091 | 9,651 | 61,3489 | 35,032 | 92,34 |
| 71 | 5 | 5,2 | 1051 | 9,884 | 83,3058 | 34,979 | 92,605 |
| 72 | 6 | 5,2 | 337 | 9,899 | 104,346 | 34,754 | 95,6 |
| 73 | 3 | 6 | 535 | 9,224 | 44,6408 | 37,613 | 100 |
| 74 | 4 | 6 | 505 | 9,413 | 82,3081 | 39,494 | 96,195 |
| 75 | 5 | 6 | 1149 | 10,701 | 106,722 | 37,338 | 84,818 |
| 76 | 6 | 6 | 1015 | 10,892 | 138,359 | 37,181 | 85,325 |
| 77 | 3 | 8 | 473 | 9,941 | 73,6699 | 47,258 | 100 |
| 78 | 4 | 8 | 396 | 10,078 | 167,952 | 48,21 | 98,516 |
| 79 | 5 | 8 | 452 | 10,246 | 261,633 | 46,87 | 89,919 |
| 80 | 6 | 8 | 576 | 10,743 | 432,583 | 46,606 | 89,592 |
| Sim. ID | Penalization | Filter Radius | Iterations |
It. Time [s] |
Objective | Non-Discreteness | Machinability |
| 81 | 3 | 10 | 381 | 10,982 | 118,666 | 53,618 | 100 |
| 82 | 4 | 10 | 1144 | 13,666 | 284,998 | 53,272 | 98,14 |
| 83 | 5 | 10 | 1811 | 14,05 | 219,921 | 38,502 | 100 |
| 84 | 6 | 10 | 3986 | 17,087 | 314,672 | 37,534 | 100 |
| 85 | 3 | 15 | 238 | 19,017 | 230,282 | 59,919 | 100 |
| 86 | 4 | 15 | 1083 | 20,813 | 363,853 | 51,092 | 100 |
| 87 | 5 | 15 | 5000 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 88 | 6 | 15 | 5000 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 89 | 3 | 20 | 119 | 30,664 | 281,498 | 61,537 | 100 |
| 90 | 4 | 20 | 189 | 33,328 | 1150,9 | 61,91 | NaN |
| 91 | 5 | 20 | 5000 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 92 | 6 | 20 | 5000 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
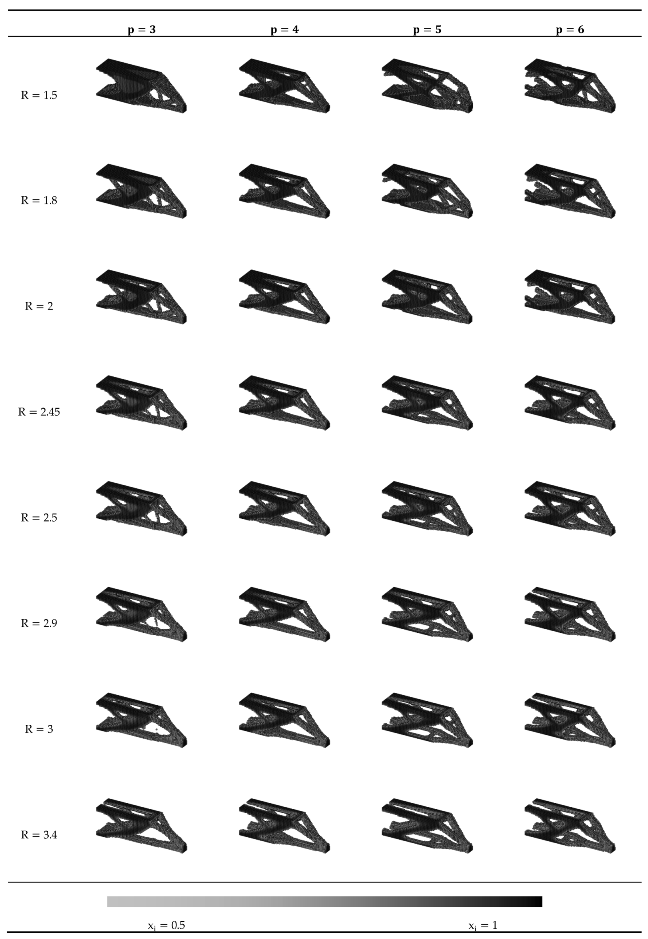
Appendix B.2. Results of the sensitivity analysis for 1.5 ≤ R ≤ 3.4

Appendix B.3. Results of the Sensitivity Analysis for 3.47 ≤ R ≤ 4.7
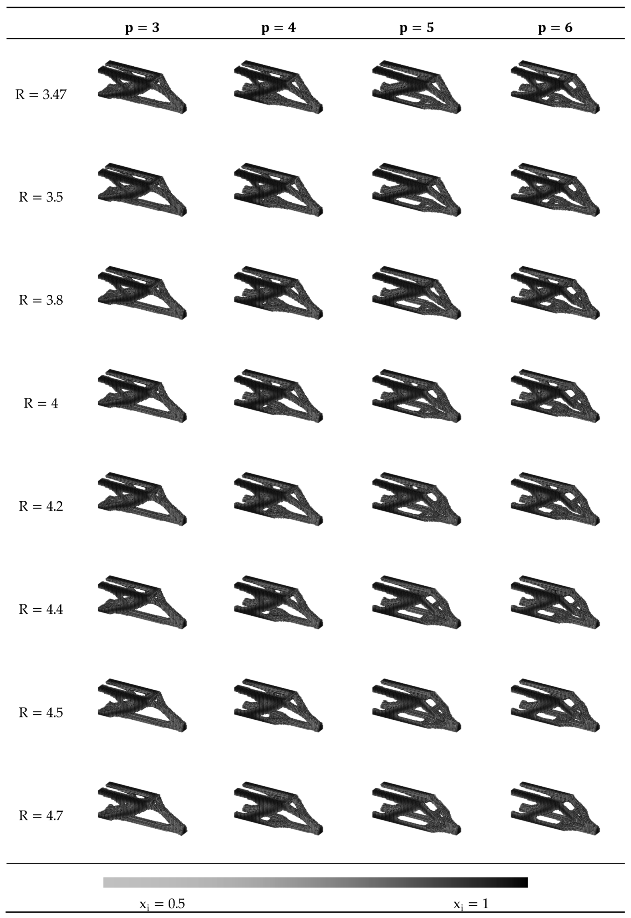
Appendix B.4. Results of the Sensitivity Analysis for 5 ≤ R ≤ 20
Appendix C
Appendix C.1. Verifications: Superior Perspective View
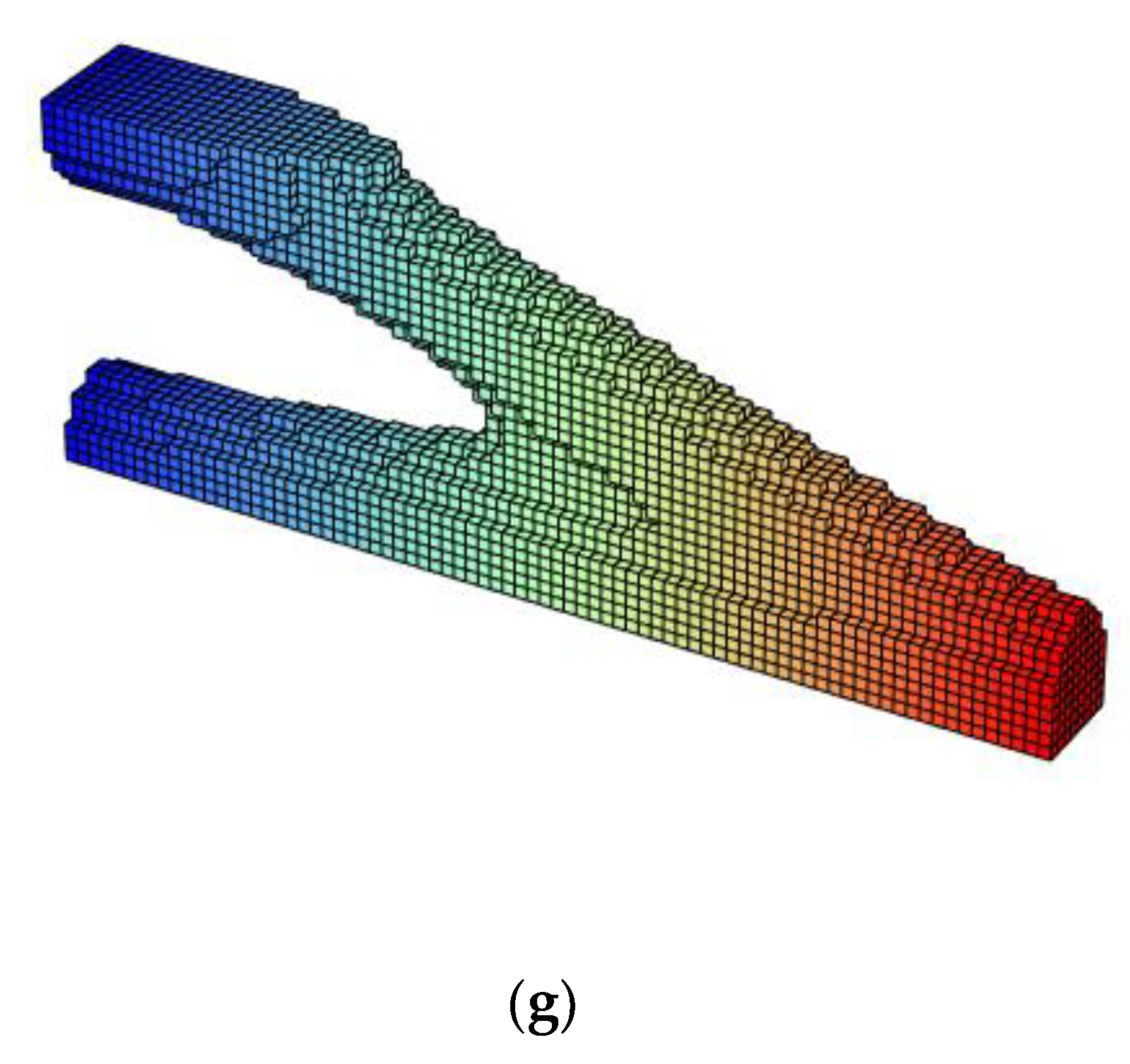
Appendix C.2. Verifications: Inferior Perspective View
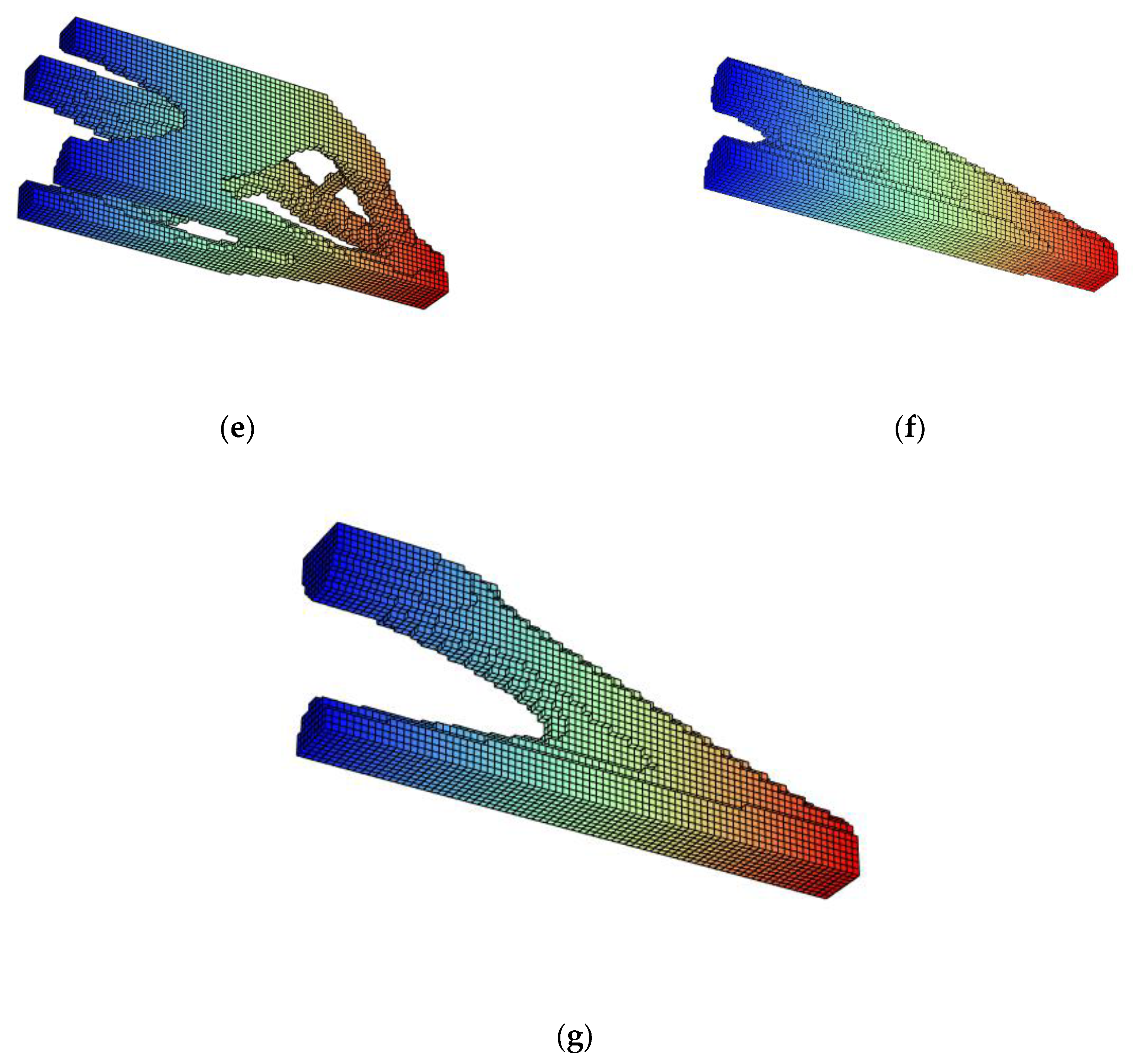
Appendix C.3. Verifications: Lateral View
Appendix C.4. Verifications: Front View
References
- Shiye, B.; Jiejiang, Z. Topology Optimization Design of 3D Continuum Structure with Reserved Hole Based on Variable Density Method. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 2016, 9, 121–128. [CrossRef]
- Michell, A.G.M. LVIII. The Limits of Economy of Material in Frame-Structures. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science 1904, 8, 589–597. [CrossRef]
- Dorn, W.S.; Gomory, R.E.; Greenberg, H.J. Automatic Design of Optimal Structures. Journal de Mécanique 1964, 3.
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Kikuchi, N. Generating Optimal Topologies in Structural Design Using a Homogenization Method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 1988, 71, 197–224. [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, O.; Maute, K. Topology Optimization Approaches. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2013, 48, 1031–1055. [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Tovar, A. An Efficient 3D Topology Optimization Code Written in Matlab. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2014, 50, 1175–1196. [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, F.; Sigmund, O. A New Generation 99 Line Matlab Code for Compliance Topology Optimization and Its Extension to 3D. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2020, 62, 2211–2228. [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P. Optimal Shape Design as a Material Distribution Problem. Structural Optimization 1989, 1, 193–202. [CrossRef]
- Mlejnek, H.P. Some Aspects of the Genesis of Structures. Structural Optimization 1992, 5, 64–69. [CrossRef]
- Kohn, R. V.; Strang, G. Optimal Design and Relaxation of Variational Problems, II. Commun Pure Appl Math 1986, 39, 139–182. [CrossRef]
- Haber, R.B.; Jog, C.S.; Bendsøe, M.P. A New Approach to Variable-Topology Shape Design Using a Constraint on Perimeter. Structural Optimization 1996, 11, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Jog, C.S. A Robust Dual Algorithm for Topology Design of Structures in Discrete Variables. Int J Numer Methods Eng 2001, 50, 1607–1618. [CrossRef]
- Duysinx, P. Layout Optimization: A Mathematical Programming Approach; Lyngby, 1997;
- Bendsøe, M.P. Optimal Shape Design as a Material Distribution Problem. Structural Optimization 1989, 1, 193–202. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Rozvany, G.I.N. The COC Algorithm, Part II: Topological, Geometrical and Generalized Shape Optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 1991, 89, 309–336. [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, E.; Clausen, A.; Schevenels, M.; Lazarov, B.S.; Sigmund, O. Efficient Topology Optimization in MATLAB Using 88 Lines of Code. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2011, 43, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Tyflopoulos, E.; Flem, D.T.; Steinert, M.; Olsen, A. State of the Art of Generative Design and Topology Optimization and Potential Research Needs.; Linköping, Sweden, August 14 2018.
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods, and Applications.; 2nd ed.; Springer Science & Business Media, 2003;
- Bruns, T.E.; Tortorelli, D.A. Topology Optimization of Non-Linear Elastic Structures and Compliant Mechanisms. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 2001, 190, 3443–3459. [CrossRef]
- Altair Engineering Inc. Altair OptiStruct Help Guide.
- Butze, M.; Sert, E.; Öchsner, A. Development of a Topology-optimized Indoor Crane Trolley for Additive Manufacturing. Materwiss Werksttech 2022, 53, 526–535. [CrossRef]
- Dassault Systèmes SolidWorks Help Page.
- PTC; Tonny Abbey PTC Creo Blogs.
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. Material Interpolation Schemes in Topology Optimization. Archive of Applied Mechanics (Ingenieur Archiv) 1999, 69, 635–654. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wu, C.W. Topology Optimization of Energy Storage Flywheel. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2017, 55, 1917–1925. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Zhu, M.; Guest, J.K. Topology Optimization Considering Multi-Axis Machining Constraints Using Projection Methods. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 2022, 390, 114464. [CrossRef]
- Langelaar, M. Topology Optimization for Multi-Axis Machining. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 2019, 351, 226–252. [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, O. Morphology-Based Black and White Filters for Topology Optimization. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2007, 33, 401–424. [CrossRef]
- Schevenels, M.; Sigmund, O. On the Implementation and Effectiveness of Morphological Close-Open and Open-Close Filters for Topology Optimization. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2016, 54, 15–21. [CrossRef]
- Pellens, J.; Lombaert, G.; Lazarov, B.; Schevenels, M. Combined Length Scale and Overhang Angle Control in Minimum Compliance Topology Optimization for Additive Manufacturing. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2019, 59, 2005–2022. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Jensen, J.; Sigmund, O. Robust Topology Optimization of Photonic Crystal Waveguides with Tailored Dispersion Properties. JOSA B 2011, 28, 387–397. [CrossRef]
- Prager, W. OPTIMALITY CRITERIA IN STRUCTURAL DESIGN. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1968, 61, 794–796. [CrossRef]
- Karush, W. Minima of Functions of Several Variables with Inequalities as Side Conditions.; 2014.
- Bendsøe, M.P. Optimization of Structural Topology, Shape, and Material; 1st ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1995; ISBN 978-3-662-03117-9.
- Sigmund, O. A 99 Line Topology Optimization Code Written in Matlab. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2001, 21, 120–127. [CrossRef]
- Svanberg, K.; Svärd, H. Density Filters for Topology Optimization Based on the Pythagorean Means. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2013, 48, 859–875. [CrossRef]
- Morillas, A.V.; Alonso, J.M.; Caballero, A.B.; Sisamón, C.C.; Ceruti, A. Adaptive Variable Design Algorithm for Improving Topology Optimization in Additive Manufacturing. Preprints (Basel) 2024. [CrossRef]
| 1.5 | 1.8 | 2 | 2.45 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 3 | 3.4 | 3.47 | 3.5 | 3.8 | 4 | |
| Reason | OS | ED | ED | ED | ED | ED | OS | ED | ED | ED | ED | ED |
| 4.2 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 5 | 5.2 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 15 | 20 | ||
| Reason | ED | ED | ED | ED | ED | ED | OS | LV | LV | LV | LV |
| Case (a) | Case (b) | Case (c) | Case (d) | Case (e) | Case (f) | Case (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iterations | 1018 | 1738 | 346 | 2086 | 1087 | 2639 | 790 |
| Mnd | 21.5065 | 0.8477 | 28.3512 | 3.901 | 1.1824 | 5.2443 | 6.1459 |
| Machinability | 89.577 | 94.381 | 95.751 | 100 | 95.479 | 100 | 100 |
| Compliance | 38.0111 | 19.5020 | 59.1714 | 136.4004 | 21.1516 | 46.4197 | 34.3937 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





