Submitted:
11 June 2024
Posted:
11 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Moisture Content
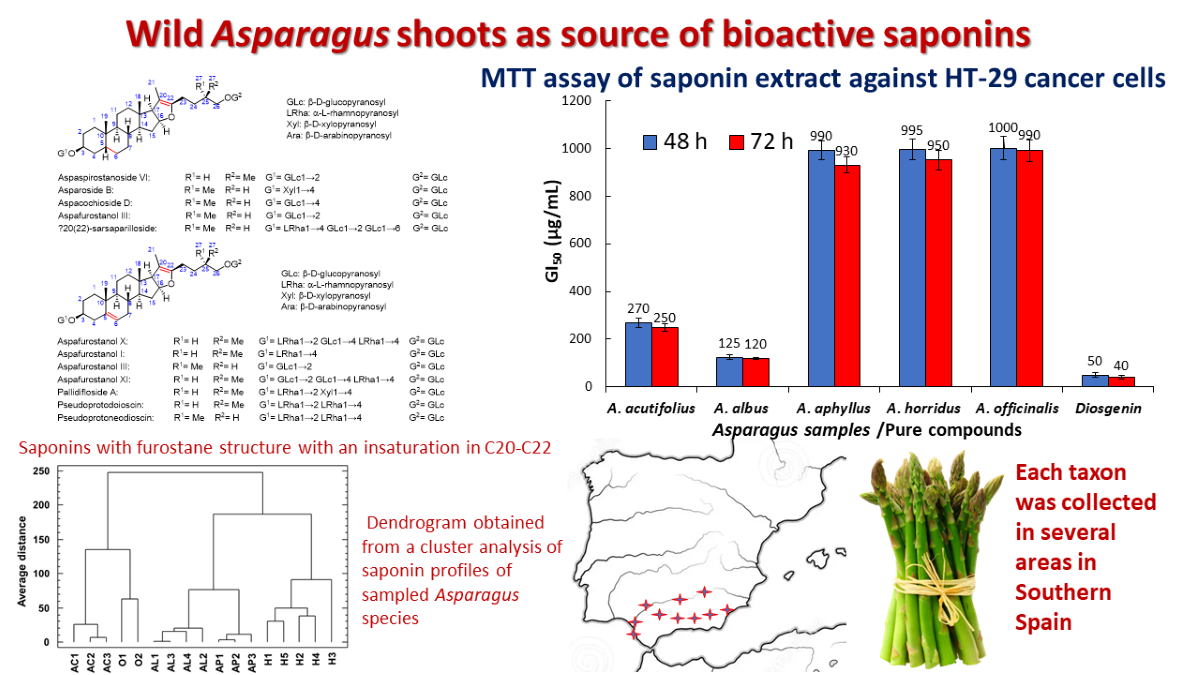
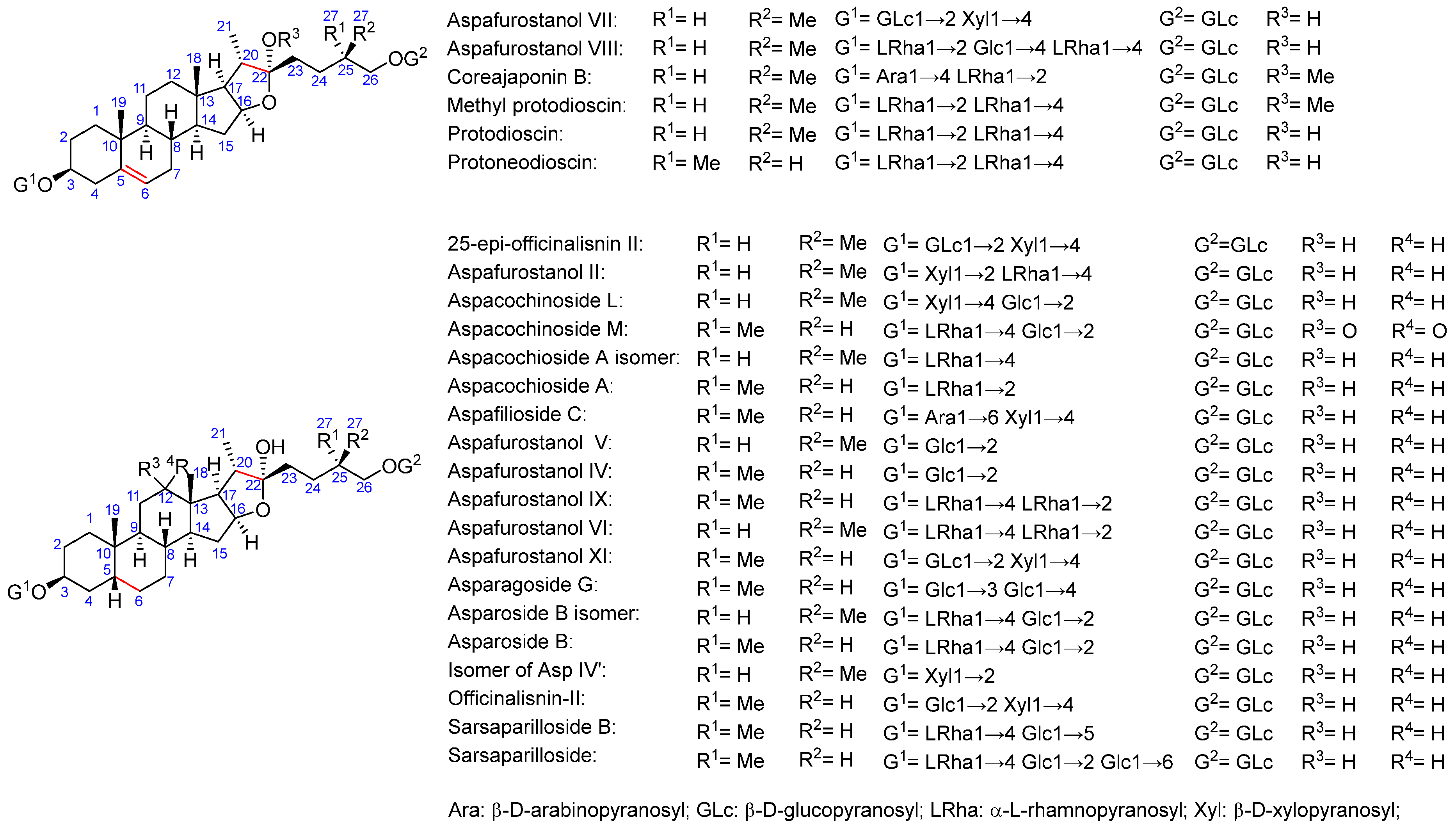
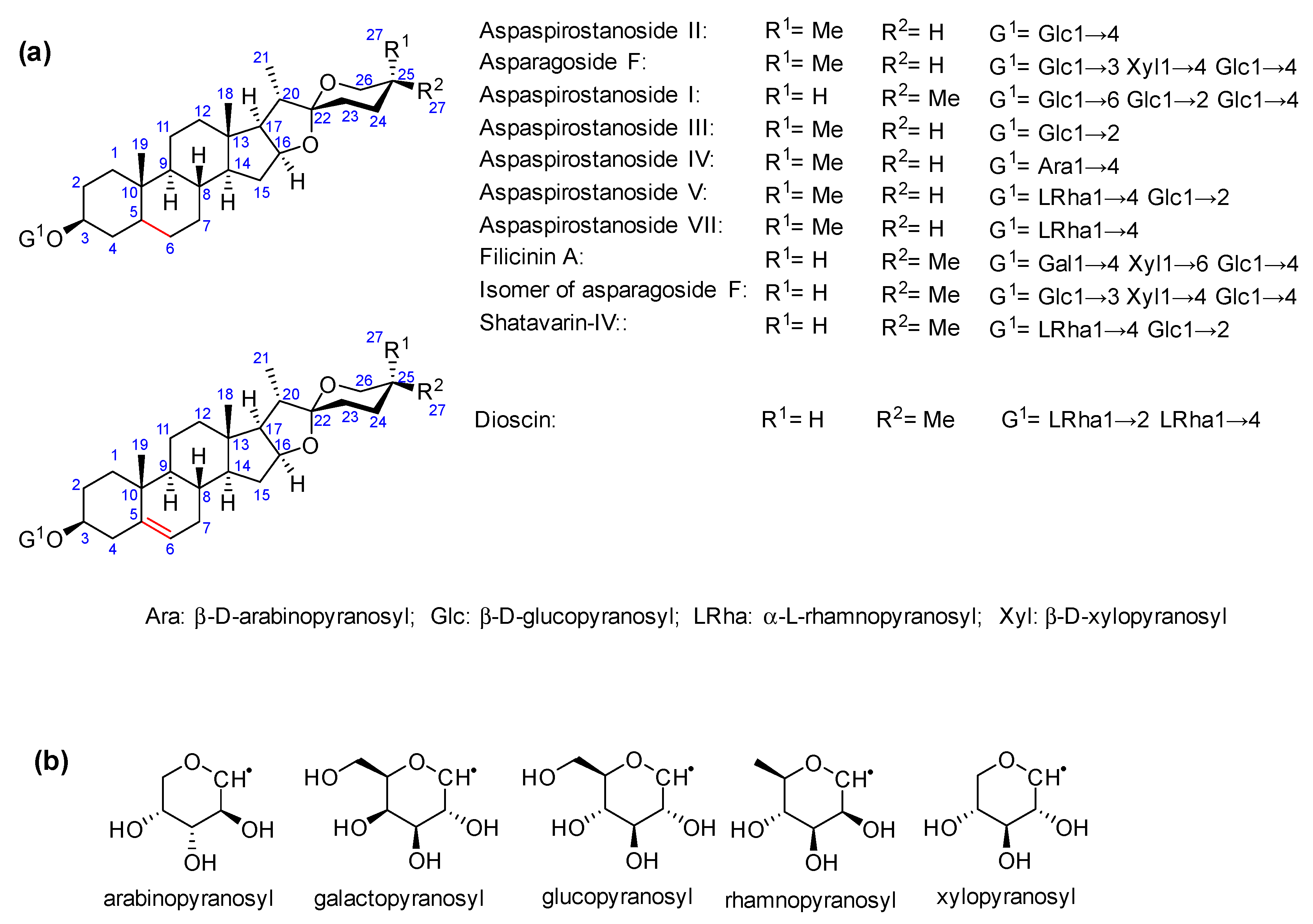
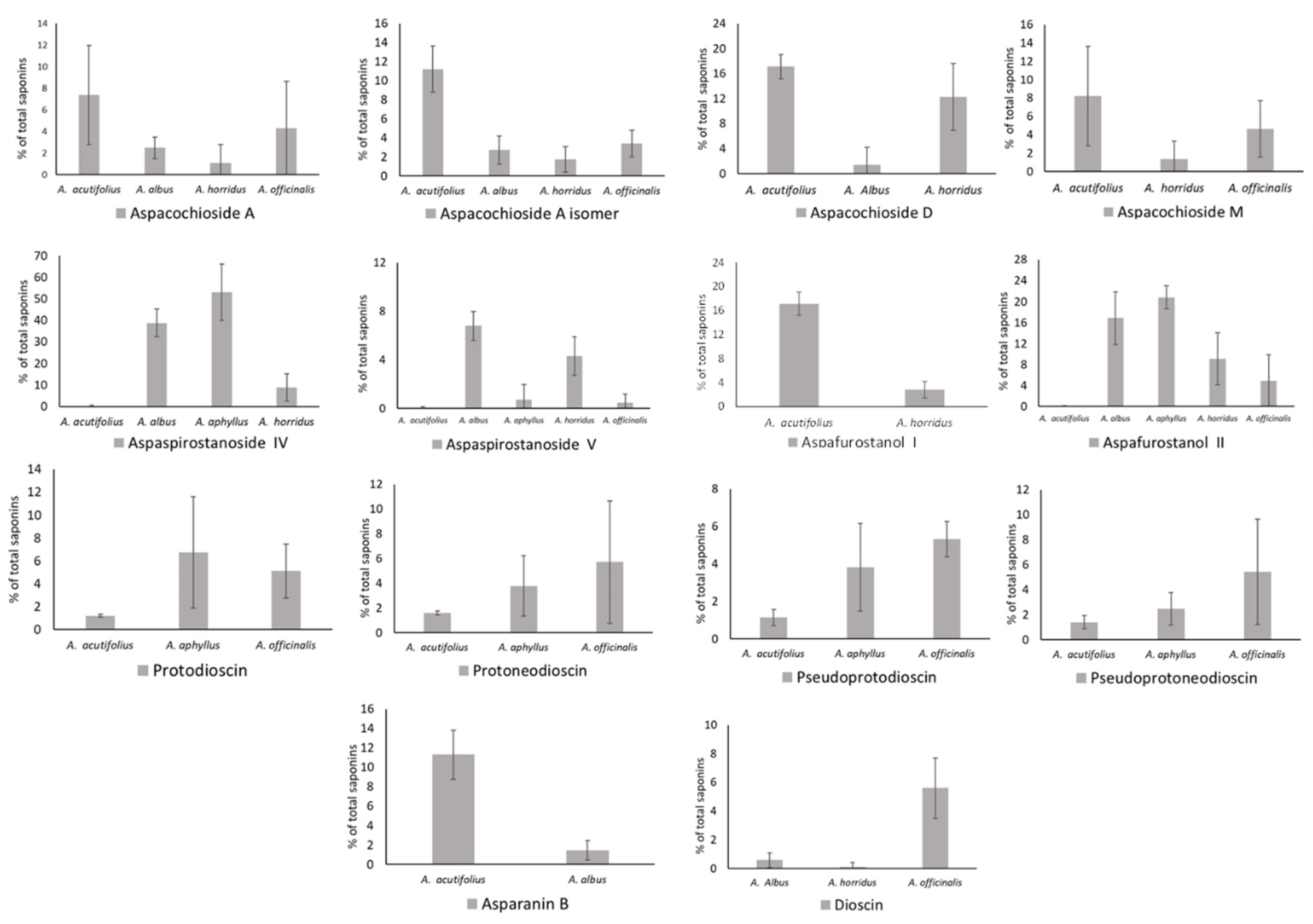
2.2. Total Saponins and Saponin Profiles
2.3. Cluster Analysis
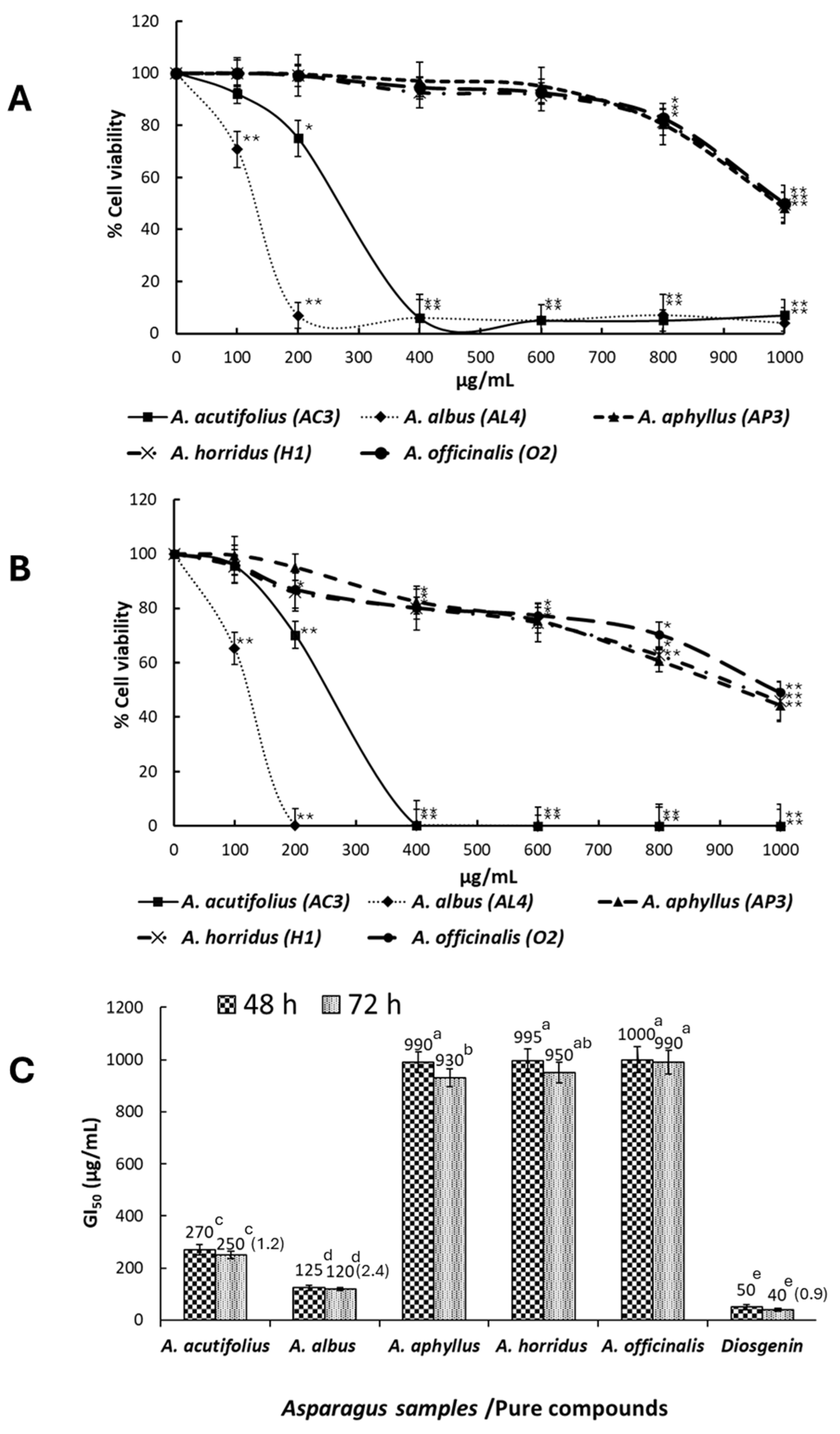
2.4. Antiproliferative Activity
3. Discussion
3.1. Saponin Profiles of the Various Asparagus Species Analyzed in This Work
3.2. Multivariable Analyses for Assessing Chemotaxonomy
3.3. Antiproliferative Activity of the Saponins Extracts of Asparagus Shoots on HT-29 Cancer Cells
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples
| Species/Location | Code | Geographical coordinates | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Asparagus acutifolius (Raviscanina) Punta Entinas, El Ejido, Almería Algámitas, Sevilla |
|||
| AC1 | 36.690831 -2.7732501 | 04/04/2023 | |
| AC2 | 37.018445 -5.161181 | 07/03/2023 | |
| Fonelas, Granada Asparagus albus (White asparagus) |
AC3 | 37.409918 -3.200831 | 10/05/2023 |
| Darrícal, Almería Sierra Cabrera, Almería Barranco de las Lastras, Adra, Almería El Toyo, Almería |
AL1 | 36.917674 -3.028230 | 17/03/2023 |
| AL2 | 37.134984 -1.868005 | 05/01/2023 | |
| AL3 | 36.790886 -3.100039 | 03/03/2023 | |
| AL4 | 36.847975, -2.332920 | 03/02/2023 | |
| Asparagus aphyllus (Prickly asparagus) | |||
| Zahara de la Sierra, Cádiz | AP1 | 36.841757 -5.395525 | 20/03/2023 |
| Mijas, Málaga | AP2 | 36.591142 -4.606242 | 23/03/2023 |
| Torremolinos, Málaga | AP3 | 36.605964 -4.526782 | 20/03/2023 |
| Asparagus horridus (Esparraguera) | |||
| Cabo de Gata, Almería | H1 | 36.723495, -2.183220 | 19/03/2023 |
| Vícar, Almería | H2 | 36.813587 -2.60462 | 11/03/2023 |
| Enix, Almería | H3 | 36.875594, -2.609560 | 12/03/2023 |
| Las Amoladeras Almería | H4 | 36.817729, -2.253485 | 07/03/2023 |
| Rodalquilar, Níjar | H5 | 36.849231, -2.043093 | 148/02/2023 |
| Asparagus officinalis (Garden asparagus) | |||
| Láchar, Granada | O1 | Purchased | 01/04/2023 |
| Loja, Granada | O2 | Purchased | 05/10/2023 |
4.2. Extraction of Saponins
4.3. Total Saponin Content
4.4. Characterization of Saponins by LC-MS
4.5. Antitumor Assays
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adouni, K.; Chahdoura, H.; Mosbah, H.; Santos-Buelga, C.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Fernandes, Â.; Achour, L. Revalorization of wild Asparagus stipularis Forssk. as a traditional vegetable with nutritional and functional properties. Food & function 2018, 9, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Boik, J. (2001). Natural Compounds in Cancer Therapy. Princeton (MN): Oregon Medical Press.
- Bousserouel, S.; Le Grandois, J.; Gossé, F.; Werner, D.; Barth, S.W.; Marchioni, E.; Marescaux, J.; Raul, F. Methanolic extract of white asparagus shoots activates TRAIL apoptotic death pathway in human cancer cells and inhibits colon carcinogenesis in preclinical model. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Song, H.S.; Ukeda, H.; Sawamura, M.; Hwang, Y.S. Radical-scavenging activities of asparagus shoot extracts. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2012, 60, 11451. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdi, A.; Jaramillo-Carmona, S.; Beji, R.S.; Tej, R.; Zaoui, S.; Rodríguez-Arcos, R.; Guillén-Bejarano, R. The phytochemical and bioactivity profiles of wild Asparagus albus L. plant. Food Research International 2017, 99, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, A.; Jaramillo-Carmona, S.; Rodríguez-Arcos, R.; Jiménez-Araujo, A.; Lachaal, M.; Karray-Bouraoui, N.; Guillén-Bejarano, R. Phytochemical Characterization and Bioactivity of Asparagus acutifolius: A Focus on Antioxidant, Cytotoxic, Lipase Inhibitory and Antimicrobial Activities. Molecules 2021, 26, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.K.; Sumiyoshi, M.; Zheng, Y.N. Effects of edible asparagus on biochemical markers and histopathological examination of aged rats. Experimental Gerontology 2012, 47, 842–849. [Google Scholar]
- Heywood, V.H.; Dulloo, M.E. (2006). Wild Edible Plants: A Global Overview of Their Use and Importance to People. FAO.
- Jaramillo, S.; Muriana, F.J.G.; Guillen, R.; Jimenez-Araujo, A.; Rodriguez-Arcos, R.; Lopez, S. Saponins from edible spears of wild asparagus inhibit AKT, p70S6K, and ERK signalling, and induce apoptosis through G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in human colon cancer HCT-116 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Carmona, S.; Guillén-Bejarano, R.; Jiménez-Araujo, A.; Rodríguez-Arcos, R.; López, S. In Vitro Toxicity of Asparagus Saponins in Distinct Multidrug-Resistant Colon Cancer Cells. Chemistry & Biodiversity 2018, 15, e1800282. [Google Scholar]
- Johns, T.; Eyzaguirre, P.B. Linking biodiversity, diet and health in policy and practice. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2006, 65, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Chung, H.J.; Nam, J.W.; Park, H.J.; Seo, E.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.K. Cytotoxic and antineoplastic activity of timosaponin A-III for human colon cancer cells. Journal of natural products 2011, 74, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.M.; Nahar, L.; Mannan, A.; Arfan, M.; Khan, G.A.; Al-Groshi, A.; Sarker, S.D. Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry analysis and cytotoxicity of Asparagus adscendens roots against human cancer cell lines. Pharmacognosy Magazine 2017, 13 (Suppl 4), S890. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnlein, H.V.; Erasmus, B.; Spigelski, D. (2013). Indigenous peoples’ food systems: The many dimensions of culture, diversity and environment for nutrition and health. FAO.
- Lee, E.J.; Yoo, K.S.; Patil, B.S. Development of a rapid HPLC-UV method for simultaneous quantification of protodioscin and rutin in white and green asparagus spears. Journal of food science 2010, 75, C703–C709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyashenko, S.; González-Fernández, M.J.; Gomez-Mercado, F.; Yunusova, S.; Denisenko, O.; Guil-Guerrero, J.L. Ribes taxa: A promising source of γ-linolenic acid-rich functional oils. Food chemistry 2019, 301, 125309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.K.; Prakash, N.S.; Sundaram, R. Shatavarins (containing Shatavarin IV) with anticancer activity from the roots of Asparagus racemosus. Indian journal of pharmacology 2012, 44, 732. [Google Scholar]
- Ncube, B.; Ngunge VN, P.; Finnie, J.F.; Van Staden, J. A comparative study of the antimicrobial and phytochemical properties between outdoor grown and micropropagated Tulbaghia violacea Harv. plants. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2011, 134, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bot, M.; Thibault, J.; Pottier, Q.; Boisard, S.; Guilet, D. An accurate, cost-effective and simple colorimetric method for the quantification of total triterpenoid and steroidal saponins from plant materials. Food Chemistry 2022, 383, 132597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, X.F.; Qi, Q.; Dai, Q.S.; Yang, L.; Nie, F.F.; Guo, Q.L. Asparanin A induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2009, 381, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ning, R.; Chen, R.N.; Huang, X.F.; Dai, Q.S.; Hu, J.H.; Wang, H. Aspafilioside B induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by up-regulating H-Ras and N-Ras via ERK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Molecular Carcinogenesis 2016, 55, 440–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuki, T.; Ozaki, Y.; Kuroda, M. Immunostimulatory effects of saponin from Asparagus officinalis L. on macrophage cells. Journal of Health Science 2007, 53, 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Pegiou, E.; Mumm, R.; Acharya, P.; Vos, R.; Hall, R.D. Green and white asparagus (Asparagus officinalis): A source of developmental, chemical and urinary intrigue. Metabolites 2020, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieroni, A.; Price, L.L. (2006). Eating and Healing: Traditional Food as Medicine. Haworth Press.
- Shao, Y.; Chin, C.K.; Ho, C.T.; Ma, W.; Garrison, S.A.; Huang, M.T. Anti-tumor activity of the crude saponins obtained from asparagus. Cancer letters 1996, 104, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanowicz-Hajduk, J.; Król-Kogus, B.; Sparzak-Stefanowska, B.; Kimel, K.; Ochocka, J.R.; Krauze-Baranowska, M. Cytotoxic activity of standardized extracts, a fraction, and individual secondary metabolites from fenugreek seeds against SKOV-3, HeLa and MOLT-4 cell lines. Pharmaceutical Biology 2021, 59, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suffness, M.; Pezzuto, J.M. (1990) Assays related to cancer drug discovery. In Methods in Plant Biochemistry: Assays for Bioactivity; In Methods in Plant Biochemistry: Assays for Bioactivity; Hostettmann, K., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, pp. 71–133.
- Vázquez-Castilla, S.; Jaramillo-Carmona, S.; Fuentes-Alventosa, J.M.; Jimenez-Araujo, A.; Rodriguez-Arcos, R.; Cermeno-Sacristan, P.; Guillen-Bejarano, R. Optimization of a method for the profiling and quantification of saponins in different green Asparagus genotypes. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 2013, 61, 6250–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tadmor, Y.; Wu, Q.L.; Chin, C.K.; Garrison, S.A.; Simon, J.E. Quantification of protodioscin and rutin in asparagus shoots by LC/MS and HPLC methods. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 2003, 51, 6132–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Pang, X. Saponins extracted from by-product of Asparagus officinalis L. suppress tumour cell migration and invasion through targeting Rho GTPase signalling pathway (2013). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Lin, S.; Xin, D.; Liu, X.; Weng, L.; Zhang, M. Anticancer effects of deproteinized asparagus polysaccharide on hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Tumor Biology 2014, 35, 3517–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ren, S.; Xu, F.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. Recent advances in the pharmacological activities of dioscin. BioMed Research International 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, L.; Yang, D. Saponins from edible plants: chemistry and bioactivity. Food Research International 2015, 76, 616–630. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, Y.S.; Ma, R.H.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.G.; Wei, Z.J. Asparanin A from Asparagus officinalis L. induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human endometrial carcinoma ishikawa cells via mitochondrial and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2019, 68, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.J. 2012. Biological activity of woody stem of Asparagus officinalis L. East China Normal University 10–12.


| Species/samples | Moisture (g/100 g) | Saponins (mg/100 g dry weight) |
|---|---|---|
| A. acutifolius | ||
| AC1 | 81.4 ± 0.0 h | 1094.9 ± 21.2 def |
| AC2 | 84.6 ± 0.3 fg | 1529.3 ± 107.8 a |
| AC3 | 85.2 ± 0.3 ef | 1151.5 ± 7.9 de |
| Mean ± SD | 84.5 ± 2.3 B | 1258.6 ± 236.2 A |
| A. albus | ||
| AL1 | 88.0 ± 0.2 bc | 1405.2 ± 176.3 ab |
| AL2 | 88.1 ± 0.2 bc | 996.9 ± 39.1 efg |
| AL3 | 86.4 ± 1.2 de | 1387.4 ± 107.9 abc |
| AL4 | 89.0 ± 0.5 b | 930.5 ± 98.5 fgh |
| Mean ± SD | 87.9 ± 1.1 AB | 1180.0 ± 251.3 AB |
| A. aphyllus | ||
| AP1 | 83.7 ± 0.9 g | 907.8 ± 27.3 fgh |
| AP2 | 85.3 ± 0.5 ef | 860.8 ± 115.0 gh |
| AP3 | 86.5 ± 1.2 de | 909.3 ± 7.7 fgh |
| Mean ± SD | 85.2 ± 1.4 B | 892.6 ± 27.6 AB |
| A. horridus | ||
| H1 | 80.7 ± 1.4 h | 1211.5 ± 60.3 cd |
| H2 | 84.0 ± 0.7 fg | 1422.9 ± 70.8 ab |
| H3 | 83.3 ± 1.1 g | 838.3 ± 174.1 ghi |
| H4 | 87.5 ± 0.1 cd | 838.1 ± 55.5 ghi |
| H5 | 87.3 ± 0.5 cd | 794.9 ± 31.2 hi |
| Mean ± SD | 84.6 ± 2.9 B | 1021.1 ± 281.0 AB |
| A. officinalis | ||
| O1 | 91.1 ± 0.2 a | 750.9 ± 112.0 hi |
| O2 | 90.9 ± 0.3 a | 669.1 ± 101.0 i |
| Mean ± SD | 91.0 ± 0.1 A | 710.0 ± 57.8 B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





