Submitted:
07 June 2024
Posted:
11 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Study Participants
Whole Exome Sequencing
Chemicals
Antibodies
ACE Activity Assay
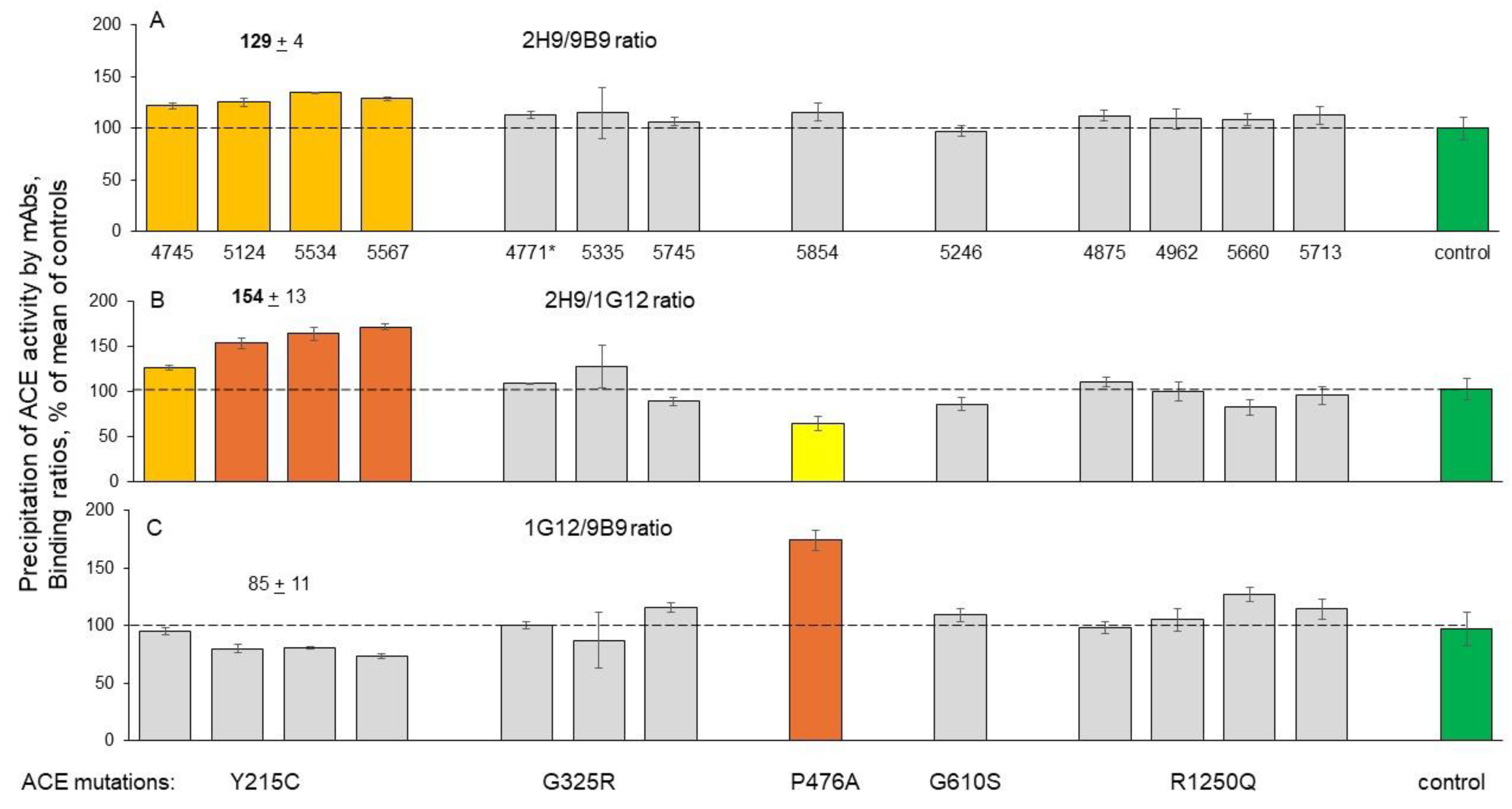
Immunological Characterization of the Blood ACE
Statistical Analysis
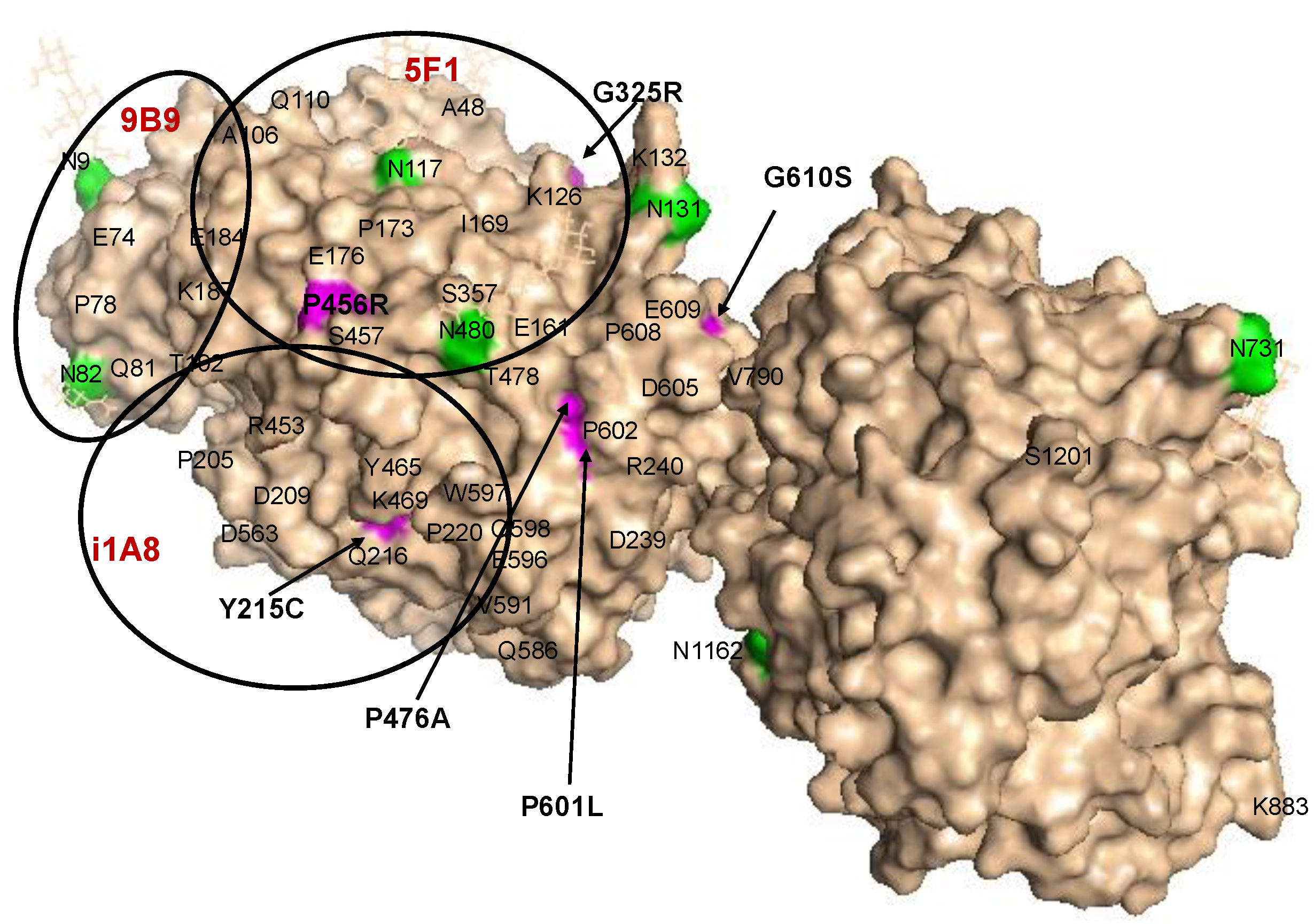
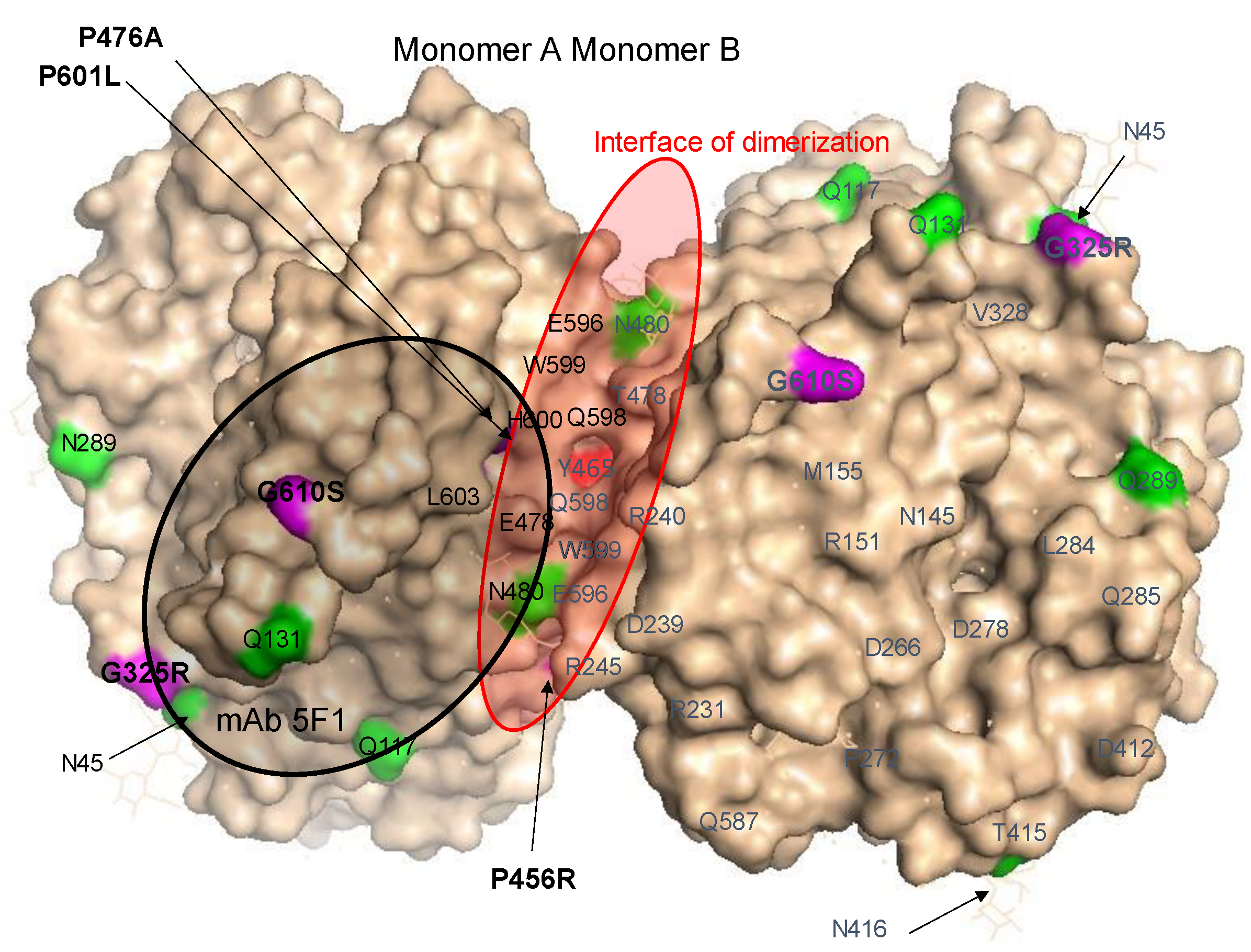
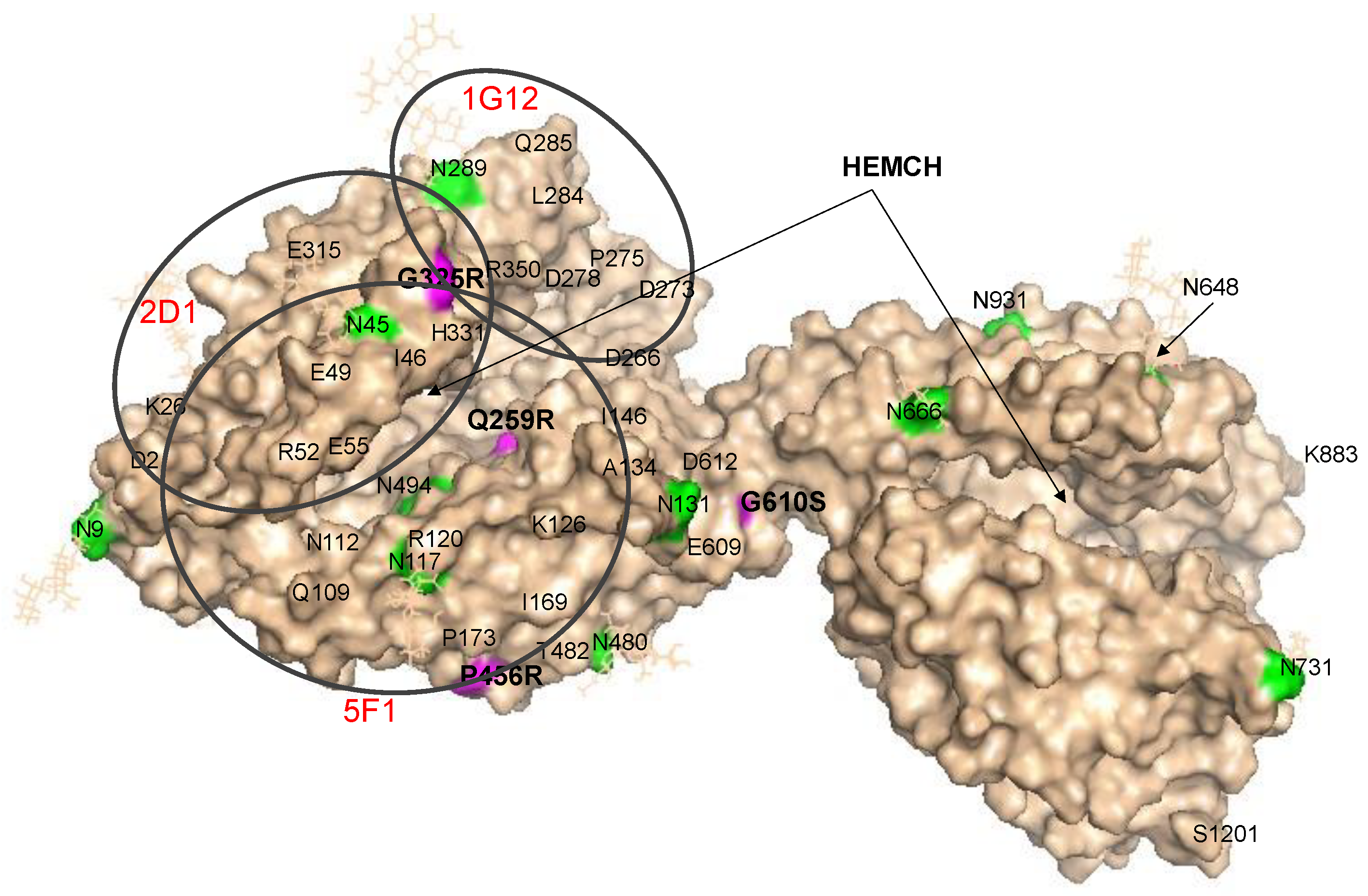
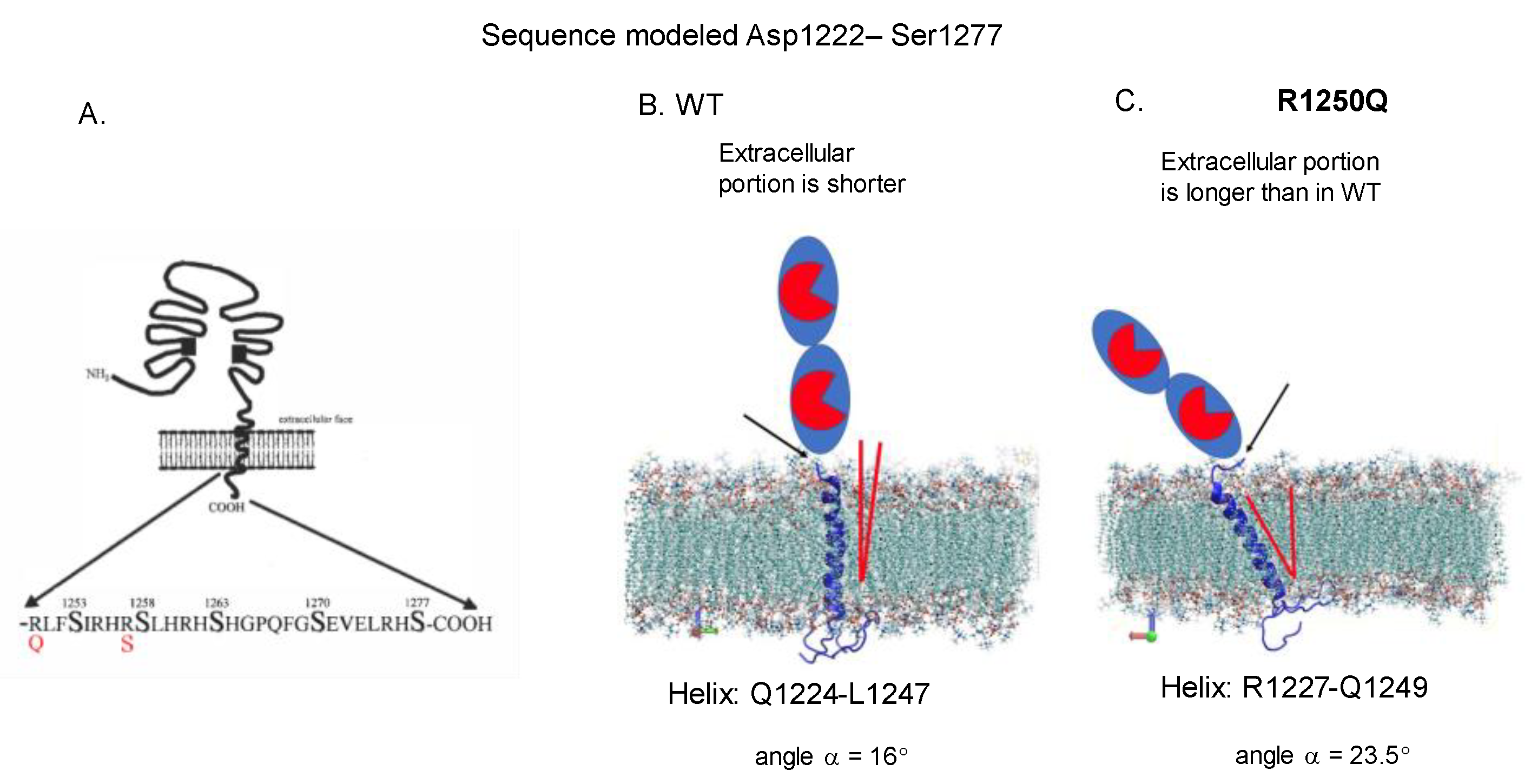
Localization of AD-Associated ACE Mutations on ACE Globule
3. Results and Discussion
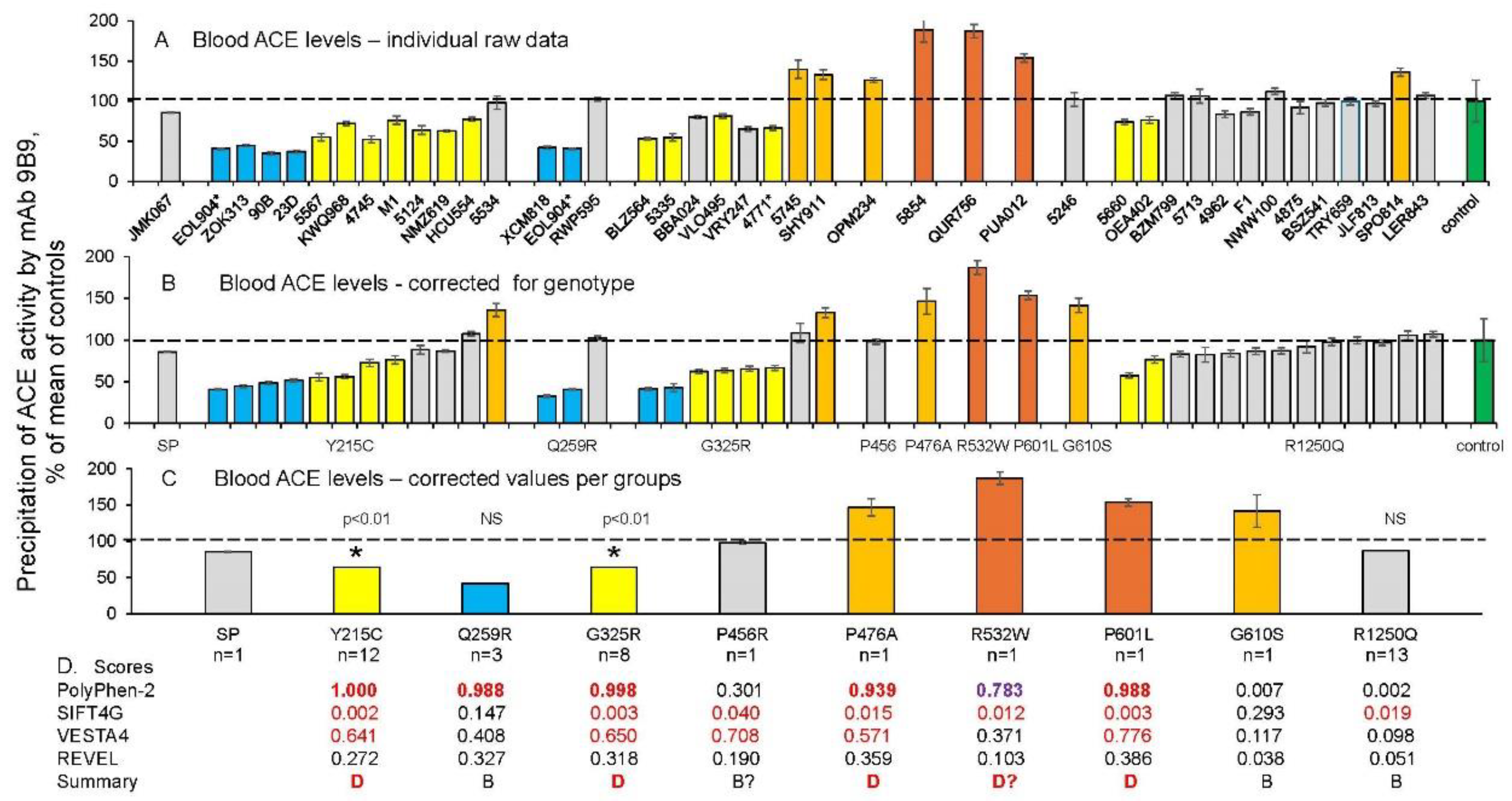
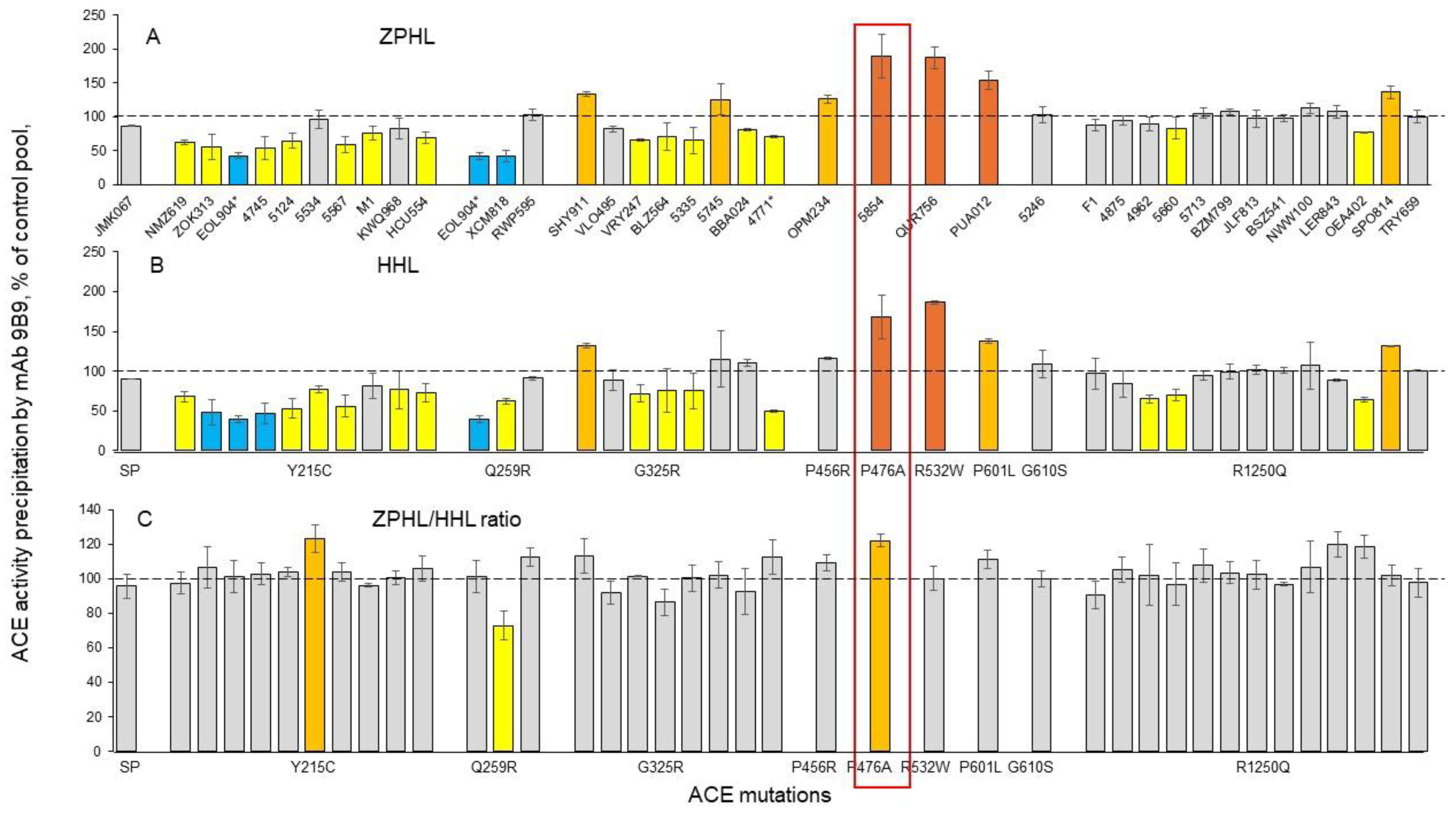
Quantification of blood ACE in Carriers of ACE Mutations
Detection of Catalytic Abnormalities of Mutant ACEs Using EDTA-Plasma Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selkoe DJ, Hardy J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol Med 2016; 8: 595–608. [CrossRef]
- Sims R, Hill M, Williams J. The multiplex model of the genetics of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Neurosci 2020; 23: 311–322. [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Guerrero J, Santiago-Balmaseda A, Jeronimo-Aguilar P, et al. Alzheimer’s Disease: An Updated Overview of Its Genetics. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24: 3754. [CrossRef]
- Kehoe PG, Russ C, McIlory S, et al. Variation in DCP1, encoding ACE, is associated with susceptibility to Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet1999;21: 71–72. [CrossRef]
- Sassi C, Brown KS, Medway C, et al. Influence of coding variability in APP-Aβ metabolism genes in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. PLOS One 2016; 11: e0150079. [CrossRef]
- Schwartzentruber J, Cooper S, Liu JZ, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis, fine-mapping and integrative prioritization implicate new Alzheimer’s disease risk genes. Nat Genet 2021; 53: 392–402. [CrossRef]
- Sturrock ED, Anthony CS, Danilov SM. Peptidyl-dipeptidase a/angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes, 2012; pp.480–494. [CrossRef]
- Bernstein KE, Ong FS, Blackwell WL, et al. A modern understanding of the traditional and nontraditional biological functions of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Pharmacol Rev 2012; 65: 1–46. [CrossRef]
- Zou K, Maeda T, Watanabe A, et al. Aβ42-to-Aβ40- and angiotensin-converting activities in different domains of angiotensin-converting enzyme.J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 31914–31920. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM, Adzhubei IA, Kozuch AS, et al. Carriers of heterozygous loss-of-function ACE mutations are at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedicines 2024; 12: 162. [CrossRef]
- Corvol P, Michaud A, Gribouval O, Gasc JM, Gubler MC. Can we live without a functional renin-angiotensin system? Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2008; 35: 431-433. [CrossRef]
- Gribouval O, Moriniere V, Pawtowski A, et al. Spectrum of mutations in the renin-angiotensin system genes in autosomal recessive renal tubular dysgenesis. Hum Mut 2011; 33: 316–326. [CrossRef]
- Cuddy LK, Prokopenko D, Cunningham EP, et al. Aβ-accelerated neurodegeneration caused by Alzheimer’s-associated ACE variant R1279Q is rescued by angiotensin system inhibition in mice. Sci Transl Med2020;.12: eaaz2541. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM, Kalinin S, Chen Z, et al. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme Gln1069Arg mutation impairs trafficking to the cell surface resulting in selective denaturation of the C-domain. PLoS One 2010; 5: e10438. [CrossRef]
- Belova V, Pavlova A, Afasizhev R, et al. System analysis of the sequencing quality of human whole exome samples on BGI NGS platform. Sci Rep 2022; 12: 609. [CrossRef]
- Wingett SW, Andrews S. FastQ Screen: A tool for multi-genome mapping and quality control. F1000Res; 2018; 7: 138. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 2078–2079. [CrossRef]
- Li H.A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2011;27: 2987-2993. [CrossRef]
- Poplin R, Chang P-C, Alexander D, et al. A universal SNP and small-indel variant caller using deep neural networks. Nat Biotech 2018; 6: 983–987. [CrossRef]
- Tan A, Abecasis GR, Kang HM. Unified Representation of Genetic Variants. Bioinformatics 2015; 31: 2202-2204. [CrossRef]
- Li Q, Wang K. InterVar: Clinical interpretation of genetic variants by ACMG-AMP 2015 guideline. Am J Hum Genet 2017; 100: 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM, Balyasnikova IV, Danilova AS, et al. Conformational fingerprinting of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE). 1. application in sarcoidosis. J Proteome Res 2010; 9: 5782–5793. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM. Conformational fingerprinting using monoclonal antibodies (on the example of angiotensin I-converting enzyme-ACE). Mol Biol (Moscow) 2017;51: 906–920. [CrossRef]
- Popova IA, Lubbe L, Petukhov PF, et al. Epitope mapping of novel monoclonal antibodies to human angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Protein Sci2021; 30: 1577–1593. [CrossRef]
- Danilov S, Savoie F, Lenoir B, et al. Development of enzyme-linked immunoassays for human angiotensin I converting enzyme suitable for large-scale studies. J Hypertens 1996; 14: 719–727.
- Samokhodskaya LM, Jain MS, Kurilova OV, et al. Phenotyping angiotensin-converting enzyme in blood: A necessary approach for precision medicine. J Appl Lab Med 2021; 6: 1179–1191. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM, Balyasnikova IV, Albrecht RF, Kost OA. Simultaneous determination of ACE activity with 2 substrates provides information on the status of somatic ace and allows detection of inhibitors in human blood. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2008; 52: 90–103. [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 2010; 7: 248–249. [CrossRef]
- Lubbe L, Sewell BT, Woodward JD, Sturrock ED. Cryo-EM reveals mechanisms of angiotensin I-converting enzyme allostery and dimerization. EMBO J 2022; 41: e110550. [CrossRef]
- Anthony CS, Corradi HR, Schwager SL, et al. The N domain of human angiotensin-I- converting enzyme: the role of N glycosylation and crystal structure in complex with N domain specific phosphinic inhibitor, RXP407. J Biol Chem 2010;285: 35685-35693. [CrossRef]
- Petrov MN, Shilo VY, Tarasov AV, et al. Conformational changes of blood ACE in uremia. PLoS One 2012; 7: e49290. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM, Jain MS, Petukhov PA, et al. Blood ACE phenotyping for personalized medicine: revelation of patients with conformationally altered ACE. Biomedicines 2023;11: 534. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM, Lunsdorf H, Akinbi HT, et al. Lysozyme and bilirubin bind to ACE and regulate its conformation and shedding. Sci Rep 2016; 6: 34913. [CrossRef]
- Rigat B, Hubert C, Alhenc-Gelas F, et al. An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene accounting for half the variance of serum enzyme levels. J Clin Invest 1990; 86: 1343–1346. [CrossRef]
- Costerousse O, Allegrini J, Lopez M, et al. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme in human circulating mononuclear cells: genetic polymorphism of expression in T-lymphocytes. Biochem J 1993; 290 (Pt.1): 33-40. [CrossRef]
- Danser AH, Schalekamp MA, Bax WA, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme in the human heart. Effect of the deletion/insertion polymorphism. Circulation 1995; 92:1387-1388. [CrossRef]
- Tiret L, Rigat B, Visvikis S, et al. Evidence, from combined segregation and linkage analysis, that a variant of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) gene controls plasma ACE levels. Am J Hum Genet 1992; 51: 197-205.
- Biller H, Zissel G, Ruprecht B, et al. Genotype-corrected reference values for serum angiotensin-converting enzyme. Eur Resp J 2006; 28: 1085-1090. [CrossRef]
- Kruit A, Grutters JC, Gerritsen WB, et al. ACE I/D-corrected Z-scores to identify normal and elevated ACE activity in sarcoidosis. Respir Med 2007; 101: 510-515. [CrossRef]
- Lopera F, Marino C, Chandrahas AS, et al. Resilience to autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease in a Reelin-COLBOS heterozygous man. Nat Med 2023;29: 1243-1252. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM, Gordon K, Nesterovitch AB, et al. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme mutation (Y465D) cause dramatic increase in blood ACE via accelerated ACE shedding due to changes of ACE dimerization. PLoS One 2011; 6: e25952. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM, Jain MS, Petukhov PA, et al. Novel ACE mutations mimicking sarcoidosis by increasing blood ACE levels. Transl Res 2021; 230: 5–20. [CrossRef]
- Kryukova OV, Tikhomirova VE, Golukhova EZ, et al. Tissue Specificity of Human Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0143455. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM, Tikhomirova VE, Metzger R, et al. ACE phenotyping in Gaucher disease. Mol Genet Metab 2018; 123: 501-510. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM, Watermeyer JM, Balyasnikova IV, et al. Fine epitope mapping of mAb 5F1 reveals anticatalytic activity. Biochemistry2007; 46: 9019-9031.
- Naqvi N, Liu K, Graham RM, Husain A. Molecular basis of exopeptidase activity in the C-terminal domain of human angiotensin I-converting enzyme: insights into the origins of its exopeptidase activity. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 6669-6675. [CrossRef]
- Cozier GE, Lubbe L, Sturrock ED, Acharya KR. Angiotensin-converting enzyme open for business: Structural insights into the subdomain dynamics. FEBS J 2020; 288: 2238–2256. [CrossRef]
- Kozuch AJ, Petukhov PA, Fagyas M, et al. Urinary ACE phenotyping as a research and diagnostic tool: identification of sex-dependent ACE immunoreactivity. Biomedicines 2023; 11: 953. [CrossRef]
- Danilov SM, Tikhomirova VE, Kryukova OV, et al. Conformational fingerprint of blood and tissue ACEs: Personalized approach. PLoS One 2018;13: e0209861. [CrossRef]
- Kohlstedt K, Shoghi F, Müller-Esterl W, Busse R, Fleming I. CK2 phosphorylates the angiotensin-converting enzyme and regulates its retention in the endothelial cell plasma membrane. Circ Res 2002; 91: 749–756. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




