Submitted:
05 June 2024
Posted:
07 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Ethics Statement
2.2. Parasite and Probiotic Strain
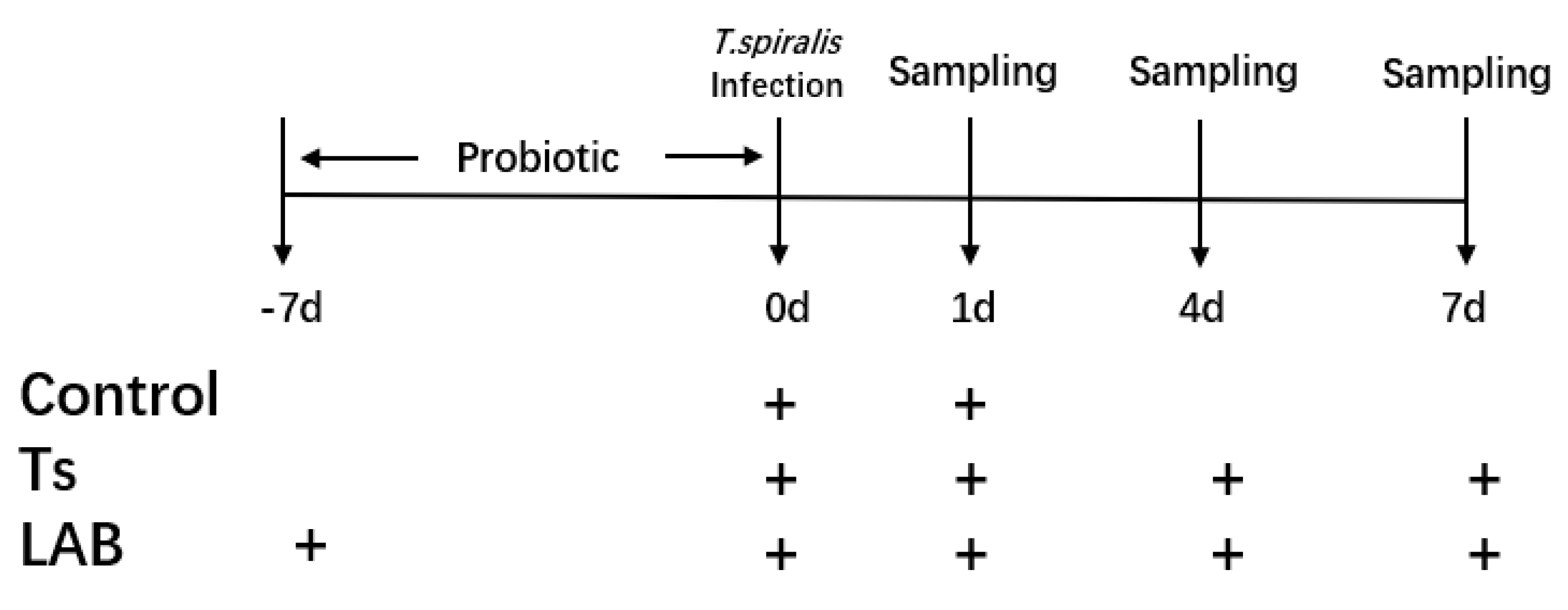
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Intestinal Worm Burdens
2.5. Oxidative Stress Assay
2.6. Measurement of Inflammatory Cytokines
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Adult Worm Reduction
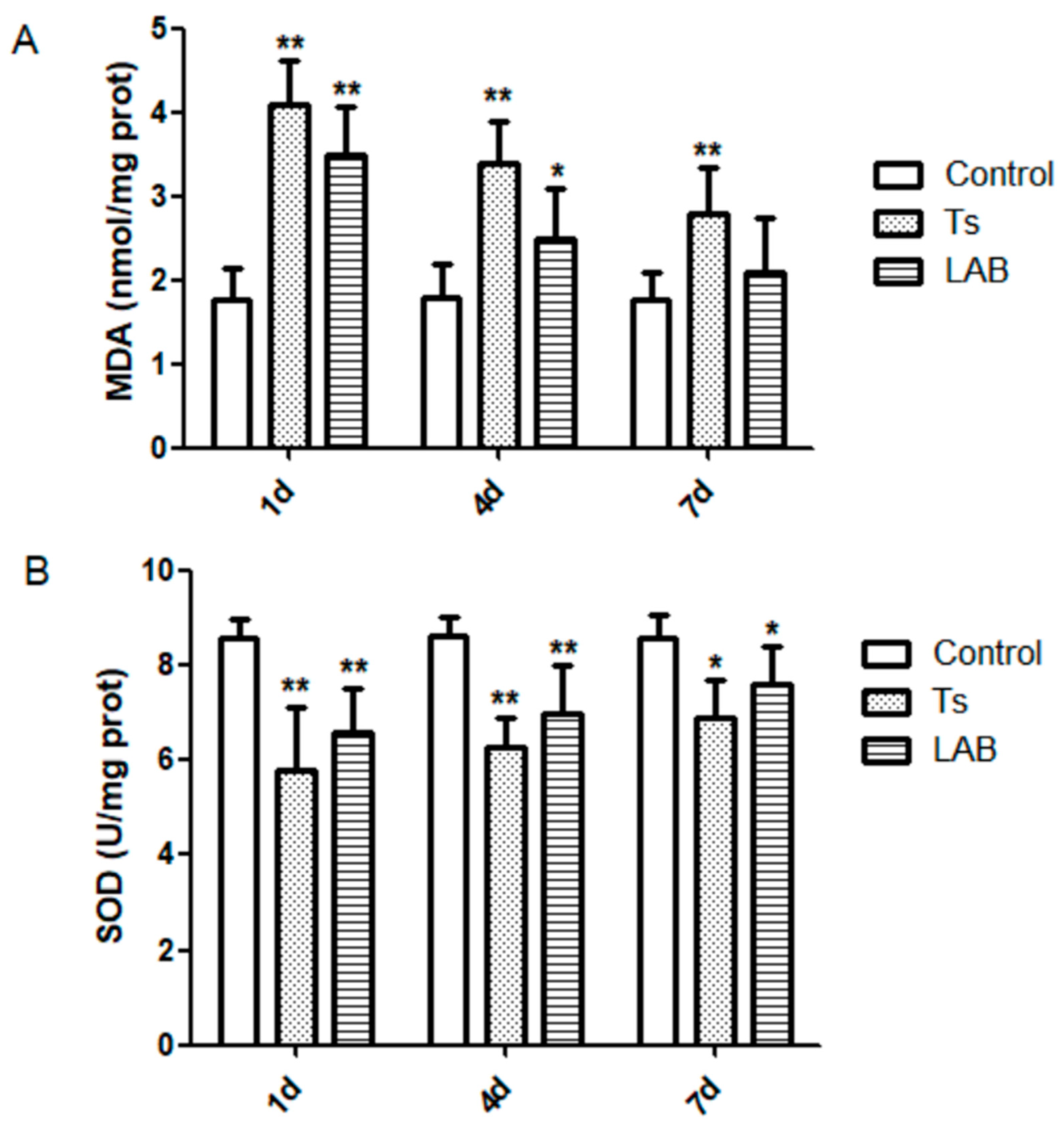
3.2. Oxidative Stress Marker Levels
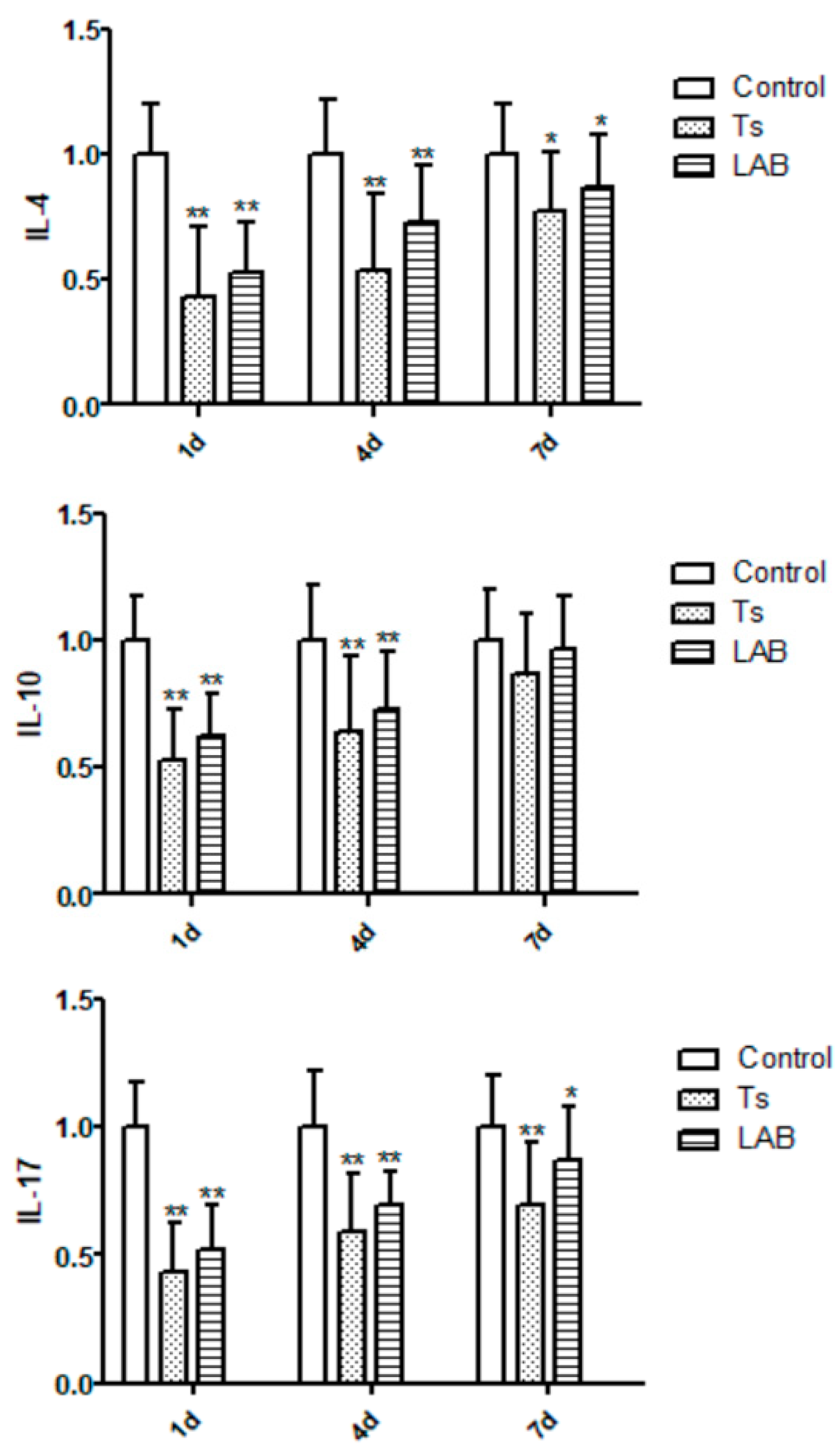
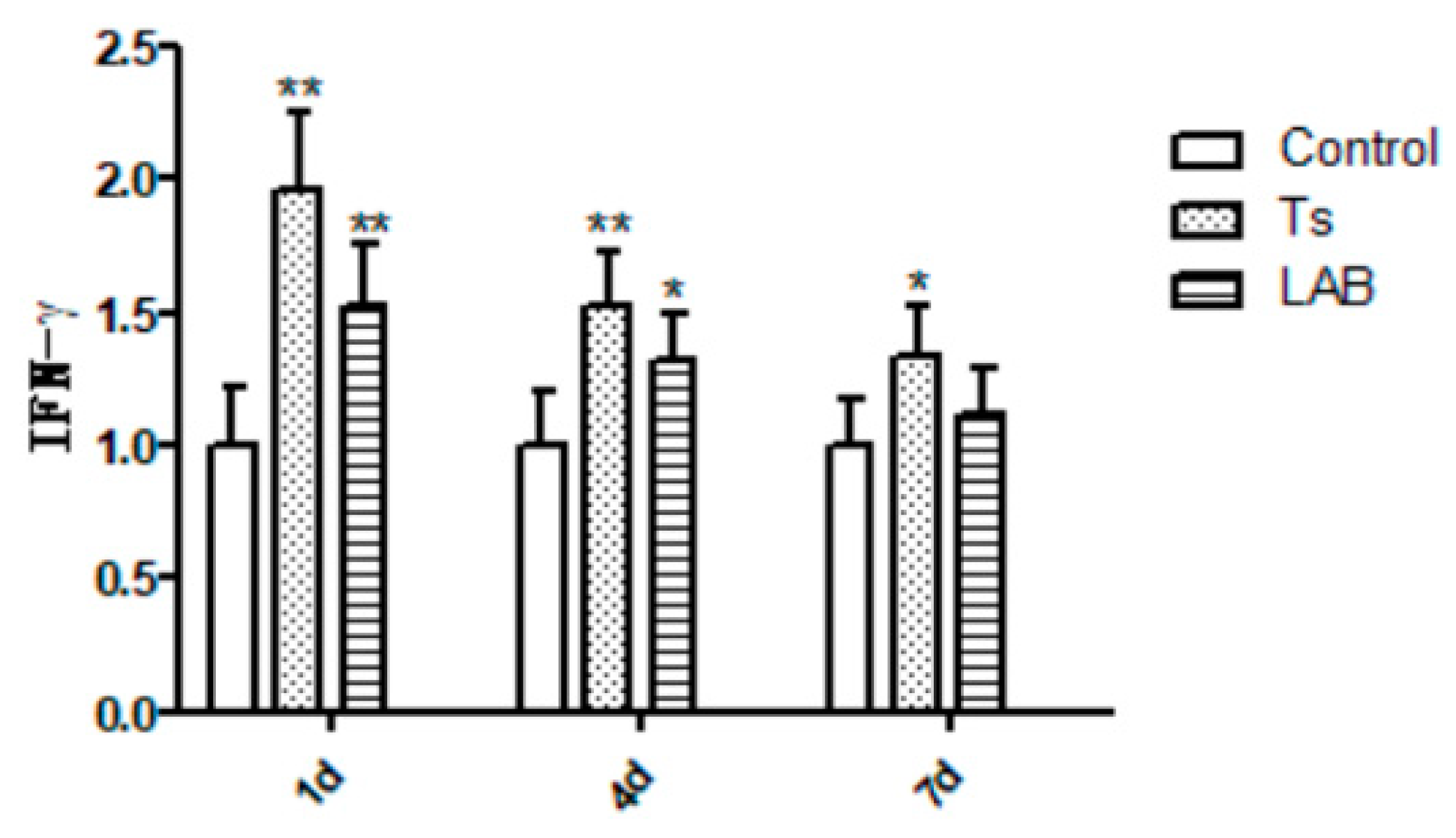
3.3. Inflammatory Response
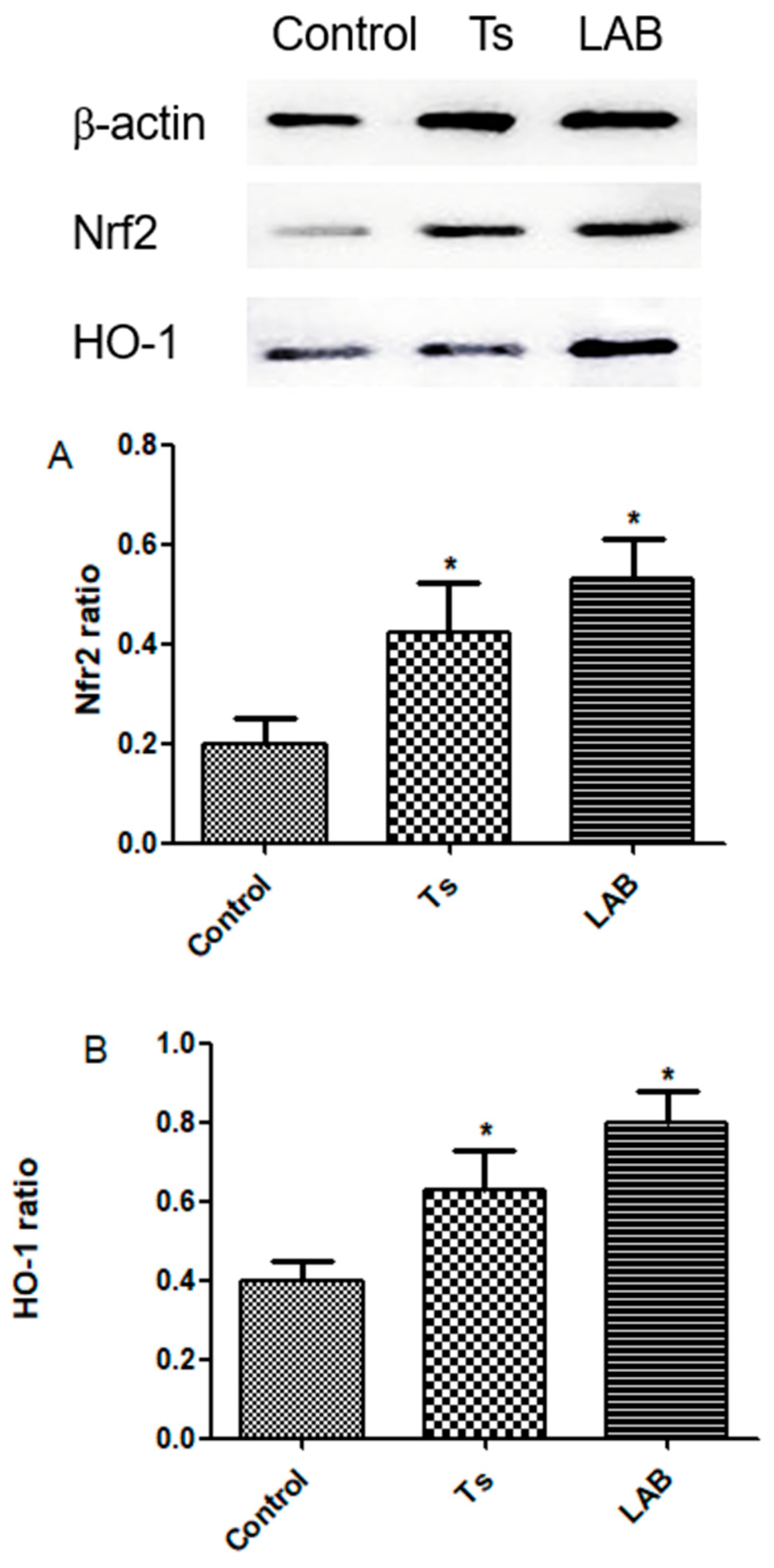
3.4. Nrf2 and HO-1 Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasby Saad, M.; Safwat, O.; El-Guindy, D.; Raafat, R.; Elgendy, D.; Hasby, E. Biomolecular Changes and Cortical Neurodegenerative Lesions in Trichinella Spiralis Infected BALB/c Mice: A Preliminary Study Elucidating a Potential Relationship Between Systemic Helminthic Infections and Idiopathic Parkinson's. Helminthologia 2018, 55, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pan, J.; Meng, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, X. Trichinella spiralis infection decreases the diversity of the intestinal flora in the infected mouse. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2021, 54, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, E.; Sjölund, M.; Wallgren, T.; Lind, E.O.; Höglund, J.; Wallgren, P. Management practices related to the control of gastrointestinal parasites on Swedish pig farms. Porcine Health Manag 2021, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajíčková, M.; Nguyen, L.T.; Skálová, L.; Raisová Stuchlíková, L.; Matoušková, P. Anthelmintics in the future: current trends in the discovery and development of new drugs against gastrointestinal nematodes. Drug Discov Today 2020, 25, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargová, M.; Hurníková, Z.; Revajová, V.; Lauková, A.; Dvorožňáková, E. Probiotic Bacteria can Modulate Murine Macrophage's Superoxide Production in Trichinella Spiralis Infection. Helminthologia 2020, 57, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Garfias, C.R.; Ixta, O.; Orduña, M.; Martínez, F.; Aguilar, B.; Cortés, A. Enhancement of resistance in mice treated with Lactobacillus casei: effect on Trichinella spiralis infection. Vet Parasitol 1999, 80, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Gómez, F.; Fuentes-Castro, B.E.; Bautista-Garfias, C.R. The intraperitoneal inoculation of Lactobacillus casei in mice induces total protection against Trichinella spiralis infection at low challenge doses. Parasitol Res 2011, 109, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Temsahy, M.M.; Ibrahim, I.R.; Mossallam, S.F.; Mahrous, H.; Abdel Bary, A.; Abdel Salam, S.A. Evaluation of newly isolated probiotics in the protection against experimental intestinal trichinellosis. Vet Parasitol 2015, 214, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorožňáková, E.; Bucková, B.; Hurníková, Z.; Revajová, V.; Lauková, A. Effect of probiotic bacteria on phagocytosis and respiratory burst activity of blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNL) in mice infected with Trichinella spiralis. Vet Parasitol 2016, 231, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucková, B.; Hurníková, Z.; Lauková, A.; Revajová, V.; Dvorožňáková, E. The Anti-parasitic Effect of Probiotic Bacteria via Limiting the Fecundity of Trichinella Spiralis Female Adults. Helminthologia 2018, 55, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, M.A.; Florent, I.; Kohl, L.; Grellier, P. Probiotics for the control of parasites: an overview. J Parasitol Res 2011, 2011, 610769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, N.L. Intimate gut interactions: helminths and the microbiota. Cell Res 2016, 26, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gause, W.C.; Maizels, R.M. Macrobiota - helminths as active participants and partners of the microbiota in host intestinal homeostasis. Curr Opin Microbiol 2016, 32, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peachey, L.E.; Jenkins, T.P.; Cantacessi, C. This Gut Ain't Big Enough for Both of Us. Or Is It? Helminth-Microbiota Interactions in Veterinary Species. Trends Parasitol 2017, 33, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Su, L.; Li, Y.; Long, S.R.; Chang, J.; Zhang, W.; Walker, W.A.; Xavier, R.J.; Cherayil, B.J.; Shi, H.N. Helminth-induced alterations of the gut microbiota exacerbate bacterial colitis. Mucosal Immunol 2018, 11, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, J. Ecological role of lactobacilli in the gastrointestinal tract: implications for fundamental and biomedical research. Appl Environ Microbiol 2008, 74, 4985–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rheinallt, M.J.; Chirayu, D.; Trevor, M.D.; Liping, L.; Alexandra, A.W.; Christopher, D.S.; Courtney, S. A; April. R.R; Erin. S.K.; Andrew, S.N. Lactobacilli Modulate Epithelial Cytoprotection through the Nrf2 Pathway[J]. Cell Reports, 2015; 12, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolas-Fernández, F. Biological variation in Trichinella species and genotypes. J Helminthol 2003, 77, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, H.R.; Bessonov, A.S.; Cuperlovic, K.; Gajadhar, A.A.; van Knapen, F.; Noeckler, K.; Schenone, H.; Zhu, X. International Commission on Trichinellosis: recommendations on methods for the control of Trichinella in domestic and wild animals intended for human consumption. Vet Parasitol 2000, 93, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.; Lee, Y.; Goo, D.; Zimmerman, N.P.; Smith, A.H.; Rehberger, T.; Lillehoj, H.S. The effects of dietary Bacillus subtilis supplementation, as an alternative to antibiotics, on growth performance, intestinal immunity, and epithelial barrier integrity in broiler chickens infected with Eimeria maxima. Poult Sci 2020, 99, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Tsapieva, A.N.; Zhang, L.; Han, J. Heat-Killed Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Repairs Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Damage via MLCK/MLC Pathway Activation. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozio, E. Searching for Trichinella: not all pigs are created equal. Trends Parasitol 2014, 30, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.N.; Sun, G.G.; Qi, X.; Yang, F.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, X.; Cui, J.; Wang, Z.Q. Characterization of a serine protease inhibitor from Trichinella spiralis and its participation in larval invasion of host's intestinal epithelial cells. Parasit Vectors 2018, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.Y.; Zhu, X.P.; Xu, K.C.; Lu, Q.; Boireau, P. Biological and genetic characteristics of two Trichinella isolates in China; comparison with European species. Parasite 2001, 8, S34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakelin, D.; Goyal, P.K. Trichinella isolates: parasite variability and host responses. Int J Parasitol 1996, 26, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S. , et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saracino, M.P.; Vila, C.C.; Baldi, P.C.; González Maglio, D.H. Searching for the one(s): Using Probiotics as Anthelmintic Treatments. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 714198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Cheng, P.C.; Pan, T.M. The immunomodulatory effects of lactic acid bacteria for improving immune functions and benefits. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2012, 96, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mido, S.; Fath, E.M.; Farid, A.S.; Nonaka, N.; Oku, Y.; Horii, Y. Trichinella spiralis : Infection changes serum paraoxonase -1 levels, lipid profile, and oxidative status in rats[J]. Experimental Parasitology 2012, 131, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farid, A.S.; Mido, S.; Linh, B. K.; Hayashi, T.; Horii, Y. An atherogenic lipid profile with low serum paraoxonase-1 activity during nematode infection in rats[J]. European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2010; 40, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.E.; Maizels, R.M. Diversity and dialogue in immunity to helminths. Nat Rev Immunol 2011, 11, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Garfias, C.R.; Ixta-Rodríguez, O.; Martínez-Gómez, F.; López, M.G.; Aguilar-Figueroa, B.R. Effect of viable or dead Lactobacillus casei organisms administered orally to mice on resistance against Trichinella spiralis infection. Parasite 2001, 8, S226–S228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudner, X.L.; Happel, K.I.; Young, E.A.; Shellito, J.E. Interleukin-23 (IL-23)-IL-17 cytokine axis in murine Pneumocystis carinii infection. Infect Immun 2007, 75, 3055–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, C.S.; Hu, C.M.; Chiu, W.T.; Lam, C.S.; Ting, Y.; Tsai, S.H.; Wang, T.C. Suppression of lipopolysaccharide-induced of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 by Sanguis Draconis, a dragon's blood resin, in RAW 264.7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2008, 115, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanmani, P.; Kim, H. Protective Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Against TLR4 Induced Inflammatory Response in Hepatoma HepG2 Cells Through Modulation of Toll-Like Receptor Negative Regulators of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and NF-κB Signaling. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roselli, M.; Finamore, A.; Britti, M.S.; Mengheri, E. Probiotic bacteria Bifidobacterium animalis MB5 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG protect intestinal Caco-2 cells from the inflammation-associated response induced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88. Br J Nutr 2006, 95, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kirpich, I.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Barve, S.; McClain, C.J.; Feng, W. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment potentiates intestinal hypoxia-inducible factor, promotes intestinal integrity and ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury. Am J Pathol 2011, 179, 2866–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Yunyi, Y.; Hui, H.; Hua, H.; Mingzhong, Y. Xanthohumol attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through inhibiting NF-κB and activating Nrf2 signaling pathways[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2018; 61, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Day 4 | Day 7 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean±SD | reduction | mean±SD | reduction | |
| Ts | 296±31 | —— | 227±15 | —— |
| LAB | 242±26 | 18.24% | 126±23* | 44.49% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





