Submitted:
04 June 2024
Posted:
06 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and study protocol:
2.2. Measurements:
2.3. Orthopedic assessment:
2.4. Ethical approval:
2.5. Statistical analysis:
3. Results
3.1. Study population:
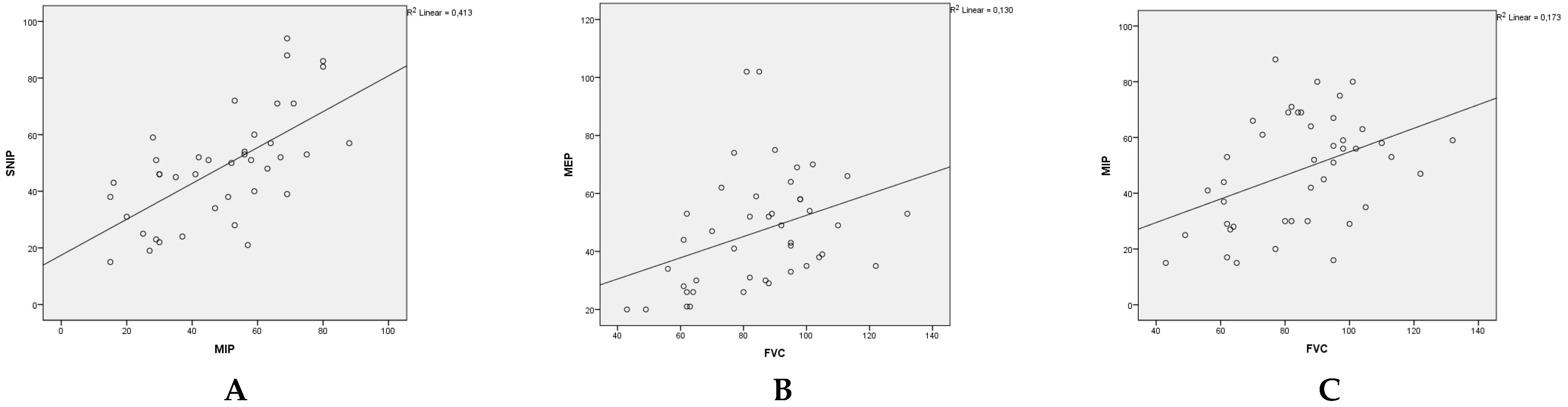
3.2. Respiratory assessments:
3.3. Effect of kyphoscoliosis, chest deformity and malnutrition:
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wasilewska, E.; Sobierajska-Rek, A.; Malgorzewicz, S.; Solinski, M.; Jassem, E. Benefits of Telemonitoring of Pulmonary Function-3-Month Follow-Up of Home Electronic Spirometry in Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J Clin Med 2022, 11(3). [published Online First: 2022/02/16]. [CrossRef]
- Leon-Astudillo, C.; Okorie, C. U. A.; McCown, M. Y.; Dy, F. J.; Puranik, S.; Prero, M.; ElMallah, M. K.; Treat, L.; Gross, J. EATS Core Curriculum 2022. Pediatric Pulmonary Medicine: Updates in pediatric neuromuscular disease. Pediatr Pulmonol 2023, 58(7): p. 1866-1874. [published Online First: 2023/05/05]. [CrossRef]
- Finder, J. D.; Birnkrant, D.; Carl, J.; Farber, H. J.; Gozal, D.; Iannaccone, S. T.; Kovesi, T.; Kravitz, R. M.; Panitch, H.; Schramm, C. et al. Respiratory care of the patient with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: ATS consensus statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004, 170(4): p. 456-65. [published Online First: 2004/08/11]. [CrossRef]
- Gauld, L. M.; Boynton, A.; Betts, G. A.; Johnston, H. Spirometry is affected by intelligence and behavior in muscular dystrophy. Pediatr Pulmonol 2005, 40(5): p. 408-13. [published Online First: 2005/09/08]. [CrossRef]
- Choi, W. H.; Shin, M. J.; Jang, M. H.; Lee, J. S.; Kim, S. Y.; Kim, H. Y.; Hong, Y.; Kim, C.; Shin, Y. B. Maximal Inspiratory Pressure and Maximal Expiratory Pressure in Healthy Korean Children. Ann Rehabil Med 2017, 41(2): p. 299-305. [published Online First: 2017/05/16]. [CrossRef]
- Nicot, F.; Hart, N.; Forin, V.; Boule, M.; Clement, A.; Polkey, MI.; Lofaso, F.; Fauroux, B. Respiratory muscle testing: A valuable tool for children with neuromuscular disorders. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006, 174(1):67-74. [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Chiang, J.; Qian, H.; Amin, R. Maximal static respiratory and sniff pressures in healthy children. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019, 16(4):478-487. [published Online First: 2018/12/19]. [CrossRef]
- Birnkrant, D.J.; Bushby, K.; Bann, C.M.; Alman, B.A.; Apkon, S.D.; Blackwell, A.; Case, L.E.; Cripe, L.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Olson, A.K. et al. Diagnosis and management of duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 2: Respiratory, cardiac, bone health, and orthopaedic management. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17(4):347-361. [published Online First: 2018/02/06]. [CrossRef]
- Khirani, S.; Ramirez, A.; Aubertin, G.; Boule, M.; Chemouny, C.; Forin, V.; Fauroux, B. Respiratory muscle decline in duchenne muscular dystrophy. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2014, 49(5):473-481. [published Online First: 2013/07/10]. [CrossRef]
- Laveneziana, P.; Albuquerque, A.; Aliverti, A.; Babb, T.; Barreiro, E.; Dres, M.; Dube, B.P.; Fauroux, B.; Gea, J.; Guenette, J.A.; et al. Ers statement on respiratory muscle testing at rest and during exercise. Eur Respir J. 2019, 53(6). [published Online First: 2019/04/09]. [CrossRef]
- Neve, V.; Cuisset, J.M.; Edme, J.L.; Carpentier, A.; Howsam, M.; Leclerc, O.; Matran, R. Sniff nasal inspiratory pressure in the longitudinal assessment of young duchenne muscular dystrophy children. Eur Respir J. 2013, 42(3):671-680. [published Online First: 2012/12/22]. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Mei, Q.Q.; Xin, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wu, S.W.; Liu, C.F. The assessment of sniff nasal inspiratory pressure in patients with duchenne muscular dystrophy in china. Brain Dev. 2018, 40(5):391-396 [published Online First: 2018/02/27]. [CrossRef]
- Fauroux, B.; Aubertin, G.; Cohen, E.; Clement, A.; Lofaso, F. Sniff nasal inspiratory pressure in children with muscular, chest wall or lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2009, 33(1):113-117. [published Online First: 2008/09/19]. [CrossRef]
- Pennati, F.; Arrigoni, F.; LoMauro, A.; Gandossini, S.; Russo, A.; D'Angelo, M.G.; Aliverti, A. Diaphragm involvement in duchenne muscular dystrophy (dmd): An mri study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020, 51(2):461-471. [published Online First: 2019/07/14]. [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.H.; Choi, W.A.; Kim, D.H.; Kang, S.W. Postural vital capacity difference with aging in duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 2015, 52(5):722-727. [published Online First: 2015/03/03]. [CrossRef]
- Pandit, C.; Kennedy, B.; Waters, K.; Young, H.; Jones, K.; Fitzgerald, D.A. Can postural changes in spirometry in children with duchenne muscular dystrophy predict sleep hypoventilation? Paediatr Respir Rev. 2023. [published Online First: 2023/09/12]. [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Suh, M.R.; Choi, W.A.; Kang, S.W.; Oh, H.J. Correlation of serum creatine kinase level with pulmonary function in duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann Rehabil Med. 2017, 41(2):306-312. [published Online First: 2017/05/16]. [CrossRef]
- Rodillo, E.; Noble-Jamieson, C.M.; Aber, V.; Heckmatt, J.Z.; Muntoni, F.; Dubowitz, V. Respiratory muscle training in duchenne muscular dystrophy. Arch Dis Child. 1989, 64(5):736-738. [published Online First: 1989/05/01]. [CrossRef]
- Lott, D.J.; Taivassalo, T.; Senesac, C.R.; Willcocks, R.J.; Harrington, A.M.; Zilke, K.; Cunkle, H.; Powers, C.; Finanger, E.L.; Rooney, W.D.; et al. Walking activity in a large cohort of boys with duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 2021, 63(2):192-198. [published Online First: 2020/11/15]. [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.A.; Martinez, F.E.; Manco, J.C. Correlation between standing height, sitting height, and arm span as an index of pulmonary function in 6-10-year-old children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2003, 36(3):202-208. [published Online First: 2003/08/12]. [CrossRef]
- Kuczmarski, R.J.; Ogden, C.L.; Guo, S.S.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M.; Flegal, K.M.; Mei, Z.; Wei, R.; Curtin, L.R.; Roche A.F.; Johnson, C.L. 2000 cdc growth charts for the united states: Methods and development. Vital Health Stat 11. 2002, (246):1-190.
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J. 2005, 26(2):319-338. [CrossRef]
- Quanjer, P.H., Tammeling, G.J.; Cotes, J.E.; Pedersen, O.F.; Peslin, R.; Yernault, J.C. Lung volumes and forced ventilatory flows. Report working party standardization of lung function tests, european community for steel and coal. Official statement of the european respiratory society. Eur Respir J Suppl. 1993, 16:5-40.
- LoMauro, A.; Romei, M.; Gandossini, S.; Pascuzzo, R.; Vantini, S.; D'Angelo, M.G.; Aliverti, A. Evolution of respiratory function in duchenne muscular dystrophy from childhood to adulthood. Eur Respir J. 2018, 51(2). [published Online First: 2018/02/14]. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.S.; Valentine, R.E. Clinical measurement of the thoracic kyphosis. A study of the intra-rater reliability in subjects with and without shoulder pain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010, 11:39. [published Online First: 2010/03/03]. [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.A.; Whitelaw, W.A. The assessment of maximal respiratory mouth pressures in adults. Respir Care. 2009, 54(10):1348-1359.
- Fitting, J.W.; Paillex, R.; Hirt, L.; Aebischer, P.; Schluep, M. Sniff nasal pressure: A sensitive respiratory test to assess progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1999, 46(6):887-893.
- Janssens, J.P.; Adler, D.; Iancu Ferfoglia, R.; Poncet, A.; Genton Graf, L.; Leuchter, I.; Escher Imhof, M.; Heritier Barras, A.C. Assessing inspiratory muscle strength for early detection of respiratory failure in motor neuron disease: Should we use mip, snip, or both? Respiration. 2019, 98(2):114-124. [published Online First: 2019/04/25]. [CrossRef]
- Kaslow, J.A.; Soslow, J.H.; Burnette, W.B.; Raucci, F.J.; Hills, T.J.; Ibach, M.G.; Hebblethwaite, R.C.; Arps, K.M.; Sokolow, A.G. Improving access and guideline adherence in pulmonary care in patients with duchenne muscular dystrophy. Respir Care. 2022, 67(3):347-352. [published Online First: 2021/12/09]. [CrossRef]
- Levine, H.; Goldfarb, I.; Katz, J.; Carmeli, M.; Shochat, T.; Mussaffi, H.; Aharoni, S.; Prais, D.; Nevo, Y. Pulmonary function tests for evaluating the severity of duchenne muscular dystrophy disease. Acta Paediatr. 2023, 112(4):854-860. [published Online First: 2023/01/04]. [CrossRef]
- Sobierajska-Rek, A.; Wasilewska, E.; Sledzinska, K.; Jablonska-Brudlo, J.; Malgorzewicz, S.; Wasilewski, A.; Szalewska, D. The association between the respiratory system and upper limb strength in males with duchenne muscular dystrophy: A new field for intervention? Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022, 19(23). [published Online First: 2022/12/12]. [CrossRef]
- Inkley, S.R.; Oldenburg, F.C.; Vignos, P.J., Jr. Pulmonary function in duchenne muscular dystrophy related to stage of disease. Am J Med. 1974, 56(3):297-306. [published Online First: 1974/03/01]. [CrossRef]
- Stedman, H.H.; Sweeney, H.L.; Shrager, J.B.; Maguire, H.C.; Panettieri, R.A.; Petrof, B.; Narusawa, M.; Leferovich, J.M.; Sladky, J.T.; Kelly, A.M. The mdx mouse diaphragm reproduces the degenerative changes of duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1991, 352(6335):536-539. [published Online First: 1991/08/08]. [CrossRef]
- Fromageot, C.; Lofaso, F.; Annane, D.; Falaize, L.; Lejaille, M.; Clair, B.; Gajdos, P.; Raphael, J.C. Supine fall in lung volumes in the assessment of diaphragmatic weakness in neuromuscular disorders. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001, 82(1):123-128. [published Online First: 2001/03/10]. [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, S.; Khirani, S.; Dabaj, I.; Cavassa, E.; Amaddeo, A.; Arroyo, J.O.; Desguerre, I.; Richard, P.; Cutrera, R.; Ferreiro, A.; et al. Diaphragmatic dysfunction in sepn1-related myopathy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2017, 27(8):747-755. [published Online First: 2017/06/14]. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kang, S.W.; Lee, S.C.; Choi, W.A.; Kim, D.H. How respiratory muscle strength correlates with cough capacity in patients with respiratory muscle weakness. Yonsei Med J. 2010, 51(3):392-397 [published Online First: 2010/04/09]. [CrossRef]
- Poussel, M.; Kaminsky, P.; Renaud, P.; Laroppe, J.; Pruna, L.; Chenuel, B. Supine changes in lung function correlate with chronic respiratory failure in myotonic dystrophy patients. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2014, 193:43-51. [published Online First: 2014/01/21]. [CrossRef]
- Fayssoil, A.; Chaffaut, C.; Prigent, H.; Laforet, P.; Clair, B.; Orlikowski, D.; Ogna, A.; Chevret, S.; Meng, P.; Annane, D.; et al. Nutritional status, swallowing disorders, and respiratory prognosis in adult duchenne muscular dystrophy patients. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2021, 56(7):2146-2154. [published Online First: 2021/05/04]. [CrossRef]
- Willig, T.N.; Carlier, L.; Legrand, M.; Riviere, H.; Navarro, J. Nutritional assessment in duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1993, 35(12):1074-1082. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Oh, H.J.; Choi, W.A.; Kim, D.J.; Kang, S.W. Relationship between eating and digestive symptoms and respiratory function in advanced duchenne muscular dystrophy patients. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2020, 7(2):101-107. [published Online First: 2020/01/07]. [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.; Carey, K.; Ho, G.; Mallitt, K.A.; Widger, J.; Farrar, M. The relationship of body habitus and respiratory function in duchenne muscular dystrophy. Respir Med. 2016, 119:35-40. [published Online First: 2016/10/04]. [CrossRef]
- Manzur, A.Y.; Kuntzer, T.; Pike, M.; Swan, A. Glucocorticoid corticosteroids for duchenne muscular dystrophy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008, (1):CD003725. [published Online First: 2008/02/07]. [CrossRef]
- Canapari, C.A.; Barrowman, N.; Hoey, L.; Walker, S.W.; Townsend, E.; Tseng, B.S.; Katz, S.L. Truncal fat distribution correlates with decreased vital capacity in duchenne muscular dystrophy. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2015. 50(1):63-70. [published Online First: 2014/03/20]. [CrossRef]
- Inal-Ince, D.; Savci, S.; Arikan, H.; Saglam, M.; Vardar-Yagli, N.; Bosnak-Guclu, M.; Dogru, D. Effects of scoliosis on respiratory muscle strength in patients with neuromuscular disorders. Spine J. 2009, 9(12):981-986. [published Online First: 2009/10/13]. [CrossRef]
- Ramappa, M. Can 'sniff nasal inspiratory pressure' determine severity of scoliosis in paediatric population? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009, 129(11):1461-1464. [published Online First: 2008/12/17]. [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.M.; Hunt, B.; Green, M. Fall in vital capacity with posture. Br J Dis Chest. 1985, 79(3):267-271.
| All patients (n:44) |
Ambulatory patients (n:25) |
Non-ambulatory patients (n:19) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), (mean±std) | 10.8±2.9 | 9.2±2.1 | 13±2.3 |
| Male, n (%) | 42 (95.5) | 23 (92) | 19 (100) |
| Body-mass index percentile (BMIp) (median)(25-75p) | 52.5 (12.9-86.4) | 49.6 (27-81.5) | 55.5 (0.9-84) |
| Age at diagnosis (years), (median)(25-75p) | 3.5 (1.6-5) | 4 (1.8-5) | 3 (1.5-5) |
| Consanguineous marriage,n (%) | 11 (25) | 5 (20) | 6 (31.6) |
| Family history of DMD patients, n (%) | 11 (25) | 8 (32) | 3 (15.8) |
| Kyphosis, n (%) | 13 (29.5) | 11 (44) | 2 (10.5) |
| Scoliosis, n (%) | 12 (27.3) | 2 (8) | 10 (52.6) |
| COBB angle, °, (median)(25-75p) | 6 (2-11) | 5 (0-7.7) | 10 (4-16) |
| Chest deformity, n (%) | 12 (27.3) | 4 (16) | 8 (42.1) |
| Other orthopedic problems (limb contractures, pes equinovarus etc…) n (%) | 25 (56.8) | 9 (36) | 16 (84.2) |
| Cardiological problems, n (%) | 6 (13.6) | 0 (0) | 6 (31.6) |
| Venous blood gas pCO2 (mmHg) (mean±std) | 37.7±4.1 | 36.8±3.1 | 39.0±5.1 |
| Steroid treatment, (years), (median)(25-75p) | 4 (2-6) | 3 (1.5-5) | 6 (4-11.1) |
| Ambulatory patients (n:25) |
Non-ambulatory patients (n:19) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upright position | Supine position | p value | Upright Position | Supine position | P value | |
| FVC (%) (mean±std) | 92.3±17.4 | 87.3±19.2 | 0.000* | 75.7±18.9 | 71.1±19.0 | 0.021* |
| FEV1 (%) (mean±std) | 98.2±17.0 | 91.8±18.9 | 0.000* | 83.8±18.5 | 77.6±18.8 | 0.002* |
| FEV1/FVC (%) (mean±std) | 103.3±4.2 | 102.4±4.8 | 0.330 | 107.0±6.1 | 106.4±6.0 | 0.457 |
|
FEF2575 (%) (mean±std) |
100.8±14.3 | 92.8±16.3 | 0.001* | 97.1±25.9 | 88.3±26.1 | 0.040* |
|
MIP (cmH2O) (mean± std) |
51.0±20.2 | NA | NA | 44.5±19.3 | NA | NA |
|
SNIP (cmH2O) (mean± std) |
52.6±15.7 | NA | NA | 42.1±23.3 | NA | NA |
| MEP (cmH2O) (median, 25-75p) | 49 (35-67.5) | NA | NA | 39 (26-53.2) | NA | NA |
| Malnourished group (n:28) |
Non-malnourished group (n:16) |
P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIP (mean± std) | 39.6±18.6 | 61.7±14.0 | 0.000* |
| MEP (median, 25-75p) | 35 (26-49.7) | 54 (47-64) | 0.001* |
| SNIP (mean± std) | 40.9±14.3 | 61.7±21.7 | 0.001* |
| FVC (%) (mean±std) | 84.1±22.4 | 85.1±14.9 | 0.854 |
| FEV1 (%) (mean±std) | 91.0±21.5 | 92.0±14.0 | 0.867 |
| FEV1/FVC (%) (mean±std) | 105.4±4.7 | 104.5±6.6 | 0.627 |
| FEF2575 (%) (mean±std) | 95.2±17.1 | 104.1±22.8 | 0.159 |
| *p<0.05 significancy |
| Postural FVC difference < % 7.5 (n:27) |
Postural FVC difference > % 7.5 (n:17) |
P value | |
| MIP (cmH2O) (mean±std) | 52,38±19,79 | 43,81±18,13 | 0,168 |
| SNIP (cmH2O) (mean±std) | 53,40±19 | 41,93±17,54 | 0,049* |
| MEP (cmH2O) (median, 25-75p) | 47 (31-59) | 38 (28,50-53,75) | 0,407 |
| FVC (%) (mean±std) | 85,07±17,51 | 85,35±23,50 | 0,838 |
| FEV1 (%) (mean±std) | 94±15,73 | 91,53±21,39 | 0,665 |
| FEV1/FVC (%) (mean±std) | 104,96±5,71 | 104,88±5,04 | 0,946 |
| FEF2575 (%) (mean±std) | 98,80±19,48 | 103,17±16,35 | 0,449 |
| * p<0.05 significancy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





