Submitted:
31 May 2024
Posted:
03 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Background
AI and its Usage in Medicine and Health Care
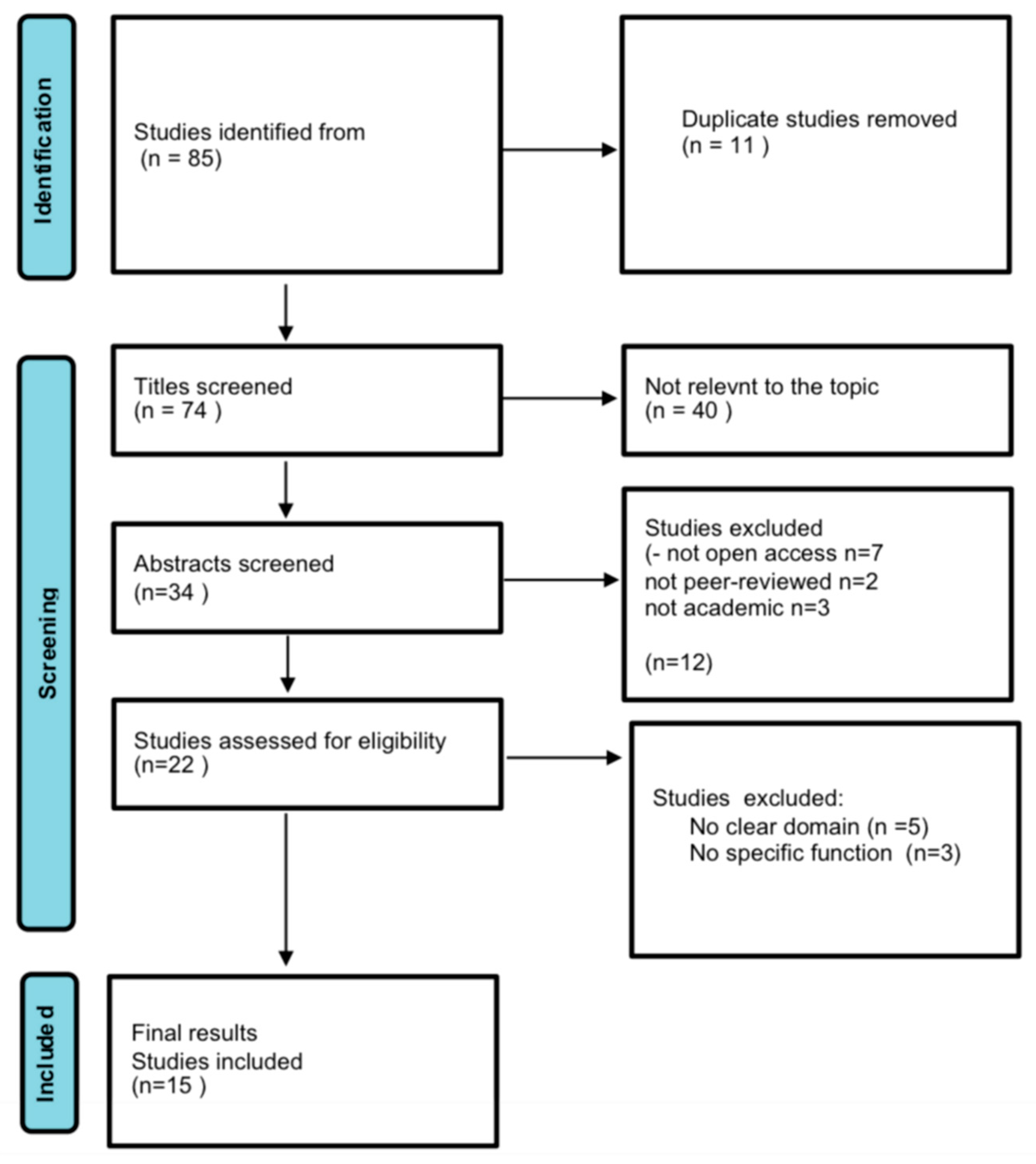
Methods
Results and Analysis
Discussion
- Impact of AI on the Quality and Credibility of Scientific Writing: Exploring how AI influences the quality and trustworthiness of scientific publications.
- Development of Various AI tools Specifically Designed for Scientific Writing: Some Generative AI tools are specifically prepared for scientific writing. Exploring their reliability and benefits could be a valuable thing for the stakeholders.
- Ethical Guidelines for AI Use in Scientific Writing: Some guidelines for responsible usage of Generative AI in the field of science already exist. National legislations also make efforts to regulate the area. Analysis of the existing status and its impact on the process is also a valuable contribution.
Conclusion
Funding Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Lindsay DM: Scientific Writing = Thinking in Words writing. Europhysics Letters, 143. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Gopen GD, Swan JA: The science of scientific writing. American scientist, 78(6), 550-558. 1990, Available at https://www.usenix.org/sites/default/files/gopen_and_swan_science_of_scientific_writing.pdf.
- Heard SB: The Scientist's Guide to Writing: How to Write More Easily and Effectively throughout Your Scientific Career, Princeton: Princeton University Press. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Okwemba RK: Introduction To Scientific Writing A Review. International Journal of Scientific Research in Science and Technology. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Giglio AD, Costa MU: The use of artificial intelligence to improve the scientific writing of non-native English speakers. Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira, 69. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Khalifa M, Albadawy M: Using artificial intelligence in academic writing and research: An essential productivity tool. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine Update, 100145. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Kaliyadan F, Seetharam KA: ChatGPT-Quo Vadis?. Indian Dermatology Online Journal, 14(4), 457-458. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elsalam KA, Abdel-Momen SM: Artificial Intelligence's Development and Challenges in Scientific Writing. Egyptian Journal of Agricultural Research. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Liang W, Zhang Y, Wu Z, et al.: Mapping the Increasing Use of LLMs in Scientific Papers. 2024, https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.01268.
- Muga G: Editorial —Artificial Intelligence language models in scientific. 2023, https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/link_gateway/2023EL....14320000G/. [CrossRef]
- Vitente AC, Lazaro RT, Escuadra CJ, et al.: The Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Assisted Technologies in Scientific Discourse. Philippine Journal of Physical Therapy. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Nazarovets S, Teixeira da Silva JA: ChatGPT as an “author”: Bibliometric analysis to assess the validity of authorship. Accountability in Research, 1-11. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Grimm LJ, Harvey JA: Practical steps to writing a scientific manuscript. Journal of Breast Imaging, 4(6), 640-648. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Somashekhar SP: Art of Scientific Writing. Indian Journal of Gynecologic Oncology, 18, 1-3. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Lunsford TR, Lunslord BR: How to Critically Read a Journal Research Article. JPO Journal of Prosthetics and Orthotics, 8, 24-31. 1996, https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.oandp.org/resource/resmgr/docs/skc/journal-club/How_to_Critically_Read.pdf.
- Fischer BA, Zigmond MJ: Components of a Research Article. 2009, Retrieved from www.survival.pitt.edu.
- Nielsen E, Reilly PL: A Guide to Understanding and Evaluating Research Articles. Gifted Child Quarterly, 29, 90 – 92. 1985. [CrossRef]
- Watson R: Avoiding Desk Rejection of a Manuscript. Nurse Author & Editor. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Carobene A, Padoan A, Cabitza F, et al.: Rising adoption of artificial intelligence in scientific publishing: evaluating the role, risks, and ethical implications in paper drafting and review process. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM). 2023. [CrossRef]
- Khan NA, Osmonaliev K, Sarwar MZ: Pushing the Boundaries of Scientific Research with the use of Artificial Intelligence tools: Navigating Risks and Unleashing Possibilities. Nepal Journal of Epidemiology, 13, 1258 – 1263. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Razack HIA, Mathew ST, Saad FFA, et al.: Artificial intelligence-assisted tools for redefining the communication landscape of the scholarly world. Science Editing, 8(2), 134-144. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Boyko J, Cohen J, Fox N, et al.: An Interdisciplinary Outlook on Large Language Models for Scientific Research. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Fonseca M, Cohen SB: Can Large Language Model Summarizers Adapt to Diverse Scientific Communication Goals? 2024. [CrossRef]
- Salimi A, Saheb H: Large language models in ophthalmology scientific writing: ethical considerations blurred lines or not at all? American Journal of Ophthalmology. 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilat R, Cole B J: How will artificial intelligence affect scientific writing, reviewing and editing? The future is here…. Arthroscopy, 39(5), 1119-1120. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Dashti M, Londono J, Ghasemi S, et al.: How much can we rely on artificial intelligence chatbots such as the ChatGPT software program to assist with scientific writing?. The Journal of prosthetic dentistry. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Vallath AL, Sivasubramanian BP, Chatterjee A, et al.: Ventricular septal rupture and artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted healthcare. Cureus, 15(3). 2023. [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag NM, Sumaida AB, Binz T, et al.: Integrating Artificial Intelligence Into Radiation Oncology: Can Humans Spot AI?. Cureus, 15(12). 2023. [CrossRef]
- Salazar GZ, Zúñiga D, Vindel CL, et al.: Efficacy of AI Chats to determine an emergency: a comparison between OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google Bard, and Microsoft Bing AI Chat. Cureus, 15(9). 2023. [CrossRef]
- Dossantos J, An J, Javan R: Eyes on AI: ChatGPT's transformative potential impact on ophthalmology. Cureus, 15(6). 2023. [CrossRef]
- Uppalapati VK, Nag DS: A Comparative Analysis of AI Models in Complex Medical Decision-Making Scenarios: Evaluating ChatGPT, Claude AI, Bard, and Perplexity. Cureus, 16(1). 2024. [CrossRef]
- Pais C, Liu J, Voigt R, et al.: Large language models for preventing medication direction errors in online pharmacies. Nat Med (2024). [CrossRef]
- Haidar O, Jaques A, McCaughran PW, et al.: AI-Generated Information for Vascular Patients: Assessing the Standard of Procedure-Specific Information Provided by the ChatGPT AI-Language Model. Cureus, 15(11). 2023. [CrossRef]
- Tan Y, Zhang Z, Li M, et al.: MedChatZH: A tuning LLM for traditional Chinese medicine consultations. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 172, 108290. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Altamimi I, Altamimi A, Alhumimidi AS, et al.: Snakebite advice and counseling from artificial intelligence: an acute venomous snakebite consultation with ChatGPT. Cureus. 2023, 15:e40351. [CrossRef]
- Kim JK, Chua M, Rickard M, et al.: ChatGPT and large language model (LLM) chatbots: The current state of acceptability and a proposal for guidelines on utilization in academic medicine. Journal of Pediatric Urology. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ong JCL, Chang SYH, William W, et al.: Ethical and regulatory challenges of large language models in medicine. The Lancet Digital Health. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Lozic E, Stular B: ChatGPT v Bard v Bing v Claude 2 v Aria v human-expert. How good are AI chatbots at scientific writing?. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kacena, M. A., Plotkin, L. I., & Fehrenbacher, J. C. (2024). The use of artificial intelligence in writing scientific review articles. Current Osteoporosis Reports, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Aydin, O., & Karaarslan, E. (2022). OpenAI ChatGPT generated literature review: Digital twin in healthcare. Aydın, Ö., Karaarslan, E.(2022). OpenAI ChatGPT Generated Literature Review: Digital Twin in Healthcare. In Ö. Aydın (Ed.), Emerging Computer Technologies, 2. https://acikerisim.mu.edu.tr/xmlui/bitstream/handle/20.500.12809/10483/Omer.pdf?sequence=1.
- Salvagno M, Taccone FS, Gerli AG, et al.: Can artificial intelligence help for scientific writing?. Critical care, 27(1), 75. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Hwang T, Aggarwal N, Khan PZ, et al.: Can ChatGPT assist authors with abstract writing in medical journals? Evaluating the quality of scientific abstracts generated by ChatGPT and original abstracts. PLoS ONE 19(2): e0297701. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Donlon, E., & Tiernan, P. (2023). Chatbots and Citations: An experiment in academic writing with Generative AI. Irish Journal of Technology Enhanced Learning, 7(2), 75-87. [CrossRef]
- Altmäe S, Sola-Leyva A, Salumets A: Artificial intelligence in scientific writing: a friend or a foe?. Reproductive BioMedicine Online, 47(1), 3-9. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kung JY: Elicit. The Journal of the Canadian Health Libraries Association, 44(1), 15. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Huang J, Tan M: The role of ChatGPT in scientific communication: writing better scientific review articles. American journal of cancer research, 13(4), 1148. 2023, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc10164801/.
- Burger B, Kanbach DK, Kraus S, et al.: On the use of AI-based tools like ChatGPT to support management research. European Journal of Innovation Management, 26(7), 233-241. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Athaluri SA, Manthena SV, Kesapragada VKM, et al.: Exploring the boundaries of reality: investigating the phenomenon of artificial intelligence hallucination in scientific writing through ChatGPT references. Cureus, 15(4). 2023. [CrossRef]
- Mugaanyi J, Cai L, Cheng S, et al.: Evaluation of Large Language Model Performance and Reliability for Citations and References in Scholarly Writing: Cross-Disciplinary Study. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 26, e52935. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Jenko N, Ariyaratne S, Jeys L, et al.: An evaluation of AI generated literature reviews in musculoskeletal radiology. The Surgeon. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H. P. (2023). Can Generative Artificial Intelligence Write an Academic Journal Article? Opportunities, Challenges, and Implications. Irish Journal of Technology Enhanced Learning, 7(2), 158-171. [CrossRef]
- Smith P, Smith L: This season’s artificial intelligence (AI): is today’s AI really that different from the AI of the past? Some reflections and thoughts. AI and Ethics, 1-4. 2023. [CrossRef]
| Authors and year | Title | Main Focus | Key findings | AI Benefits | AI limitations |
| 1. Altmae et al. 2023 | Artificial intelligence in scientific writing: A friend or a foe | Chat GPT for scientific writing | ChatGPT has shown a high potential in scientific writing | Material organization, draft creation, and proofreading | Inaccuracy and non-existing references |
| 2. Athaluri et al. 2023 | Exploring the boundaries of reality: Investigating the phenomenon of artificial intelligence hallucination in scientific writing through ChatGPT references | Chat GPT-3 hallucination | Partly Inaccurate references | In general, AI-generated content can be trusted but must be monitored and revised | Some non-existing references |
| 3. Kacena et al. 2024 | The use of artificial intelligence in writing scientific review articles | ChatGPT-4 writing draft manuscript | It can reduce the time for writing but the content must be revised by humans | AI usage in scientific writing is time-saving | Inaccurate references up to 70%, likelihood of plagiarism, and does not include the newest literature |
| 4. Lozic & Stular 2023 | ChatGPT v Bard v Bing v Claude 2 v Aria v human-expert. How good are AI chatbots at scientific writing? | Comparing different AI chatbots for scholarly writing | All chatbots are proficient in merging existing knowledge; however, understanding their limitations is essential | ChatGPT-4 outperforms the other chatbots in quantitative accuracy. | AI bots in their current versions are not capable of creating original content. |
| 5. Salvagno et al. 2023 | Can artificial intelligence help with scientific writing? | ChatGPT assistance in scientific writing | ChatGPT has a potential for scientific writing accompanied by ethical concerns and challenges | ChatGPT can help with the research questions, literature review, formatting, and language review. It can also save time in clinical practice | To be used only as an assistant and not replacement for experts. Potential plagiarism and inaccuracies. Paid versions can cause disbalance |
| 6. Aydin & Karaarslan 2022. | #break# OpenAI ChatGPT Generated Literature Review: Digital Twin in Healthcare | ChatGPT and its assistance in academic writing | AI will facilitate the scientific writing process | / | High level of similarity in the AI-generated content. |
| 7. Babal & Babal 2023. | Generative artificial intelligence: Can ChatGPT write a#break#quality abstract? | ChatGPT preparation of a conference abstract | ChatGPT can become a valuable writing tool.#break# | The AI-generated abstract was well-written and without errors | One fictitious citation was spotted. |
| 8. Donlon & Tiernan, 2023. | Chatbots and Citations: An experiment in academic writing with Generative AI | ChatGPT-3.5 (free version) writing an academic paper | The bot generated a credible base and was particularly useful in some aspects | Useful for generation of title, introduction, and conclusion, including the first draft of a paper. | / |
| 9. Hsu 2023 | Can Generative Artificial Intelligence Write an Academic Journal Article? Opportunities, Challenges, and Implications | ChatGPT-4 tested for preparation of a short academic paper. | Although AI is a game-changer for academia the need for balance is evident | A valuable tool for idea generation, design, and English writing. | Lack of critical thinking is something very important for accuracy. Ethical considerations. |
| 10. Hwang et al. 2024 | Can ChatGPT assist authors with abstract writing in medical journals? Evaluating the quality of scientific abstracts generated by ChatGPT and original abstracts | ChatGPT 3.5 and 4 versions in preparation of paper abstract following journal templates | ChatGPT exhibited proficiency in the content with minimal errors in the abstract | ChatGPT generates concise and readable abstracts of scientific articles.#break#Authentic and well-structured abstracts. | Minimal errors were spotted.#break#The general quality of the author-generated abstracts was higher. |
| 11. Mugaanyi et al. 2024 | Evaluation of Large Language Model Performance and Reliability#break#for Citations and References in Scholarly Writing:#break#Cross-Disciplinary Study | ChatGPT 3.5 usage for citations and references in scholarly publishing | ChatGPT-generated references and citations vary across various academic disciplines | In general, ChatGPT 3.5 generated relevant references and citations. | Hallucinations in the identifications of the DOI numbers of the generated references. |
| 12. Kung, J. 2023 | Elicit | "Elicit" AI as a research assistant | "Elicit" is a unique AI tool for summarizing academic literature | A useful tool for reviewing literature and answering questions based on scholarly articles. | It retrieves articles from one database only |
| 13. Jenko et al. 2024 | An evaluation of AI-generated literature reviews in musculoskeletal radiology | Assessment of AI-generated literature reviews | Although current AI tools are not reliable for routine use, they are capable of producing impressive literature reviews | AI saves time. ChatGPT-4 generates good literature reviews. | Cannot identify all relevant publications. Requires human oversight. |
| 14. Burger et al. 2023 | On the use of AI-based tools like ChatGPT to support management research | AI use to support research | AI will be integrated into the research to improve some domains | Improving the objectivity and the accuracy of the results. Avoid human errors and improve the reproducibility of research. Making the research process faster, more reliable, and more convenient | AI does not provide reasoning and causality. |
| 15. Huang &Tan, 2023#break# | The role of ChatGPT in scientific communication: Writing better scientific review articles | ChatGPT and its application in drafting scientific articles | ChatGPT is a powerful tool that facilitates the process of scientific writing, making it more efficient and effective | Enhance quality and efficiency in writing literature reviews. It makes the process faster, creates outlines, adds details, and improves the writing style. | The generated text must be edited to avoid plagiarism. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




